Fabrication and Characterization of Functional Biobased Membranes from Postconsumer Cotton Fabrics and Palm Waste for the Removal of Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibers
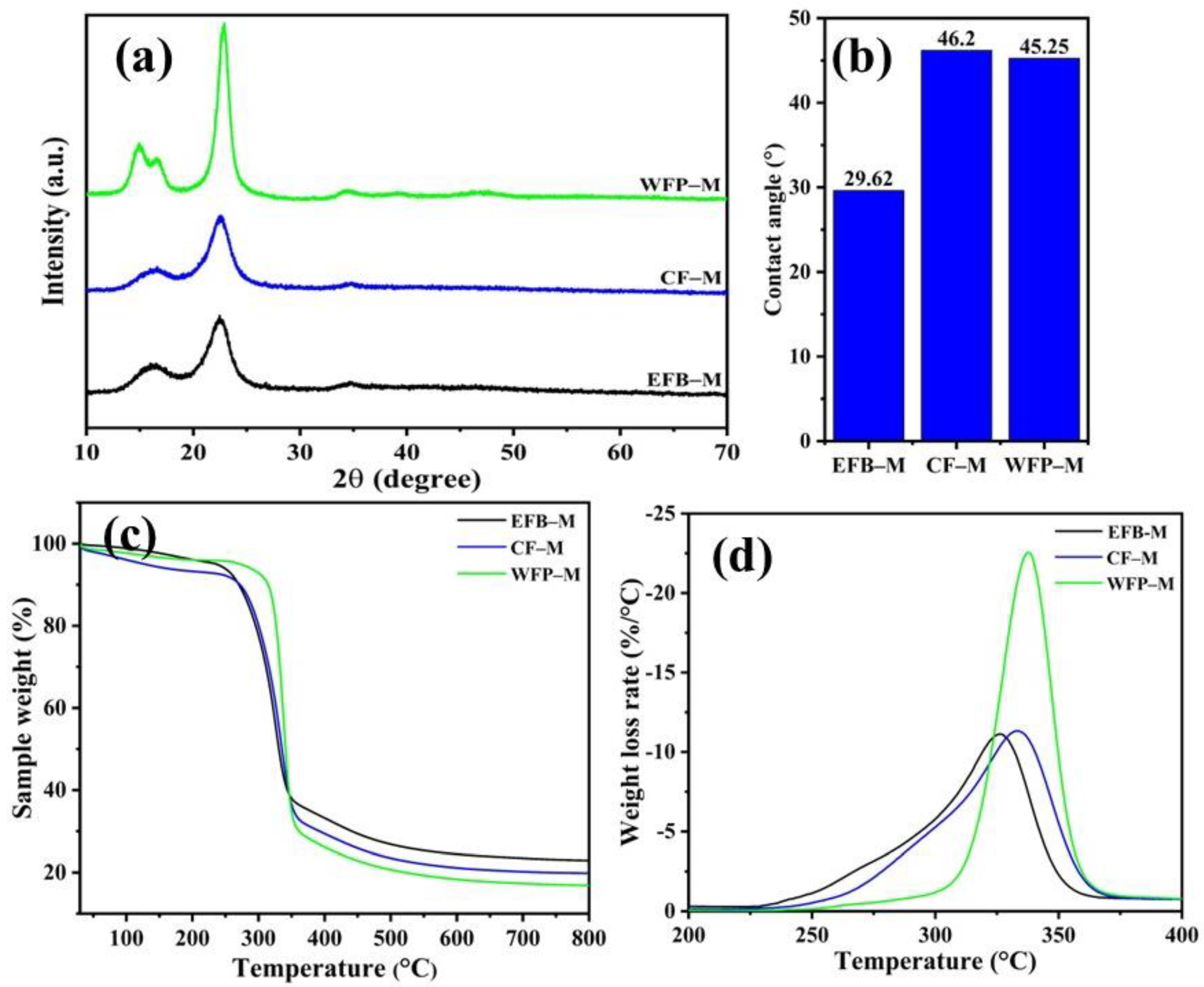
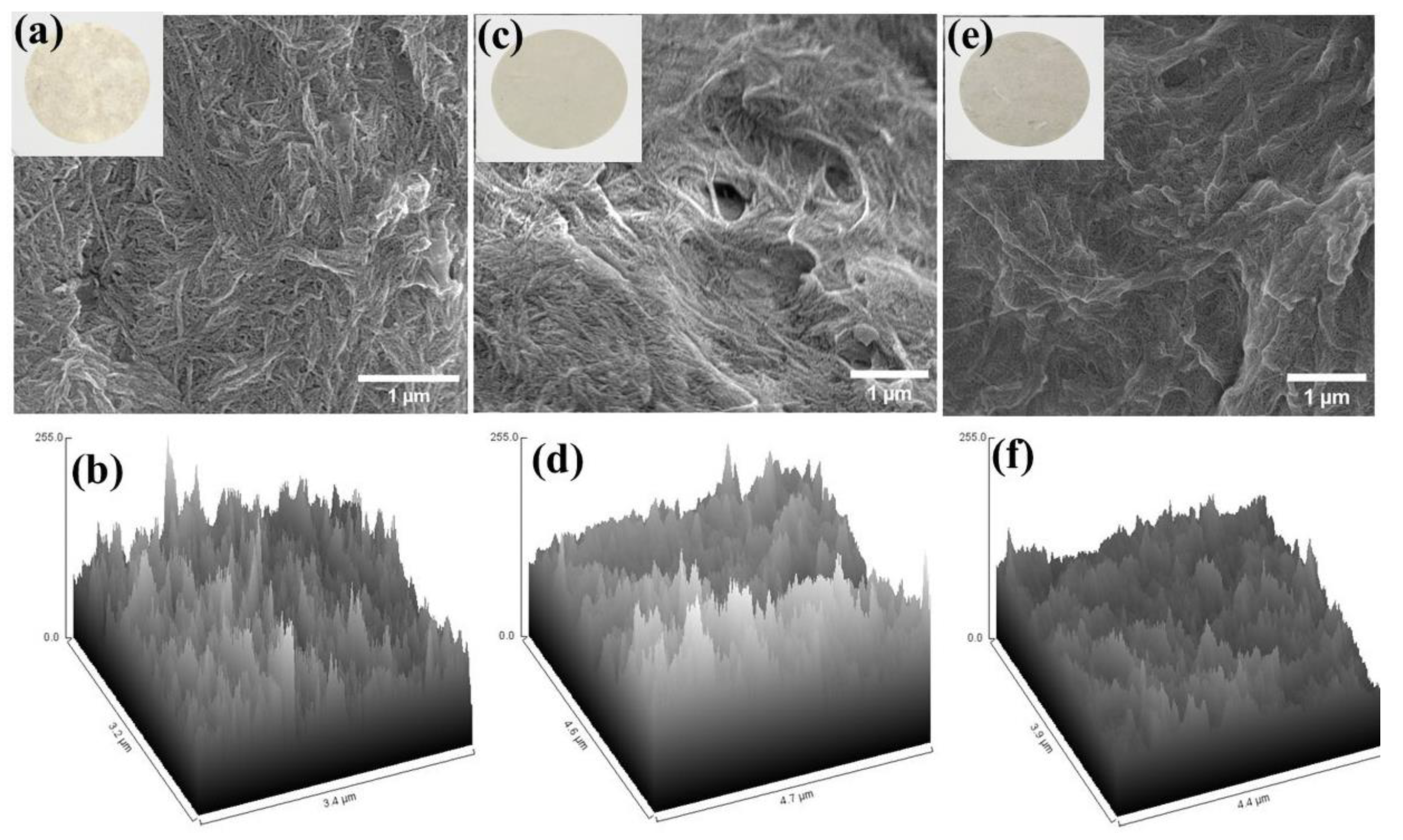
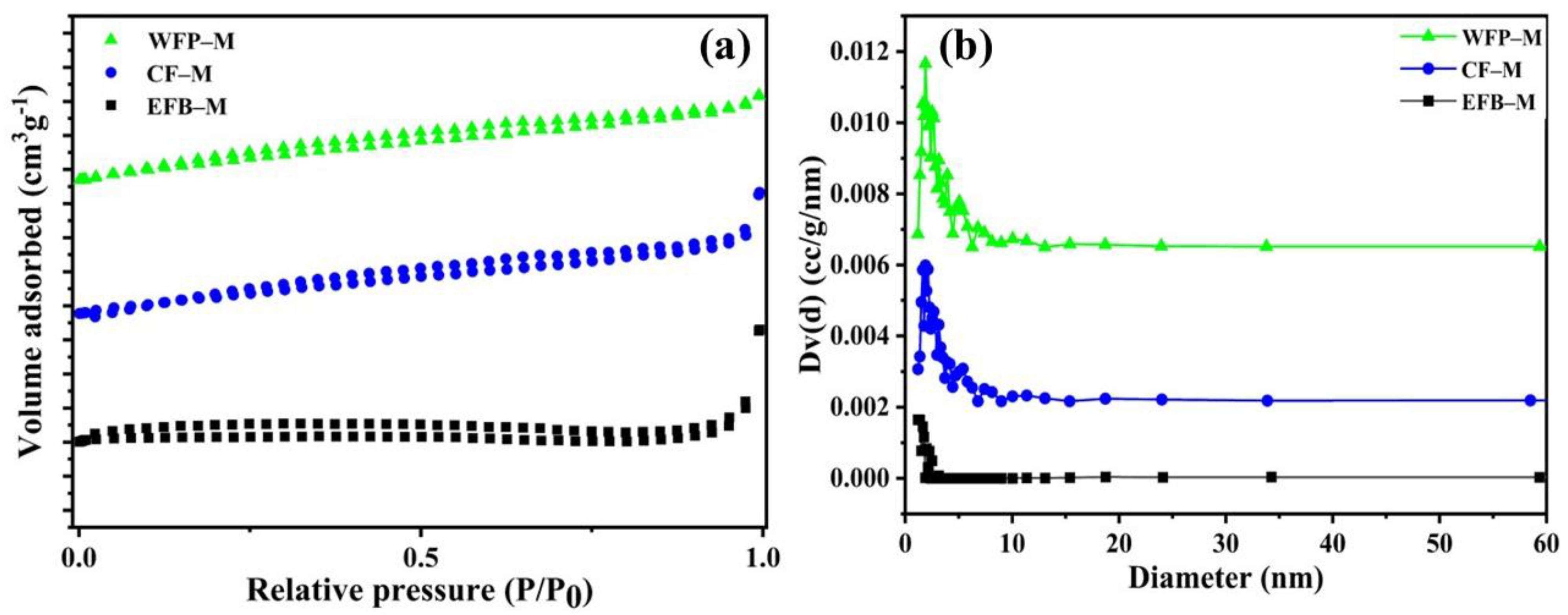
2.2. Characterization of CNF Membrane Framework
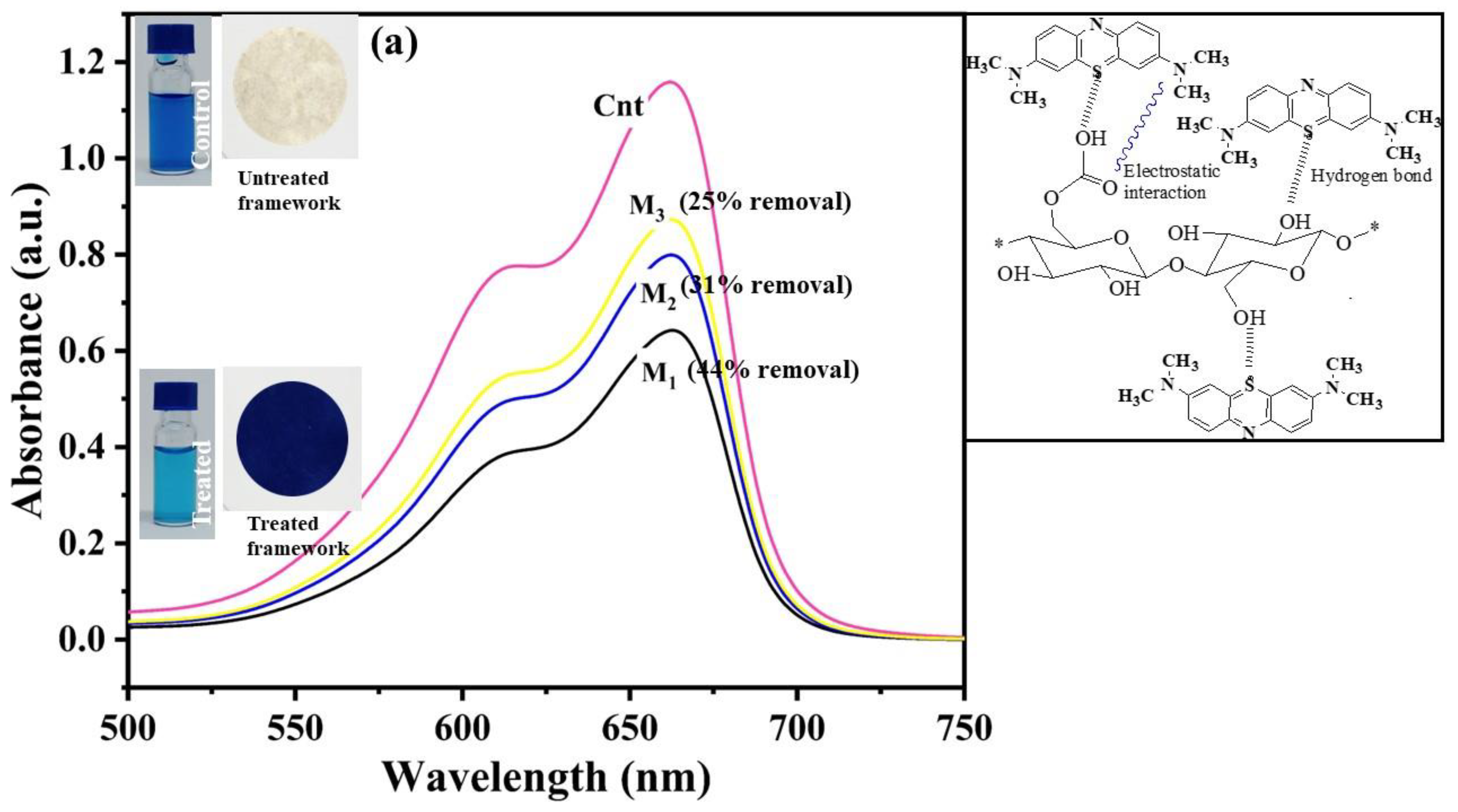
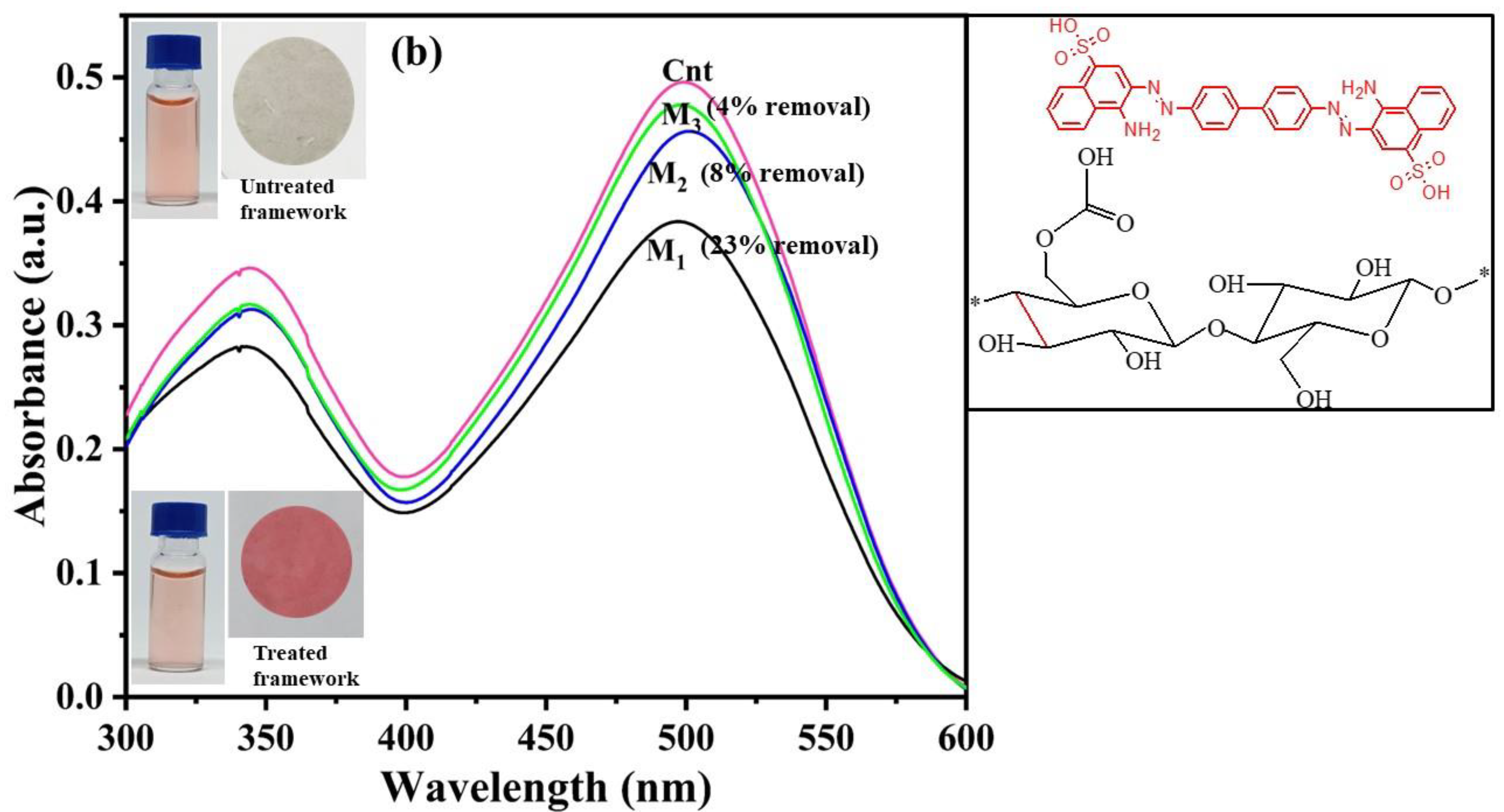
2.3. Dye Removal Using Fabricated Nanocellulose Membrane
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Delignification and Bleaching of Palm Empty Fruit Bunch
3.3. Synthesis of Cellulose Nanofibers
3.4. Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibers
3.5. Fabrication of Functional Cellulose Membranes
3.6. Characterization of Functional Cellulosic Membranes
3.7. Removal of Dyes from Model Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutton, M.; Shafahi, M. Water Pollution Caused by Leather Industry: A Review. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 13th International Conference on Energy Sustainability Collocated with the ASME 2019 Heat Transfer Summer Conference, Bellevue, WA, USA, 14–17 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, K.; Shezad, N.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Akhtar, F.; Jamil, F.; Shafique, S.; Park, Y.-K.; Hussain, M. A review on activated carbon modifications for the treatment of wastewater containing anionic dyes. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; Alonso, M.C.; Riu, J.; Barceló, D. Identification of Polar, Ionic, and Highly Water Soluble Organic Pollutants in Untreated Industrial Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Shabir, M.; Yasin, M.; Hussain, M.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Nizami, A.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Park, Y.-K. A review on recent advances in the treatment of dye-polluted wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.