Molecular Anatomy of the EML4-ALK Fusion Protein for the Development of Novel Anticancer Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Genetic Composition of the EML4-ALK Fusion Gene
3. Structural Analysis of EML4-ALK
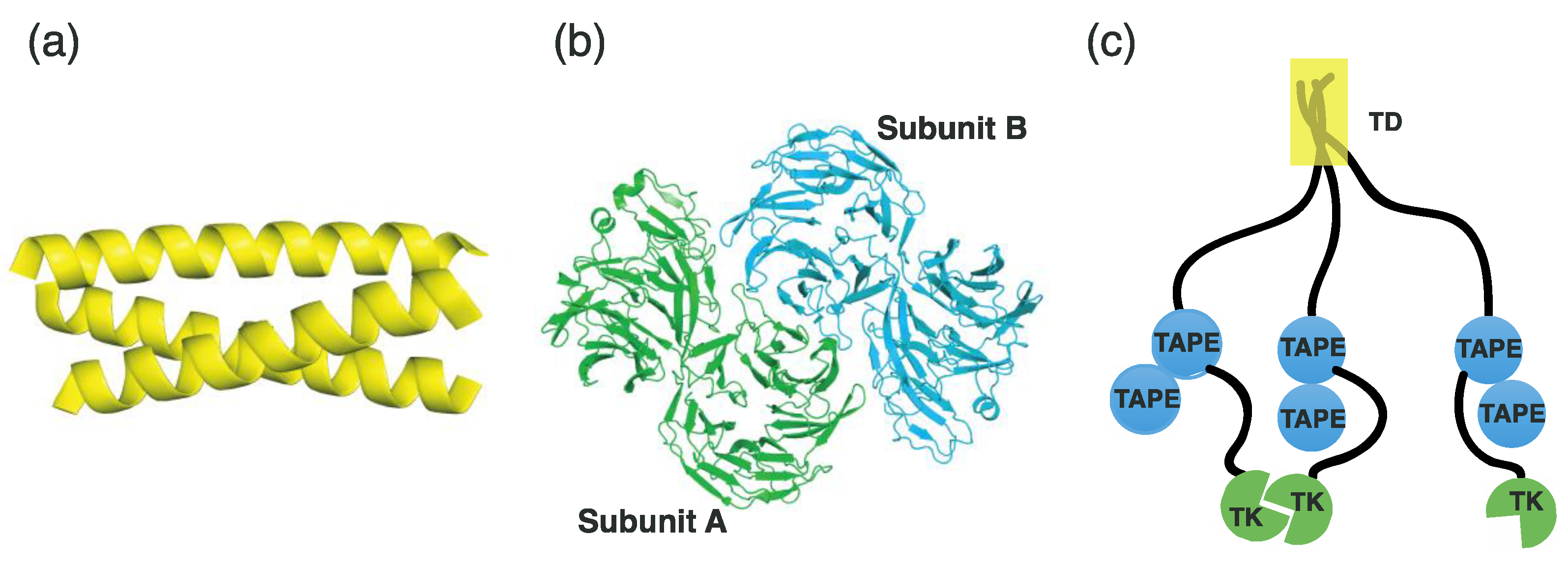
3.1. Overall Architecture of EML
3.2. TK Domain Structure of ALK
3.3. Substrate-Binding Mode of the TK Domain for Catalysis
4. EML4-ALK Inhibitors
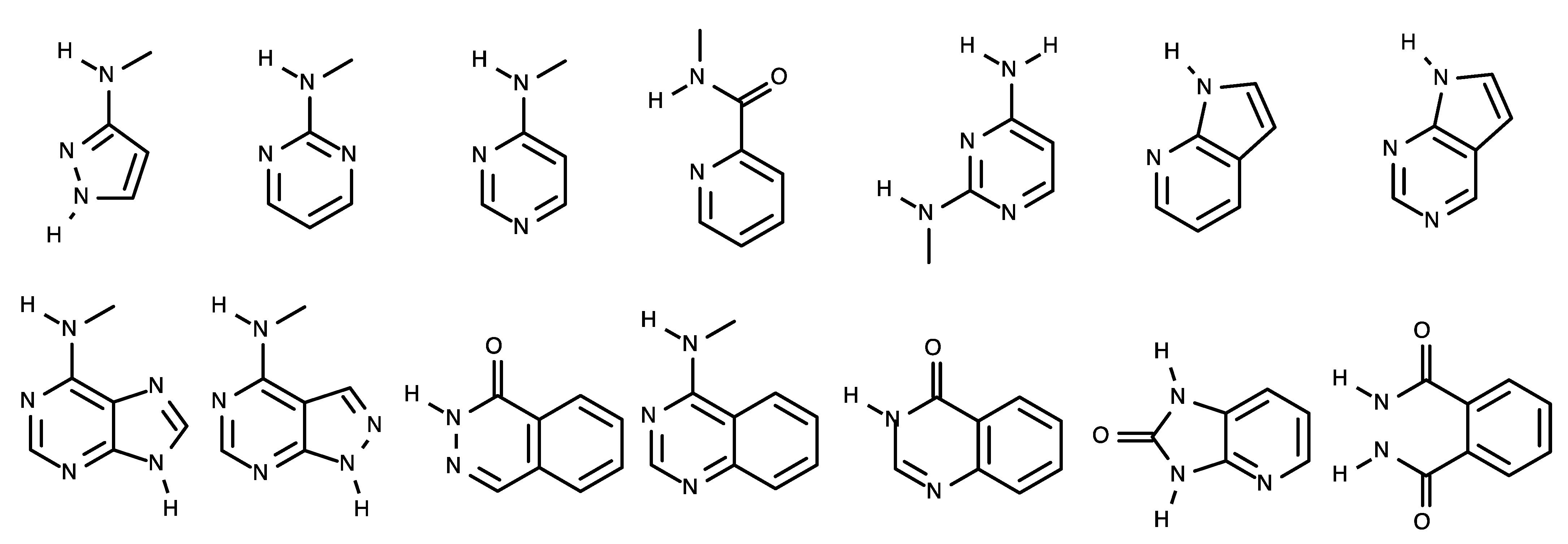
4.1. Representative ALK Inhibitors
4.2. Structures of ALK–Inhibitor Complexes
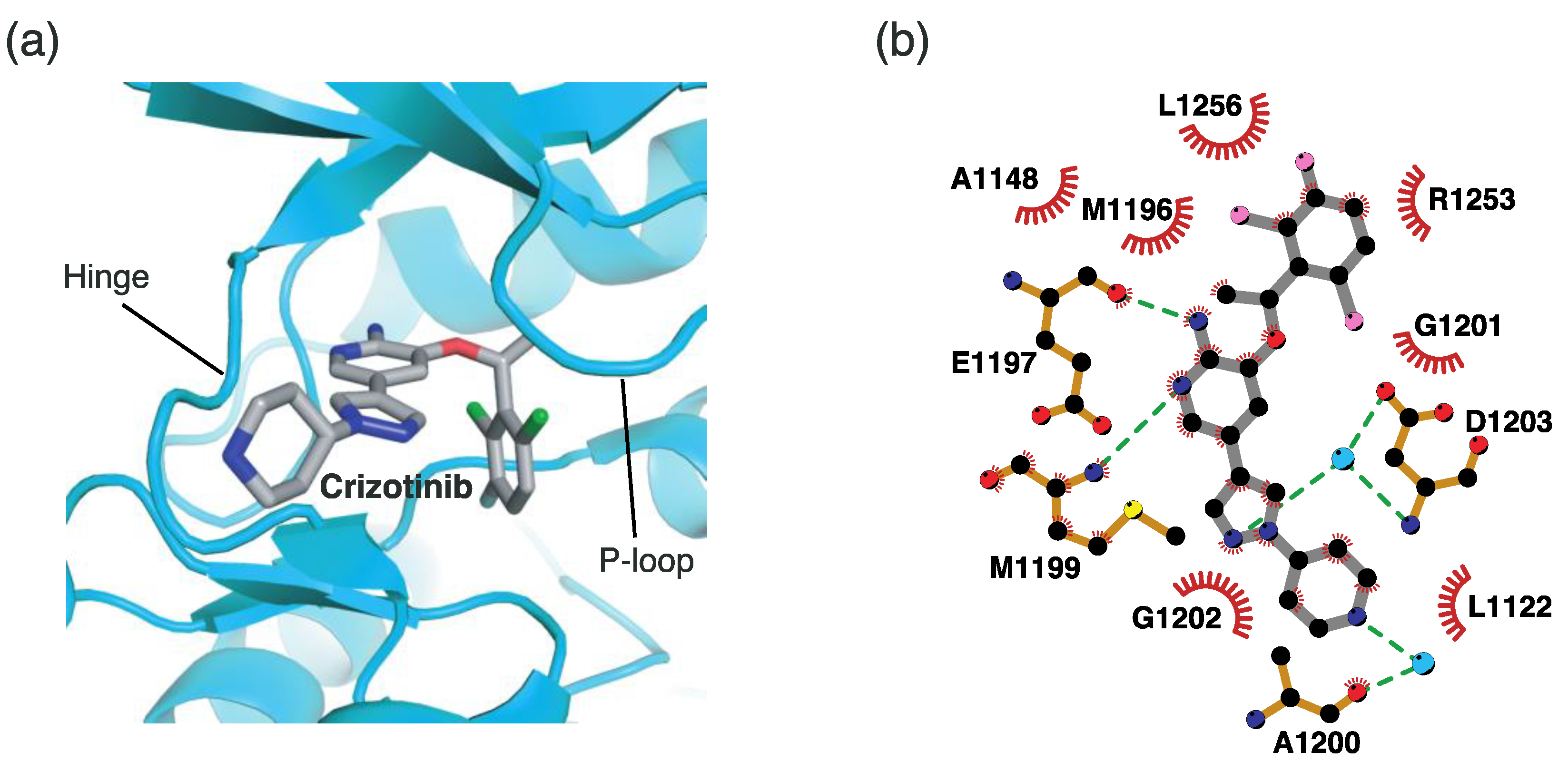
4.2.1. Binding Mode of the ALK–Crizotinib Complex
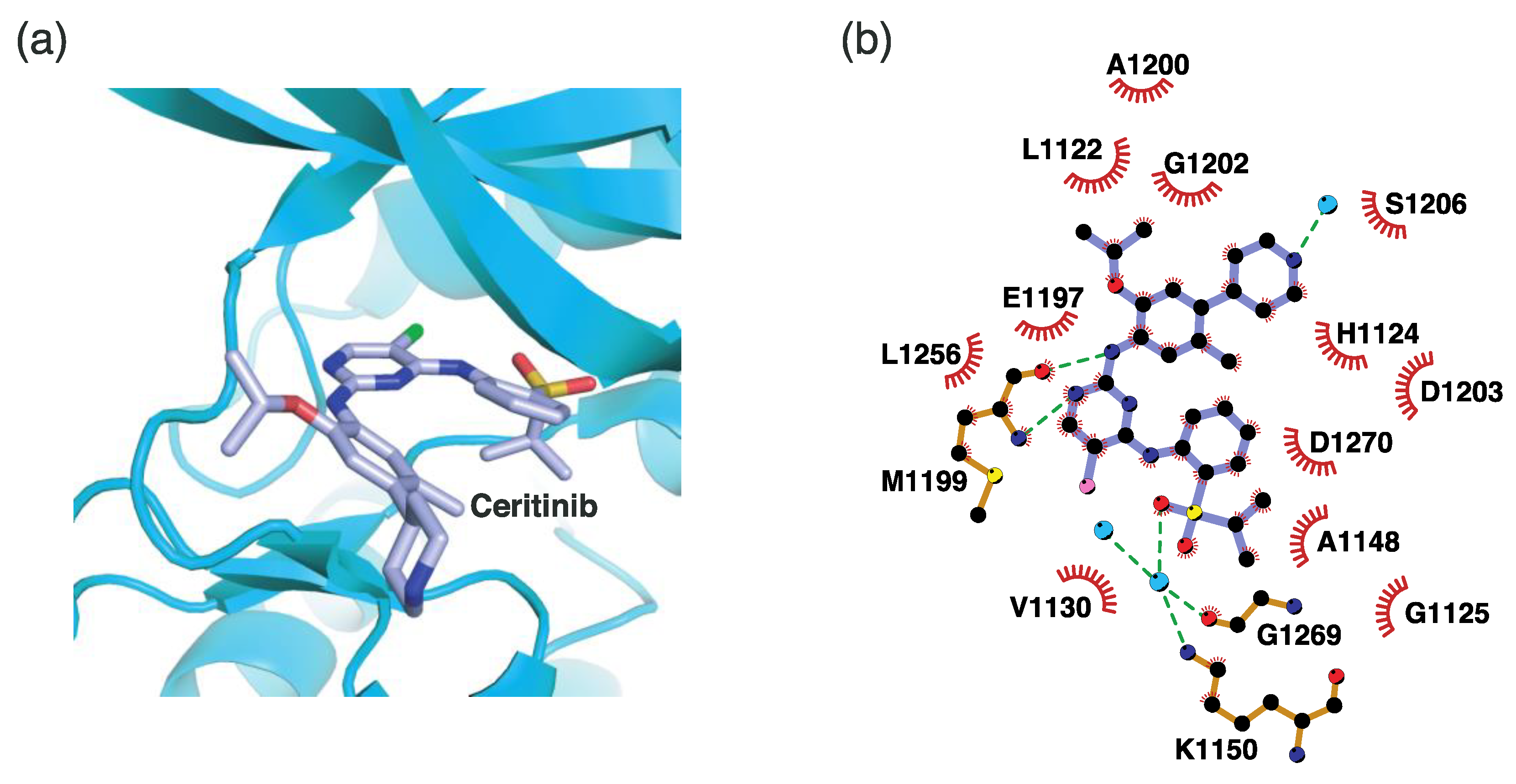
4.2.2. Binding Mode of the ALK–Ceritinib Complex
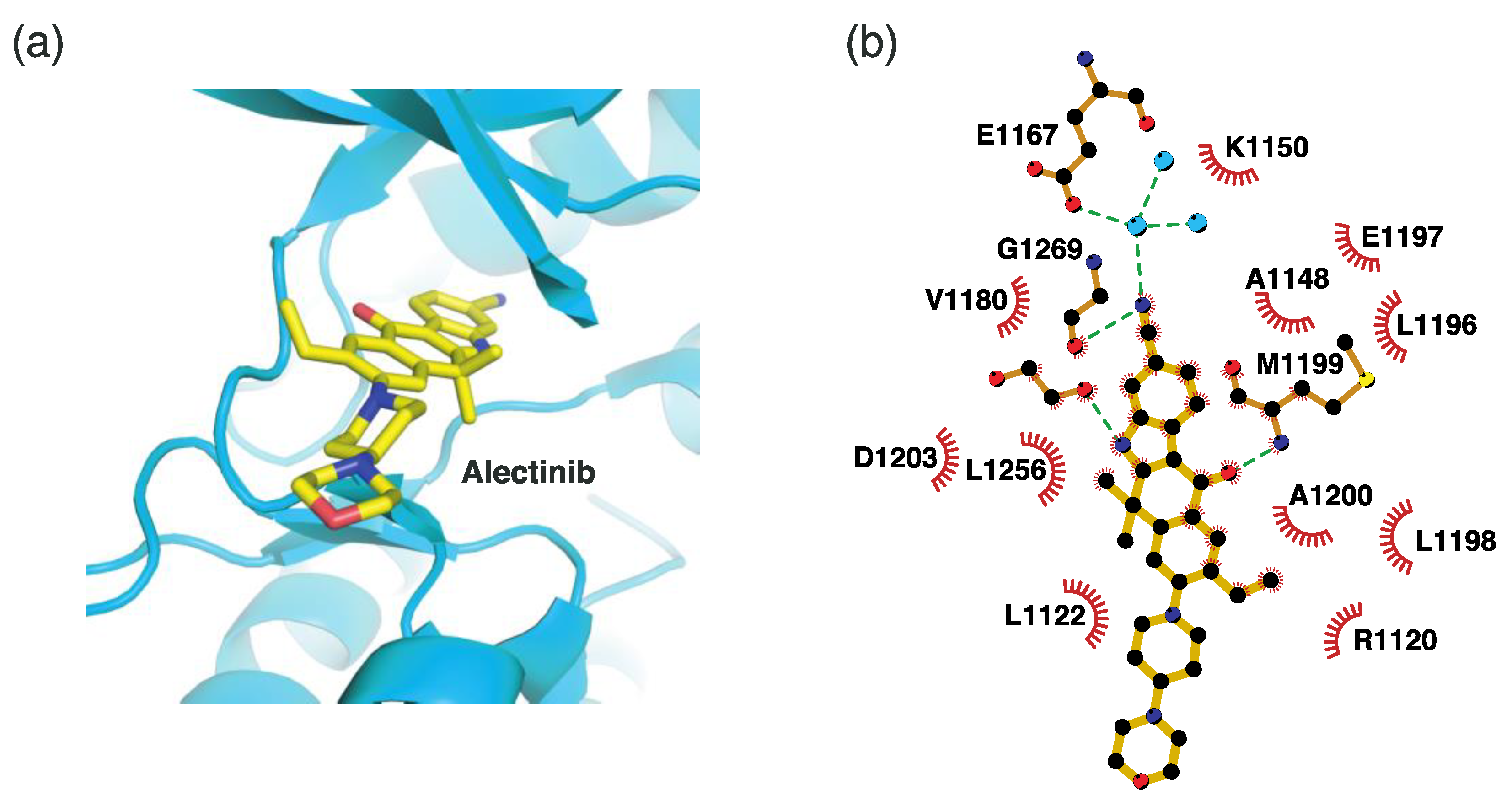
4.2.3. Binding Mode of the ALK–Alectinib Complex
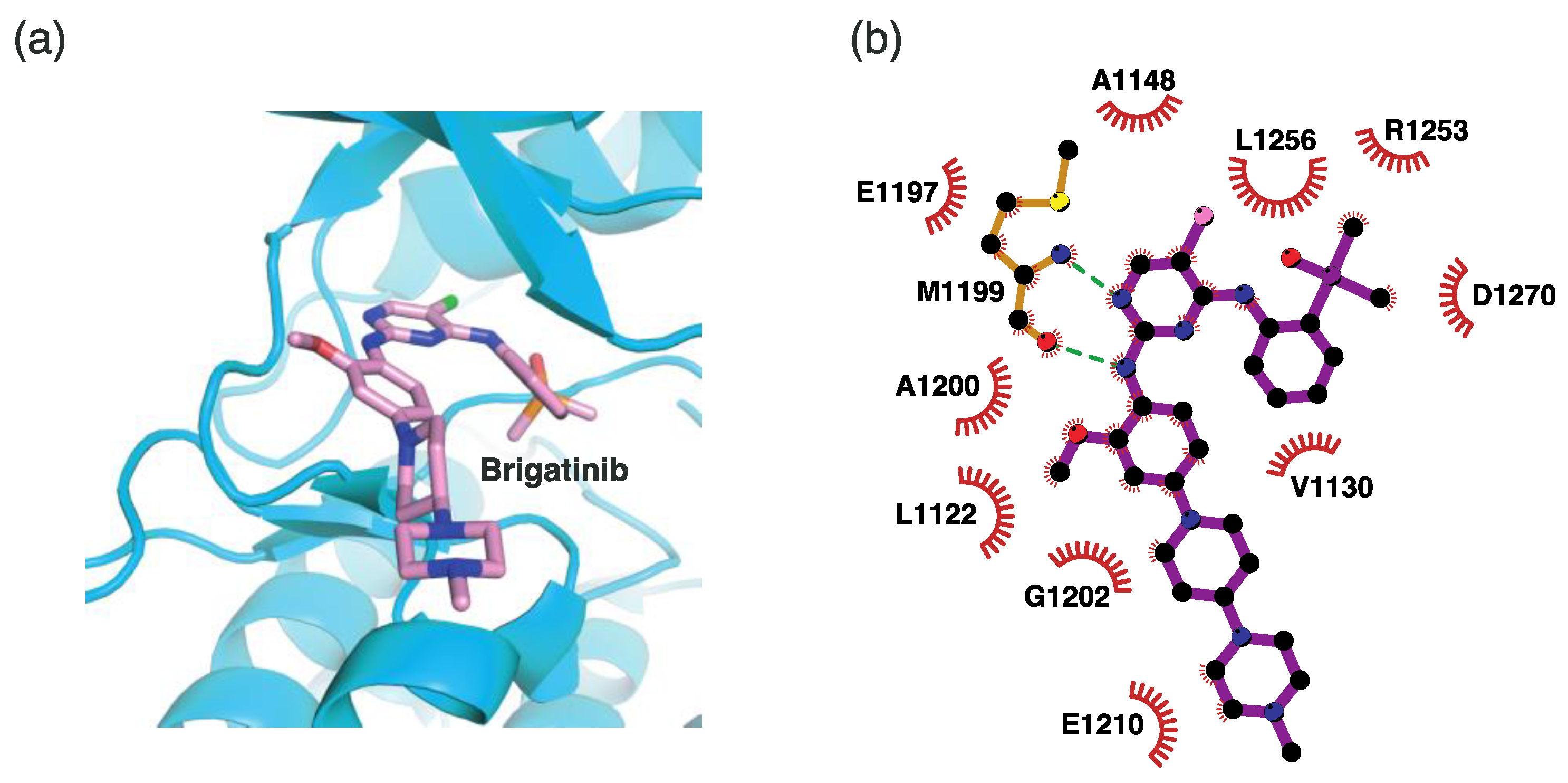
4.2.4. Binding Mode of the ALK–Brigatinib Complex
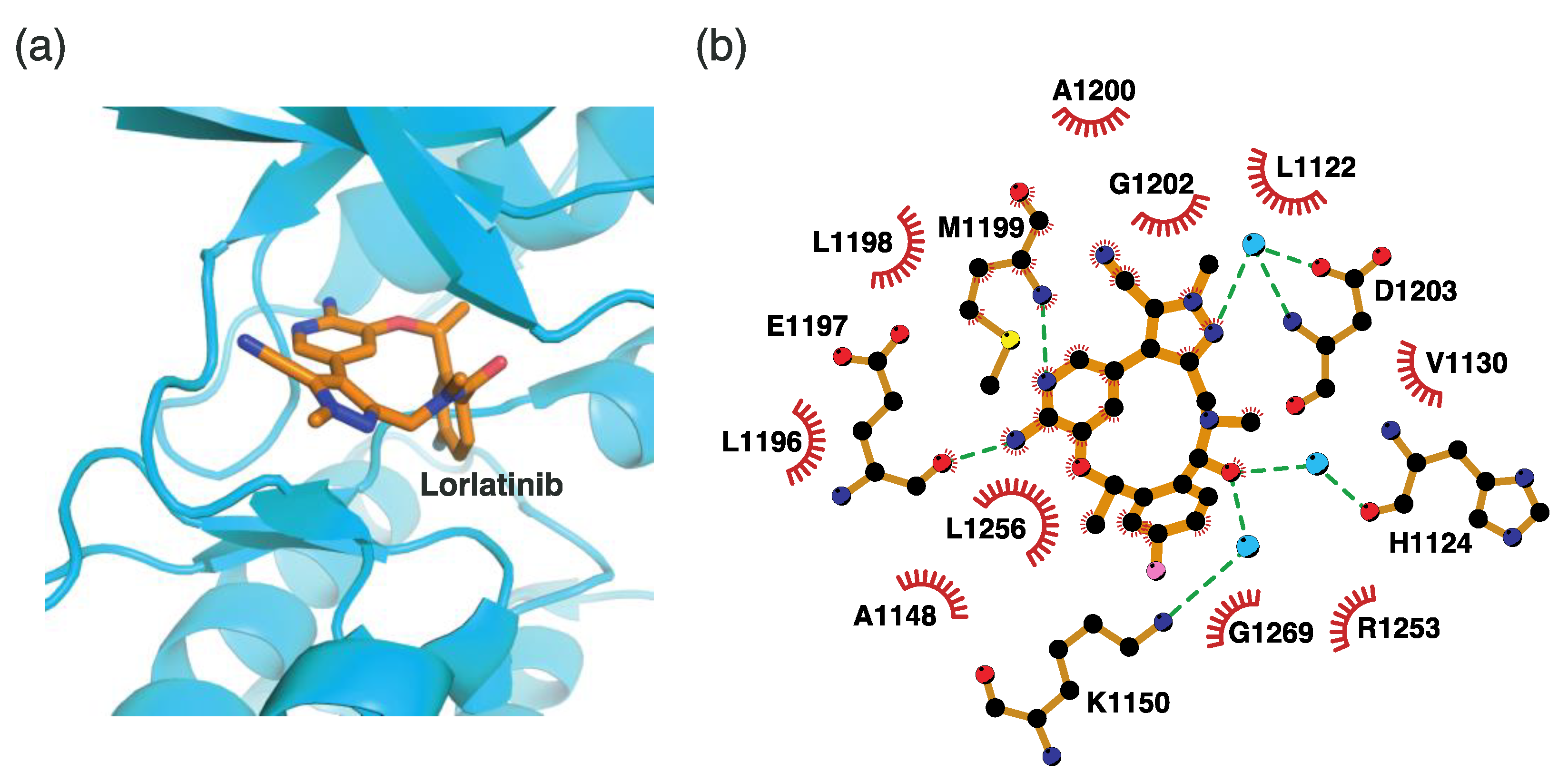
4.2.5. Binding Mode of the ALK–Lorlatinib Complex
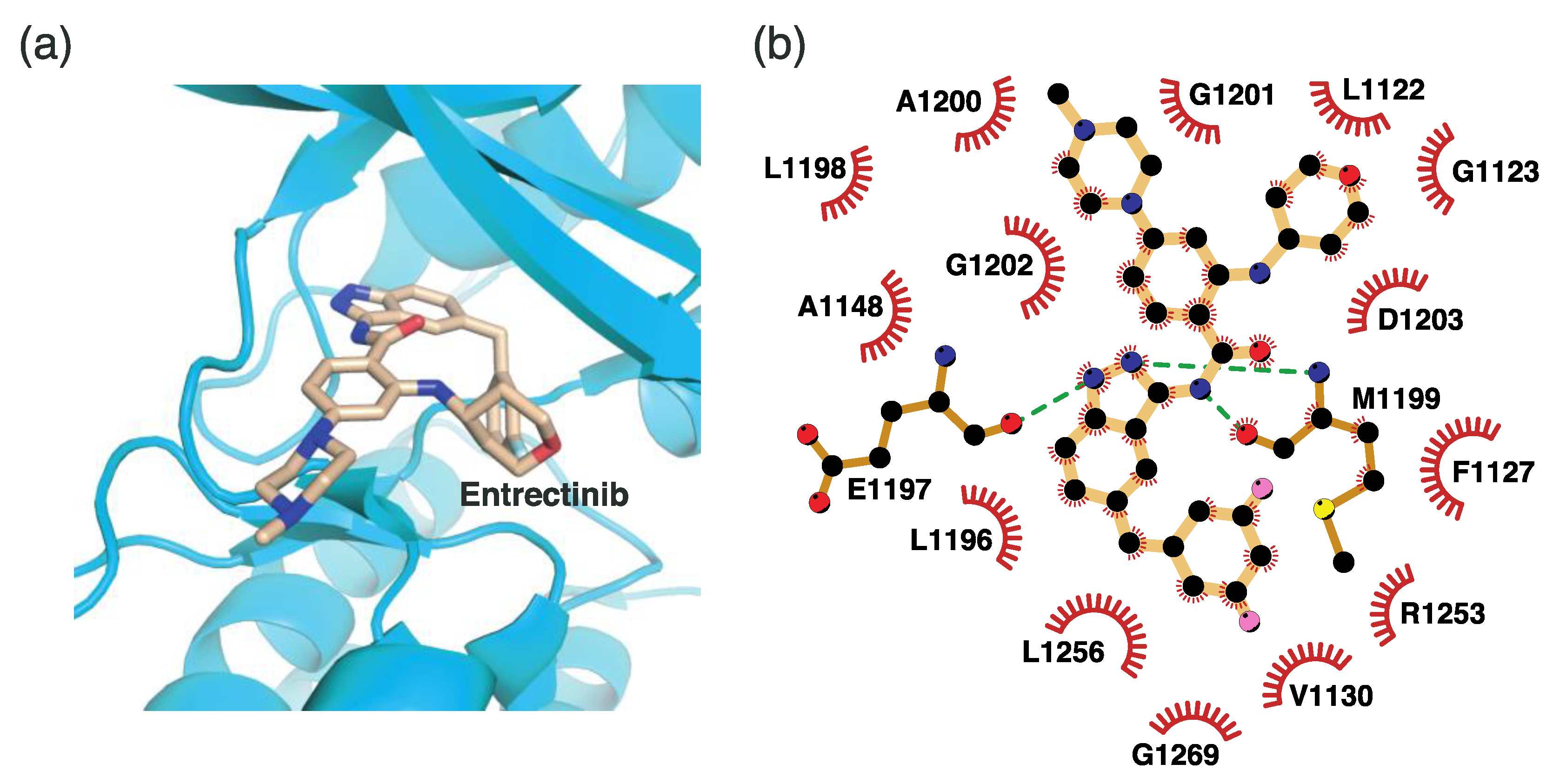
4.2.6. Binding Mode of the ALK–Entrectinib Complex
4.3. Molecular Mechanism of EML-ALK Inhibitor Resistance
5. Strategies for the Development of Novel EML4-ALK Therapies
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sher, T.; Dy, G.K.; Adjei, A.A. Small cell lung cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprenant, K.A.; Dean, K.; McKee, J.; Hake, S. EMAP, an echinoderm microtubule-associated protein found in microtubule-ribosome complexes. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprenant, K.A.; Tuxhorn, J.A.; Daggett, M.A.; Ahrens, D.P.; Hostetler, A.; Palange, J.M.; VanWinkle, C.E.; Livingston, B.T. Conservation of the WD-repeat, microtubule-binding protein, EMAP, in sea urchins, humans, and the nematode C. elegans. Dev. Genes Evol. 2000, 210, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Fujimoto, J.; Semba, T.; Satoh, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Mori, S. Hyperphosphorylation of a novel 80 kDa protein-tyrosine kinase similar to Ltk in a human Ki-1 lymphoma cell line, AMS3. Oncogene 1994, 9, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.; Shapiro, D.N.; Look, A.T.; Saltman, D.L. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1995, 267, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, M.; Dean, M.; Cooper, C.S.; Schmidt, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Blair, D.G.; Vande Woude, G.F. Mechanism of met oncogene activation. Cell 1986, 45, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiora, P.; Marchio, S.; Stella, M.C.; Giai, M.; Belfiore, A.; De Bortoli, M.; Di Renzo, M.F.; Costantino, A.; Sismondi, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Overexpression of the RON gene in human breast carcinoma. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoro, M.M.; Penengo, L.; Minetto, M.; Orecchia, S.; Cilli, M.; Gaudino, G. Point mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain release the oncogenic and metastatic potential of the Ron receptor. Oncogene 1998, 17, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The role of the ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Takada, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Ueno, T.; Haruta, H.; Hamada, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. A mouse model for EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19893–19897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwak, E.L.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.; Maki, R.G.; Ou, S.H.; Dezube, B.J.; Janne, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, H.R.; Li, H.R.; Bruey, J.M.; Scheerle, J.A.; Meloni-Ehrig, A.M.; Kelly, J.C.; Novick, C.; Albitar, M. Exon scanning by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for detection of known and novel EML4-ALK fusion variants in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Soriano, R.; Rivers, C.S.; Mohan, S.; Pandita, A.; Tang, J.; Modrusan, Z. Exon array profiling detects EML4-ALK fusion in breast, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.B.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Zhou, C.; Shreeve, S.M.; Selaru, P.; Polli, A.; et al. Clinical Experience With Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camidge, D.R.; Bang, Y.J.; Kwak, E.L.; Iafrate, A.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Fox, S.B.; Riely, G.J.; Solomon, B.; Ou, S.H.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated results from a phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.T.; Yeap, B.Y.; Solomon, B.J.; Riely, G.J.; Gainor, J.; Engelman, J.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; Ou, S.H.; Butaney, M.; et al. Effect of crizotinib on overall survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ALK gene rearrangement: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.L.; Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Enomoto, M.; Hamada, T.; Haruta, H.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4971–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Inamura, K.; Togashi, Y.; Hatano, S.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y.; et al. Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for EML4-ALK fusion transcripts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6618–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horn, L.; Pao, W. EML4-ALK: Honing in on a new target in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, 4232–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Choi, Y.L.; Togashi, Y.; Soda, M.; Hatano, S.; Inamura, K.; Takada, S.; Ueno, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Satoh, Y. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.J.; Tran-Dube, M.; Shen, H.; Nambu, M.; Kung, P.P.; Pairish, M.; Jia, L.; Meng, J.; Funk, L.; Botrous, I.; et al. Structure based drug design of crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) kinase and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6342–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Johnson, T.W.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Bunker, K.D.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cook, A.S.; Cui, J.J.; Dack, K.N.; et al. Design of potent and selective inhibitors to overcome clinical anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutations resistant to crizotinib. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1170–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Gainor, J.F.; Bergqvist, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Deng, Y.L.; Liu, W.; Dardaei, L.; et al. Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friboulet, L.; Li, N.; Katayama, R.; Lee, C.C.; Gainor, J.F.; Crystal, A.S.; Michellys, P.Y.; Awad, M.M.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.; et al. The ALK inhibitor ceritinib overcomes crizotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, H.; Tsukaguchi, T.; Hiroshima, S.; Kodama, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukami, T.A.; Oikawa, N.; Tsukuda, T.; Ishii, N.; Aoki, Y.; et al. CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.S.; Liu, S.; Zou, D.; Thomas, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Romero, J.; Kohlmann, A.; Li, F.; Qi, J.; et al. Discovery of Brigatinib (AP26113), a Phosphine Oxide-Containing, Potent, Orally Active Inhibitor of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4948–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.L.; Dinh, D.; et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Menichincheri, M.; Ardini, E.; Magnaghi, P.; Avanzi, N.; Banfi, P.; Bossi, R.; Buffa, L.; Canevari, G.; Ceriani, L.; Colombo, M.; et al. Discovery of Entrectinib: A New 3-Aminoindazole As a Potent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK), c-ros Oncogene 1 Kinase (ROS1), and Pan-Tropomyosin Receptor Kinases (Pan-TRKs) inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3392–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.W.; Law, E.W.; Rennalls, L.P.; Busacca, S.; O’Regan, L.; Fry, A.M.; Fennell, D.A.; Bayliss, R. Crystal structure of EML1 reveals the basis for Hsp90 dependence of oncogenic EML4-ALK by disruption of an atypical beta-propeller domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, M.W.; O’Regan, L.; Roth, D.; Montgomery, J.M.; Straube, A.; Fry, A.M.; Bayliss, R. Microtubule association of EML proteins and the EML4-ALK variant 3 oncoprotein require an N-terminal trimerization domain. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.L.; Soda, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Ueno, T.; Takashima, J.; Nakajima, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Hamada, T.; Haruta, H.; et al. EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Koivunen, J.; Ogino, A.; Yanagita, M.; Nikiforow, S.; Zheng, W.; Lathan, C.; Marcoux, J.P.; Du, J.; Okuda, K.; et al. A novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doebele, R.C.; Pilling, A.B.; Aisner, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Le, A.T.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Kondo, K.L.; Linderman, D.J.; Heasley, L.E.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katayama, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Khan, T.M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Solomon, B.J.; Halmos, B.; Jessop, N.A.; Wain, J.C.; Yeo, A.T.; Benes, C.; et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rolfo, C.; Passiglia, F.; Castiglia, M.; Raez, L.E.; Germonpre, P.; Gil-Bazo, I.; Zwaenepoel, K.; De Wilde, A.; Bronte, G.; Russo, A.; et al. ALK and crizotinib: After the honeymoon…what else? Resistance mechanisms and new therapies to overcome it. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eichenmuller, B.; Everley, P.; Palange, J.; Lepley, D.; Suprenant, K.A. The human EMAP-like protein-70 (ELP70) is a microtubule destabilizer that localizes to the mitotic apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepley, D.M.; Palange, J.M.; Suprenant, K.A. Sequence and expression patterns of a human EMAP-related protein-2 (HuEMAP-2). Gene 1999, 237, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegha-Dunghu, J.; Neumann, B.; Reber, S.; Krause, R.; Erfle, H.; Walter, T.; Held, M.; Rogers, P.; Hupfeld, K.; Ruppert, T.; et al. EML3 is a nuclear microtubule-binding protein required for the correct alignment of chromosomes in metaphase. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollmann, M.; Parwaresch, R.; Adam-Klages, S.; Kruse, M.L.; Buck, F.; Heidebrecht, H.J. Human EML4, a novel member of the EMAP family, is essential for microtubule formation. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.R.; Yeoh, S.; Jackson, G.; Bayliss, R. EML4-ALK Variants: Biological and Molecular Properties, and the Implications for Patients. Cancers 2017, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, L.F.; Chen, H.; Emkey, R.; Whittington, D.A. The R1275Q neuroblastoma mutant and certain ATP-competitive inhibitors stabilize alternative activation loop conformations of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37447–37457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.C.; Jia, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, X.; Ng, K.; Ambing, E.; Gao, M.Y.; Hua, S.; Chen, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Crystal structure of the ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) catalytic domain. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, H.Y.; Li, Q.; Engstrom, L.D.; West, M.; Appleman, V.; Wong, K.A.; McTigue, M.; Deng, Y.L.; Liu, W.; Brooun, A.; et al. PF-06463922 is a potent and selective next-generation ROS1/ALK inhibitor capable of blocking crizotinib-resistant ROS1 mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3493–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forde, P.M.; Rudin, C.M. Crizotinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert. Opin. Pharm. 2012, 13, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J. Clinical use of crizotinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Biologics 2013, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deeks, E.D. Ceritinib: A Review in ALK-Positive Advanced NSCLC. Target. Oncol. 2016, 11, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Alectinib: A review of its use in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Drugs 2015, 75, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M.; Ge, Y.; Sukari, A.; Kukreja, G.; Ou, S.I. A user’s guide to lorlatinib. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 151, 102969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Banfi, P.; Bosotti, R.; De Ponti, C.; Pulci, R.; Ballinari, D.; Ciomei, M.; Texido, G.; Degrassi, A.; et al. Entrectinib, a Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor with Activity in Multiple Molecularly Defined Cancer Indications. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, L.; Klug-Mcleod, J.; Rai, B.; Lunney, E.A. Kinase hinge binding scaffolds and their hydrogen bond patterns. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, D.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Moebitz, H. Ten things you should know about protein kinases: IUPHAR Review 14. Br. J. Pharm. 2015, 172, 2675–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gainor, J.F.; Varghese, A.M.; Ou, S.H.; Kabraji, S.; Awad, M.M.; Katayama, R.; Pawlak, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Yeap, B.Y.; Riely, G.J.; et al. ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: An analysis of 1683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorre, M.E.; Mohammed, M.; Ellwood, K.; Hsu, N.; Paquette, R.; Rao, P.N.; Sawyers, C.L. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001, 293, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.J.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, J.; Stover, E.H.; Boulton, C.L.; Gotlib, J.; Legare, R.D.; Amaral, S.M.; Curley, D.P.; Duclos, N.; Rowan, R.; Kutok, J.L.; et al. PKC412 overcomes resistance to imatinib in a murine model of FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha-induced myeloproliferative disease. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daub, H.; Specht, K.; Ullrich, A. Strategies to overcome resistance to targeted protein kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blencke, S.; Zech, B.; Engkvist, O.; Greff, Z.; Orfi, L.; Horvath, Z.; Keri, G.; Ullrich, A.; Daub, H. Characterization of a conserved structural determinant controlling protein kinase sensitivity to selective inhibitors. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, J.; Mentens, N.; Furet, P.; Fabbro, D.; Clark, J.J.; Griffin, J.D.; Marynen, P.; Gilliland, D.G. Prediction of resistance to small molecule FLT3 inhibitors: Implications for molecularly targeted therapy of acute leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6385–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dibb, N.J.; Dilworth, S.M.; Mol, C.D. Switching on kinases: Oncogenic activation of BRAF and the PDGFR family. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, R.; Choi, J.; Fennell, D.A.; Fry, A.M.; Richards, M.W. Molecular mechanisms that underpin EML4-ALK driven cancers and their response to targeted drugs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1209–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, R.; Khan, T.M.; Benes, C.; Lifshits, E.; Ebi, H.; Rivera, V.M.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Iafrate, A.J.; Engelman, J.A.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic strategies to overcome crizotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancers harboring the fusion oncogene EML4-ALK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7535–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Normant, E.; Paez, G.; West, K.A.; Lim, A.R.; Slocum, K.L.; Tunkey, C.; McDougall, J.; Wylie, A.A.; Robison, K.; Caliri, K.; et al. The Hsp90 inhibitor IPI-504 rapidly lowers EML4-ALK levels and induces tumor regression in ALK-driven NSCLC models. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sang, J.; Acquaviva, J.; Friedland, J.C.; Smith, D.L.; Sequeira, M.