Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pharmacological Effects
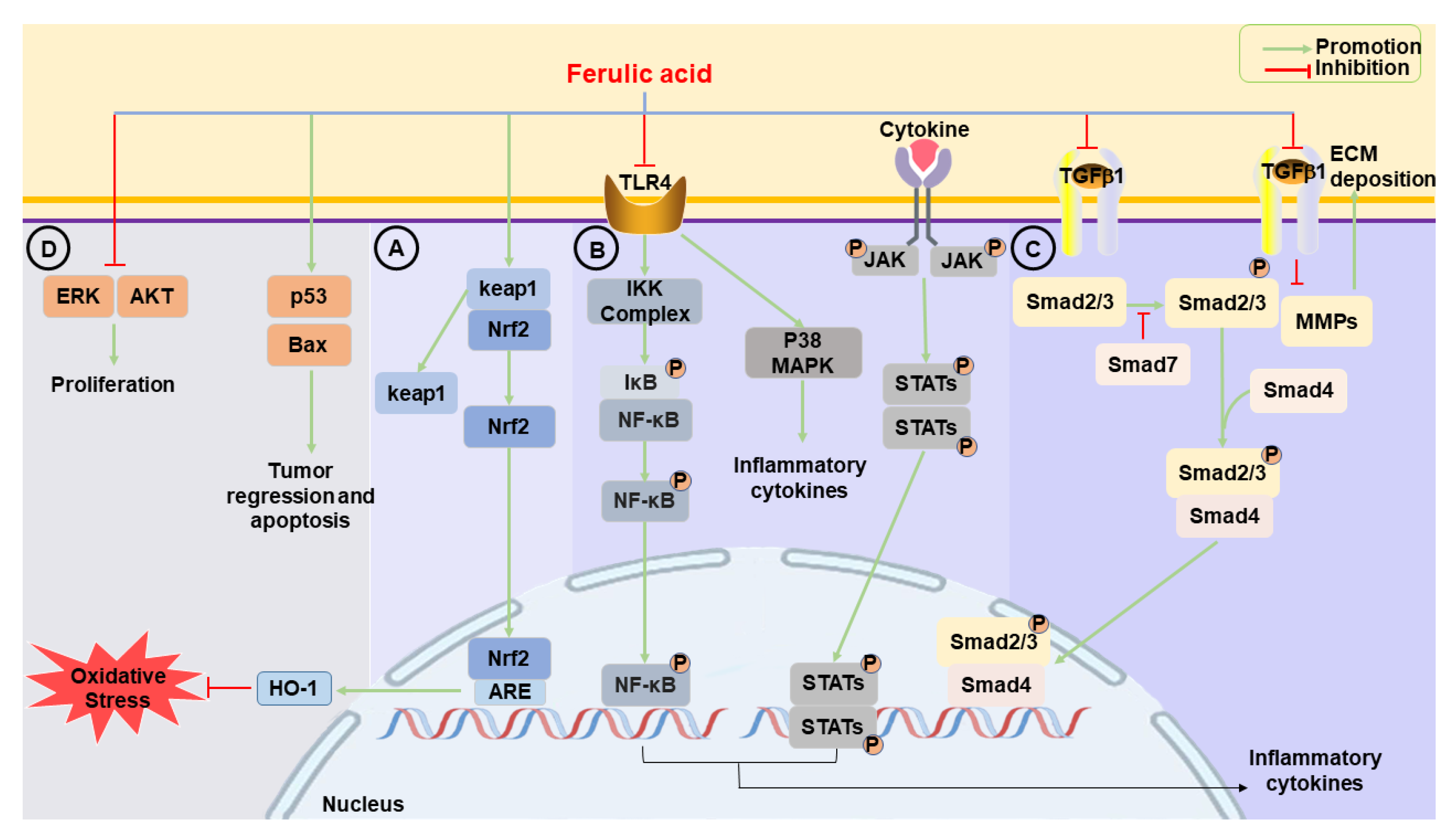
2.1. Anti-Oxidative Effects
2.1.1. ROS
2.1.2. Free Radical Scavenging
2.1.3. Nrf2/HO-1
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.2.1. p38 MAPK
2.2.2. NF-κB
2.2.3. JAK/STAT
2.2.4. NLRP3
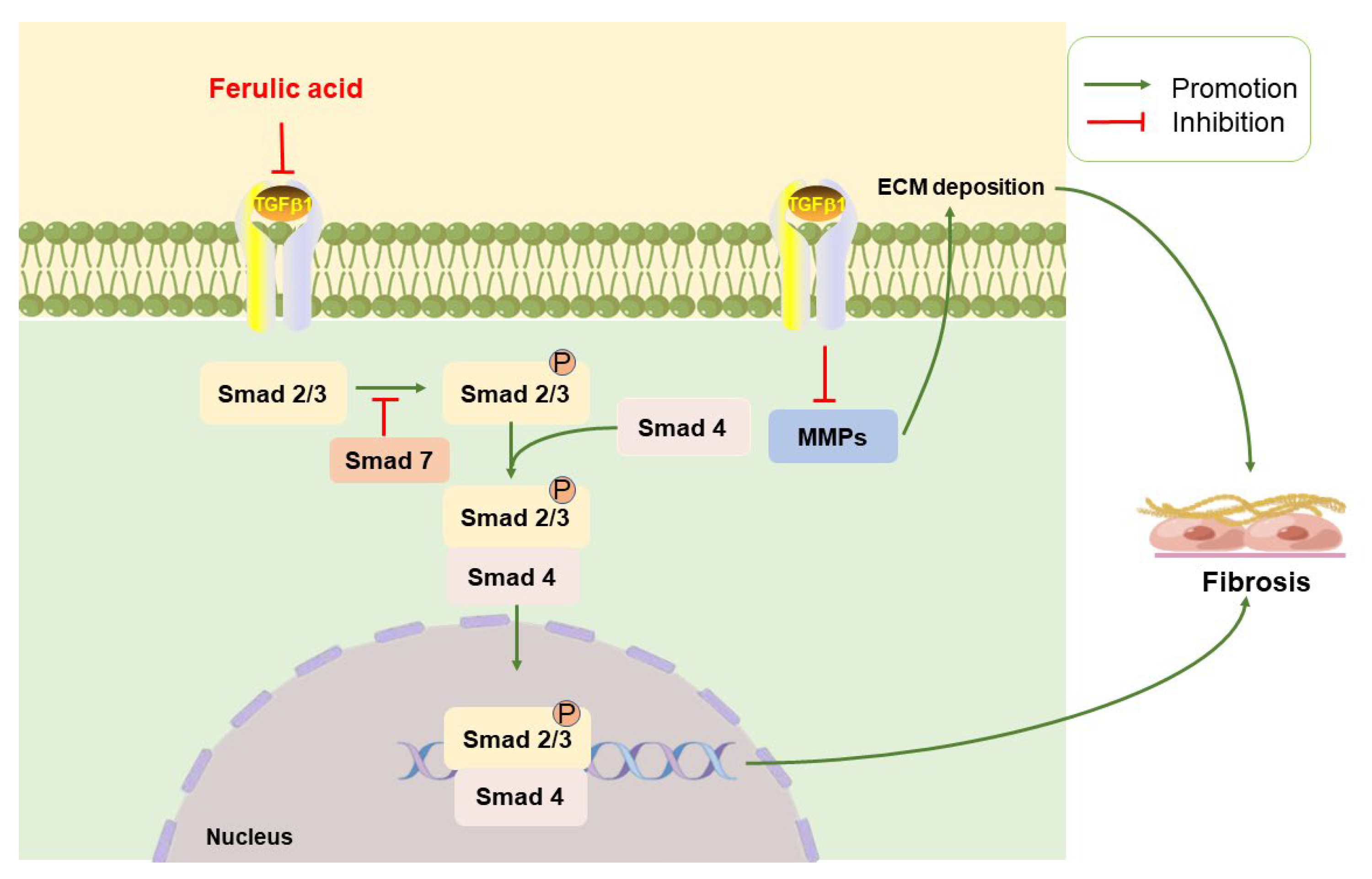
2.3. Anti-Fibrotic Effects
2.3.1. TGF-β/Small Mothers against Decapentaplegic
2.3.2. MMPs/TIMPs
2.4. Anti-Cancer Effects
2.4.1. p53
2.4.2. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase
2.4.3. Protein Kinase B
2.4.4. Programmed Cell Death
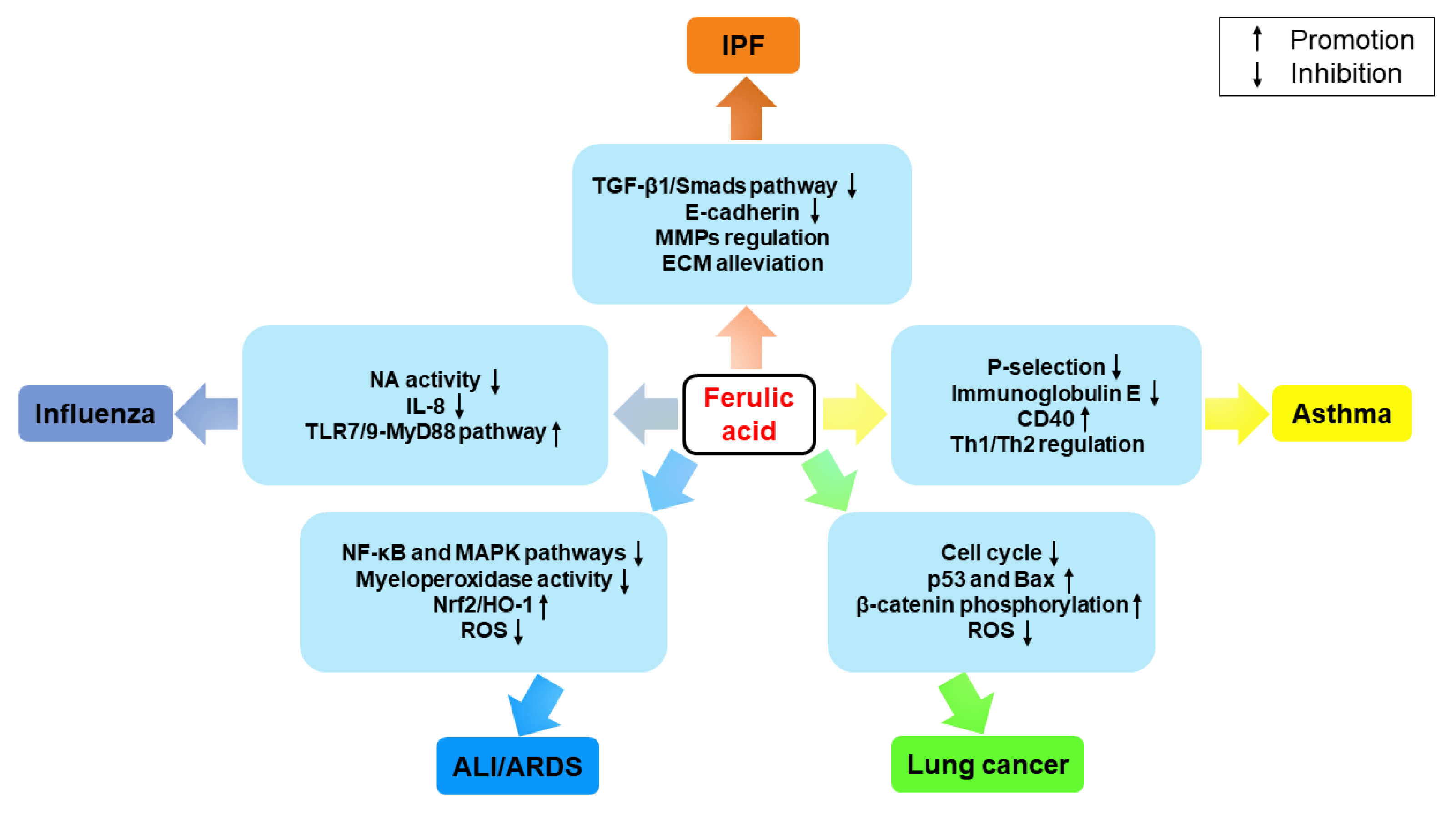
3. Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases
3.1. IPF
3.2. Asthma
3.3. Lung Cancer
3.4. ALI/ARDS
3.5. Influenza
3.6. Other Pulmonary Diseases
4. Toxicological Effects
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wakefield, J.; Hassan, H.M.; Jaspars, M.; Ebel, R.; Rateb, M.E. Dual Induction of New Microbial Secondary Metabolites by Fungal Bacterial Co-cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, I.; Sapountzaki, E.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. Ferulic Acid from Plant Biomass: A Phytochemical with Promising Antiviral Properties. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 777576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento-Silva, A.; Patto, M.C.V.; do Rosario Bronze, M. Relevance, structure and analysis of ferulic acid in maize cell walls. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Moghadasian, M.H. Chemistry, natural sources, dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid: A review. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.G.; Harris, P.J. Ferulic acid is esterified to glucuronoarabinoxylans in pineapple cell walls. Phytochemistry 2001, 56, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pruthi, V. Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, P. Dietary ferulic acid supplementation improves antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism in weaned piglets. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, C.L.; Leu, S.J.; Lee, Y.L. Ferulic acid induces Th1 responses by modulating the function of dendritic cells and ameliorates Th2-mediated allergic airway inflammation in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 678487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibitoye, O.B.; Ajiboye, T.O. Ferulic acid potentiates the antibacterial activity of quinolone-based antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerito, C.; Emanuele, S.; Ferrante, F.; Celesia, A.; Giuliano, M.; Fiore, T. Tributyltin(IV) ferulate, a novel synthetic ferulic acid derivative, induces autophagic cell death in colon cancer cells: From chemical synthesis to biochemical effects. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 205, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Wei, X.L.; Xie, M. The effect of sodium ferulate in experimental pulmonary fibrosis via NALP3 inflammasome. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2017, 48, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Zeni, A.L.B.; Camargo, A.; Dalmagro, A.P. Ferulic acid reverses depression-like behavior and oxidative stress induced by chronic corticosterone treatment in mice. Steroids 2017, 125, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, L.; Subbiah, K.; Arumugam, A.; Senapathy, J.G. Ferulic acid modulates fluoride-induced oxidative hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 151, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadar, S.S.; Vyawahare, N.S.; Bodhankar, S.L. Ferulic acid ameliorates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress, iNOs, COX-2, and apoptosis in laboratory rats. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.J.; Wu, M.Y.; Lu, J.H. Ferulic Acid in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Cells 2021, 10, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.; Badawy, D.; Neamatallah, T.; Fahmy, A. Ferulic acid, a natural polyphenol, alleviates insulin resistance and hypertension in fructose fed rats: Effect on endothelial-dependent relaxation. Chem-Biol. Interact. 2016, 254, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, M.; Huang, Z.Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Jia, Y.H.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhou, F.H. Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Injury by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Liu, D.H.; Hu, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhou, S.B. Ferulic acid ameliorates pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures by reducing neuron cell death. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 156, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Cui, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.X.; He, T.T.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.W. Ferulic acid ameliorates isoproterenol-induced heart failure by decreasing oxidative stress and inhibiting cardiocyte apoptosis via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Lin, S.; Kang, H.; Ma, X. Ferulic acid against cyclophosphamide-induced heart toxicity in mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 1261270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani, M.; Kalantari, H.; Khodayar, M.J.; Khorsandi, L.; Kalantar, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, H. Alleviation of Liver Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Underlies the Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid in Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Drug. Des. Devel Ther. 2020, 14, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanski, J.; Aksenova, M.; Stoyanova, A.; Butterfield, D.A. Ferulic acid antioxidant protection against hydroxyl and peroxyl radical oxidation in synaptosomal and neuronal cell culture systems in vitro: Structure-activity studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuinness, A.J.; Sapey, E. Oxidative Stress in COPD: Sources, Markers, and Potential Mechanisms. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Oxidative stress-based therapeutics in COPD. Redox Biol. 2020, 33, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S.; Das, A.K.; Sil, P.C. Ferulic Acid Protects Hyperglycemia-Induced Kidney Damage by Regulating Oxidative Insult, Inflammation and Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Ferulic acid alleviates retinal neovascularization by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization through the ROS/NF-kappaB axis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 976729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.; Kim, B.H.; Naowaboot, J.; Lee, M.Y.; Hyun, M.R.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Chung, C.H. Effects of ferulic acid on diabetic nephropathy in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Manna, K.; Adhikary, A.; Mishra, S.; Das Saha, K.; Sharma, R.D.; Majumder, B.; Dey, S. Ferulic acid enhances the radiation sensitivity of lung and liver carcinoma cells by collapsing redox homeostasis: Mechanistic involvement of Akt/p38 MAPK signalling pathway. Free. Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 944–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A. Anti-hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, D.K.; Devasagayam, T.P. Antioxidant and prooxidant nature of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives ferulic and caffeic acids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3369–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Yazaki, K.; Sawaki, K.; Ozawa, T.; Kawaguchi, M. Hydroxyl radical scavenging effects of guaiacol used in traditional dental pulp sedation: Reaction kinetic study. Biomed. Res 2005, 26, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanont, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Tohda, M.; Vajragupta, O.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. Evaluation of the nitric oxide radical scavenging activity of manganese complexes of curcumin and its derivative. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H.; Fikrig, S.M.; Smithwick, E.M. Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils. A diagnostic acid. Lancet 1968, 2, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.T.; Ching, L.C.; Yen, G.C. Inducing gene expression of cardiac antioxidant enzymes by dietary phenolic acids in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, A.; Khanduja, K.L. Plant polyphenols inhibit benzoyl peroxide-induced superoxide anion radical production and diacylglyceride formation in murine peritoneal macrophages. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 35, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanduja, K.L.; Avti, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Mittal, N.; Sohi, K.K.; Pathak, C.M. Anti-apoptotic activity of caffeic acid, ellagic acid and ferulic acid in normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: A Bcl-2 independent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Cassano, R.; Ferrarelli, T.; Barone, E.; Picci, N.; Mancuso, C. Trans-ferulic acid-based solid lipid nanoparticles and their antioxidant effect in rat brain microsomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 109, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Lv, H.; Li, J.; Che, Y.; Xu, B.; Tao, Z.; Jiang, W. Roles of Nrf2/HO-1 and HIF-1alpha/VEGF in lung tissue injury and repair following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7695–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, H.X.Y.; Li, R.L.; Peng, W.; Wu, C.J. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, R.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.F.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.H.; Qu, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.Y. Methane Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7067619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Saad, M.A. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2021, 335, 109368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Kan, Y.W. Nrf2 is essential for protection against acute pulmonary injury in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12731–12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.M.; Maltagliati, A.J. Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.C.; Hong, Q.; Wang, Y.G.; Liang, Q.D.; Tan, H.L.; Xiao, C.R.; Tang, X.L.; Shao, S.; Zhou, S.S.; Gao, Y. Ferulic acid induces heme oxygenase-1 via activation of ERK and Nrf2. Drug Discov. Ther. 2011, 5, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. Ferulic acid protects against heat stress-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in IEC-6 cells via the PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 35, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Latunde-Dada, G.O. Upregulation of Nrf2 Signalling and the Inhibition of Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis by Ferulic Acid in MIN6 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Ghatreh-Samani, K.; Amini-Khoei, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Heidarian, E.; Najafi, M. Ferulic acid prevents cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through exerting anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and suppression of NF-kappaB/TNF-alpha axis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Hussein, O.E.; Hozayen, W.