Actionable Driver Events in Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Mutational Profile and Molecular Landscape of SCLC
1.2. Tumor Heterogeneity and Plasticity in SCLC
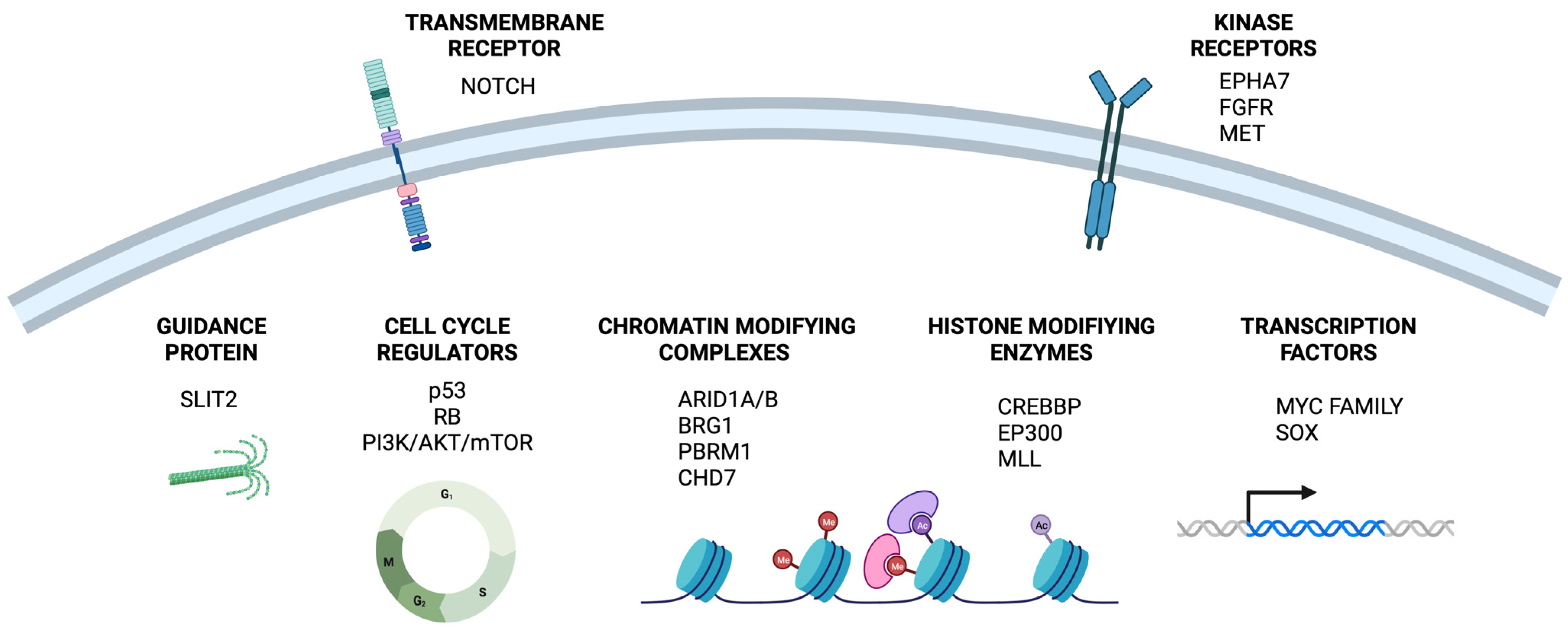
2. Actionable Drivers in SCLC
2.1. Targeting Transcription Factors and Epigenomic Regulators
2.2. Targeting DNA Damage Response Proteins
2.3. Kinase Inhibitors
2.4. Targeting Metabolic Pathways
2.5. Other Targetable Proteins and Lipids Involved in SCLC
2.6. Targeting Pathways and Biological Processes
2.7. Angiogenesis Related Therapies
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer Statistics for the Year 2020: An Overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, A.M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Yu, H.A.; Won, H.H.; Riely, G.J.; Krug, L.M.; Kris, M.G.; Rekhtman, N.; Ladanyi, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Small-Cell Lung Cancers in Patients Who Never Smoked Cigarettes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basumallik, N.; Agarwal, M. Small Cell Lung Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Früh, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Besse, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hendriks, L.E.; Lantuejoul, S.; Peters, S.; Reguart, N.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemkerian, G.P.; Akerley, W.; Bogner, P.; Borghaei, H.; Chow, L.Q.; Downey, R.J.; Gandhi, L.; Ganti, A.K.P.; Govindan, R.; Grecula, J.C.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2013, 11, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.U.; Kang, H.S. A Narrative Review of Current and Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Callahan, M.K.; Awad, M.M.; Calvo, E.; Ascierto, P.A.; Atmaca, A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hirsch, F.R.; Selvaggi, G.; Szustakowski, J.D.; et al. Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Nivolumab Monotherapy and in Combination with Ipilimumab in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 853–861.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab, with or without Tremelimumab, plus Platinum–Etoposide versus Platinum–Etoposide Alone in First-Line Treatment of Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer (CASPIAN): Updated Results from a Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiles of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-B.; Dunn, C.T.; Park, K.-S. Recent Progress in Mapping the Emerging Landscape of the Small-Cell Lung Cancer Genome. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kim, K.-C.; Kim, K.-B.; Dunn, C.T.; Park, K.-S. Transcriptional Deregulation Underlying the Pathogenesis of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peifer, M.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Sos, M.L.; George, J.; Seidel, D.; Kasper, L.H.; Plenker, D.; Leenders, F.; Sun, R.; Zander, T.; et al. Integrative Genome Analyses Identify Key Somatic Driver Mutations of Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, S.; Mimaki, S.; Makinoshima, H.; Tada, S.; Ishii, G.; Ohmatsu, H.; Niho, S.; Yoh, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Therapeutic Priority of the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway in Small Cell Lung Cancers as Revealed by a Comprehensive Genomic Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, A.S.; Micinski, A.M.; Kastner, D.W.; Guo, B.; Wait, S.J.; Spainhower, K.B.; Conley, C.C.; Chen, O.S.; Guthrie, M.R.; Soltero, D.; et al. MYC Drives Temporal Evolution of Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes by Reprogramming Neuroendocrine Fate. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 60–78.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, E.; Wallenburg, M.; Wollenzien, H.; Thompson, E.; Kumar, K.; Feiner, J.; McNally, M.; Friesen, H.; Mukherjee, M.; Afeworki, Y.; et al. Sox2 Is an Oncogenic Driver of Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Promotes the Classic Neuroendocrine Subtype. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-S.; Liang, M.-C.; Raiser, D.M.; Zamponi, R.; Roach, R.R.; Curtis, S.J.; Walton, Z.; Schaffer, B.E.; Roake, C.M.; Zmoos, A.-F.; et al. Characterization of the Cell of Origin for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyn, A.; Borromeo, M.; Wang, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Shao, C.; Dospoy, P.D.; Lee, V.; Tan, C.; Sullivan, J.P.; Larsen, J.E.; et al. ASCL1 Is a Lineage Oncogene Providing Therapeutic Targets for High-Grade Neuroendocrine Lung Cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14788–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Denny, S.K.; Greenside, P.G.; Chaikovsky, A.C.; Brady, J.J.; Ouadah, Y.; Granja, J.M.; Jahchan, N.S.; Lim, J.S.; Kwok, S.; et al. Intertumoral Heterogeneity in SCLC Is Influenced by the Cell Type of Origin. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferone, G.; Lee, M.C.; Sage, J.; Berns, A. Cells of Origin of Lung Cancers: Lessons from Mouse Studies. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offin, M.; Guo, R.; Wu, S.L.; Sabari, J.; Land, J.D.; Ni, A.; Montecalvo, J.; Halpenny, D.F.; Buie, L.W.; Pak, T.; et al. Immunophenotype and Response to Immunotherapy of RET-Rearranged Lung Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzutilo, E.G.; Pedrani, M.; Amatu, A.; Ruggieri, L.; Lauricella, C.; Veronese, S.M.; Signorelli, D.; Cerea, G.; Giannetta, L.; Siena, S.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Either De Novo or Transformed: Systematic Review of Different Applications and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, S.; Morstyn, G.; Carney, D.N.; Modesti, A.; Triche, T.J. Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines: Pure and Variant Types Can Be Distinguished by Their Extracellular Matrix Synthesis. Eur. Respir. J. 1988, 1, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Girard, L.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Haruki, T.; Papari-Zareei, M.; Stastny, V.; Ghayee, H.K.; Pacak, K.; Oliver, T.G.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumors and Preclinical Models Display Heterogeneity of Neuroendocrine Phenotypes. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borromeo, M.D.; Savage, T.K.; Kollipara, R.K.; He, M.; Augustyn, A.; Osborne, J.K.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Cobb, M.H.; et al. ASCL1 and NEUROD1 Reveal Heterogeneity in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors and Regulate Distinct Genetic Programs. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baine, M.K.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Lai, W.V.; Egger, J.V.