Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptional Profiling in DAPK1-KO Mice
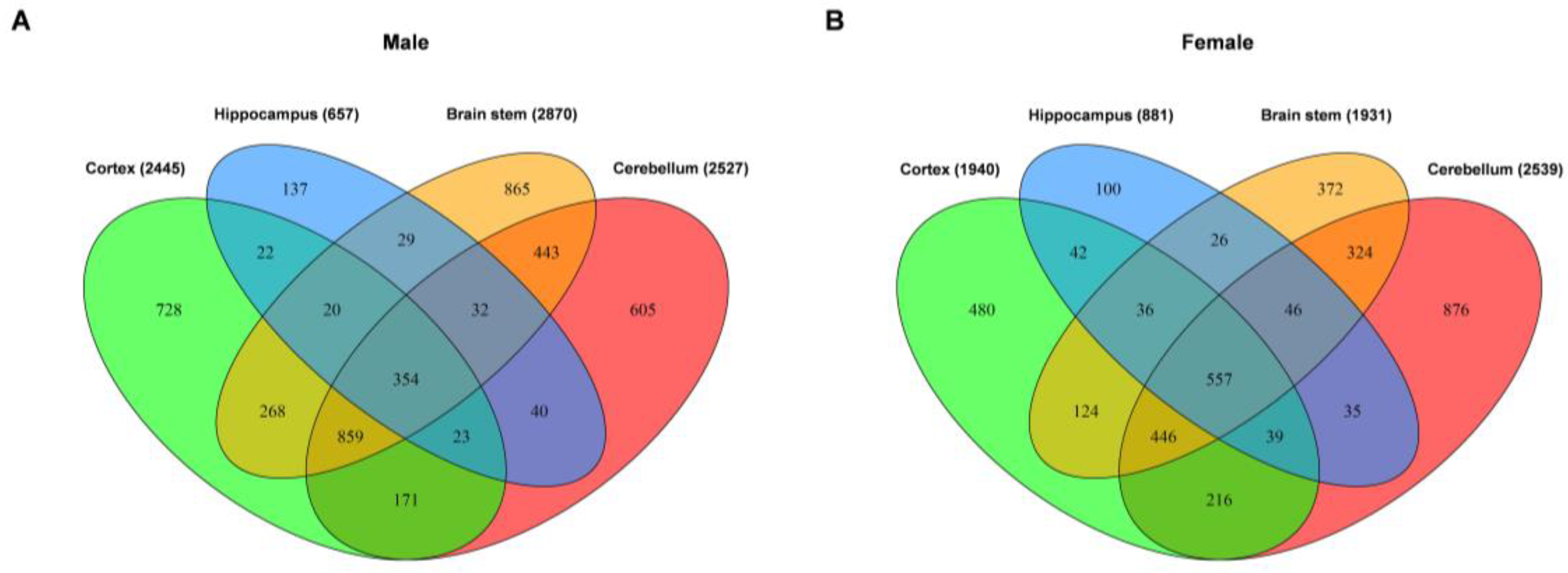
2.2. Common and Unique DEGs in the Tissues from Four Brain Regions
2.3. GO Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
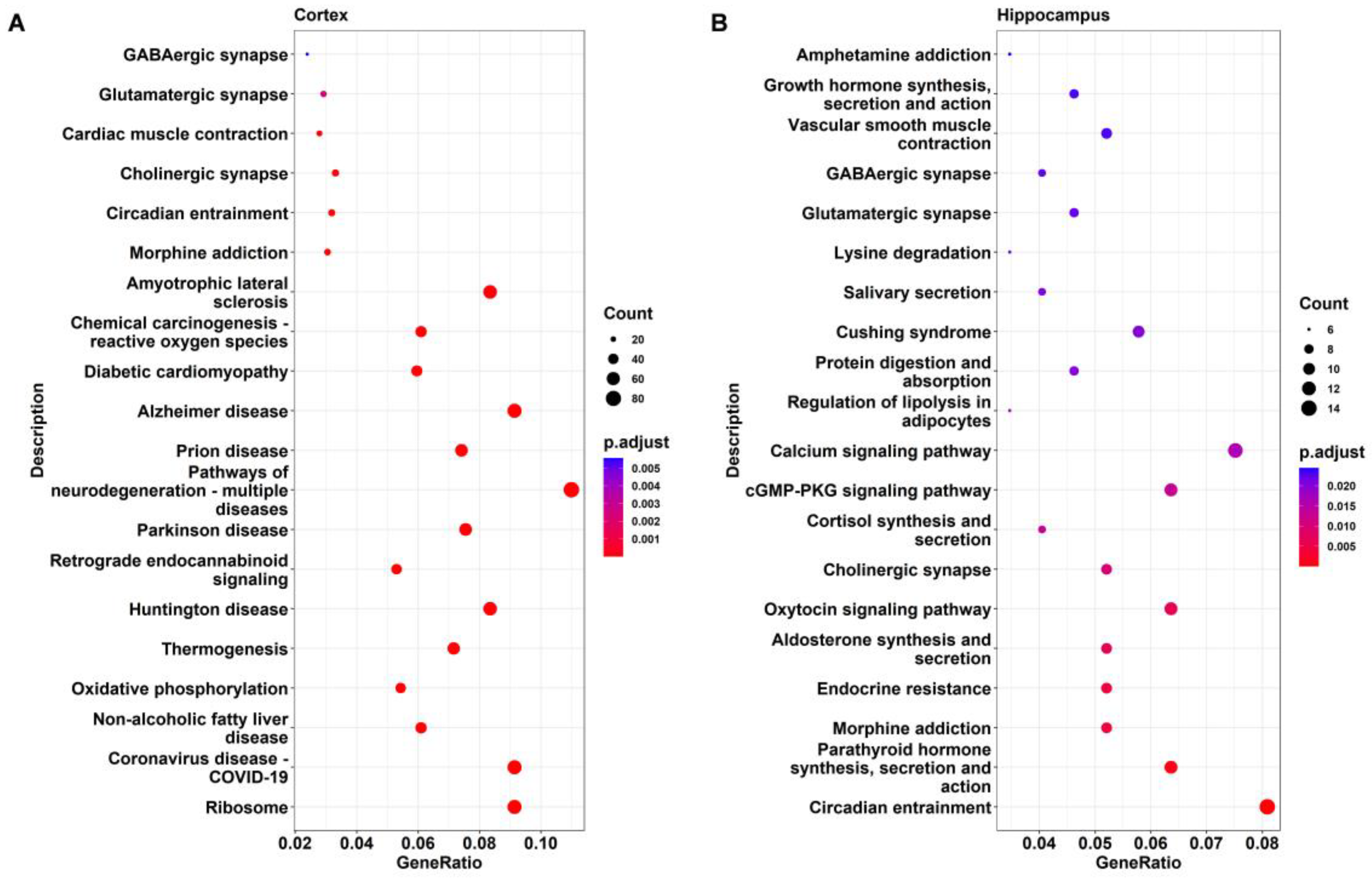
2.4. KEGG Pathway Analysis of DEGs
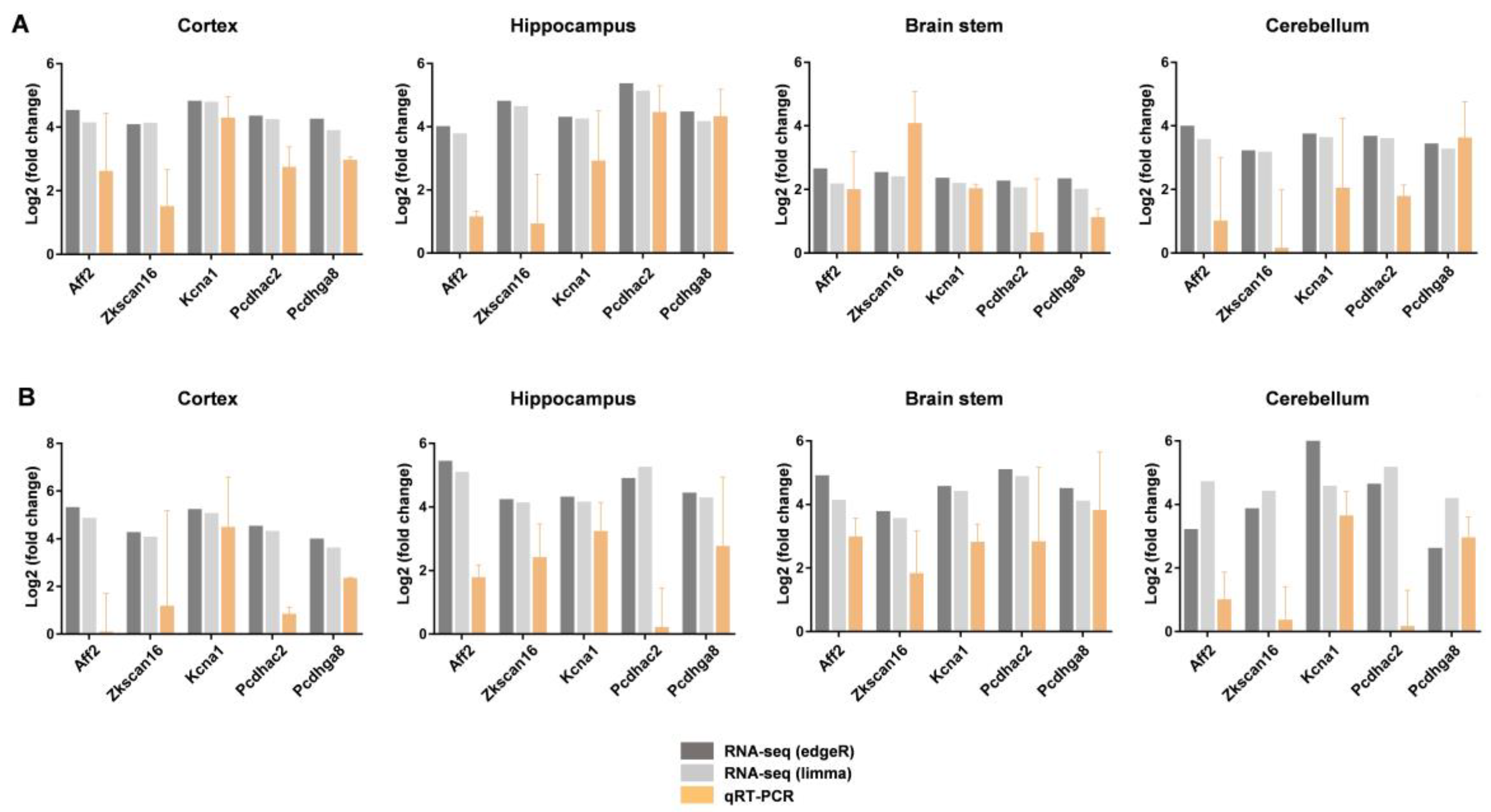
2.5. Gene Expression Validation by RT-PCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.3. Transcriptome Sequencing
4.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, N.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lee, T.H. Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Phosphorylation in Neuronal Cell Death and Neurodegenerative Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiloh, R.; Bialik, S.; Kimchi, A. The DAPK family: A structure-function analysis. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2014, 19, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiss, L.P.; Feinstein, E.; Berissi, H.; Cohen, O.; Kimchi, A. Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lee, T.H. Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 as a Promising Drug Target in Cancer and Alzheimer’s Disease. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Hioki, T.; Nagayama, S.; Ooashi, N.; Sun, X.; Ishii, T.; Kudo, Y.; Nakajima-Iijima, S.; et al. Developmental changes in distribution of death-associated protein kinase mRNAs. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 58, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Yamashita, T. Role of DAPK in neuronal cell death. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2014, 19, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Salomon, V.; Bialik, S.; Kimchi, A. DAP-kinase and autophagy. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2014, 19, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.X.; Chai, G.S.; Ni, Z.F.; Hu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, X.S.; Chen, N.N.