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abd El-Twab, S.M. Ferulic acid prevents oxidative stress, inflammation, and liver injury via upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in methotrexate-induced rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7910–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, S.; Zheng, J.; Gong, X.; Xiao, B. Ferulic acid alleviates alveolar epithelial barrier dysfunction in sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting ferroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Meng, H.; Sun, X.; Xue, C. Ferulic acid protects human lens epithelial cells against ionizing radiation-induced oxidative damage by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6932188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Cao, X.; Zhao, M.; Du, J.; Peng, M.; et al. Physalis alkekengi L. var. franchetii (Mast.) Makino: A review of the pharmacognosy, chemical constituents, pharmacological effects, quality control, and applications. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afroz, R.; Tanvir, E.M.; Tania, M.; Fu, J.; Kamal, M.A.; Khan, M.A. LPS/TLR4 pathways in breast cancer: Insights into cell signalling. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 2274–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Shen, J.D.; Xu, L.P.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.C.; Yi, L.T. Ferulic acid inhibits neuro-inflammation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 45, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Jin, N.; Zou, W.; Gao, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, F. Ferulic acid inhibits bovine endometrial epithelial cells against LPS-induced inflammation via suppressing NK-kappaB and MAPK pathway. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 126, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, P.; Milara, J.; Roger, I.; Cortijo, J. Role of JAK/STAT in Interstitial Lung Diseases; Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, G.; So, A. Regulation of inflammasome activity. Immunology 2010, 130, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodzik, P.; Tajdel-Zielinska, M.; Ciesla, A.; Marczak, M.; Ludwikow, A. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Plant Hormone Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.Y.; Koh, M.S.; Moon, A. The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Buckman, S.Y.; Pentland, A.P.; Templeton, D.J.; Morrison, A.R. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by the activated MEKK1 → SEK1/MKK4 → p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12901–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Y.T.; Aziz, F.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Arguelles, S. Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietersma, A.; Tilly, B.C.; Gaestel, M.; de Jong, N.; Lee, J.C.; Koster, J.F.; Sluiter, W. p38 mitogen activated protein kinase regulates endothelial VCAM-1 expression at the post-transcriptional level. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 230, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, A.M.; Cook, M.N.; Lark, M.W.; Newman-Tarr, T.M.; Swift, B.A.; Nelson, A.H.; Barone, F.C.; Kumar, S. SB 203580 inhibits p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, nitric oxide production, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in bovine cartilage-derived chondrocytes. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Han, J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: Activation and function. Cell. Signal. 2000, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jing, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, G. Ferulic acid alleviates sciatica by inhibiting peripheral sensitization through the RhoA/p38MAPK signalling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 106, 154420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellendorf, F.T.; Bonkat, N.; Dalkner, N.; Schonthaler, E.M.D.; Manchia, M.; Fuchs, D.; Reininghaus, E.Z. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-activity in Severe Psychiatric Disorders: A Systemic Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiguchi, M.; Komazaki, H.; Hirai, S.; Egashira, Y. Ferulic acid suppresses expression of tryptophan metabolic key enzyme indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase via NFkappaB and p38 MAPK in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglial cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, E.H.M.