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Daneshbod, Y.; Beras, A.; Spencer, R.; Lopardo, J.; Bodd, F.; et al. SCLC Subtypes Defined by ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1: A Comprehensive Immunohistochemical and Histopathologic Characterization. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriuranpong, V.; Borges, M.W.; Strock, C.L.; Nakakura, E.K.; Watkins, D.N.; Blaumueller, C.M.; Nelkin, B.D.; Ball, D.W. Notch Signaling Induces Rapid Degradation of Achaete-Scute Homolog 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 3129–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Fetsch, P.; Thomas, A.; Pommier, Y.; Schrump, D.S.; Miettinen, M.M.; Chen, H. Molecular Subtypes of Primary SCLC Tumors and Their Associations With Neuroendocrine and Therapeutic Markers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, J.T.; George, J.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Berns, A.; Brambilla, E.; Byers, L.A.; Carbone, D.; Chen, H.J.; Christensen, C.L.; Dive, C.; et al. New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Poirier, J.T.; Byers, L.A.; Dive, C.; Dowlati, A.; George, J.; Heymach, J.V.; Johnson, J.E.; Lehman, J.M.; MacPherson, D.; et al. Molecular Subtypes of Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Synthesis of Human and Mouse Model Data. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, M.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, M.; Sato, Y.; Takata, S.; Takai, E.; Miyashita, N.; Saito, A.; Nakatani, Y.; Yachida, S. An Integrative Epigenomic Approach Identifies ELF3 as an Oncogenic Regulator in ASCL1 -positive Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2596–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dwivedi, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Barwick, B.; Ernani, V.; Zhang, G.; Gilbert-Ross, M.; Carlisle, J.; Khuri, F.R.; et al. YAP1 Expression in SCLC Defines a Distinct Subtype With T-Cell–Inflamed Phenotype. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Klingbeil, O.; He, X.-Y.; Wu, X.S.; Arun, G.; Lu, B.; Somerville, T.D.D.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Demerdash, O.E.; et al. POU2F3 Is a Master Regulator of a Tuft Cell-like Variant of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shue, Y.T.; Lim, J.S.; Sage, J. Tumor Heterogeneity in Small Cell Lung Cancer Defined and Investigated in Pre-Clinical Mouse Models. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Saito, A.; Ohshima, M.; Suzuki, H.I.; Nagase, T. YAP and TAZ Modulate Cell Phenotype in a Subset of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, S.M.; Ildefonso, G.V.; McAtee, C.O.; Ozawa, P.M.M.; Ireland, A.S.; Stauffer, P.E.; Wasdin, P.T.; Huang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Lim, J.S.; et al. Archetype Tasks Link Intratumoral Heterogeneity to Plasticity and Cancer Hallmarks in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Systems 2022, 13, 690–710.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouadah, Y.; Rojas, E.R.; Riordan, D.P.; Capostagno, S.; Kuo, C.S.; Krasnow, M.A. Rare Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells Are Stem Cells Regulated by Rb, P53, and Notch. Cell 2019, 179, 403–416.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, K.K.; Simpson, K.L.; Dive, C. Small Cell Lung Cancer Enters the Era of Precision Medicine. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Park, E.M.; Diao, L.; Groves, S.M.; Heeke, S.; Nabet, B.Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis, L.M.; Lu, W.; et al. Patterns of Transcription Factor Programs and Immune Pathway Activation Define Four Major Subtypes of SCLC with Distinct Therapeutic Vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 346–360.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chung, C.; Xie, T.; Ozeck, M.; Nichols, T.C.; Frey, J.; Udyavar, A.R.; Sharma, S.; Paul, T.A. Intrinsic and Acquired Drug Resistance to LSD1 Inhibitors in Small Cell Lung Cancer Occurs through a TEAD4-driven Transcriptional State. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 1309–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augert, A.; Eastwood, E.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Wu, N.; Grunblatt, E.; Basom, R.; Liggitt, D.; Eaton, K.D.; Martins, R.; Poirier, J.T.; et al. Targeting NOTCH Activation in Small Cell Lung Cancer through LSD1 Inhibition. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaau2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiatt, J.B.; Sandborg, H.; Garrison, S.M.; Arnold, H.U.; Liao, S.-Y.; Norton, J.P.; Friesen, T.J.; Wu, F.; Sutherland, K.D.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; et al. Inhibition of LSD1 with Bomedemstat Sensitizes Small Cell Lung Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Blockade and T-Cell Killing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4551–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Martinez-Marti, A.; Trigo, J.M.; Moreno, V.; Garrido, P.; Ferron-Brady, G.; Wu, Y.; Park, J.; Collingwood, T.; et al. Phase I, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Efficacy of GSK2879552 in Relapsed/Refractory SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oser, M.G.; Sabet, A.H.; Gao, W.; Chakraborty, A.A.; Schinzel, A.C.; Jennings, R.B.; Fonseca, R.; Bonal, D.M.; Booker, M.A.; Flaifel, A.; et al. The KDM5A/RBP2 Histone Demethylase Represses NOTCH Signaling to Sustain Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Promote Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1718–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, F.; Koinuma, D.; Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Fukayama, M.; Miyaozono, K.; Ehata, S. EZH2 Promotes Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer by Suppressing the TGF-β-Smad-ASCL1 Pathway. Cell Discov. 2015, 1, 15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, E.E.; Lok, B.H.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Desmeules, P.; Miles, L.A.; Arnold, P.K.; Ni, A.; Khodos, I.; de Stanchina, E.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Chemosensitive Relapse in Small Cell Lung Cancer Proceeds through an EZH2-SLFN11 Axis. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, M.