Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
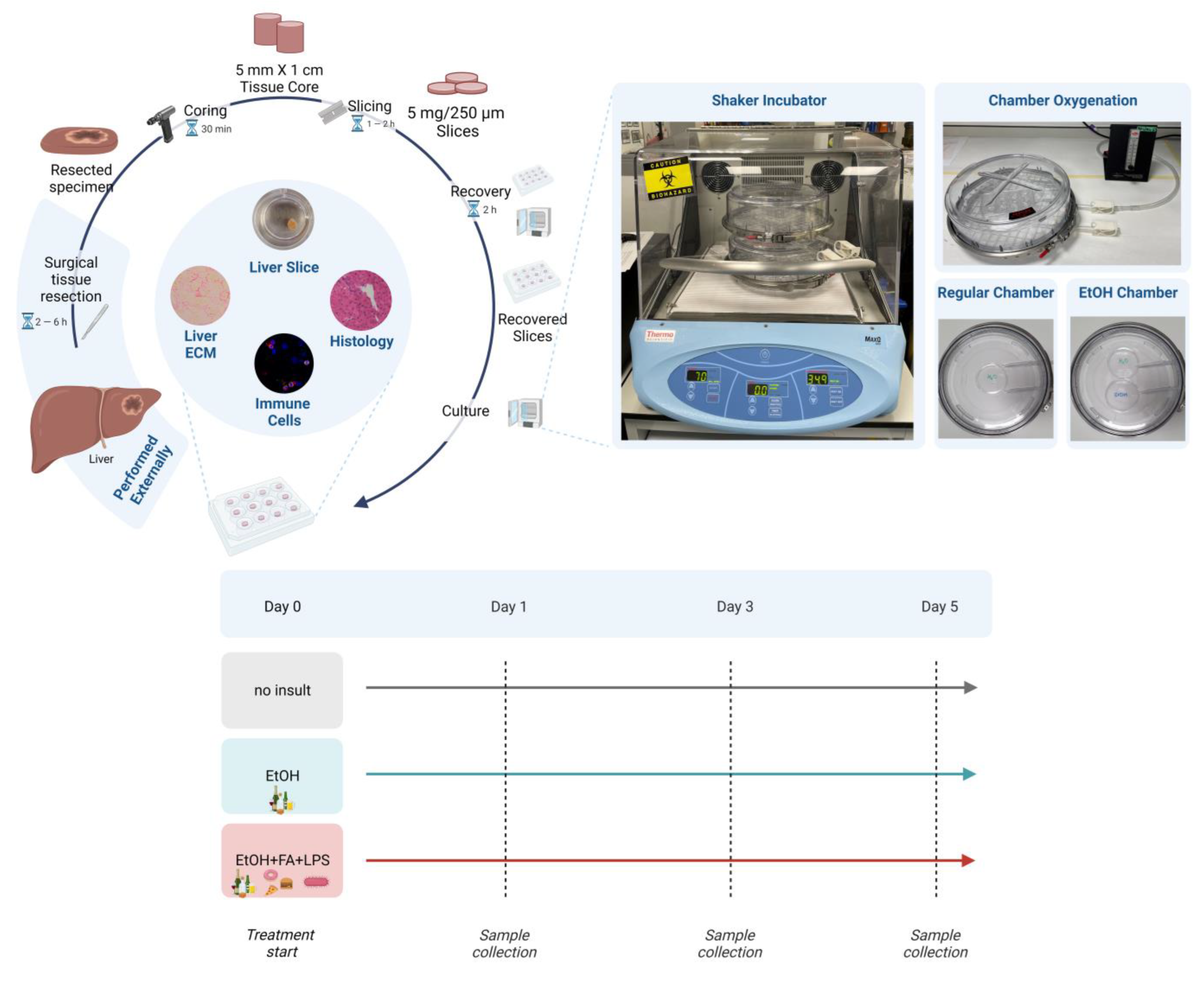
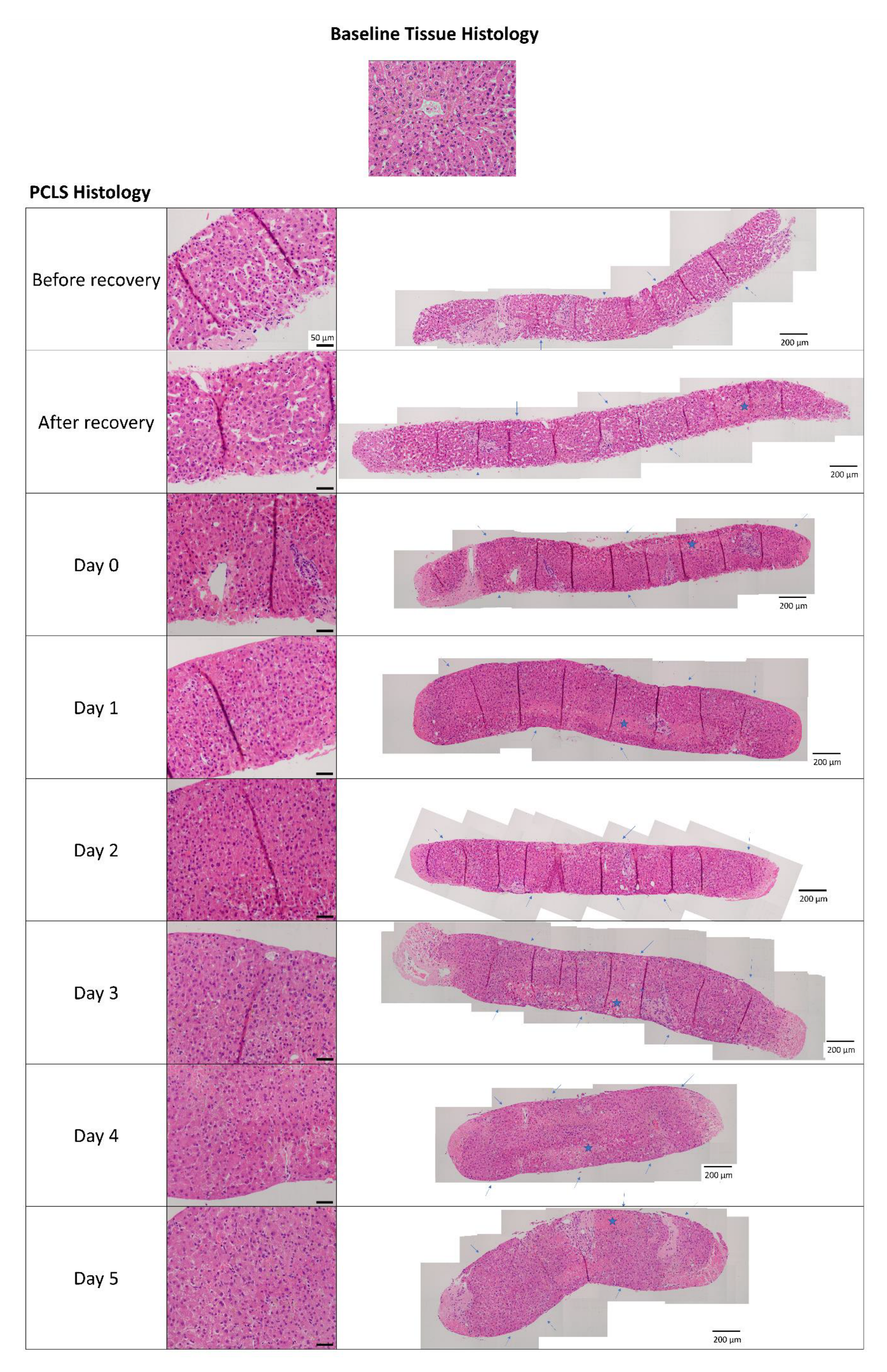
2.1. Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices Are Viable up to Six Days in Culture
2.2. Upregulation of Lipid Synthesis in Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices Exposed to Alcohol
2.3. Alcohol Insults Induce Hepatocyte Damage in Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices
2.4. Differential Inflammatory Responses Are Triggered by EtOH Alone or in Combination with FA and LPS Treatment in Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices
2.5. Fibrogenic Activity Was Observed in Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices Independently from Alcohol Stimuli
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment
4.2. Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices Preparation and Culturing Conditions
4.3. Histology
4.4. Quantification of the ATP Content in the PCLS
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. QuantiGene Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Analysis of Soluble Markers in Culture Supernatants
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565639 (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Mandrekar, P.; Bataller, R.; Tsukamoto, H.; Gao, B. Alcoholic Hepatitis: Translational Approaches to Develop Targeted Therapies. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndugga, N.; Lightbourne, T.G.; Javaherian, K.; Cabezas, J.; Verma, N.; Barritt, A.S.; Bataller, R. Disparities between Research Attention and Burden in Liver Diseases: Implications on Uneven Advances in Pharmacological Therapies in Europe and the USA. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e013620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, C.; Stauber, R.E.; Davies, S.; Denk, H.; Dienes, H.P.; Gnemmi, V.; Guido, M.; Miquel, R.; Paradis, V.; Schirmacher, P.; et al. Development and Prognostic Relevance of a Histologic Grading and Staging System for Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current Management. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riva, A.; Palma, E.; Devshi, D.; Corrigall, D.; Adams, H.; Heaton, N.; Menon, K.; Preziosi, M.; Zamalloa, A.; Miquel, R.; et al. Soluble TIM3 and Its Ligands Galectin-9 and CEACAM1 Are in Disequilibrium During Alcohol-Related Liver Disease and Promote Impairment of Anti-Bacterial Immunity. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwick, L.J.L.; Riva, A.; Ryan, J.M.; Cooksley, H.; Palma, E.; Tranah, T.H.; Manakkat Vijay, G.K.; Vergis, N.; Thursz, M.; Evans, A.; et al. Blockade of PD1 and TIM3 Restores Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Patients with Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 590–602.