Aging of the Arterial System
Abstract
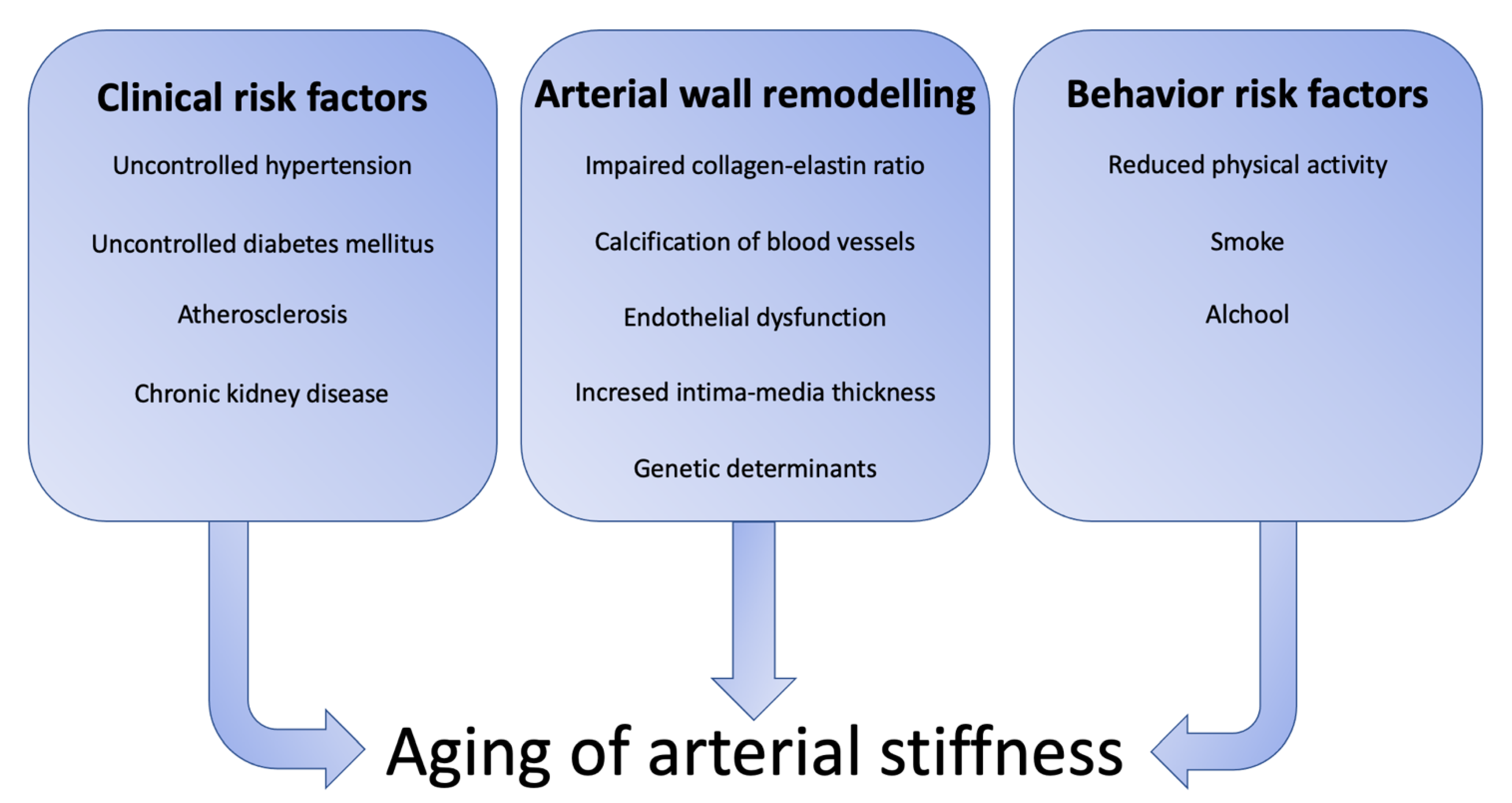
:1. Introduction
2. Arterial Wall Remodeling during Aging
2.1. Collagen and Elastin
2.2. Calcification
2.3. Endothelial Dysfunction and Intima-Media Thickening
2.4. Genetic Determinants
3. Method to Assess Arterial Stiffness
4. Clinical Risk Factor for Arterial Stiffness
4.1. Hypertension
4.2. Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Atherosclerosis
4.4. Chronic Kidney Disease
5. Behavior Risk Factors
5.1. Smoking
5.2. Alcohol
5.3. Physical Activity
6. Increased Arterial Stiffness and Clinical Outcome
6.1. Atrial Fibrillation
6.2. Stroke
6.3. Declined Cognitive Function
7. Pharmacological Treatment of Arterial Stiffness
7.1. Antihypertensive Drug
7.2. Antidiabetic-Drugs
7.3. Lipid-Lowering Drugs
7.4. Perspective
| Drug Class | PWV | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-hypertensive drugs | ||
| ACE Inhibitors | ↓ | ↓ RAS and acts as antifibrotic agents [105] |
| Angiotensin receptors blockers | ↓ | ↓ RAS and acts as antifibrotic agents [106] |
| Calcium channel antagonists | ↔ or ↓ | None or reduce wave reflection [107] |
| β-blockers | ↓ | Reduce heart rate and modulate visco-elastic properties of arterial wall [89] |
| Nitrates | ↔ | None documented |
| Diuretics | ↔ | None documented |
| Aldosterone antagonists | ↔ or ↓ | None or modulate fibronectin expression and vascular tone [108] |
| α-blockers | ↔ or ↓ | None or increase nitrogen oxygen [109] |
| Antidiabetic drugs | ||
| Glitazones | ↓ | ↓ AGE and its interaction with RAGE [91] |
| Metformin | ↔ or ↓ | ↓ AGE and its interaction with RAGE; increase adiponectin [110] |
| Lipid-lowering drugs | ||
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | ↓ | Modulate inflammation [97] |
| PCSK9 inhibitors | ↓ | Modulate inflammation [111] |
| Ezetimibe | ↓ | Modulate inflammation [101] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Limpijankit, T.; Vathesatogkit, P.; Matchariyakul, D.; Wiriyatanakorn, S.; Siriyotha, S.; Thakkinstian, A.; Sritara, P. Cardio-ankle vascular index as a predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events in metabolic syndrome patients. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tu, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Determinants of arterial elastic function in middle-aged and elderly people: A population-based cross-sectional study from a low-income population in China. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1037227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P. The structural factor of hypertension: Large and small artery alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatner, S.F.; Zhang, J.; Vyzas, C.; Mishra, K.; Graham, R.M.; Vatner, D.E. Vascular Stiffness in Aging and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 762437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritze, O.; Romero, B.; Schleicher, M.; Jacob, M.P.; Oh, D.; Starcher, B.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Bujan, J.; Stock, U.A. Age-related changes in the elastic tissue of the human aorta. J. Vasc. Res. 2012, 49, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.P.; Baugh, R.; Wilson, C.A.; Burns, J. Age related changes in the tunica media of the vertebral artery: Implications for the assessment of vessels injured by trauma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babici, D.; Kudej, R.K.; McNulty, T.; Zhang, J.; Oydanich, M.; Berkman, T.; Nishimura, K.; Bishop, S.P.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F. Mechanisms of increased vascular stiffness down the aortic tree in aging, premenopausal female monkeys. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H222–H234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Depre, C.; Ghosh, K.; Resuello, R.G.; Natividad, F.F.; Rossi, F.; Peppas, A.; Shen, Y.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F. Mechanism of gender-specific differences in aortic stiffness with aging in nonhuman primates. Circulation 2007, 116, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamiot-Clerc, P.; Renaud, J.F.; Safar, M.E. Pulse pressure, aortic reactivity, and endothelium dysfunction in old hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2001, 37, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aronson, D. Cross-linking of glycated collagen in the pathogenesis of arterial and myocardial stiffening of aging and diabetes. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, Y.; Kawano, K.; Yamasawa, F.; Ishii, T.; Shibata, T.; Inayama, S. Age-dependent changes of collagen and elastin content in human aorta and pulmonary artery. Angiology 1984, 35, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, J.; Engelen, L.; Ferreira, I.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Boutouyrie, P.; Laurent, S.; Segers, P.; Reesink, K.; Van Bortel, L.M. Reference values for local arterial stiffness. Part B: Femoral artery. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetos, A.; Laurent, S.; Hoeks, A.P.; Boutouyrie, P.H.; Safar, M.E. Arterial alterations with aging and high blood pressure. A noninvasive study of carotid and femoral arteries. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1993, 13, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, G.F.; Parise, H.; Benjamin, E.J.; Larson, M.G.; Keyes, M.J.; Vita, J.A.; Vasan, R.S.; Levy, D. Changes in arterial stiffness and wave reflection with advancing age in healthy men and women: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Windham, B.G.; Griswold, M.E.; Farasat, S.M.; Ling, S.M.; Carlson, O.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Najjar, S.S. Influence of leptin, adiponectin, and resistin on the association between abdominal adiposity and arterial stiffness. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolajevic, J.; Sabovic, M. Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Coagulation Effects on Medial Arterial Calcification in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescatore, L.A.; Gamarra, L.F.; Liberman, M. Multifaceted Mechanisms of Vascular Calcification in Aging. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribarren, C.; Sidney, S.; Sternfeld, B.; Browner, W.S. Calcification of the aortic arch: Risk factors and association with coronary heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. JAMA 2000, 283, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Toorn, J.E.; Rueda-Ochoa, O.L.; van der Schaft, N.; Vernooij, M.W.; Ikram, M.A.; Bos, D.; Kavousi, M. Arterial calcification at multiple sites: Sex-specific cardiovascular risk profiles and mortality risk-the Rotterdam Study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahousse, L.; Bos, D.; Wijnant, S.R.A.; Kavousi, M.; Stricker, B.H.; Van Der Lugt, A.; Vernooij, M.W.; Brusselle, G.G. Atherosclerotic calcification in major vessel beds in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The Rotterdam Study. Atherosclerosis 2019, 291, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donato, A.J.; Machin, D.R.; Lesniewski, L.A. Mechanisms of Dysfunction in the Aging Vasculature and Role in Age-Related Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Su, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhuo, D.; Ma, C.; Fan, G. The Induction of Endothelial Autophagy and Its Role in the Development of Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 831847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikkineth, A.C.; AlGhatrif, M.; Oberdier, M.T.; Morrell, C.; Palchamy, E.; Strait, J.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Lakatta, E.G. Sex Differences in Longitudinal Determinants of Carotid Intima Medial Thickening With Aging in a Community-Dwelling Population: The Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Aging. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Gao, L.; Ziegelbauer, K.; Norata, G.D.; Empana, J.P.; Schmidtmann, I.; Lin, H.; McLachlan, S.; Bokemark, L.; Ronkainen, K.; et al. Correction: Predictive value for cardiovascular events of common carotid intima media thickness and its rate of change in individuals at high cardiovascular risk—Results from the PROG-IMT collaboration. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Laurent, S. Mechanisms of Arterial Stiffening: From Mechanotransduction to Epigenetics. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.; Ramirez, J.; Warren, H.R.; Aung, N.; Lee, A.M.; Tzanis, E.; Petersen, S.E.; Munroe, P.B. Genome-wide association study identifies loci for arterial stiffness index in 127,121 UK Biobank participants. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Harst, P.; Verweij, N. Identification of 64 Novel Genetic Loci Provides an Expanded View on the Genetic Architecture of Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygui, F.; Wild, P.S.; Zeller, T.; Germain, M.; Castagné, R.; Lackner, K.J.; Münzel, T.; Montalescot, G.; Mitchell, G.F.; Verwoert, G.C.; et al. Adrenomedullin and arterial stiffness: Integrative approach combining monocyte ADM expression, plasma MR-Pro-ADM, and genome-wide association study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, G.F.; Verwoert, G.C.; Tarasov, K.V.; Isaacs, A.; Smith, A.V.; Rietzschel, E.R.; Tanaka, T.; Liu, Y.; Parsa, A.; Najar, S.S.; et al. Common genetic variation in the 3′-BCL11B gene desert is associated with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity and excess cardiovascular disease risk: The AortaGen Consortium. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yucel, C.; Demir, S.; Demir, M.; Tufenk, M.; Nas, K.; Molnar, F.; Illyes, M.; Acarturk, E. Left ventricular hypertrophy and arterial stiffness in essential hypertension. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2015, 116, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzik, T.J.; Hoch, N.E.; Brown, K.A.; McCann, L.A.; Rahman, A.; Dikalov, S.; Goronzy, J.; Weyand, C.; Harrison, D.G. Role of the T cell in the genesis of angiotensin II induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bortel, L.M.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Cruickshank, J.K.; De Backer, T.; Filipovsky, J.; Huybrechts, S.; Mattace-Raso, R.U.S.; Protogerou, A.D.; et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecelja, M.; Ruijsink, B.; Puyol-Anton, E.; Li, Y.; Godwin, H.; King, A.P.; Razavi, R.; Chowienczyk, P. Aortic Distensibility Measured by Automated Analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Events in UK Biobank. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Joh, H.S.; Lim, W.H.; Seo, J.; Kim, S.; Zo, J.; Kim, M. One-month changes in blood pressure-adjusted pulse wave velocity for predicting long-term cardiovascular outcomes in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Hypertens. 2022, 41, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.Y. Arterial stiffness and stroke: De-stiffening strategy, a therapeutic target for stroke. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giudici, A.; Khir, A.W.; Reesink, K.D.; Delhaas, T.; Spronck, B. Five years of cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) and CAVI0: How close are we to a pressure-independent index of arterial stiffness? J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuteri, A.; Morrell, C.H.; Orru, M.; Strait, J.B.; Tarasov, K.V.; Ferreli, L.A.P.; Loi, F.; Pilia, M.G.; Delitala, A.; Spurgeon, H.; et al. Longitudinal perspective on the conundrum of central arterial stiffness, blood pressure, and aging. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scuteri, A.; Morrell, C.H.; Fegatelli, D.A.; Fiorillo, E.; Delitala, A.; Orrù, M.; Marongiu, M.; Schlessinger, D.; Cucca, F. Arterial stiffness and multiple organ damage: A longitudinal study in population. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delitala, A.P.; Orru, M.; Filigheddu, F.; Pilia, M.G.; Delitala, G.; Ganau, A.; Saba, P.S.; Decandia, F.; Scuteri, A.; Marongiu, M.; et al. Serum free thyroxine levels are positively associated with arterial stiffness in the SardiNIA study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakatta, E.G.; AlunniFegatelli, D.; Morrell, C.H.; Fiorillo, E.; Orrù, M.; Delitala, A.; Marongiu, M.; Schelssinger, D.; Cucca, F.; Scuteri, A. Impact of Stiffer Arteries on the Response to Antihypertensive Treatment: A Longitudinal Study of the SardiNIA Cohort. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; McCurley, A.T.; DuPont, J.J.; Aronovitz, M.; Moss, M.E.; Stillman, I.E.