Development of A Radiomic Model for MGMT Promoter Methylation Detection in Glioblastoma Using Conventional MRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selected Radiomic Features
2.2. Classification Performances of the Two ML Algorithms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
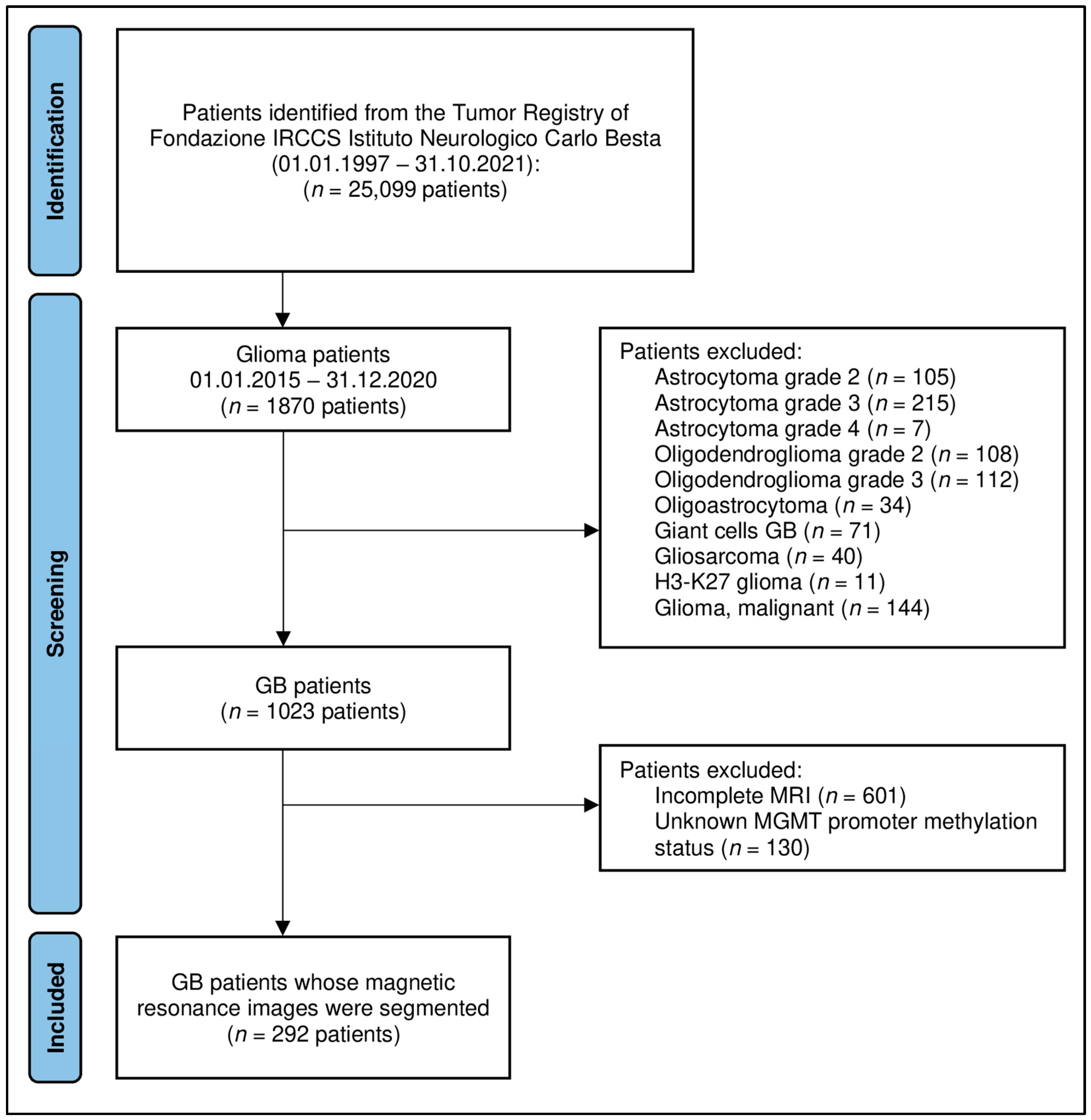
4.1. Patient Selection
4.2. MRI Acquisition
4.3. MGMT Promoter Methylation Status Testing
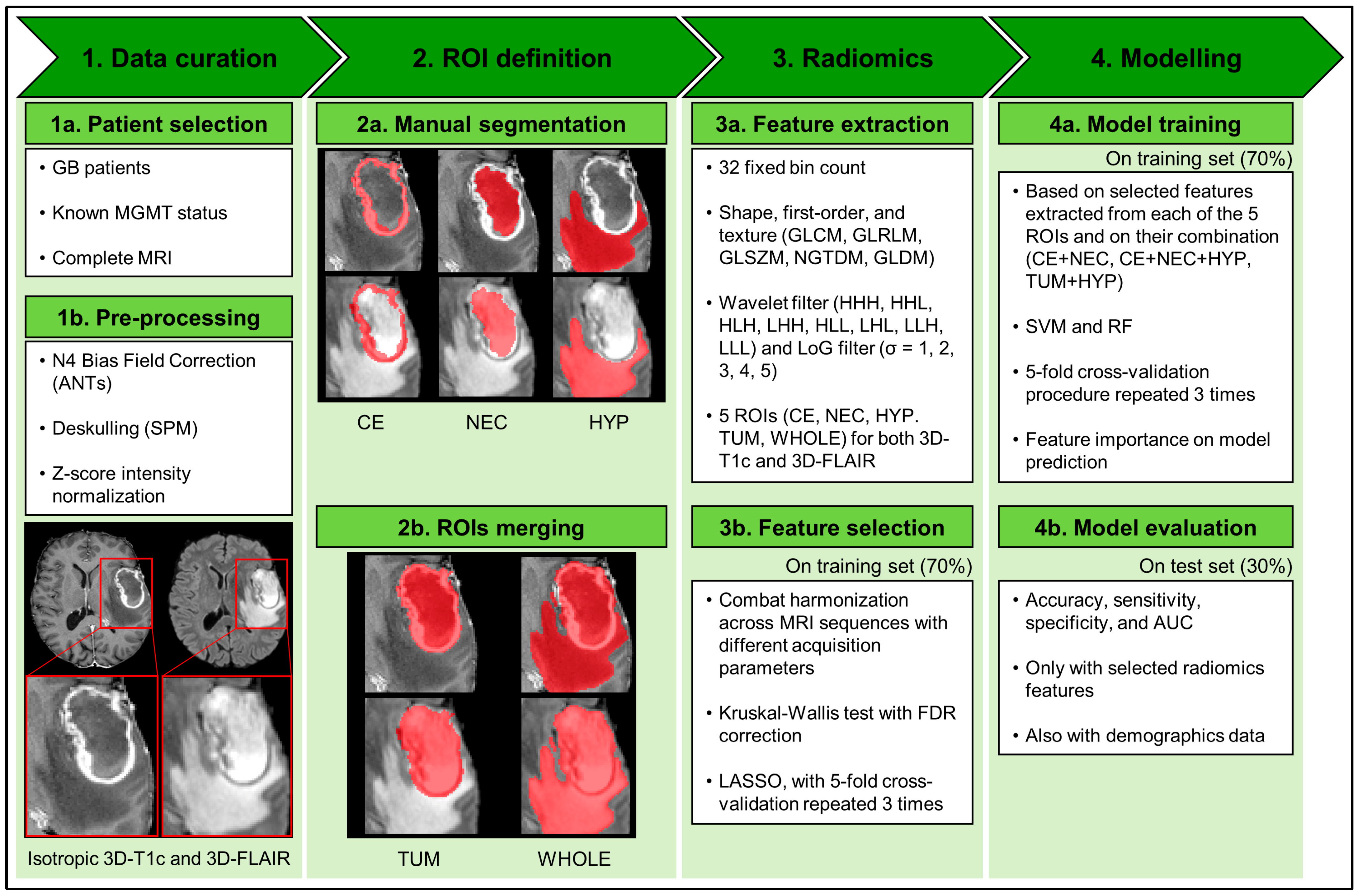
4.4. Image Analysis and Modeling Pipeline
4.4.1. Data Curation: Image Pre-Processing
4.4.2. ROI Definition
4.4.3. Radiomics: Feature Extraction and Selection from Multiregional and Multiparametric MRI
4.4.4. Modelling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 21, v1–v100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Stupp, R.; Reifenberger, G.; Brandes, A.A.; van den Bent, M.J.; Wick, W.; Hegi, M.E. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: Ready for personalized medicine? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Q.; Shao, A. O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase (MGMT): Challenges and New Opportunities in Glioma Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.R.; O’neill, B.P. Glioblastoma survival in the United States before and during the temozolomide era. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 107, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT Gene Silencing and Benefit from Temozolomide in Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Godard, S.; Dietrich, P.-Y.; Regli, L.; Ostermann, S.; Otten, P.; Van Melle, G.; de Tribolet, N.; Stupp, R. Clinical trial substantiates the predictive value of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma patients treated with temozolomide. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Pongor, L.; Su, Y.-T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Quezado, M.; Trepel, J.; Aldape, K.; Pommier, Y.; Wu, J. MGMT Status as a Clinical Biomarker in Glioblastoma. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.; Lai, A.; Nghiemphu, P.; Kim, H.; Phillips, H.; Kharbanda, S.; Moftakhar, P.; Lalaezari, S.; Yong, W.; Ellingson, B.; et al. Relationship between tumor enhancement, edema, IDH1 Mutational status, MGMT promoter methylation, and survival in glioblastoma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Calabria, L.F.; Tavanti, F.; Minniti, G.; Rossi-Espagnet, M.C.; Coppola, V.; Pugliese, S.; Guida, D.; Francione, G.; Colonnese, C.; et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient obtained by magnetic resonance imaging as a prognostic marker in glioblastomas: Correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Bent, M.J.v.D. Imaging Correlates of Adult Glioma Genotypes. Radiology 2017, 284, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Bang, J.-I.; Cheon, G.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.-K.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, K.W.; Chung, J.