Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Maximal Load Capacity
2.2. Body Composition and Caloric Intake of Mice after 8 Weeks of ST
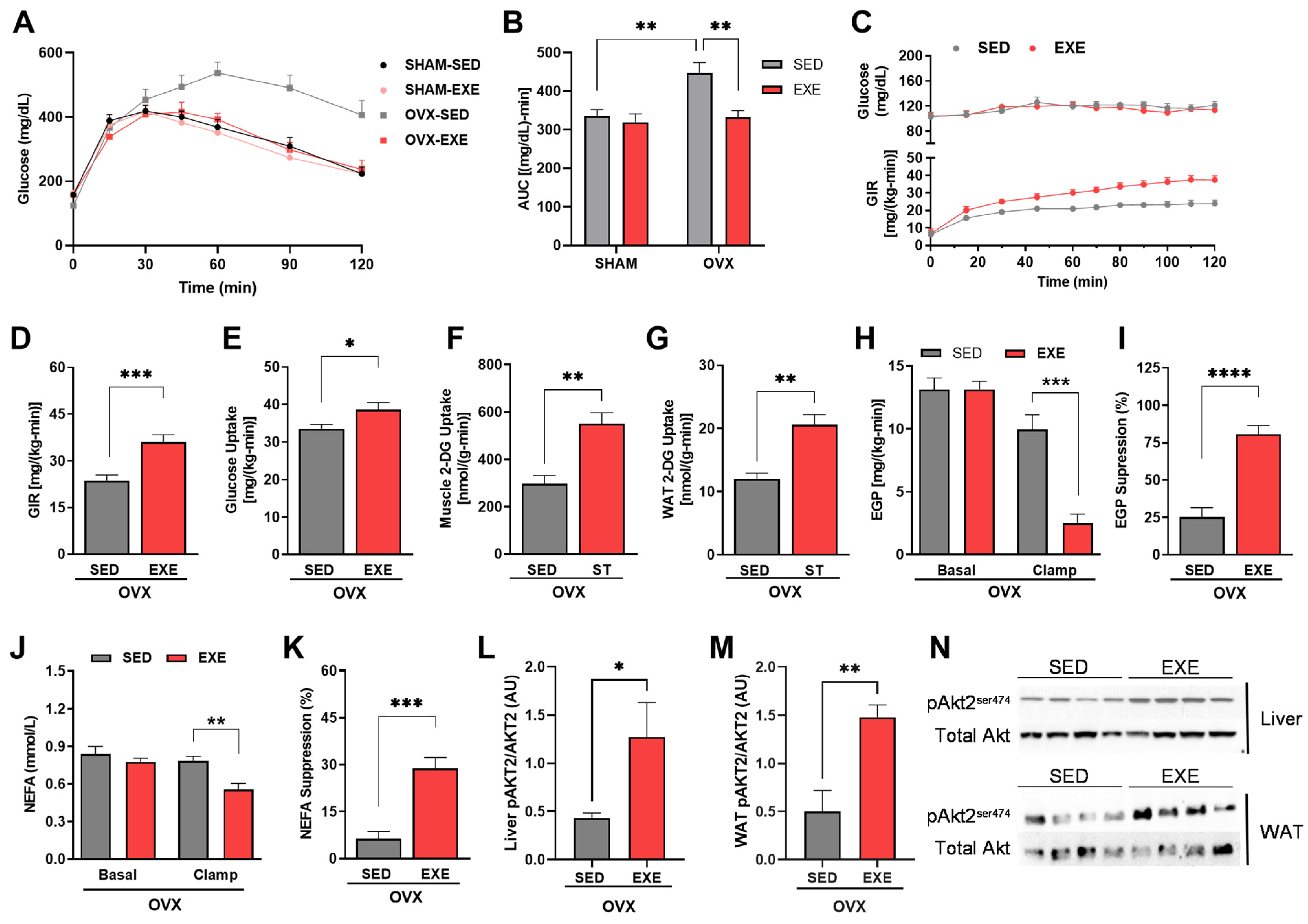
2.3. ST Improves Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity in Ovariectomized Mice
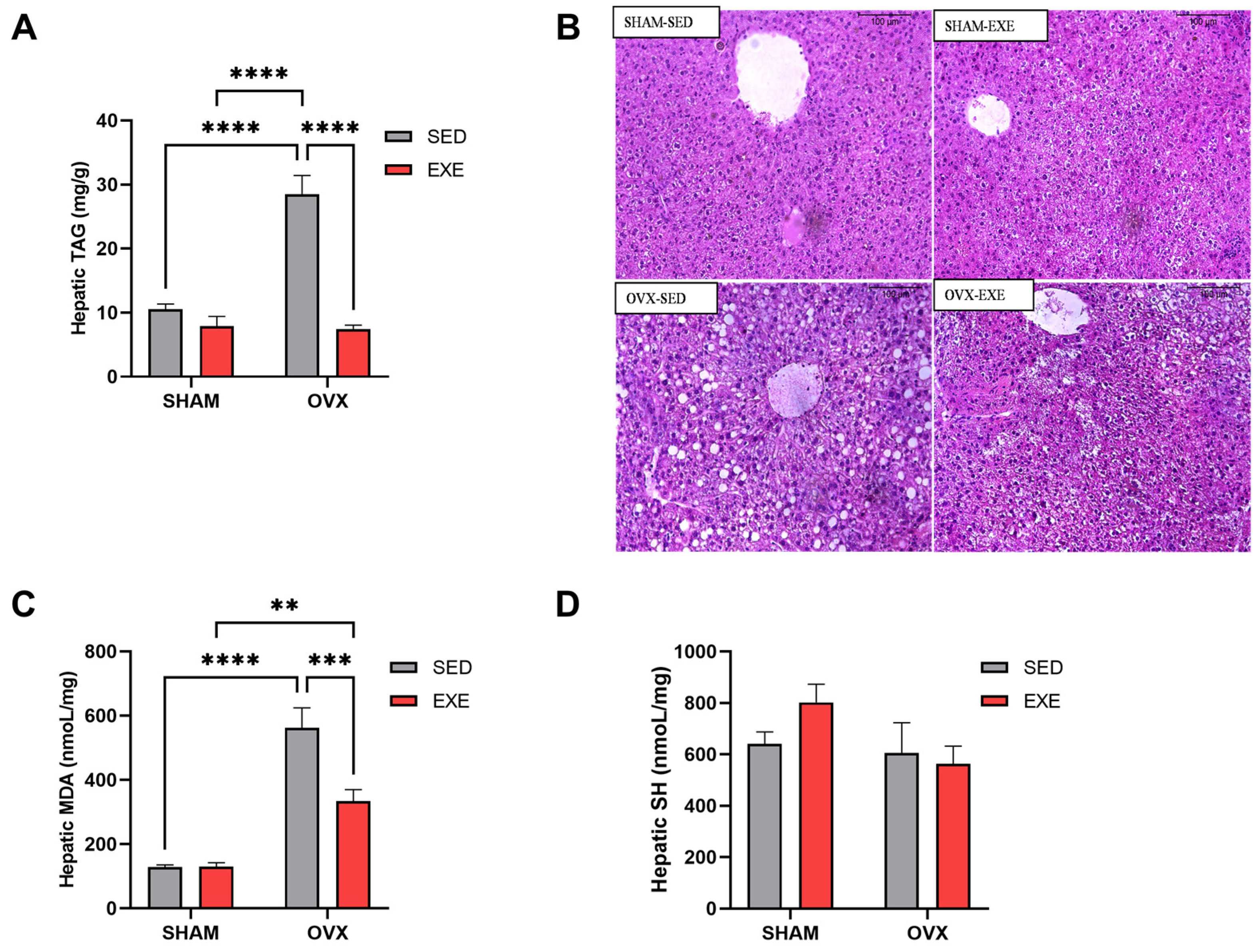
2.4. Lipid Profile and Oxidative Stress in the Liver after 8 Weeks of ST
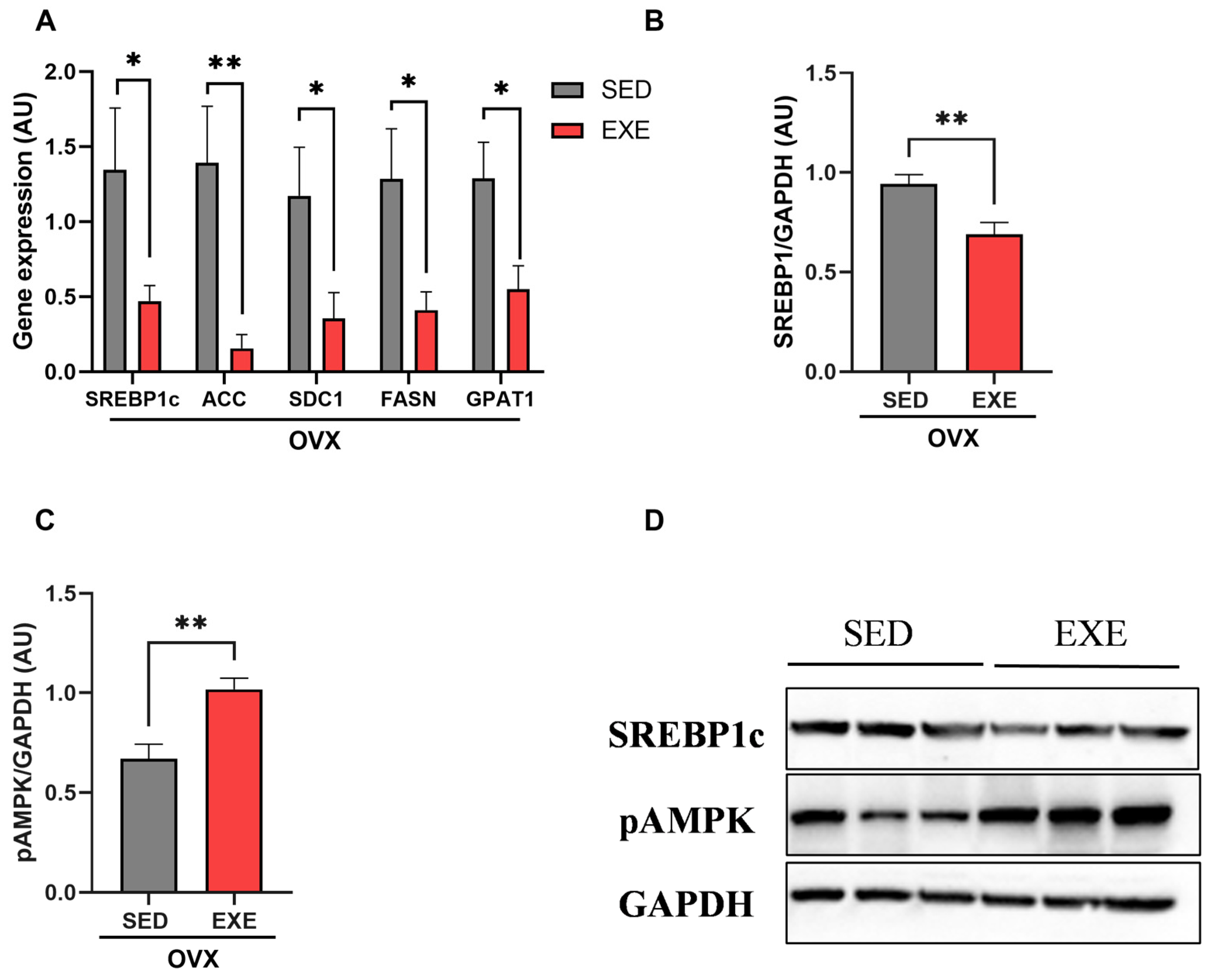
2.5. Effects of ST on Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Pathways
2.6. ST in the Gene and Protein Expression of Cytokines in the Liver of Ovariectomized Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
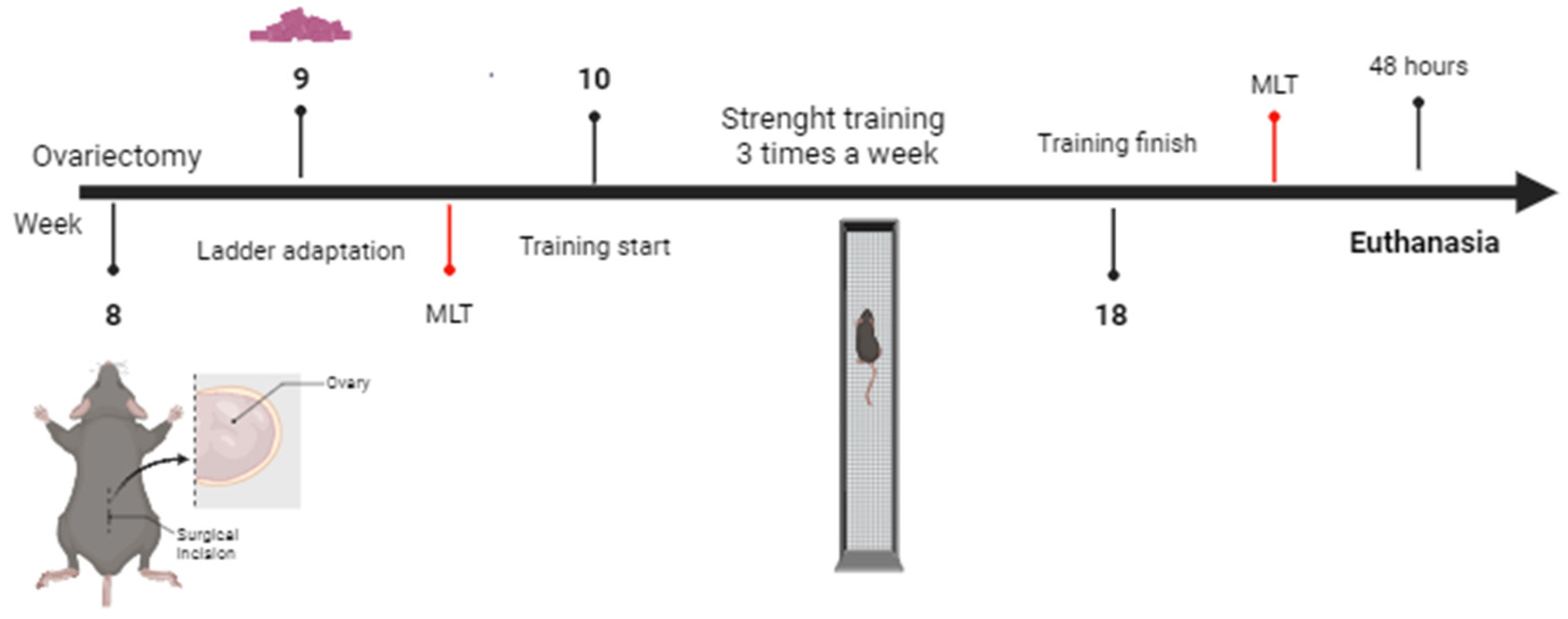
4.1. Animals
4.2. Ovariectomy
4.3. Ladder Adaptation
4.4. Maximum Load Capacity (MLC)
4.5. Strength Training Protocol (ST)
4.6. Glucose Tolerance Test
4.7. Magnetic Resonance
4.8. Tissue Lipid Content
4.9. In Vivo Assessment of Insulin Sensitivity
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. Assessment of Gene Expression—Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
4.12. Analysis of Oxidative Stress Markers
4.13. Liver Morphology
4.14. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, H.G.; Park, H. Metabolic Disorders in Menopause. Metabolites 2022, 12, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, P.; Mascagni, G.; Giannini, A.; Genazzani, A.R.; Simoncini, T. Symptoms of menopause—Global prevalence, physiology and implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shufelt, C.; Manson, J. Managing Menopause by Combining Evidence With Clinical Judgment. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Menopause-Associated Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Foods Beneficial for Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkin, M.J. Menopause: Hormones, Lifestyle, and Optimizing Aging. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 46, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidlinger, S.; Winterberger, K.; Pape, J.; Weidlinger, M.; Janka, H.; von Wolff, M.; Stute, P. Impact of estrogens on resting energy expenditure: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrinoudaki, I.; Armeni, E. Understanding of and clinical approach to cardiometabolic transition at the menopause. Climacteric 2024, 27, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Jung, Y. Energy Metabolism Changes and Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism in Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus, A.N.; Henry, B.A. The role of oestrogen in determining sexual dimorphism in energy balance. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, E.; Hayashi, T.; Nakatani, M.; Aida, N.; Suda, R.; Fujii, T.; Wakatsuki, T.; Honda, S.; Harada, N.; Shimono, Y. Lack of association of ovariectomy-induced obesity with overeating and the reduction of physical activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2019, 20, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, F.N.; Matos, S.L.; Araujo, L.C.C.; Carvalho, C.R.O.; Amaral, A.G.; Camporez, J.P. Western Diet-Fed ApoE Knockout Male Mice as an Experimental Model of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4692–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kanda, S.; Guigni, B.A.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Carvalho, C.R.; Petersen, K.F.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Cellular mechanism by which estradiol protects female ovariectomized mice from high-fat diet-induced hepatic and muscle insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboobifard, F.; Pourgholami, M.H.; Jorjani, M.; Dargahi, L.; Amiri, M.; Sadeghi, S.; Tehrani, F.R. Estrogen as a key regulator of energy homeostasis and metabolic health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.; Lyu, K.; Goldberg, E.L.; Zhang, D.; Cline, G.W.; Jurczak, M.J.; Dixit, V.D.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Anti-inflammatory effects of oestrogen mediate the sexual dimorphic response to lipid-induced insulin resistance. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3885–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, A.; Tramunt, B.; Montagner, A.; Mouly, C.; Riant, E.; Calmy, M.L.; Adlanmerini, M.; Fontaine, C.; Burcelin, R.; Lenfant, F.; et al. Membrane estrogen receptor-alpha contributes to female protection against high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1215947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.G.; Kursawe, R.; Titchenell, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Perry, C.J.; Jurczak, M.J.; Abudukadier, A.; Han, M.S.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Cell 2015, 160, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Samuel, V.T.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2014, 510, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorr, M.; Dichtel, L.E.; Gerweck, A.V.; Valera, R.D.; Torriani, M.; Miller, K.K.; Bredella, M.A. Sex differences in body composition and association with cardiometabolic risk. Biol. Sex Differ. 