Osteogenic Potential of Autologous Dentin Graft Compared with Bovine Xenograft Mixed with Autologous Bone in the Esthetic Zone: Radiographic, Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
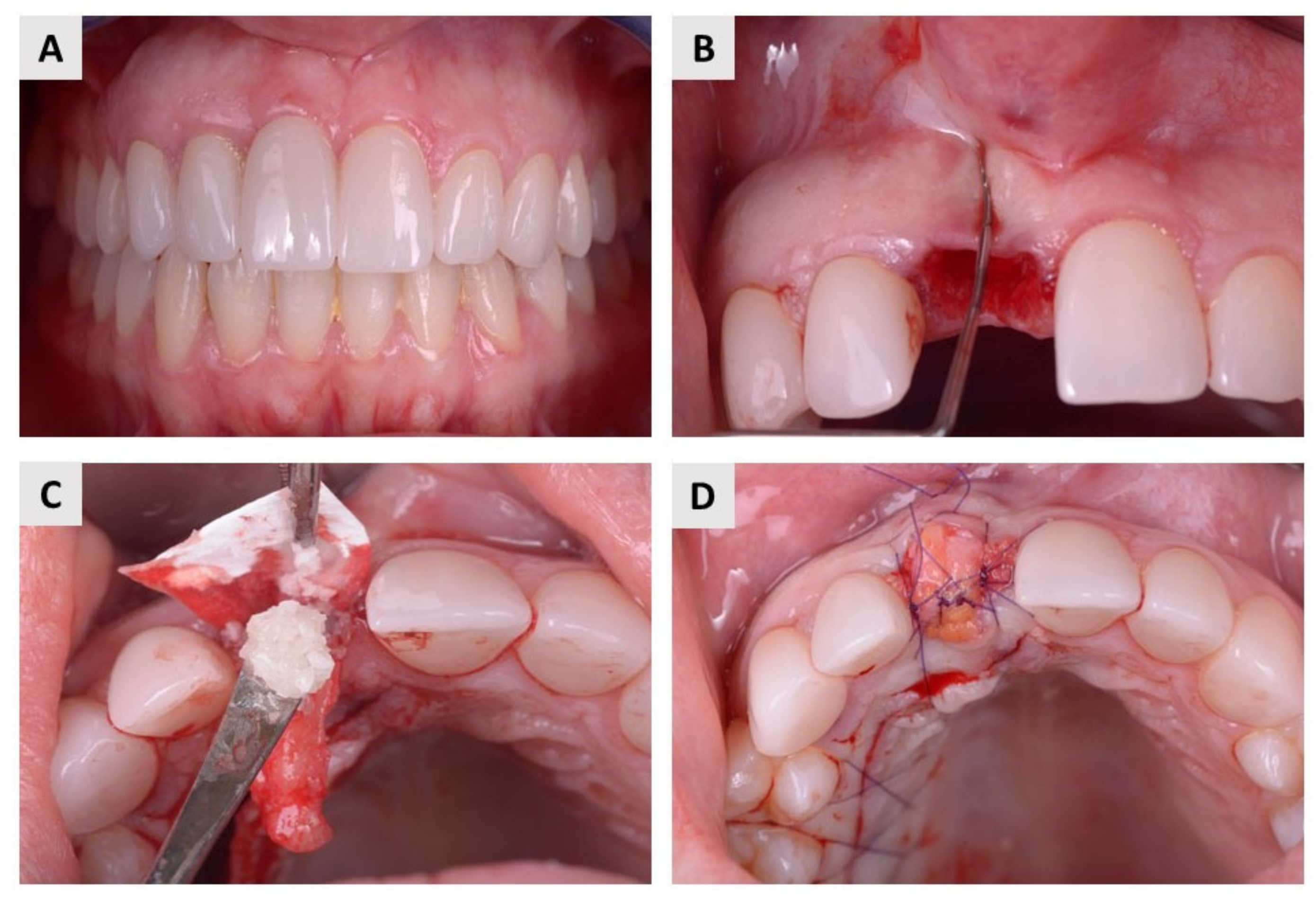
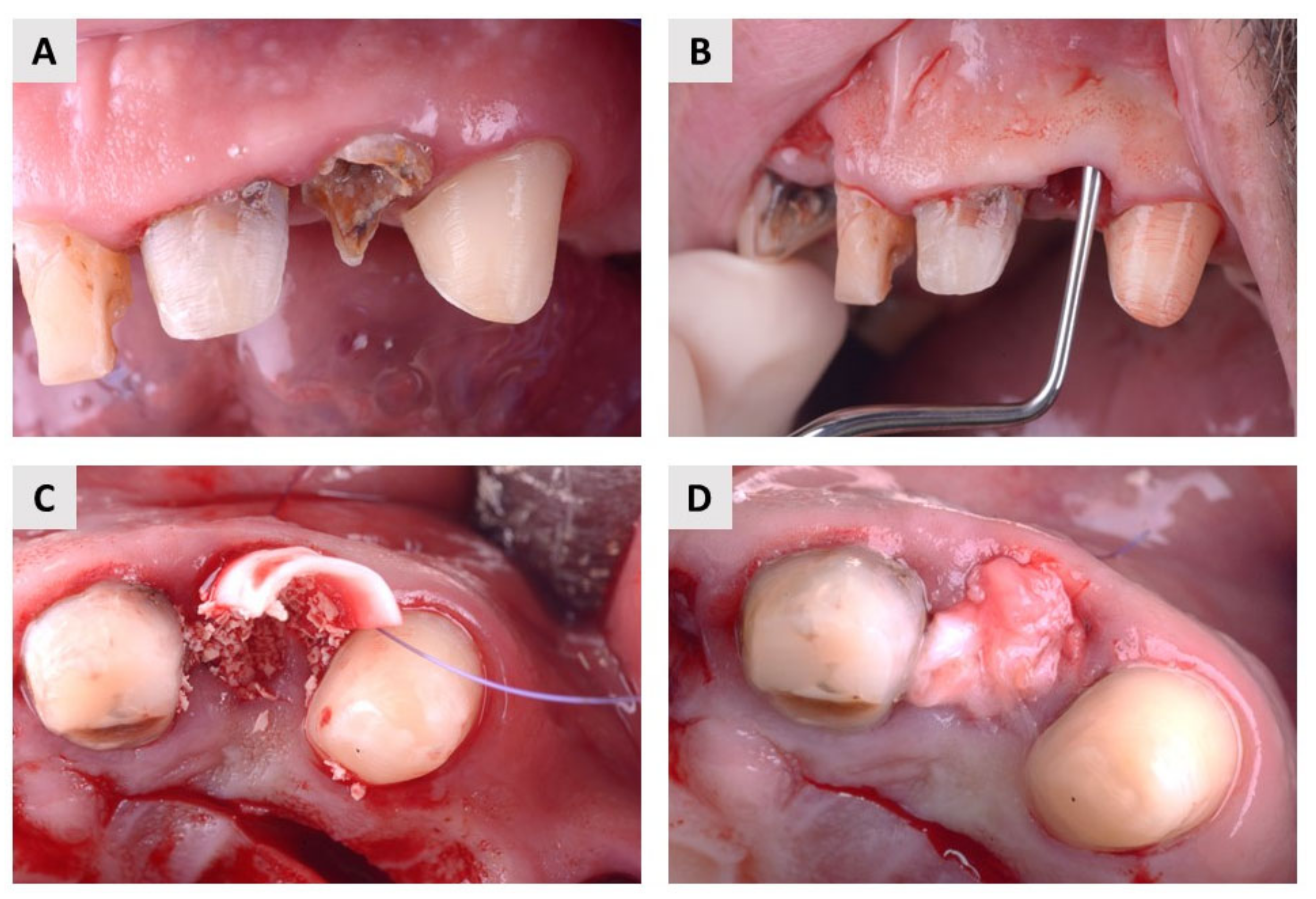
2.1. Clinical Evaluation
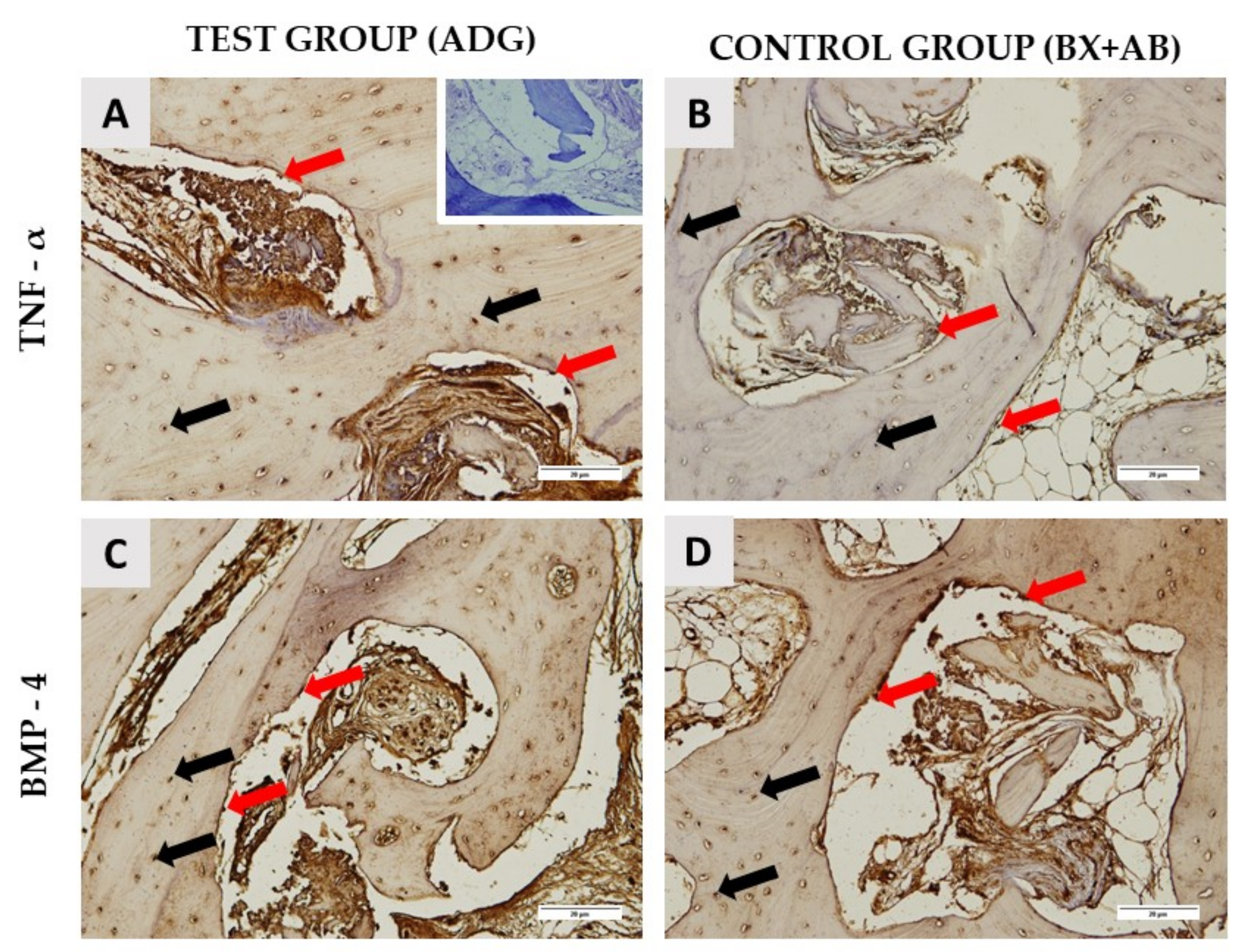
2.2. Histological Results
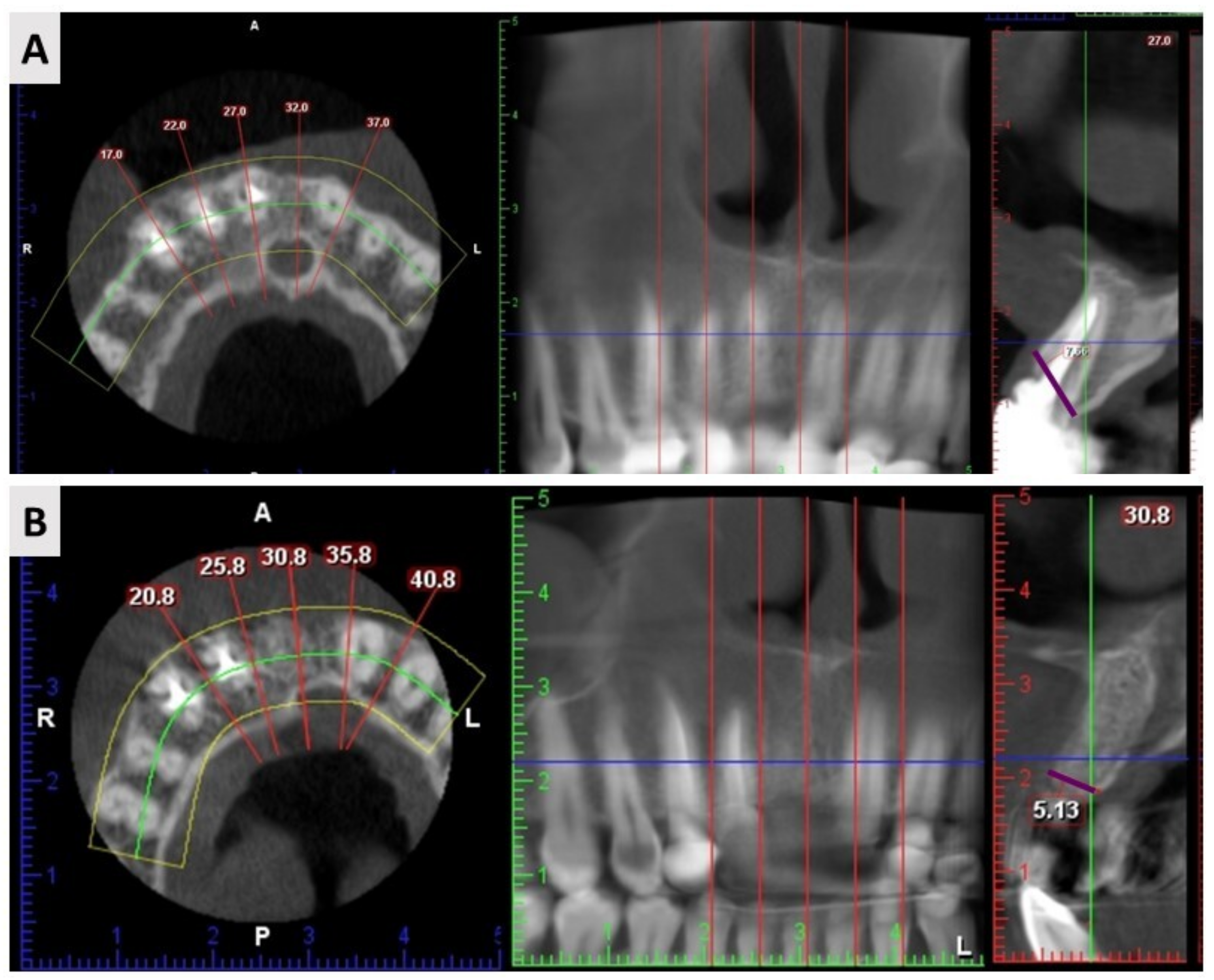
2.3. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection Criteria and Preoperative Assessment
4.2. Surgical Procedure and Postoperative Follow-Up
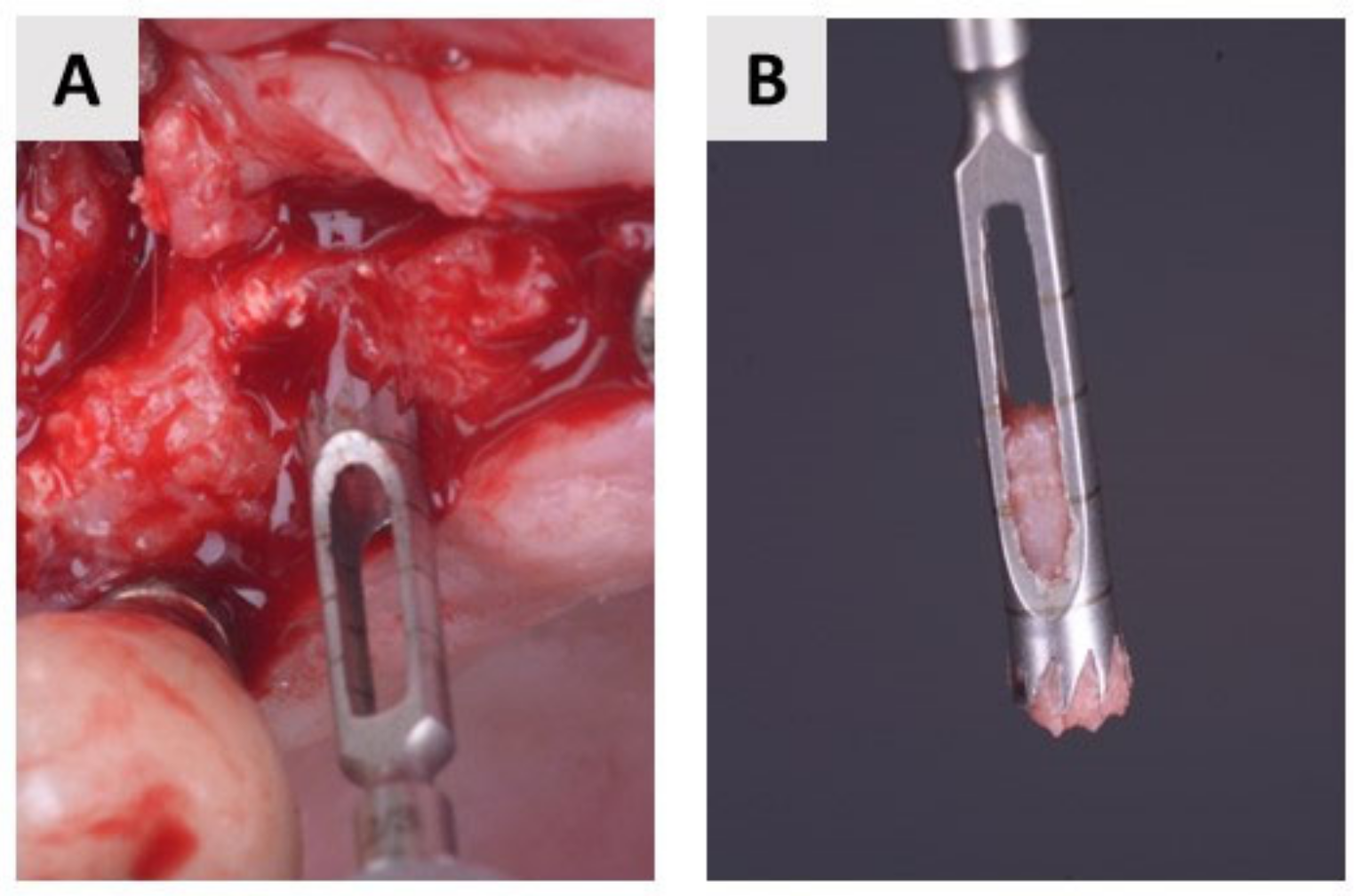
4.3. Bone Biopsy Collection
4.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Radiological Assessment
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horowitz, R.; Holtzclaw, D.; Rosen, P.S. A review on alveolar ridge preservation following tooth extraction. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.L.; Wong, T.L.T.; Wong, M.C.M.; Lang, N.P. A systematic review of post-extractional alveolar hard and soft tissue dimensional changes in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S5), 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappuis, V.; Engel, O.; Reyes, M.; Shahim, K.; Nolte, L.P.; Buser, D. Ridge alterations post-extraction in the esthetic zone: A 3D analysis with CBCT. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 195S–201S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassir, S.; Alhareky, M.; Wangsrimongkol, B.; Jia, Y.; Karimbux, N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Hard Tissue Outcomes of Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, T.; Takano-yamamoto, T.; Yabuuchi, T.; Ando, R.; Roberts, W.E. Histomorphometric evaluation of alveolar bone turnover between the maxilla and the mandible during experimental tooth movement in dogs. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenke, E.; Hahn, M.; Weinzierl, K.; Radespiel-Tröger, M.; Neukam, F.W.; Engelke, K. Implant stability and histomorphometry: A correlation study in human cadavers using stepped cylinder implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.L.; Lee, J.K.; Um, H.S.; Chang, B.S. Esthetic evaluation of maxillary single-tooth implants in the esthetic zone. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2010, 40, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalsi, A.S.; Kalsi, J.S.; Bassi, S. Alveolar ridge preservation: Why, when and how. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 227, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, I.B.; Chen, S.T.; Buser, D. Ridge preservation for implant therapy. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 260–271. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriou, R.; Tsiridis, E.; Giannoudis, P.V. Current concepts of molecular aspects of bone healing. Injury 2005, 36, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, H.J.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Rossi, F.; Perale, G. Bone grafts: Which is the ideal biomaterial? J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Egusa, H. Current bone substitutes for implant dentistry. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsoddin, E.; Houshmand, B.; Golabgiran, M. Biomaterial selection for bone augmentation in implant dentistry: A systematic review. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Misch, C.M. Implant Dentistry, 4th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2010; p. 361. [Google Scholar]
- Sakkas, A.; Wilde, F.; Heufelder, M.; Winter, K.; Schramm, A. Autogenous bone grafts in oral implantology—Is it still a “gold standard”? A consecutive review of 279 patients with 456 clinical procedures. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2017, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultekin, B.A.; Bedeloglu, E.; Kose, T.E.; Mijiritsky, E. Comparison of Bone Resorption Rates after Intraoral Block Bone and Guided Bone Regeneration Augmentation for the Reconstruction of Horizontally Deficient Maxillary Alveolar Ridges. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4987437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiorana, C.; Beretta, M.; Salina, S.; Santoro, F. Reduction of autogenous bone graft resorption by means of bio-oss coverage: A prospective study-PubMed. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kacarevic, Z.P.; Kavehei, F.; Houshmand, A.; Franke, J.; Smeets, R.; Rimashevskiy, D.; Wenisch, S.; Schnettler, R.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. Purification processes of xenogeneic bone substitutes and their impact on tissue reactions and regeneration. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 41, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.M.; Doering, H.; Schmidt, T.; Lutz, R.; Neukam, F.W.; Schlegel, K.A. Histological results after maxillary sinus augmentation with Straumann® BoneCeramic, Bio-Oss®, Puros®, and autologous bone: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Tamimi, F.; Alkhraisat, M.H.; Manchón, Á.; Linares, R.; Prados-Frutos, J.C.; Hernández, G.; López Cabarcos, E. Platelet-rich plasma may prevent titanium-mesh exposure in alveolar ridge augmentation with anorganic bovine bone. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindhe, J.; Cecchinato, D.; Donati, M.; Tomasi, C.; Liljenberg, B. Ridge preservation with the use of deproteinized bovine bone mineral. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberi, A.; Samarani, A.; Nader, N.; Noujeim, Z.; Dagher, M.; Kanj, W.; Mearawi, R.; Salemeh, Z.; Badran, B. Physicochemical characteristics of bone substitutes used in oral surgery in comparison to autogenous bone. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 320790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urist, M.R.; SIlverman, B.F.; Buring, K.; Dubuc, F.L.; Rosenberg, J.M. The bone induction principle. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1967, 53, 243–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessho, K.; Tanaka, N.; Matsumoto, J.; Tagawa, T.; Murata, M. Human dentin-matrix-derived bone morphogenetic protein. J. Dent. Res. 1991, 70, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.T.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. Bone morphogenetic protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Originalni, R.; Xhaferi, B.; Petreska, M.P.; Xheladini, A.; Papić, I. Use of mineralized dentin graft in augmentation of different indication areas in the jaw bones. Serb. Dent. J. 2021, 68, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-W.; Um, I.-W.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-K. Bone Healing Capacity of Demineralized Dentin Matrix Materials in a Mini-pig Cranium Defect. J. Korean Dent. Sci. 2012, 5, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Yang, K.Y.; Lee, J.K. Porcine study on the efficacy of autogenous tooth bone in the maxillary sinus. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 39, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrantes Pinheiro Carvalho, V.; De Olivera Tosello, D.; de Castillo Salgado, M.A.; Fernandes Gomes, M. Histomorphometric analysis of homogenous demineralized dentin matrix as osteopromotive material in rabbit mandibles. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 679–686. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, S.; Binderman, I.; Tomac, J. Maintenance of Alveolar Ridge Dimensions Utilizing an Extracted Tooth Dentin Particulate Autograft and Platelet-Rich fibrin: A Retrospective Radiographic Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study. Materials 2020, 13, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, K.M.; Um, I.W.; Kim, Y.K.; Woo, J.M.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Autogenous demineralized dentin matrix from extracted tooth for the augmentation of alveolar bone defect: A prospective randomized clinical trial in comparison with anorganic bovine bone. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.; Worthington, H.; Coulthard, P. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Bone augmentation techniques for dental implant treatment. In Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Esposito, M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Ortiz, G.; Chambrone, L.; Vignoletti, F. Effect of alveolar ridge preservation interventions following tooth extraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cenicante, J.; Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Mendes, J.J.; Mascarenhas, P.; Alcoforado, G.; Santos, A. The Use of Autogenous Teeth for Alveolar Ridge Preservation: A Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Labrador Martínez de Morentin, L.; Martínez-Pereda, M.; Martínez, L.