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, G.P. Phosphorylation of tau by death-associated protein kinase 1 antagonizes the kinase-induced cell apoptosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2013, 37, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xia, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, D.; Gan, C.L.; Wang, L.; Mei, Y.; Lan, G.; Shui, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. Death-associated protein kinase 1 mediates Aβ42 aggregation-induced neuronal apoptosis and tau dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.L.; Zou, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, D.; Lan, G.; Mei, Y.; Wang, L.; Shui, X.; Hu, L.; et al. Inhibition of Death-associated Protein Kinase 1 protects against Epileptic Seizures in mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.L.; Zou, Y.; Chen, D.; Shui, X.; Hu, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Mei, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Blocking ERK-DAPK1 Axis Attenuates Glutamate Excitotoxicity in Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman Alsaadi, M. Role of DAPK1 in neuronal cell death, survival and diseases in the nervous system. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2019, 74, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonarati, O.R.; Cook, S.G.; Goodell, D.J.; Chalmers, N.E.; Rumian, N.L.; Tullis, J.E.; Restrepo, S.; Coultrap, S.J.; Quillinan, N.; Herson, P.S.; et al. CaMKII versus DAPK1 Binding to GluN2B in Ischemic Neuronal Cell Death after Resuscitation from Cardiac Arrest. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1–8.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodell, D.J.; Zaegel, V.; Coultrap, S.J.; Hell, J.W.; Bayer, K.U. DAPK1 Mediates LTD by Making CaMKII/GluN2B Binding LTP Specific. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, S.; Jin, H.; Bi, L.; Wei, N.; Yan, H.; Yang, X.; Yao, C.; Xu, M.; Shu, S.; et al. A Novel Mechanism of Spine Damages in Stroke via DAPK1 and Tau. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 4559–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Zhu, H.; Tang, N.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Pei, L.