-L.; Thanh, D.T.H.; Show, P.-L.; How, S.-C.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Hsu, M.; Chia, S.R.; Chen, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-K. Studies of protein wastes adsorption by chitosan-modified nanofibers decorated with dye wastes in batch and continuous flow processes: Potential environmental applications. Membranes 2022, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Ooi, C.W.; Show, P.L.; Hoe, B.C.; Chai, W.S.; Chiu, C.-Y.; Wang, S.S.-S.; Chang, Y.-K. Removal of ionic dyes by nanofiber membrane functionalized with chitosan and egg white proteins: Membrane preparation and adsorption efficiency. Membranes 2022, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Chai, W.S.; Chen, S.-J.; Shih, J.-Y.; Koyande, A.K.; Liu, B.-L.; Chang, Y.-K. Removal of soluble microbial products and dyes using heavy metal wastes decorated on eggshell. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajidariyor, T.; Nuntawad, N.; Somsaen, P.; Prukdamrongchai, R.; Cherdchoo, H.; Posoknistakul, P.; Khemthong, P.; Wanmolee, W.; Arjfuk, P.; Pongchaikul, P.; et al. Cryo-Induced Cellulose-Based Nanogel from Elaeis guineensis for Antibiotic Delivery Platform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Pan, S.; Rodrigues, J.; Elkodous, M.A.; Danquah, M.K. Medical applications of biopolymer nanofibers. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 4107–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, C.R.; Callaway, K.; Spencer, E.; Leisy, K.; Jiang, G.; Yang, S.; Hu, X. Biopolymer-Based Filtration Materials. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11804–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamba, F.B.; Mbuli, B.S.; Ramontja, J. Recent Advances in Biopolymeric Membranes towards the Removal of Emerging Organic Pollutants from Water. Membranes 2021, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Raj, M.C.; Joy, J.; Moores, A.; Drisko, G.L.; Sanchez, C. Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: From biosources to materials and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11575–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.T.; Cherian, R.M.; Antony, T.; Tharayil, A.; Das, H.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Chirayil, C.J.; Thomas, S. A review on the best bioadsorbent membrane- nanocellulose for effective removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, Z. Nanocellulose Based Filtration Membrane in Industrial Waste Water Treatment: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Caldas, M.-X.; Carlsson, J.; Sadiktsis, I.; Jaworski, A.; Nilsson, U.; Mathew, A.P. Cellulose Nanocrystals from Postconsumer Cotton and Blended Fabrics: A Study on Their Properties, Chemical Composition, and Process Efficiency. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3787–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Lima, M.M.; Wong, J.T.; Paillet, M.; Borsali, R.; Pecora, R. Translational and Rotational Dynamics of Rodlike Cellulose Whiskers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Reuse of waste cotton cloth for the extraction of cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tao, R.; Ismail, A.; Wang, Y. Cellulose Nanocrystals Derived from Textile Waste through Acid Hydrolysis and Oxidation as Reinforcing Agent of Soy Protein Film. Polymers 2020, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Medeiros, E.; Malmonge, J.; Gregorski, K.; Wood, D.; Mattoso, L.; Glenn, G.; Orts, W.; Imam, S. Cellulose nanowhiskers from coconut husk fibers: Effect of preparation conditions on their thermal and morphological behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supian, M.A.F.; Amin, K.N.M.; Jamari, S.S.; Mohamad, S. Production of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) from empty fruit bunch (EFB) via mechanical