Dexamethasone Modulates the Cytokine Response but Not COVID-19-Induced Coagulopathy in Critically Ill
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients Baseline Characteristics
2.2. Clinical Outcome
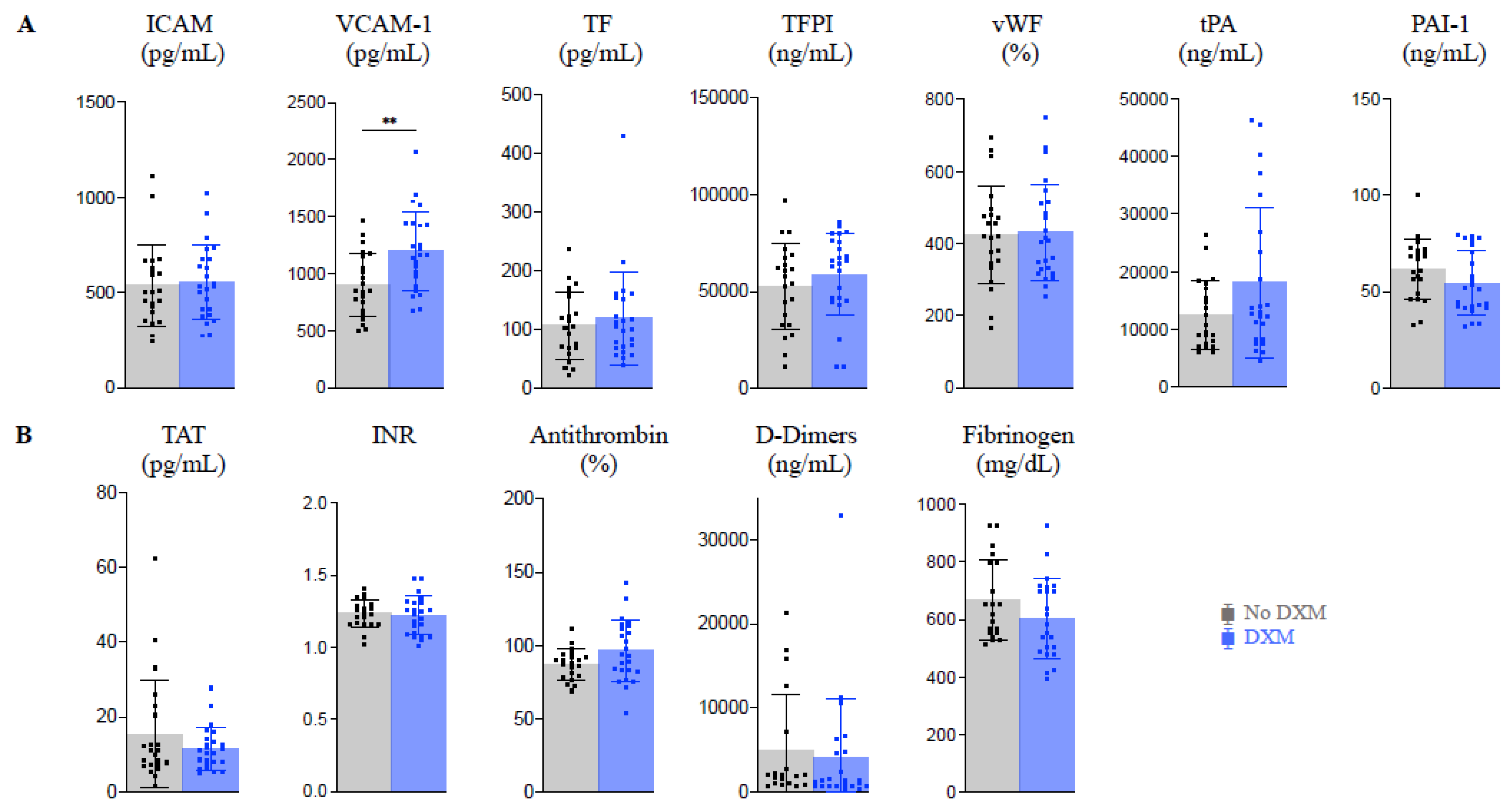
2.3. Endothelial Activation and Coagulopathy (Figure 1)
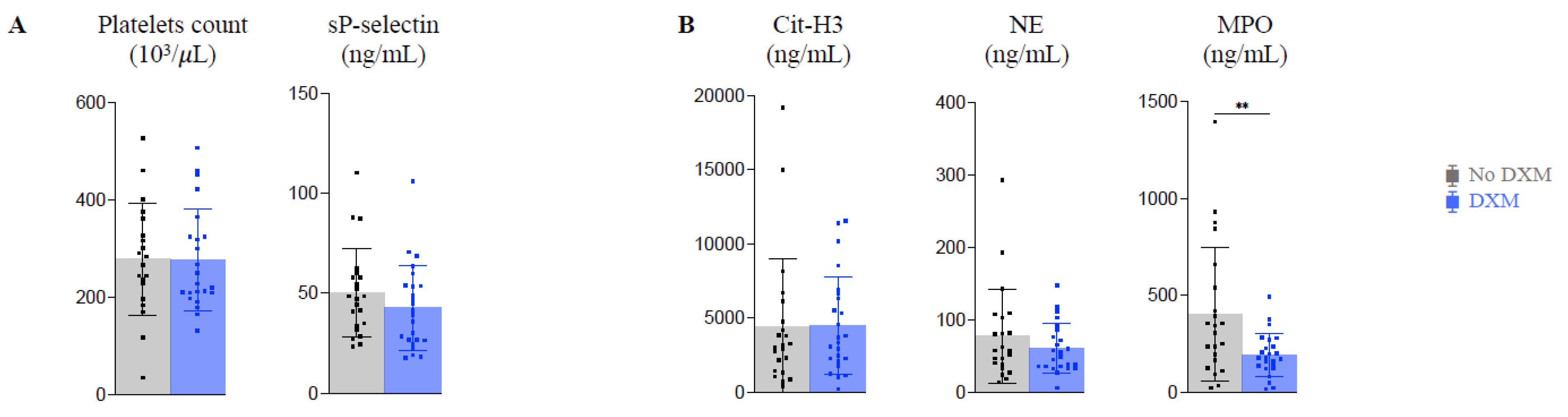
2.4. Platelet Activation and NETosis (Figure 2)
2.5. Inflammatory Reaction and Immune Response
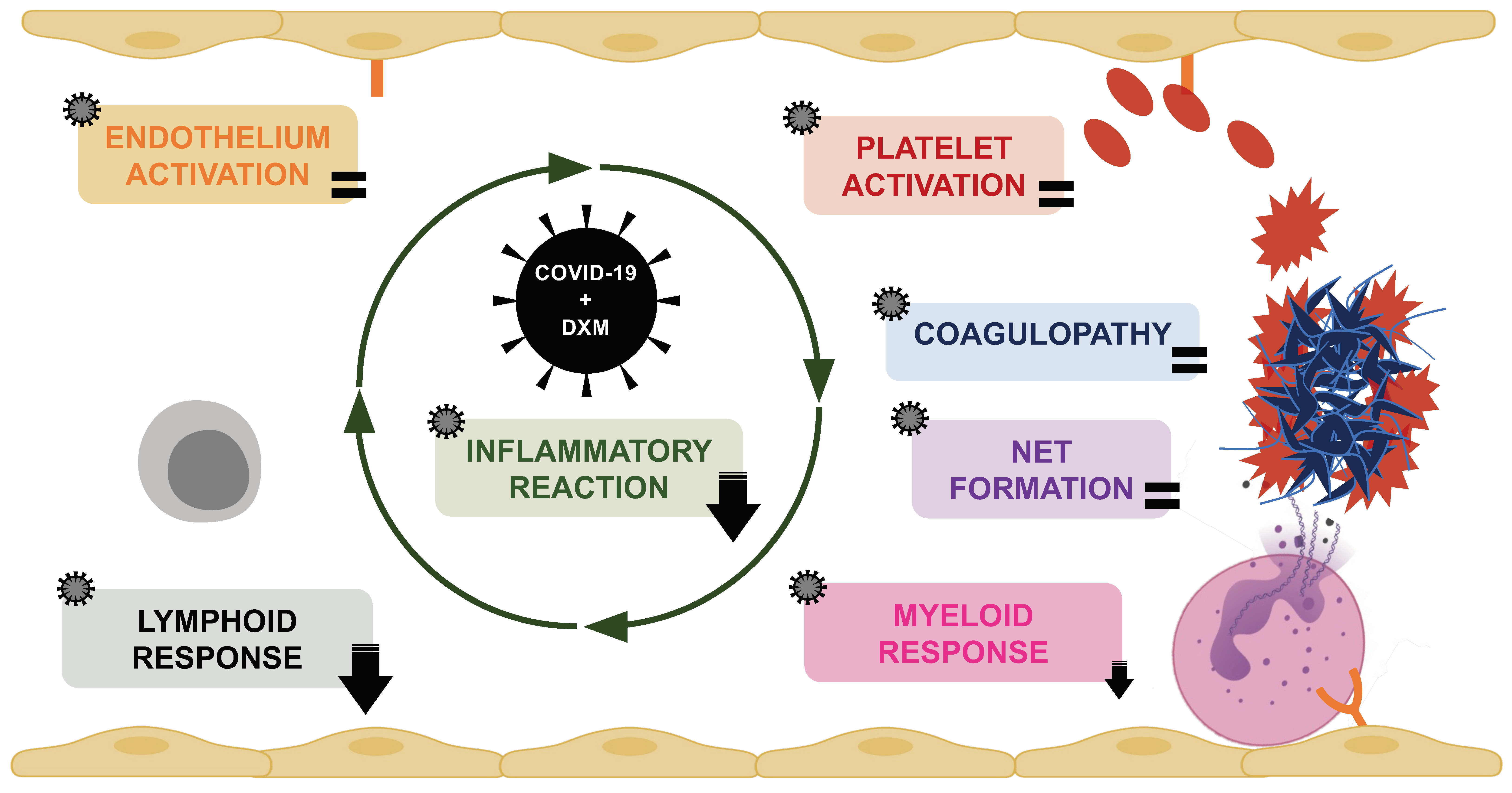
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design and Setting of the Study
4.2. Population
4.3. Clinical Outcomes
4.4. Sampling
4.5. Measurement of Biomarkers
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Puri, B.K.; Marx, W.; O’Neil, A.; Athan, E.; Walder, K.; Berk, M.; Olive, L.; Carvalho, A.F.; et al. The cytokine storms of COVID-19, H1N1 influenza, CRS and MAS compared. Can one sized treatment fit all? Cytokine 2021, 144, 155593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechamps, M.; De Poortere, J.; Martin, M.; Gatto, L.; Daumerie, A.; Bouzin, C.; Octave, M.; Ginion, A.; Robaux, V.; Pirotton, L.; et al. Inflammation-Induced Coagulopathy Substantially Differs Between COVID-19 and Septic Shock: A Prospective Observational Study. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaklamanos, A.; Belogiannis, K.; Skendros, P.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Tzioufas, A.G. COVID-19 Immunobiology: Lessons Learned, New Questions Arise. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, F.; Araf, Y.; Hosen, M.J. Corticosteroids for COVID-19: Worth it or not? Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Gong, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Qin, H.; Hu, J.; Huang, J. Associations of immunological features with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, B.; Massberg, S. Thrombosis as an intravascular effector of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, P.; Hékimian, G.; Lejeune, M.; Chommeloux, J.; Desnos, C.; De Chambrun, M.P.; Martin-Toutain, I.; Nieszkowska, A.; Lebreton, G.; Bréchot, N.; et al. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Is a Major Contributor to COVID-19–Associated Coagulopathy: Insights From a Prospective, Single-Center Cohort Study. Circulation 2020, 142, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, A.; Vecchié, A.; Dagna, L.; Martinod, K.; Dixon, D.L.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dentali, F.; Montecucco, F.; Massberg, S.; Levi, M.