On the Nature of Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Collagen Powder from Bovine Achilles Tendon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fluorescence Excitation and Emission Spectra of Collagen from Bovine Achilles Tendon
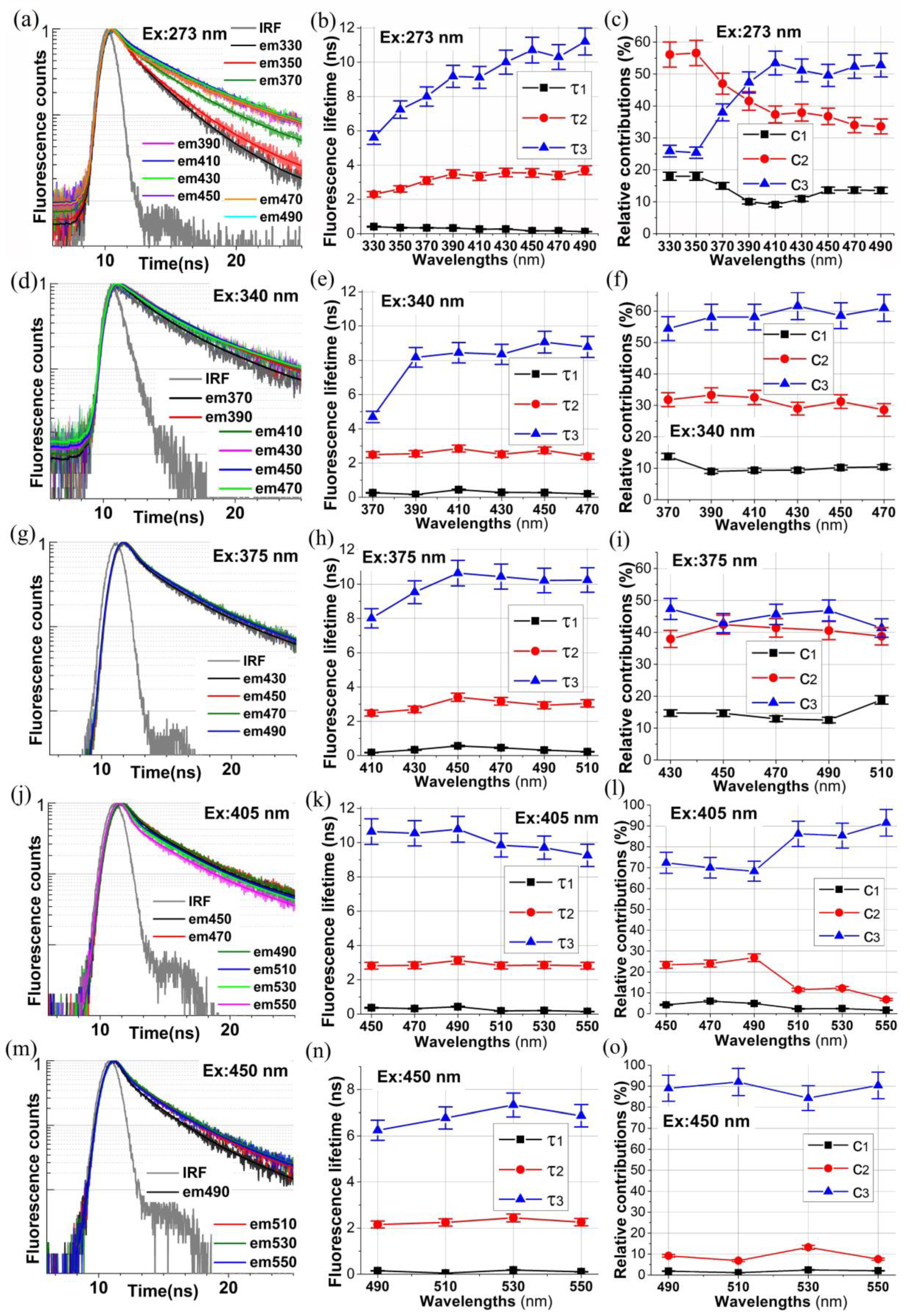
2.2. Time-Resolved Autofluorescence Decays of Collagen from Bovine Achilles Tendon
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfano, R.; Pu, Y. Optical biopsy for cancer detection. In Lasers for Medical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 325–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtschafter, Z.; Bentley, J. Hernias as a collagen maturation defect. Ann. Surg. 1964, 160, 852–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagh, P.V.; Read, R.C. Defective collagen synthesis in inguinal herniation. Am. J. Surg. 1972, 124, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.; Osier, C.; Gletsu, N.; Jeansonne, L.; Baghai, M.; Sherman, M.; Smith, C.D.; Ramshaw, B.; Lin, E. Abnormal primary tissue collagen composition in the skin of recurrent incisional hernia patients. Am. Surg. 2007, 73, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczęsny, W.; Fisz, J.; Żuchowski, P.; Niedojadło, J.; Szmytkowski, J.; Dąbrowiecki, S. Ultrastructural Differences in Rectus Sheath of Hernia Patients and Healthy Controls. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 167, e171–e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, V.M.; Kohn, R.R.; Cerami, A. Accelerated age-related browning of human collagen in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, G.; Rajaram, R.; Bhuyan, K.C.; Oronsky, A.L.; Goidl, J.A. Administration of an aldose reductase inhibitor induces a decrease of collagen fluorescence in diabetic rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Kamińska, A. Changes induced by ultraviolet light in fuorescence of collagen in the presence of b-carotene. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 120, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.D.; Rogatkin, D.A.; Litvinova, K.S. Collagen as in vivo quantitative fluorescent biomarkers of abnormal tissue changes. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2012, 5, 1250010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, W.; Li, G. The aggregation behavior of native collagen in dilute solution studied by intrinsic fluorescence and external probing. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, I.; Dragnea, A.M.; Gaidaub, C.; Dragomirb, T. Collagen fluorescence measurements on nanosilver treated leather. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2010, 62, 634–643. [Google Scholar]