method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichosz, S.; Masek, A. Cellulose Fibers Hydrophobization via a Hybrid Chemical Modification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romruen, O.; Karbowiak, T.; Tongdeesoontorn, W.; Shiekh, K.A.; Rawdkuen, S. Extraction and Characterization of Cellulose from Agricultural By-Products of Chiang Rai Province, Thailand. Polymers 2022, 14, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, B.; Hassan, E.B.; Mahmoud, B. Chemical isolation and characterization of different cellulose nanofibers from cotton stalks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, H.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Thermo-Responsive Cellulose-Based Material with Switchable Wettability for Controllable Oil/Water Separation. Polymers 2018, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Du, H.; Yang, X.; Si, C. Recent Strategies in Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibrils Derived from Raw Cellulose Materials. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7923068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnol, C.; Rodrigues, F.H.; Pereira, A.G.; Fajardo, A.R.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Superabsorbent hydrogel composite made of cellulose nanofibrils and chitosan-graft-poly (acrylic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Jawaid, M.; Parveez, B.; Zuriyati, A.; Khan, A. Morphological, chemical and thermal analysis of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from bamboo fibre. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, M.-X.; Chen, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-Z. Full-Biobased Nanofiber Membranes toward Decontamination of Wastewater Containing Multiple Pollutants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11783–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Z.; Georgouvelas, D.; Svedberg, A.; Monti, S.; Mathew, A.P. Upscaled engineered functional microfibrillated cellulose