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Ali, F.E.M.; Abd El-Ghafar, O.A.M.; Kozman, M.R.; Sharkawi, S.M.Z. Trans-ferulic acid ameliorates cisplatin-induced testicular damage via suppression of TLR4, P38-MAPK, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 41948–41964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caamano, J.; Hunter, C.A. NF-kappaB family of transcription factors: Central regulators of innate and adaptive immune functions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Santani, D. Role of NF-kappa B in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, R.; Akashi, S.; Ogata, H.; Nagai, Y.; Fukudome, K.; Miyake, K.; Kimoto, M. MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohto, U.; Fukase, K.; Miyake, K.; Satow, Y. Crystal structures of human MD-2 and its complex with antiendotoxic lipid IVa. Science 2007, 316, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 2009, 458, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, D.; Bo, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Ferulic acid inhibits LPS-induced apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells by regulating the NF-kappaB and Nrf2 signalling pathways to restore mitochondrial dynamics and ROS generation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Ali, T.; Alam, S.I.; Ullah, R.; Zeb, A.; Lee, K.W.; Rutten, B.P.F.; Kim, M.O. Ferulic acid rescues LPS-induced neurotoxicity via modulation of the TLR4 receptor in the mouse hippocampus. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2774–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, S.M.; Ravuri, H.G.; Pradhan, R.K.; Narra, S.; Kumar, J.M.; Kuncha, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Sistla, R. Ferulic acid protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammatory events and upregulating antioxidant defenses in Balb/c mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.; Manna, K.; Sinha, M.; Datta, S.; Das, D.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Ghosh, M.; Saha, K.D.; Dey, S. Role of ferulic acid in the amelioration of ionizing radiation induced inflammation: A murine model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, S. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, P.; Sarmiento, M. JAK/STAT Pathway Inhibition May Be a Promising Therapy for COVID-19-Related Hyperinflammation in Hematologic Patients. Acta Haematol. 2021, 144, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, N.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J.; Ren, Z.; Meng, F.; Yang, L. Anti-arthritic activity of ferulic acid in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in rats: JAK2 inhibition. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, G.; Qi, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. Inhibition of the Inflammasome Activity of NLRP3 Attenuates HDM-Induced Allergic Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 718779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Yang, Y.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Huo, C.; Ji, X.L.; Qu, Y.Q. Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome-A Key Player in Antiviral Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Qian, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Z. Ferulic acid relieved ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway in rats. Cell Biol. Int. 2023, 47, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Qiu, W.; Shi, Y. Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inducing autophagy and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Weiskirchen, S.; Tacke, F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Mauviel, A. Transforming growth factor-beta and fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3056–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Shi, L.B.; Zhang, S.Y. Ovarian Fibrosis: A Phenomenon of Concern. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Sun, H.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D.W. New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: The macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakshir, P.; Hinz, B. The big five in fibrosis: Macrophages, myofibroblasts, matrix, mechanics, and miscommunication. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68–69, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Pan, Z.; Dong, M.; Yu, C.; Niu, Y. Ferulic acid suppresses activation of hepatic stellate cells through ERK1/2 and Smad signaling pathways in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Saifi, M.A.; Pulivendala, G.; Godugu, C.; Talla, V. Ferulic acid ameliorates the progression of pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of TGF-beta/smad signalling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-beta: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Chen, D.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Feng, Y.L.; Cao, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.Y. New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Lu, D.W.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.L.; Chen, H.; Chen, D.Q.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.Y. Central role of dysregulation of TGF-beta/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Peng, W.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Smad2 and Smad3 play antagonistic roles in high glucose-induced renal tubular fibrosis via the regulation of SnoN. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 113, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.G.; Sun, W.; He, W.M.; Ni, L.; Yang, Y.Y. Ferulic acid attenuates TGF-beta1-induced renal cellular fibrosis in NRK-52E cells by inhibiting Smad/ILK/Snail pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 619720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, M.; Zuo, S.; Wu, R.M.; Deng, K.S.; Lu, S.; Zhu, J.J.; Zou, G.L.; Yang, J.; Cheng, M.L.; Zhao, X.K. Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 4107–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.N.; Niu, Y.C. Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to alleviate hepatic fibrosis in bile duct-ligated cirrhotic rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2925–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukkumani, R.; Priyanka, A.; Sankar, P.; Menon, V.P. Ferulic acid influences hepatic expression pattern of matrix metalloproteinases during alcohol and PUFA induced toxicity. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craig, V.J.; Zhang, L.; Hagood, J.S.; Owen, C.A. Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, M.G.; Parks, W.C. Matrix remodeling by MMPs during wound repair. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 904–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.S.; Wei, Q.H.; Wei, J.H.; Xu, P.L.; Chen, Y. Combination of ferulic acid, ligustrazine and tetrahydropalmatine inhibits invasion and metastasis through MMP/TIMP signaling in endometriosis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniforth, V.; Huang, W.C.; Aravindaram, K.; Yang, N.S. Ferulic acid, a phenolic phytochemical, inhibits UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinases in mouse skin via posttranslational mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Loka, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Bishayee, A. Ferulic acid-mediated modulation of apoptotic signaling pathways in cancer. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 125, 215–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, D.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Li, H. Ferulic acid exerts antitumor activity and inhibits metastasis in breast cancer cells by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Yu, H.; Guo, W.K.; Kong, Y.; Gu, L.N.; Li, Q.; Yang, S.S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.X. The anticancer effects of ferulic acid is associated with induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicke, B.; Hegardt, C.; Krogh, M.; Onning, G.; Akesson, B.; Cirenajwis, H.M.; Oredsson, S.M. The antiproliferative effect of dietary fiber phenolic compounds ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid on the cell cycle of Caco-2 cells. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Y.; Tang, C.C.; Hu, H.T.; Fang, H.Y.; Chen, B.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Wang, H.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Teng, Y.N.; et al. Inhibitory effect of trans-ferulic acid on proliferation and migration of human lung cancer cells accompanied with increased endogenous reactive oxygen species and beta-catenin instability. Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhazendar, M.; Chalak, J.; El-Huneidi, W.; Vinod, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of ferulic acid in breast and liver cancer cell lines. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghari-Tabari, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Qujeq, D.; Andevari, A.N.; Sabahi, Z.; Moein, S. Signaling, metabolism, and cancer: An important relationship for therapeutic intervention. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 5512–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, Y.; Rotter, V.; Aloni-Grinstein, R. Gain-of-Function Mutant p53: All the Roads Lead to Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Illana, V.; Fahraeus, R. p53 isoforms gain functions. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5113–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, E.; Tsuchiya, A.; Imoto, M. Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenglee, S.; Jogloy, S.; Patanothai, A.; Leid, M.; Senawong, T. Cytotoxic effects of peanut phenolics possessing histone deacetylase inhibitory activity in breast and cervical cancer cell lines. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xue, F.; Han, C.; Yang, H.; Han, L.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Yuan, B.; et al. Ferulic acid ameliorated placental inflammation and apoptosis in rat with preeclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2019, 41, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafim, T.L.; Carvalho, F.S.; Marques, M.P.; Calheiros, R.; Silva, T.; Garrido, J.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Silva, E.T.; et al. Lipophilic caffeic and ferulic acid derivatives presenting cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmanno, K.; Cook, S.J. Tumour cell survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, G. Therapeutic effects and mechanism of ferulic acid and icariin in mammary gland hyperplasia model rats via regulation of the ERK pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.R.; Yuan, Y.J. Ferulic acid inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by angiotensin II. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 499, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.; Yuan, Y. Ferulic acid inhibits endothelial cell proliferation through NO down-regulating ERK1/2 pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 93, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.J.; Zhang, P.X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, N.G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, R.Y.; Yan, H.; Shi, X.Q.; et al. A ferulic acid derivative FXS-3 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of human lung cancer A549 cells via positive JNK signaling pathway and negative ERK/p38, AKT/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting AKT for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; Lee, M.H. AKT as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gong, X.