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osna, N.A.; Rasineni, K.; Ganesan, M.; Donohue, T.M.; Kharbanda, K.K. Pathogenesis of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Xu, M.J.; Bertola, A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Liangpunsakul, S. Animal Models of Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Relevance. Gene Expr. 2017, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, M.B. Why Animal Studies Are Often Poor Predictors of Human Reactions to Exposure. J. R. Soc. Med. 2009, 102, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delire, B.; Stärkel, P.; Leclercq, I. Animal Models for Fibrotic Liver Diseases: What We Have, What We Need, and What Is under Development. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas-Paz, A.; Hao, F.; Nelson, L.J.; Vázquez, M.T.; Canals, S.; del Moral, M.G.; Martínez-Naves, E.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Cubero, F.J. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Utility of Animal Models. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkin, R.J.W.; Lalor, P.F.; Parker, R.; Newsome, P.N. Murine Models of Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis and Their Relevance to Human Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevzorova, Y.A.; Boyer-Diaz, Z.; Javier Cubero, F.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Animal Models for Liver Disease—A Practical Approach for Translational Research. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.M.; Sjövall, J.; Strom, S.; Bodin, K.; Nowak, G.; Einarsson, C.; Ellis, E. Ethanol Stimulates Bile Acid Formation in Primary Human Hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Babuta, M.; Catalano, D.; Saiju, A.; Szabo, G. Alcohol Promotes Exosome Biogenesis and Release via Modulating Rabs and MiR-192 Expression in Human Hepatocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 787356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ma, Y.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Chronic Alcohol Exposure Induces Hepatocyte Damage by Inducing Oxidative Stress, SATB2 and Stem Cell-like Characteristics, and Activating Lipogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawroth, J.C.; Petropolis, D.B.; Manatakis, D.V.; Maulana, T.I.; Burchett, G.; Schlünder, K.; Witt, A.; Shukla, A.; Kodella, K.; Ronxhi, J.; et al. Modeling Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease in a Human Liver-Chip. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, J.; Chang, M.; Yan, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, T.; Li, C.; et al. Human ESC-Derived Expandable Hepatic Organoids Enable Therapeutic Liver Repopulation and Pathophysiological Modeling of Alcoholic Liver Injury. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Bravo, B.; Ariño, S.; Blaya, D.; Pose, E.; Martinez García de la Torre, R.A.; Latasa, M.U.; Martínez-Sánchez, C.; Zanatto, L.; Sererols-Viñas, L.; Cantallops-Vilà, P.; et al. Hepatocyte Dedifferentiation Profiling in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Identifies CXCR4 as a Driver of Cell Reprogramming. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewyse, L.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. Best Practices and Progress in Precision-Cut Liver Slice Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Doornebal, E.J.; Chokshi, S. Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Versatile Tool to Advance Liver Research. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.F.; Gandolfi, A.J.; Krumdieck, C.L.; Putnam, C.W.; Zukoski, C.F.; Davis, W.M.; Brendel, K. Dynamic Organ Culture of Precision Liver Slices for in Vitro Toxicology. Life Sci. 1985, 36, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kanter, R.; De Jager, M.H.; Draaisma, A.L.; Jurva, J.U.; Olinga, P.; Meijer, D.K.F.; Groothuis, G.M.M. Drug-Metabolizing Activity of Human and Rat Liver, Lung, Kidney and Intestine Slices. Xenobiotica 2002, 32, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, I.A.M.; Olinga, P.; De Jager, M.H.; Merema, M.T.; De Kanter, R.; Van De Kerkhof, E.G.; Groothuis, G.M.M. Preparation and Incubation of Precision-Cut Liver and Intestinal Slices for Application in Drug Metabolism and Toxicity Studies. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paish, H.L.; Reed, L.H.; Brown, H.; Bryan, M.C.; Govaere, O.; Leslie, J.; Barksby, B.S.; Garcia Macia, M.; Watson, A.; Xu, X.; et al. A Bioreactor Technology for Modeling Fibrosis in Human and Rodent Precision-Cut Liver Slices. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Bovenkamp, M.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Meijer, D.K.F.; Olinga, P. Precision-Cut Fibrotic Rat Liver Slices as a New Model to Test the Effects of Anti-Fibrotic Drugs in Vitro. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewyse, L.; De Smet, V.; Verhulst, S.; Eysackers, N.; Kunda, R.; Messaoudi, N.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. Improved Precision-Cut Liver Slice Cultures for Testing Drug-Induced Liver Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 862185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, I.M.; Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Luangmonkong, T.; Hadi, M.; Oosterhuis, D.; de Jong, K.P.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P. Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices as a Model to Test Antifibrotic Drugs in the Early Onset of Liver Fibrosis. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 35, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, L.W.; Thiele, G.M.; Duryee, M.J.; Schaffert, C.S.; DeVeney, A.L.; Hunter, C.D.; Olinga, P.; Tuma, D.J. An in Vitro Method of Alcoholic Liver Injury Using Precision Cut Liver Slices from Rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffert, C.S.; Duryee, M.J.; Bennett, R.G.; DeVeney, A.L.; Tuma, D.J.; Olinga, P.; Easterling, K.C.; Thiele, G.M.; Klassen, L.W. Exposure of