-E.; Jauset, T.; Massó-Vallés, D.; Martínez-Martín, S.; Rahl, P.; Maltais, L.; Zacarias-Fluck, M.F.; Casacuberta-Serra, S.; Serrano del Pozo, E.; Fiore, C.; et al. Intrinsic Cell-Penetrating Activity Propels Omomyc from Proof of Concept to Viable Anti-MYC Therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaar5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, F.P.; Tokgün, E.; Solé-Sánchez, S.; Giampaolo, S.; Tokgün, O.; Jauset, T.; Kohno, T.; Perucho, M.; Soucek, L.; Yokota, J. Growth Suppression by MYC Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells with TP53 and RB1 Inactivation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31014–31028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massó-Vallés, D.; Soucek, L. Blocking Myc to Treat Cancer: Reflecting on Two Decades of Omomyc. Cells 2020, 9, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting Oncogenic Myc as a Strategy for Cancer Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy to Target C-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollaoglu, G.; Guthrie, M.R.; Böhm, S.; Brägelmann, J.; Can, I.; Ballieu, P.M.; Marx, A.; George, J.; Heinen, C.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Tong, P.; Stewart, C.A.; Cristea, S.; Valliani, A.; Shames, D.S.; Redwood, A.B.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, L.; Glisson, B.S.; et al. CHK1 Inhibition in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Produces Single-Agent Activity in Biomarker-Defined Disease Subsets and Combination Activity with Cisplatin or Olaparib. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gesumaria, L.; Park, Y.-K.; Oliver, T.G.; Singer, D.S.; Ge, K.; Schrump, D.S. BET Inhibitors Target the SCLC-N Subtype of Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Blocking NEUROD1 Transactivation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2023, 21, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhan, C.; Feng, M.; Leblanc, M.; Ke, E.; Yeddula, N.; Verma, I.M. Targeting CREB Pathway Suppresses Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.; Augert, A.; Kim, D.-W.; Eastwood, E.; Wu, N.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Kim, K.-B.; Dunn, C.T.; Pillai, S.P.S.; Gazdar, A.F.; et al. Crebbp Loss Drives Small Cell Lung Cancer and Increases Sensitivity to HDAC Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megyesfalvi, Z.; Gay, C.M.; Popper, H.; Pirker, R.; Ostoros, G.; Heeke, S.; Lang, C.; Hoetzenecker, K.; Schwendenwein, A.; Boettiger, K.; et al. Clinical Insights into Small Cell Lung Cancer: Tumor Heterogeneity, Diagnosis, Therapy, and Future Directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 620–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Saito-Adachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takai, E.; Shibata, S.; Seki, M.; Rokutan, H.; Maeda, D.; Horie, M.; et al. E74-like Factor 3 Is a Key Regulator of Epithelial Integrity and Immune Response Genes in Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfield, K.S.S.; Marshall, E.A.; Anderson, C.; Ng, K.W.; Rahmati, S.; Xu, Z.; Fuller, M.; Milne, K.; Lu, D.; Shi, R.; et al. Epithelial Tumor Suppressor ELF3 Is a Lineage-Specific Amplified Oncogene in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Choi, Y.E.; Kim, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Goh, S.-H. ELF3 Is a Target That Promotes Therapeutic Efficiency in EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Inhibiting PKCί. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shia, D.W.; Choi, W.; Vijayaraj, P.; Vuong, V.; Sandlin, J.M.; Lu, M.M.; Aziz, A.; Marin, C.; Aros, C.J.; Sen, C.; et al. Targeting PEA3 Transcription Factors to Mitigate Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Oncogene 2023, 42, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, R.; Iriki, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Pan, C.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sakagami, T.; Komohara, Y. Onionin A Inhibits Small-Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation through Suppressing STAT3 Activation Induced by Macrophages-Derived IL-6 and Cell–Cell Interaction with Tumor-Associated Macrophage. Human Cell 2023, 36, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aix, S.P.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Navarro, A.; Cousin, S.; Bonanno, L.; Smit, E.F.; Chiappori, A.; Olmedo, M.E.; Horvath, I.; Grohé, C.; et al. Combination Lurbinectedin and Doxorubicin versus Physician’s Choice of Chemotherapy in Patients with Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ATLANTIS): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaría Nuñez, G.; Robles, C.M.G.; Giraudon, C.; Martínez-Leal, J.F.; Compe, E.; Coin, F.; Aviles, P.; Galmarini, C.M.; Egly, J.-M. Lurbinectedin Specifically Triggers the Degradation of Phosphorylated RNA Polymerase II and the Formation of DNA Breaks in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, F.; Martínez Diez, M.; Santamaría Nuñez, G.; Díaz-Hernandéz, J.I.; Genes Robles, C.M.; Díez Pérez, J.; Compe, E.; Ricci, R.; Li, T.; Coin, F.; et al. Promoters of ASCL1- and NEUROD1-dependent Genes Are Specific Targets of Lurbinectedin in SCLC Cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Jaigirdar, A.A.; Mulkey, F.; Cheng, J.; Hamed, S.S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Goheer, A.; Helms, W.S.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Lurbinectedin for the Treatment of Metastatic Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2378–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, J.; Subbiah, V.; Besse, B.; Moreno, V.; López, R.; Sala, M.A.; Peters, S.; Ponce, S.; Fernández, C.; Alfaro, V.; et al. Lurbinectedin as Second-Line Treatment for Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Basket Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Wang, J.; Nilsson, M.B.; Fujimoto, J.; Saintigny, P.; Yordy, J.; Giri, U.; Peyton, M.; Fan, Y.H.; Diao, L.; et al. Proteomic Profiling Identifies Dysregulated Pathways in Small Cell Lung Cancer and Novel Therapeutic Targets Including PARP1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barayan, R.; Ran, X.; Lok, B.H. PARP Inhibitors for Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Potential for Integration into Current Treatment Approaches. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sica, G.L.; Wagner, L.I.; Wade, J.L.; Srkalovic, G.; Lash, B.W.; Leach, J.W.; Leal, T.B.; Aggarwal, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide in Combination With Veliparib or Placebo for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ECOG-ACRIN 2511 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Waqar, S.N.; Krug, L.M.; Dowlati, A.; Hann, C.L.; Chiappori, A.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Woo, K.M.; Cardnell, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination With Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients With Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ramkumar, K.; Cardnell, R.J.; Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Wang, W.