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, L.; Lovly, C.M.; Jimenez, J.P.; et al. Targeted inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 overcomes ALK inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murano, H.; Matsubara, T.; Takahashi, I.; Hara, M. A purine-type heat shock protein 90 inhibitor promotes the heat shock response in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucherat, O.; Chabot, S.; Paulin, R.; Trinh, I.; Bourgeois, A.; Potus, F.; Lampron, M.C.; Lambert, C.; Breuils-Bonnet, S.; Nadeau, V.; et al. HDAC6: A Novel Histone Deacetylase Implicated in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucherat, O.; Peterlini, T.; Bourgeois, A.; Nadeau, V.; Breuils-Bonnet, S.; Boilet-Molez, S.; Potus, F.; Meloche, J.; Chabot, S.; Lambert, C.; et al. Mitochondrial HSP90 Accumulation Promotes Vascular Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özgür, A. Investigation of anticancer activities of STA-9090 (ganetespib) as a second generation HSP90 inhibitor in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells. J. Chemother. 2021, 33, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.Y.; Nepali, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang YS, H.; Hsu, K.C.; Yen, Y.; Pan, S.L.; Liou, J.P.; Lee, S.B. A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor MPT0L184 dysregulates cell-cycle checkpoints and initiates unscheduled mitotic signaling. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 138, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakasa, H.; Tsugami, Y.; Koyama, T.; Han, L.; Nishimura, T.; Isobe, N.; Kobayashi, K. Adverse Effects of High Temperature On Mammary Alveolar Development In Vitro. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2022, 27, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Fong, S.Y.; Shon, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Brooks, R.; Lahens, N.F.; Chen, D.; Dang, C.V.; Field, J.M.; Sehgal, A. Time-of-day specificity of anticancer drugs may be mediated by circadian regulation of the cell cycle. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heider, M.; Eichner, R.; Stroh, J.; Morath, V.; Kuisl, A.; Zecha, J.; Lawatscheck, J.; Baek, K.; Garz, A.K.; Rudelius, M.; et al. The IMiD target CRBN determines HSP90 activity toward transmembrane proteins essential in multiple myeloma. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 1170–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, B.; Bornmann, W.G.; Pellicena, P.; Schindler, T.; Veach, D.R.; Miller, W.T.; Clarkson, B.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal structures of the kinase domain of c-Abl in complex with the small molecule inhibitors PD173955 and imatinib (STI-571). Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.; Yamazaki, Y.; Chand, D.; van Dijk, J.R.; Ruuth, K.; Palmer, R.H.; Hallberg, B. Novel Mechanisms of ALK Activation Revealed by Analysis of the Y1278S Neuroblastoma Mutation. Cancers 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, N.; Sasaki, T.; Okumura, S.; Minami, Y.; Chiba, S.; Ohsaki, Y. Monomerization of ALK Fusion Proteins as a Therapeutic Strategy in ALK-Rearranged Non-small Cell Lung Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Generation | Generic Name | Trade Name | Chemical Structure | Target | Type | Approval Year | Approval Country | PDB ID a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Crizotinib | Xalkori | 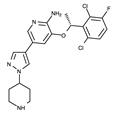 | ALK/ROS1 | I | 2011 (ALK) 2016 (ROS1) | US/EU | 2XP2, 2YFX, 4ANQ, 4ANS, 5AAA, 5AAB, 5AAC |
| II | Ceritinib | Zykadia |  | ALK | I | 2014 | US | 4MKC |
| II | Alectinib | Alecensa | 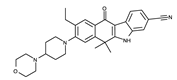 | ALK | I | 2014/ 2015/ 2017 | Japan/ US/ EU | 3AOX |
| II | Brigatinib | Alunbrig |  | ALK/EGFR | I | 2016 | US | 6MX8 |
| III | Lorlatinib | Lorbrena | 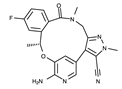 | ALK/ROS1 | I | 2015/2019 | US/EU | 4CLI, 4CLJ, 5AA8, 5AA9, 5A9U |
| III | Entrectinib | Rozlytrek | 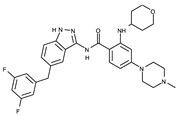 | ALK/ROS1/TRK b | I | 2019/2020 | US/ Australia/EU | 5FTO |
| Name | Chemical Structure | Potency a | Molecular Weight | Kd | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KW-24783 | 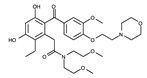 | ++++ b | 574.7 | 3.8 nM | [75] |
| Onalespib | 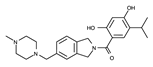 | +++ c | 409.5 | 18 nM | [75,76,77] |
| Ganetespib | 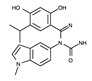 | +++ | 364.4 | 4 nM | [75,78] |
| BIIB021 | 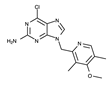 | ++++ | 318.8 | 1.7 nM | [75,79] |
| Luminespib | 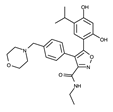 | +++ | 465.5 | 13 nM | [75,80] |
| Tanespimycin | 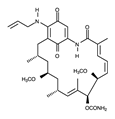 | +++ | 585.7 | 5 nM | [81] |
| HSP990 | 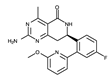 | ++++ | 379.4 | 0.6 nM | [82] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheon, S.Y.; Kwon, S. Molecular Anatomy of the EML4-ALK Fusion Protein for the Development of Novel Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065821
Cheon SY, Kwon S. Molecular Anatomy of the EML4-ALK Fusion Protein for the Development of Novel Anticancer Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065821
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheon, So Yeong, and Sunghark Kwon. 2023. "Molecular Anatomy of the EML4-ALK Fusion Protein for the Development of Novel Anticancer Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065821
APA StyleCheon, S. Y., & Kwon, S. (2023). Molecular Anatomy of the EML4-ALK Fusion Protein for the Development of Novel Anticancer Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065821