2018, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Brown, W.C.; Cai, Q.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Stafford, J.M. Estrogen treatment after ovariectomy protects against fatty liver and may improve pathway-selective insulin resistance. Diabetes 2013, 62, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiriglia, A.; Lorito, N.; Serra, M.; Perra, A.; Morandi, A.; Kowalik, M.A. Sex difference in liver diseases: How preclinical models help to dissect the sex-related mechanisms sustaining NAFLD and hepatocellular carcinoma. iScience 2023, 26, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, L.C.C.; Cruz, A.G.; Camargo, F.N.; Sucupira, F.G.; Moreira, G.V.; Matos, S.L.; Amaral, A.G.; Murata, G.M.; Carvalho, C.R.O.; Camporez, J.P. Estradiol Protects Female ApoE KO Mice against Western-Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F. NAFLD: Mechanisms, Treatments, and Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.Q.; Bai, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Fang, C.W.; Wang, F.; Qin, X.J. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santana, D.A.; Castro, A.; Cavaglieri, C.R. Strength Training Volume to Increase Muscle Mass Responsiveness in Older Individuals: Weekly Sets Based Approach. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 759677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, J.M.; Pieri, B.; Luciano, T.F.; Marques, S.O.; Guglielmo, L.G.A.; Souza, C.T. Muscular resistance, hypertrophy and strength training equally reduce adiposity, inflammation and insulin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. Einstein 2020, 