-Q. Use of Autogenous Dentin as Graft Material in Oral Surgery Martín-Ares, María Martínez-González, José María. Cient. Dent. 2019, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Binderman, I.; Hallel, G.; Nardi, C.; Yaffe, A.; Sapoznikov, L. A novel procedure to process extracted teeth for immediate grafting of autogenous dentin. J. Interdiscipl. Med. Dent. Sci. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, G.S.; Miziara, M.N.; Silva, E.R.D.; Ferreira, E.L.; Biulchi, A.P.F.; Alves, J.B. Enhanced bone formation during healing process of tooth sockets filled with demineralized human dentine matrix. Aust. Dent. J. 2013, 58, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, C.R.; Silva, E.R.; Martins, A.B.; Pessoa, F.F.; Gomes, P.V.N.; De Araújo, M.S.C.; Miziara, M.N.; Alves, J.B. Demineralised human dentine matrix stimulates the expression of VEGF and accelerates the bone repair in tooth sockets of rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, Z.; Horowitz, R.; Prasad, H.; Kotsakis, G. Healing Dynamics Following Alveolar Ridge Preservation with Autologous Tooth Structure. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2019, 39, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derner, R.; Anderson, A.C. The bone morphogenic protein. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2005, 22, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.F.; Xing, L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 473, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algate, K.; Haynes, D.R.; Bartold, P.M.; Crotti, T.N.; Cantley, M.D. The effects of tumour