-K.; Kim, E.E.; Lee, D.S. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine positron emission tomography in relation to methyl-guanine methyltransferase promoter methylation in high-grade gliomas. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2015, 36, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eoli, M.; Menghi, F.; Bruzzone, M.G.; De Simone, T.; Valletta, L.; Pollo, B.; Bissola, L.; Silvani, A.; Bianchessi, D.; D’Incerti, L.; et al. Methylation of O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase and loss of heterozygosity on 19q and/or 17p are overlapping features of secondary glioblastomas with prolonged survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzone, M.G.; Eoli, M.; Cuccarini, V.; Grisoli, M.; Valletta, L.; Finocchiaro, G. Genetic signature of adult gliomas and correlation with MRI features. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levner, I.; Drabycz, S.; Roldan, G.; De Robles, P.; Cairncross, J.G.; Mitchell, R. Predicting MGMT methylation status of glioblastomas from MRI texture. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2009, London, UK, 20–24 September 2009; pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Drabycz, S.; Roldán, G.; de Robles, P.; Adler, D.; McIntyre, J.B.; Magliocco, A.M.; Cairncross, J.G.; Mitchell, J.R. An analysis of image texture, tumor location, and MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma using magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Albano, D.; Chianca, V.; Messina, C.; Gambino, A.; Ugga, L.; Cortese, M.C.; Lazzara, A.; Ricci, D.; et al. MRI radiomics-based machine-learning classification of bone chondrosarcoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 128, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, L.-Y.; Yin, X.-P.; Gao, B.-L. Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Evaluation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 689509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, I.; Rundo, L.; Codari, M.; Di Leo, G.; Salvatore, C.; Interlenghi, M.; Gallivanone, F.; Cozzi, A.; D’Amico, N.C.; Sardanelli, F. AI applications to medical images: From machine learning to deep learning. Phys. Medica 2021, 83, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-C.; Bai, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.; Zheng, H. Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme: A multicentre study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, P.; Alberts, E.; Delbridge, C.; Trebeschi, S.; Valentinitsch, A.; Bette, S.; Huber, T.; Gempt, J.; Meyer, B.; Schlegel, J.; et al. Diffusion tensor image features predict IDH genotype in newly diagnosed WHO grade II/III gliomas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xing, Z.; She, D.