Sevoflurane Induces a Cyclophilin D-Dependent Decrease of Neural Progenitor Cells Migration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
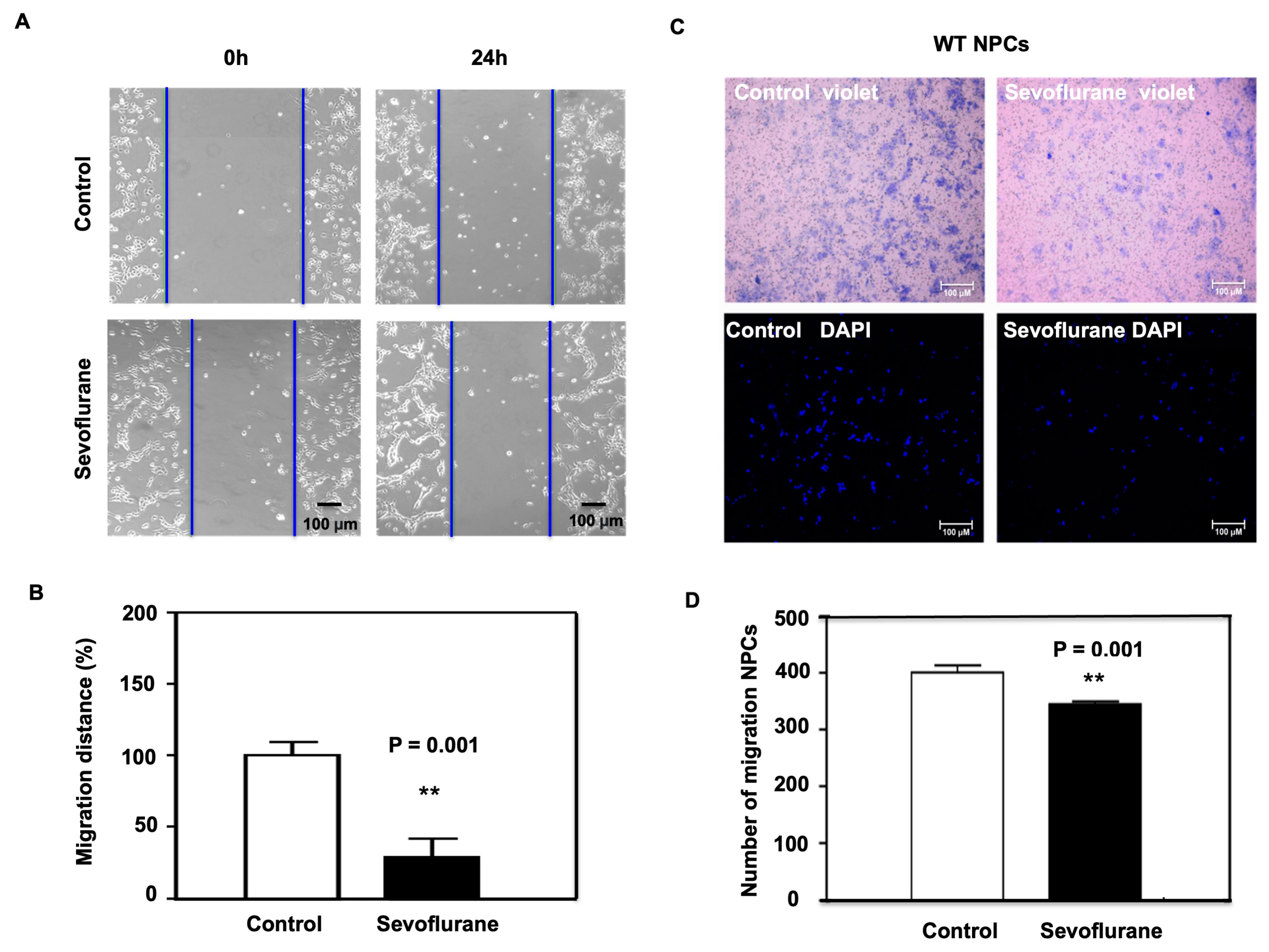
2.1. Sevoflurane Induced the Decrease of Migration in NPCs Harvested from WT Mice
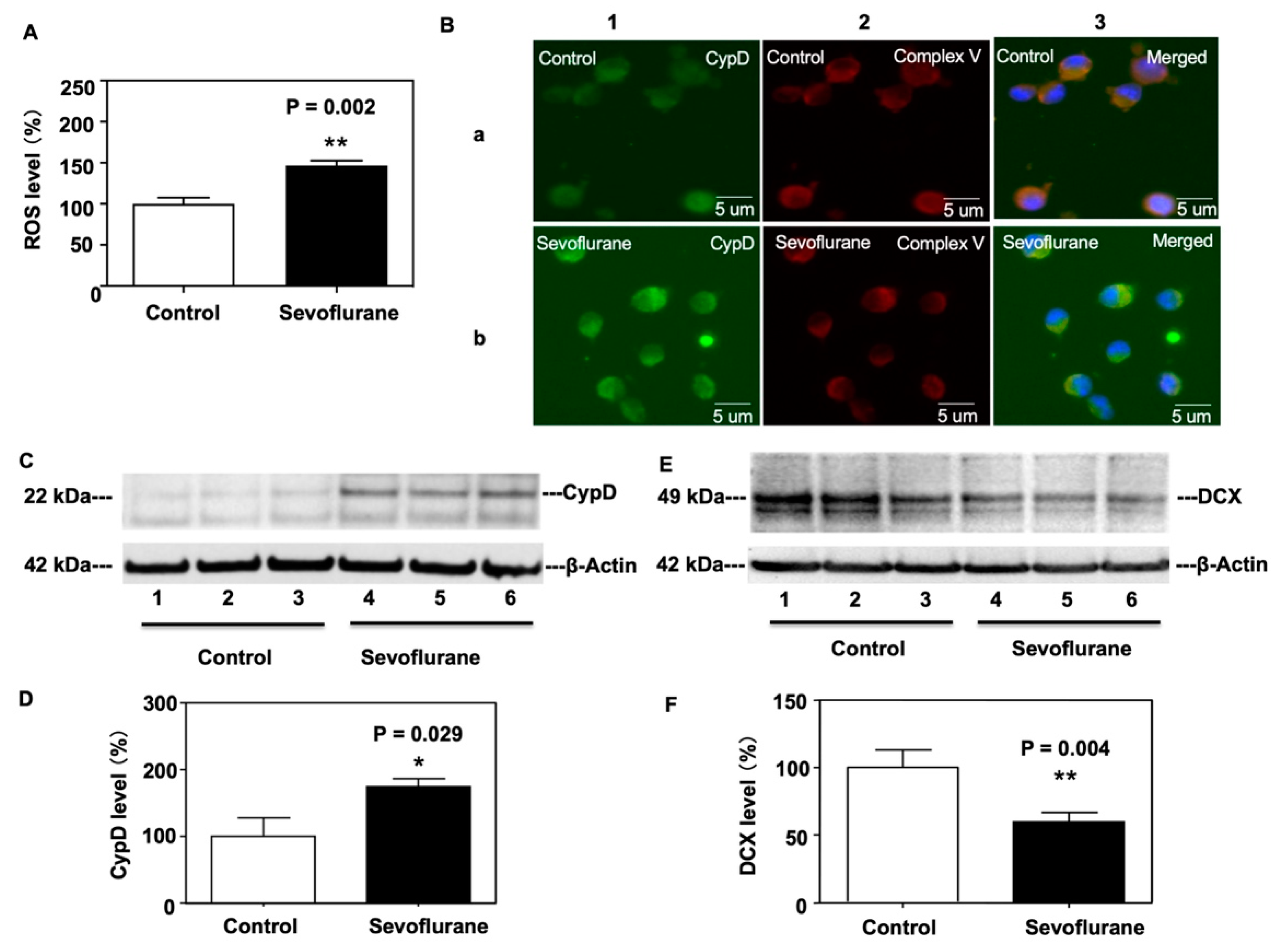
2.2. Sevoflurane Increased CypD and ROS Levels and Decreased DCX Levels in NPCs Harvested from WT Mice
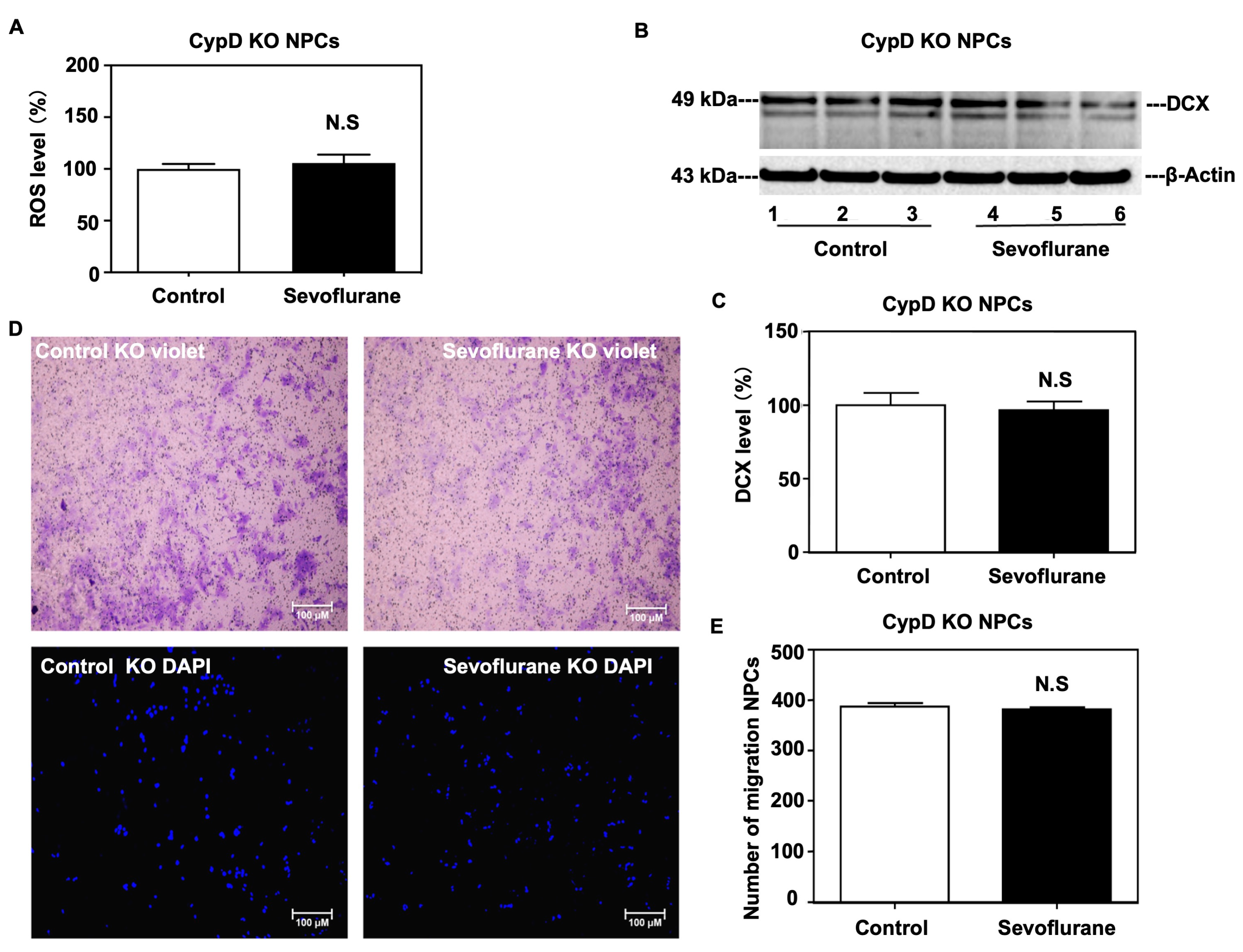
2.3. Sevoflurane Induced a CypD-Dependent Impairment of Migration of NPCs
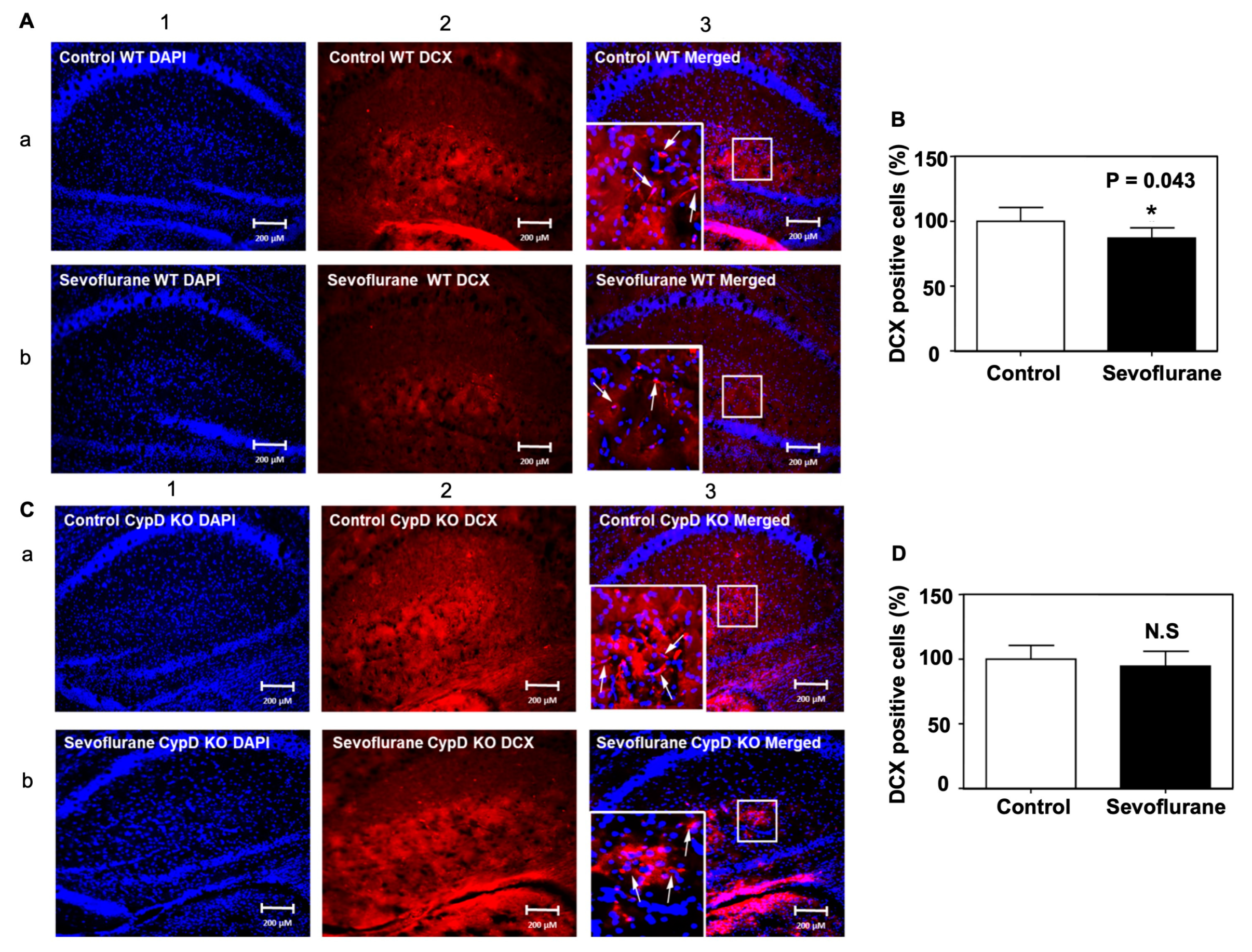
2.4. Sevoflurane Induced a CypD-Dependent Decrease of DCX-Positive Cells in Hippocampus of Young WT Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
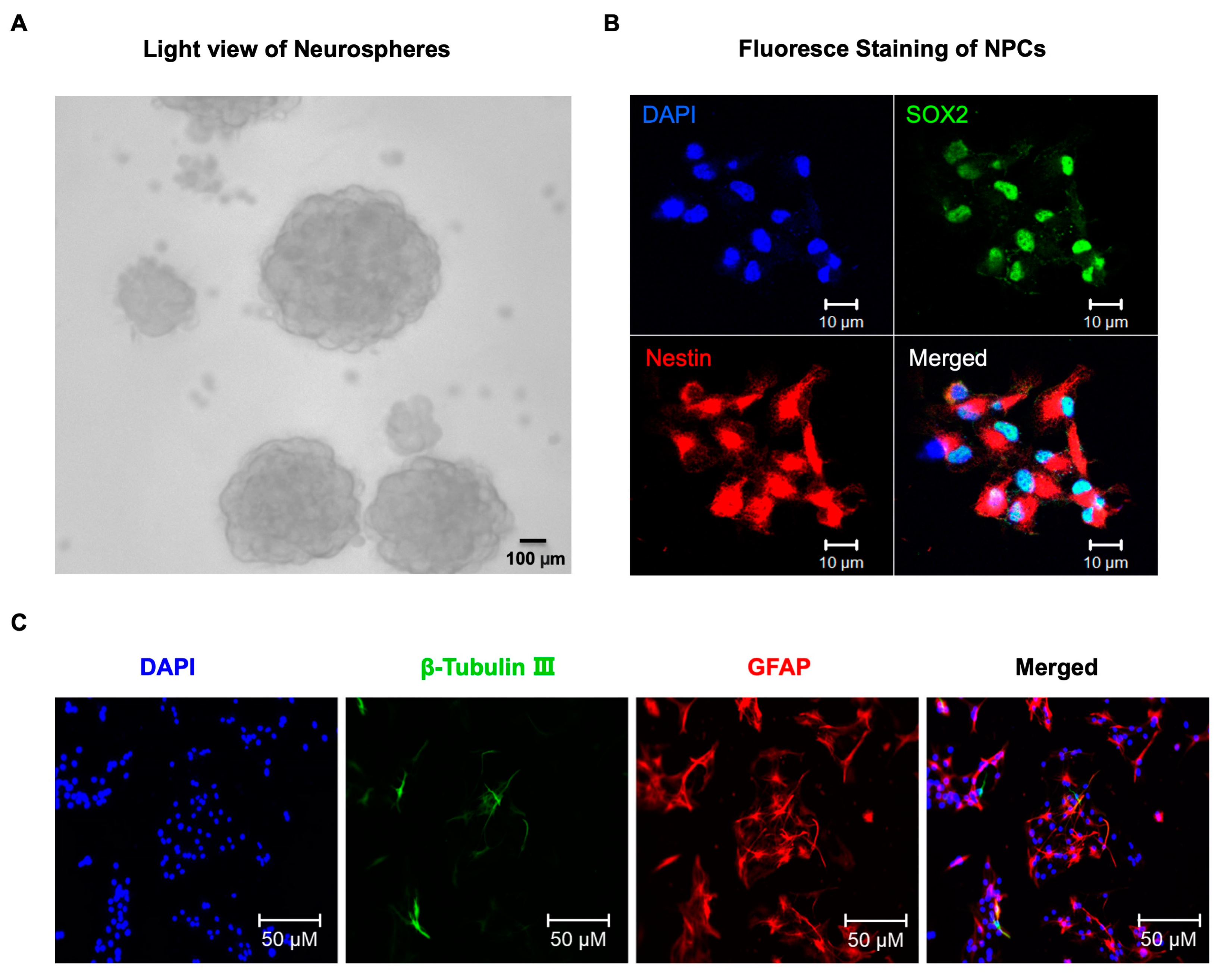
4.1. Neural Progenitor Cells (NPCs) Culture and Treatment
4.2. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.3. Wound Healing Assay
4.4. Transwell Migration Assay
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Measurement
4.7. Mice Anesthesia
4.8. Brain Tissue Collection
4.9. A Tandem Mass Tag (TMT)-Labeling and Sample Cleaning up for MASS Spectrometry Study
4.10. Proteomic Data Analysis
4.11. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Soriano, S.G.; Vutskits, L.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Hemmings, H.C.; Davidson, A.; Warner, D.O.; Sun, L.S. Thinking, fast and slow: Highlights from the 2016 BJA seminar on anaesthetic neurotoxicity and neuroplasticity. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilder, R.T.; Flick, R.P.; Sprung, J.; Katusic, S.K.; Barbaresi, W.J.; Mickelson, C.; Gleich, S.J.; Schroeder, D.R.; Weaver, A.L.; Warner, D.O. Early exposure to anesthesia and learning disabilities in a population-based birth cohort. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.S.; Li, G.; Miller, T.L.; Salorio, C.; Byrne, M.W.; Bellinger, D.C.; Ing, C.; Park, R.; Radcliffe, J.; Hays, S.R.; et al. Association Between a Single General Anesthesia Exposure Before Age 36 Months and Neurocognitive Outcomes in Later Childhood. JAMA 2016, 315, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, A.J.; Disma, N.; de Graaff, J.C.; Withington, D.E.; Dorris, L.; Bell, G.; Stargatt, R.; Bellinger, D.C.; Schuster, T.; Arnup, S.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years of age after general anaesthesia and awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): An international multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, D.O.; Chelonis, J.J.; Paule, M.G.; Frank, R.D.; Lee, M.; Zaccariello, M.J.; Katusic, S.K.; Schroeder, D.R.; Hanson, A.C.; Schulte, P.J.; et al. Performance on the Operant Test Battery in young children exposed to procedures requiring general anaesthesia: The MASK study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vutskits, L.; Xie, Z. Lasting impact of general anaesthesia on the brain: Mechanisms and relevance. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ing, C.; Warner, D.O.; Sun, L.S.; Flick, R.P.; Davidson, A.J.; Vutskits, L.; McCann, M.E.; O’Leary, J.; Bellinger, D.C.; Rauh, V.; et al. Anesthesia and Developing Brains: Unanswered Questions and Proposed Paths Forward. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, N.; Ori, C.; Erisir, A.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. General anesthesia causes long-lasting disturbances in the ultrastructural properties of developing synapses in young rats. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, G. Autophagy activation prevents sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in H4 human neuroglioma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Qin, J.; Ge, P.; Feng, C. Sevoflurane Exposure Induces Neuronal Cell Parthanatos Initiated by DNA Damage in the Developing Brain via an Increase of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 583782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Yang, Q.