flat sheet membranes for removing charged water pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, D.; Sun, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, F. An environmentally tolerant, highly stable, cellulose nanofiber-reinforced, conductive hydrogel multifunctional sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, N.; Sonawane, S.H.; Anand Kishore, K. Synthesis of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) from cotton using ultrasound-assisted acid hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 70, 105353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kian, L.K.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, H.; Karim, Z. Isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from roselle-derived microcrystalline cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandura, P.; Riedl, B.; Kokta, B.V. Thermal degradation behavior of cellulose fibers partially esterified with some long chain organic acids. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 70, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Chlebicki, S.; Mamleev, V. Thermal degradation of cotton under linear heating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 78, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, M.H.; Pohan, N.A.; Garba, Z.N.; Kassim, M.J.; Rahim, A.A.; Brosse, N.; Yemloul, M.; Fazita, M.N.; Haafiz, M.M. Physicochemical of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm fronds as potential methylene blue adsorbents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Guo, F.; Zhu, J.; Cao, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y. A comparative study on the crystalline structure of cellulose isolated from bamboo fibers and parenchyma cells. Cellulose 2021, 28, 5993–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.; Cristelo, C.; Silvestre, S.; Fortunato, E.; Sousa, A.; Alves, A.; Correia, D.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Gama, M. Hydrophobic modification of bacterial cellulose using oxygen plasma treatment and chemical vapor deposition. Cellulose 2020, 27, 10733–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Du, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, K.; Lv, X.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y. Facile preparation of BiOBr/cellulose composites by in situ synthesis and its enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Zhou, Q.; Ikkala, O.; Berglund, L.A. Strong and Tough Cellulose Nanopaper with High Specific Surface Area and Porosity. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3638–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, P.; Michen, B.; Huch, A.; Tingaut, P.; Caseri, W.R.; Zimmermann, T. Characterization of Pores in Dense Nanopapers and Nanofibrillated Cellulose Membranes: A Critical Assessment of Established Methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25884–25897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebald, C.; Wurzbacher, J.A.; Tingaut, P.; Zimmermann, T.; Steinfeld, A. Amine-based nanofibrillated cellulose as adsorbent for CO2 capture from air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9101–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Santos, J.M.N.; Rodrigues, I.L.; Rosa, R.; Pavan, F.A.; Lima, E.C. Adsorption of Methylene Blue by ultrasonic surface modified chitin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 446, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Macedo, J.; da Costa Júnior, N.B.; Almeida, L.E.; da Silva Vieira, E.F.; Cestari, A.R.; de Fátima Gimenez, I.; Barreto, L.S. Kinetic and calorimetric study of the adsorption of dyes on mesoporous activated carbon prepared from coconut coir dust. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapson, R.W. Amyloid from a histochemical perspective. A review of the structure, properties and types of amyloid, and a proposed staining mechanism for Congo red staining. Biotech. Histochem. 