- Deyl, Z.; Praus, R.; Šulcová, H.; Goldman, J.N. Fluorescence of collagen—Properties of tyrosine residues and another fluorescent element in calf skin collagen. FEBS Lett. 1969, 5, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, N.; Gillies, R.; Moran, M.; Kochevar, I.E.; Anderson, R.R. Endogenous Skin Fluorescence Includes Bands that may Serve as Quantitative Markers of Aging and Photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.; Zonios, G.; Anderson, R.R.; Kollias, N. Fluorescence Excitation Spectroskopy Provides Information About Human Skin In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Alfano, R.R. Stokes shift spectroscopic analysis of multifluorophores for human cancer detection in breast and prostate tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, S.P. Cross-linking of collagen. Isolation, structural characterization and glycosylation of pyridinoline. Biochem. J. 1983, 215, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, S.P.; Duncan, A.; Wilson, N.; Evans, B.J. Standardization of pyridinium crosslinks, pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline, for use as biochemical markers of collagen degradation. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, J.; Kokkonen, H.T.; Kovanen, V.; Hauta-Kasari, M.; Vahimaa, P.; Lammi, M.J.; Töyräs, J.; Jurvelin, J.S. Nondestructive fluorescence-based quantification of threose-induced collagen cross-linking in bovine articular cartilage. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 0970031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahunia, H.K.; Lough, A.; Vieth, R.; Pritzker, K. A cartilage derived novel compound DDP (2,6-dimethyldifuro-8-pyrone): Isolation, purification, and identification. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakaram, M.; Cheng, Q.; Feather, M.S.; Ortwerth, B.J. Structural elucidation of a novel lysine-lysine crosslink generated in a glycation reaction with L-threose. Amino Acids. 