miRNA-378 Is Downregulated by XBP1 and Inhibits Growth and Migration of Luminal Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
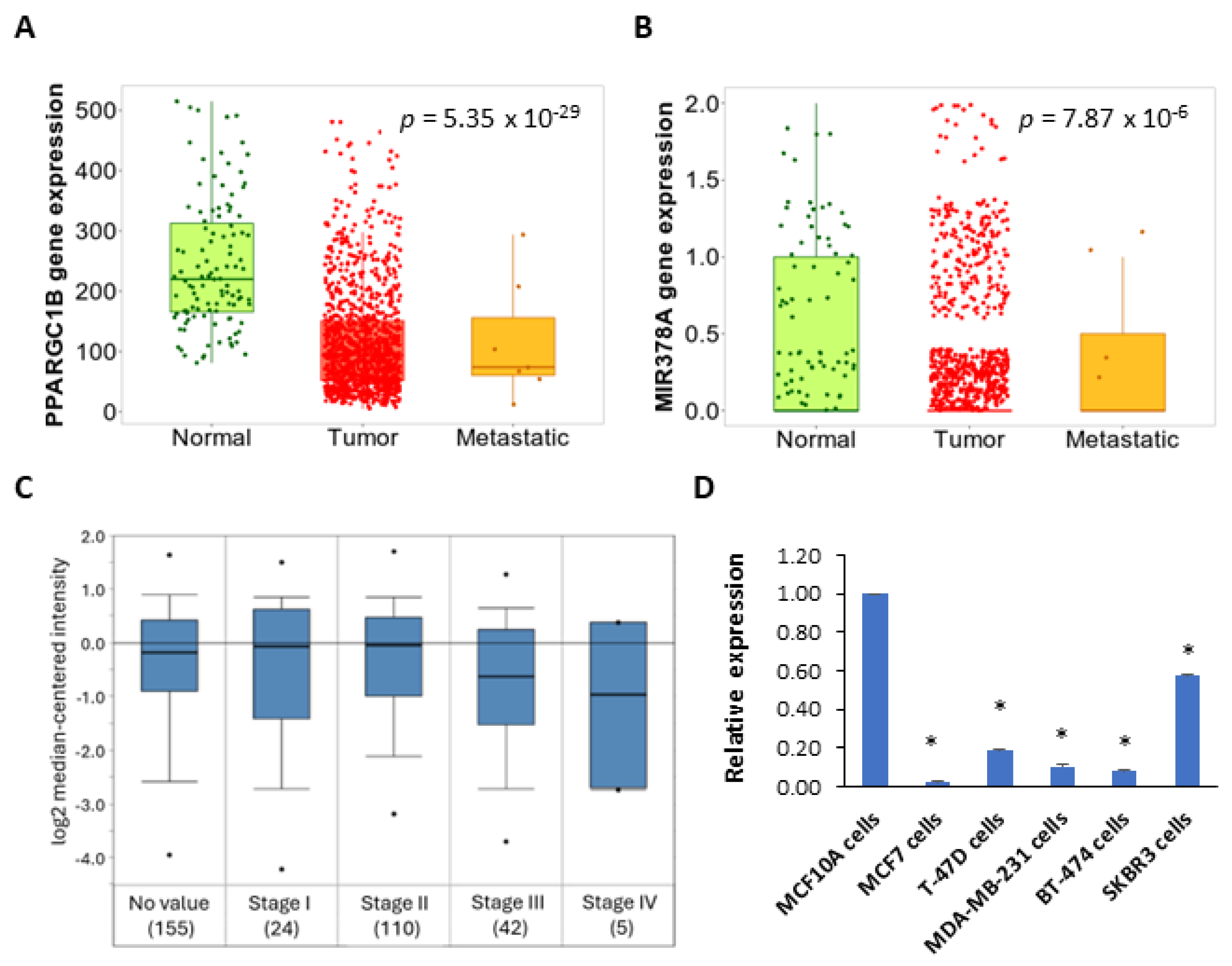
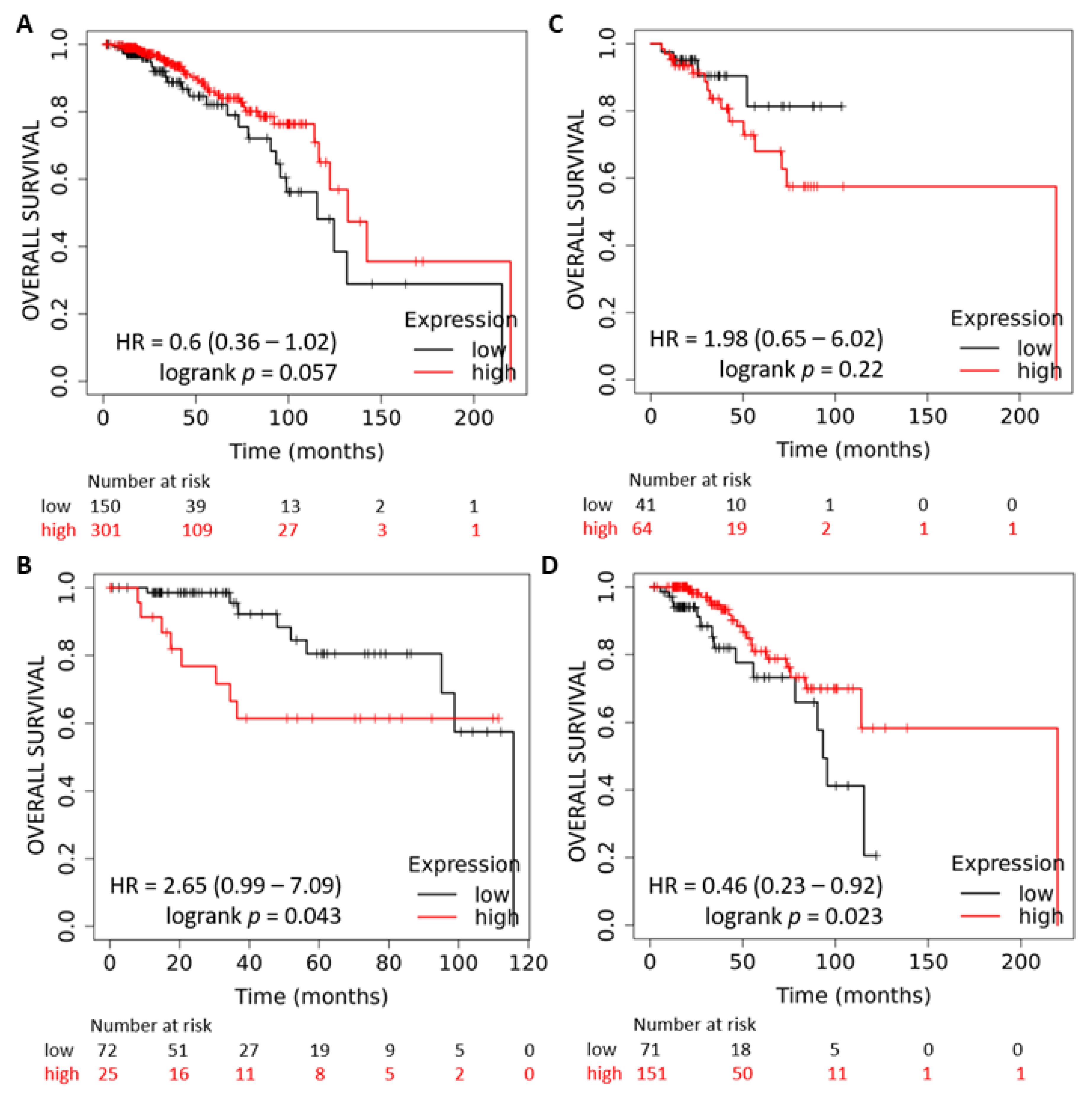
2.1. Expression and Prognostic Value of the miR-378 in Subtypes of Breast Cancer
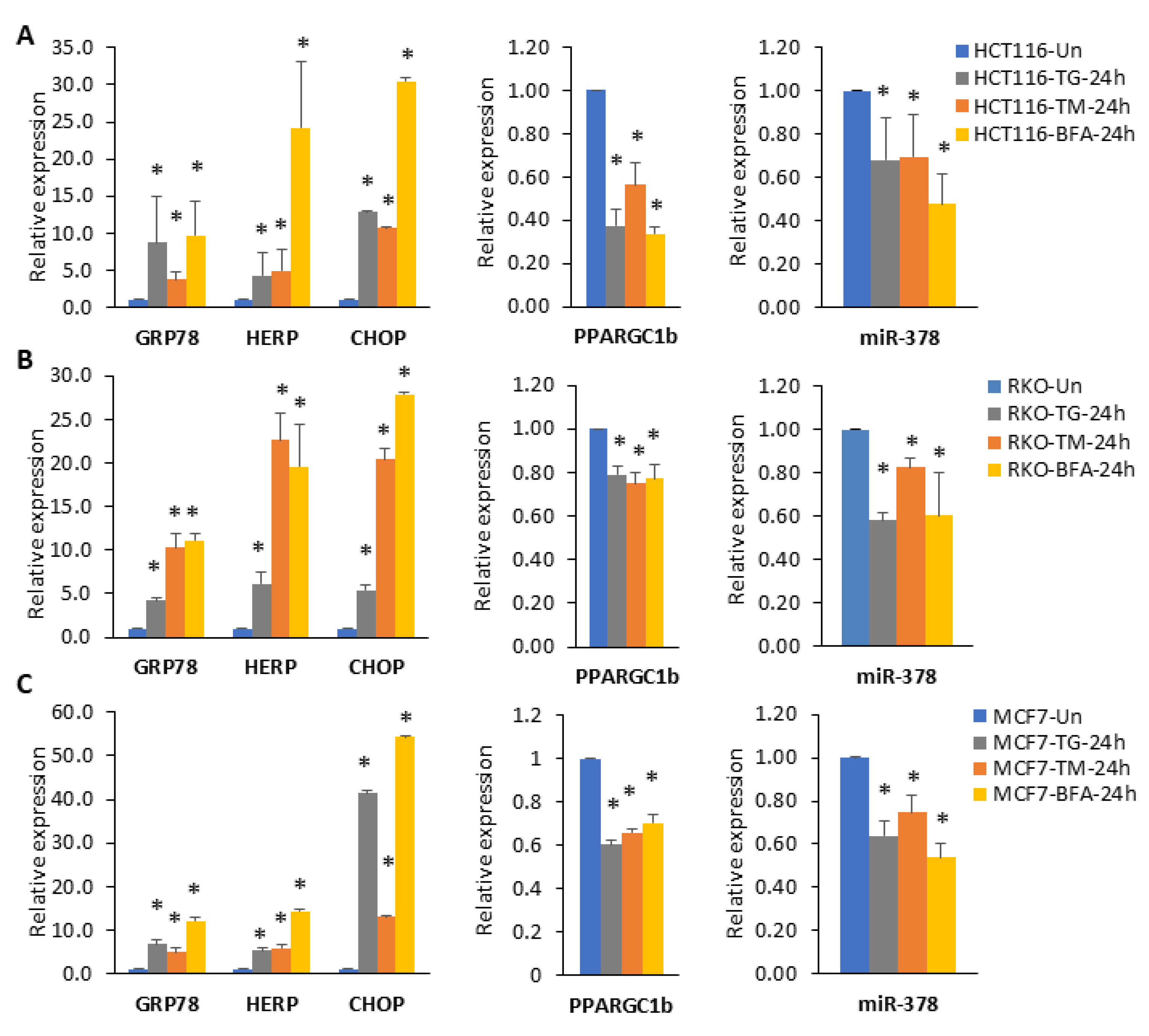
2.2. miR-378 Is Downregulated during Conditions of UPR
2.3. XBP1 Is Required for Downregulation of miR-378
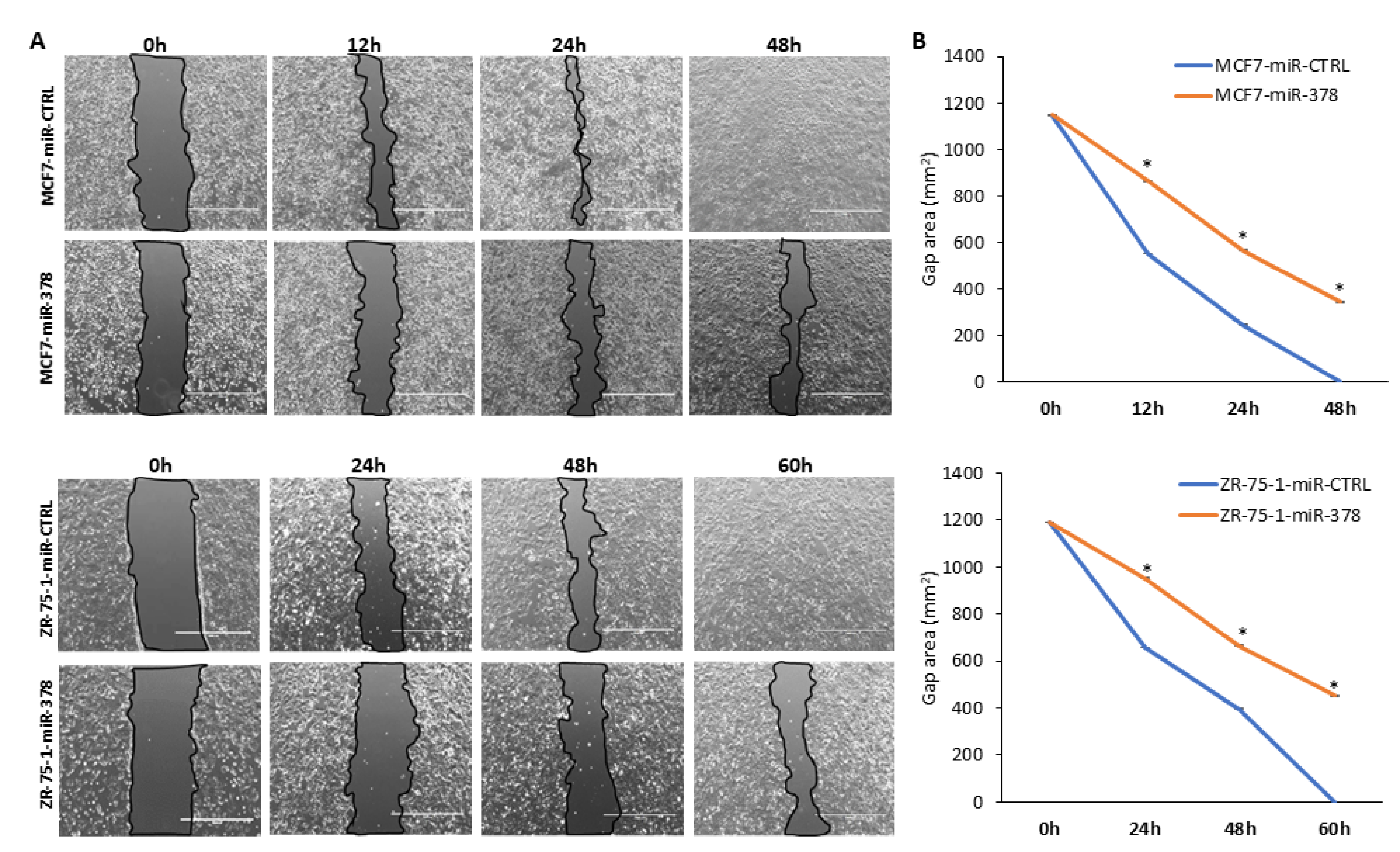
2.4. miR-378 Reduces Cell Proliferation and Migration of Luminal Cells
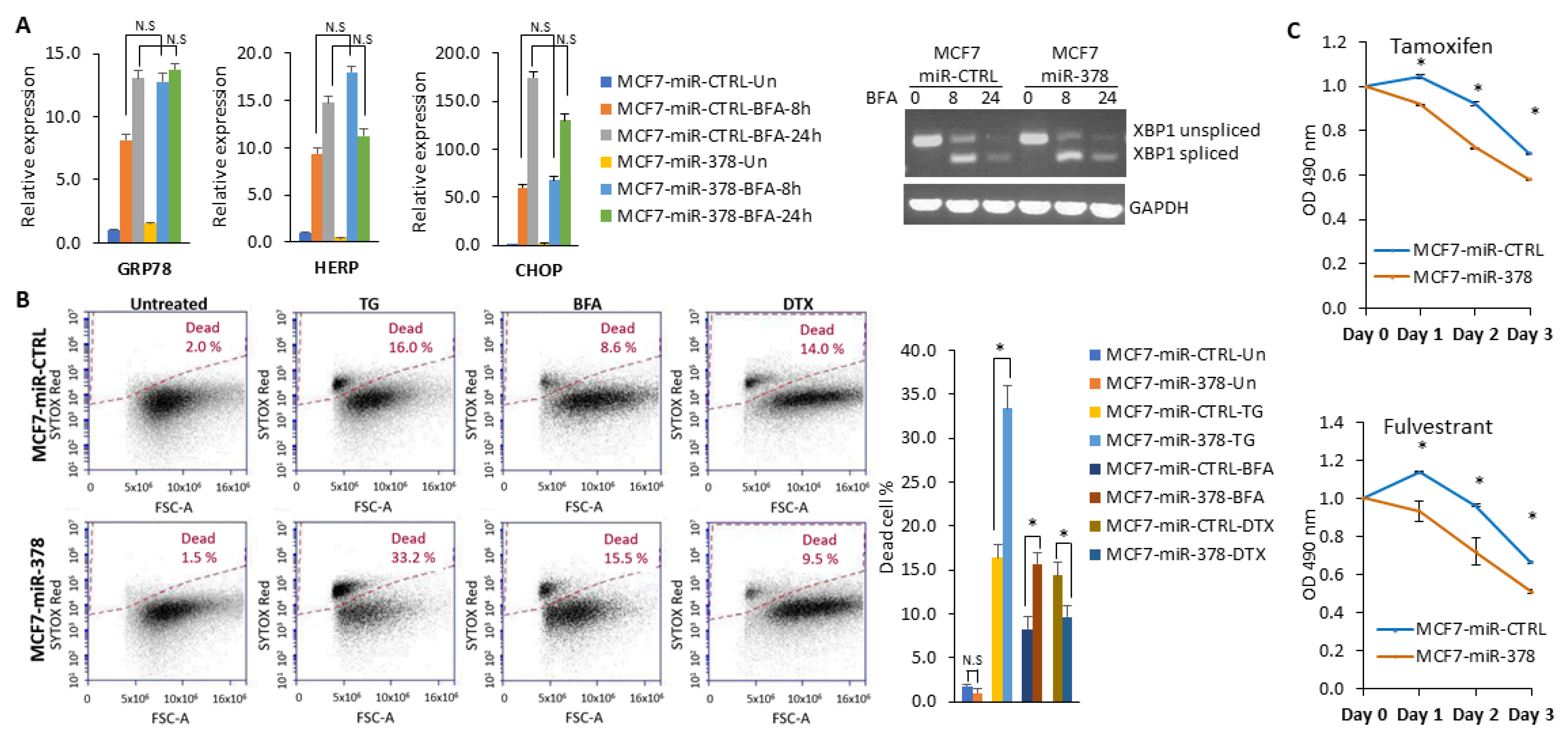
2.5. miR-378 Sensitises Cells to Anti-Estrogens and EnR Stress-Induced Cell Death
2.6. miR-378 Dependent Gene Signature Is Associated with Good Outcome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
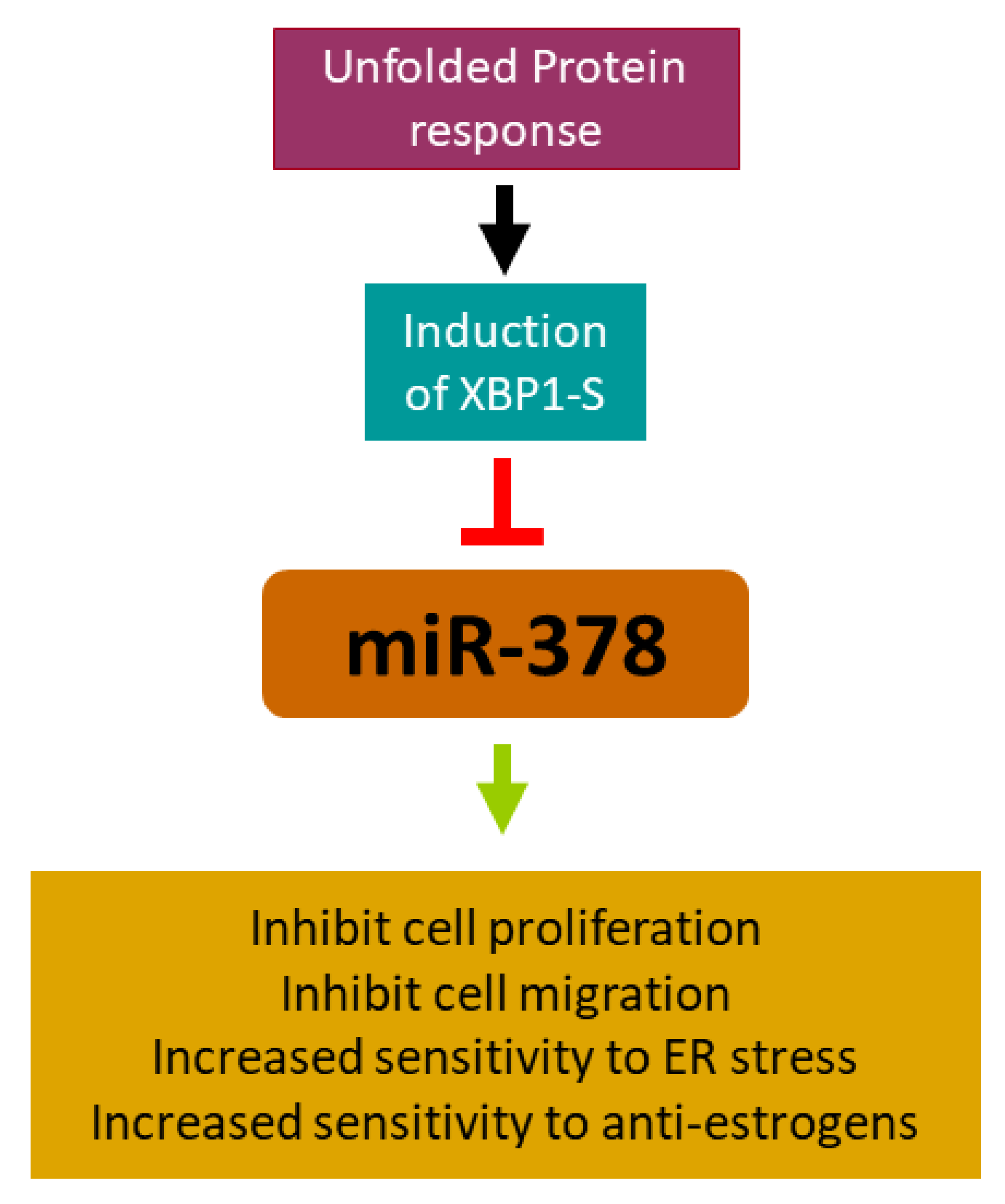
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
References
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Shang, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, J.; Sha, B. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathways: Activation and Diseases. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, S.J.; Chambers, J.E.; Ron, D. Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 21, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Axten, J.M.; Patterson, J.B. Pharmacological targeting of the unfolded protein response for disease intervention. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 764–775, Correction in 2019, 15, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Martinon, F.; Rodriguez, D.; Glimcher, L.H. The Unfolded Protein Response: Integrating Stress Signals through the Stress Sensor Ire1 Alpha. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1219–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Yu, C.; Yin, F.; Xu, W.; Pan, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, T.; Chen, S.; Luo, W.; Su, T.; et al. IRE1α-XBP1 regulates PDK1-dependent induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 421, 113376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Yan, W.; Ruan, J.; Fang, M.; Yu, C.; Du, S.; Rai, G.; Tao, D.; Henderson, M.J.; Fang, S. XBP1 variant 1 (Xv1) promotes mitosis of cancer cells involving upregulation of the polyglutamylase TTLL6. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ma, R.; Li, G. Dual Role of Inositol-requiring Enzyme 1α–X-box Binding protein 1 Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuroscience 2022, 505, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karali, E.; Bellou, S.; Stellas, D.; Klinakis, A.; Murphy, C.; Fotsis, T. VEGF Signals through ATF6 and PERK to Promote Endothelial Cell Survival and Angiogenesis in the Absence of ER Stress. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Chen, X.; Lee, A.-H.; Glimcher, L.H. TLR activation of the transcription factor XBP1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruska, N.; Zheng, X.; Yang, X.; Helferich, W.G.; Shapiro, D.J. Anticipatory estrogen activation of the unfolded protein response is linked to cell proliferation and poor survival in estrogen receptor α-positive breast cancer. Oncogene 2014, 34, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, K.; Noblin, D.J.; Serebrenik, Y.V.; Adams, A.; Zhao, C.; Crews, C.M. Targeted protein destabilization reveals an estrogen-mediated ER stress response. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, J.S.; Liu, X.S.; Brodsky, A.S.; Li, W.; Meyer, C.A.; Szary, A.J.; Eeckhoute, J.; Shao, W.; Hestermann, E.V.; Geistlinger, T.R.; et al. Chromosome-Wide Mapping of Estrogen Receptor Binding Reveals Long-Range Regulation Requiring the Forkhead Protein FoxA1. Cell 2005, 122, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Sharma, C.G.; Jordan, V.C. Estrogen regulation of X-box binding protein-1 and its role in estrogen induced growth of breast and endometrial cancer cells. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2010, 2, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, B.P.; Riggins, R.B.; Shajahan, A.N.; Klimach, U.; Wang, A.; Crawford, A.C.; Zhu, Y.; Zwart, A.; Wang, M.; Clarke, R. Human X-Box binding protein-1 confers both estrogen independence and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cell lines. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 4013–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ramirez, L.; Cao, H.; Nelson, D.; Hammond, E.; Lee, A.-H.; Yoshida, H.; Mori, K.; Glimcher, L.H.; Denko, N.C.; Giaccia, A.J.; et al. XBP1 Is Essential for Survival under Hypoxic Conditions and Is Required for Tumor Growth. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 5943–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.P.; Barraclough, D.L.; Stewart, C.; Joyce, K.A.; Eccles, R.M.; Barraclough, R.; Rudland, P.S.; Sibson, D.R. Expression and splicing of the unfolded protein response gene XBP-1 are significantly associated with clinical outcome of endocrine-treated breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Ruan, S.; Wang, M.; Ye, D.; Fan, N.; Meng, Q.; Tian, B.; Huang, T. A novel chemical, STF-083010, reverses tamoxi-fen-related drug resistance in breast cancer by inhibiting