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tian, Q.; et al. Selective Degeneration of Entorhinal-CA1 Synapses in Alzheimer’s Disease via Activation of DAPK1. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10843–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.H.; Kim, B.M.; Chen, C.H.; Begley, M.J.; Cantley, L.C.; Lee, T.H. Death-associated protein kinase 1 phosphorylates NDRG2 and induces neuronal cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Z.; Li, B.Q.; Jia, J.P. DAPK1: A Novel Pathology and Treatment Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; You, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lee, S.; Hong, Y.; Hong, Y.; Kimchi, A.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lee, T.H. Death-associated protein kinase 1 has a critical role in aberrant tau protein regulation and function. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; You, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Suh, J.; Tanzi, R.E.; Lee, T.H. Inhibition of death-associated protein kinase 1 attenuates the phosphorylation and amyloidogenic processing of amyloid precursor protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 2498–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Deng, M.F.; Xiong, W.; Xie, A.J.; Guo, J.; Liang, Z.H.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.G.; Zhu, X.; Man, H.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-26a/Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Signaling Induces Synucleinopathy and Dopaminergic Neuron Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. LncRNA MALAT1 targeting miR-124-3p regulates DAPK1 expression contributes to cell apoptosis in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.E.; Caron, N.S.; Aly, A.E.; Lemarié, F.L.; Dal Cengio, L.; Ko, Y.; Lazic, N.; Anderson, L.; Nguyen, B.; Raymond, L.A.; et al. DAPK1 Promotes Extrasynaptic GluN2B Phosphorylation and Striatal Spine Instability in the YAC128 Mouse Model of Huntington Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 590569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Wang, B.; Koikawa, K.; Nezu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Lee, T.H.; Zhou, X.Z. Inhibition