Precision-Cut Rat Liver Slices to Ethanol Accelerates Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duryee, M.J.; Willis, M.S.; Schaffert, C.S.; Reidelberger, R.D.; Dusad, A.; Anderson, D.R.; Klassen, L.W.; Thiele, G.M. Precision-Cut Liver Slices from Diet-Induced Obese Rats Exposed to Ethanol Are Susceptible to Oxidative Stress and Increased Fatty Acid Synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G208–G217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stärkel, P.; Schnabl, B.; Leclercq, S.; Komuta, M.; Bataller, R.; Argemi, J.; Palma, E.; Chokshi, S.; Hellerbrand, C.; Maccioni, L.; et al. Deficient IL-6/Stat3 Signaling, High TLR7, and Type I Interferons in Early Human Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Triad for Liver Damage and Fibrosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Riva, A.; Moreno, C.; Odena, G.; Mudan, S.; Manyakin, N.; Miquel, R.; Degré, D.; Trepo, E.; Sancho-Bru, P.; et al. Perturbations in Mitochondrial Dynamics Are Closely Involved in the Progression of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A.E.M.; Saulnier, M.; Cruz, E.; Merema, M.T.; Rose, K.; Bentley, P.; Olinga, P. Organ Slice Viability Extended for Pathway Characterization: An in Vitro Model to Investigate Fibrosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 82, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Arteel, G.E. Effect of Ethanol on Lipid Metabolism. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, T.; Song, Z. Chronic Alcohol Consumption Disrupted Cholesterol Homeostasis in Rats: Downregulation of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor and Enhancement of Cholesterol Biosynthesis Pathway in the Liver. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaka, T.; Shimano, H. Elovl6: A New Player in Fatty Acid Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorhauge, K.H.; Thiele, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Johansen, S.; Madsen, B.S.; Antonsen, S.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Lindvig, K.P.; Krag, A. Serum Keratin-18 Detects Hepatic Inflammation and Predicts Progression in Compensated Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.R.; Grove, J.I.; Liebig, S.; Astbury, S.; Vergis, N.; Goldin, R.; Quaglia, A.; Bantel, H.; Guha, I.N.; Thursz, M.R.; et al. In Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis, Serum Keratin-18 Fragments Are Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Theragnostic Biomarkers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsalya, V.; Cave, M.C.; Kong, M.; Gobejishvili, L.; Falkner, K.C.; Craycroft, J.; Mitchell, M.; Szabo, G.; McCullough, A.; Dasarathy, S.; et al. Keratin 18 Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Factor for Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobie, R.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Henderson, B.E.P.; Smith, J.R.; Matchett, K.P.; Portman, J.R.; Wallenborg, K.; Picelli, S.; Zagorska, A.; Pendem, S.V.