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Ke, Z.J. Sevoflurane decreases self-renewal capacity and causes c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated damage of rat fetal neural stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, R.; Ling, X.; Peng, M.; Xue, Z.; Cang, J.; Fang, F. Maternal Sevoflurane Exposure Causes Abnormal Development of Fetal Prefrontal Cortex and Induces Cognitive Dysfunction in Offspring. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 6158468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Joseph, D.J.; Inan, S.; Wei, H. Dual effects of isoflurane on proliferation, differentiation, and survival in human neuroprogenitor cells. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, P.; Liang, F.; Liufu, N.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, J.C.; Xie, Z. Cyclophilin D Contributes to Anesthesia Neurotoxicity in the Developing Brain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. Sevoflurane inhibits embryonic stem cell self-renewal and subsequent neural differentiation by modulating the let-7a-Lin28 signaling pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Shie, V.; Wang, H.; Busscher, J.J.; Yue, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, Z. Sevoflurane inhibits neurogenesis and the Wnt-catenin signaling pathway in mouse neural progenitor cells. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Song, R.; Ling, X.; Peng, M.; Xue, Z.; Cang, J. Multiple sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant mice inhibits neurogenesis of fetal hippocampus via repressing transcription factor Pax6. Life Sci. 2017, 175, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Shi, H.N.; Culley, D.J.; Crosby, G.