Plasma Circular-RNA 0005567 as a Potential Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
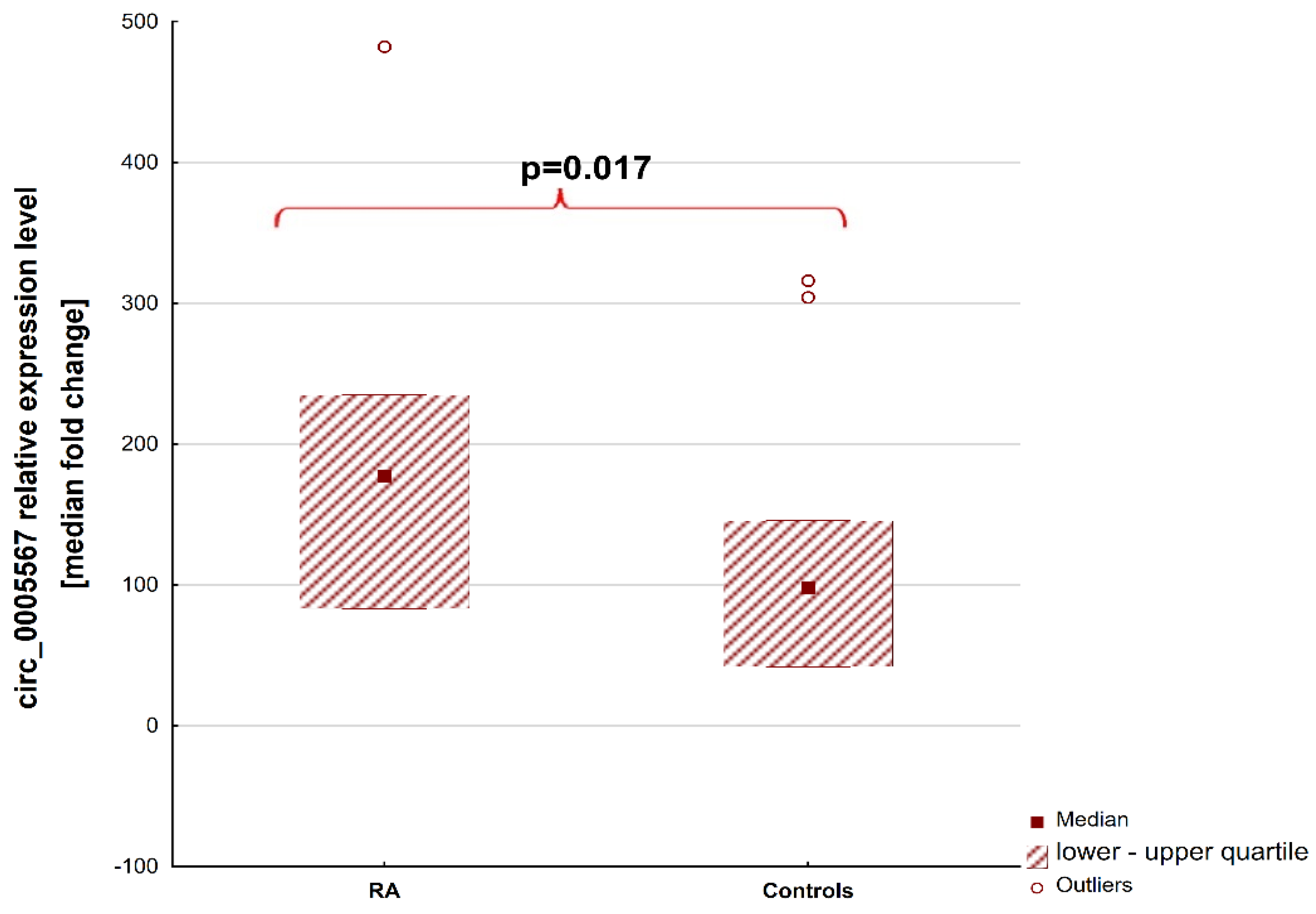
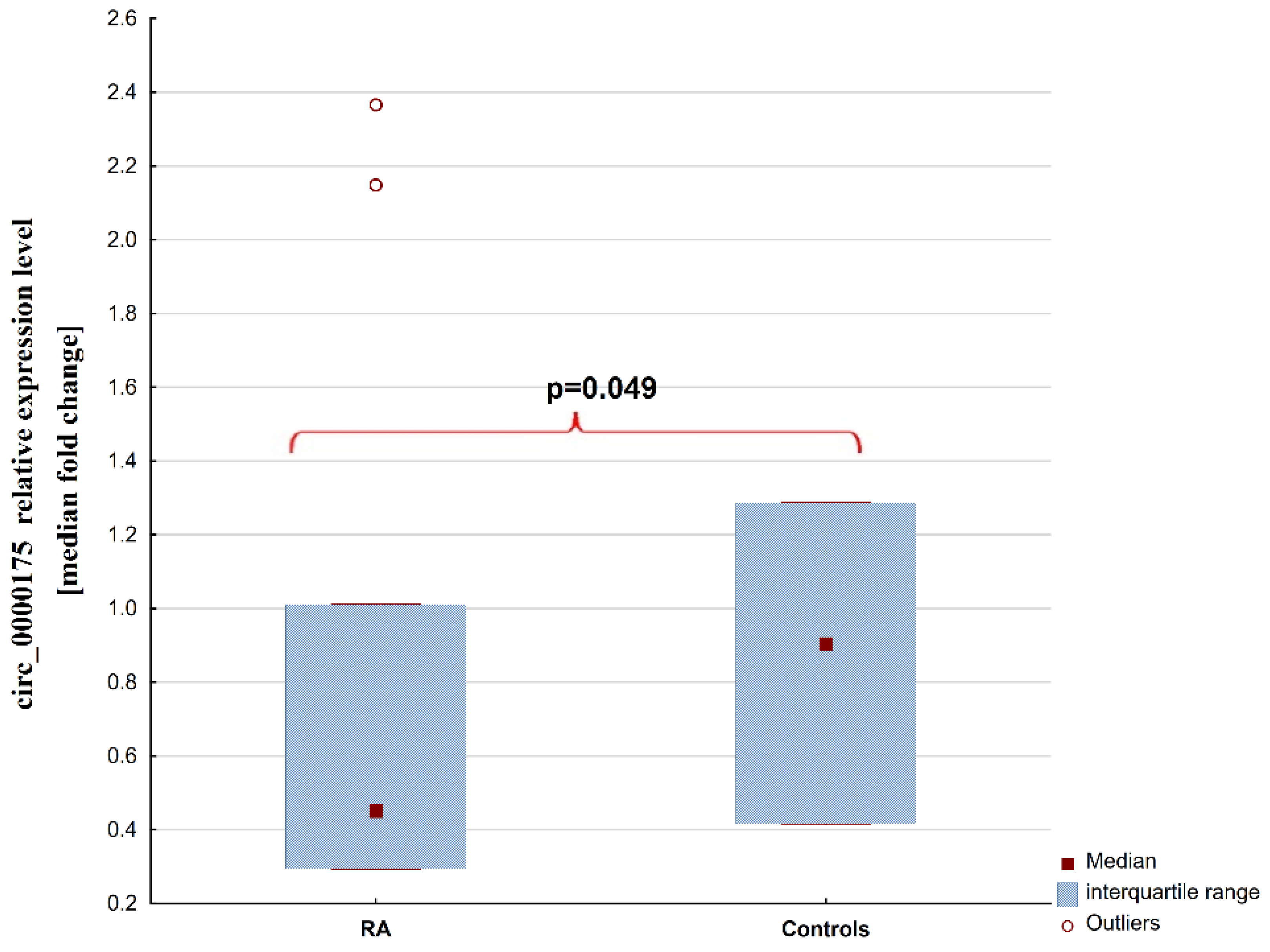
2. Results
2.1. Patients
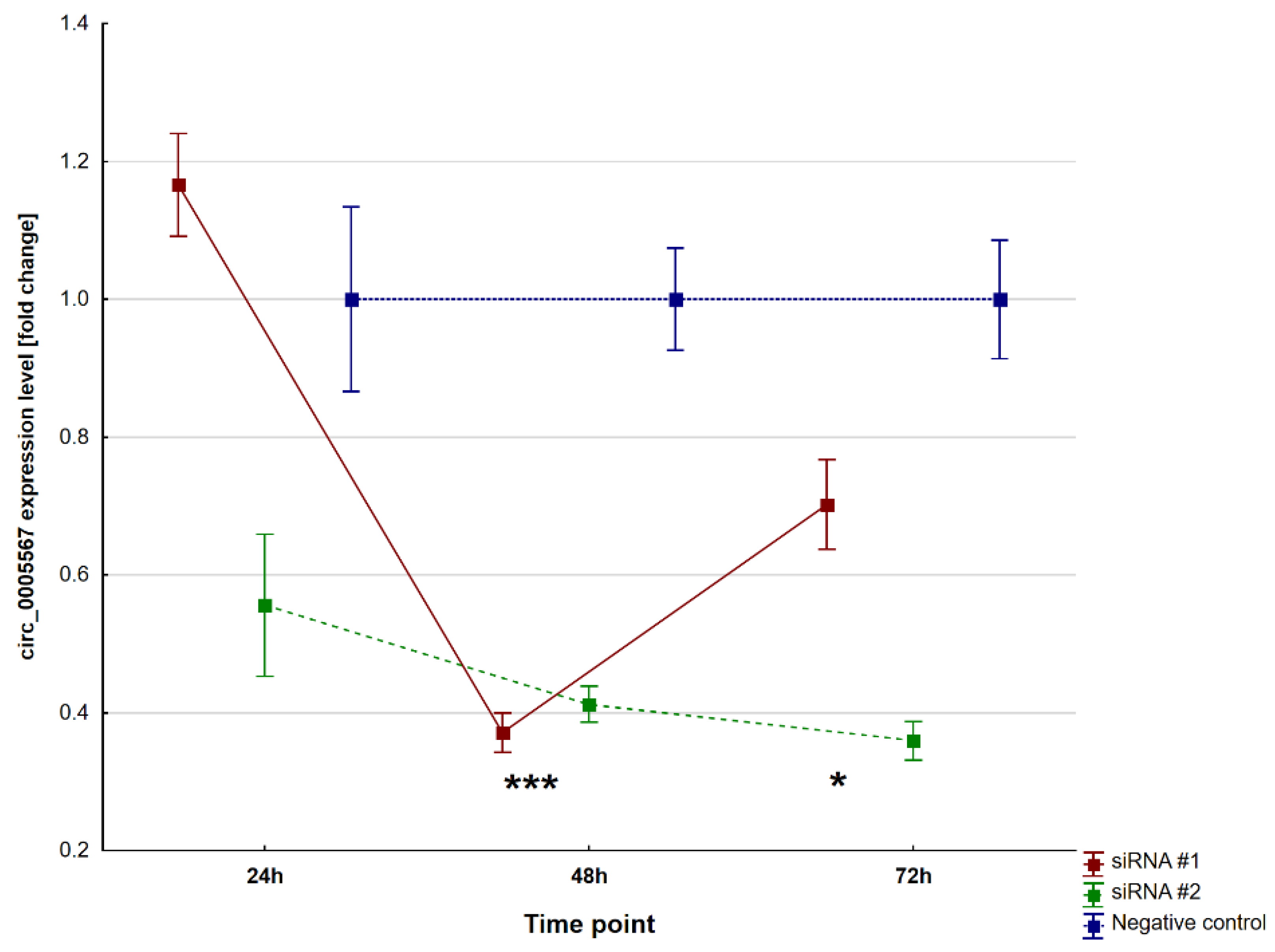
2.2. Circ_0005567 Silencing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Circular-RNA Analysis in Plasma Samples
4.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.4. Interactions between circRNA, microRNA, and mRNA
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Yao, F.; Rao, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.; Luo, Q. Circular RNAs hsa-circ0000175 and hsa-circ0044235 in plasma are novel biomarkers for new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmunity 2021, 54, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Yang, J.; Lu, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z. Non-coding RNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Q.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Liang, R.; Zhao, J.; Yang, M. Identification of Circular RNAs Circ_0005008 and Circ_0005198 in Plasma as Novel Biomarkers for New-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 722017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolcino, M.; Tinazzi, E.; Puccetti, A.; Lunardi, C. Long Non-Coding RNAs Target Pathogenetically Relevant Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2019, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, M.; Eghtedarian, R.; Dinger, M.E.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs in Rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofigh, R.; Hosseinpourfeizi, M.; Baradaran, B.; Teimourian, S.; Safaralizadeh, R. Rheumatoid arthritis and non-coding RNAs; how to trigger inflammation. Life Sci. 2023, 315, 121367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, F.; Wu, L.; Cao, H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, W. The emerging landscape of circular RNAs in immunity: Breakthroughs and challenges. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, F. Current Status of Functional Studies on Circular RNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Potential Role as Diagnostic Biomarkers. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zeng, L.; Zeng, L.; Rao, J.