The Interactions of Magnesium Sulfate and Cromoglycate in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain; The Role of Magnesium on Mast Cell Degranulation in Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effects of Cromoglycate and Magnesium Sulfate Alone in the Formalin Orofacial Test in Rats
2.2. The Effect of the Combination of Cromoglycate and Magnesium Sulfate in the Formalin Orofacial Test in Rats
2.2.1. Different Doses of Cromoglycate (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg) Were Combined and Tested with Low-Effective Dose of Magnesium Sulfate (5 mg/kg) (Figure 2)


2.2.2. Different Doses of Cromoglycate (1, 10, and 30 mg/kg) Were Combined and Tested with High Effective Dose of Magnesium Sulfate (15 mg/kg) (Figure 3)

2.3. Interactions between Cromoglycate and Magnesium Sulfate
2.3.1. Interaction between Cromoglycate and Magnesium Sulfate in Phase 1 of Formalin Test—Acute Nociceptive Orofacial Pain
2.3.2. Interaction between Cromoglycate and Magnesium Sulfate in Phase 2 of Formalin Test—Acute Inflammatory Orofacial Pain
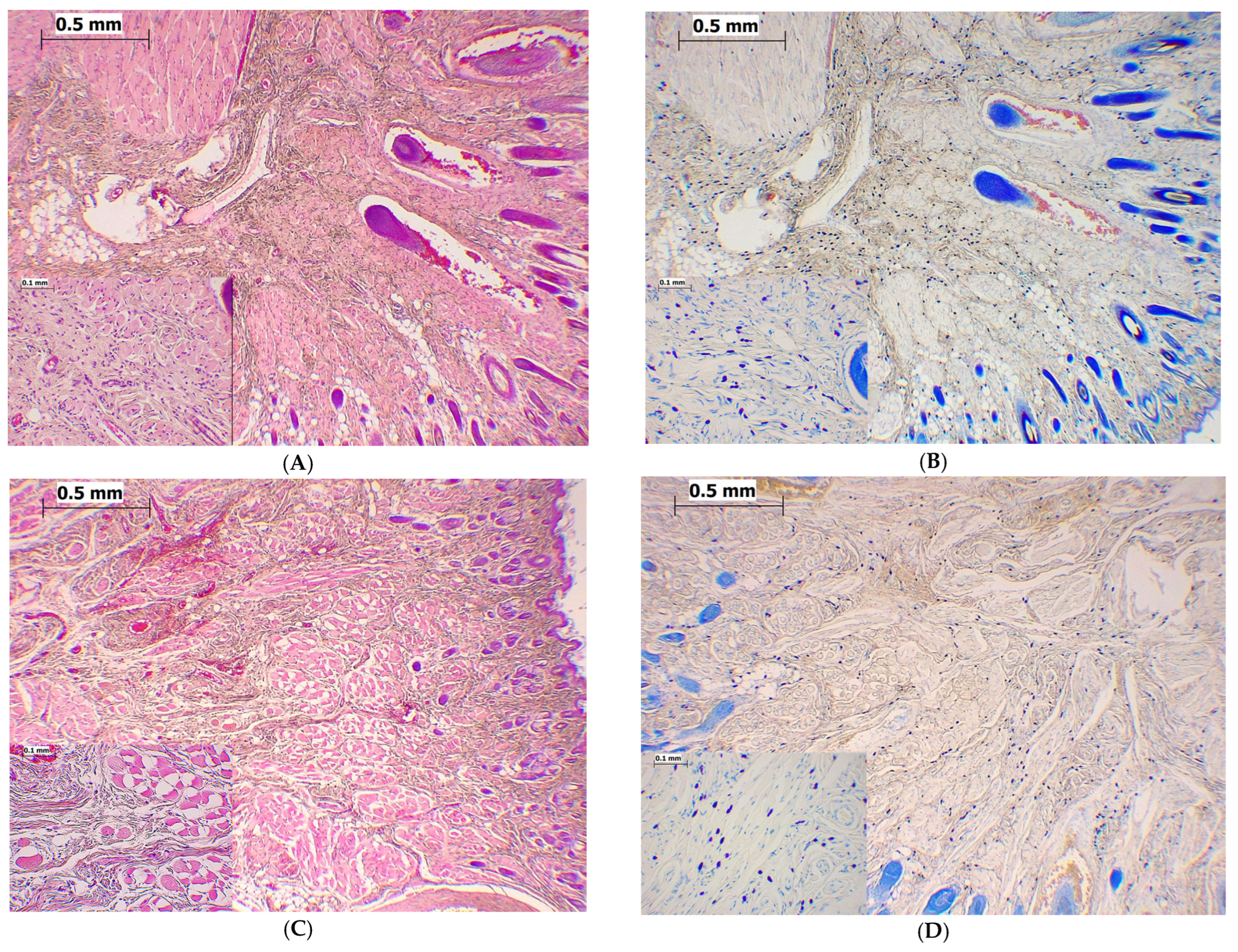
2.4. Magnesium Sulfate Reduced the Total Number of Mast Cells in Orofacial Region in the Formalin-Induced Orofacial Pain Test
2.5. Magnesium Sulfate Reduced Degranulation of Mast Cells in the Formalin-Induced Orofacial Pain Test
2.6. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Ethics Statement
4.3. Drugs and Protocol for Drug Administration
4.4. The Model of Orofacial Pain
4.5. Data Analysis in Pain Testing
4.6. Upper Lip Tissue Collection and Staining
4.7. Data Analysis for Mast Cells
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benoliel, R.; May, A.; Svensson, P.; Pigg, M.; Law, A.; Nixdorf, D.; Renton, T.; Sharav, Y.; Ernberg, M.; Peck, C.; et al. International Classification of Orofacial Pain, 1st edition (ICOP). Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 129–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegeler, C.; Brauns, G.; May, A. Characteristics and natural disease history of persistent idiopathic facial pain, trigeminal neuralgia, and neuropathic facial pain. Headache 2021, 61, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeson, J.P. The classification of orofacial pains. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 20, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.M. Orofacial pain. Pain 2011, 152, S25–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kubo, A.; Iwata, K. Pathophysiological mechanisms of persistent orofacial pain. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 62, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Blokhuis, B.R.; Garssen, J.; Redegeld, F.A. Non-IgE mediated mast cell activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, T.; Kneilling, M.; Mailhammer, R.; Maier, K.; Sander, C.A.; Kollias, G.; Kunkel, S.L.; Hültner, L.; Röcken, M. Mast cells control neutrophil recruitment during T cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions through tumor necrosis factor and macrophage inflammatory protein 2. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, C.A.; Tambeli, C.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ferreira, S.H. The major role of peripheral release of histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in formalin-induced nociception. Neuroscience 2001, 102, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Perkins, N.M.; Tracey, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Inflammation and hyperalgesia induced by nerve injury in the rat: A key role of mast cells. Pain 2003, 105, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenhaar, F.; Magerl, M.; Peters, E.M.; Hendrix, S.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M. Mast cell-driven skin inflammation is impaired in the absence of sensory nerves. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.J.; Moalem-Taylor, G. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: Involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 229, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.J. Mast cells and oral inflammation. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2003, 14, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Kainz, V.; Burstein, R.; Strassman, A.M. Mast cell degranulation distinctly activates trigemino-cervical and lumbosacral pain pathways and elicits widespread tactile pain hypersensitivity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, I.M. Infection, Pain, and Itch. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjea, D.; Martinov, T. Mast cells: Versatile gatekeepers of pain. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebro, D.P.; Vučković, S.M.; Dožić, I.S.; Dožić, B.S.; Savić Vujović, K.R.; Milovanović, A.P.; Karadzic, B.; Prostran, M. Magnesium sulfate reduces formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats with normal magnesium serum levels. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessle, B.J. Peripheral and central mechanisms of orofacial pain and their clinical correlates. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005, 71, 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars, D.; Gozariu, M.; Cadden, S.W. Animal models of nociception. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 597–652. [Google Scholar]
- Zouikr, I.; Ahmed, A.F.; Horvat, J.C.; Beagley, K.W.; Clifton, V.L.; Ray, A.; Thorne, R.F.; Jarnicki, A.G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Hodgson, D.M. Programming of formalin-induced nociception by neonatal LPS exposure: Maintenance by peripheral and central neuroimmune activity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.M.; Bustanji, Y.; El-Maraghy, S.A.; Taha, M.O.; Al Ghussein, M.A. Naproxen and cromolyn as new glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibitors for amelioration of diabetes and obesity: An investigation by docking simulation and subsequent in vitro/in vivo biochemical evaluation. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawi, T.M.; Bustanji, Y.; El-Maraghy, S.; Taha, M.O.; Al-Ghussein, M.A. Evaluation of naproxen and cromolyn activities against cancer cells viability, proliferation, apoptosis, p53 and gene expression of survivin and caspase-3. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaggi, A.S.; Kaur, G.; Bali, A.; Singh, N. Pharmacological investigations on mast cell stabilizer and histamine receptor antagonists in vincristine-induced neuropathic pain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebro, D.P.; Vučković, S.; Vujović, K.S.; Prostran, M. Anti-hyperalgesic effect of systemic magnesium sulfate in carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain in rats: Influence of the nitric oxide pathway. Magnes. Res. 2014, 27, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovic, S.; Srebro, D.; SavicVujovic, K.; Prostran, M. The antinociceptive effects of magnesium sulfate and MK-801 in visceral inflammatory pain model: The role of NO/cGMP/K(+)ATP pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srebro, D.; Vuckovic, S.; Milovanovic, A.; Kosutic, J.; Vujovic, K.S.; Prostran, M. Magnesium in Pain Research: State of the Art. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujović, K.S.; Vučković, S.; Vasović, D.; Medić, B.; Knežević, N.; Prostran, M. Additive and antagonistic antinociceptive interactions between magnesium sulfate and ketamine in the rat formalin test. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2017, 77, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebro, D.; Vučković, S.; Milovanović, A.; Savić Vujović, K.; Prostran, M. Evaluation of Prophylactic and Therapeutic Effects of Tramadol and Tramadol Plus Magnesium Sulfate in an Acute Inflammatory Model of Pain and Edema in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, K.; Żyżyńska-Granica, B.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kurowski, P.; Gajewska, M.; Bujalska-Zadrożny, M. Magnesium and Morphine in the Treatment of Chronic Neuropathic Pain-A Biomedical Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebro, D.P.; Vučković, S.M.; Savić Vujović, K.R.; Prostran, M.Š. TRPA1, NMDA receptors and nitric oxide mediate mechanical hyperalgesia induced by local injection of magnesium sulfate into the rat hind paw. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebro, D.; Vučković, S.; Prostran, M. Inhibition of neuronal and inducible nitric synthase does not affect the analgesic effects of NMDA antagonists in visceral inflammatory pain. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2016, 76, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Toro, C.; Koroleva, K.; Ermakova, E.; Gafurov, O.; Abushik, P.; Tavi, P.; Sitdikova, G.; Giniatullin, R. Testing the Role of Glutamate NMDA Receptors in Peripheral Trigeminal Nociception Implicated in Migraine Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S.; Sim, J.; Jang, K.S. Mast cell number, substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, S.I. The mast cell and synovial inflammation. Or, what’s a nice cell like you doing in a joint like this? Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Lu, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; Liu, M. Mast cell degranulation in human periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheethal, H.S.; Uma, K.; Rao, K.; Priya, N.S.; Umadevi, H.S.; Smitha, T. A quantitative analysis of mast cells in inflammatory periapical and gingival lesions. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2014, 15, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, P.R.; Lopes-Rocha, R.; Pereira, E.M.; Marinho, S.A.; de Miranda, J.L.; Lima, N.L.; Verli, F.D. Effect of propolis on mast cells in wound healing. Inflammopharmacology 2012, 20, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.H.; Zou, G.; Ding, S.J.; Li, T.T.; Zhu, L.B.; Wang, J.Z.; Yao, Y.X.; Zhang, X.M. Mast cell stabilizer ketotifen reduces hyperalgesia in a rodent model of surgically induced endometriosis. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, A.L.; Siqueira, R.M.; Araujo, J.C.; Gondim, D.V.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Quetz, J.S.; Havt, A.; Lima, A.A.M.; Vale, M.L. Role of NMDA receptors in the trigeminal pathway, and the modulatory effect of magnesium in a model of rat temporomandibular joint arthritis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2013, 121, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.M.; Locatelli, L.; Fedele, G.; Cazzaniga, A.; Mazur, A. Magnesium and the Brain: A Focus on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, V.N.; Meyerowitz, J.; Zou, B.; Klukinov, M.; Yan, N.; Sharma, K.; Clark, D.J.; Xie, X.; Yeomans, D.C. Impact of Magnesium on Oxytocin Receptor Function. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebro, D.; Vučković, S.; Prostran, M. Participation of peripheral TRPV1, TRPV4, TRPA1 and ASIC in a magnesium sulfate-induced local pain model in rat. Neuroscience 2016, 339, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kanju, P.; Fang, Q.; Lee, S.H.; Parekh, P.K.; Lee, W.; Moore, C.; Brenner, D.; Gereau, R.W., 4th; Wang, F.; et al. TRPV4 is necessary for trigeminal irritant pain and functions as a cellular formalin receptor. Pain 2014, 155, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves Rodrigues Santos, S.A.; de Barros Mamede Vidal Damasceno, M.; Alves Magalhães, F.E.; Sessle, B.J.; Amaro de Oliveira, B.; Alves Batista, F.L.; Vieira-Neto, A.E.; Rolim Campos, A. Transient receptor potential channel involvement in antinociceptive effect of citral in orofacial acute and chronic pain models. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omote, K.; Kawamata, T.; Kawamata, M.; Namiki, A. Formalin-induced release of excitatory amino acids in the skin of the rat hindpaw. Brain Res. 1998, 787, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddonfard, E.; Erfanparast, A.; Farshid, A.A.; Khalilzadeh, E. Interaction between histamine and morphine at the level of the hippocampus in the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfanparast, A.; Tamaddonfard, E.; Taati, M.; Dabbaghi, M. Effects of crocin and safranal, saffron constituents, on the formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 392–402. [Google Scholar]
- Luccarini, P.; Cadet, R.; Saade, M.; Woda, A. Antinociceptive effect of morphine microinjections into the spinal trigeminal subnucleus oralis. Neuroreport 1995, 6, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, K.; Sasaki, M.; Karasawa, S.; Obata, H.; Nara, T.; Goto, F. The effect of intrathecal magnesium sulphate on nociception in rat acute pain models. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Sato, E.; Kaneko, T.; Sato, I. Antihyperalgesic effects of intrathecally administered magnesium sulfate in rats. Pain 2000, 84, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, L.; Kesmati, M.; Najafzadeh, H. Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of nanoparticles of magnesium oxide in mice with and without ketamine. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Isiordia-Espinoza, M.A.; Zapata-Morales, J.R.; Castañeda-Santana, D.I.; de la Rosa-Coronado, M.; Aragon-Martinez, O.H. Synergism between tramadol and parecoxib in the orofacial formalin test. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.H.; Yaksh, T.L. Evaluation of interaction between gabapentin and ibuprofen on the formalin test in rats. Anesthesiology 1999, 91, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vastani, N.; Seifert, B.; Spahn, D.R.; Maurer, K. Sensitivities of rat primary sensory afferent nerves to magnesium: Implications for differential nerve blocks. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 30, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimaru, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Ra, C. L-type Ca2+ channels in mast cells: Activation by membrane depolarization and distinct roles in regulating mediator release from store-operated Ca2+ channels. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradding, P. Mast cell ion channels. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2005, 87, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.J.; Paulussen, J.J.; Tollenaere, J.P.; De Mol, N.J.; Janssen, L.H. Structure-activity relationships of astemizole derivatives for inhibition of store operated Ca2+ channels and exocytosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 350, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, H.; del Carmen, K.A.; Stokes, A. Link between TRPV channels and mast cell function. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2007, 179, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rixecker, T.; Mathar, I.; Medert, R.; Mannebach, S.; Pfeifer, A.; Lipp, P.; Tsvilovskyy, V.; Freichel, M. TRPM4-mediated control of FcεRI-evoked Ca(2+) elevation comprises enhanced plasmalemmal trafficking of TRPM4 channels in connective tissue type mast cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryana, P.; Rajaei, S.; Bagheri, A.; Karimi, F.; Dabbagh, A. Acute effect of intravenous administration of magnesium sulfate on serum levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in