Establishment of the Myeloid TBX-Code Reveals Aberrant Expression of T-Box Gene TBX1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
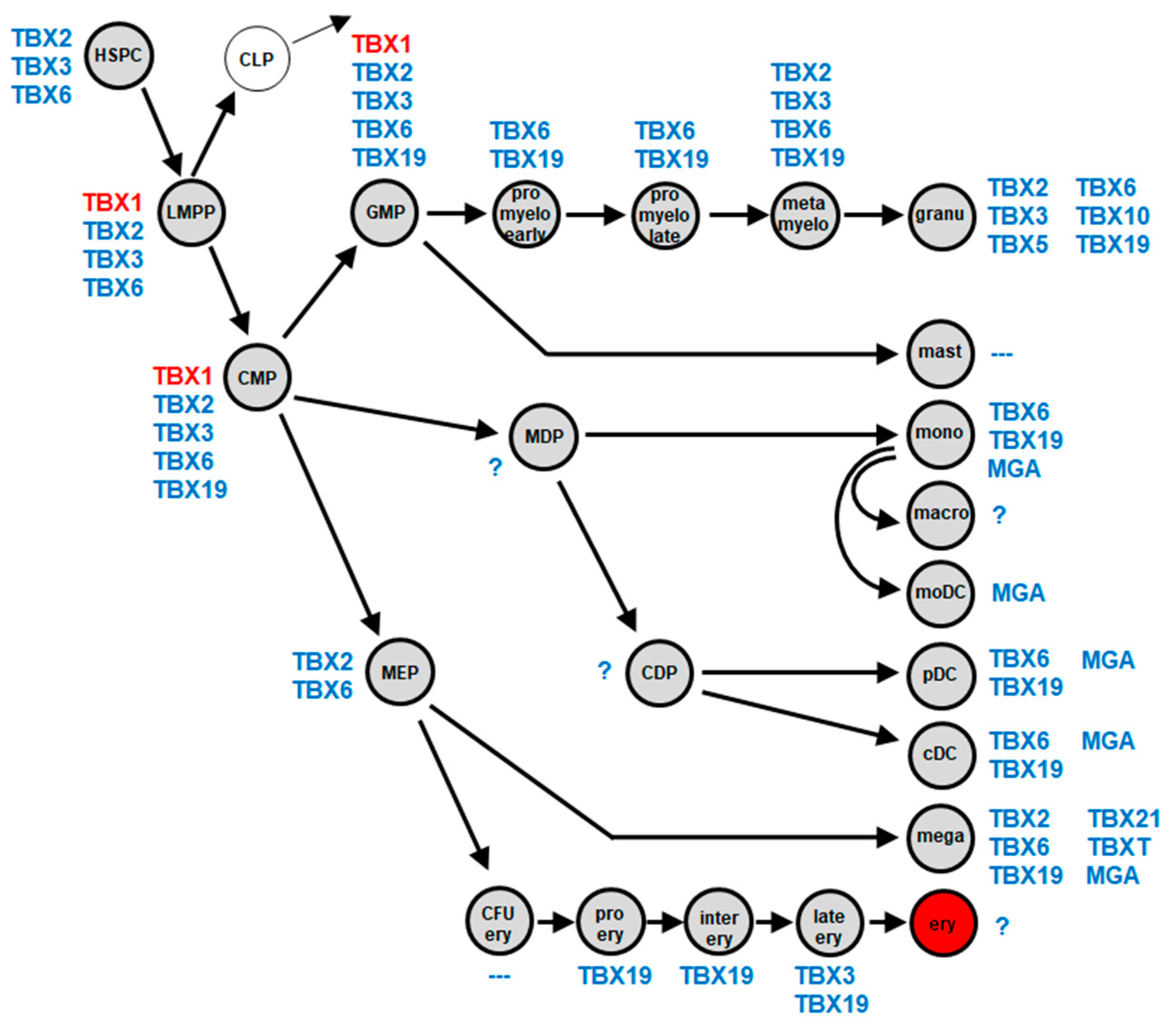
2.1. Myeloid TBX-Code
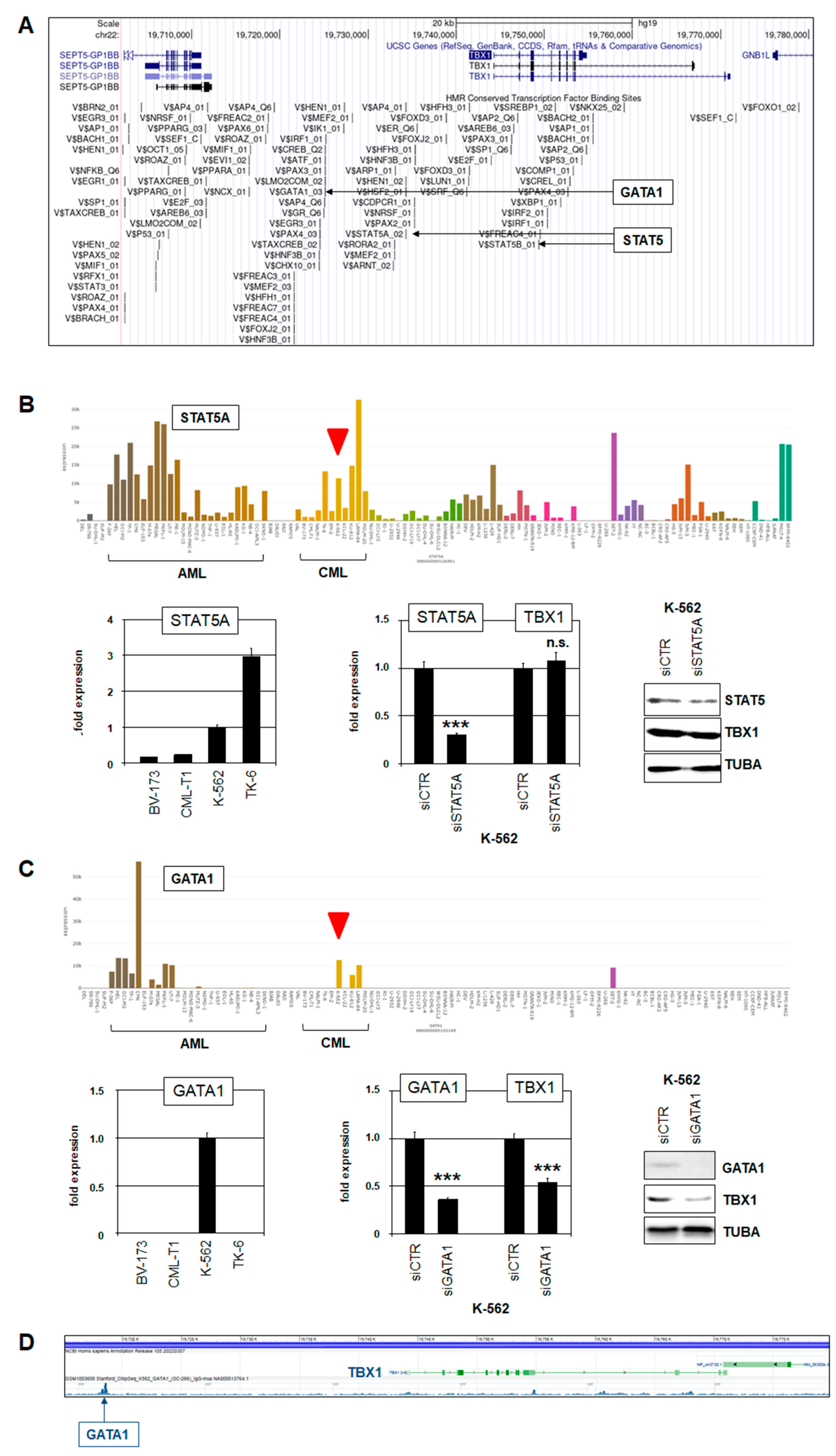
2.2. Expression of TBX1 in Myeloid Malignancies
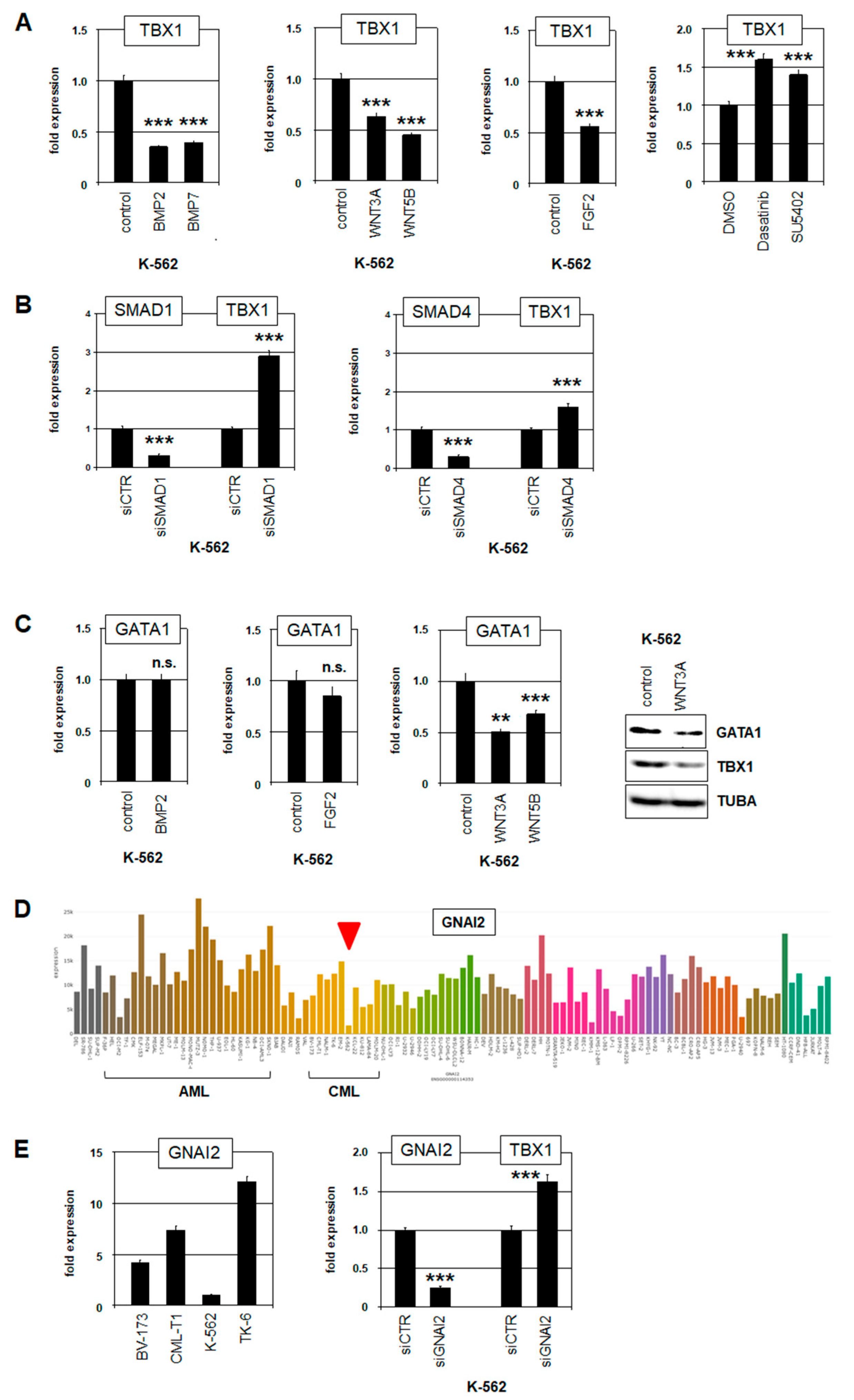
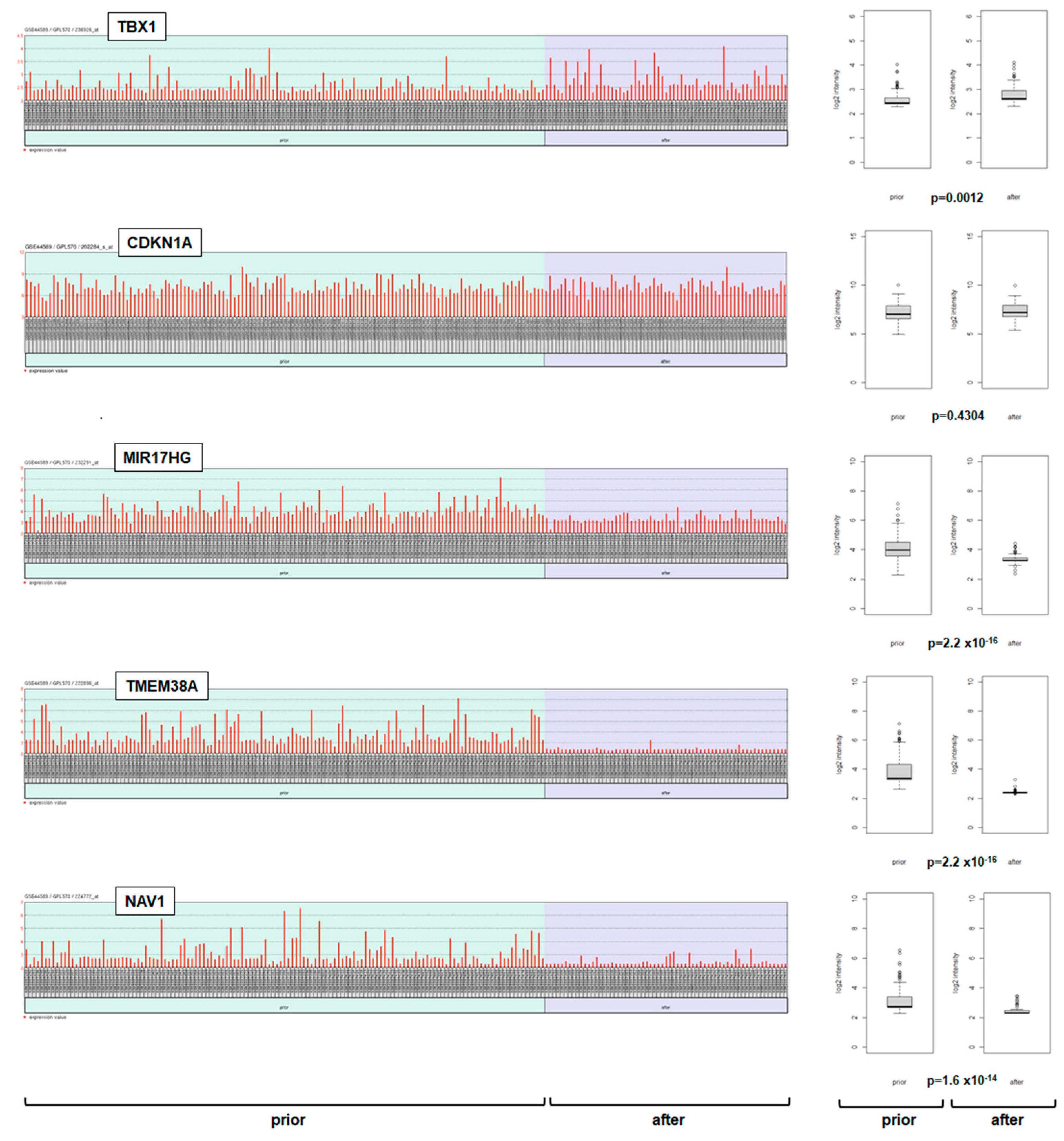
2.3. Deregulation of TBX1 in CML
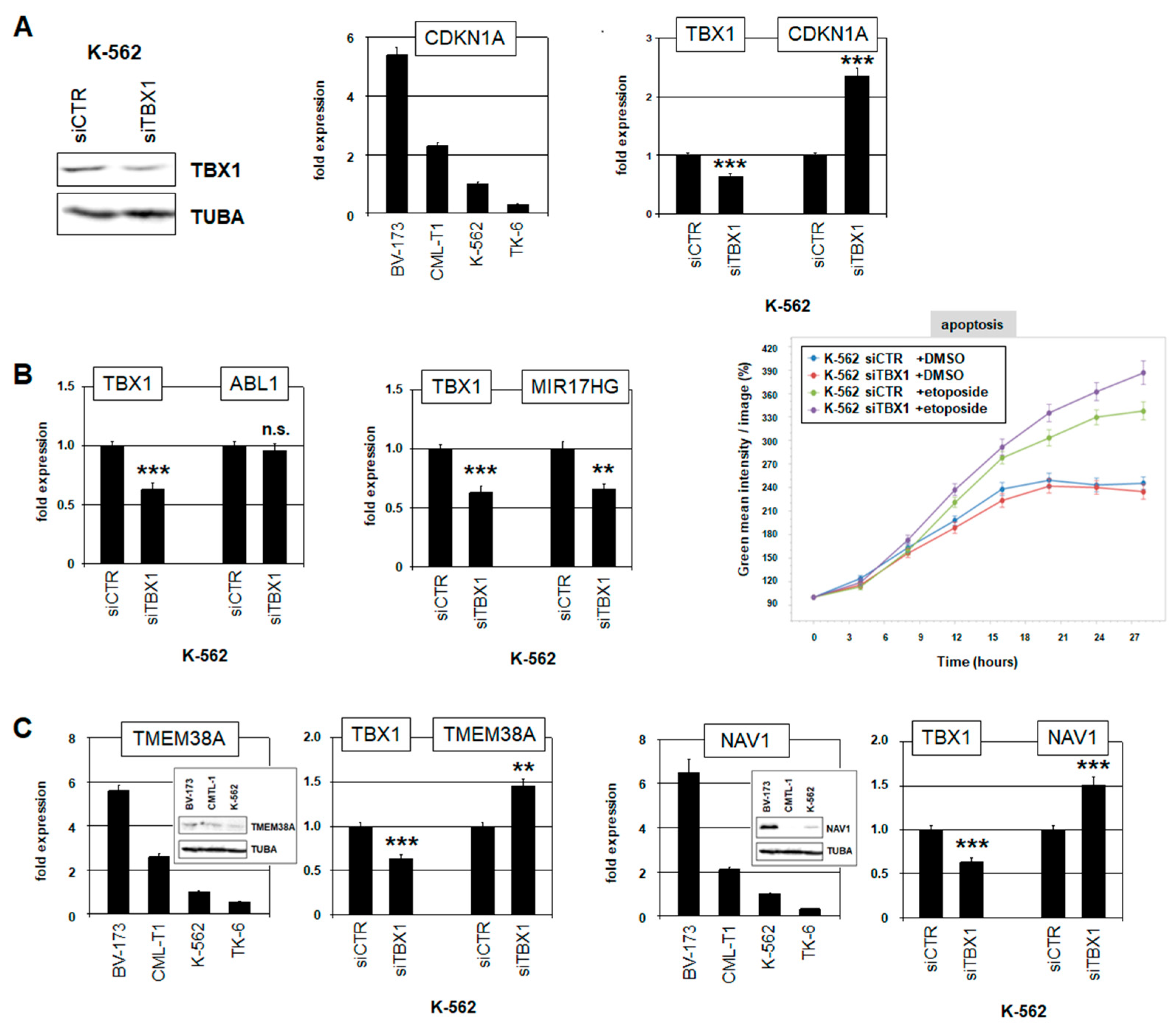
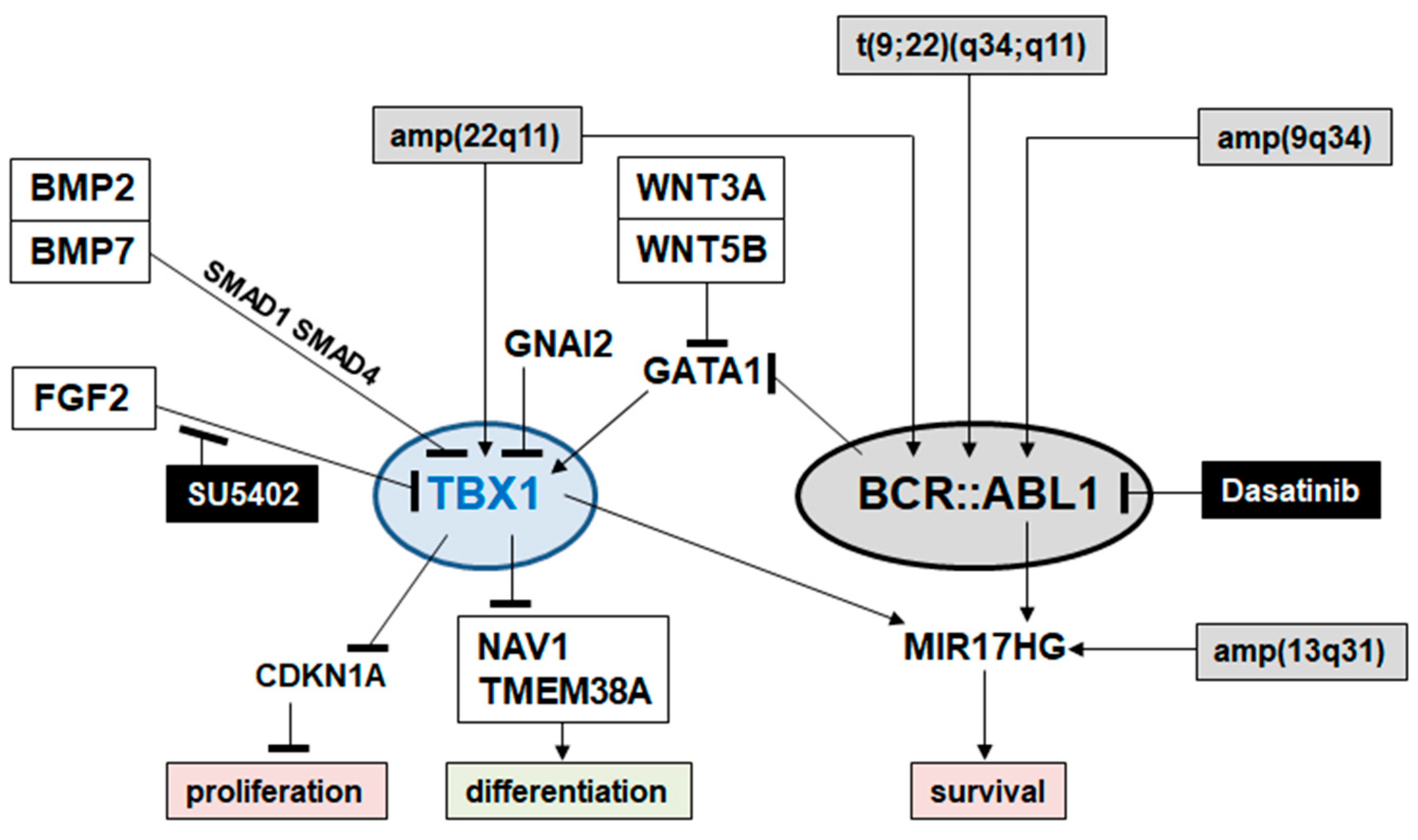
2.4. Target Genes of TBX1 in CML
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatic Analyses of Gene Expression Data
4.2. Cell Lines and Treatments
4.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
4.4. Protein Analysis
4.5. Karyotyping and Genomic Profiling Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothenberg, E.V. Transcriptional Control of Early T and B Cell Developmental Choices. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 283–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.D. Transcriptional control of granulocyte and monocyte development. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6816–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avellino, R.; Delwel, R. Expression and regulation of C/EBPα in normal myelopoiesis and in malignant transformation. Blood 2017, 129, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T. GATA Transcription Factors: Basic Principles and Related Human Disorders. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 242, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, E.A. The role of HOX genes in myeloid leukemogenesis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2006, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Harada, Y.; Harada, H. Myeloid neoplasms and clonal hematopoiesis from the RUNX1 perspective. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, P.; Chan, S. PU.1: A crucial and versatile player in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 175, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotto, D.B.; Siena, Á.D.D.; de Barros, I.I.; Carvalho, S.D.C.E.S.; Muys, B.R.; Goedert, L.; Cardoso, C.; Plaça, J.R.; Ramão, A.; Squire, J.A.; et al. Contributions of HOX genes to cancer hallmarks: Enrichment pathway analysis and review. Tumor Biol. 2020, 42, 1010428320918050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S. NKL-Code in Normal and Aberrant Hematopoiesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, V.E. The T-box gene family: Emerging roles in development, stem cells and cancer. Development 2014, 141, 3819–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Brook, J.D.; Wilsdon, A. T-Box Genes in Human Development and Disease. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 122, 383–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W.J.; Qian, Y.Q.; Billeter, M.; Furukubo-Tokunaga, K.; Schier, A.F.; Resendez-Perez, D.; Affolter, M.; Otting, G.; Wüthrich, K. Homeodomain-DNA recognition. Cell 1994, 78, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, P.W.; Booth, H.A.F.; Bruford, E.A. Classification and nomenclature of all human homeobox genes. BMC Biol. 2007, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, M.; Seidman, J.G.; Müller, C.W. Structure of the DNA-bound T-box domain of human TBX3, a transcription factor re-sponsible for ulnar-mammary syndrome. Structure 2002, 10, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, V.; Conlon, F.L. The T-box family. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, reviews3008.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S. The Role of NKL Homeobox Genes in T-Cell Malignancies. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S. The Role of IRX Homeobox Genes in Hematopoietic Progenitors and Leukemia. Genes 2023, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S.; Meyer, C. Establishment of the TBX-code reveals aberrantly activated T-box gene TBX3 in Hodgkin lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.; Meyer, C.; Pommerenke, C. Establishment of the lymphoid ETS-code reveals deregulated ETS genes in Hodgkin lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.; Scherr, M.; MacLeod, R.A.F.; Pommerenke, C.; Koeppel, M.; Meyer, C.; Kaufmann, M.; Dallmann, I.; Drexler, H.G. NKL homeobox gene activities in normal and malignant myeloid cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S.; Pommerenke, C.; Meyer, C.; MacLeod, R.A.F. The Hematopoietic TALE-Code Shows Normal Activity of IRX1 in Myeloid Progenitors and Reveals Ectopic Expression of IRX3 and IRX5 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.L.; Szabo, S.J.; Glimcher, L.H. T-bet regulates IgG class switching and pathogenic autoantibody production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5545–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, M.J.; Weinmann, A.S.; Matsuda, J.L.; Salomon, R.; Farnham, P.J.; Biron, C.A.; Gapin, L.; Glimcher, L.H. T-bet regulates the terminal maturation and homeostasis of NK and Valpha14i NKT cells. Immunity 2004, 20, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Mesa, N.; Schroeder, J.-H.; Stolarczyk, E.; Gallagher, A.L.; Lo, J.W.; Bailey, C.; Campbell, L.; Sexl, V.; MacDonald, T.T.; Howard, J.K.; et al. T-bet controls intestinal mucosa immune responses via repression of type 2 innate lymphoid cell function. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Marotel, M.; Fauteux-Daniel, S.; Mathieu, A.; Viel, S.; Marçais, A.; Walzer, T. T-bet and Eomes govern differentiation and function of mouse and human NK cells and ILC1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, E.L.; Mullen, A.C.; Martins, G.A.; Krawczyk, C.M.; Hutchins, A.S.; Zediak, V.P.; Banica, M.; DiCioccio, C.B.; Gross, D.A.; Mao, C.A.; et al. Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin. Science 2003, 302, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.M.; Carty, S.A.; Kim, J.S.; Zou, T.; Smith-Garvin, J.; Alonzo, E.S.; Haimm, E.; Sant’angelo, D.B.; Koretzky, G.A.; Reiner, S.L.; et al. Requirements for Eomesodermin and Promyelocytic Leukemia Zinc Finger in the Development of Innate-Like CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4573–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.H.; Klawon, D.E.J.; Zeng, S.; Lee, V.; Socci, N.D.; Savage, P.A. Eomes identifies thymic precursors of self-specific memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.A.; Wong, P.; Schappe, T.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Cubitt, C.; Jaeger, N.; Lee, M.; Keppel, C.R.; Marin, N.D.; Foltz, J.A.; et al. Stage-Specific Requirement for Eomes in Mature NK Cell Homeostasis and Cytotoxicity. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernink, J.H.; Krabbendam, L.; Germar, K.; de Jong, E.; Gronke, K.; Kofoed-Nielsen, M.; Munneke, J.M.; Hazenberg, M.D.; Villaudy, J.; Buskens, C.J.; et al. Interleukin-12 and -23 Control Plasticity of CD127+ Group 1 and Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Intestinal Lamina Propria. Immunity 2015, 43, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Kumar, R.; Krause, D.S. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future. Cells 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G. Hematopoietic and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: Multi-Stability versus Lineage Restriction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochi, Y. Genetic landscape of chronic myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 117, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, J.; Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Short, N.J. Pathogenesis and management of accelerated and blast phases of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 37, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quentmeier, H.; Pommerenke, C.; Dirks, W.G.; Eberth, S.; Koeppel, M.; MacLeod, R.A.F.; Nagel, S.; Steube, K.; Uphoff, C.C.; Drexler, H.G. The LL-100 panel: 100 cell lines for blood cancer studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warsch, W.; Walz, C.; Sexl, V. JAK of all trades: JAK2-STAT5 as novel therapeutic targets in BCR-ABL1+ chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Fu, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Dou, L.; Gao, X.; Luo, X.; et al. BCR-ABL/GATA1/miR-138 mini circuitry contributes to the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2014, 33, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Fang, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Gαi2 regulates the adult myogenesis of masticatory muscle satellite cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoupa, M.; Xavier, G.M.; Bryan, S.; Theologidis, I.; Arno, M.; Cobourne, M.T. Gene expression profiling in the developing sec-ondary palate in the absence of Tbx1 function. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, N.N.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. The Multifaceted p21 (Cip1/Waf1/CDKN1A) in Cell Differentiation, Migration and Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, L.; Battmer, K.; Castoldi, M.; Schultheis, B.; Hochhaus, A.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Ganser, A.; Eder, M.; Scherr, M. Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 2007, 109, 4399–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, S.; Pommerenke, C.; MacLeod, R.A.; Meyer, C.; Kaufmann, M.; Drexler, H.G. The NKL-code for innate lymphoid cells reveals deregulated expression of NKL homeobox genes HHEX and HLX in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). Oncotarget 2020, 11, 3208–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, A.; Fulcoli, F.G.; Illingworth, E. Tbx1: Transcriptional and Developmental Functions. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 122, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klusóczki, Á.; Veréb, Z.; Vámos, A.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Wabitsch, M.; Bacso, Z.; Fésüs, L.; Kristóf, E. Differentiating SGBS adipocytes respond to PPARγ stimulation, irisin and BMP7 by functional browning and beige characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funato, N. Craniofacial Phenotypes and Genetics of DiGeorge Syndrome. J. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, C.; Nagaso, H.; Jin, H.; Frasch, M. Org-1, the Drosophila ortholog of Tbx1, is a direct activator of known identity genes during muscle specification. Development 2012, 139, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, C.; März, J.; Reim, I.; Frasch, M. Org-1-dependent lineage reprogramming generates the ventral longitudinal mus-culature of the Drosophila heart. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-H.; Norris, A.; Weiss, J.B.; Frasch, M. Jelly belly protein activates the receptor tyrosine kinase Alk to specify visceral muscle pioneers. Nature 2003, 425, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.R.; Martinelli, V.; Rinaldi, P.; Ciancia, R.; del Vecchio, L. GATA1 is overexpressed in patients with essential throm-bocythemia and polycythemia vera but not in patients with primary myelofibrosis or chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Yuan, X.; Racioppi, C.; Leslie, M.; Stutt, N.; Aleksandrova, A.; Christiaen, L.; Wilson, M.D.; Scott, I.C. GATA4/5/6 family transcription factors are conserved determinants of cardiac versus pharyngeal mesoderm fate. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabg0834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Fu, Q.; Li, F.; Chen, S.; Sun, K.; Xu, R.; Xu, Y. Variants in a cis-regulatory element of TBX1 in conotruncal heart defect patients impair GATA6-mediated