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Uncovers Zonation of Function in the Mesenchyme during Liver Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Liaskou, E.; Hadley, S.; Youster, J.; Faint, J.; Adams, D.H.; Lalor, P.F. An in Vitro Model of Human Acute Ethanol Exposure That Incorporates CXCR3- and CXCR4-Dependent Recruitment of Immune Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriguga, S.; Li, M.; Luangmonkong, T.; Boersema, M.; De Jong, K.P.; Oosterhuis, D.; Gorter, A.R.; Beljaars, L.; Olinga, P. Distinct Responses between Healthy and Cirrhotic Human Livers upon Lipopolysaccharide Challenge: Possible Implications for Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G114–G125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijnikman, A.S.; Davids, M.; Herrema, H.; Aydin, O.; Tremaroli, V.; Rios-Morales, M.; Levels, H.; Bruin, S.; de Brauw, M.; Verheij, J.; et al. Microbiome-Derived Ethanol in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, I.M.; Pham, B.T.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P. Evaluation of Fibrosis in Precision-Cut Tissue Slices. Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver Fibrosis and Repair: Immune Regulation of Wound Healing in a Solid Organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Espinoza, L.; Huch, M. The Balancing Act of the Liver: Tissue Regeneration versus Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, A.M. Recent Events in Alcoholic Liver Disease: V. Effects of Ethanol on Liver Regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G1–G6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Petitjean, L.; Petitjean, M.; Pavlides, M. Liver Fibrosis Phenotyping and Severity Scoring by Quantitative Image Analysis of Biopsy Slides. Liver Int. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wershof, E.; Park, D.; Barry, D.J.; Jenkins, R.P.; Rullan, A.; Wilkins, A.; Schlegelmilch, K.; Roxanis, I.; Anderson, K.I.; Bates, P.A.; et al. A FIJI Macro for Quantifying Pattern in Extracellular Matrix. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ishac, E.J.N.; Dent, P.; Kunos, G.; Gao, B. Effects of Ethanol on Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Normal and Regenerating Liver. Biochem. J. 1998, 334 Pt 3, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koteish, A.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Diehl, A.M. Ethanol Induces Redox-Sensitive Cell-Cycle Inhibitors and Inhibits Liver Regeneration after Partial Hepatectomy. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Ma, X.; Riva, A.; Iansante, V.; Dhawan, A.