necrosis factor-α on bone cells involved in periodontal alveolar bone loss; osteoclasts, osteoblasts and osteocytes. J. Periodontal Res. 2016, 51, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.E.; Nowzari, H. The long-term risks and complications of bovine-derived xenografts: A case series. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2019, 23, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhu, H.C.; Huang, D.H. Autogenous DDM versus Bio-Oss granules in GBR for immediate implantation in periodontal postextraction sites: A prospective clinical study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ADG 1 | BX+AB 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 7 (35%) | 12 (70.5%) |
| Male | 13 (65%) | 5 (29.5%) |
| n | 20 | 17 |
| Age (years) | ||
| Mean | 52.4 | 55.9 |
| SD | 10.8 | 8.8 |
| Min | 26 | 38 |
| Max | 71 | 74 |
| Incisor | Canine | Premolar | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADG 1 | 12 | 3 | 5 | 20 |
| BX+AB 2 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 17 |
| Total | 25 | 6 | 6 | 37 |
| Newly Formed Bone (NB) | Residual Biomaterial (BM) | Soft Tissue (ST) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADG 1 | 72.55 ± 12.14% | 10.61 ± 5.37% | 16.84 ± 9.18% |
| BX+AB 2 | 69.61 ± 13.53% | 12.31 ± 7.83% | 18.07 ± 6.93% |
| p-value * | 0.613 | 0.570 | 0.742 |
| Mean Value ADG 1 ± SD 2 | Mean Value BX+AB 3 ± SD | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α around biomaterial | 140.89 ± 4.92 | 149.96 ± 6.64 | 0.0027 |
| TNF-α new bone area | 77.49 ± 3.61 | 88.72 ± 7.1 | 0.0003 |
| BMP-4 around biomaterial | 131.26 ± 9.1 | 171.75 ± 10.5 | 0.0001 |
| BMP-4 new bone area | 108.76 ± 7.54 | 108.66 ± 8.2 | 0.9761 |