of death-associated protein kinase 1 attenuates cis P-tau and neurodegeneration in traumatic brain injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 203, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cui, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Han, L.; Du, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-124/Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Signaling Regulates Neuronal Apoptosis in Traumatic Brain Injury via Phosphorylating NR2B. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 892197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, T.; Shirooie, S.; Sureda, A.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Dehpour, A.R.; Saldías, M.; Akkol, E.K. Regulation of DAPK1 by Natural Products: An Important Target in Treatment of Stroke. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2142–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Pang, P.; Pei, L.; Shen, H.; Lu, Y. DAPK1 Signaling Pathways in Stroke: From Mechanisms to Therapies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4716–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Xu, X.; Peng, L.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, W.; Soundarapandian, M.M.; Balel, C.; Wang, M.; Jia, N.; Zhang, W.; et al. DAPK1 interaction with NMDA receptor NR2B subunits mediates brain damage in stroke. Cell 2010, 140, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mei, Y.; Kim, N.; Lan, G.; Gan, C.L.; Fan, F.; Zhang, T.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.; et al. Melatonin directly binds and inhibits death-associated protein kinase 1 function in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 69, e12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shui, X.; Mei, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lan, G.; Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Gan, C.L.; Li, R.; Tian, Y.; et al. miR-143-3p Inhibits Aberrant Tau Phosphorylation and Amyloidogenic Processing of APP by Directly Targeting DAPK1 