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Du, W.; Kuang, G. Ferulic acid inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis via blockage of PI3K/Akt pathway in osteosarcoma cell. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhu, S.; Tong, Y.; Peng, S. Ferulic Acid Induces Apoptosis of HeLa and Caski Cervical Carcinoma Cells by Down-Regulating the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Akt Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e920095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Chiu, J.H.; Wu, I.H.; Wang, B.W.; Pan, C.M.; Chen, Y.H. Ferulic acid augments angiogenesis via VEGF, PDGF and HIF-1 alpha. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.W.; Jiang, J.S.; Lu, W.Q. Ferulic acid exerts anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activity by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-mediated angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24011–24031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moujalled, D.; Strasser, A.; Liddell, J.R. Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Lv, J.; Chen, M.; Guo, N.; Fang, Y.; Tong, J.; He, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, Z. Serinc2 deficiency causes susceptibility to sepsis-associated acute lung injury. J. Inflamm. 2022, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, S.M.; Cooney, J.P.; Pellegrini, M.; Doerflinger, M. Programmed cell death: The pathways to severe COVID-19? Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Deng, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, H.; Lv, X. Role of Ferroptosis in Lung Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhi, L.L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Chen, C.Q.; Qi, Y.F.; Gao, W.T.; He, W.X.; et al. RBMS1 regulates lung cancer ferroptosis through translational control of SLC7A11. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e152067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, X.; Yu, M. Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies Potential Ferroptosis Key Genes in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 788417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Dong, M.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Wang, W.; Li, M.; Teng, F.; Yi, L.; Dong, J.; Wei, Y. Ferroptosis, novel therapeutics in asthma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Qi, K.; Gong, Y.; Long, X.; Zhu, S.Q.; Lu, F.; Lin, K.; Xu, J.J. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Via Upregulating AMPK alpha 2 Expression-Mediated Ferroptosis Depression. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2022, 79, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamarchuk, A.; Efanov, A.; Maximov, V.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Croce, C.M.; Pekarsky, Y. Akt phosphorylates and regulates Pdcd4 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chen, Q.; Li, M.; He, L.; Riaz, F.; Zhang, T.; Li, D. Programmed cell death factor 4 (PDCD4), a novel therapy target for metabolic diseases besides cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 159, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitomsky, N.; Bohm, M.; Klempnauer, K.H. Transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 interferes with JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and recruitment of the coactivator p300 by c-Jun. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7484–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Giovannini, L. Inhibition of mTOR/S6K1/4E-BP1 Signaling by Nutraceutical SIRT1 Modulators. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrello, N.V.; Peschiaroli, A.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Colburn, N.H.; Sherman, N.E.; Pagano, M. S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 2006, 314, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortality, G.B.D.; Causes of Death, C. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yin, B.; Xia, G.; Shen, Z.; Gu, W.; Wu, M. Role of the stromal cell derived factor-1/CXC chemokine receptor 4 axis in the invasion and metastasis of lung cancer and mechanism. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 4947–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.J. Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases. Comprehensive review of the recent literature 2010-2012. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, S45–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.J. Concise review: Current status of stem cells and regenerative medicine in lung biology and diseases. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, S.; Vos, R.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verleden, G.M. Survival in adult lung transplantation: Where are we in 2020? Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2020, 25, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Chen, S.Y.; Lerbs, T.; Lee, J.W.; Domizi, P.; Gordon, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Nolan, G.; Betancur, P.; Wernig, G. Activation of JUN in fibroblasts promotes pro-fibrotic programme and modulates protective immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Patterson, C.M.; Reed, A.K.; Thillai, M. Lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, N.; Sakai, S.; Kitagawa, M. Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis, with focus on pathways related to TGF-beta and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Wells, A.U.; Jenkins, R.G. Pulmonary fibrosis and COVID-19: The potential role for antifibrotic therapy. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Liu, H.; Cao, F.; Jiao, Y. Astragaloside IV synergizing with ferulic acid ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8845798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, R.; Overstreet, J.M.; Higgins, S.P.; Higgins, P.J. TGF-beta1 --> SMAD/p53/USF2 --> PAI-1 transcriptional axis in ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.M.; Tang, P.M.; Li, J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-beta/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Chang, K.; Wu, H.; Su, G.; Gong, J. Notch signaling pathway mediates the immunomodulatory mechanism of Yangfei Huoxue decoction alleviating bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Su, G.; Song, P.; Jiang, M.; Gong, J. An animal research and a chemical composition analysis of a Chinese prescription for pulmonary fibrosis: Yangfei Huoxue Decoction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 245, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mims, J.W. Asthma: Definitions and pathophysiology. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, I.D.; Beasley, R.; Agusti, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Bel, E.; Brusselle, G.; Cullinan, P.; Custovic, A.; Ducharme, F.M.; Fahy, J.V.; et al. After asthma: Redefining airways diseases. Lancet 2018, 391, 350–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugiolo, A.S.S.; Gouveia, A.C.C.; de Souza Alves, C.C.; de Castro, E.S.F.M.; de Oliveira, É.E.; Ferreira, A.P. Ferulic acid supresses Th2 immune response and prevents remodeling in ovalbumin-induced pulmonary allergy associated with inhibition of epithelial-derived cytokines. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, G.; Bachmair, E.M.; Wood, S.; Mateos, R.; Bravo, L.; de Roos, B. The colonic metabolites dihydrocaffeic acid and dihydroferulic acid are more effective inhibitors of in vitro platelet activation than their phenolic precursors. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morianos, I.; Semitekolou, M. Dendritic cells: Critical regulators of allergic asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayanandamoorthy, Y.; Antoniraj, M.G.; Kandregula, C.A.B.; Kandasamy, R. Aerosolized hyaluronic acid decorated, ferulic acid loaded chitosan nanoparticle: A promising asthma control strategy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 591, 119958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, D.; He, J.; Krasna, M.J. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.; Manna, K.; Khan, A.; Sinha, M.; Biswas, S.; Sengupta, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Dey, S. Ferulic acid (FA) abrogates gamma-radiation induced oxidative stress and DNA damage by up-regulating nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and activation of NHEJ pathway. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Gawish, R.A.; Sallam, A.M.; Fahmy, H.A.; Nada, A.S. Ferulic acid protects against radiation-induced testicular damage in male rats: Impact on SIRT1 and PARP1. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 6218–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandugula, V.R.; Rajendra, P.N. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose and ferulic acid modulates radiation response signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzaiene, N.N.; Jaziri, S.K.; Kovacic, H.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Ghedira, K.; Luis, J. The effects of caffeic, coumaric and ferulic acids on proliferation, superoxide production, adhesion and migration of human tumor cells in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 766, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, Y.; Kurdowska, A.; Allen, T.C. Acute lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Horvath, V.; Datler, H.; Hell, L.; Ay, C.; Niederreiter, B.; Jilma, B.; Schmid, J.A.; Assinger, A.; et al. Myeloid but not epithelial tissue factor exerts protective anti-inflammatory effects in acid aspiration-induced acute lung injury. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lin, L.; Wu, H. Ferulic acid alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Tao, Z.; Xiong, K. High expression of KITLG is a new hallmark activating the MAPK pathway in type A and AB thymoma. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Gong, G. Ethyl ferulate contributes to the inhibition of the inflammatory responses in murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cells and acute lung injury in mice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, D.; Hu, Z.; Xu, M.; Xu, M.; Liu, Z. The effects of the combination of sodium ferulate and oxymatrine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation 2012, 35, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, W.; Gao, H.; Jiao, Y. Pretreatment of ferulic acid attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 394632017750518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Yue, L.; Cui, W.; Zhou, W.; Gao, J.; Yao, H. Molecular pathogenesis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and therapeutic potential by targeting AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, G.; Wan, B.B.; Jiang, F.J.; Wei, M.X.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, J.; et al. Ethyl ferulate protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, D.Y.; Moore, F.C.; Morgan, M.K. Influenza: Diagnosis and treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Xu, L.; Lin, D.; Lian, W.; Cui, M.