patients undergoing elective coronary bypass graft with cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth. Pain Med. 2014, 4, e16316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebro, D.; Dožić, B.; Savić Vujović, K.; Medić Brkić, B.; Vučković, S. Magnesium Sulfate Reduces Carrageenan-Induced Rat Paw Inflammatory Edema Via Nitric Oxide Production. Dose Response 2023, 21, 15593258231155788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.M.; Denk, F.; Chisholm, K.I.; Suddason, T.; Durrieux, C.; Thakur, M.; Gentry, C.; McMahon, S.B. Peripheral inflammatory pain sensitisation is independent of mast cell activation in male mice. Pain 2017, 158, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnúsdóttir, E.I.; Grujic, M.; Roers, A.; Hartmann, K.; Pejler, G.; Lagerström, M.C. Mouse mast cells and mast cell proteases do not play a significant role in acute tissue injury pain induced by formalin. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918808161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begon, S.; Alloui, A.; Eschalier, A.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y.; Dubray, C. Assessment of the relationship between hyperalgesia and peripheral inflammation in magnesium-deficient rats. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjea, D.; Wetzel, A.; Mack, M.; Engblom, C.; Allen, J.; Mora-Solano, C.; Paredes, L.; Balsells, E.; Martinov, T. Mast cell degranulation mediates compound 48/80-induced hyperalgesia in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Luk, K.; Vang, D.; Soto, W.; Vincent, L.; Robiner, S.; Saavedra, R.; Li, Y.; Gupta, P.; Gupta, K. Morphine stimulates cancer progression and mast cell activation and impairs survival in transgenic mice with breast cancer. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, i4–i13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J. Drug Synergism and Dose-Effect Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grabovsky, Y.; Tallarida, R. Isobolographic Analysis for Combinations of a Full and Partial Agonist: Curved Isoboles. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J.; Murray, R.B. Manual of Pharmacologic Calculations with Computer Program, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, E.S.; Post, T.J.; Vigderman, R.J. Density heterogeneity of human lung mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srebro, D.; Dožić, B.; Vučković, S.; Savić Vujović, K.; Medić Brkić, B.; Dožić, I.; Srebro, M. The Interactions of Magnesium Sulfate and Cromoglycate in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain; The Role of Magnesium on Mast Cell Degranulation in Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076241
Srebro D, Dožić B, Vučković S, Savić Vujović K, Medić Brkić B, Dožić I, Srebro M. The Interactions of Magnesium Sulfate and Cromoglycate in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain; The Role of Magnesium on Mast Cell Degranulation in Neuroinflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076241
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrebro, Dragana, Branko Dožić, Sonja Vučković, Katarina Savić Vujović, Branislava Medić Brkić, Ivan Dožić, and Milorad Srebro. 2023. "The Interactions of Magnesium Sulfate and Cromoglycate in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain; The Role of Magnesium on Mast Cell Degranulation in Neuroinflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076241
APA StyleSrebro, D., Dožić, B., Vučković, S., Savić Vujović, K., Medić Brkić, B., Dožić, I., & Srebro, M. (2023). The Interactions of Magnesium Sulfate and Cromoglycate in a Rat Model of Orofacial Pain; The Role of Magnesium on Mast Cell Degranulation in Neuroinflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076241





