PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Proteolysis in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
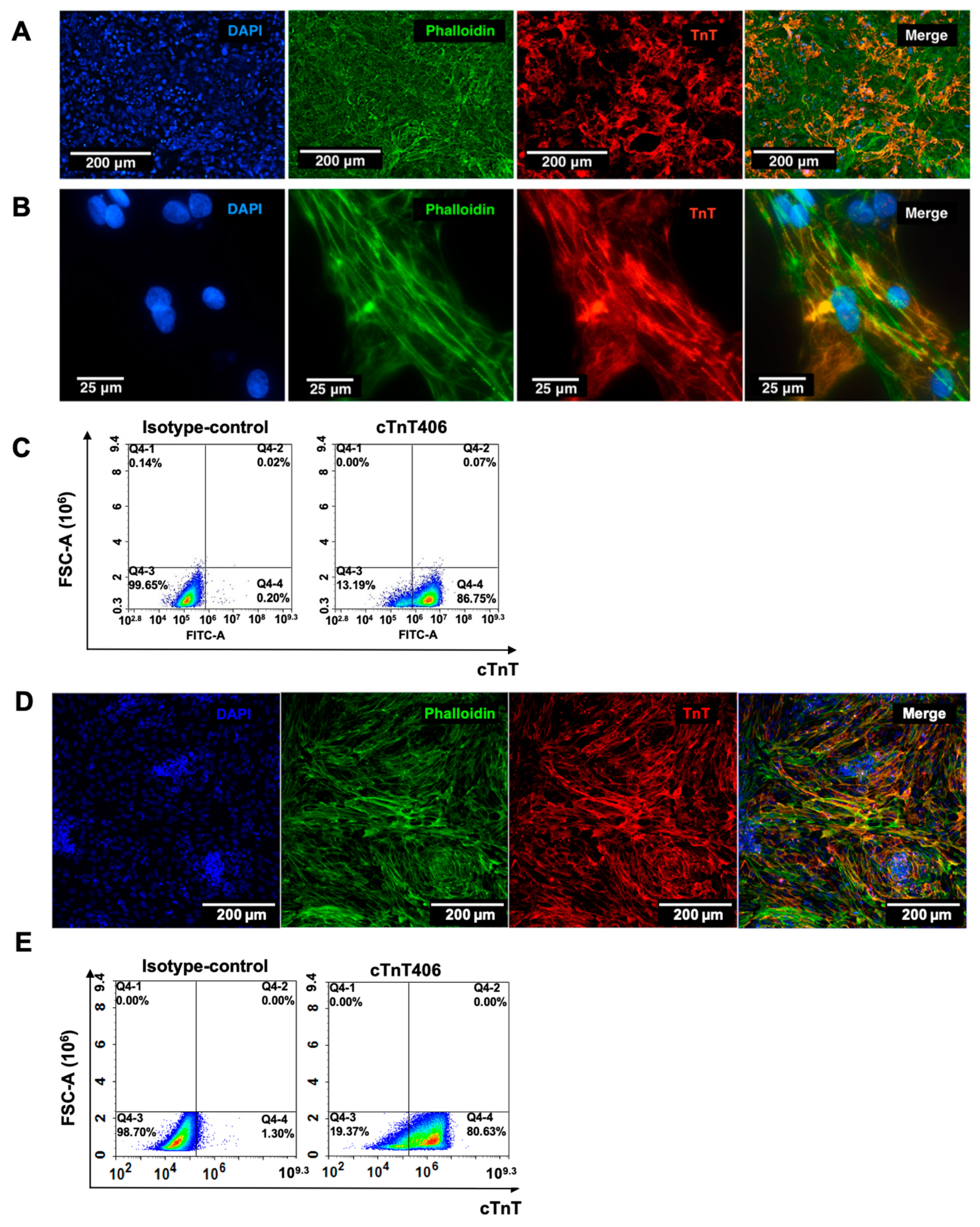
2.1. Generation and Characterization of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes
2.2. IGFBP-4 Is Proteolytically Cleaved by PAPP-A in hiPSC-CM-Conditioned Medium
2.3. PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Cleavage Proceeds Both on the Cell Surface and in the Conditioned Medium of hiPSC-CMs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Differentiation of hiPSCs into Cardiomyocytes
4.2. Immunocytochemistry
4.3. Flow Cytometry
4.4. Proteolytic Cleavage of IGFBP-4 in Cell-Conditioned Medium
4.5. Detection of NT-IGFBP-4 and PAPP-A by Sandwich-Type FIA
4.6. Cell Lysate Preparation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ren, J.; Samson, W.K.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin-like growth factor I as a cardiac hormone: Physiological and pathophysiological implications in heart disease. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1999, 31, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, A.; Nederlof, R.; Panjwani, P.; Spychala, A.; Tschaidse, T.; Reffelt, H.; Boy, J.; Raupach, A.; Gödecke, S.; Petzsch, P.; et al. IGF1 Treatment Improves Cardiac Remodeling after Infarction by Targeting Myeloid Cells. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Li, H.; Pi, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, S. Cardioprotective effect of IGF-1 against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway in rats in vivo. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmons, D.R. Role of IGF-binding proteins in regulating IGF responses to changes in metabolism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T139–T169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortebjerg, R. IGFBP-4 and PAPP-A in normal physiology and disease. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2018, 41, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, L.S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Weyer, K.; Boldt, H.B.; Ebbesen, P.; Christiansen, M.; Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Giudice, L.C.; Oxvig, C. Cell surface targeting of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A proteolytic activity. Reversible adhesion is mediated by two neighboring short consensus repeats. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47225–47234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, M.T.; Sorensen, E.S.; Stachowiak, D.; Boldt, H.B.; Kristensen, L.; Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Oxvig, C. Complex of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A and the proform of eosinophil major basic protein. Disulfide structure and carbohydrate attachment. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, L.S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Nielsen, C.G.; Boldt, H.B.; Hopmann, K.H.; Conover, C.A.; Oxvig, C. Substrate specificity of the metalloproteinase pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) assessed by mutagenesis and analysis of synthetic peptides: Substrate residues distant from the scissile bond are critical for proteolysis. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, C.A.; Oxvig, C.; Overgaard, M.T.; Christiansen, M.; Giudice, L.C. Evidence that the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 protease in human ovarian follicular fluid is pregnancy associated plasma protein-A. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 4742–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazerbourg, S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Oxvig, C.; Christiansen, M.; Conover, C.A.; Laurendeau, I.; Vidaud, M.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; Zapf, J.; Monget, P. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) in ovine, bovine, porcine, and equine ovarian follicles: Involvement in IGF binding protein-4 proteolytic degradation and mRNA expression during follicular development. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5243–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.B.; Oxvig, C.; Overgaard, M.T.; Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Gleich, G.J.; Hays, L.G.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Conover, C.A. The insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-dependent IGF binding protein-4 protease secreted by human fibroblasts is pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3149–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, C.A.; Faessen, G.F.; Ilg, K.E.; Chandrasekher, Y.A.; Christiansen, M.; Overgaard, M.T.; Oxvig, C.; Giudice, L.C. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-a is the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 protease secreted by human ovarian granulosa cells and is a marker of dominant follicle selection and the corpus luteum. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Schwartz, R.S.; Lewis, D.A.; Overgaard, M.T.; Christiansen, M.; Oxvig, C.; Ashai, K.; Holmes, D.R.J.; Conover, C.A. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 protease produced by smooth muscle cells increases in the coronary artery after angioplasty. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, L.C.; Conover, C.; Bale, L.; Faessen, G.; Ilg, K.; Sun, I.; Imani, B.; Suen, L.; Irwin, J.; Christiansen, M.; et al. Identification and regulation of the IGFBP-4 protease and its physiological inhibitor in human trophoblasts and endometrial stroma: Evidence for paracrine regulation of IGF-II bioavailability in the placental bed during human implantation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, C.A.; Bale, L.K.; Frye, R.L.; Schaff, H.V. Cellular characterization of human epicardial adipose tissue: Highly expressed PAPP-A regulates insulin-like growth factor I signaling in human cardiomyocytes. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, C.A.; Harrington, S.C.; Bale, L.K. Differential regulation of pregnancy associated plasma protein-A in human coronary artery endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2008, 18, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, P.; Ionta, V.; Chimenti, I.; Angelini, F.; Miraldi, F.; Pala, A.; Messina, E.; Giacomello, A. Analysis of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A production in human adult cardiac progenitor cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 190178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Conover, C.A.; Overgaard, M.T.; Bailey, K.R.; Christiansen, M.; Holmes, D.R.; Virmani, R.; Oxvig, C.; Schwartz, R.S. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A as a marker of acute coronary syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konev, A.A.; Kharitonov, A.V.; Rozov, F.N.; Altshuler, E.P.; Serebryanaya, D.V.; Lassus, J.; Harjola, V.; Katrukha, A.G.; Postnikov, A.B. CT-IGFBP-4 as a novel prognostic biomarker in acute heart failure. ESC Heart Fail 2020, 7, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikov, A.B.; Smolyanova, T.; Kharitonov, A.; Serebryanaya, D.; Kozlovsky, S.; Tryshina, Y.; Malanicev, R.; Arutyunov, A.; Murakami, M.; Apple, F.; et al. N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of IGFBP-4 as novel biomarkers for short-term risk assessment of major adverse cardiac events in patients presenting with ischemia. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebryanaya, D.V.; Adasheva, D.A.; Konev, A.A.; Artemieva, M.M.; Katrukha, I.A.; Postnikov, A.B.; Medvedeva, N.A.; Katrukha, A.G. IGFBP-4 Proteolysis by PAPP-A in a Primary Culture of Rat Neonatal Cardiomyocytes under Normal and Hypertrophic Conditions. Biochemistry 2021, 86, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortebjerg, R.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Gude, M.F.; Irmukhamedov, A.; Riber, L.P.; Frystyk, J.; De Mey, J.G.R. Local IGF Bioactivity Associates with High PAPP-A Activity in the Pericardial Cavity of Cardiovascular Disease Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e4083–e4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkel, P.; Jakobsen, J.C.; Hilden, J.; Jensen, G.B.; Kjøller, E.; Sajadieh, A.; Kastrup, J.; Kolmos, H.J.; Iversen, K.K.; Bjerre, M.; et al. Prognostic value of 12 novel cardiological biomarkers in stable coronary artery disease. A 10-year follow-up of the placebo group of the Copenhagen CLARICOR trial. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Garcia, O.; Pelacho, B.; Prosper, F. Induced pluripotent stem cells as a new strategy for cardiac regeneration and disease modeling. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2013, 62, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakikes, I.; Ameen, M.; Termglinchan, V.; Wu, J.C. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Insights into molecular, cellular, and functional phenotypes. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Yang, L.; Lin, B.; Zhu, X.; Sun, B.; Kaplan, A.D.; Bett, G.C.; Rasmusson, R.L.; London, B.; Salama, G. Mechanism of automaticity in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 81, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wei, H.; Lu, J.; Wong, P.; Shim, W. Identification and characterization of calcium sparks in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55266. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.O.; Rahman, G.A.; Yin, K.; Long, S. Enhancing Matured Stem-Cardiac Cell Generation and Transplantation: A Novel Strategy for Heart Failure Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; Suhail, Y.; Zong, P.; Feng, J.; Ajeti, V.; Sayyad, W.A.; Nikolaus, J.; Yankova, M.; et al. Cardiac ultrastructure inspired matrix induces advanced metabolic and functional maturation of differentiated human cardiomyocytes. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hua, Y.; Miyagawa, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Sawa, Y. hiPSC-Derived Cardiac Tissue for Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchenko, C.Y.; Pipes, G.C.; Lozinskaya, I.M.; Lin, Z.; Xiaoping, X.; Needle, S.; Grygielko, E.T.; Hu, E.; Toomey, J.R.; Lepore, J.J.; et al. Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes exhibit temporal changes in phenotype. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H913–H922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.E.; Anzai, T.; Chanthra, N.; Uosaki, H. A Brief Review of Current Maturation Methods for Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Chao, B.S.; Wu, J.C. Strategies for Improving the Maturity of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, Z.T.; Oxvig, C.; Bale, L.K.; Conover, C.A. Stress-activated signaling pathways mediate the stimulation of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A expression in cultured human fibroblasts. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, C.A.; Bale, L.K.; Harrington, S.C.; Resch, Z.T.; Overgaard, M.T.; Oxvig, C. Cytokine stimulation of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A expression in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells: Inhibition by resveratrol. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C183–C188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, C.A.; Kiefer, M.C.; Zapf, J. Posttranslational regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 in normal and transformed human fibroblasts. Insulin-like growth factor dependence and biological studies. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxvig, C. The role of PAPP-A in the IGF system: Location, location, location. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 9, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.P.; Kokkala, S.; Lund, J.; Tamm, N.; Voipio-Pulkki, L.-M.; Pettersson, K. Molecular distinction of circulating pregnancy-associated plasma protein A in myocardial infarction and pregnancy. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konev, A.A.; Serebryanaya, D.V.; Koshkina, E.V.; Rozov, F.N.; Filatov, V.L.; Kozlovsky, S.V.; Kara, A.N.; Katrukha, A.G.; Postnikov, A.B. Glycosylated and non-glycosylated NT-IGFBP-4 in circulation of acute coronary syndrome patients. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 55, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konev, A.A.; Smolyanova, T.I.; Kharitonov, A.V.; Serebryanaya, D.V.; Kozlovsky, S.V.; Kara, A.N.; Feygina, E.E.; Katrukha, A.G.; Postnikov, A.B. Characterization of endogenously circulating IGFBP-4 fragments-Novel biomarkers for cardiac risk assessment. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, N.; Pisselet, C.; Monniaux, D.; Monget, P. Proteolytic activity degrading insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2, -3, -4, and -5 in healthy growing and atretic follicles in the pig ovary. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 56, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutova, M.V.; Surdina, A.V.; Ischenko, D.S.; Naumov, V.A.; Bogomazova, A.N.; Vassina, E.M.; Alekseev, D.G.; Lagarkova, M.A.; Kiselev, S.L. An integrative analysis of reprogramming in human isogenic system identified a clone selection criterion. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmqvist, S.; Lehtonen, S.; Chumarina, M.; Puttonen, K.A.; Azevedo, C.; Lebedeva, O.; Ruponen, M.; Oksanen, M.; Djelloul, M.; Collin, A.; et al. Creation of a library of induced pluripotent stem cells from Parkinsonian patients. npj Park. Dis. 2016, 2, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, L.S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Søe, R.; Boldt, H.B.; Sottrup-Jensen, L.; Giudice, L.C.; Conover, C.A.; Oxvig, C. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) cleaves insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-5 independent of IGF: Implications for the mechanism of IGFBP-4 proteolysis by PAPP-A. FEBS Lett. 2001, 504, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adasheva, D.A.; Lebedeva, O.S.; Goliusova, D.V.; Postnikov, A.B.; Teriakova, M.V.; Kopylova, I.V.; Lagarkova, M.A.; Katrukha, A.G.; Serebryanaya, D.V. PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Proteolysis in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098420
Adasheva DA, Lebedeva OS, Goliusova DV, Postnikov AB, Teriakova MV, Kopylova IV, Lagarkova MA, Katrukha AG, Serebryanaya DV. PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Proteolysis in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(9):8420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdasheva, Daria A., Olga S. Lebedeva, Daria V. Goliusova, Alexander B. Postnikov, Maria V. Teriakova, Irina V. Kopylova, Maria A. Lagarkova, Alexey G. Katrukha, and Daria V. Serebryanaya. 2023. "PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Proteolysis in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 9: 8420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098420
APA StyleAdasheva, D. A., Lebedeva, O. S., Goliusova, D. V., Postnikov, A. B., Teriakova, M. V., Kopylova, I. V., Lagarkova, M. A., Katrukha, A. G., & Serebryanaya, D. V. (2023). PAPP-A-Specific IGFBP-4 Proteolysis in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098420