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shui, X.; Zhang, M.; Mei, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lan, G.; Hu, L.; Gan, C.L.; Tian, Y.; Li, R.; et al. MiR-191-5p Attenuates Tau Phosphorylation, Aβ Generation, and Neuronal Cell Death by Regulating Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 3554–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Ke, X.; Deng, M.; Wu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Afewerky, H.K.; Zhang, X.; Pei, L.; Lu, Y. Degradation of Caytaxin Causes Learning and Memory Deficits via Activation of DAPK1 in Aging. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3368–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukawa, K.; Tanaka, T.; Bai, T.; Li, L.; Tsubota, Y.; Owada-Makabe, K.; Maeda, M.; Hoshino, K.; Akira, S.; Iso, H. Deletion of the kinase domain from death-associated protein kinase enhances spatial memory in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Pei, L.; Hu, L.; Pan, S.; Xiong, W.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Shang, Y.; Yao, S. Death-associated protein kinase 1 mediates interleukin-1β production through regulating inlfammasome activation in Bv2 microglial cells and mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansoub, H.; Tang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.Q.; Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Salissou, M.T.M.; Lu, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhou, L.T.; Almansob, Y.A.M.; et al. Oxytocin Alleviates MPTP-Induced Neurotoxicity in Mice by Targeting MicroRNA-26a/Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Pathway. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2020, 74, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, M.; Soriano, L.; Wieloch, T.; Nikolich, K.; Urfer, R.; Oksenberg, D. Death-associated protein kinase is activated by dephosphorylation in response to cerebral ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42290–42299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.B.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhao, R.; Shi, T.Y.; Feng, S.