transactivation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompouki, E.; Bowman, T.V.; Lawton, L.N.; Fan, Z.P.; Wu, D.C.; DiBiase, A.; Martin, C.S.; Cech, J.N.; Sessa, A.K.; Leblanc, J.L.; et al. Lineage regulators direct BMP and Wnt pathways to cell-specific programs during differentiation and regeneration. Cell 2011, 147, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, F.; Rudat, C.; Kispert, A. Mechanisms of T-box gene function in the developing heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H. MicroRNAs and lymphomagenesis: A functional review. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 160, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happo, L.; Cragg, M.S.; Phipson, B.; Haga, J.M.; Jansen, E.S.; Herold, M.J.; Dewson, G.; Michalak, E.M.; Vandenberg, C.J.; Smyth, G.K.; et al. Maximal killing of lymphoma cells by DNA damage–inducing therapy requires not only the p53 targets Puma and Noxa, but also Bim. Blood 2010, 116, 5256–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, R.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, D.; Cvekl, A.; Morrow, B.E. Mammalian TBX1 Preferentially Binds and Regulates Downstream Targets Via a Tandem T-site Repeat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcoli, F.G.; Franzese, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Angelini, C.; Baldini, A. Rebalancing gene haploinsufficiency in vivo by targeting chromatin. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, A.; Lin, P.-H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, J. TRIC-A regulates intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. Pflügers Arch. 2021, 473, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwocka, K.; Vejda, S.; Cotter, T.G.