Decasubstituted Pillar[5]arene Derivatives Containing L-Tryptophan and L-Phenylalanine Residues: Non-Covalent Binding and Release of Fluorescein from Nanoparticles
Abstract
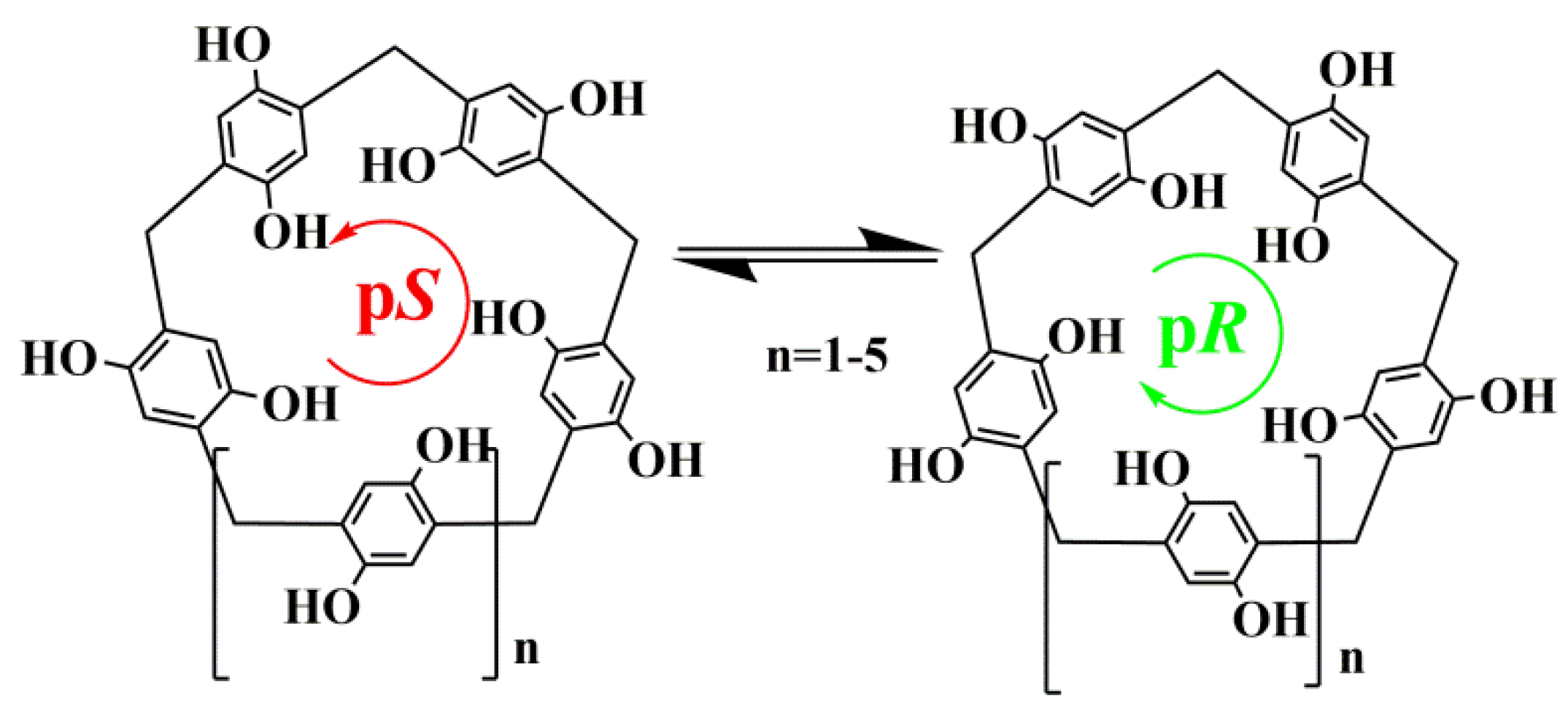
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 2, 3
2.2. Analysis of Cytotoxicity of 2 and 3 by Colorimetric MTT Test against PC-3 and MCF-7 Tumor Cell Lines
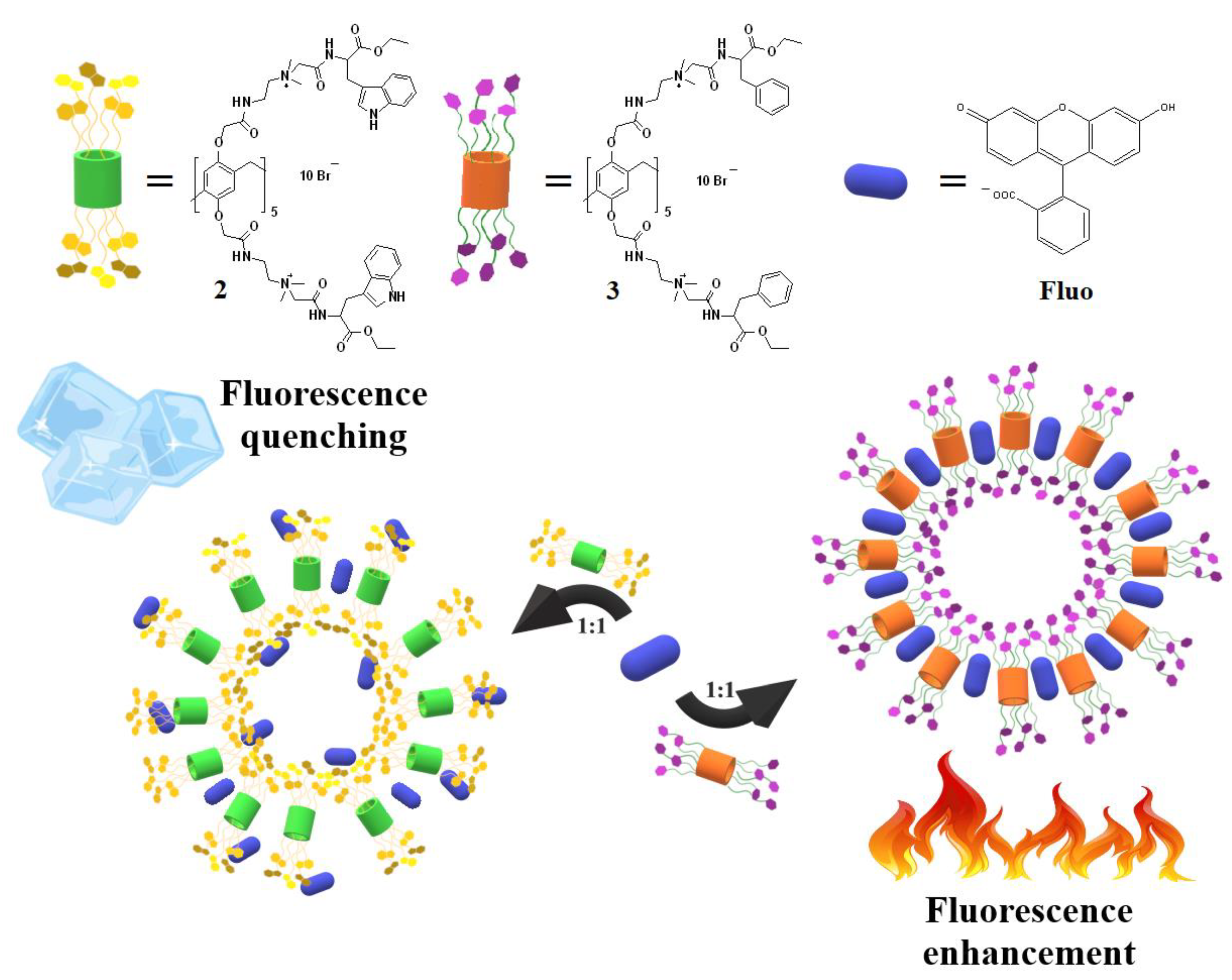
2.3. Pillar[5]arene/Fluorescein Nanoparticles
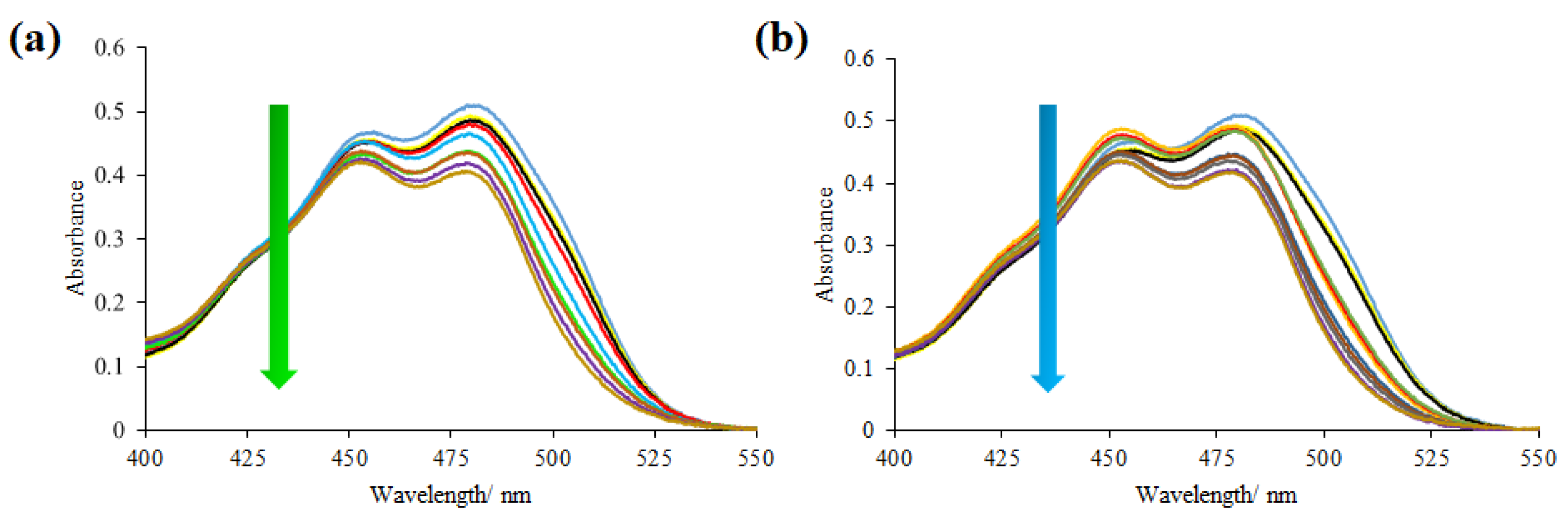
2.3.1. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
2.3.2. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
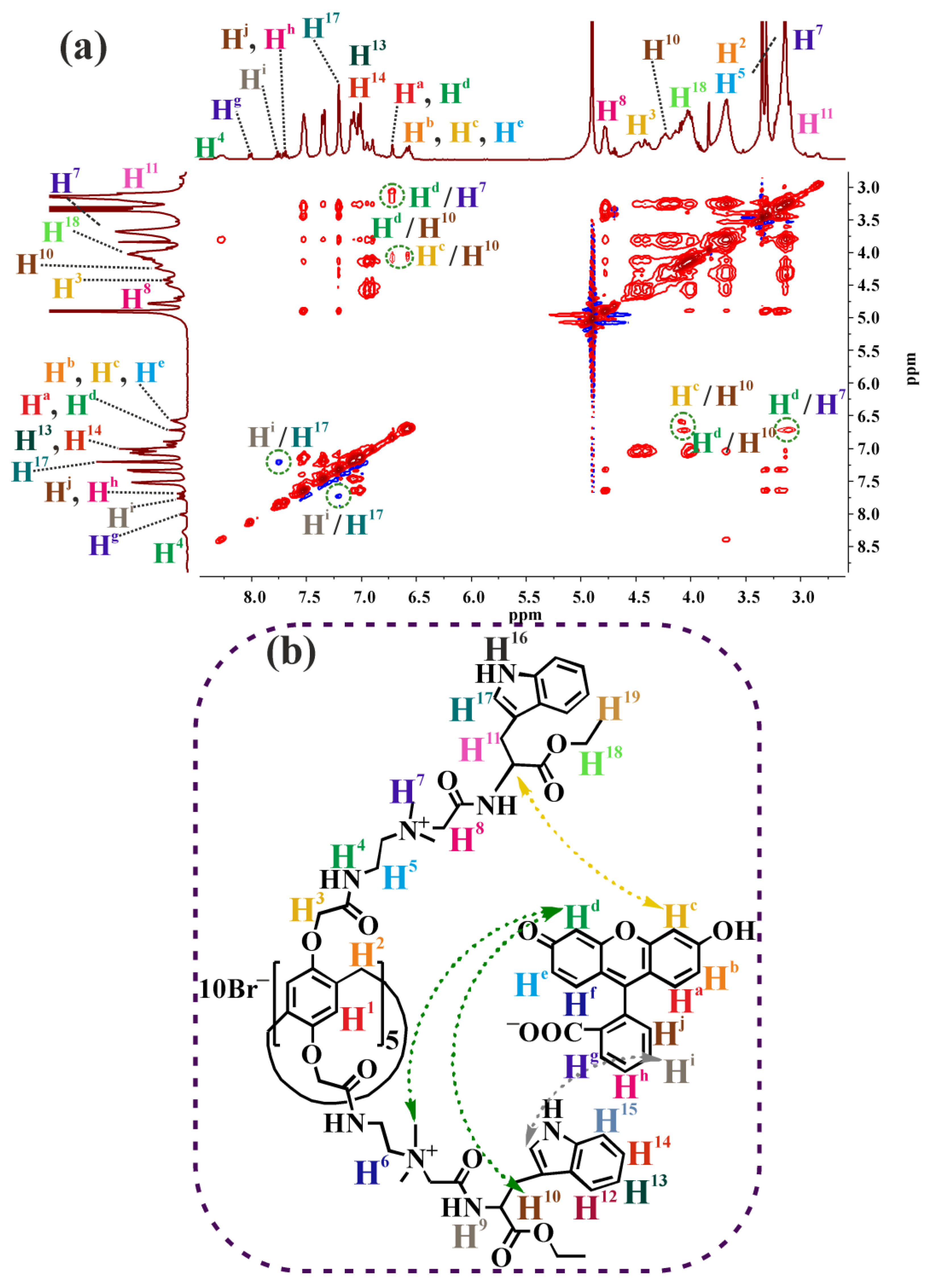
2.3.3. 2D NOESY NMR Spectroscopy of Pillar[5]arene–Fluorescein Mixtures
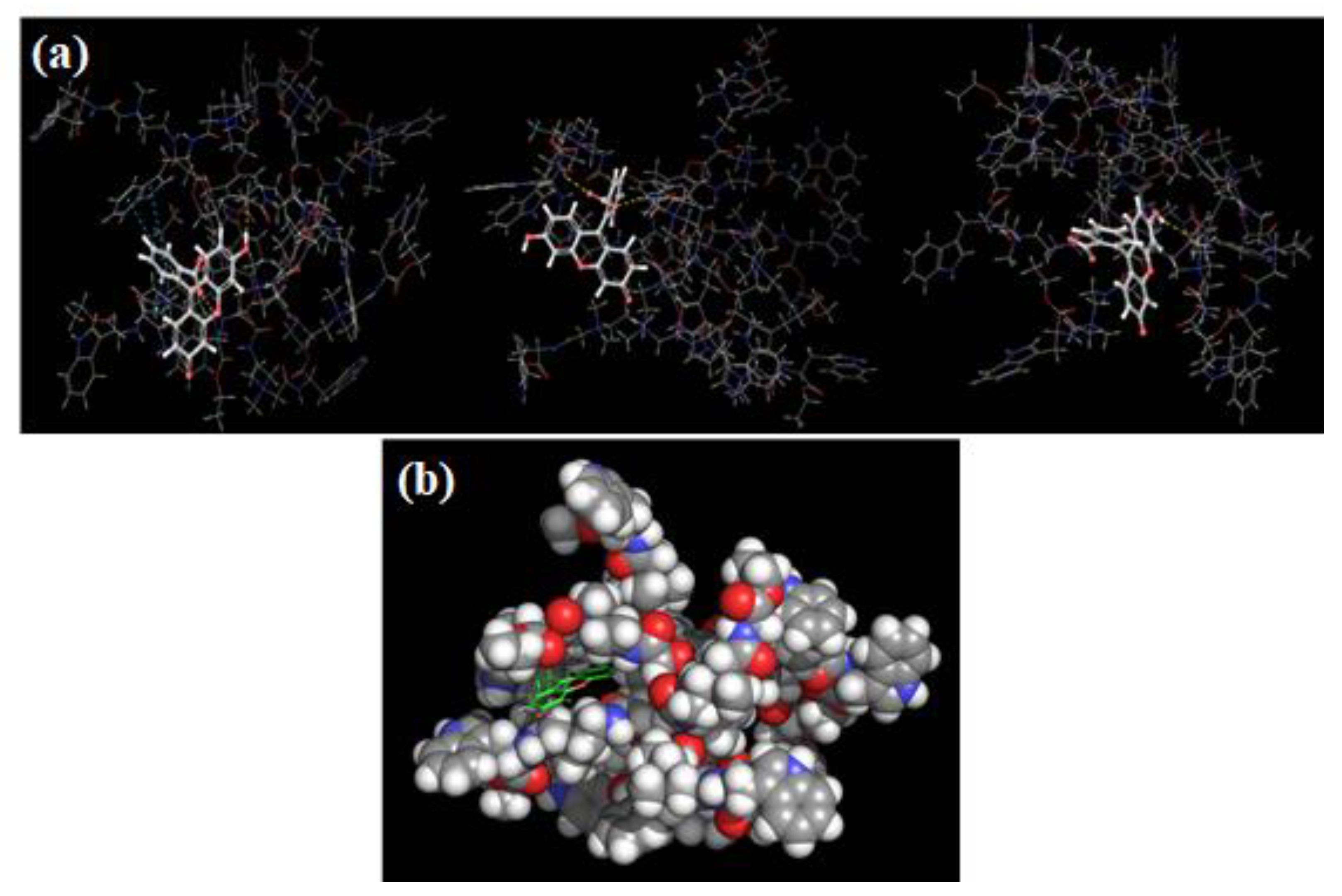
2.3.4. Computer Simulation Studies
2.3.5. Self-Assembly of Pillar[5]arene Derivatives 2, 3 and Fluorescein
2.3.6. Aggregation Study of Pillar[5]arenes 2 and 3 with Fluo by DLS and TEM
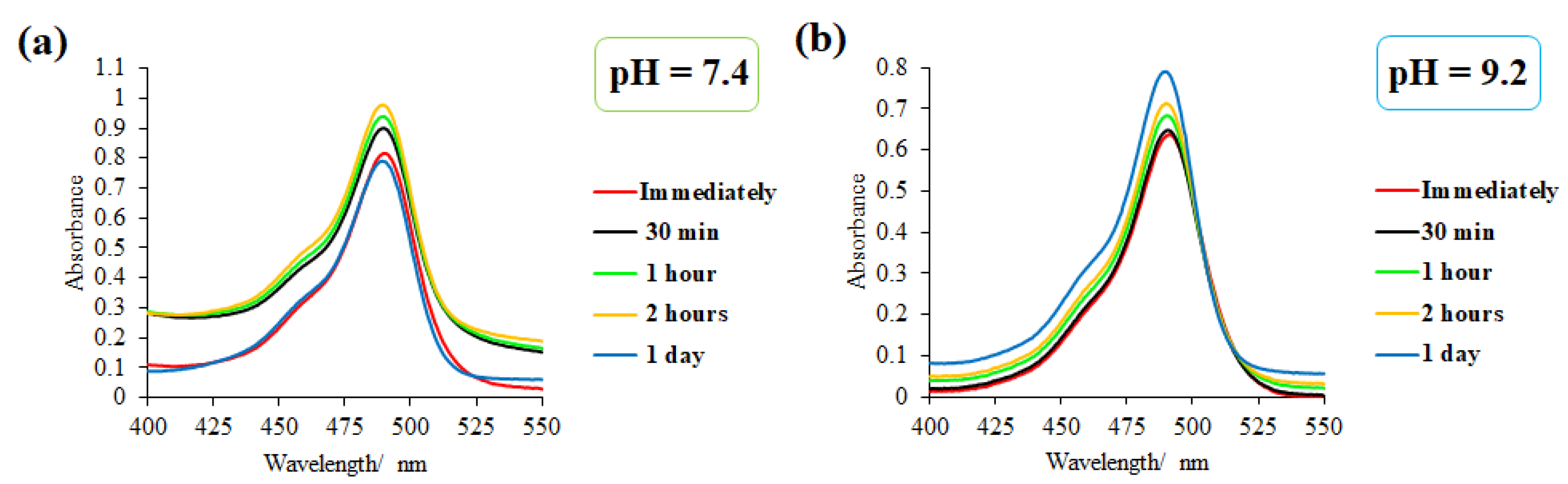
2.3.7. Study of the Fluorescein Release from Pillar[5]arene/Fluorescein Nanoparticles at Different pH
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 2, 3
3.3. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
3.4. Determination of the Association Constant by Spectrophotometric Titration
3.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.6. The Study of Fluorescein Release from the Associates with Pillar[5]arenes 2, 3 over Time by UV–Visible Spectroscopy
3.7. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.8. Zeta Potentials
3.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.10. Computer Simulation Studies
3.11. Cytotoxicity Analysis of Compounds 2 and 3 by Colorimetric MTT-Test against PC-3 and MCF-7 Tumor Cell Lines