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Tanzi, R.E.; Xie, Z. Anesthetics isoflurane and desflurane differently affect mitochondrial function, learning, and memory. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, G.; Sall, J.W.; May, L.D.; Bell, J.S.; Magnusson, K.R.; Rau, V.; Visrodia, K.H.; Alvi, R.S.; Ku, B.; Lee, M.T.; et al. Isoflurane differentially affects neurogenesis and long-term neurocognitive function in 60-day-old and 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, W.; Ryu, M.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoon, S.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, S.H.; et al. Sevoflurane Exposure during the Critical Period Affects Synaptic Transmission and Mitochondrial Respiration but Not Long-term Behavior in Mice. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrock, L.G.; Starner, M.L.; Murphy, K.L.; Baxter, M.G. Long-term effects of single or multiple neonatal sevoflurane exposures on rat hippocampal ultrastructure. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, E.; Fante, L.; Fowlkes, J.; Petronilli, V.; Forte, M.A.; Bernardi, P. Properties of the permeability transition pore in mitochondria devoid of Cyclophilin D. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18558–18561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baines, C.P.; Kaiser, R.A.; Purcell, N.H.; Blair, N.S.; Osinska, H.; Hambleton, M.A.; Brunskill, E.W.; Sayen, M.R.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Dorn, G.W.; et al. Loss of cyclophilin D reveals a critical role for mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death. Nature 2005, 434, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Rydzewska, M.; Yan, S. Cyclophilin D deficiency improves mitochondrial function and learning/memory in aging Alzheimer disease mouse model. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Guo, L.; Wu, X.; Sosunov, A.A.; McKhann, G.M.; Chen, J.X.; Yan, S.S. Cyclophilin D deficiency rescues Abeta-impaired PKA/CREB signaling and alleviates synaptic degeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Guo, L.; Fang, F.; Chen, D.; Sosunov, A.A.; McKhann, G.M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Molkentin, J.D.; et al. Cyclophilin D deficiency attenuates mitochondrial and neuronal perturbation and ameliorates learning and memory in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, C.; Cerpa, W.; Tapia-Rojas, C.; Quintanilla, R.A. Tau Deletion Prevents Cognitive Impairment and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Age Associated by a Mechanism Dependent on Cyclophilin-D. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 586710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Gao, J.; Karlsson, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Kuhn, H.G.; Blomgren, K. Isoflurane anesthesia induced persistent, progressive memory impairment, caused a loss of neural stem cells, and reduced neurogenesis in young, but not adult, rodents. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2010, 30, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.; Shi, P.; Mao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. Effect of apoptosis in neural stem cells treated with sevoflurane. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, H.; Peng, Z.; Lao, N.; Dong, H.; Xiong, L. Effects of sevoflurane on self-renewal capacity and differentiation of cultured neural stem cells. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, D.J.; Boyd, J.D.; Palanisamy, A.; Xie, Z.; Kojima, K.; Vacanti, C.A.; Tanzi, R.E.; Crosby, G. Isoflurane decreases self-renewal capacity of rat cultured neural stem cells. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, W.; Hapfelmeier, G.; Kochs, E.; Zieglgansberger, W.; Rammes, G. Isoflurane blocks synaptic plasticity in the mouse hippocampus. Anesthesiology 2001, 94, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, F.; Koulakoff, A.; Boucher, D.; Chafey, P.; Schaar, B.; Vinet, M.C.; Friocourt, G.; McDonnell, N.; Reiner, O.; Kahn, A.; et al. Doublecortin is a developmentally regulated, microtubule-associated protein expressed in migrating and differentiating neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Quarm, A.K.; Xi, S.; Sun, T.; Zhang, D.; Qian, J.; Ding, H.; Gao, J. Cyclophilin D-mediated angiotensin II-induced NADPH oxidase 4 activation in endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction that can be rescued by gallic acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 940, 175475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Carlsson, Y.; Basso, E.; Zhu, C.; Rousset, C.I.; Rasola, A.; Johansson, B.R.; Blomgren, K.; Mallard, C.; Bernardi, P.; et al. Developmental shift of cyclophilin D contribution to hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2588–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akter, M.; Kaneko, N.; Sawamoto, K. Neurogenesis and neuronal migration in the postnatal ventricular-subventricular zone: Similarities and dissimilarities between rodents and primates. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 167, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, F.C.; de Chevigny, A.; Falace, A.; Cardoso, C. Disorders of neurogenesis and cortical development. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accogli, A.; Addour-Boudrahem, N.; Srour, M. Neurogenesis, neuronal migration, and axon guidance. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 173, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Miao, C.; Soriano, S.G.; Sun, D.; Baxter, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Selective Anesthesia-induced Neuroinflammation in Developing Mouse Brain and Cognitive Impairment. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Y.; Yu, B.; Crosby, G.; Culley, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Sevoflurane induces tau phosphorylation and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta activation in young mice. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tan, H.; Boukhali, M.; Khatri, A.; Yu, Y.; Hua, F.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Yang, G.; et al. Tau Contributes to Sevoflurane-induced Neurocognitive Impairment in Neonatal Mice. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, Z. Propofol and magnesium attenuate isofluraneinduced caspase-3 activation via inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Med. Gas. Res. 2012, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Lu, H.; Dong, Y.; Shapoval, D.; Soriano, S.G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Coenzyme Q10 reduces sevoflurane-induced cognitive deficiency in young mice. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drobish, J.K.; Gan, Z.S.; Cornfeld, A.D.; Eckenhoff, M.F. From the Cover: Volatile Anesthetics Transiently Disrupt Neuronal Development in Neonatal Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
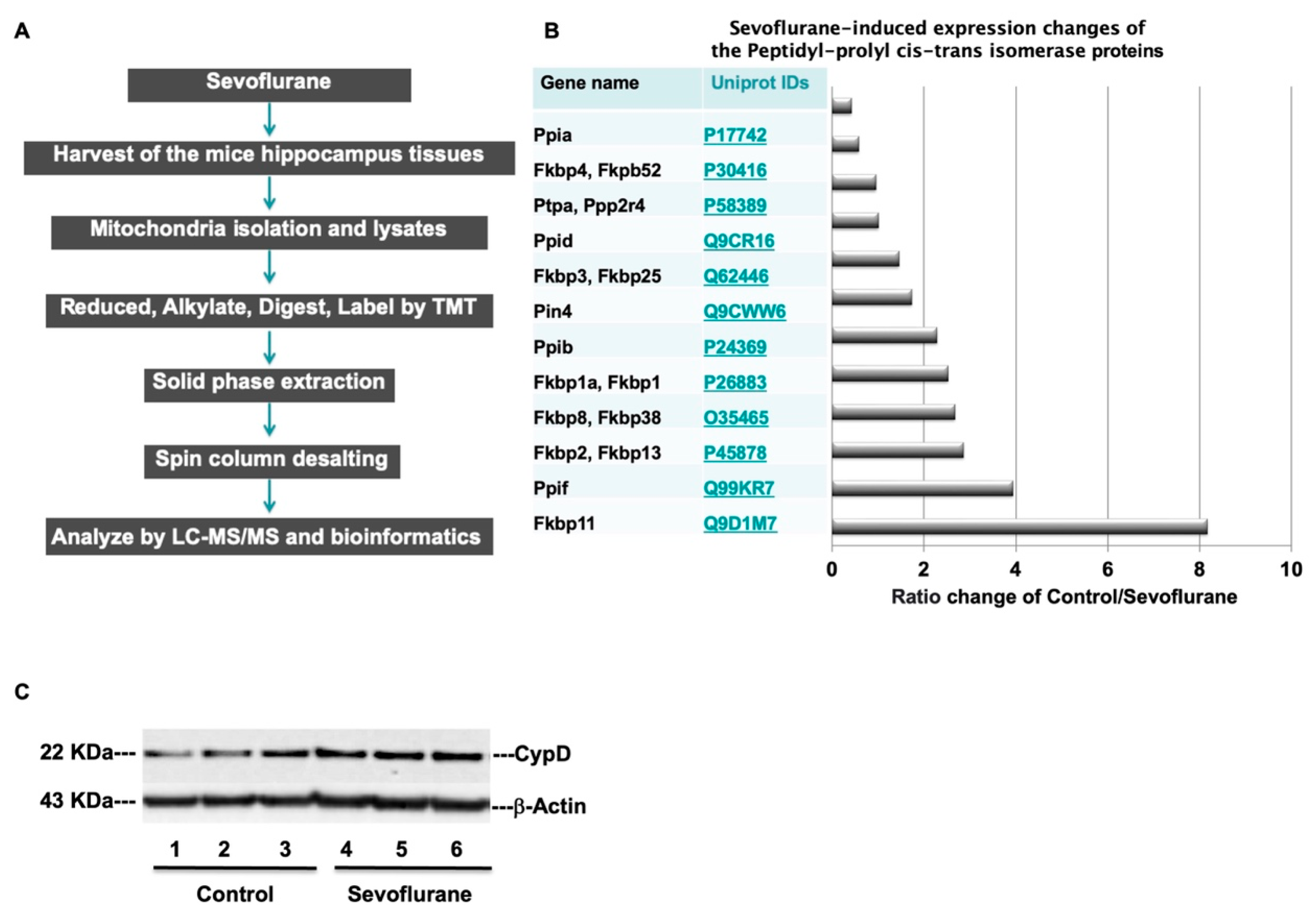

| Uniport IDs | Protein Full Name | Gene Name | MW | Control vs. Sevoflurane Abundance Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9D1M7 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP11 | Fkbp11 | 22.2 | 8.167487685 |
| Q99KR7 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase F, mitochondrial | Ppif | 22 | 3.931292942 |
| P45878 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP2 | Fkbp2, Fkbp13 | 15.6 | 2.857343838 |