-L.; Fujimoto, J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Byers, L.A. A Wake-up Call for Cancer DNA Damage: The Role of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) across Multiple Cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, K.; Cardnell, R.J.; Zhang, B.; Shen, L.; Stewart, C.A.; Ramkumar, K.; Cargill, K.R.; Wang, J.; Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A. SLFN11 Biomarker Status Predicts Response to Lurbinectedin as a Single Agent and in Combination with ATR Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4095–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-W.; Thomas, A.; Murai, J.; Trepel, J.B.; Bates, S.E.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Pommier, Y. Overcoming Resistance to DNA-Targeted Agents by Epigenetic Activation of Schlafen 11 ( SLFN11) Expression with Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.G.; Delord, J.-P.; Jeffry Evans, T.R.; De Jonge, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Meurer, M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Angell, H.K.; Rocher-Ros, V.; et al. Olaparib and Durvalumab in Patients with Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer (MEDIOLA): An Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2, Basket Study. Lung Cancer 2023, 180, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, J.H.; Lok, B.H.; Ma, J.; Bell, A.; de Stanchina, E.; Poirier, J.T.; Rudin, C.M. Talazoparib Is a Potent Radiosensitizer in Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines and Xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Takahashi, N.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ceribelli, M.; Wilson, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Beck, E.; Sciuto, L.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of ATR Yields Durable Regressions in Small Cell Lung Cancers with High Replication Stress. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 566–579.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Miao, N.; Liu, G.; Deng, L.; Wei, S.; Hou, J. Immunogenicity of Small-cell Lung Cancer Associates with STING Pathway Activation and Is Enhanced by ATR and TOP1 Inhibition. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 4864–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.W.; Zhang, Y.; Elmeskini, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Fu, H.; Murai, Y.; Wangsa, D.; Kumar, S.; Takahashi, N.; Atkinson, D.; et al. ATR Inhibition Augments the Efficacy of Lurbinectedin in Small-cell Lung Cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, K.; Yokouchi, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Ninomiya, H.; Sakakibara, R.; Subat, S.; Nagano, H.; Nomura, K.; Okumura, S.; Shibutani, T.; et al. Association of Tumor TROP2 Expression with Prognosis Varies among Lung Cancer Subtypes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28725–28735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautschi, O.; Heighway, J.; Mack, P.C.; Purnell, P.R.; Lara, P.N.; Gandara, D.R. Aurora Kinases as Anticancer Drug Targets. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, K.E.; Garza, S.J.; Lira, M.E.; Ching, K.A.; Lee, N.V.; Cao, J.; Yuan, J.; Ye, J.; Ozeck, M.; Shi, S.T.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Approach to Identify Predictive Biomarkers of Response to the Aurora Kinase Inhibitor PF-03814735. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich, B.A.; Kim, J.; Gao, D.; Chan, D.C.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, A.-C.; Bunn, P.A. Barasertib (AZD1152), a Small Molecule Aurora B Inhibitor, Inhibits the Growth of SCLC Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2314–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.L.; Wang, J.S.; Falchook, G.; Greenlees, C.; Jones, S.; Strickland, D.; Fabbri, G.; Kennedy, C.; Elizabeth Pease, J.; Sainsbury, L.; et al. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Aurora Kinase B Inhibitor AZD2811: A Phase 1 Dose-Finding Study in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Niu, H.; Nackaerts, K.; Csoszi, T.; Ostoros, G.; Mark, Z.; Baik, C.; Joy, A.A.; Chouaid, C.; Jaime, J.C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Paclitaxel plus Alisertib versus Paclitaxel plus Placebo as Second-Line Therapy for SCLC: Primary and Correlative Biomarker Analyses. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Piro, G.; Schietroma, F.; Strusi, A.; Vita, E.; Fiorani, S.; Barone, D.; Monaca, F.; Sparagna, I.; Valente, G.; et al. Unweaving the Mitotic Spindle: A Focus on Aurora Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1026020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Checkpoint Kinase 1 in DNA Damage Response and Cell Cycle Regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4009–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; Kim, I.-K.; Rao, G.; McCutcheon, J.; Hsu, S.-T.; Teicher, B.; Kallakury, B.; Dowlati, A.; et al. Checkpoint Kinase 1 Inhibition Enhances Cisplatin Cytotoxicity and Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance in SCLC by Promoting Mitotic Cell Death. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kim, I.; Kallakury, B.; Chahine, J.J.; Iwama, E.; Pierobon, M.; Petricoin, E.; McCutcheon, J.N.; Zhang, Y.; Umemura, S.; et al. Acquired Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistance to Chk1 Inhibitors Involves Wee1 Up-regulation. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1130–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Navarro, A.; Schaefer, E.; Johnson, M.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Han, J.-Y.; Bondarenko, I.; Cicin, I.; Dragnev, K.H.; Abel, A.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Prexasertib (LY2606368) in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.; Plummer, R.; Moreno, V.; Carter, L.; Roda, D.; Garralda, E.; Kristeleit, R.; Sarker, D.; Arkenau, T.; Roxburgh, P.; et al. A Phase I/II Trial of Oral SRA737 (a Chk1 Inhibitor) Given in Combination with Low-Dose Gemcitabine in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Della Corte, C.M.; Milutinovic, S.; Cardnell, R.J.; Diao, L.; Ramkumar, K.; Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Fan, Y.; Shen, L.; et al. Combination Treatment of the Oral CHK1 Inhibitor, SRA737, and Low-Dose Gemcitabine Enhances the Effect of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Blockade by Modulating the Immune Microenvironment in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.M.; Moore, K.N.; Rader, J.S.; Simpkins, F.; Mita, A.C.; Beck, J.T.; Hart, L.; Chu, Q.; Oza, A.; Tinker, A.V.; et al. A Phase Ib Study Assessing the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of the First-in-Class Wee1 Inhibitor Adavosertib (AZD1775) as Monotherapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Target. Oncol. 