3.11.1. Cell Culture Cultivation
3.11.2. Addition of the Studied Compounds to Cells
3.11.3. Cytotoxicity Analysis of the Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazarova, A.A.; Yakimova, L.S.; Padnya, P.L.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Osin, Y.N.; Cragg, P.J.; Stoikov, I.I. Monosubstituted pillar[5]arene functionalized with (amino) phosphonate fragments are “smart” building blocks for constructing nanosized structures with some s-and p-metal cations in the organic phase. NJC 2019, 43, 14450–14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Shi, B.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F. Pillararene host–guest complexation induced chirality amplification: A new way to detect cryptochiral compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10868–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, T.; Kanai, S.; Fujinami, S.; Yamagishi, T.A.; Nakamoto, Y. para-Bridged symmetrical pillar[5]arenes: Their Lewis acid catalyzed synthesis and host–guest property. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5022–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, L.E.; Patel, B.A.; Fagan-Murphy, A.; Kothur, R.R.; Cragg, P.J. Detection of clinically important cations by a pillar[5]arene-modified electrochemical sensor. Chem. Sens. 2013, 3, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Ogoshi, T.; Kitajima, K.; Aoki, T.; Yamagishi, T.A.; Nakamoto, Y. Effect of an intramolecular hydrogen bond belt and complexation with the guest on the rotation behavior of phenolic units in pillar[5]arenes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Yamagishi, T.A. Pillararenes: Versatile