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Expression and clinical significance of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0000175 and hsa_circ_0008410 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z. Clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis patients with peripheral neuropathy and potential related risk factors. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarz, B.; Ciesla, M.; Dryglewska, M.; Rosenthal, A.K.; Majdan, M. Hypermethylation of the miR-155 gene in the whole blood and decreased plasma level of miR-155 in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; Rong, G.; Tang, Z.; Gui, B. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 8920–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; Rong, G.; Tang, Z.; Gui, B. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, P. Pharmacogenetics of rheumatoid arthritis: Potential targets from susceptibility genes and present therapies. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2010, 3, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequerré, T.; Gauthier-Jauneau, A.-C.; Bansard, C.; Derambure, C.; Hiron, M.; Vittecoq, O.; Daveau, M.; Mejjad, O.; Daragon, A.; Tron, F.; et al. Gene profiling in white blood cells predicts infliximab responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khansai, M.; Phitak, T.; Klangjorhor, J.; Udomrak, S.; Fanhchaksai, K.; Pothacharoen, P.; Kongtawelert, P. Effects of sesamin on primary human synovial fibroblasts and SW982 cell line induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha as a synovitis-like model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Yoo, D.-H.; Kang, T.-Y. Validity of SW982 synovial cell line for studying the drugs against rheumatoid arthritis in fluvastatin-induced apoptosis signaling model. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Lyu, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, Z.; Yang, N.; Zheng, Z.; et al. miR-194 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal pigment epithelial cells by directly targeting ZEB1. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.-C.; Kang, I.-H.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-H.; Koh, J.-T. MicroRNA-194 reciprocally stimulates osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis via regulating COUP-TFII expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Rao, X.