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; McKenna, S.L. Bcr-Abl reduces endoplasmic reticulum releasable calcium levels by a Bcl-2–independent mechanism and inhibits calcium-dependent apoptotic signaling. Blood 2006, 107, 4003–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.I.; de Las Heras, J.I.; Czapiewski, R.; Lê Thành, P.; Booth, D.G.; Kelly, D.A.; Webb, S.; Kerr, A.R.W.; Schirmer, E.C. Tis-sue-Specific Gene Repositioning by Muscle Nuclear Membrane Proteins Enhances Repression of Critical Developmental Genes during Myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, R.M.; Hevner, R.F.; Halpain, S. The Neuron Navigators: Structure, function, and evolutionary history. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1099554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Cwynarski, K.; Entwistle, A.; Marelli-Berg, F.; Dazzi, F.; Simpson, E.; Goldman, J.M.; Melo, J.V.; Lechler, R.I.; Bellantuono, I.; et al. Dendritic cells from CML patients have altered actin organization, reduced antigen processing, and impaired migration. Blood 2003, 101, 3560–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLeod, R.A.F.; Kaufmann, M.; Drexler, H.G. Cytogenetic harvesting of commonly used tumor cell lines. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagel, S.; Haake, J.; Pommerenke, C.; Meyer, C.; MacLeod, R.A.F. Establishment of the Myeloid TBX-Code Reveals Aberrant Expression of T-Box Gene TBX1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010032
Nagel S, Haake J, Pommerenke C, Meyer C, MacLeod RAF. Establishment of the Myeloid TBX-Code Reveals Aberrant Expression of T-Box Gene TBX1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagel, Stefan, Josephine Haake, Claudia Pommerenke, Corinna Meyer, and Roderick A. F. MacLeod. 2024. "Establishment of the Myeloid TBX-Code Reveals Aberrant Expression of T-Box Gene TBX1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010032
APA StyleNagel, S., Haake, J., Pommerenke, C., Meyer, C., & MacLeod, R. A. F. (2024). Establishment of the Myeloid TBX-Code Reveals Aberrant Expression of T-Box Gene TBX1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010032