synthetic receptors for supramolecular chemistry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 2961–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, P.J.; Sharma, K. Pillar[5]arenes: Fascinating cyclophanes with a bright future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, S.; Zeng, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, R. The chiral interfaces fabricated by d/l-alanine-pillar[5]arenes for selectively adsorbing ctDNA. Chem. Comm. 2019, 55, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarova, A.A.; Sultanaev, V.R.; Yakimova, L.S.; Stoikov, I.I. Synthesis and supramolecular properties of water-soluble pillar[5]arenes containing amino acid residues. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 58, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qin, D.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H. Self-assembly, rheological properties and antioxidant activities of chitosan grafted with tryptophan and phenylalanine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 597, 124763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.; Johnson, J.; Liyanage, W.; Nilsson, B.L. Impact of gelation method on thixotropic properties of phenylalanine-derived supramolecular hydrogels. Soft Matter. 2020, 16, 10158–10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ravinder, R.; Bais, S.S.; Basak, S.; Krishnan, N.A.; Haridas, V. Redox sensitive self-assembling dipeptide for sustained intracellular drug delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Neo, T.L.; Liu, D.X.; Tam, J.P. Importance of SARS-CoV spike protein Trp-rich region in viral infectivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekar, M.; Mohan Das, T. Synthesis and antioxidant properties of novel fluorescein-based quinoline glycoconjugates. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2014, 33, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, T.; Zhuang, S.; Lu, Q.; Li, P.; Huang, B. Synthesis of pH-sensitive fluorescein grafted cellulose nanocrystals with an amino acid spacer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4842–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylevich, A.; Patsenker, L.D.; Gellerman, G. Exploiting fluorescein based drug conjugates for fluorescent monitoring in drug delivery. Dyes Pigm. 2017, 139, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimova, L.S.; Shurpik, D.N.; Guralnik, E.G.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Osin, Y.N.; Stoikov, I.I. Fluorescein-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles based on monoamine pillar[5]arene: Synthesis and interaction with DNA. ChemNanoMat 2018, 4, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimova, L.S.; Guralnik, E.G.; Shurpik, D.N.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Osin, Y.N.; Subakaeva, E.V.; Stoikov, I.I. Morphology, structure and cytotoxicity of dye-loaded lipid nanoparticles based on monoamine pillar[5]arenes. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzębski, M.; Peplińska, B.; Florczak, P.; Gapiński, J.; Flak, D.; Mała, P.; Szwajca, A. Fluorescein ether-ester dyes for labeling of fluorinated methacrylate nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Scharff-Poulsen, A.M.; Gu, H.; Almdal, K. Synthesis and characterization of ratiometric, pH sensing nanoparticles with covalently attached fluorescent dyes. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3381–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaverzneva, E.D.; Zvorykina, V.K.; Kiseleva, V.V. Synthesis of N-(6-benzylthio-9H-9-purinyl) acetylamino acids. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Div. Chem. Sci. 1970, 19, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, A.; Shurpik, D.; Padnya, P.; Mukhametzyanov, T.; Cragg, P.; Stoikov, I. Self-assembly of supramolecular architectures by the effect of amino acid residues of quaternary ammonium pillar[5]arenes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T.; Hashizume, M.; Yamagishi, T.A.; Nakamoto, Y. Synthesis, conformational and host–guest properties of water-soluble pillar[5]arene. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3708–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, T.; Tajiri, Y.; Shinkai, S. New water-soluble calixarenes modified with amino acids at the upper rim. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas. 1993, 112, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Mondal, S.; Rencus-Lazar, S.; Gazit, E. Organization of amino acids into layered supramolecular secondary structures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görbitz, C.H.; Törnroos, K.W.; Day, G.M. Single-crystal investigation of l-tryptophan with Z′= 16. Acta Crystallogr. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2012, 68, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, A.; Khannanov, A.; Boldyrev, A.; Yakimova, L.; Stoikov, I. Self-assembling systems based on pillar[5]arenes and surfactants for encapsulation of diagnostic dye dapi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.W.; Floyd, A.J.; Sainsbury, M. Organic Spectroscopy; J. Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, E.; Pardo, A.; Guijarro, M.S.; Fernandez-Alonso, J.I. Photophysic properties of fluorescein in alcohol medium for different pH. J. Mol. Struct. 1986, 142, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Feng, X.; Yang, D.; Yi, C.; Qiu, X. Pi-pi stacking of the aromatic groups in lignosulfonates. BioResources. 2012, 7, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbert, B.; Thordarson, P. The death of the Job plot, transparency, open science and online tools, uncertainty estimation methods and other developments in supramolecular chemistry data analysis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Sreeramulu, K.; Sharma, H.C. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching as a binding assay to monitor protein conformation changes in the membrane of intact mitochondria. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2016, 48, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padnya, P.L.; Khripunova, I.A.; Mostovaya, O.A.; Mukhametzyanov, T.A.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Vorobev, V.V.; Stoikov, I.I. Self-assembly of chiral fluorescent nanoparticles based on water-soluble L-tryptophan derivatives of p-tert-butylthiacalix[4]arene. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakovich, J. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder, D. Physical Biochemistry: Applications to Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1982; 761p. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Song, N.; Yang, Y.-W. A stimuli-responsive pillar[5]arene-based hybrid material with enhanced tunable multicolor luminescence and ion-sensing ability. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8, nwaa281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorovska, V.I.; Labyntseva, R.D.; Bevza, O.V.; Pugach, A.Y.; Drapailo, A.B.; Cherenok, S.O.; Kalchenko, V.I. Thiacalix[4]arene phosphonate C-800 as a novel fluorescent probe for zinc in living cells. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2021, 93, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Aljaroudi, N. Energy transfer between Ir(ppy)3 molecules in neat film and concentration quenching of phosphorescence. Opt. Mater. 2008, 30, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Meng, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, P. Pillar[5]arenes: A new class of AIE gen macrocycles used for luminescence sensing of Fe3+ ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 11747–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lam, J.W.; Kwok, R.T.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Fundamental understanding and future developments. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4, 5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.; Renggli, K.; Razumovitch, J.; Vebert, C. Dynamic light scattering in supramolecular materials chemistry. In Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential–what they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J.W.; Tang, B.Z. Restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM): Investigating AIE mechanism from experimental and theoretical studies. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2021, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wei, Q.; Qian, J.; Ruan, R.; Yang, H. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery in synergistic cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultanaev, V.; Yakimova, L.; Nazarova, A.; Mostovaya, O.; Sedov, I.; Davletshin, D.; Gilyazova, E.; Bulatov, E.; Li, Z.