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.Q.; Wu, Y.M.; et al. G-protein-coupled receptor 30 mediates rapid neuroprotective effects of estrogen via depression of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4887–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, D.C.; Schindler, C.K.; So, N.K.; Lan, J.Q.; Meller, R.; Simon, R.P. Death-associated protein kinase expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Hossain, M.; Mishra, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Najm, I.; Ghosh, C. Expression and Functional Relevance of Death-Associated Protein Kinase in Human Drug-Resistant Epileptic Brain: Focusing on the Neurovascular Interface. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4904–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Shinoda, S.; Schindler, C.K.; Quan-Lan, J.; Meller, R.; Taki, W.; Simon, R.P.; Henshall, D.C. Expression, interaction, and proteolysis of death-associated protein kinase and p53 within vulnerable and resistant hippocampal subfields following seizures. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, D.C.; Araki, T.; Schindler, C.K.; Shinoda, S.; Lan, J.Q.; Simon, R.P. Expression of death-associated protein kinase and recruitment to the tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway following brief seizures. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Das, S.; Sheng, Z.H. Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of syntaxin-1A by the death-associated protein (DAP) kinase regulates its interaction with Munc18. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26265–26274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozuacik, D.; Bialik, S.; Raveh, T.; Mitou, G.; Shohat, G.; Sabanay, H.; Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Kimchi, A. DAP-kinase is a mediator of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase activation and autophagic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Liang, T.; Ye, Z.