2018, 93, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flauzino Neto, W.; Silvério, H.; Dantas, N.; Pasquini, D. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from agro-industrial residue—Soy hulls. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 42, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, A.; Afewerki, S.; Alimohammadzadeh, R.; Sanhueza, I.; Tai, C.-W.; Osong, S.H.; Engstrand, P.; Ibrahem, I. A sustainable strategy for production and functionalization of nanocelluloses. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 91, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Singh, R.; Joshi, K.; Vinayak, V. TiO2 doped polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and Luffa cylindrica based photocatalytic nanosponge to absorb and desorb oil in diatom solar panels. RSC Adv. 2021, 9, 22410–22416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.-D.; Buema, G. Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriem, O.A.; Kamel, A.M.; Shaaban, W.; Elkady, M.F. Enhancement of Dye Separation Performance of Eco-Friendly Cellulose Acetate-Based Membranes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
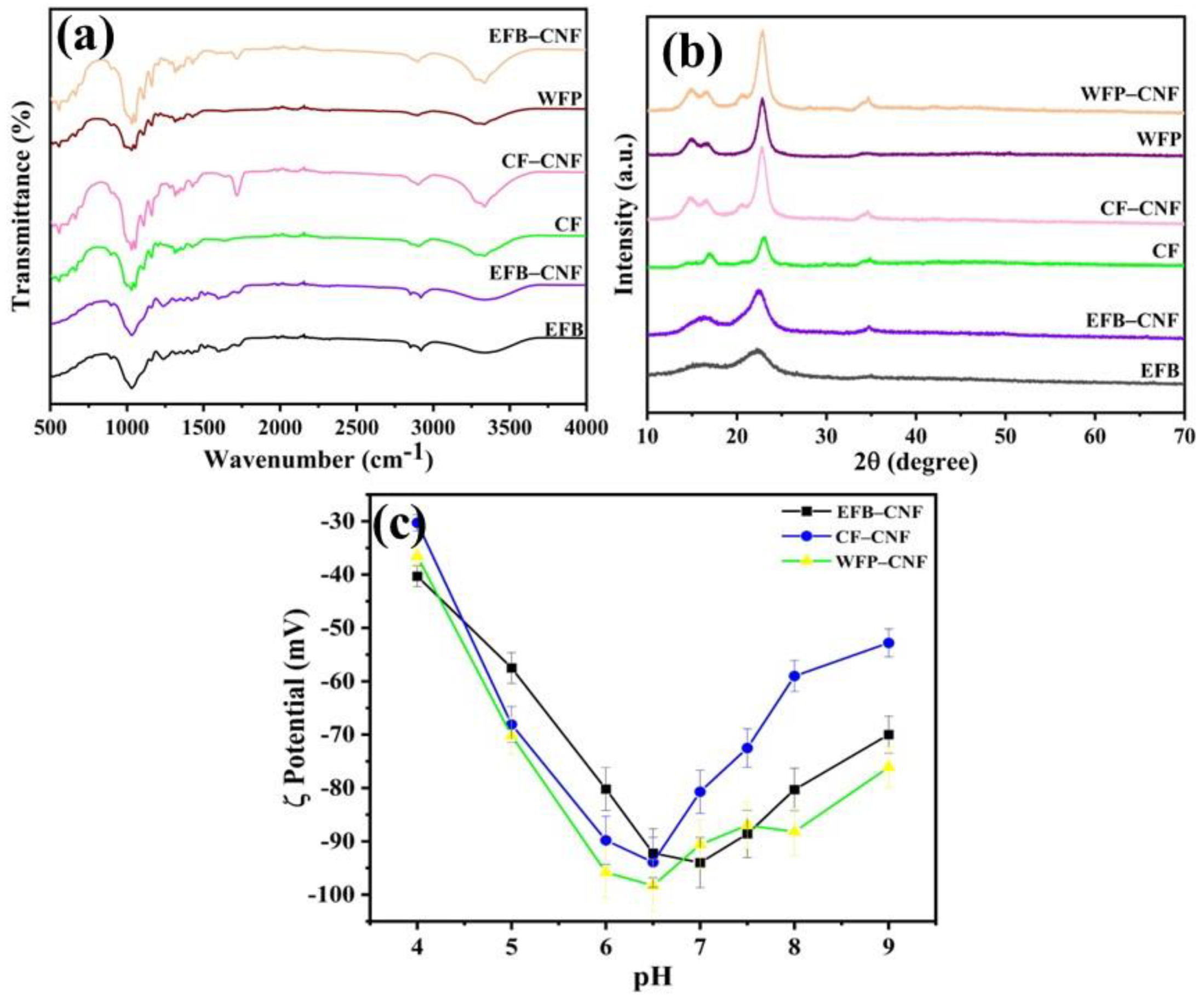
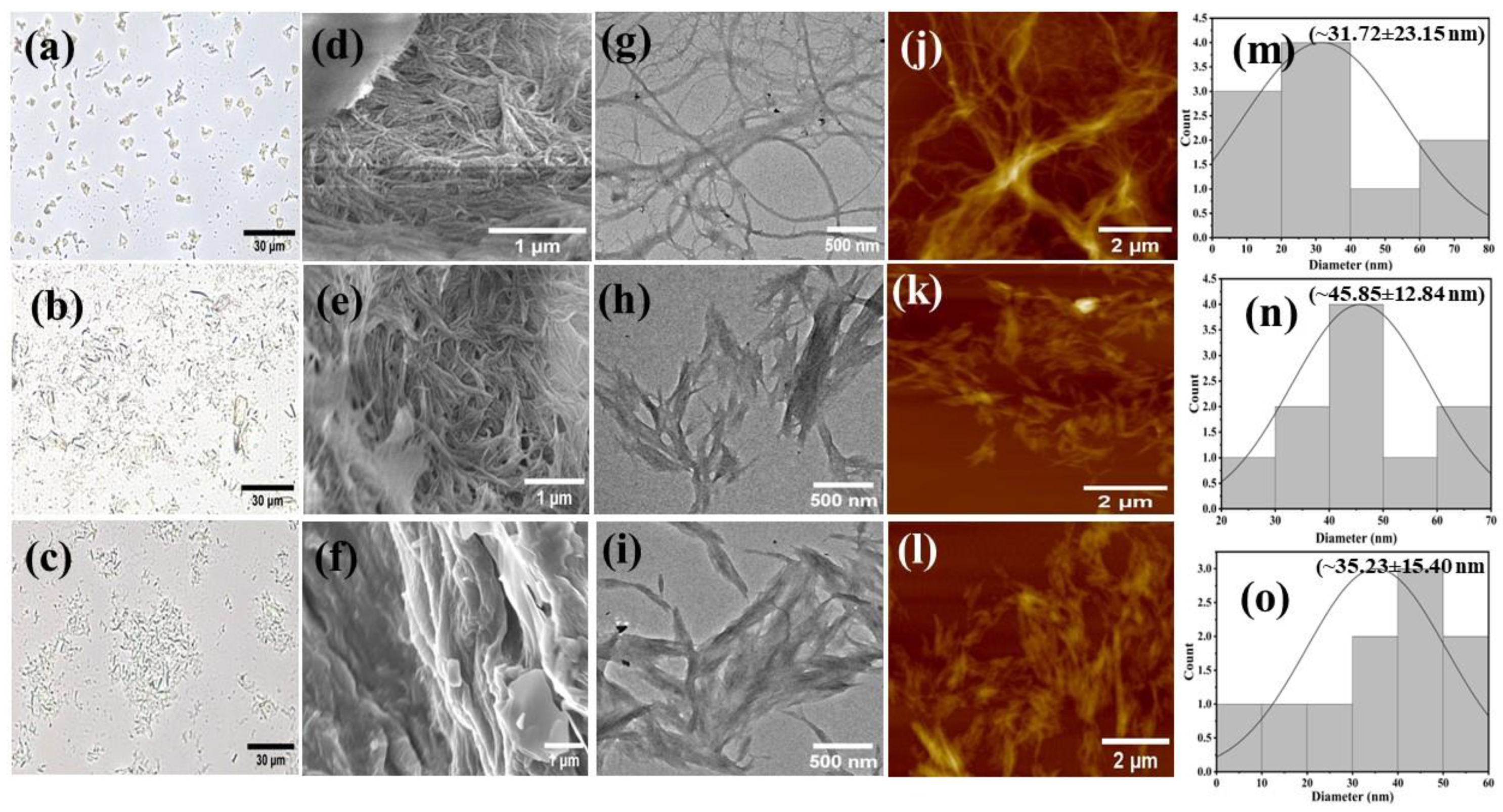


| Samples | Yield (%) | Surface ζ-Potential (mV) at pH 7.0 | Crystallite Size (nm) | Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EFB–CNF | NA | −94.0 ± 4.70 | 26.99 | 56.11% |
| CF–CNF | 76.74% | −80.7 ± 4.04 | 25.38 | 56.17% |
| WFP–CNF | 52.50% | −90.6 ± 4.53 | 6.52 | 61.18% |
| Samples | TGA and DTG Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset Degradation Temperature (°C) | Max Degradation Temperature (°C) | Char Residue at 898.4 °C (%) | |
| EFB | 293.9 | 335.8 | 15.9 |
| EFB–CNF | 277.9 | 315.7 | 20.1 |
| CF | 327.6 | 349.5 | 6.1 |
| CF–CNF | 321.9 | 339.0 | 5.0 |
| WFP | 328.4 | 348.6 | 7.0 |
| WFP–CNF | 308.2 | 343.9 | 12.5 |
