Palmitic Acid Inhibits Myogenic Activity and Expression of Myosin Heavy Chain MHC IIb in Muscle Cells through Phosphorylation-Dependent MyoD Inactivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
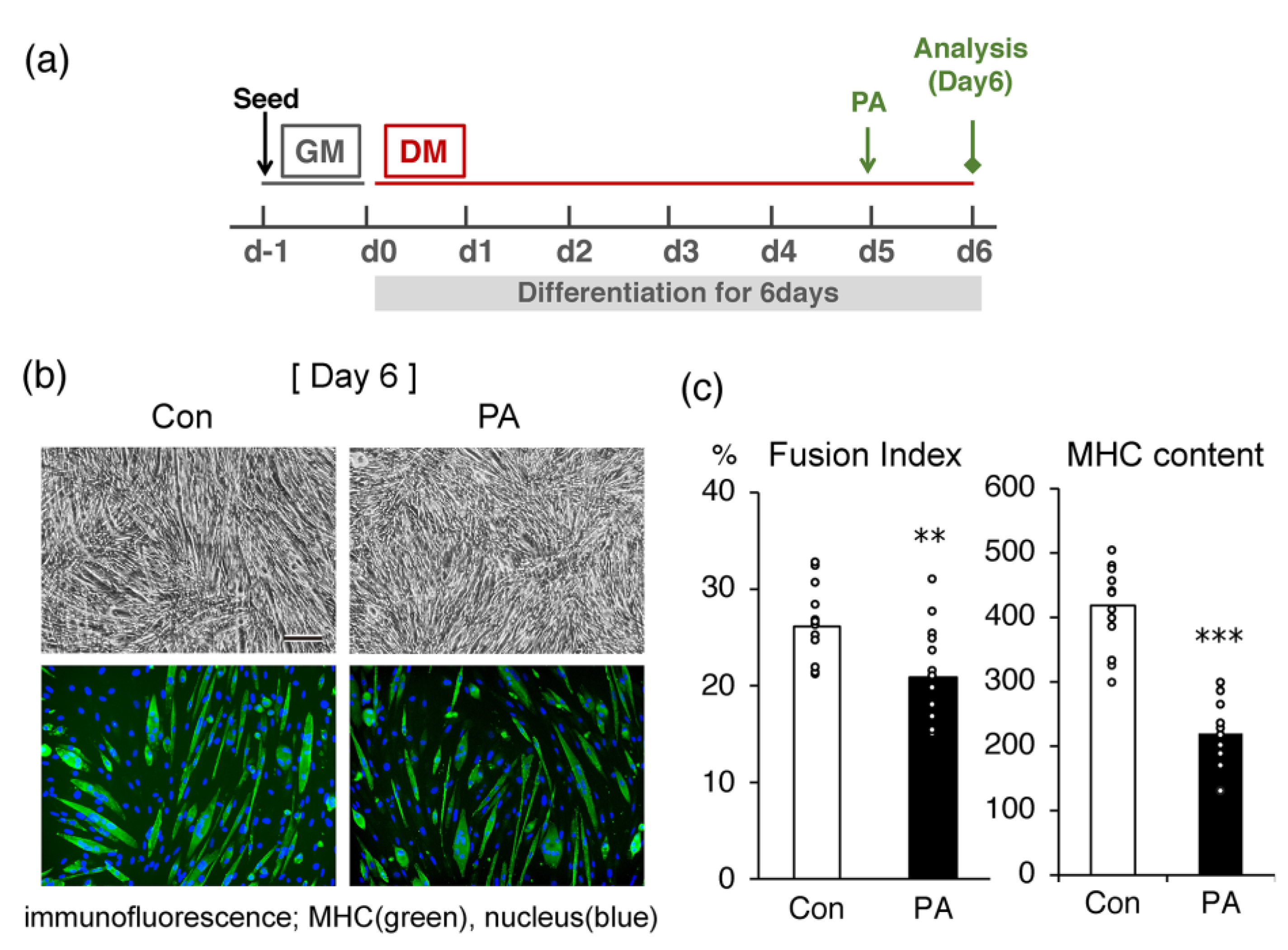
2.1. PA Inhibits the Terminal Differentiation of Myoblasts into Myotubes
2.2. PA Primarily Inhibits the Expression of MHC IIb in Differentiated Cells
2.3. The Inhibitory Effect of PA on MHC Expression in Myotubes Is Not Mediated via TLR-4
2.4. PA Suppresses MyoD-Induced Activation of Myh4 Promoter in C2C12 Cells
2.5. The Inhibitory Effect of PA on Myh4 Promoter Activation by MyoD Requires Ser Residues That Are Targets for Phosphorylation
2.6. Inhibition of PKC Partially Recovers PA-Induced Inhibition of MHC IIb Gene Expression in C2C12 Myotubes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Palmitic Acid Complex Preparation
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis Using Real-Time PCR
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Immunofluorescence and Calculation of the Myogenic Index
4.7. Reporter Assays
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.J.; Paolisso, G.; Abbatecola, A.M.; Corsonello, A.; Bustacchini, S.; Strollo, F.; Lattanzio, F. Frailty and muscle metabolism dysregulation in the elderly. Biogerontology 2010, 11, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, M.; Landi, F.; Vellas, B.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Sarcopenia and physical frailty: Two sides of the same coin. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, S.; Luo, L.; Guang, L.; Liang, K.; Ma, W.; et al. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: Descriptive review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivlin, R.S. Keeping the young-elderly healthy: Is it too late to improve our health through nutrition? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1572S–1576S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C.; Wang, Z.M.; Heymsfield, S.B. Skeletal muscle mass and aging: Regional and whole-body measurement methods. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 26, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slawik, M.; Vidal-Puig, A.J. Adipose tissue expandability and the metabolic syndrome. Genes Nutr. 2007, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A.B. What is lipotoxicity? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.N.; Choi, K.M. The implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity on cardiometabolic disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Choi, K.M. Sarcopenic obesity, insulin resistance, and their implications in cardiovascular and metabolic consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Trompier, D.; Andreoletti, P.; Le Borgne, F.; Demarquoy, J.; Lizard, G. Fatty acids-induced lipotoxicity and inflammation. Curr. Drug. Metab. 2012, 13, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. Palmitic acid: Physiological role, metabolism and nutritional implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.; Hu, X.; Gong, R.H.; Huang, C.; Chen, M.; Wong, H.L.X.; Bian, Z.; Kwan, H.Y. Palmitic acid is an intracellular signaling molecule involved in disease development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2547–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, D.; Montecucco, F.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21630–21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, B.D.; Rahnert, J.A.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, B.; Woodworth-Hobbs, M.E.; Price, S.R. Palmitate-induced ER stress and inhibition of protein synthesis in cultured myotubes does not require toll-like receptor 4. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth-Hobbs, M.E.; Hudson, M.B.; Rahnert, J.A.; Zheng, B.; Franch, H.A.; Price, S.R. Docosahexaenoic acid prevents palmitate-induced activation of proteolytic systems in C2C12 myotubes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deldicque, L.; Cani, P.D.; Philp, A.; Raymackers, J.M.; Meakin, P.J.; Ashford, M.L.; Delzenne, N.M.; Francaux, M.; Baar, K. The unfolded protein response is activated in skeletal muscle by high-fat feeding: Potential role in the downregulation of protein synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E695–E705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, K.R.; McMillan, J.D.; Kumar, A. Emerging roles of er stress and unfolded protein response pathways in skeletal muscle health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Min, K.H.; Lee, W. Palmitic acid-induced MiR-429-3p impairs myoblast differentiation by downregulating cfl2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Lee, W. MiR-320-3p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of myogenic progenitor cells by modulating actin remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschenes, M.R. Effects of aging on muscle fibre type and size. Sports Med. 2004, 34, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Williams, J.; Atherton, P.; Larvin, M.; Lund, J.; Narici, M. Sarcopenia, dynapenia, and the impact of advancing age on human skeletal muscle size and strength; a quantitative review. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.S.; Justice, J.N.; Thompson, L. Lipotoxicity, aging, and muscle contractility: Does fiber type matter? Geroscience 2019, 41, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.S.; Jones, D.A.; Wagenmakers, A.J. Network distribution of mitochondria and lipid droplets in human muscle fibres. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortreed, K.E.; Krause, M.P.; Huang, J.H.; Dhanani, D.; Moradi, J.; Ceddia, R.B.; Hawke, T.J. Muscle-specific adaptations, impaired oxidative capacity and maintenance of contractile function characterize diet-induced obese mouse skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiaffino, S.; Reggiani, C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1447–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagopal, P.; Schimke, J.C.; Ades, P.; Adey, D.; Nair, K.S. Age effect on transcript levels and synthesis rate of muscle MHC and response to resistance exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E203–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.R.; Vittone, J.L.; Bigelow, M.L.; Proctor, D.N.; Coenen-Schimke, J.M.; Rys, P.; Nair, K.S. Changes in myosin heavy chain mRNA and protein expression in human skeletal muscle with age and endurance exercise training. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Parr, T.; Brameld, J.M. Myosin heavy chain mrna isoforms are expressed in two distinct cohorts during C2C12 myogenesis. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2012, 32, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.H.