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Cao, D. IDH mutant and 1p/19q co-deleted oligodendrogliomas: Tumor grade stratification using diffusion-, susceptibility-, and perfusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology 2017, 59, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, S.; Akbari, H.; Doshi, J.; Shukla, G.; Rozycki, M.; Bilello, M.; Lustig, R.A.; Davatzikos, C.A. Radiomic signature of infiltration in peritumoral edema predicts subsequent recurrence in glioblastoma: Implications for personalized radiotherapy planning. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 021219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitto, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Albano, D.; Morelli, F.; Pescatori, L.C.; Messina, C.; Imbriaco, M.; Sconfienza, L.M. CT and MRI radiomics of bone and soft-tissue sarcomas: A systematic review of reproducibility and validation strategies. Insights Into Imaging 2021, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, B.; An, C.; Kim, D.; Ahn, S.S.; Han, K.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Chang, J.H.; Lee, S.-K. Radiomics-based prediction of multiple gene alteration incorporating mutual genetic information in glioblastoma and grade 4 astrocytoma, IDH-mutant. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 155, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Ye, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Predicting MGMT Promoter Methylation in Diffuse Gliomas Using Deep Learning with Radiomics. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.S. What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Do, D.T.; Chiu, F.-Y.; Yapp, E.K.Y.; Yeh, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y. XGBoost improves classification of MGMT promoter methylation status in IDH1 wildtype glioblastoma. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.T.; Yang, M.-R.; Lam, L.H.T.; Le, N.Q.K.; Wu, Y.-W. Improving MGMT methylation status prediction of glioblastoma through optimizing radiomics features using genetic algorithm-based machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.-b.; Guo, F.; Xu, Z.-l.; Li, C.; Wei, W.; Tian, P.; Liu, T.-t.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Ye, J.; et al. Radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for the prediction of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisi, G.; Filice, S. Predicting MGMT Promoter Methylation of Glioblastoma from Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion: A Radiomic Approach. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfiatis, P.; Kline, T.L.; Coufalova, L.; Lachance, D.H.; Parney, I.F.; Carter, R.E.; Buckner, J.C.; Erickson, B.J. MRI texture features as biomarkers to predict MGMT methylation status in glioblastomas. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G.M. Transparent Reporting of a Multivariable Prediction Model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): The TRIPOD statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 68, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihira, S.; Mei, X.; Mahmoudi, K.; Liu, Z.; Dogra, S.; Belani, P.; Tsankova, N.; Hormigo, A.; Fayad, Z.A.; Doshi, A.; et al. U-Net Based Segmentation and Characterization of Gliomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduin, M.; Primakov, S.; Compter, I.; Woodruff, H.C.