2023, 18, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallo, A.; Frese, K.K.; Morrow, C.J.; Sloane, R.; Gulati, S.; Schenk, M.W.; Trapani, F.; Simms, N.; Galvin, M.; Brown, S.; et al. The Combination of the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib and the WEE1 Inhibitor AZD1775 as a New Therapeutic Option for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5153–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Caeser, R.; Chavan, S.S.; Zhan, Y.A.; Chow, A.; Manoj, P.; Uddin, F.; Kitai, H.; Qu, R.; Hayatt, O.; et al. WEE1 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Immune Response to PD-L1 Blockade by the Concomitant Activation of STING and STAT1 Pathways in SCLC. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Christensen, C.L.; Dries, R.; Oser, M.G.; Deng, J.; Diskin, B.; Li, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; et al. CDK7 Inhibition Potentiates Genome Instability Triggering Anti-Tumor Immunity in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 37–54.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Schultz, C.W.; Pommier, Y.; Thomas, A. CDK7 Inhibition Synergizes with Topoisomerase I Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Inducing Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteolysis of RNA Polymerase II. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, S.; Gao, X.; Tian, D.; Tian, S.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Dong, R.; et al. KC-180-2 Exerts Anti-SCLC Effects via Dual Inhibition of Tubulin Polymerization and Src Signaling. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32164–32175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redin, E.; Garrido-Martin, E.M.; Valencia, K.; Redrado, M.; Solorzano, J.L.; Carias, R.; Echepare, M.; Exposito, F.; Serrano, D.; Ferrer, I.; et al. YES1 Is a Druggable Oncogenic Target in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1387–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Morita, M.; Tanuma, N. A Metabolic Vulnerability of Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32278–32279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, M.; Toyokawa, G.; Sugahara, O.; Sugiyama, S.; Haratake, N.; Yamada, Y.; Wada, R.; Takamori, S.; Shimokawa, M.; Takenaka, T.; et al. Modulation of Host Glutamine Anabolism Enhances the Sensitivity of Small Cell Lung Cancer to Chemotherapy. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ng, S.R.; Colón, C.I.; Drapkin, B.J.; Hsu, P.P.; Li, Z.; Nabel, C.S.; Lewis, C.A.; Romero, R.; Mercer, K.L.; et al. Identification of DHODH as a Therapeutic Target in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, S.; Coles, G.L.; Hornburg, D.; Gershkovitz, M.; Arand, J.; Cao, S.; Sen, T.; Williamson, S.C.; Kim, J.W.; Drainas, A.P.; et al. The MEK5–ERK5 Kinase Axis Controls Lipid Metabolism in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Fdez, A.; Re-Louhau, M.F.; Rodríguez-Núñez, P.; Ludeña, D.; Matilla-Almazán, S.; Pandiella, A.; Esparís-Ogando, A. Clinical, Genetic and Pharmacological Data Support Targeting the MEK5/ERK5 Module in Lung Cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalishazar, M.D.; Wait, S.J.; Huang, F.; Ireland, A.S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Lee, Y.; Schuman, S.S.; Guthrie, M.R.; Berrett, K.C.; Vahrenkamp, J.M.; et al. MYC-Driven Small-Cell Lung Cancer Is Metabolically Distinct and Vulnerable to Arginine Depletion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5107–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucantoni, F.; Salvucci, M.; Düssmann, H.; Lindner, A.U.; Lambrechts, D.; Prehn, J.H.M. BCL(X)L and BCL2 Increase the Metabolic Fitness of Breast Cancer Cells: A Single-Cell Imaging Study. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1512–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ezra, J.M.; Kornstein, M.J.; Grimes, M.M.; Krystal, G. Small Cell Carcinomas of the Lung Express the Bcl-2 Protein. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Lochmann, T.L.; Floros, K.V.; Naseri, M.; Powell, K.M.; Cook, W.; March, R.J.; Stein, G.T.; Greninger, P.; Maves, Y.K.; Saunders, L.R.; et al. Venetoclax Is Effective in Small-Cell Lung Cancers with High BCL-2 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Hann, C.L.; Garon, E.B.; Ribeiro de Oliveira, M.; Bonomi, P.D.; Camidge, D.R.; Chu, Q.; Giaccone, G.; Khaira, D.; Ramalingam, S.S.; et al. Phase II Study of Single-Agent Navitoclax (ABT-263) and Biomarker Correlates in Patients with Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Salgia, R.; Wang, X.; Hodgson, L.D.; Masters, G.A.; Green, M.; Vokes, E.E. Randomized Phase II Study of Carboplatin and Etoposide with or without the Bcl-2 Antisense Oligonucleotide Oblimersen for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: CALGB 30103. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploumaki, I.; Triantafyllou, E.; Koumprentziotis, I.-A.; Karampinos, K.; Drougkas, K.; Karavolias, I.; Trontzas, I.; Kotteas, E.A. Bcl-2 Pathway Inhibition in Solid Tumors: A Review of Clinical Trials. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 1554–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, K.; Tanimoto, A.; Della Corte, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Cardnell, R.J.; Wang, J.; Polanska, U.M.; Andersen, C.; et al. Targeting BCL2 Overcomes Resistance and Augments Response to Aurora Kinase B Inhibition by AZD2811 in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3237–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, J.M.; Hoeksema, M.D.; Staub, J.; Qian, J.; Harris, B.; Callison, J.C.; Miao, J.; Shi, C.; Eisenberg, R.; Chen, H.; et al. Somatostatin Receptor 2 Signaling Promotes Growth and Tumor Survival in Small-cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whalen, K.A.; White, B.H.; Quinn, J.M.; Kriksciukaite, K.; Alargova, R.; Au Yeung, T.P.; Bazinet, P.; Brockman, A.; DuPont, M.M.; Oller, H.; et al. Targeting the Somatostatin Receptor 2 with the Miniaturized Drug Conjugate, PEN-221: A Potent and Novel Therapeutic for the Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiga, Y.; Drainas, A.P.; Baron, M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Barkal, A.A.; Ahrari, Y.; Mancusi, R.; Ross, J.B.; Takahashi, N.; Thomas, A.; et al. Radiotherapy in Combination with CD47 Blockade Elicits a Macrophage-Mediated Abscopal Effect. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsumoto, T.; Maemura, K.; Watanabe, K.; Amano, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Zokumasu, K.; Ando, T.; Kawakami, M.; Kage, H.; Nakajima, J.; et al. NRXN1 as a Novel Potential Target of Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 3590–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemeyer, W.R.; Gavrilyuk, J.; Schammel, A.; Zhao, X.; Sarvaiya, H.; Pysz, M.; Gu, C.; You, M.; Isse, K.; Sullivan, T.; et al. ABBV-011, A Novel, Calicheamicin-Based Antibody–Drug Conjugate, Targets SEZ6 to Eradicate Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelenis, D.P.; Rodarte, K.E.; Kollipara, R.K.; Pozo, K.; Choudhuri, S.P.; Spainhower, K.B.; Wait, S.J.; Stastny, V.; Oliver, T.G.; Johnson, J.E. Inhibition of Karyopherin Β1-Mediated Nuclear Import Disrupts Oncogenic Lineage-Defining Transcription Factor Activity in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3058–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groux-Degroote, S.; Delannoy, P. Cancer-Associated Glycosphingolipids as Tumor Markers and Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Leighl, N.B.; Surmont, V.; van Herpen, C.; Sibille, A.; Markman, B.; Clarke, S.; Juergens, R.A.; Rivera, M.A.; Andelkovic, V.; et al. BMS-986012, an Anti–Fucosyl-GM1 Monoclonal Antibody as Monotherapy or in Combination With Nivolumab in Relapsed/Refractory SCLC: Results From a First-in-Human Phase 1/2 Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-S.; Martelotto, L.G.; Peifer, M.; Sos, M.L.; Karnezis, A.N.; Mahjoub, M.R.; Bernard, K.; Conklin, J.F.; Szczepny, A.; Yuan, J.; et al. A Crucial Requirement for Hedgehog Signaling in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Champiat, S.; Lai, W.V.; Izumi, H.; Govindan, R.; Boyer, M.; Hummel, H.-D.; Borghaei, H.; Johnson, M.L.; Steeghs, N.; et al. Tarlatamab, a First-in-Class DLL3-Targeted Bispecific T-Cell Engager, in Recurrent Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2893–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.H.; Devarakonda, S.; Skidmore, Z.L.; Krysiak, K.; Ramu, A.; Trani, L.; Kunisaki, J.; Masood, A.; Waqar, S.N.; Spies, N.C.; et al. Recurrent WNT Pathway Alterations Are Frequent in Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-B.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, Y.; Tang, J.; Kirk, N.; Gan, Y.; Kim, B.; Fang, B.; Park, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. WNT5A–RHOA Signaling Is a Driver of Tumorigenesis and Represents a Therapeutically Actionable Vulnerability in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4219–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, M.; Genno, S.; Takeda, T.; Matsuda, T.; Kimura, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Morii, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Nishida, S. Rhosin Suppressed Tumor Cell Metastasis through Inhibition of Rho/YAP Pathway and Expression of RHAMM and CXCR4 in Melanoma and Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.-C.; Wang, W.-P.; Chi, Y.-H. AKT Phosphorylation as a Predictive Biomarker for PI3K/MTOR Dual Inhibition-Induced Proteolytic Cleavage of MTOR Companion Proteins in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, X.; Hubert, S.M.; Li, Q.; Su, D.; Xu, H.; Fan, Y.; Yu, X.; et al. Activation of PI3K/AKT Pathway Is a Potential Mechanism of Treatment Resistance in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanal-Villalonga, A.; Taniguchi, H.; Zhan, Y.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Chavan, S.S.; Meng, F.; Uddin, F.; Manoj, P.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; Won, H.H.; et al. Multiomic Analysis of Lung Tumors Defines Pathways Activated in Neuroendocrine Transformation. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 3028–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Kawada, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Mukae, H.; Yano, S. Impact of MET Inhibition on Small-cell Lung Cancer Cells Showing Aberrant Activation of the Hepatocyte Growth Factor/ MET Pathway. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, L.A.; Horn, L.; Ghandi, J.; Kloecker, G.; Owonikoko, T.; Waqar, S.N.; Krzakowski, M.; Cardnell, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.; Taverna, P.; et al. A Phase 2, Open-Label, Multi-Center Study of Amuvatinib in Combination with Platinum Etoposide Chemotherapy in Platinum-Refractory Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 81441–81454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glisson, B.; Besse, B.; Dols, M.C.; Dubey, S.; Schupp, M.; Jain, R.; Jiang, Y.; Menon, H.; Nackaerts, K.; Orlov, S.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1b/2 Study of Rilotumumab or Ganitumab in Combination With Platinum-Based Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 615–625.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy-Werbin, M.; del Rey-Vergara, R.; Galindo-Campos, M.A.; Moliner, L.; Arriola, E. MET Inhibitors in Small Cell Lung Cancer: From the Bench to the Bedside. Cancers 2019, 11, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekido, Y.; Obata, Y.; Ueda, R.; Hida, T.; Suyama, M.; Shimokata, K.; Ariyoshi, Y.; Takahashi, T. Preferential Expression of C-Kit Protooncogene Transcripts in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 2416–2419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, J.-O.; Park, J.-Y.; Seo, M.-D.; Park, S.G. Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting c-Kit for the Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaudin, D.; de Cremoux, P.; Sastre, X.; Judde, J.-G.; Nemati, F.; Tran-Perennou, C.; Fréneaux, P.; Livartowski, A.; Pouillart, P.; Poupon, M.-F. In Vivo Efficacy of STI571 in Xenografted Human Small Cell Lung Cancer Alone or Combined with Chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.E.; Fischer, T.; Fischer, B.; Dunlop, D.; Rischin, D.; Silberman, S.; Kowalski, M.O.; Sayles, D.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Fletcher, C.; et al. Phase II Study of Imatinib in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5880–5887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dy, G.K.; Miller, A.A.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Aubry, M.-C.; Langdon, R.M.; Morton, R.F.; Schild, S.E.; Jett, J.R.; Adjei, A.A. A Phase II Trial of Imatinib (ST1571) in Patients with c-Kit Expressing Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A CALGB and NCCTG Study. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Hausmann, S.; Flores, N.M.; Benitez, A.M.; Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Person, M.D.; Gayatri, S.; Cheng, D.; Lu, Y.; et al. The NFIB/CARM1 Partnership Is a Driver in Preclinical Models of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Aparnathi, M.K.; Nixon, K.C.J.; Venkatasubramanian, V.; Rahman, F.; Song, L.; Weiss, J.; Barayan, R.; Sugumar, V.; Barghout, S.H.; et al. Targeting the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System Using the UBA1 Inhibitor TAK-243 Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Han, B.; Chen, G.; He, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Anlotinib vs Placebo as Third- or Further-Line Treatment for Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Study. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-M.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, H.-G.; Min, Y.J.; Yi, S.Y.; Yun, H.J.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Pazopanib Maintenance after First-Line Etoposide and Platinum Chemotherapy in Patients with Extensive Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study (KCSG-LU12-07). Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Camrelizumab Plus Apatinib in Extensive-Stage SCLC (PASSION): A Multicenter, Two-Stage, Phase 2 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhou, R.; Li, X.; Pan, D. Combination of Bevacizumab and Dual Immunotherapy for Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report. Immunotherapy 2021, 13, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target | Targeting Molecule | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| AURKB | Barasertib | Barasertib has growth-inhibitory effects in some SCLC lines and suppresses tumor growth xenografts. C-MYC amplification or high gene expression or C-MYC gene signature is a useful predictive biomarker. | [85] |
| c-Src | KC-180-2 | KC-180-2 suppresses SCLC lines proliferation and inhibits the growth of SCLC xenograft tumors. | [100] |
| YES1 | CH6953755 | CH6953755 presents anti-tumor activity in organoids and in cell- and patient-derived xenografts. | [101] |
| HPRT1 | 6-MP | 6-MP in combination with MTX attenuates the growth of mouse SCLC xenograft models. The glutamine synthetase inhibitor methionine sulfoximine (MSO) enhances this effect. | [103] |
| DHODH | Brequinar | Brequinar reduces SCLC cells viability in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in PDX and mouse models. | [104] |
| SSTR2 | PEN-221 | PEN-221 inhibits in vitro cellular proliferation and suppresses tumor growth in SSTR2-positive SCLC xenografts. | [116] |
| CD47 | CD47-blocking antibody | CD47 blockade plus irradiation inhibits tumor growth in SCLC xenograft models, promoting abscopal effects. | [117] |
| NRXN1 | ADC | The combination of a primary anti-NRXN1 monoclonal antibody and a secondary ADC exhibits anti-tumor activity in SCLC cell lines in vitro. | [118] |
| KPNB1 | INI-43 | INI-43 disrupts SCLC-A and SCLC-N cells proliferation in vitro and suppresses the growth of SCLC-A PDX tumors. | [120] |
| WNT5A/RHOA | Rhosin | Rhosin inhibits SCLC cell proliferation in vitro. | [126] |
| c-Kit | 4C9-DM1 | 4C9-DM1 suppresses SCLC proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model, with synergistic effects when combined with carboplatin-etoposide therapy. | [136] |
| NFIB/CARM1 | TP-064 | TP-064 alone cannot cause cancer regression; however, in combination with cisplatin-etoposide chemotherapy, it exhibits anti-tumor activity in a SCLC xenograft model. | [140] |
| UBA1 | TAK-243 | The combination of TAK-243 and genotoxic therapies (e.g., olaparib) exhibits a synergistic effect in cell lines and PDX models. | [141] |
| KDM5A/RBP2 | KDM5-C70 | KDM5-C70 decreases ASCL1 levels and inhibits cellular proliferation of a subset of SCLC lines. Combining KDM5-C70 and the LSD1 inhibitor ORY-1001 synergistically suppresses ASCL1 levels. | [46] |
| FGFR/PEA3 | LY2874455 | LY2874455 presents anti-tumor activity when used alone or in combination with cisplatin-etoposide in vitro and in SCLC xenografts. | [63] |
| STAT3 activation | Onionin A | By suppressing STAT3 activation, onionin A inhibits SCLC cells proliferation and suppresses tumor growth in a murine model. | [64] |
| Target | Targeting Molecule | Stage | Study | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncogenic transcription | Lurbinectedin | Approved | NCT04291937 | Used as a second line treatment. |
| Phase 3 | NCT05153239 | Ongoing; as a single agent or combined with irinotecan. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT05091567 | Ongoing; combined with atezolizumab. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT02566993 | Did not improve OS vs. topotecan. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT05578326 | Ongoing; combined with trilaciclib. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT05572476 | Ongoing; combined with durvalumab in pre-treated patients. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04607954 | Ongoing; combined with durvalumab. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT04358237 | Ongoing; combined with pembrolizumab. | ||
| PARP | Veliparib | Phase 2 | NCT02289690 | Potentiates chemotherapy. |
| Phase 2 | NCT01638546 | Improved PFS and OS in SLFN11-positive patients. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT01642251 | Demonstrated efficacy in patients with extensive stage SCLC when combined with chemotherapy. | ||
| Talazoparib | Phase 2 | NCT04334941 | Ongoing; in SLFN11-positive patients. | |
| Phase 2 | NCT03672773 | Ongoing; combined with temozolomide in low doses. | ||
| Olaparib | Phase 3 | NCT04624204 | Ongoing; in combination with pembrolizumab in pre-treated patients with chemotherapy. | |
| Phase 2 | NCT03009682 | In patients with gene mutations in the homologous recombination pathway; no results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04538378 | Ongoing; in combination with durvalumab in SCLC transformed from EGFR-mutated adenocarcinomas. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT05623319 | Ongoing; in combination with pembrolizumab. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04939662 | Ongoing; in combination with bevacizumab. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02498613 | Ongoing; in combination with cediranib in metastatic tumors. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT05245994 | Ongoing; in combination with durvalumab. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03428607 | In combination with AZD6738; no results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02937818 | In combination with AZD6738 in refractory patients. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT02446704 | Ongoing; in recurrent patients. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT05975944 | Ongoing; in combination with selinexor. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT02769962 | Ongoing; in combination with EP0057. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT02734004 | Ongoing; in combination with MEDI4736. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT04728230 | Ongoing; in combination with carboplatin, etoposide and/or radiation. | ||