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, J.; MacArthur, T.A.; Sridharan, M.; Pruthi, R.K.; McBane, R.D.; Witzig, T.E.; Park, M.S. A Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Management Options of COVID-19 Associated Coagulopathy. Shock 2020, 55, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, T.; Wood, M.K.; Hughes, D.M.; Talor, M.V.; Ma, Z.; Schneider, J.; Skinner, J.T.; Asady, B.; Goerlich, E.; Halushka, M.K.; et al. Endothelial thrombomodulin downregulation caused by hypoxia contributes to severe infiltration and coagulopathy in COVID-19 patient lungs. Ebiomedicine 2022, 75, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel, V.; Lobysheva, I.; Gérard, L.; Vermeersch, M.; Perez-Morga, D.; Castelein, T.; Mesland, J.-B.; Hantson, P.; Collienne, C.; Gruson, D.; et al. Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and decreased vascular nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients. Ebiomedicine 2022, 77, 103893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimont, L.; Dechamps, M.; David, C.; Bouvy, C.; Gillot, C.; Haguet, H.; Favresse, J.; Ronvaux, L.; Candiracci, J.; Herzog, M.; et al. NETosis and Nucleosome Biomarkers in Septic Shock and Critical COVID-19 Patients: An Observational Study. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D., Jr.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, M.B.; Naazie, I.N.; Elsayed, N.; Mathlouthi, A.; Marmor, R.; Clary, B. Thromboembolism risk of COVID-19 is high and associated with a higher risk of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eclinicalmedicine 2020, 29–30, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Tacquard, C.; Severac, F.; Leonard-Lorant, I.; Ohana, M.; Delabranche, X.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Gandet, F.F.; et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, J.G.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehra, M.R.; Lavie, C.J.; Rizk, Y.; Forthal, D.N. Pharmaco-Immunomodulatory Therapy in COVID-19. Drugs 2020, 80, 1267–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Goldin, M.; Giannis, D.; Diab, W.; Wang, J.; Khanijo, S.; Mignatti, A.; Gianos, E.; Cohen, M.; Sharifova, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Therapeutic-Dose Heparin vs Standard Prophylactic or Intermediate-Dose Heparins for Thromboprophylaxis in High-risk Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: The HEP-COVID Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, P.R.; Goligher, E.C.; Berger, J.S.; Neal, M.D.; McVerry, B.J.; Nicolau, J.C. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inspiration Investigators; Sadeghipour, P.; Talasaz, A.H.; Rashidi, F.; Sharif-Kashani, B.; Beigmohammadi, M.T.; Farrokhpour, M.; Sezavar, S.H.; Payandemehr, P.; Dabbagh, A.; et al. Effect of Intermediate-Dose vs Standard-Dose Prophylactic Anticoagulation on Thrombotic Events, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Treatment, or Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: The INSPIRATION Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligher, E.C.; Bradbury, C.A.; McVerry, B.J.; Lawler, P.R.; Berger, J.S.; Gong, M.N. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators; Angus, D.C.; Derde, L.; Al-Beidh, F.; Annane, D.; Arabi, Y.; Beane, A.; Van Bentum-Puijk, W.; Berry, L.; Bhimani, Z.; et al. Effect of Hydrocortisone on Mortality and Organ Support in Patients With Severe COVID-19: The REMAP-CAP COVID-19 Corticosteroid Domain Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazini, B.M.; Maia, I.S.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Berwanger, O.; Rosa, R.G.; Veiga, V.C.; Avezum, A.; Lopes, R.D.; Bueno, F.R.; Silva, M.V.A.O.; et al. Effect of Dexamethasone on Days Alive and Ventilator-Free in Patients With Moderate or Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19: The CoDEX Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Paassen, J.; Vos, J.S.; Hoekstra, E.M.; Neumann, K.M.I.; Boot, P.C.; Arbous, S.M. Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group; Sterne, J.A.C.; Murthy, S.; Diaz, J.V.; Slutsky, A.S.; Villar, J.; Angus, D.C.; Annane, D.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Berwanger, O.; et al. Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis. JAMA 2020, 324, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Colunga-Lozano, L.E.; Prasad, M.; Tangamornsuksan, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Yao, L.; Motaghi, S.; Couban, R.J.; Ghadimi, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids in COVID-19 based on evidence for COVID-19, other coronavirus infections, influenza, community-acquired pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2020, 192, E756–E767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. How corticosteroids control inflammation: Quintiles Prize Lecture 2005. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, J.; Novosad, S.A.; Winthrop, K.L. Infection Risk and Safety of Corticosteroid Use. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, S.; Frithiof, R.; Larsson, A.; Franzén, S.; Anderberg, S.B.; Kristensen, B.; Hultström, M.; Lipcsey, M. Immuno-Modulatory Effects of Dexamethasone in Severe COVID-19—A Swedish Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, Z.; Razzack, A.A.; Patel, G.; Sarfraz, M. Venous Thromboembolism, Corticosteroids and COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2021, 27, 1076029621993573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesland, J.-B.; Carlier, E.; François, B.; Serck, N.; Gerard, L.; Briat, C.; Piagnerelli, M.; Laterre, P.-F.; on behalf of the COVCORVAP Collaboration Group. Early Corticosteroid Therapy May Increase Ventilator-Associated Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.-F.; Wu, H.; Yan, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Temperton, N.J.; Weiss, R.A.; Brenchley, J.M.; et al. T Cell Responses to Whole SARS Coronavirus in Humans. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5490–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, D.; Sperhake, J.P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Steurer, S.; Edler, C.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Mushumba, H.; Kniep, I.; Schröder, A.S.; et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuwen, L.-A.; Geldhof, V.; Pasut, A.; Carmeliet, P. COVID-19: The vasculature unleashed. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Di Nisio, M.; Levy, J.H.; Kitamura, N.; Thachil, J. New criteria for sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) following the revised sepsis definition: A retrospective analysis of a nationwide survey. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, F.B., Jr.; Toh, C.H.; Hoots, W.K.; Wada, H.; Levi, M.; Scientific Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH). Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, M.D.; Lemaire, L.C.; Giebelen, I.A.; van Zoelen, M.A.D.; Pater, J.M.; Pangaart, P.S.V.D.; Groot, A.P.; de Vos, A.F.; Elliott, P.J.; Meijers, J.C.M.; et al. Prednisolone Dose-Dependently Influences Inflammation and Coagulation during Human Endotoxemia. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brabander, J.; Michels, E.H.A.; van Linge, C.C.A.; Chouchane, O.; Douma, R.A.; Reijnders, T.D.Y.; Schuurman, A.R.; van Engelen, T.S.R.; Wiersinga, W.J.; van der Poll, T.; et al. Association between dexamethasone treatment and the host response in COVID-19 patients admitted to the general ward. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarre, P.; Urbina, T.; Cunat, S.; Merdji, H.; Bonny, V.; Lavillegrand, J.-R.; Raia, L.; Bige, N.; Baudel, J.-L.; Maury, E.; et al. Impact of corticosteroids on the procoagulant profile of critically ill COVID-19 patients: A before-after study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2022, 89, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Goyal, A.; Cusick, A.; Lahan, S.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Bhyan, P.; Bhattad, P.B.; Aslam, F.; Ranka, S.; Dalia, T.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine: A comprehensive review and its controversial role in coronavirus disease 2019. Ann. Med. 2020, 53, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-D.; Chang, S.-Y.; Lan, T.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Kao, J.-H.; Liao, C.-H.; Tsai, M.-J.; Kuo, P.-H.; Huang, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-T.; et al. Experience of the use of hydroxychloroquine on patients with COVID-19: A perspective on viral load and cytokine kinetics. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 120, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARDS Definition of Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, W.A.; Draper, E.A.; Wagner, D.P.; Zimmerman, J.E. APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit. Care Med. 1985, 13, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.E.; Trzeciak, S.M.; Kline, J.A. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No DXM Group n = 22 | DXM Group n = 24 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEMOGRAPHICS | |||
| Men | 15 (68) | 19 (79) | 0.51 |
| Women | 7 (32) | 5 (21) | |
| Age (years) | 59.9 ± 10.4 | 64.45 ± 8.9 | 0.12 |
| MEDICAL HISTORY | |||
| Hypertension | 13 (59) | 17 (71) | 0.54 |
| BMI > 25 | 15 (68) | 17 (71) | >0.99 |
| Diabetes | 5 (23) | 10 (42) | 0.22 |
| History of smoking | 2 (9) | 1(4) | 0.60 |
| COPD | 3 (14) | 1 (4) | 0.34 |
| CKD | 0 (0) | 2 (8) | 0.49 |
| Cancer | 0 (0) | 4 (17) | 0.11 |
| ROUTINE LABORATORY TESTING | |||
| CRP (mg/dL) | 199.3 ± 88.9 | 118.8 ± 76.6 | <0.01 * |
| Highest CRP (mg/dL) | 315.0 ± 126.4 | 285.8 ± 104.6 | 0.40 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 ± 0.60 | 1.46 ± 2.44 | 0.40 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.2 ± 2.1 | 12.4 ± 2.2 | 0.07 |
| WBCs (/µL) | 9497 ± 3563 | 10,739 ± 4167 | 0.29 |