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.M.; Sesaki, H.; Williams, R.; Ding, W.X.; et al. Dynamin-1–Like Protein Inhibition Drives Megamitochondria Formation as an Adaptive Response in Alcohol-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, P.J. Species Differences in the Structure and Function of the Immune System. Toxicology 2003, 188, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J. FDA Modernization Act 2.0 Allows for Alternatives to Animal Testing. Artif. Organs 2023, 47, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadman, M. FDA No Longer Has to Require Animal Testing for New Drugs. Science 2023, 379, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Shah, V.H. Current Trials and Novel Therapeutic Targets for Alcoholic Hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornebal, E.J.; Harris, N.; Riva, A.; Jagatia, R.; Pizanias, M.; Prachalias, A.; Menon, K.; Preziosi, M.; Zamalloa, A.; Miquel, R.; et al. Human Immunocompetent Model of Neuroendocrine Liver Metastases Recapitulates Patient-Specific Tumour Microenvironment. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 909180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Demographics | Background Liver | Tumour | Treatment (Y/N) | Alcohol | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUBJECT ID | Sex | Age | Ethnicity | BMI | Fibrosis Score | Other Observations | Aetiology | Current/Former | Units/Week | |
| PCLS-130-KCH | F | 81 | Caucasian | 28.97 | F0–F1 * | Areas of parenchyma atrophy and F1 with mild CL PSF. 10% steatosis | CRLM | Y | N | UA |
| PCLS-132-KCH | M | 39 | Caucasian | UA | F0–F3 * | Areas of F2–3, secondary to SOS with marked PSF and NRH20% steatosis | CRLM | N | UA | UA |
| PCLS-149-KCH | F | 37 | Caucasian | 19.36 | F0 | Rare pp delicate fibrous spurs | CRLM | Y | UA | UA |
| PCLS-156-KCH | F | 69 | Caucasian | 17.3 | F0 * | Very focal pp delicate expansion and focal CL PSF | CRLM | Y | current | <14 |
| PCLS-159-KCH | M | 40 | Asian | 24.8 | F0 | <5% steatosis | CRLM | N | N | UA |
| PCLS-190-KCH | M | 60 | Caucasian | 26.7 | F0 | 30% steatosis | CRLM | N | N | UA |
| PCLS-215-KCH | M | 50 | Caucasian | 28.7 | F0–F1 | Variable pp delicate fibrosis and patchy CL PSF (mild SOS) | CRLM | N | UA | UA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rastovic, U.; Bozzano, S.F.; Riva, A.; Simoni-Nieves, A.; Harris, N.; Miquel, R.; Lackner, C.; Zen, Y.; Zamalloa, A.; Menon, K.; et al. Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010150
Rastovic U, Bozzano SF, Riva A, Simoni-Nieves A, Harris N, Miquel R, Lackner C, Zen Y, Zamalloa A, Menon K, et al. Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleRastovic, Una, Sergio Francesco Bozzano, Antonio Riva, Arturo Simoni-Nieves, Nicola Harris, Rosa Miquel, Carolin Lackner, Yoh Zen, Ane Zamalloa, Krishna Menon, and et al. 2024. "Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010150
APA StyleRastovic, U., Bozzano, S. F., Riva, A., Simoni-Nieves, A., Harris, N., Miquel, R., Lackner, C., Zen, Y., Zamalloa, A., Menon, K., Heaton, N., Chokshi, S., & Palma, E. (2024). Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010150