| ATR | Berzosertib | Phase 2 | NCT04768296 | No results posted yet. |
| Phase 1/2 | NCT04802174 | Ongoing; in combination with lurbinectedin. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT04826341 | Ongoing; in combination with sacituzumab-govitecan. | ||
| Alisertib | Phase 2 | NCT06095505 | Ongoing; in patients with extensive stage. | |
| Phase 2 | NCT01045421 | An objective response was noted in 21% of the patients. | ||
| Chk1 | LY2606368 | Phase 2 | NCT02735980 | Availability limitations. Another compound has been developed and is currently being tested in other neoplasms. |
| SRA-737 | Phase 1/2 | NCT02797977 | Used in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin; no results posted yet. | |
| WEE1 | AZD1775 | Phase 2 | NCT02688907 | Ongoing; in patients with MYC amplification or CDKN2A + TP53 mutation. |
| Phase 2 | NCT02593019 | Used as a single agent in relapsed patients; no results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02688907 | Terminated, regimen change. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02937818 | Ongoing; in combination carboplatin and olaparib. | ||
| Arginine | ADI-PEG 20 | Phase 2 | NCT01266018 | Terminated for lack of efficacy. |
| Phase 1/2 | NCT05616624 | Ongoing; in combination with gemcitabine and docetaxel. | ||
| BCR-ABL, PDGFR, c-Kit | Imatinib | Phase 2 | NCT00156286 | No results posted. |
| Phase 2 | NCT00248482 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00052949 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00193349 | No results posted. | ||
| EZH2 | DS-3201b | Phase 1/2 | NCT03879798 | In combination with irinotecan; no results posted. |
| XNW5004 | Phase 1/2 | NCT06022757 | Ongoing; in combination with pembrolizumab. | |
| VEGFR, PDGFR and c-Kit | Pazopanib | Phase 2 | NCT01253369 | Notable rate of stable disease and slightly improve of PFS compared to second-line therapies. |
| BCL2 | Oblimersen Sodium | Phase 2 | NCT00042978 | No results posted yet. |
| GM1 | BMS-986012 | Phase 1/2 | NCT04702880 | Ongoing; in combination with carboplatin, etoposide and nivolumab. |
| Phase 1/2 | NCT02247349 | No results posted yet. | ||
| LSD1 | Iadademstat | Phase 2 | NCT05420636 | Ongoing; in combination with paclitaxel in relapsed patients. |
| DLL3 | AMG 757 | Phase 3 | NCT05740566 | Ongoing; in combination with chemotherapy. |
| Phase 2 | NCT05060016 | Ongoing; in relapsed patients. | ||
| HPN328 | Phase 1/2 | NCT04471727 | Ongoing; in patients with DDL3 expression. | |
| Phase 1/2 | NCT05879978 | Ongoing; in combination with ezabenlimab in patients with DDL3 expression. | ||
| BI764532 | Phase 2 | NCT05882058 | Ongoing; different doses of the compound tested. | |
| CREBBP | Tinostamustine | Phase 1/2 | NCT03345485 | No results posted yet. |
| VEFGR | Sunitinib | Phase 2 | NCT00695292 | No OS and PFS results posted. |
| Phase 2 | NCT00620347 | Approved as a second-line treatment in China. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00616109 | No improvements over control. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT01306045 | Ongoing; tested among several drugs. | ||
| Phase 1/2 | NCT00453154 | Safe and improved PFS. | ||
| Anlotinib | Phase 4 | NCT03890055 | In combination with chemotherapy in relapsed patients. | |
| Phase 3 | NCT04073550 | In combination with topotecan. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT04234607 | In combination with benmelstobart, etoposide and carboplatin. No results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT04192682 | In combination with sintilimab. | ||
| Aflibercept | Phase 2 | NCT00828139 | In combination with topotecan. Improved PFS but increased toxicity. | |
| VEGF | Bevacizumab | Phase 2/3 | NCT00930891 | In combination with chemotherapy, did not improve outcome in extensive SCLC patients. |
| Phase 2 | NCT00403403 | In combination with cisplatin or carboplatin plus etoposide for treatment of extensive-stage SCLC, improved PFS with an acceptable toxicity profile. No improvement in OS was observed. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04730999 | Ongoing; in patients with extensive disease. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04939662 | Ongoing; in combination with olaparib. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00698516 | After treatment with topotecan-bevacizumab, improvement in PFS. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT05588388 | Ongoing; in combination with chemo-immunotherapy and atezolizumab. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00193375 | 2-Year PFS: 22% of participants. Overall response rate: 80%. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT00726986 | Terminated due to extreme toxicity when combined with cisplatin and etoposide. | ||
| VEGFR2 | Apatinib | Phase 3 | NCT03651219 | No results posted. |
| Phase 3 | NCT04490421 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT02875457 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 3 | NCT03100955 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03547804 | Successful, already in Phase 3. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04901754 | In combination with camrelizumab; no results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04128800 | In combination with S-1; no results posted yet. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04683198 | Ongoing; in combination with cambralizumab, carboplatin and etoposide. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02945852 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02995187 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03135977 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03389087 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT02980809 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03129698 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT03417895 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04659785 | No results posted. | ||
| Phase 2 | NCT04453930 | No results posted. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez, M.; Zamora, I.; Freeman, M.R.; Encío, I.J.; Rotinen, M. Actionable Driver Events in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010105
Gutiérrez M, Zamora I, Freeman MR, Encío IJ, Rotinen M. Actionable Driver Events in Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez, Mirian, Irene Zamora, Michael R. Freeman, Ignacio J. Encío, and Mirja Rotinen. 2024. "Actionable Driver Events in Small Cell Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010105
APA StyleGutiérrez, M., Zamora, I., Freeman, M. R., Encío, I. J., & Rotinen, M. (2024). Actionable Driver Events in Small Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010105






