Polycondensed Peptide-Based Polymers for Targeted Delivery of Anti-Angiogenic siRNA to Treat Endometriosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
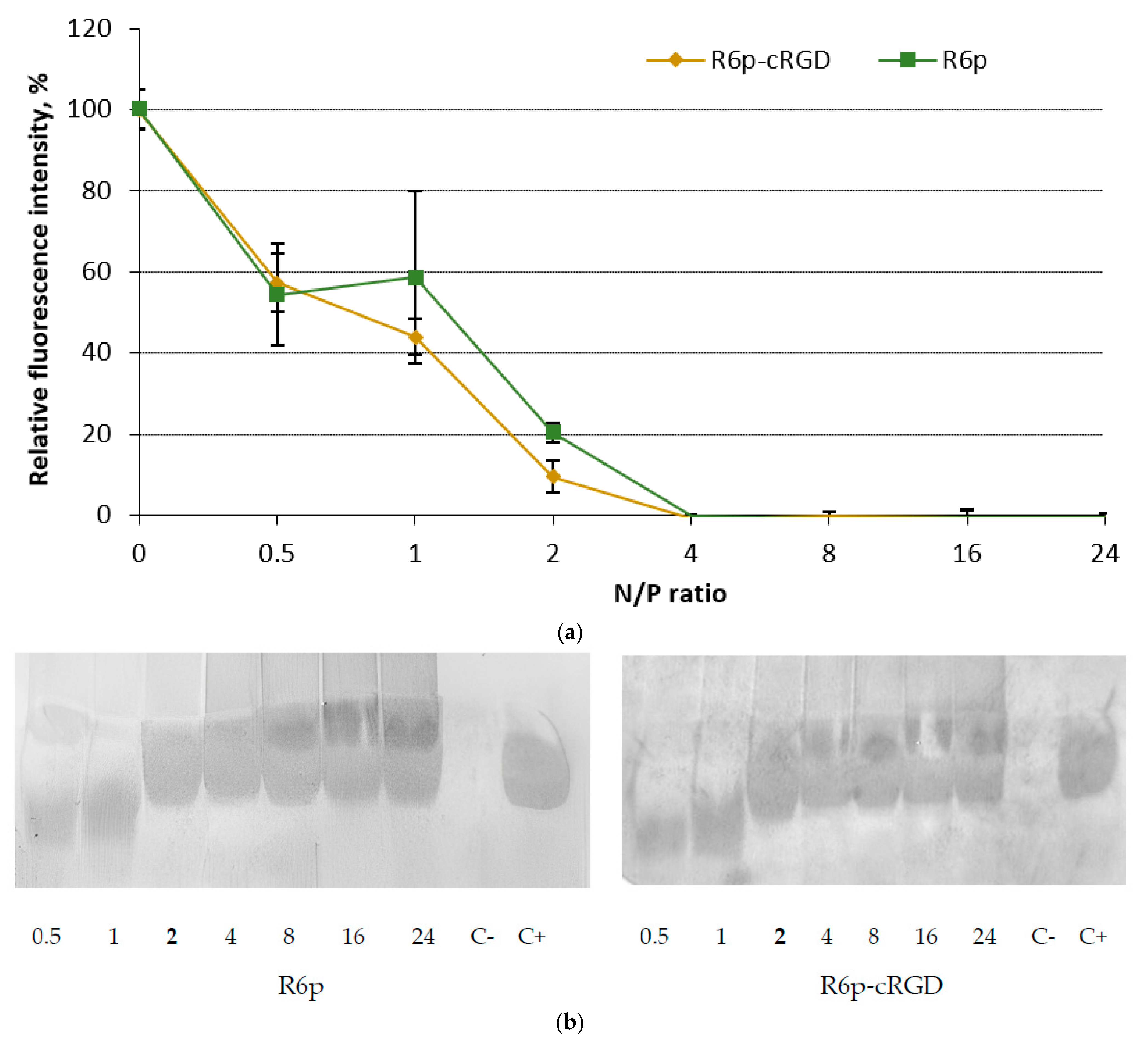
2.1. siRNA-Binding and siRNA Protection Properties of the Carriers
2.2. Size and ʐ-Potential of siRNA-Complexes
2.3. Assessment of Cytotoxicity of siRNA-Complexes
2.4. Assessment of GFP and VEGFA Gene Expression Silencing by siRNA-Complexes
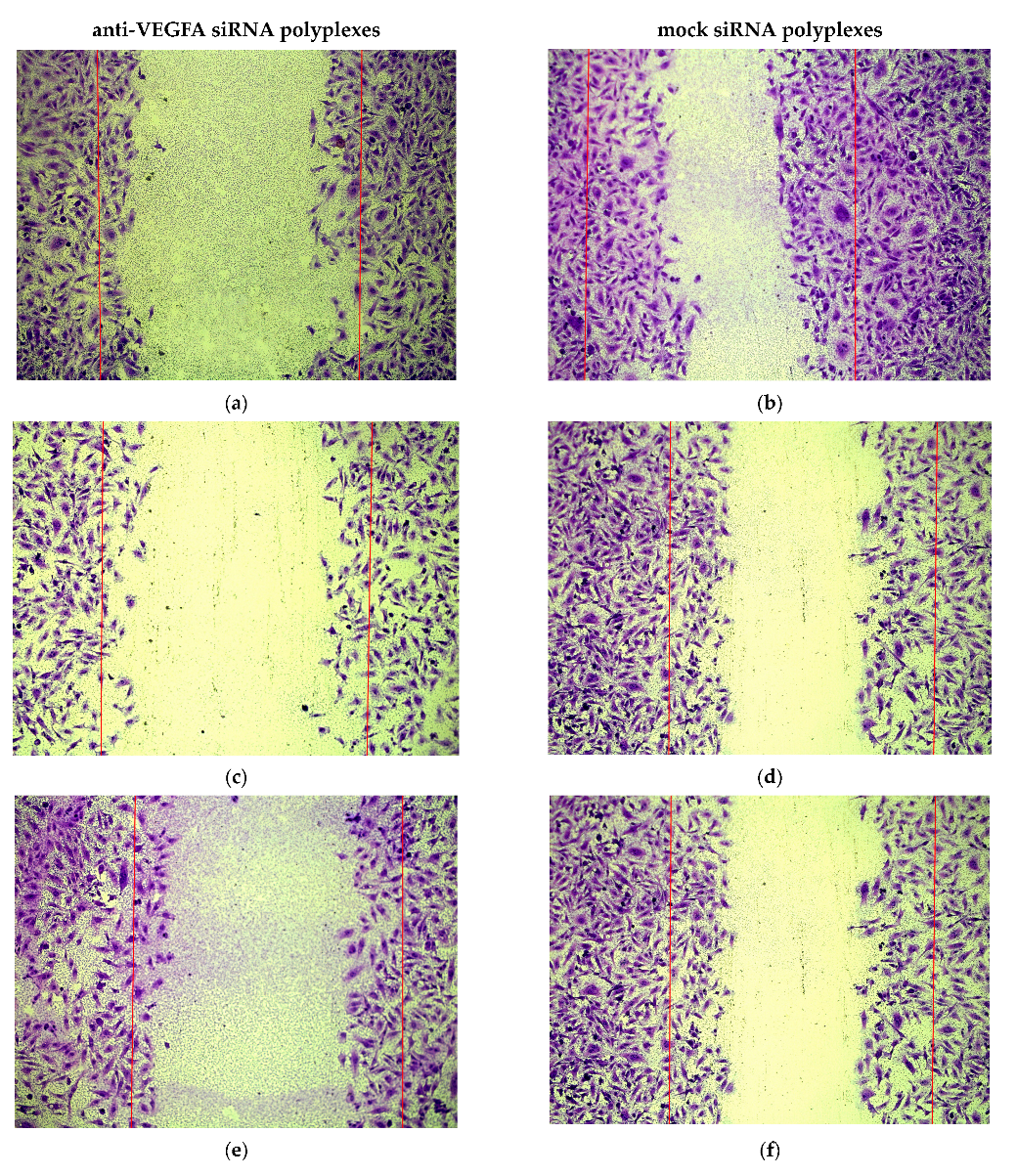
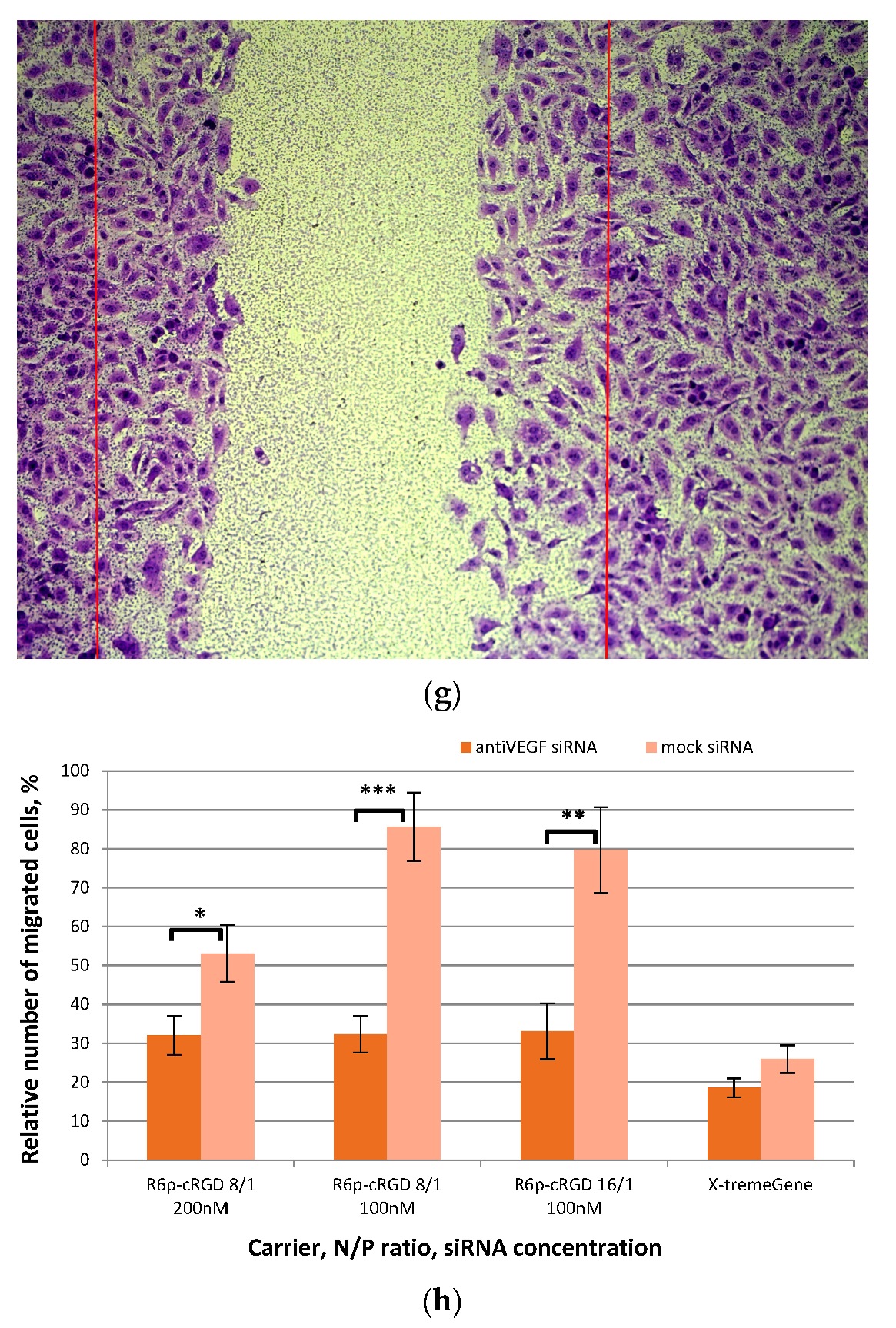
2.5. Assessment of Endothelial Cells Migration and Proliferation Inhibition by siRNA-Complexes
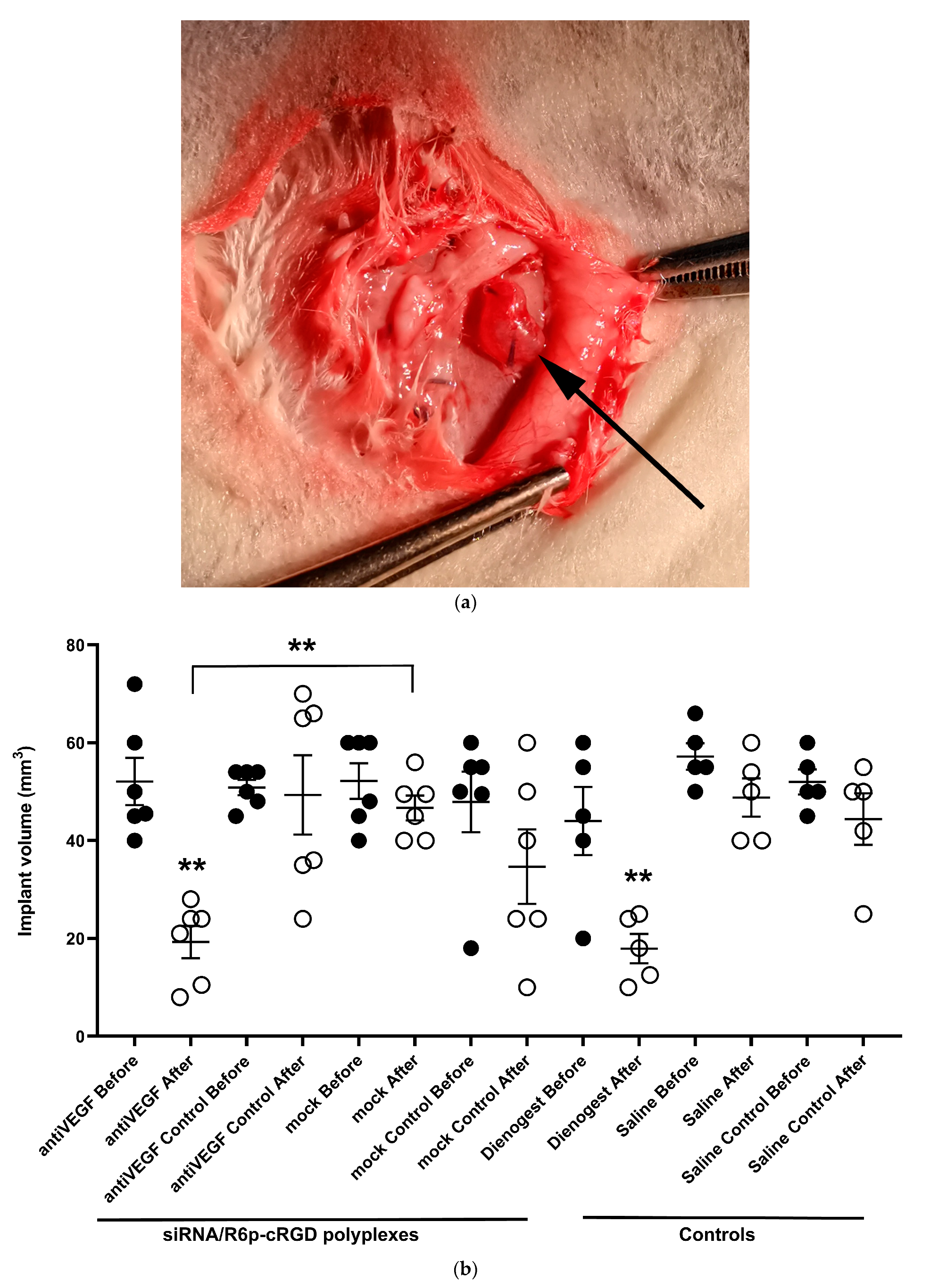
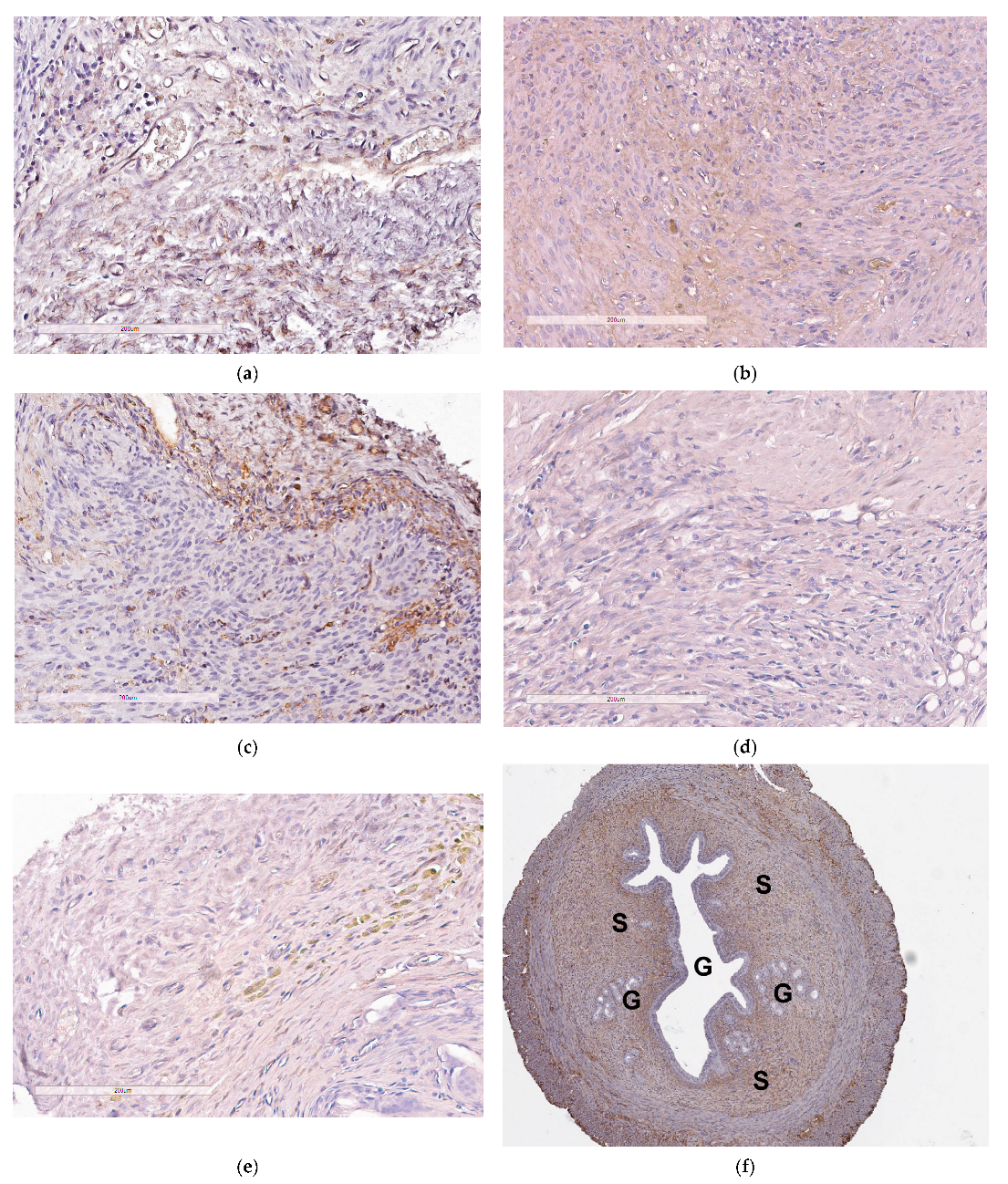
2.6. Assessement of Anti-Angiogenic Properties of siRNA-Complexes In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Lines and Animals
3.2. Synthesis of Peptide Carriers
3.3. siRNAs Sequences
3.4. Preparation of siRNA-Polymplexes
3.5. siRNA Binding Assay
3.6. RNase A Protection Assay
3.7. Measurement of Size and Zeta-Potential of siRNA-Complexes
3.8. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of siRNA-Complexes
3.9. siRNA Transfer to MDA-MB-231 Cells and GFP Fluorescence Detection
3.10. siRNA Transfer to EA.hy926 Cells and Quantitative RT-PCR
3.11. Quantitative Measurement of VEGFA Production
3.12. Scratch Migration Assay
3.13. Induction of EM Rat Model and In Vivo siRNA Transfer
3.14. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes-Coelho, F.; Martins, F.; Pereira, S.A.; Serpa, J. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah, A.; Sadeghinia, A.; Kahroba, H.; Samadi, A.; Heidari, H.R.; Bradaran, B.; Zeinali, S.; Molavi, O. Therapeutic targeting of angiogenesis molecular pathways in angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, S.; Takashima, Y.; Udagawa, R.; Ibaraki, H.; Seta, Y.; Ishihara, H. A Multifunctional Hybrid Nanocarrier for Non-Invasive siRNA Delivery to the Retina. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, H. Current status and future of anti-angiogenic drugs in lung cancer. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, A.S.; Demessie, A.A.; Taratula, O.; Korzun, T.; Slayden, O.D.; Taratula, O. Nanomedicines for Endometriosis: Lessons Learned from Cancer Research. Small 2021, 17, 2004975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zondervan, K.T.; Becker, C.M.; Missmer, S.A. Endometriosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedaiwy, M.A.; Allaire, C.; Alfaraj, S. Long-term medical management of endometriosis with dienogest and with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist and add-back hormone therapy. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.G.; Olivares, C.N.; Bilotas, M.A.; Meresman, G.F.; Barañao, R.I. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition on endometrial implant development in a murine model of endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 18, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H.; Boztosun, A.; Açmaz, G.; Atılgan, R.; Akkar, O.B.; Kosar, M.I. The Efficacy of Bevacizumab, Sorafenib, and Retinoic Acid on Rat Endometriosis Model. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 20, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschke, M.W.; Menger, M.D. Anti-angiogenic treatment strategies for the therapy of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2012, 18, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquet de Joliniere, J.; Fruscalzo, A.; Khomsi, F.; Stochino Loi, E.; Cherbanyk, F.; Ayoubi, J.M.; Feki, A. Antiangiogenic Therapy as a New Strategy in the Treatment of Endometriosis? The First Case Report. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 791686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrosin, C.; Gyorffy, S.; Margetts, P.; Ross, C.; Gauldie, J. Therapeutic Effect of Angiostatin Gene Transfer in a Murine Model of Endometriosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, S.A.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Bohlen, P.; Posser, R.; Hartman, T.; Sauer, M.V.; Kitajewski, J.; Zimmermann, R.C. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor 2 pathway is critical for blood vessel survival in corpora lutea of pregnancy in the rodent. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pytela, R.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell 1985, 40, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Targeting of drugs and nanoparticles to tumors. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehring, J.; Jeelani, R. Human implantation: The complex interplay between endometrial receptivity, inflammation, and the microbiome. Placenta 2022, 117, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Langendonckt, A.; Donnez, J.; Defrère, S.; Dunselman, G.A.J.; Groothuis, P.G. Antiangiogenic and vascular-disrupting agents in endometriosis: Pitfalls and promises. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 14, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, D.L.; Rogers, P.A.W.; Hii, L.; Wingfield, M. Angiogenesis: A new theory for endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Update 1998, 4, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, O.; Lessey, B.A. Alterations in expression of endometrial endothelial nitric oxide synthase and α vβ 3 integrin in women with endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 78, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.A.; Kiselev, A.V. Peptide modules for overcoming barriers of nucleic acids transport to cells. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrobattista, E.; van der Aa, M.A.E.M.; Hennink, W.E.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Artificial viruses: A nanotechnological approach to gene delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, C. Why gene therapies must go virus-free. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M. Peptides, polypeptides and peptide-polymer hybrids as nucleic acid carriers. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2188–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Feng, F.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Glutathione-responsive nano-vehicles as a promising platform for targeted intracellular drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, A.; Selutin, A.; Maretina, M.; Selkov, S.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Shtykalova, S.; Selutin, A.; Shved, N.; Maretina, M.; Selkov, S.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Development of iRGD-Modified Peptide Carriers for Suicide Gene Therapy of Uterine Leiomyoma. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Shtykalova, S.; Maretina, M.; Selutin, A.; Shved, N.; Deviatkin, D.; Selkov, S.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Polycondensed Peptide Carriers Modified with Cyclic RGD Ligand for Targeted Suicide Gene Delivery to Uterine Fibroid Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Selutin, A.; Maretina, M.; Selkov, S.; Kiselev, A. Peptide-Based Nanoparticles for αvβ3 Integrin-Targeted DNA Delivery to Cancer and Uterine Leiomyoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Petrosyan, M.; Maretina, M.; Bazian, E.; Krylova, I.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. iRGD-Targeted Peptide Nanoparticles for Anti-Angiogenic RNAi-Based Therapy of Endometriosis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, D.L.; Smiley, E.; Kwok, K.Y.; Rice, K.G. Low molecular weight disulfide cross-linking peptides as nonviral gene delivery carriers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2000, 11, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundara Manickam, D.; Bisht, H.S.; Wan, L.; Mao, G.; Oupicky, D. Influence of TAT-peptide polymerization on properties and transfection activity of TAT/DNA polyplexes. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerman, P.J. Flexibility of RNA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1997, 26, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnou, S.; Miller, A.D.; Keller, M. Lipidic Carriers of siRNA: Differences in the Formulation, Cellular Uptake, and Delivery with Plasmid DNA. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 13348–13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Manickam, D.S.; Oupický, D.; Mao, G. DNA release dynamics from reducible polyplexes by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12474–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, A.; Egorova, A.; Laukkanen, A.; Baranov, V.; Urtti, A. Characterization of reducible peptide oligomers as carriers for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Tong, H.; Shi, Q.; Fernandes, J.C.; Jin, T.; Dai, K.; Zhang, X. Uptake mechanisms of non-viral gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.A.; Kogure, K.; Akita, H.; Harashima, H. Uptake pathways and subsequent intracellular trafficking in nonviral gene delivery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litzinger, D.C.; Buiting, A.M.J.; van Rooijen, N.; Huang, L. Effect of liposome size on the circulation time and intraorgan distribution of amphipathic poly(ethylene glycol)-containing liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1994, 1190, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbold, T.; Han, S.; Hasi, A.; Baigude, H. Receptor-mediated delivery of therapeutic RNA by peptide functionalized curdlan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Manning, C.D.; Millar, H.; McCabe, F.L.; Ferrante, C.; Sharp, C.; Shahied-Arruda, L.; Doshi, P.; Nakada, M.T.; Anderson, G.M. CNTO 95, a fully human anti αv integrin antibody, inhibits cell signaling, migration, invasion, and spontaneous metastasis of human breast cancer cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatkowska, M.; Szymański, J.; Padula, G.; Cierniewski, C.S. Interaction and functional association of protein disulfide isomerase with αvβ3 integrin on endothelial cells. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgell, C.J.S.; McDonald, C.C.; Graham, J.B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3734–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiradharma, N.; Khan, M.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.-Y. Self-assembled Cationic Peptide Nanoparticles Capable of Inducing Efficient Gene Expression In Vitro. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Güell, M.; Serrano, L. Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, N.M.; Dhalla, N.S.; Santani, D.D. Angiogenesis—A new target for future therapy. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 44, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart-King, C.A. Chapter 3 Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Migration. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 45–64. ISBN 9780123743152. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Crivellato, E.; Vacca, A. The structure of the vascular network of tumors. Cancer Lett. 2007, 248, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Petrosyan, M.; Maretina, M.; Balashova, N.; Polyanskih, L.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Anti-angiogenic treatment of endometriosis via anti-VEGFA siRNA delivery by means of peptide-based carrier in a rat subcutaneous model. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murji, A.; Biberoğlu, K.; Leng, J.; Mueller, M.D.; Römer, T.; Vignali, M.; Yarmolinskaya, M. Use of dienogest in endometriosis: A narrative literature review and expert commentary. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mönckedieck, V.; Sannecke, C.; Husen, B.; Kumbartski, M.; Kimmig, R.; Tötsch, M.; Winterhager, E.; Grümmer, R. Progestins inhibit expression of MMPs and of angiogenic factors in human ectopic endometrial lesions in a mouse model. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, H.; Katayama, T.; Uematsu, K.; Hiratsuka, M.; Kiyomura, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Sugita, A.; Ito, M. Effect of dienogest administration on angiogenesis and hemodynamics in a rat endometrial autograft model. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, O.M.; Kaufmann-Reiche, U.; Moeller, C.; Fuhrmann, U. Effects of dienogest on surgically induced endometriosis in rats after repeated oral administration. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2011, 72, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.D.; Sun, Y.M.; Fu, G.F.; Du, Y.Z.; Chen, F.Y.; Yuan, H.; Zheng, C.