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Ramaekers, B.L.T.; Dorsthorst, M.T.; Revenich, E.G.M.; ter Laan, M.; Pegge, S.A.H.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of integrated qualitative and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analysis in glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vils, A.; Bogowicz, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Vuong, D.; Saltybaeva, N.; Kraft, J.; Wirsching, H.-G.; Gramatzki, D.; Wick, W.; Rushing, E.; et al. Radiomic Analysis to Predict Outcome in Recurrent Glioblastoma Based on Multi-Center MR Imaging From the Prospective DIRECTOR Trial. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 636672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihira, S.; Tsankova, N.M.; Bauer, A.; Sakai, Y.; Mahmoudi, K.; Zubizarreta, N.; Houldsworth, J.; Khan, F.; Salamon, N.; Hormigo, A.; et al. Multiparametric MRI texture analysis in prediction of glioma biomarker status: Added value of MR diffusion. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, M.; Gersey, Z.C.; Ak, M.; Elakkad, A.; Kotrotsou, A.; Zenkin, S.; Elshafeey, N.; Mamindla, P.; Kumar, V.A.; Kumar, A.J.; et al. Pre-operative MRI radiomics model non-invasively predicts key genomic markers and survival in glioblastoma patients. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 160, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The image biomarker standardization initiative: Standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Lucignani, M.; Tagliente, E.; Dellepiane, F.; Rossi-Espagnet, M.C.; Ritrovato, M.; Vidiri, A.; Villani, V.; Ranazzi, G.; et al. AI and High-Grade Glioma for Diagnosis and Outcome Prediction: Do All Machine Learning Models Perform Equally Well? Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 601425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.Y.; Park, Y.W.; Ahn, S.S.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.-K. Quality assessment of meningioma radiomics studies: Bridging the gap between exploratory research and clinical applications. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 138, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Quality of science and reporting of radiomics in oncologic studies: Room for improvement according to radiomics quality score and TRIPOD statement. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdá-Alberich, L.; Solana, J.; Mallol, P.; Ribas, G.; García-Junco, M.; Alberich-Bayarri, A.; Marti-Bonmati, L. MAIC–10 brief quality checklist for publications using artificial intelligence and medical images. Insights Into Imaging 2023, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.; Hamilton, S.R.; Burger, P.C.