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. MicroRNA–Messenger RNA Regulatory Network Mediates Disrupted TH17 Cell Differentiation in Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 824209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Zuo, Q. miR-194-5p inhibits LPS-induced astrocytes activation by directly targeting neurexophilin 1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 471, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-194 reduces inflammatory response and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells permeability through suppression of TGF-β/SMAD pathway by inhibiting THBS1 in chronic idiopathic urticaria. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.C.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Sánchez-Corona, J.; Castillo-Ortiz, J.D.; Castañeda-Sánchez, J.J.; Bastian, Y.; Romo-García, M.F.; Ochoa-González, F.; Monsivais-Urenda, A.E.; González-Amaro, R.; et al. Analysis of miRNA expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis during remission and relapse after a 5-year trial of tofacitinib treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 63, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsson, M.C.; Silfverswärd, S.T.; Nadali, M.; Turkkila, M.; Svensson, M.N.; Jonsson, I.-M.; Andersson, K.M.; Bokarewa, M.I. IGF-1R signalling contributes to IL-6 production and T cell dependent inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhartz, C.; Heesel, B.; Sasse, J.; Hemmann, U.; Landgraf, C.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Horn, F.; Heinrich, P.C.; Graeve, L. Differential activation of acute phase response factor/STAT3 and STAT1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. I. Definition of a novel phosphotyrosine motif mediating STAT1 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12991–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Arakawa, F.; Higuchi, F.; Ishibashi, Y.; Goto, M.; Sugita, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Niino, D.; Shimizu, K.; Aoki, R.; et al. Gene expression analysis of rheumatoid arthritis synovial lining regions by cDNA microarray combined with laser microdissection: Up-regulation of inflammation-associated STAT1, IRF1, CXCL9, CXCL10, and CCL5. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 41, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollereau, B.; Garijo, A.P.; Bergmann, A.; Miura, M.; Gerlitz, O.; Ryoo, H.D.; Steller, H.; Morata, G. Compensatory proliferation and apoptosis-induced proliferation: A need for clarification. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, F.L.P.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Morales-Prieto, D.M.; Ospina-Prieto, S.; Weber, M.; Photini, S.M.; Sass, N.; Daher, S.; Schleussner, E.; Markert, U.R. Involvement of STAT1 in proliferation and invasiveness of trophoblastic cells. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 17, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, S. Knockdown of miR-194-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in breast cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, F.; Fu, W.; Wang, X.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Yin, J.; Cai, L.; Tang, P.; et al. Increased expression of miR-194-5p through the circPVRL3/miR-194-5p/SOCS2 axis promotes proliferation and metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Han, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, K.; Wang, C.; Hai, P.; Bian, A.; Guo, R. Effect of miR-194-5p regulating STAT1/mTOR signaling pathway on the biological characteristics of ectopic endometrial cells from mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 6136–6148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orr, C.K.; Najm, A.; Young, F.; McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D.J. The Utility and Limitations of CRP, ESR and DAS28-CRP in Appraising Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokka, T.; Pincus, T. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, C-Reactive Protein, or Rheumatoid Factor Are Normal at Presentation in 35%–45% of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Seen Between 1980 and 2004: Analyses from Finland and the United States. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarz, B.; Ciesla, M.; Rosenthal, A.K.; Dryglewska, M.; Majdan, M. The value of anti-CarP and anti-PAD4 as markers of rheumatoid arthritis in ACPA/RF negative rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X21989868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.C.; Dudekula, D.B.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Analysis of Circular RNAs Using the Web Tool Cir-cInteractome. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1724, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudekula, D.B.; Panda, A.C.; Grammatikakis, I.; De, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. CircInteractome: A web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieśla, M.; Kolarz, B.; Majdan, M.; Darmochwał-Kolarz, D. Plasma micro-RNA-22 is associated with disease activity in well-established rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórski, R.; Cieśla, M.; Podgórska, D.; Bajorek, W.; Płonka, A.; Czarny, W.; Trybulski, R.; Król, P. Plasma microRNA-320a as a Potential Biomarker of Physiological Changes during Training in Professional Volleyball Players. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busk, P.K. A tool for design of primers for microRNA-specific quantitative RT-qPCR. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koressaar, T.; Remm, M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Li, J.; Huang, K.-Y.; Shrestha, S.; Hong, H.-C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.-G.; Jin, C.-N.; Yu, Y.; et al. miRTarBase 2020: Updates to the experimentally validated microRNA–target interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D148–D154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Yang, J.-C.; Chang, J.-B.; Tsai, S.-C. Down-Regulation of miR-194-5p for Predicting Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kang, Y.; Liao, W.-M.; Yu, L. MiR-194 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by targeting Sox5. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-C.; Chen, R.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.-H.; Luo, S.-Z.; Xu, M.-Y. MicroRNA-194 inactivates hepatic stellate cells and alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting AKT2. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4468–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, J. miR-194-5p protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via MAPK1/PTEN/AKT pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Jiang, S. miR-194-5p serves a suppressive role in human keloid fibroblasts via targeting NR2F2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xia, L.; Guo, Q.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qin, S.; Leng, W.; Li, D. Genome-wide association studies identify miRNA-194 as a prognostic biomarker for gastrointestinal cancer by targeting ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1025594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | RA Overall n = 45 | Controls n = 26 | p-Value RA Overall vs. HC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 50.3 ± 13.4 | 51.8 ± 7.8 | 0.6 |