| Width before Extraction | Width after Extraction | Net Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADG 1 | 8.06 ± 1.34 mm | 7.18 ± 1.48 mm | −0.88 ± 0.76 |
| BX+AB 2 | 7.88 ± 1.08 mm | 6.64 ± 0.85 mm | −1.24 ± 0.99 |
| p-value * | 0.654 | 0.172 | 0.219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oguić, M.; Čandrlić, M.; Tomas, M.; Vidaković, B.; Blašković, M.; Jerbić Radetić, A.T.; Zoričić Cvek, S.; Kuiš, D.; Cvijanović Peloza, O. Osteogenic Potential of Autologous Dentin Graft Compared with Bovine Xenograft Mixed with Autologous Bone in the Esthetic Zone: Radiographic, Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076440
Oguić M, Čandrlić M, Tomas M, Vidaković B, Blašković M, Jerbić Radetić AT, Zoričić Cvek S, Kuiš D, Cvijanović Peloza O. Osteogenic Potential of Autologous Dentin Graft Compared with Bovine Xenograft Mixed with Autologous Bone in the Esthetic Zone: Radiographic, Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076440
Chicago/Turabian StyleOguić, Matko, Marija Čandrlić, Matej Tomas, Bruno Vidaković, Marko Blašković, Ana Terezija Jerbić Radetić, Sanja Zoričić Cvek, Davor Kuiš, and Olga Cvijanović Peloza. 2023. "Osteogenic Potential of Autologous Dentin Graft Compared with Bovine Xenograft Mixed with Autologous Bone in the Esthetic Zone: Radiographic, Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076440
APA StyleOguić, M., Čandrlić, M., Tomas, M., Vidaković, B., Blašković, M., Jerbić Radetić, A. T., Zoričić Cvek, S., Kuiš, D., & Cvijanović Peloza, O. (2023). Osteogenic Potential of Autologous Dentin Graft Compared with Bovine Xenograft Mixed with Autologous Bone in the Esthetic Zone: Radiographic, Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076440