IRE1/XBP1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40692–40703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Miller, N.; Kerin, M.; Callagy, G.; Gupta, S. NCOA3 coactivator is a transcriptional target of XBP1 and regulates PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4 signalling in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5860–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Warri, A.; Jin, L.; Zwart, A.; Riggins, R.B.; Fang, H.B.; Clarke, R. NF-kappaB signaling is required for XBP1 (unspliced and spliced)-mediated effects on antiestrogen responsiveness and cell fate decisions in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, D.; Abbasi, B.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. XBP1 increases transactivation of somatic mutants of ESR1 and loss of XBP1 reverses endocrine resistance conferred by gain-of-function Y537S ESR1 mutation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, D.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. Targeting the IRE1-XBP1 axis to overcome endocrine resistance in breast cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Cancer Lett. 2020, 486, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, D.; Sultana, A.; Islam, N.; Cox, F.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. RRM2 and CDC6 are novel effectors of XBP1-mediated endocrine resistance and predictive markers of tamoxifen sensitivity. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Liang, R.; Lu, P.; Lai, L.; Zhu, X. Depicting the Implication of miR-378a in Cancers. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Ueno, T.; Suzuki, T.; Sato, W.; Shigekawa, T.; Osaki, A.; Saeki, T.; Berezikov, E.; Mano, H.; et al. miR-378a-3p modulates tamoxifen sensitivity in breast cancer MCF-7 cells through targeting GOLT1A. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearing, L.J.; Cumming, H.E.; Chapman, R.; Finkel, A.M.; Woodhouse, I.B.; Luu, K.; Gould, J.A.; Forster, S.C.; Hertzog, P.J. CiiiDER: A tool for predicting and analysing transcription factor binding sites. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0215495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Iliopoulos, D.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Lim, E.; Tam, W.L.; Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; et al. XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HIF1α pathway. Nature 2014, 508, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Zhou, C.; Han, S.; Hou, X.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-378 enhances migration and invasion in cervical cancer by directly targeting autophagy-related protein 12. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6319–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, M.; Cao, W.; Yang, Z. miR-378 functions as an onco-miRNA by targeting the ST7L/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cervical cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.X.; Cui, F.; Qu, D.; Sun, R.Y.; Sun, P.; Chen, F.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Sun, H.-S. MiR-378 promotes the cell proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting FOXG1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.S.; Noor, S.M.; Nagoor, N.H. MiR-378 and MiR-1827 Regulate Tumor Invasion, Migration and Angiogenesis in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting RBX1 and CRKL, Respectively. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypek, K.; Tertil, M.; Golda, S.; Ciesla, M.; Weglarczyk, K.; Collet, G.; Guichard, A.; Kozakowska, M.; Boczkowski, J.; Was, H.; et al. Interplay Between Heme Oxygenase-1 and miR-378 Affects Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Growth, Vascularization, and Metastasis. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Gerweck, L.E.; Fukumura, D.; Loeffler, J.S.; Yang, B.B.; et al. MicroRNA-378 enhances radiation response in ectopic and orthotopic implantation models of glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 136, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Deng, Z.; Wang, C.-H.; Yang, B.B. MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20350–20355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Du, W.W.; Fang, L.; Shan, S.W.; Qian, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, W.; Ma, J.; Rutnam, Z.J.; Yang, B.B. The Intermediate Filament Vimentin Mediates MicroRNA miR-378 Function in Cellular Self-renewal by Regulating the Expression of the Sox2 Transcription Factor*. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.L.; Peng, X.H.; Zhao, F.P.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Chen, H.H.; Li, X.P. MicroRNA-378 functions as an onco-miR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing TOB2 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Kang, C. miR-378 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Ji, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Sun, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; et al. MicroRNA-378-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting BRAF. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, F.X.; Yu, M.J.; Xue, J.S.; Zhao, J.S. MicroRNA-378 inhibits cell growth and enhances L-OHP-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T. MiR-378 is an independent prognostic factor and inhibits cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgeris, M.; Stravodimos, K.; Scorilas, A. Loss of miR-378 in prostate cancer, a common regulator of KLK2 and KLK4, correlates with aggressive disease phenotype and predicts the short-term relapse of the patients. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.G.; Zhou, W.; Han, T.; Du, S.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, G.Y.; Kong, C.Z. MiR-378 suppresses prostate cancer cell growth through downregulation of MAPK1 in vitro and in vivo. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Xu, T.; Lu, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G. MicroRNA-378 regulates cell proliferation and migration by repressing RNF31 in pituitary adenoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, X.W.; Zhan, Y.B.; Bao, J.J.; Zhou, J.Q.; Zhang, F.J.; Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Regulation of UHRF1 by microRNA-378 modulates medulloblastoma cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3078–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Chi, J.; Wang, L. miR-378 inhibits cell growth and enhances apoptosis in human myelodysplastic syndromes. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, G.; Dragon, J.A.; Hong, D.; Messier, T.L.; Gordon, J.A.R.; Farina, N.H.; Boyd, J.R.; VanOudenhove, J.J.; Perez, A.W.; Zaidi, S.K.; et al. MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 8825–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winsel, S.; Mäki-Jouppila, J.; Tambe, M.; Aure, M.R.; Pruikkonen, S.; Salmela, A.-L.; Halonen, T.; Leivonen, S.-K.; Kallio, L.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; et al. Excess of miRNA-378a-5p perturbs mitotic fidelity and correlates with breast cancer tumourigenesis in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Barua, D.; Arabkari, V.; Islam, N.