1997, 12, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishth, D. Advanced Glycation End-products and Bone Fractures. IBMS Bonekey 2009, 6, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séro, L.; Sanguinet, L.; Blanchard, P.; Dang, B.; Morel, S.; Richomme, P.; Séraphin, D.; Derbré, S. Tuning a 96-Well Microtiter Plate Fluorescence-Based Assay to Identify AGE Inhibitors in Crude Plant Extracts. Molecules 2013, 18, 14320–14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, G.S.; Pauls, S.W.; Hedstrom, J.F.; Johnson, C.K. Tyrosyl Fluorescence Decays and Rotational Dynamics in Tyrosine Monomers and in Dipeptides. J. Fluoresc. 1997, 4, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, J.R. Origin of Tryptophan Fluorescence Lifetimes. Part 2: Fluorescence Lifetimes Origin of Tryptophan in Proteins. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Responte, D.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Fatakdawala, H.; Hu, J.; Athanasiou, K.A.; Marcu, L. Nondestructive Evaluation of Tissue Engineered Articular Cartilage Using Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Ultrasound Backscatter Microscopy. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2012, 18, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarek, J.-M.I.; Marcu, L.; Snyder, W.J.; Grundfest, W.S. Time-resolved Fluorescence Spectra of Arterial Fluorescent Compounds: Reconstruction with the Laguerre Expansion Technique. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 71, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
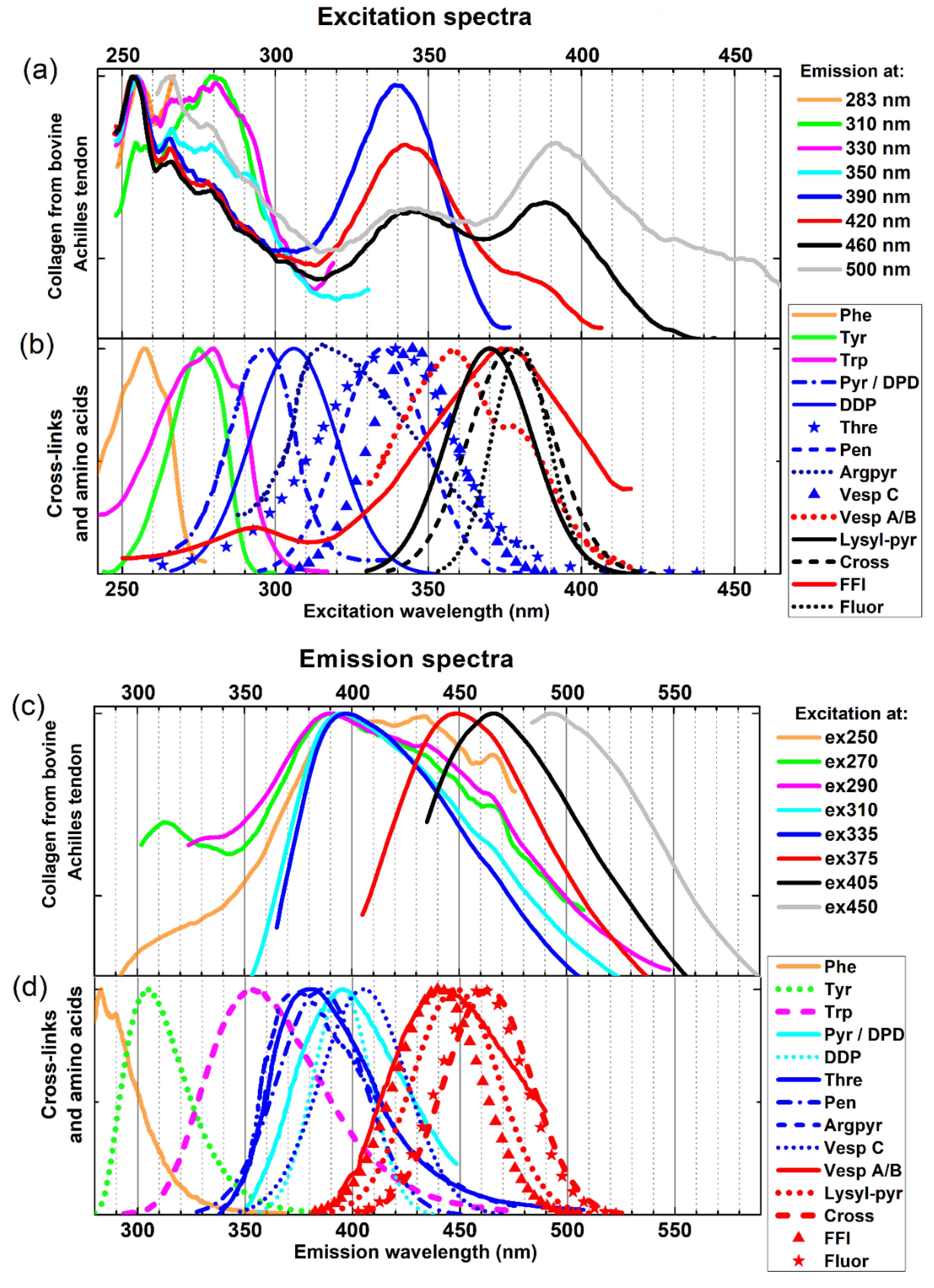
| Cross-Link | Ex/Em [nm] | References |
|---|---|---|
| Trivalent cross-link | ||
| Pyridinoline (Pyr), | 295 (acid), 325 (neutral)/340 (alkaline)/395 | [17,18] |
| Deoxypyridinoline (DPD) | 294 (acid), 325 (neutral)/395 | [18,19] |
| 2,6-dimethyldifuro-8-pyrone (DDP) | 306/395 | [19,20] |
| Advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) | ||
| Threosidine (Thre) | 328/402 | [21] |
| Pentosidine (Pen) | 335/385 | [19,22,23] |
| Argpyrimidine (Argpyr) | 335/400 | [23] |
| Vesperlysine C (Vesp C) | 345/405 | [22,23] |
| Vesperlysine A/B (Vesp A/B) | 366/442 | [22,23] |
| Lysyl-pyrropyridine (Lysyl-pyr) | 370/448 | [23] |
| Crossline (Cross) | 379/463 | [22,23] |
| 2-(2-furoyl)-4(5)-(2-furanyl)-1H-imidazole (FFI) | 380/440 | [23] |
| Fluorolink (Fluor) | 380/460 | [23] |