| O35465 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP8 | Fkbp8, Fkbp38 | 44.5 | 2.669543147 |
| P26883 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1A | Fkbp1a, Fkbp1 | 11.9 | 2.519260401 |
| P24369 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | Ppib | 23.7 | 2.282234957 |
| Q9CWW6 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 4 | Pin4 | 13.8 | 1.732792463 |
| Q62446 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP3 | Fkbp3, Fkbp25 | 25.2 | 1.453658537 |
| Q9CR16 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase D | Ppid | 40.7 | 1.001914608 |
| P58389 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A activator | Ptpa, Ppp2r4 | 40.6 | 0.948455804 |
| P30416 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP4 | Fkbp4, Fkpb52 | 51.8 | 0.578207406 |
| P17742 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | Ppia | 18 | 0.414748708 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, P.; Liang, F.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y. Sevoflurane Induces a Cyclophilin D-Dependent Decrease of Neural Progenitor Cells Migration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076746
Lu P, Liang F, Dong Y, Xie Z, Zhang Y. Sevoflurane Induces a Cyclophilin D-Dependent Decrease of Neural Progenitor Cells Migration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076746
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Pan, Feng Liang, Yuanlin Dong, Zhongcong Xie, and Yiying Zhang. 2023. "Sevoflurane Induces a Cyclophilin D-Dependent Decrease of Neural Progenitor Cells Migration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076746
APA StyleLu, P., Liang, F., Dong, Y., Xie, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Sevoflurane Induces a Cyclophilin D-Dependent Decrease of Neural Progenitor Cells Migration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076746