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. Hyperactivation of nuclear receptor coactivators induces PERK-dependent cell death. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 11707–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Read, D.; Gupta, A.; Ladilov, Y.; Samali, A.; Gupta, S. miRNA signature of unfolded protein response in H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.R.; Yu, J.; Shanker, K.; Deshpande, N.; Varambally, R.; Ghosh, D.; Barrette, T.; Pander, A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. ONCOMINE: A Cancer Microarray Database and Integrated Data-Mining Platform. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arabkari, V.; Barua, D.; Hossain, M.M.; Webber, M.; Smith, T.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. miRNA-378 Is Downregulated by XBP1 and Inhibits Growth and Migration of Luminal Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010186
Arabkari V, Barua D, Hossain MM, Webber M, Smith T, Gupta A, Gupta S. miRNA-378 Is Downregulated by XBP1 and Inhibits Growth and Migration of Luminal Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010186
Chicago/Turabian StyleArabkari, Vahid, David Barua, Muhammad Mosaraf Hossain, Mark Webber, Terry Smith, Ananya Gupta, and Sanjeev Gupta. 2024. "miRNA-378 Is Downregulated by XBP1 and Inhibits Growth and Migration of Luminal Breast Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010186
APA StyleArabkari, V., Barua, D., Hossain, M. M., Webber, M., Smith, T., Gupta, A., & Gupta, S. (2024). miRNA-378 Is Downregulated by XBP1 and Inhibits Growth and Migration of Luminal Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010186