| λex [nm] | λem [nm] | τ1/c1 [ns]/[%] | τ2/c2 [ns]/[%] | τ3/c3 [ns]/[%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 273 | 330 | 0.410/18 | 2.30/56 | 5.60/26 |
| 350 | 0.348/18 | 2.61/57 | 7.24/25 | |
| 370 | 0.340/15 | 3.10/47 | 8.00/38 | |
| 390 | 0.329/10 | 3.48/42 | 9.17/48 | |
| 410 | 0.265/9 | 3.34/37 | 9.12/54 | |
| 430 | 0.269/11 | 3.57/38 | 10.00/51 | |
| 450 | 0.168/14 | 3.54/37 | 10.71/49 | |
| 470 | 0.169/14 | 3.40/34 | 10.30/52 | |
| 490 | 0.120/13 | 3.70/34 | 11.20/53 | |
| 340 | 370 | 0.264/14 | 2.49/32 | 4.69/54 |
| 390 | 0.167/9 | 2.54/33 | 8.17/58 | |
| 410 | 0.442/9 | 2.84/33 | 8.44/58 | |
| 430 | 0.285/9 | 2.51/29 | 8.35/62 | |
| 450 | 0.277/10 | 2.74/31 | 9.06/59 | |
| 470 | 0.201/10 | 2.38/29 | 8.78/61 | |
| 375 | 430 | 0.339/15 | 2.70/38 | 9.53/47 |
| 450 | 0.565/15 | 3.40/42 | 10.64/43 | |
| 470 | 0.459/13 | 3.17/41 | 10.44/46 | |
| 490 | 0.319/12 | 2.93/41 | 10.21/47 | |
| 510 | 0.229/19 | 3.05/39 | 10.24/42 | |
| 405 | 450 | 0.364/5 | 2.82/23 | 10.64/72 |
| 470 | 0.319/6 | 2.84/24 | 10.54/70 | |
| 490 | 0.427/5 | 3.13/27 | 10.78/68 | |
| 510 | 0.182/3 | 2.82/11 | 9.85/86 | |
| 530 | 0.203/2 | 2.86/12 | 9.71/85 | |
| 550 | 0.148/2 | 2.82/7 | 9.25/91 | |
| 450 | 490 | 0.148/2 | 2.16/9 | 6.24/89 |
| 510 | 0.049/2 | 2.24/7 | 6.77/91 | |
| 530 | 0.180/3 | 2.44/13 | 7.33/84 | |
| 550 | 0.105/3 | 2.26/7 | 6.87/90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saletnik, Ł.; Szczęsny, W.; Szmytkowski, J.; Fisz, J.J. On the Nature of Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Collagen Powder from Bovine Achilles Tendon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087631
Saletnik Ł, Szczęsny W, Szmytkowski J, Fisz JJ. On the Nature of Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Collagen Powder from Bovine Achilles Tendon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087631
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaletnik, Łukasz, Wojciech Szczęsny, Jakub Szmytkowski, and Jacek J. Fisz. 2023. "On the Nature of Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Collagen Powder from Bovine Achilles Tendon" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087631
APA StyleSaletnik, Ł., Szczęsny, W., Szmytkowski, J., & Fisz, J. J. (2023). On the Nature of Stationary and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Collagen Powder from Bovine Achilles Tendon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087631