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, J.Y. Mechanisms for the activation of toll-like receptor 2/4 by saturated fatty acids and inhibition by docosahexaenoic acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.T.; Snyder, E.C.; Patterson, M.N.; Swoap, S.J. An E-box within the MHC IIb gene is bound by MyoD and is required for gene expression in fast muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, C1069–C1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.N.; Dias, P.; Houghton, P.J. Mutation of Thr115 in MyoD positively regulates function in murine fibroblasts and human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1998, 9, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, A.; Wang, Q.; Goebl, M.G.; Harrington, M.A. Phosphorylation of nuclear myod is required for its rapid degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 4994–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzmann, M.; Vandromme, M.; Schaeffer, V.; Carnac, G.; Labbe, J.C.; Lamb, N.; Fernandez, A. Cdk1- and Cdk2-mediated phosphorylation of MyoD Ser200 in growing C2 myoblasts: Role in modulating MyoD half-life and myogenic activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintignac, L.A.; Sirri, V.; Leibovitch, M.P.; Lecluse, Y.; Castedo, M.; Metivier, D.; Kroemer, G.; Leibovitch, S.A. Mutant myod lacking cdc2 phosphorylation sites delays M-phase entry. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, L.J.; Davies, J.D.; Philpott, A. Myod phosphorylation on multiple C terminal sites regulates myogenic conversion activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 481, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Sharples, A.P.; Al-Shanti, N.; Stewart, C.E. Omega-3 fatty acid epa improves regenerative capacity of mouse skeletal muscle cells exposed to saturated fat and inflammation. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, F.; Ji, X.; Yu, H.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, F.; Bao, Z. Oleate ameliorates palmitate-induced impairment of differentiative capacity in C2C12 myoblast cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2021, 30, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.N.; Lyu, A.K.; Chen, J.L.; Sun, Y.; Lyu, Q.; Zhao, Y.X.; Guo, A.; Liao, Z.Y.; et al. Type 2 diabetes-induced overactivation of p300 contributes to skeletal muscle atrophy by inhibiting autophagic flux. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, L.R.; Fiamoncini, J.; Hirabara, S.M.; Procopio, J.; Cambiaghi, T.D.; Pinheiro, C.H.; Lopes, L.R.; Curi, R. Updating the effects of fatty acids on skeletal muscle. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Urso, C.J.; Jadeja, V. Saturated fatty acids in obesity-associated inflammation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, C.A.; Tapscott, S.J. MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 16, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.M.; Koishi, K.; Rudnicki, M.; Maggs, A.M. MyoD protein is differentially accumulated in fast and slow skeletal muscle fibres and required for normal fibre type balance in rodents. Mech. Dev. 1997, 61, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seward, D.J.; Haney, J.C.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Swoap, S.J. bHLH transcription factor MyoD affects myosin heavy chain expression pattern in a muscle-specific fashion. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C408–C413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmark, M.; Rana, Z.A.; Stewart, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Gundersen, K. De-phosphorylation of myod is linking nerve-evoked activity to fast myosin heavy chain expression in rodent adult skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Garcia, C.; Hernandez-Camacho, J.D.; Carvajal, J.J. Regulation of myogenic gene expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 419, 113299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, H.; Parker, P.J. The extended protein kinase C superfamily. Biochem. J. 1998, 332, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.D.; Affandi, T.; Black, A.R.; Reyland, M.E. PKCalpha and pkcdelta: Friends and rivals. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turban, S.; Hajduch, E. Protein kinase C isoforms: Mediators of reactive lipid metabolites in the development of insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.R.; Ha, M.Y.; Shim, S.M.; Park, T.S. Measurements of diacylglycerols in skeletal muscle by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Lipids 2013, 48, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, K.; Stretton, C.; Lipina, C.; Blachnio-Zabielska, A.; Baranowski, M.; Gorski, J.; Marley, A.; Hundal, H.S. Defining the role of DAG, mitochondrial function, and lipid deposition in palmitate-induced proinflammatory signaling and its counter-modulation by palmitoleate. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboardi, G.C.; Ramazzotti, G.; Bavelloni, A.; Piazzi, M.; Fiume, R.; Billi, A.M.; Matteucci, A.; Faenza, I.; Cocco, L. A role for pkcepsilon during C2C12 myogenic differentiation. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marcantonio, D.; Galli, D.; Carubbi, C.; Gobbi, G.; Queirolo, V.; Martini, S.; Merighi, S.; Vaccarezza, M.; Maffulli, N.; Sykes, S.M.; et al. PKCepsilon as a novel promoter of skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 339, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jove, M.; Planavila, A.; Sanchez, R.M.; Merlos, M.; Laguna, J.C.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Palmitate induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells by a mechanism involving protein kinase C and nuclear factor-kappab activation. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmio, J.; Udd, B. Borderlines between sarcopenia and mild late-onset muscle disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, S.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Nielsen, D.E.; Badawi, A.; El-Sohemy, A.; Mutch, D.M.; Ma, D.W. Comprehensive profiling of plasma fatty acid concentrations in young healthy Canadian adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizunoya, W.; Wakamatsu, J.; Tatsumi, R.; Ikeuchi, Y. Protocol for high-resolution separation of rodent myosin heavy chain isoforms in a mini-gel electrophoresis system. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 377, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Shibasaki, A.; Naka, A.; Saito, H.; Iida, K. Lactate promotes myoblast differentiation and myotube hypertrophy via a pathway involving MyoD in vitro and enhances muscle regeneration in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuba, I.; Fujita, R.; Iida, K. Palmitic Acid Inhibits Myogenic Activity and Expression of Myosin Heavy Chain MHC IIb in Muscle Cells through Phosphorylation-Dependent MyoD Inactivation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065847
Matsuba I, Fujita R, Iida K. Palmitic Acid Inhibits Myogenic Activity and Expression of Myosin Heavy Chain MHC IIb in Muscle Cells through Phosphorylation-Dependent MyoD Inactivation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065847
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuba, Izumi, Rikako Fujita, and Kaoruko Iida. 2023. "Palmitic Acid Inhibits Myogenic Activity and Expression of Myosin Heavy Chain MHC IIb in Muscle Cells through Phosphorylation-Dependent MyoD Inactivation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065847
APA StyleMatsuba, I., Fujita, R., & Iida, K. (2023). Palmitic Acid Inhibits Myogenic Activity and Expression of Myosin Heavy Chain MHC IIb in Muscle Cells through Phosphorylation-Dependent MyoD Inactivation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065847





