Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 Alters Gene Expression to Affect Acid Phosphatase Activity in Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
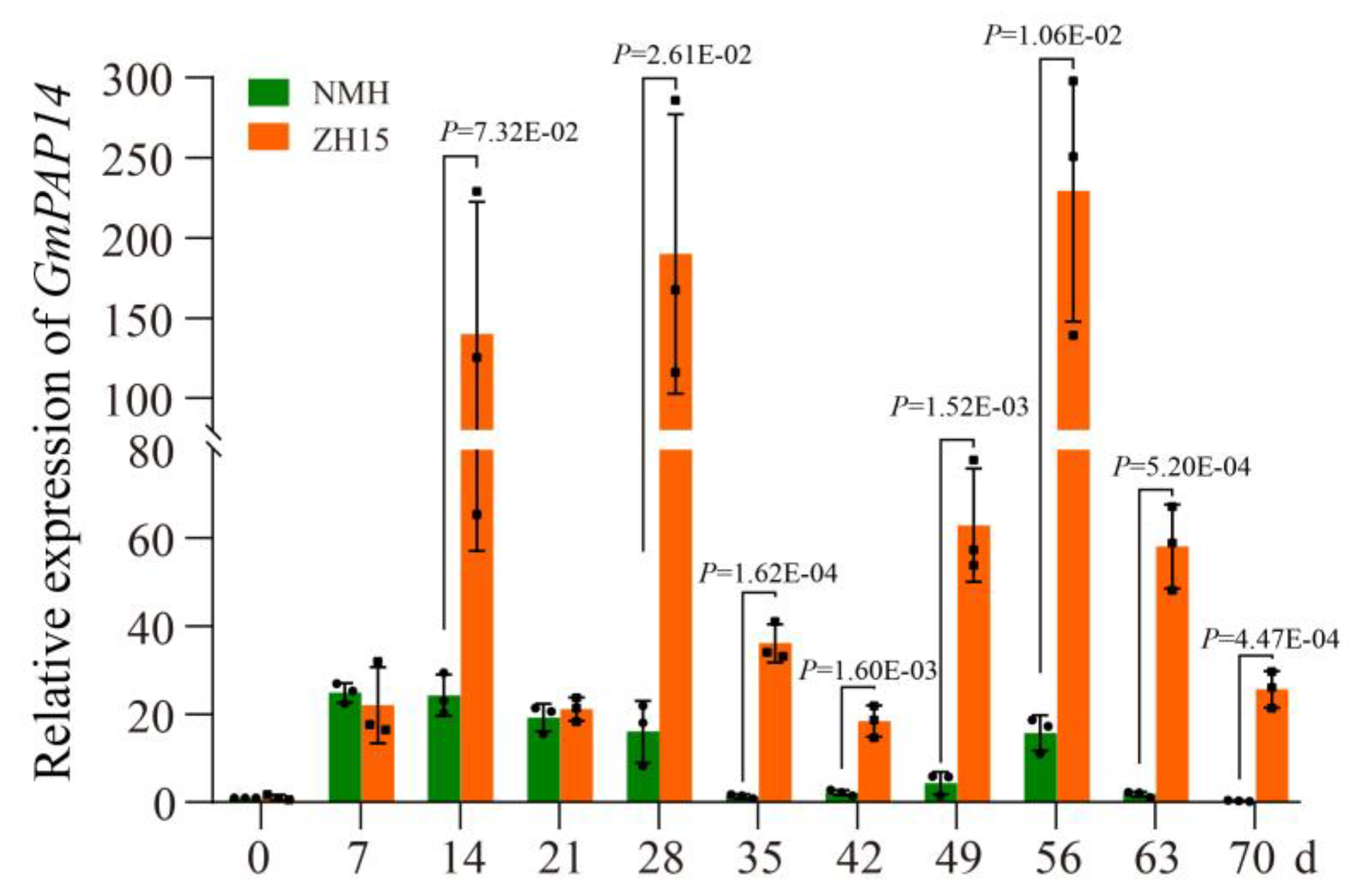
2.1. GmPAP14 Was Significantly Induced in Roots of ZH15 under Low P Conditions
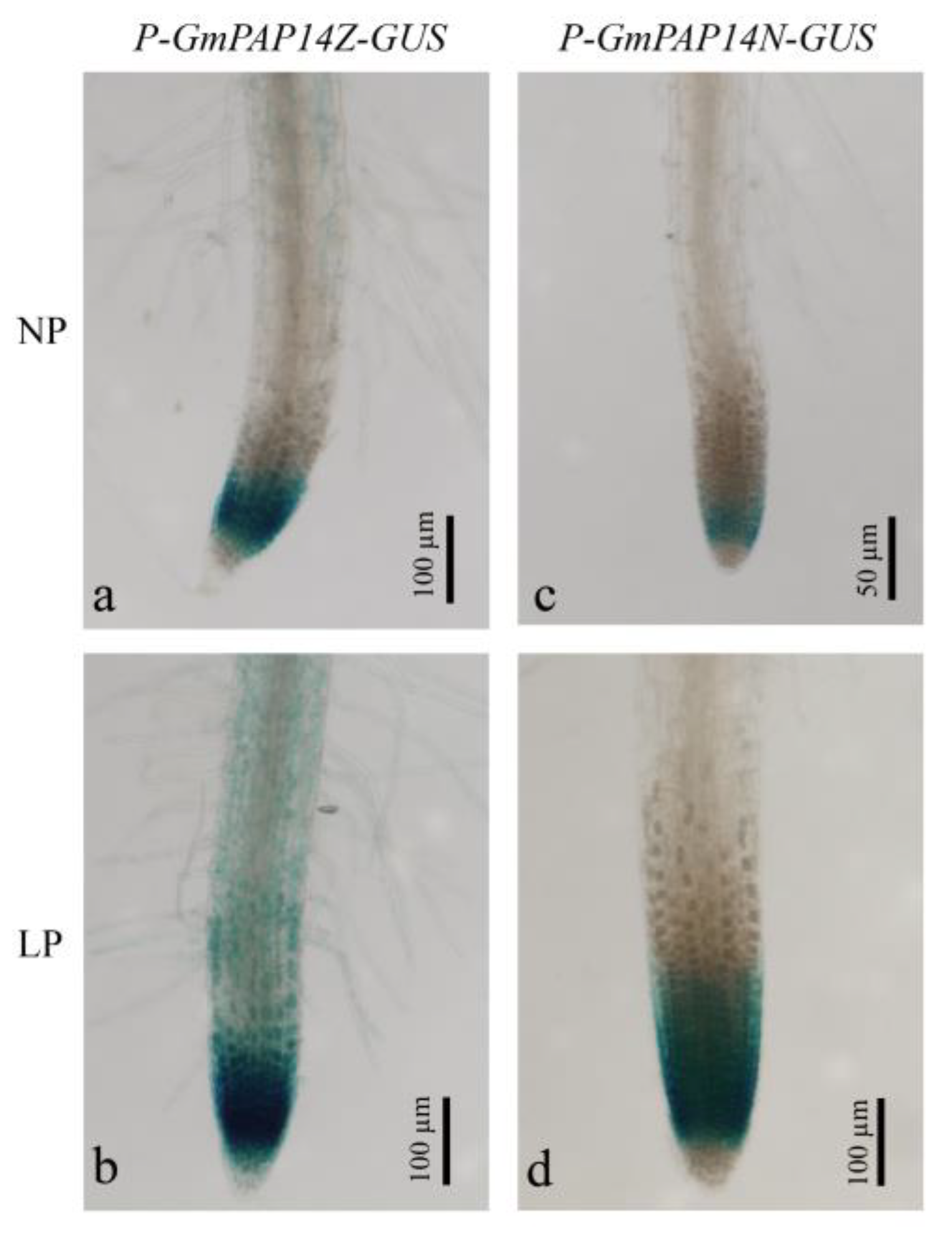
2.2. Variation in the GmPAP14 Promoter Affected Gene Expression
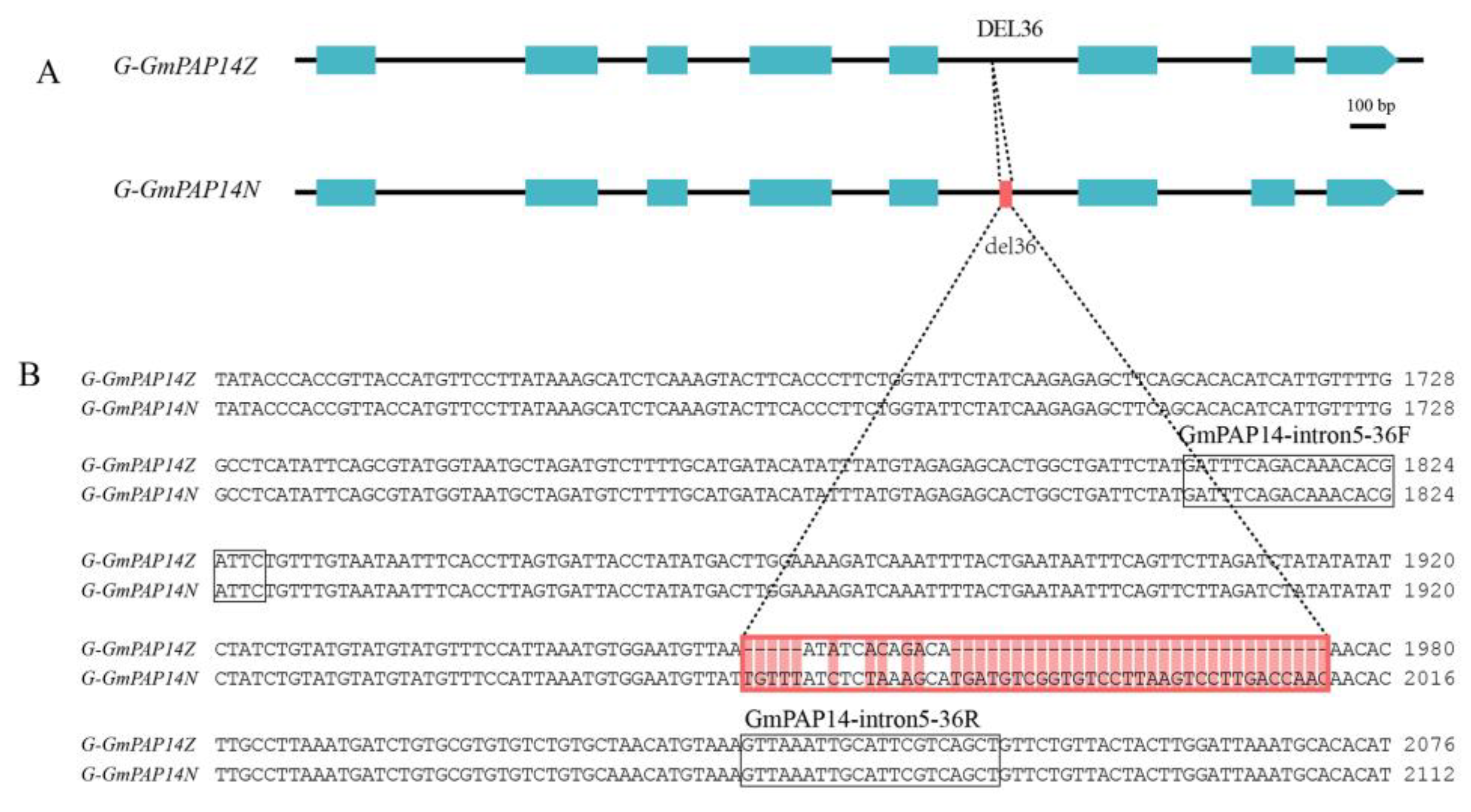
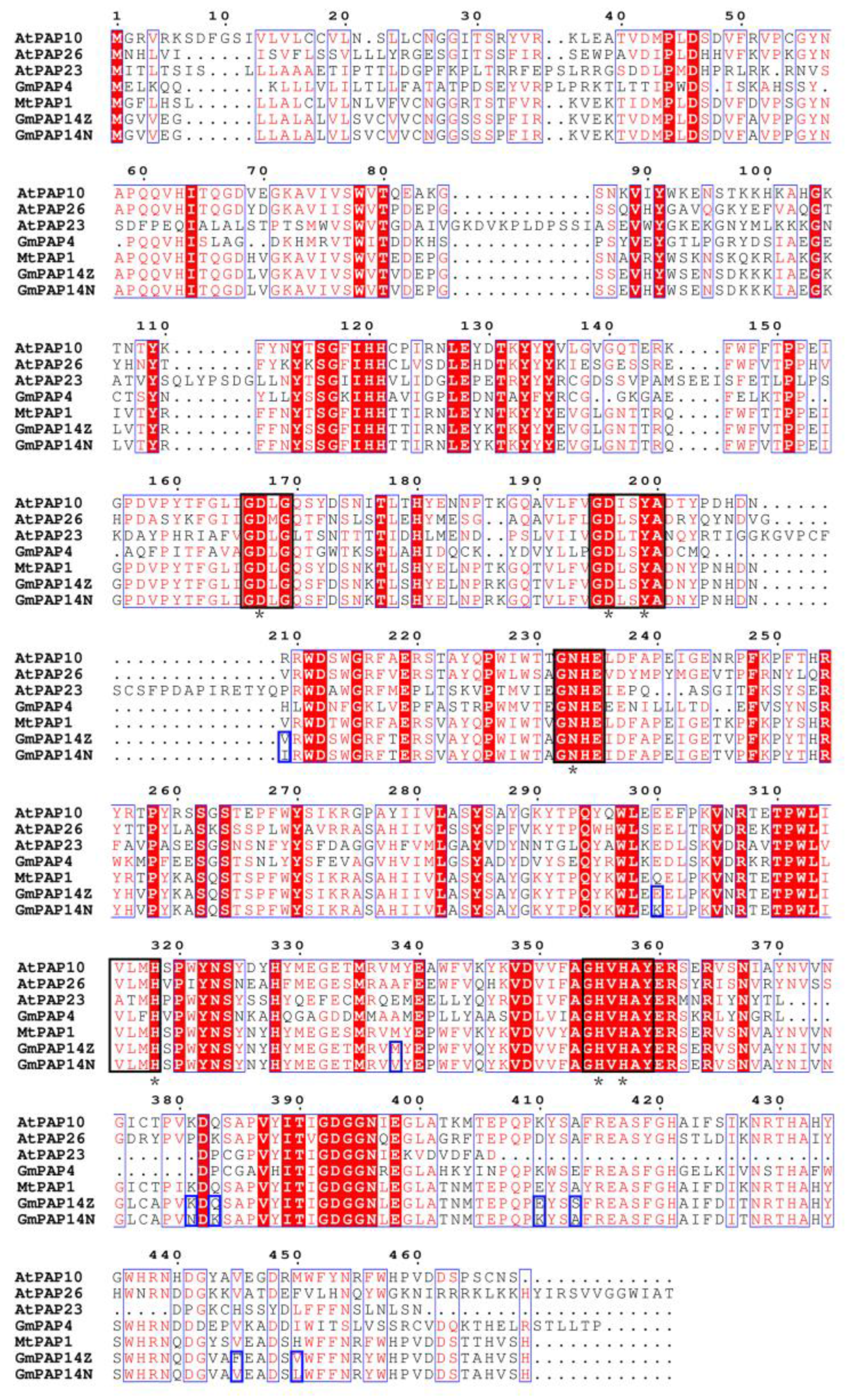
2.3. GmPAP14 gDNA Sequences Were Variational between ZH15 and NMH
2.4. G-GmPAP14Z Exhibited Higher Levels of GmPAP14 Expression and Significantly Improved Growth of Arabidopsis under Low P Conditions
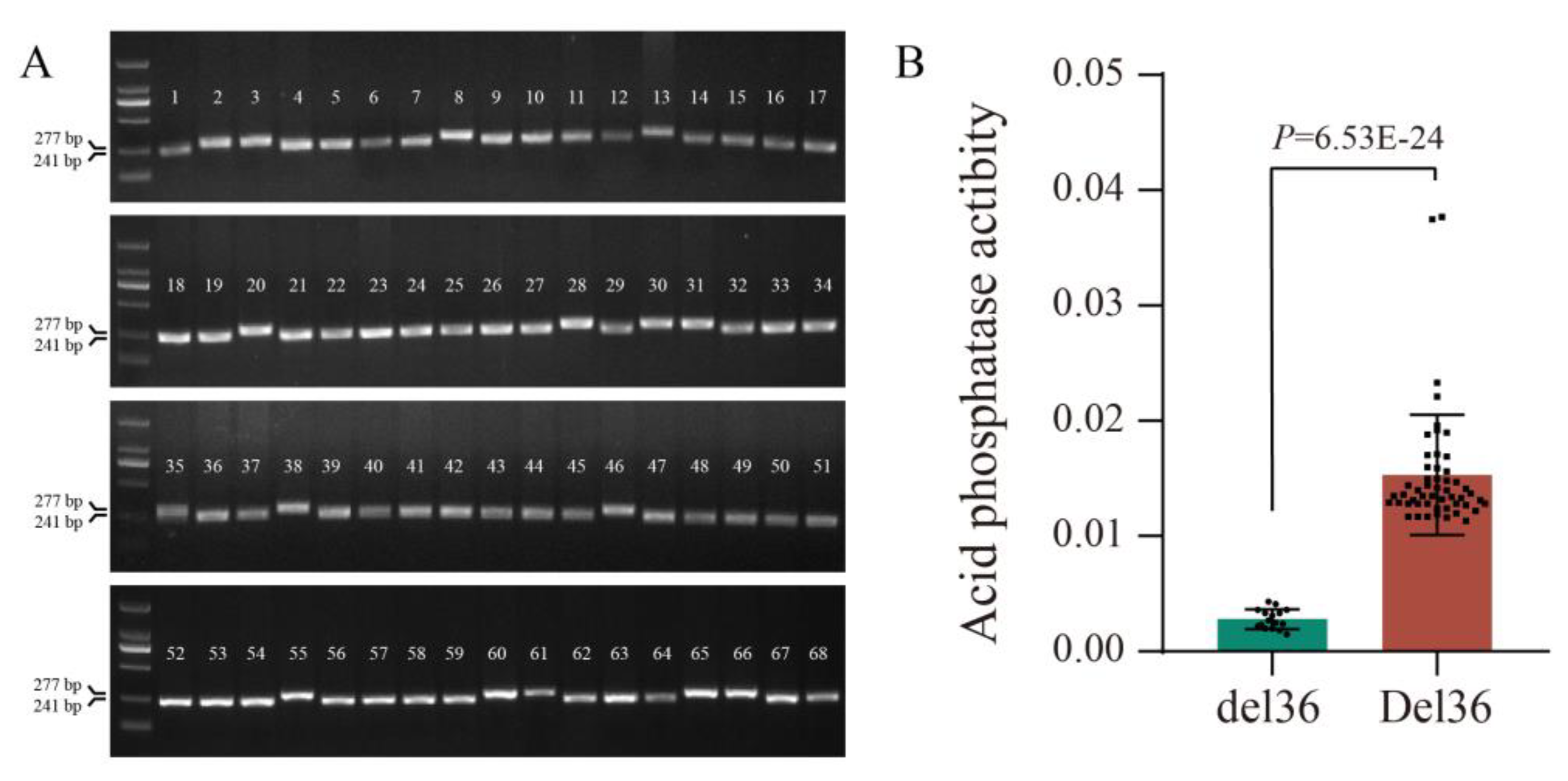
2.5. Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 was Closely Related to APase Activity in Soybean
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.3. Cloning of GmPAP14 cDNA, Genomic DNA and Promoter Sequences in Soybean
4.4. Vector Construction and Plant Transformation
4.5. Histochemical GUS Staining
4.6. Measurement of APase Activity in Transgenic Arabidopsis
4.7. Measurement of P Content in Transgenic Arabidopsis
4.8. Variation Analysis of GmPAP14 in Natural Soybean Populations
4.9. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satheesh, V.; Tahir, A.; Li, J.; Lei, M. Plant phosphate nutrition: Sensing the stress. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Qiu, W.; Gao, W.; Tyerman, S.D.; Shou, H.; Wang, C. OsPAP10c, a novel secreted acid phosphatase in rice, plays an important role in the utilization of external organic phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Ryan, M.H.; Lambers, H.; Siddique, K.H. Phosphorus acquisition and utilisation in crop legumes under global change. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; White, P.J.; Cheng, L. Mechanisms for improving phosphorus utilization efficiency in plants. Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Arredondo, D.L.; Leyva-Gonzalez, M.A.; Gonzalez-Morales, S.I.; Lopez-Bucio, J.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Phosphate nutrition: Improving low-phosphate tolerance in crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.F.; Suriyagoda, L.D.B.; Lambers, H. Tightening the Phosphorus Cycle through Phosphorus-Efficient Crop Genotypes. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, J.; Puga, M.I.; Rojas-Triana, M.; Martinez-Hevia, I.; Diaz, S.; Poza-Carrion, C.; Minambres, M.; Leyva, A. Plant adaptation to low phosphorus availability: Core signaling, crosstalks, and applied implications. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Root Developmental Responses to Phosphorus Nutrition. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1065–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, S.; Tran, L.S. Phosphorus homeostasis in legume nodules as an adaptive strategy to phosphorus deficiency. Plant Sci. 2015, 239, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, M.; Liang, C.; Xue, Y.; Lin, S.; Tian, J. Characterization