| Neutrophils (/µL) | 7803 ± 3170 | 9073 ± 3762 | 0.22 |
| Lymphocytes (/µL) | 894 ± 329 | 802 ± 425 | 0.27 |
| Lowest lymphocyte count (/µL) | 459 ± 323 | 504 ± 294 | 0.64 |
| ORGAN FAILURE AND SEVERITY SCORES | |||
| PaO2/FiO2 | 103 ± 4 | 86 ± 3 | 0.04 * |
| Apache II score | 15 ± 4 | 14 ± 4 | 0.49 |
| SOFA Score | 4 ± 1 | 6 ± 2 | <0.01 * |
| SIC score | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | >0.99 |
| DIC score | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | >0.99 |
| TREATMENT BEFORE INCLUSION | |||
| Delay symptoms—inclusion (days) | 10 ± 5 | 10 ± 4 | 0.87 |
| Delay steroids—inclusion (days) | 1.0 | 3.0 ± 2.6 | NA |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 19 (86) | 0 (0) | <0.01 |
| OUTCOME | |||
| 30-day mortality | 6 (27) | 9 (37) | 0.54 |
| 1-year mortality | 8 (36) | 12 (50) | 0.39 |
| ICU length of stay (days) | 27 ± 26 | 38 ± 42 | <0.05 * |
| Ventilation duration (days) | 21 ± 24 | 30 ± 35 | 0.08 |
| Thrombo-embolic event | 6 (27) | 3 (13) | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dechamps, M.; De Poortere, J.; Octave, M.; Ginion, A.; Robaux, V.; Pirotton, L.; Bodart, J.; Gruson, D.; Van Dievoet, M.-A.; Douxfils, J.; et al. Dexamethasone Modulates the Cytokine Response but Not COVID-19-Induced Coagulopathy in Critically Ill. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087278
Dechamps M, De Poortere J, Octave M, Ginion A, Robaux V, Pirotton L, Bodart J, Gruson D, Van Dievoet M-A, Douxfils J, et al. Dexamethasone Modulates the Cytokine Response but Not COVID-19-Induced Coagulopathy in Critically Ill. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087278
Chicago/Turabian StyleDechamps, Mélanie, Julien De Poortere, Marie Octave, Audrey Ginion, Valentine Robaux, Laurence Pirotton, Julie Bodart, Damien Gruson, Marie-Astrid Van Dievoet, Jonathan Douxfils, and et al. 2023. "Dexamethasone Modulates the Cytokine Response but Not COVID-19-Induced Coagulopathy in Critically Ill" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087278
APA StyleDechamps, M., De Poortere, J., Octave, M., Ginion, A., Robaux, V., Pirotton, L., Bodart, J., Gruson, D., Van Dievoet, M.-A., Douxfils, J., Haguet, H., Morimont, L., Derive, M., Jolly, L., Bertrand, L., Laterre, P.-F., Horman, S., & Beauloye, C. (2023). Dexamethasone Modulates the Cytokine Response but Not COVID-19-Induced Coagulopathy in Critically Ill. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087278