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Yi, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, J.; et al. Mechanism of COVID-19-Related Proteins in Spinal Tuberculosis: Immune Dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 882651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodell, D.J.; Tullis, J.E.; Bayer, K.U. Young DAPK1 knockout mice have altered presynaptic function. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 125, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Albayram, O.; Kondo, A.; Wang, B.; Kim, N.; Arai, K.; Tsai, C.Y.; Bassal, M.A.; Herbert, M.K.; Washida, K.; et al. Cis P-tau underlies vascular contribution to cognitive impairment and dementia and can be effectively targeted by immunotherapy in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Lv, F.; Shen, H.; Pei, L. Presynaptic Caytaxin prevents apoptosis via deactivating DAPK1 in the acute phase of cerebral ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, K.A.; Hallgren, J.; Bockman, C.S.; Aggarwal, A.; Kansal, V.; Netzel, L.; Iyer, S.H.; Matthews, S.A.; Deodhar, M.; Oldenburg, P.J.; et al. Respiratory dysfunction progresses with age in Kcna1-null mice, a model of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.A.; Vuong, H.E.; Yano, J.M.; Liang, Q.Y.; Nusbaum, D.J.; Hsiao, E.Y. The Gut Microbiota Mediates the Anti-Seizure Effects of the Ketogenic Diet. Cell 2018, 173, 1728–1741.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio-Simeone, K.A.; Wilke, J.C.; Milligan, H.L.; Allen, C.N.; Rho, J.M.; Maganti, R.K. Ketogenic diet treatment abolishes seizure periodicity and improves diurnal rhythmicity in epileptic Kcna1-null mice. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulhus, K.; Ammerman, L.; Glasscock, E. Clinical Spectrum of KCNA1 Mutations: New Insights into Episodic Ataxia and Epilepsy Comorbidity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Lin, Z.; Wen, S.; Jiang, Y. Potassium channels and epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 146, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowball, A.; Chabrol, E.; Wykes, R.C.; Shekh-Ahmad, T.; Cornford, J.H.; Lieb, A.; Hughes, M.P.; Massaro, G.; Rahim, A.A.; Hashemi, K.S.; et al. Epilepsy Gene Therapy Using an Engineered Potassium Channel. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinform. (Oxf. Engl.) 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthauer, K.; Kimes, P.K.; Duvallet, C.; Reyes, A.; Subramanian, A.; Teng, M.; Shukla, C.; Alm, E.J.; Hicks, S.C. A practical guide to methods controlling false discoveries in computational biology. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. ClusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lan, G.; Li, R.; Mei, Y.; Shui, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Gan, C.L.; Xia, Y.; et al. Melatonin ameliorates tau-related pathology via the miR-504-3p and CDK5 axis in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


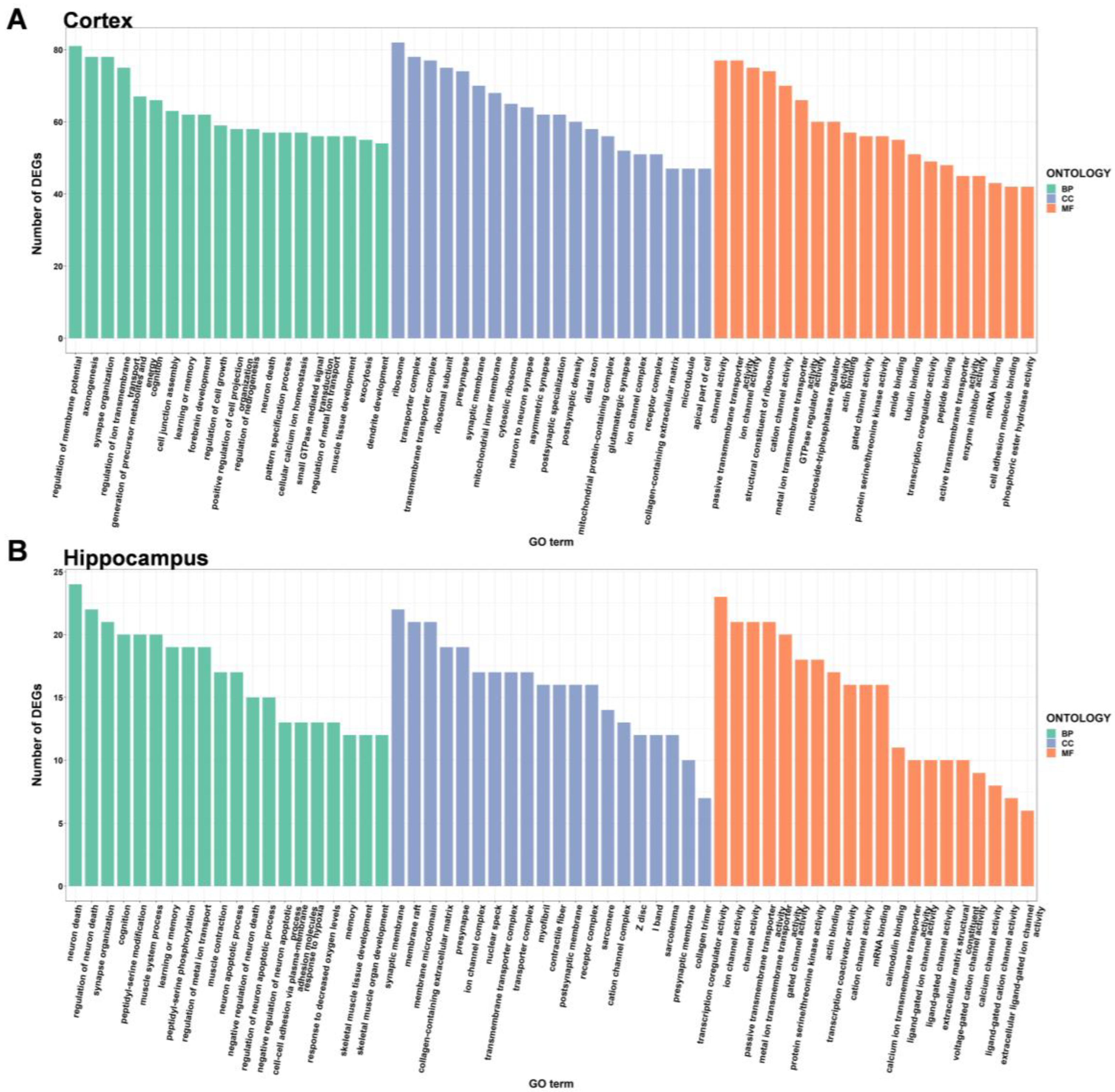
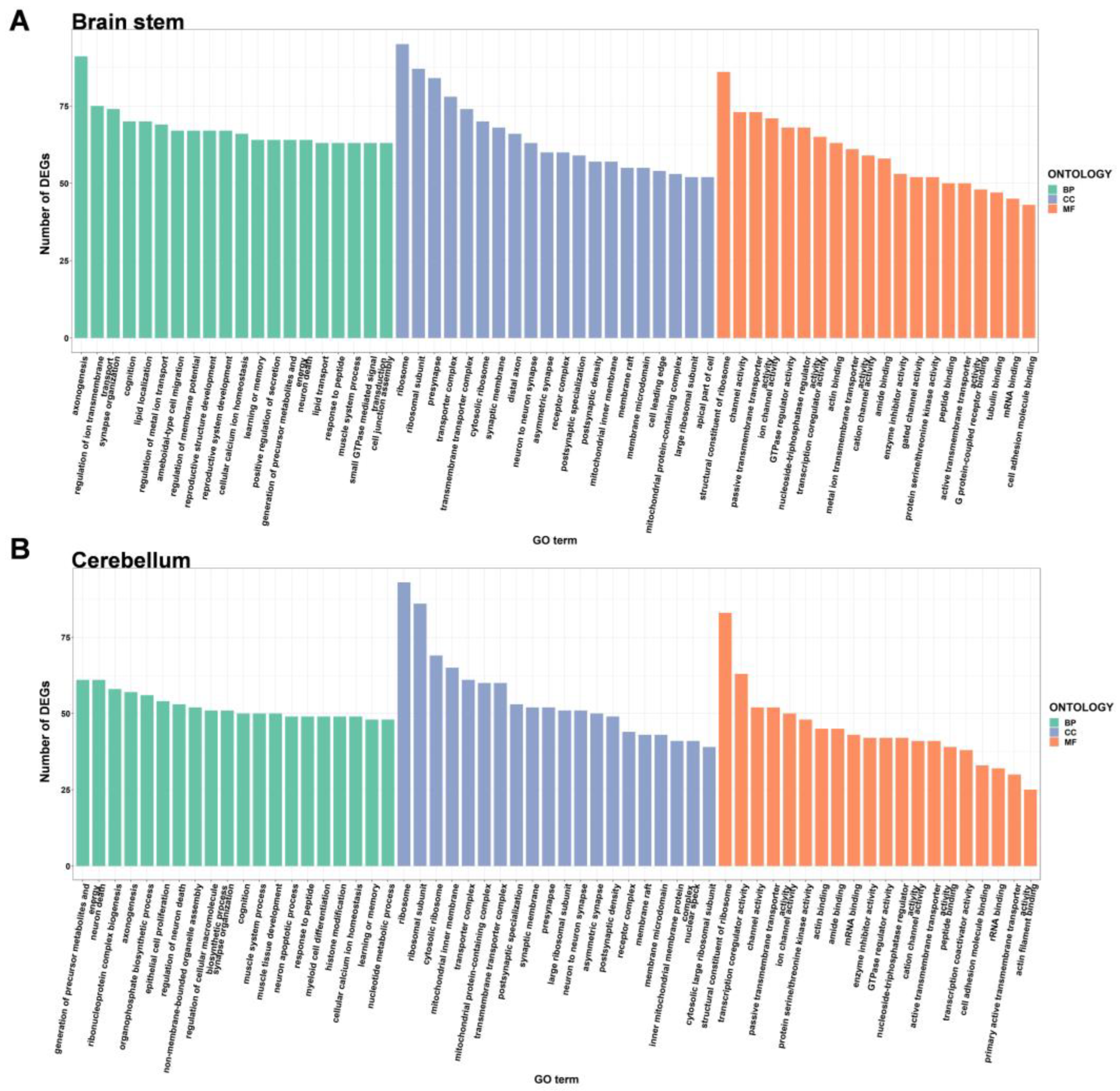

| Gender | Tissues | Total GO Categories | Biological Processes | Cell Component | Molecular Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Cortex | 983 | 727 | 139 | 117 |
| Hippocampus | 79 | 29 | 26 | 24 | |
| Brain stem | 930 | 691 | 135 | 104 | |
| Cerebellum | 440 | 275 | 107 | 58 | |
| Female | Cortex | 244 | 156 | 61 | 27 |
| Hippocampus | 32 | 21 | 1 | 10 | |
| Brain stem | 271 | 160 | 70 | 41 | |
| Cerebellum | 267 | 129 | 94 | 44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Zhi, S.; Lan, G.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lee, T.H.; Rao, S.; et al. Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076542
Li R, Zhi S, Lan G, Chen X, Zheng X, Hu L, Wang L, Zhang T, Lee TH, Rao S, et al. Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruomeng, Shuai Zhi, Guihua Lan, Xiaotong Chen, Xiuzhi Zheng, Li Hu, Long Wang, Tao Zhang, Tae Ho Lee, Shitao Rao, and et al. 2023. "Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076542
APA StyleLi, R., Zhi, S., Lan, G., Chen, X., Zheng, X., Hu, L., Wang, L., Zhang, T., Lee, T. H., Rao, S., & Chen, D. (2023). Ablation of Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Changes the Transcriptomic Profile and Alters Neural-Related Pathways in the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076542