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Christou, D.D.; Zaffe, I.Z. Smooth Muscle Cell-Mineralocorticoid Receptor as a Mediator of Cardiovascular Stiffness With Aging. Hypertension 2018, 71, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, J.J.; Lu, Q.; Moss, M.E.; Carvajal, B.; Baur, W.; Garza, A.E.; Freeman, R.; Anastasiou, M.; Ngwenyama, N.; Adler, G.K.; et al. Myeloid Mineralocorticoid Receptor Transcriptionally Regulates P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1 and Promotes Monocyte Trafficking and Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podzolkov, V.I.; Nebieridze, N.N.; Safronova, T.A. Transforming Growth Factor-beta1, Arterial Stiffness and Vascular Age in Patients With Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tai, H.C.; Sladojevic, N.; Kim, H.H.; Liao, J.K. Vascular Stiffening Mediated by Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Kinase Isoforms. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.F.; Staessen, J.A.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Duprez, D.; Plante, G.E. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, D.; Arnett, D.K.; Tyroler, H.A.; Riley, W.A.; Szklo, M.; Heiss, G. Arterial stiffness and the development of hypertension. The ARIC study. Hypertension 1999, 34, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safar, M.E.; Asmar, R.; Benetos, A.; Clacher, J.; Boutouyrie, P.; Lacolley, P.; Laurent, S.; London, G.; Pannier, B.; Protogerou, A.; et al. Interaction Between Hypertension and Arterial Stiffness. Hypertension 2018, 72, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.S.; Gustin, W.T.; Wong, N.D.; Larson, M.G.; Weber, M.A.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1997, 96, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Liao, Y.Y.; He, M.J.; Ma, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yan, Y.; Hu, J.; Xu, X.; Fan, Y.; Yang, R.; et al. Blood Pressure Trajectories From Childhood to Youth and Arterial Stiffness in Adulthood: A 30-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 894426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, A.; Beckman, J.A.; Schmidt, A.M.; Creager, M.A. Advanced glycation end products: Sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation 2006, 114, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Siva, B.V.; Ravichandiran, V. Advanced Glycation End Products: Key player of the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Glycoconj. J. 2022, 39, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.; Raman, K.G.; Lee, K.J.; Lu, Y.; Ferrran, L.J., Jr.; Chow, W.S.; Stern, D.; Schmidt, A.M. Suppression of accelerated diabetic atherosclerosis by the soluble receptor for advanced glycation endproducts. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelzinsky, J.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Seidlerova, J.; Materankova, M.; Mares, S.; Kordikova, V.; Trefil, L.; Cifkova, R.; Filipovsky, J. Serum biomarkers, skin autofluorescence and other methods. Which parameter better illustrates the relationship between advanced glycation end products and arterial stiffness in the general population? Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelzinsky, J.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Seidlerova, J.; Materankova, M.; Mares, S.; Kordikova, V.; Trefil, L.; Cifkova, R.; Filipovsky, J. Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products independently influences individual age-dependent increase of arterial stiffness. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, M.R.P.; Rospleszcz, S.; Ittermann, T.; Baumeister, S.E.; Schipf, S.; Siewert-Markus, U.; Lorbeer, R.; Storz, C.; Ptushkina, V.; Peters, A.; et al. Glucose and insulin levels are associated with arterial stiffness and concentric remodeling of the heart. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilis, P.; Oikonomou, E.; Lazaros, G.; Vogiatzi, G.; Anastasiou, M.; Mystakidi, V.C.; Goliopoulou, A.; Christoforatou, E.; Bourouki, E.; Vavouranaki, G.; et al. The association of diabetes mellitus with carotid atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness in the Corinthia study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. Aging, arterial stiffness, and hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aminuddin, A.; Lazim, M.; Hamid, A.A.; Hiu, C.K.; Yunus, M.H.M.; Kumar, J.; Ugusman, A. The Association between Inflammation and Pulse Wave Velocity in Dyslipidemia: An Evidence-Based Review. Mediators. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 4732987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecelja, M.; Hussain, T.; Greil, G.; Botnar, R.; Preston, R.; Moayyeri, A.; Spector, T.D.; Chowienczyk, P. Multimodality imaging of subclinical aortic atherosclerosis: Relation of aortic stiffness to calcification and plaque in female twins. Hypertension 2013, 61, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zagura, M.; Kals, J.; Serg, M.; Kampus, P.; Zilmer, M.; Jakobson, M.; Unt, E.; Lieberg, J.; Eha, J. Structural and biochemical characteristics of arterial stiffness in patients with atherosclerosis and in healthy subjects. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Popele, N.M.; Grobbee, D.E.; Bots, M.L.; Topouchian, J.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P.; van der Kuip, D.; Hofman, A.; Witterman, J.C. Association between arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis: The Rotterdam Study. Stroke 2001, 32, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanbay, M.; Copur, S.; Tanriover, C.; Yavuz, F.; Galassi, A.; Ciceri, P.; Cozzolino, M. The pathophysiology and management of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease patients. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2023, 21, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Coriolan, D.; Murthy, V.; Schultz, K.; Golenbock, D.T.; Beasley, D. Proinflammatory phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells: Role of efficient Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1069–H1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoli, L.; Lentini, P.; Briet, M.; Castellino, P.; House, A.A.; London, G.M.; Malatino, L.; McCullough, P.A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Boutouyrie, P. Arterial Stiffness in the Heart Disease of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhaun, N.; Goddard, J.; Webb, D.J. The endothelin system and its antagonism in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.K.; Kamble, S.H.; Krishnan, S.; Gomes, J.; To, B.; Li, S.; Liu, I.; Gumz, M.L.; Mohandas, R. Involvement of Lysyl Oxidase in the Pathogenesis of Arterial Stiffness in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2023, 324, F364–F373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, S.; Dawkins Arce, F.G.; Verwoert, G.C.; Hofman, A.; Ikram, M.A.; Franco, O.H.; Dehghan, A.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Mattace-Raso, F. Association of renal function with vascular stiffness in older adults: The Rotterdam study. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elgeti, T.; Frohlich, M.; Wismayer, K.K.; Tzschatzsch, H.; Hamm, B.; Sack, I.; Schaafs, L. The effect of smoking on quantification of aortic stiffness by ultrasound time-harmonic elastography. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoi, N.A.; Jerrard-Dunne, P.; Feely, J.; Mahmud, A. Impact of smoking and smoking cessation on arterial stiffness and aortic wave reflection in hypertension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefanadis, C.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Tsiamis, E.; Diamantopoulos, L.; Toutouzas, K.; Giatrakos, N.; Vaina, S.; Tsekpura, D.; Toutouzas, P. Unfavorable effects of passive smoking on aortic function in men. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 128, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Cooke, A.B.; Scheffler, P.; Doonan, R.J.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Alcohol Exerts a Shifted U-Shaped Effect on Central Blood Pressure in Young Adults. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlmann, C.R.; Li, F.; Ludders, D.W.; Schaefer, C.A.; Most, A.K.; Backenkohler, U.; Neumann, T.; Tillmanns, H.; Waldecker, B.; Erdogan, E.; et al. Dose-dependent activation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels by ethanol contributes to improved endothelial cell functions. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierksma, A.; Lebrun, C.E.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Grobbee, D.E.; Lamberts, S.W.J.; Hendriks, H.F.; Bots, M.L. Alcohol consumption in relation to aortic stiffness and aortic wave reflections: A cross-sectional study in healthy postmenopausal women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Safar, M.E. Influence of lifestyle modification on arterial stiffness and wave reflections. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; Zang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Ding, X.; Chen, Z.; Lan, Y.; Li, W.; Fang, W.; et al. Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Arterial Stiffness in Individuals with Different Smoking Statuses. Int. J. Sports Med. 2023, 44, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfes, J.; Ellermann, C.; Frommeyer, G.; Eckardt, L. Evidence-based treatment of atrial fibrillation around the globe: Comparison of the latest ESC, AHA/ACC/HRS, and CCS guidelines on the management of atrial fibrillation. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vio, R.; Giordani, A.S.; Stefil, M.; Madine, J.; Fairbairn, T.; Themistoclakis, S.; Salvi, P.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Shantsiila, A.; Shantsila, E.; et al. Arterial stiffness and atrial fibrillation: Shared mechanisms, clinical implications and therapeutic options. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Foo, D.C.; Wong, R.C.; Seow, S.; Gong, L.; Benditt, D.G.; Ling, L.H. Increased carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness are associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3132–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Leening, M.J.; Norby, F.L.; Roetker, N.S.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Pan, W.; Polak, J.F.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Kronmal, R.A.; et al. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study, Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), and the Rotterdam Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laurent, S.; Katsahian, S.; Fassot, C.; Tropeano, A.; Gautier, I.; Laloux, B.; Boutouyrie, P. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of fatal stroke in essential hypertension. Stroke 2003, 34, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasecki, D.; Rojek, A.; Kwarciany, M.; Kubach, M.; Boutouyrie, P.; Nyka, W.; Laurent, S.; Narkiewicz, K. Aortic stiffness predicts functional outcome in patients after ischemic stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saji, N.; Toba, K.; Sakurai, T. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Arterial Stiffness: Tsunami Effect in the Brain? Pulse 2016, 3, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Sloten, T.T.; Sedaghat, S.; Laurent, S.; London, G.M.; Pannier, B.; Ikram, M.A.; Kavousi, M.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Franco, O.H.; Boutouyrie, P.; et al. Carotid stiffness is associated with incident stroke: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, L.L.; O’Donnell, A.; Beiser, A.S.; Thibault, E.G.; Sanchez, J.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Johnson, K.A.; et al. Association of Aortic Stiffness and Pressure Pulsatility With Global Amyloid-beta and Regional Tau Burden Among Framingham Heart Study Participants Without Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Ling, L.H.; Tan, E.S.J.; Gyanwali, B.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Lim, S.L.; Gong, L.; Berboso, J.L.; Richards, A.M.; Chen, C.; et al. Effects of Carotid Artery Stiffness on Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease and Cognition. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e027295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickx, J.O.; Calus, E.; De Deyn, P.P.; Van Dam, D.; De Meyer, G.R.Y. Short-Term Pharmacological Induction of Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension with Angiotensin II Does Not Affect Learning and Memory and Cerebral Amyloid Load in Two Murine Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poels, M.M.; van Oijen, M.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Breteler, M.M. Arterial stiffness, cognitive decline, and risk of dementia: The Rotterdam study. Stroke 2007, 38, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Lacolley, P.; Briet, M.; Regnault, V.; Stanton, A.; Laurent, S.; Mahmud, A. Pharmacological modulation of arterial stiffness. Drugs 2011, 71, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.T.; Delerme, S.; Pannier, B.; Safar, M.E.; Benetos, A.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrue, P. Aortic stiffness is reduced beyond blood pressure lowering by short-term and long-term antihypertensive treatment: A meta-analysis of individual data in 294 patients. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropeano, A.I.; Boutouyrie, P.; Pannier, B.; Joannides, R.; Balkestein, E.; Katsahian, S.; Laloux, B.; Thuillez, C.; Struijker-Boudier, H.; Laurent, S. Brachial pressure-independent reduction in carotid stiffness after long-term angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic hypertensives. Hypertension 2006, 48, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Jin, N.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F.; Mao, J.; Wang, X. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist improves arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Emoto, M.; Teramura, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Hatsuda, S.; Maeno, T.; Shinohara, K.; Koyama, H.; Shoji, T.; Inaba, M. Effect of adiponectin on carotid arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetic patients treated with pioglitazone and metformin. Metabolism 2006, 55, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo Santiago, J.C.; Maraver Delgado, J.; Cayon Blanco, M.; Lopez Saez, J.B.; Gomez-Fernandez, P. Effect of dapagliflozin on arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clin. 2020, 154, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, J.D.; Hwang, W.M.; Lim, D.M. Effects of 6 Months of Dapagliflozin Treatment on Metabolic Profile and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction for Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients without Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bommel, E.J.M.; Smits, M.M.; Ruiter, D.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Touw, D.J.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Touw, D.J.; et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and gliclazide on the cardiorenal axis in people with type 2 diabetes. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, E.C.; Agouridis, A.P.; Elisaf, M.S. The effect of statin therapy on arterial stiffness by measuring pulse wave velocity: A systematic review. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 8, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.M.; Maki-Petaja, K.M.; Cheriyan, J.; Davidson, E.H.; Cherry, L.; McEniery, C.M.; Sattar, N.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Kharbanda, R.K. Simvastatin prevents inflammation-induced aortic stiffening and endothelial dysfunction. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 70, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reklou, A.; Katsiki, N.; Karagiannis, A.; Athyros, V. Effects of Lipid Lowering Drugs on Arterial Stiffness: One More Way to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk? Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Hong, Y.J. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibition in cardiovascular disease: Current status and future perspectives. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicali, R.; Mandraffino, G.; Scuruchi, M.; Lo Gullo, A.; Di Pino, A.; Ferrara, V.; Morace, C.; Aragona, C.O.; Squadrito, G.; Purrello, F.; et al. Effects of Lipid Lowering Therapy Optimization by PCSK9 Inhibitors on Circulating CD34+ Cells and Pulse Wave Velocity in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Subjects without Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Real-World Data from Two Lipid Units. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandraffino, G.; Scicali, R.; Rodriguez-Carrio, J.; Savarino, F.; Mamone, F.; Scuruchi, M.; Cinquegrani, M.; Imbalzano, E.; Di Pino, A.; Piro, S.; et al. Arterial stiffness improvement after adding on PCSK9 inhibitors or ezetimibe to high-intensity statins in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia: A Two-Lipid Center Real-World Experience. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020, 14, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.O.; Berryman-Maciel, M.; Darvish, S.; Coppock, M.E.; You, Z.; Chonchol, M.; Seals, D.R.; Rossman, M.J. Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant supplementation for improving age-related vascular dysfunction in humans: A study protocol. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 980783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, M.J.; Santos-Parker, J.R.; Steward, C.A.C.; Bispham, N.Z.; Cuevas, L.M.; Rosenberg, H.L.; Woodward, K.A.; Chonchol, M.