of Purple Acid Phosphatase Family and Functional Analysis of GmPAP7a/7b Involved in Extracellular ATP Utilization in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Qian, W.; Hurley, B.A.; She, Y.M.; Wang, D.; Plaxton, W.C. Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP12 and AtPAP26: The predominant purple acid phosphatase isozymes secreted by phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Guan, X.; Yang, M.; Law, Y.S.; Voon, C.P.; Yan, J.; Sun, F.; Lim, B.L. Overlapping Functions of the Paralogous Proteins AtPAP2 and AtPAP9 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Liu, K.; Liu, X.; Leggewie, G.; Udvardi, M.; Wang, D. Purple acid phosphatases of Arabidopsis thaliana. Comparative analysis and differential regulation by phosphate deprivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27772–27781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Tian, J.; Li, K.; Shou, H. Identification of rice purple acid phosphatases related to posphate starvation signalling. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Gui, S.; Yang, T.; Walk, T.; Wang, X.; Liao, H. Identification of soybean purple acid phosphatase genes and their expression responses to phosphorus availability and symbiosis. Ann. Bot. 2012, 109, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Munoz, E.; Avendano-Vazquez, A.O.; Montes, R.A.; de Folter, S.; Andres-Hernandez, L.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Sawers, R.J. The maize (Zea mays ssp. mays var. B73) genome encodes 33 members of the purple acid phosphatase family. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Qian, W.; Guo, W.; Gao, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, D.; et al. The Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase AtPAP10 is predominantly associated with the root surface and plays an important role in plant tolerance to phosphate limitation. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1283–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.D.; Carson, I.; Ying, S.; Ellis, K.; Plaxton, W.C. Eliminating the purple acid phosphatase AtPAP26 in Arabidopsis thaliana delays leaf senescence and impairs phosphorus remobilization. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veljanovski, V.; Vanderbeld, B.; Knowles, V.L.; Snedden, W.A.; Plaxton, W.C. Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP26, a vacuolar purple acid phosphatase up-regulated in phosphate-deprived Arabidopsis suspension cells and seedlings. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, B.A.; Tran, H.T.; Marty, N.J.; Park, J.; Snedden, W.A.; Mullen, R.T.; Plaxton, W.C. The dual-targeted purple acid phosphatase isozyme AtPAP26 is essential for efficient acclimation of Arabidopsis to nutritional phosphate deprivation. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Lu, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, C.; Shou, H. OsPAP26 Encodes a Major Purple Acid Phosphatase and Regulates Phosphate Remobilization in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Liao, H.; Wang, X. The purple acid phosphatase GmPAP21 enhances internal phosphorus utilization and possibly plays a role in symbiosis with rhizobia in soybean. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 159, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, H. A purple acid phosphatase, GmPAP33, participates in arbuscule degeneration during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in soybean. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Du, H.; Zhang, C. The Soybean Purple Acid Phosphatase GmPAP14 Predominantly Enhances External Phytate Utilization in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higo, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Korenaga, T. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadouria, J.; Giri, J. Purple acid phosphatases: Roles in phosphate utilization and new emerging functions. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 41, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Yan, G.; Zhang, C. GmPAP4, a novel purple acid phosphatase gene isolated from soybean (Glycine max), enhanced extracellular phytate utilization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, I.B.; Dionisio, G.; Madsen, C.K.; Brinch-Pedersen, H. Barley HvPAPhy_a as transgene provides high and stable phytase activities in mature barley straw and in grains. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 15, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juwattanasomran, R.; Somta, P.; Chankaew, S.; Shimizu, T.; Wongpornchai, S.; Kaga, A.; Srinives, P. A SNP in GmBADH2 gene associates with fragrance in vegetable soybean variety “Kaori” and SNAP marker development for the fragrance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagaya, Y.; Ohmiya, K.; Hattori, T. RAV1, a novel DNA-binding protein, binds to bipartite recognition sequence through two distinct DNA-binding domains uniquely found in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.; Izawa, T.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.; Bradnam, K.; Rose, A.B.; Korf, I. Comparative and functional analysis of intron-mediated enhancement signals reveals conserved features among plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5328–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.Y.; He, Z.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Sun, D.J.; Morris, C.F.; Fuerst, E.P.; Xia, X.C. Allelic variation of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) genes located on chromosomes 2A and 2D and development of functional markers for the PPO genes in common wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Qin, L.; Jin, Y.; et al. THP9 enhances seed protein content and nitrogen-use efficiency in maize. Nature 2022, 612, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.R.; Lubberstedt, T. Functional markers in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariasca-Tanaka, J.; Chin, J.H.; Drame, K.N.; Dalid, C.; Heuer, S.; Wissuwa, M. A novel allele of the P-starvation tolerance gene OsPSTOL1 from African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud) and its distribution in the genus Oryza. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gai, J.; Chang, W.; Zhang, C. Identification of phosphorus starvation tolerant soybean (Glycine max) germplasms. Front. Agric. China 2010, 4, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Du, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, C. Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 Alters Gene Expression to Affect Acid Phosphatase Activity in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065398
Kong Y, Liu Y, Li W, Du H, Li X, Zhang C. Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 Alters Gene Expression to Affect Acid Phosphatase Activity in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065398
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Youbin, Yuan Liu, Wenlong Li, Hui Du, Xihuan Li, and Caiying Zhang. 2023. "Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 Alters Gene Expression to Affect Acid Phosphatase Activity in Soybean" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065398
APA StyleKong, Y., Liu, Y., Li, W., Du, H., Li, X., & Zhang, C. (2023). Allelic Variation in GmPAP14 Alters Gene Expression to Affect Acid Phosphatase Activity in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065398