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Hu, F.Q. Gene therapy of endometriosis introduced by polymeric micelles with glycolipid-like structure. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, B.; Liang, L.; Wu, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Tan, J.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Antiangiogenesis Therapy of Endometriosis Using PAMAM as a Gene Vector in a Noninvasive Animal Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 546479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, A. Dienogest in long-term treatment of endometriosis. Int. J. Women’s Health 2011, 3, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Q.; Yan, J.; Xu, X.; Ghimire, B.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Feng, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Combination of photothermal, prodrug and tumor cell camouflage technologies for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 13, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.A.; Shtykalova, S.V.; Maretina, M.A.; Sokolov, D.I.; Selkov, S.A.; Baranov, V.S.; Kiselev, A.V. Synergistic Anti-Angiogenic Effects Using Peptide-Based Combinatorial Delivery of siRNAs Targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, and Endoglin Genes. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, R.J.; McMahon, C.; Chudasama, V. Cysteine protecting groups: Applications in peptide and protein science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11098–11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, E.; Aielli, L.; Serra, F.; De Dominicis, L.; Falasca, K.; Di Giovanni, P.; Reale, M. Evaluation of Cell Migration and Cytokines Expression Changes under the Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field on Wound Healing In Vitro Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidler, J.L.; Hilliard, P.R.; Rill, R.L. Ultrasensitive staining of nucleic acids with silver. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Che, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X. Pigment epithelial-derived factor expression in endometriotic lesions in a rat model of endometriosis. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, M.A.; Balashova, N.N.; Polyanskikh, L.S.; Baziyan, E.V.; Tral, T.G.; Fasakhutdinova, L.K.; Razygraev, A.V.; Sapronov, N.S. Influence of progesterone analogs on endometrioid heterotopia in experimental model of endometriosis. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2018, 81, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Carrier | N/P Ratio | Size (nm) ± S.D. | PDI ± S.D. | Z-Potential (mV) ± S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R6p | 8/1 | 140.3 ± 0.5132 | 0.198 ± 0.013 | 27.5 ± 1.9 |
| R6p | 16/1 | 150.3 ± 1.1 | 0.203 ± 0.012 | 33.2 ± 1.1 |
| R6p-cRGD | 8/1 | 171.8± 1.85 | 0.211 ± 0.014 | 23.1 ± 0.5 |
| R6p-cRGD | 16/1 | 188.4 ± 4.1 | 0.189 ± 0.011 | 32.1 ± 0.8 |
| Name | Composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Monomers | R6 | CHRRRRRRHC |
| cRGD | C(Npys)RGDy |___________| | |
| Polymers | R6p R6p-cRGD | (CHRRRRRRHC)n cRGD-(CHRRRRRRHC)n-cRGD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egorova, A.; Maretina, M.; Krylova, I.; Kiselev, A. Polycondensed Peptide-Based Polymers for Targeted Delivery of Anti-Angiogenic siRNA to Treat Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010013
Egorova A, Maretina M, Krylova I, Kiselev A. Polycondensed Peptide-Based Polymers for Targeted Delivery of Anti-Angiogenic siRNA to Treat Endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgorova, Anna, Marianna Maretina, Iuliia Krylova, and Anton Kiselev. 2024. "Polycondensed Peptide-Based Polymers for Targeted Delivery of Anti-Angiogenic siRNA to Treat Endometriosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010013
APA StyleEgorova, A., Maretina, M., Krylova, I., & Kiselev, A. (2024). Polycondensed Peptide-Based Polymers for Targeted Delivery of Anti-Angiogenic siRNA to Treat Endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010013