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA repair gene O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase by promoter hypermethylation is a common event in primary human neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Carré, A.; Klausner, G.; Edjlali, M.; Lerousseau, M.; Briend-Diop, J.; Sun, R.; Ammari, S.; Reuzé, S.; Andres, E.A.; Estienne, T.; et al. Standardization of brain MR images across machines and protocols: Bridging the gap for MRi-based radiomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leemput, K.; Maes, F.; Vandermeulen, D.; Suetens, P. Automated model-based bias field correction of MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.-P.; Cullen, N.; Sheline, Y.I.; Taylor, W.D.; Aselcioglu, I.; Cook, P.A.; Adams, P.; Cooper, C.; Fava, M.; McGrath, P.J.; et al. Harmonization of cortical thickness measurements across scanners and sites. NeuroImage 2017, 167, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Training Set (n = 196) | Test Set (n = 81) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 61 (11) [22–83] | 61 (12) [33–83] | 0.942 |
| Sex (M/F) | 120/76 | 51/30 | 0.892 |
| Overall survival, months | 13.2 (10.6) [0.07–51.3] | 12.6 (9.9) [0.10–46.1] | 0.753 |
| MGMTp (meth./non-meth.) | 86/110 | 35/46 | 0.999 |
| KPS 2, median (range) | 90 (50–100) | 80 (40–100) | 0.225 |
| MRI system (Scanner 1/Scanner 2) | 60/136 | 24/57 | 0.999 |
| Classification Metric | WHOLE | CE | NEC | HYP | TUM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | |
| Accuracy, % | 61.4 | 56.6 | 63.1 | 58.5 | 67.6 | 58.5 | 60.9 | 55.9 | 61.6 | 56.6 |
| (SD) | (6.9) | (6.0) | (10.0) | (6.9) | (9.0) | (7.2) | (6.9) | (10.3) | (5.0) | (7.4) |
| Sensitivity, % | 30.2 | 29.0 | 54.1 | 37.3 | 59.6 | 43.5 | 22.4 | 26.3 | 36.5 | 32.9 |
| (SD) | (19.0) | (12.7) | (15.6) | (12.3) | (9.9) | (8.6) | (18.0) | (10.9) | (18.6) | (11.9) |
| Specificity, % | 85.3 | 77.7 | 70.1 | 74.8 | 73.8 | 69.8 | 90.5 | 78.7 | 80.7 | 74.8 |
| (SD) | (13.3) | (7.4) | (16.5) | (9.8) | (14.0) | (11.5) | (8.8) | (14.4) | (15.2) | (10.1) |
| AUC | 0.661 | 0.535 | 0.688 | 0.622 | 0.759 | 0.615 | 0.610 | 0.549 | 0.669 | 0.588 |
| (SD) | (0.120) | (0.100) | (0.104) | (0.090) | (0.069) | (0.087) | (0.124) | (0.100) | (0.112) | (0.081) |
| Classification Metric | WHOLE | CE | NEC | HYP | TUM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | SVM | RF | |
| Accuracy, % | 64.2 | 61.7 | 49.4 | 50.6 | 50.6 | 53.1 | 55.6 | 53.1 | 50.6 | 51.9 |
| (95% CI) | (52.8–74.6) | (50.3–72.3) | (38.1–60.7) | (39.3–61.9) | (39.3–61.9) | (41.7–64.3) | (44.1–66.6) | (41.7–64.3) | (39.3–61.9) | (40.5–63.1) |
| Sensitivity, % | 42.9 | 37.1 | 54.3 | 25.7 | 48.6 | 48.6 | 37.1 | 25.7 | 40.0 | 28.6 |
| (n/N) | (15/35) | (13/35) | (19/35) | (9/35) | (17/35) | (17/35) | (13/35) | (9/35) | (14/35) | (10/35) |
| Specificity, % | 80.4 | 80.4 | 45.7 | 69.6 | 52.2 | 56.5 | 69.6 | 73.9 | 58.7 | 69.6 |
| (n/N) | (37/46) | (37/46) | (21/46) | (32/46) | (24/46) | (26/46) | (32/46) | (34/46) | (27/46) | (32/46) |