| Samples | TGA and DTG Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset Degradation Temperature (°C) | Max Degradation Temperature (°C) | Char Residue at 898.4 °C (%) | |
| EFB–M | 290.6 | 326.3 | 22.74 |
| CF–M | 297.4 | 333.0 | 19.81 |
| WFP–M | 321.1 | 337.6 | 16.76 |
| Samples | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | BJH Desorption Pore Width (Å) | Water Flux (L h−1 m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EFB–M | 0.64 | 0.7 ×10−2 | 11.85 | 108.00 |
| CF–M | 5.65 | 1.3×10−2 | 18.73 | 130.75 |
| WFP–M | 8.19 | 1.3×10−2 | 18.73 | 142.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.J.; Karim, Z.; Charnnok, B.; Poonsawat, T.; Posoknistakul, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Sakdaronnarong, C. Fabrication and Characterization of Functional Biobased Membranes from Postconsumer Cotton Fabrics and Palm Waste for the Removal of Dyes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076030
Khan MJ, Karim Z, Charnnok B, Poonsawat T, Posoknistakul P, Laosiripojana N, Wu KC-W, Sakdaronnarong C. Fabrication and Characterization of Functional Biobased Membranes from Postconsumer Cotton Fabrics and Palm Waste for the Removal of Dyes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Mohd Jahir, Zoheb Karim, Boonya Charnnok, Thiprada Poonsawat, Pattaraporn Posoknistakul, Navadol Laosiripojana, Kevin C.-W. Wu, and Chularat Sakdaronnarong. 2023. "Fabrication and Characterization of Functional Biobased Membranes from Postconsumer Cotton Fabrics and Palm Waste for the Removal of Dyes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076030
APA StyleKhan, M. J., Karim, Z., Charnnok, B., Poonsawat, T., Posoknistakul, P., Laosiripojana, N., Wu, K. C.-W., & Sakdaronnarong, C. (2023). Fabrication and Characterization of Functional Biobased Membranes from Postconsumer Cotton Fabrics and Palm Waste for the Removal of Dyes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076030