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Ye, J.; et al. Design, synthesis, and bioassay of 4-thiazolinone derivatives as influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariono, M.; Abdullah, N.; Damodaran, K.V.; Kamarulzaman, E.E.; Mohamed, N.; Hassan, S.S.; Shamsuddin, S.; Wahab, H.A. Potential new H1N1 neuraminidase inhibitors from ferulic acid and vanillin: Molecular modelling, synthesis and in vitro assay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuwongcharoen, N.; Shoombuatong, W.; Tantimongcolwat, T.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C. Exploring the chemical space of influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Shao, Y.; Qu, X.Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.Q. Sodium ferulate protects against influenza virus infection by activation of the TLR7/9-MyD88-IRF7 signaling pathway and inhibition of the NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decramer, M.; Janssens, W.; Miravitlles, M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegman, C.H.; Li, F.; Ryffel, B.; Togbe, D.; Chung, K.F. Oxidative Stress in Ozone-Induced Chronic Lung Inflammation and Emphysema: A Facet of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yamamoto, M.; Chen, J.; Duan, H.; Du, J.; He, L.; Shi, D.; Yao, X.; Nagai, T.; Kiyohara, H.; et al. Integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification to decipher the immunomodulatory effect of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang against poly (I:C)-induced pulmonary inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1015486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Xing, X.; Xi, S.; Jing, H.; Yuan, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, H. Trends in global, regional and national incidence of pneumoconiosis caused by different aetiologies: An analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Gan, X. The improvement effect of sodium ferulate on the formation of pulmonary fibrosis in silicosis mice through the neutrophil alkaline phosphatase 3 (NALP3)/transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1)/alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e927978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, X.; Su, S.; Ma, K.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Zhaxi, D.; Ge, R.; Li, Z.; Lu, D. Bioactive fraction of Rhodiola algida against chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension and its anti-proliferation mechanism in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 216, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Song, T.; Hao, G.; Fu, X.; Gu, X. Renal protective effect of sodium ferulate on pulmonary hypertension patients undergoing computed tomography pulmonary angiography. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiderek, K.; Moliner, V. Revealing the molecular mechanisms of proteolysis of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) by QM/MM computational methods. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10626–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, I.; Sapountzaki, E.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. The Inhibitory Potential of Ferulic Acid Derivatives against the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and ADMET Evaluation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S. In vitro and in vivo antithrombotic and cytotoxicity effects of ferulic acid. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Wang, H.E.; Chung, J.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Peng, R.Y. Ferulic acid is nephrodamaging while gallic acid is renal protective in long term treatment of chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, P.; Singh, D.K. Seasonal variation in abiotic factors and ferulic acid toxicity in snail-attractant pellets against the intermediate host snail Lymnaea acuminata. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, K.S.; Fachel, F.N.S.; de Araujo, B.V.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Oral Pharmacokinetics of Hydroxycinnamic Acids: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hu, R.; Feng, N. Ethyl oleate-containing nanostructured lipid carriers improve oral bioavailability of trans-ferulic acid as compared with conventional solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
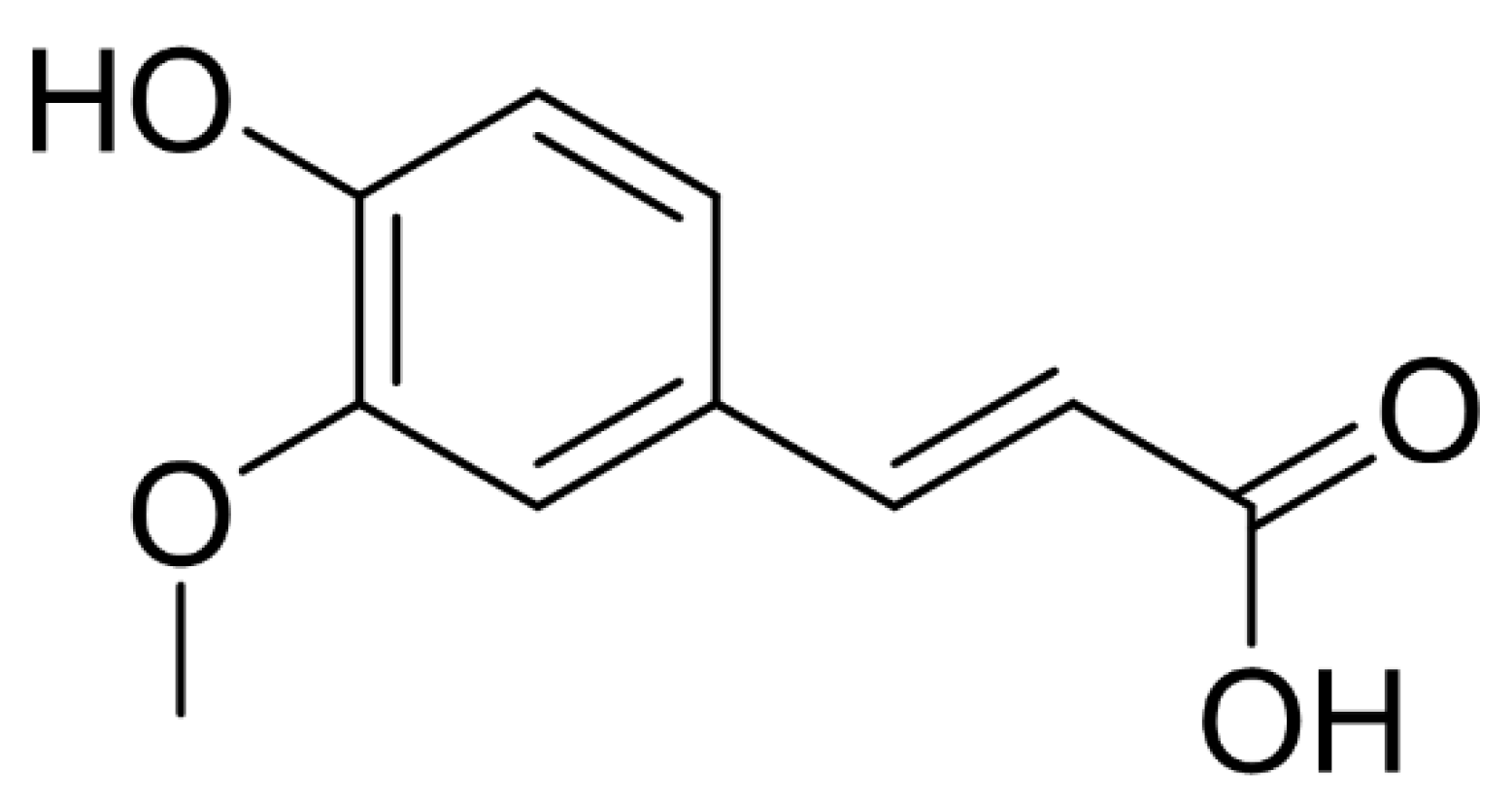

| Property | Index |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 194.18 |
| Melting point | 170.0 ± 2.0 °C |
| Boiling point | 372.3 ± 27.0 °C |
| Density | 1.316 ± 0.06 g/cm3 |
| Cis isomer | Yellow oily substance |
| Trans isomer | Monoclinic crystal |
| Solubility | Soluble in hot water, ethanol and ethyl acetate, slightly soluble in diethyl ether, and poorly soluble in benzene and petroleum ether |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Nie, H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098011
Zhai Y, Wang T, Fu Y, Yu T, Ding Y, Nie H. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098011
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yiman, Tingyu Wang, Yunmei Fu, Tong Yu, Yan Ding, and Hongguang Nie. 2023. "Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098011
APA StyleZhai, Y., Wang, T., Fu, Y., Yu, T., Ding, Y., & Nie, H. (2023). Ferulic Acid: A Review of Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutic Effects on Pulmonary Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098011