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; Murphy, M.P.; et al. Chronic Supplementation With a Mitochondrial Antioxidant (MitoQ) Improves Vascular Function in Healthy Older Adults. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Pekas, E.J.; Headid, R.J., 3rd; Son, W.; Wooden, T.K.; Song, J.; Layec, G.; Yadav, S.K.; Mishra, P.K.; Pipinios, I.I. Acute mitochondrial antioxidant intake improves endothelial function, antioxidant enzyme activity, and exercise tolerance in patients with peripheral artery disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H456–H467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, G.M.; Asmar, R.G.; O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E.; Investigators, R.P. Mechanism(s) of selective systolic blood pressure reduction after a low-dose combination of perindopril/indapamide in hypertensive subjects: Comparison with atenolol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogers, S.C.; Ko, Y.A.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Hajjar, I. Differential Sex-Specific Effects of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Therapy on Arterial Function in Hypertension: CALIBREX Trial. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janic, M.; Lunder, M.; Sabovic, M. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular therapy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 621437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacolley, P.; Labat, C.; Pujol, A.; Delcayre, C.; Benetos, A.; Safar, M. Increased carotid wall elastic modulus and fibronectin in aldosterone-salt-treated rats: Effects of eplerenone. Circulation 2002, 106, 2848–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komai, N.; Ohishi, M.; Moriguchi, A.; Yanagitani, Y.; Jinno, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Katsuya, Y.; Rakugi, H.; Higaki, J.; Ogihara, Y. Low-dose doxazosin improved aortic stiffness and endothelial dysfunction as measured by noninvasive evaluation. Hypertens. Res. 2002, 25, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, N.; Rice, S.P.; Bolusani, H.; Luzio, S.D.; Dunseath, G.; Ludgate, M.; Rees, D.A. Metformin reduces arterial stiffness and improves endothelial function in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schremmer, J.; Busch, L.; Baasen, S.; Heinen, S.; Sansone, R.; Heiss, C.; Kelm, M.; Stern, M. Chronic PCSK9 inhibitor therapy leads to sustained improvements in endothelial function, arterial stiffness, and microvascular function. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 148, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Molecule/Clinical Parameter | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Arterial hypertension | ↑ Pulse pressure ↑ Systolic blood pressure | Elastin rupture Direct vascular damage |
| Diabetes mellitus | ↑ AGE/RAGE ↓ AGE/sRAGE | ↑ resistance to enzymatic proteolysis of collagen ↑ Collagen in arterial wall |
| Chronic kidney disease | ↑ Phosphoremia | Activation of Toll-like receptor four and NK-Kappa B Activation of pro-inflammatory molecules ↑ reactive oxygen species production |
| ↑ Uric acid | ↑ nitric oxide synthetase ↑ proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells ↑ production of angiotensin II | |
| ↑ AGE/RAGE | ↑ resistance to enzymatic proteolysis of collagen ↑ Collagen in arterial wall | |
| ↑ Endothelin 1 | Endothelial dysfunction Calcification Inflammation Vasoconstriction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castelli, R.; Gidaro, A.; Casu, G.; Merella, P.; Profili, N.I.; Donadoni, M.; Maioli, M.; Delitala, A.P. Aging of the Arterial System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086910
Castelli R, Gidaro A, Casu G, Merella P, Profili NI, Donadoni M, Maioli M, Delitala AP. Aging of the Arterial System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086910
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastelli, Roberto, Antonio Gidaro, Gavino Casu, Pierluigi Merella, Nicia I. Profili, Mattia Donadoni, Margherita Maioli, and Alessandro P. Delitala. 2023. "Aging of the Arterial System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086910
APA StyleCastelli, R., Gidaro, A., Casu, G., Merella, P., Profili, N. I., Donadoni, M., Maioli, M., & Delitala, A. P. (2023). Aging of the Arterial System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086910