| AUC | 0.572 | 0.594 | 0.583 | 0.482 | 0.453 | 0.436 | 0.495 | 0.543 | 0.532 | 0.452 |
| (95% CI) | (0.439–0.705) | (0.464–0.725) | (0.457–0.710) | (0.351–0.613) | (0.323–0.583) | (0.306–0.566) | (0.360–0.630) | (0.414–0.672) | (0.403–0.660) | (0.320–0.583) |
| Name | General Description |
|---|---|
| Radiomic Quality Score (RQS) | It considers radiomics-specific aspects that fall into the following six domains: protocol quality and reproducibility in image and segmentation; feature reduction and validation; biologic/clinical validation and utility; performance index; high level of evidence; and open science [40]. |
| Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) | It provides standardized nomenclature/definitions of image biomarkers, a standardized workflow of image processing, tools for verifying the implementations of radiomics software, and reporting guidelines for radiomics studies [41]. |
| Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD) | It covers a set of recommendations for the reporting of studies developing and/or validating prediction models for both diagnosis and prognosis, for all medical domains, and all types of predictors [34]. |
| Must Artificial Intelligence Criteria-10 (MAIC-10) | It is a short quality assessment tool widely applicable to AI studies in medical imaging focusing on the following aspects: clinical need; study design; safety and privacy; data curation, annotation and partitioning; model description, robustness and explainability; and data transparency [45]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doniselli, F.M.; Pascuzzo, R.; Agrò, M.; Aquino, D.; Anghileri, E.; Farinotti, M.; Pollo, B.; Paterra, R.; Cuccarini, V.; Moscatelli, M.; et al. Development of A Radiomic Model for MGMT Promoter Methylation Detection in Glioblastoma Using Conventional MRI. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010138
Doniselli FM, Pascuzzo R, Agrò M, Aquino D, Anghileri E, Farinotti M, Pollo B, Paterra R, Cuccarini V, Moscatelli M, et al. Development of A Radiomic Model for MGMT Promoter Methylation Detection in Glioblastoma Using Conventional MRI. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010138
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoniselli, Fabio M., Riccardo Pascuzzo, Massimiliano Agrò, Domenico Aquino, Elena Anghileri, Mariangela Farinotti, Bianca Pollo, Rosina Paterra, Valeria Cuccarini, Marco Moscatelli, and et al. 2024. "Development of A Radiomic Model for MGMT Promoter Methylation Detection in Glioblastoma Using Conventional MRI" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010138
APA StyleDoniselli, F. M., Pascuzzo, R., Agrò, M., Aquino, D., Anghileri, E., Farinotti, M., Pollo, B., Paterra, R., Cuccarini, V., Moscatelli, M., DiMeco, F., & Sconfienza, L. M. (2024). Development of A Radiomic Model for MGMT Promoter Methylation Detection in Glioblastoma Using Conventional MRI. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010138