| Females | 41 (91.1) | 21 (80.8) | 0.37 |
| Disease duration, years | 10.5 [5.5–16.5] | n/a | n/a |
| RF-positive | 29 (64.4) | none | n/a |
| ACPA-positive | 40 (88.9) | none | n/a |
| ESR, mm/h | 15 [8–51] | 16 [7.5–21.5] | 0.32 |
| DAS28 | 5.22 [2.11–6.12] | n/a | n/a |
| CRP, mg/dL | 5.84 [0.44–17.47] | 0.6 [0.2–1.97] | 0.009 |
| Number of swollen joints | 3 [0–7] | n/a | n/a |
| Number of painful joints | 4 [1–12] | n/a | n/a |
| VAS PGA | 39 [9–70] | n/a | n/a |
| VAS PhGA | 30 [5–60] | n/a | n/a |
| Characteristics | RA in High Disease Activity, n = 24 | RA in Remission n = 21 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 53.5 ± 13.05 | 46.7 ± 13.2 | 0.09 |
| Females | 21 (87.5) | 20 (95.2) | 0.7 |
| Disease duration, years | 10.5 [8–17.5] | 10 [3–16.5] | 0.37 |
| RF-positive | 19 (79.2) | 10 (47.6) | 0.058 |
| ACPA-positive | 22 (91.7) | 18 (85.7) | 0.87 |
| ESR, mm/h | 49.5 [28–67] | 7 [2–10] | <0.0001 |
| DAS28 | 6.1 [5.4–6.5] | 2.1 [1.8–2.4] | <0.0001 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 16.7 [8.5–24.4] | 0.4 [0.2–1.6] | <0.0001 |
| Number of swollen joints | 6.5 [5–10] | 0 [0–1] | <0.0001 |
| Number of painful joints | 11.5 [7–14] | 1 [0–2] | <0.0001 |
| VAS PGA | 69 [51.5–77.5] | 9 [3–15] | <0.0001 |
| VAS PhGA | 60 [49–70] | 5 [2–15] | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cieśla, M.; Darmochwal-Kolarz, D.A.; Kwaśniak, K.; Pałka, A.; Kolarz, B. Plasma Circular-RNA 0005567 as a Potential Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010417
Cieśla M, Darmochwal-Kolarz DA, Kwaśniak K, Pałka A, Kolarz B. Plasma Circular-RNA 0005567 as a Potential Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010417
Chicago/Turabian StyleCieśla, Marek, Dorota A. Darmochwal-Kolarz, Konrad Kwaśniak, Anna Pałka, and Bogdan Kolarz. 2024. "Plasma Circular-RNA 0005567 as a Potential Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010417
APA StyleCieśla, M., Darmochwal-Kolarz, D. A., Kwaśniak, K., Pałka, A., & Kolarz, B. (2024). Plasma Circular-RNA 0005567 as a Potential Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010417