-T.; Zhang, D.-W.; et al. Decasubstituted Pillar[5]arene Derivatives Containing L-Tryptophan and L-Phenylalanine Residues: Non-Covalent Binding and Release of Fluorescein from Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097700
Sultanaev V, Yakimova L, Nazarova A, Mostovaya O, Sedov I, Davletshin D, Gilyazova E, Bulatov E, Li Z-T, Zhang D-W, et al. Decasubstituted Pillar[5]arene Derivatives Containing L-Tryptophan and L-Phenylalanine Residues: Non-Covalent Binding and Release of Fluorescein from Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):7700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097700
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultanaev, Vildan, Luidmila Yakimova, Anastasia Nazarova, Olga Mostovaya, Igor Sedov, Damir Davletshin, Elvina Gilyazova, Emil Bulatov, Zhang-Ting Li, Dan-Wei Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Decasubstituted Pillar[5]arene Derivatives Containing L-Tryptophan and L-Phenylalanine Residues: Non-Covalent Binding and Release of Fluorescein from Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 7700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097700
APA StyleSultanaev, V., Yakimova, L., Nazarova, A., Mostovaya, O., Sedov, I., Davletshin, D., Gilyazova, E., Bulatov, E., Li, Z.-T., Zhang, D.-W., & Stoikov, I. (2023). Decasubstituted Pillar[5]arene Derivatives Containing L-Tryptophan and L-Phenylalanine Residues: Non-Covalent Binding and Release of Fluorescein from Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 7700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24097700