18, eAO4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botezelli, J.D.; Coope, A.; Ghezzi, A.C.; Cambri, L.T.; Moura, L.P.; Scariot, P.P.; Gaspar, R.S.; Mekary, R.A.; Ropelle, E.R.; Pauli, J.R. Strength Training Prevents Hyperinsulinemia, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation Independent of Weight Loss in Fructose-Fed Animals. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Rodrigues, K.; Anaruma, C.P.; Sant’Ana, M.R.; de Campos, T.D.P.; Gaspar, R.S.; Canciglieri, R.D.S.; de Melo, D.G.; Mekary, R.A.; da Silva, A.S.R.; et al. Short-term strength training reduces gluconeogenesis and NAFLD in obese mice. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 241, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.R.P.; Castro, E.S.P.; de Oliveira, A.A.; Camilo, B.F.; Cristina-Souza, G.; Vieira-Souza, L.M.; Carneiro, M. Effect of resistance training volume on body adiposity, metabolic risk, and inflammation in postmenopausal and older females: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Sport Health Sci. 2023, 13, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Contreras, J.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Zarain-Herzberg, A.; Balderas-Villalobos, J. Ovariectomized rodents as a menopausal metabolic syndrome model. A minireview. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 475, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurina, L.M.; Gulati, M.; Everson-Rose, S.A.; Chung, P.J.; Karavolos, K.; Cohen, N.J.; Kandula, N.; Lukezic, R.; Dugan, S.A.; Sowers, M.; et al. The effect of menopause on grip and pinch strength: Results from the Chicago, Illinois, site of the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.L.; Sato, A.; Takino, Y.; Ishigami, A.; Machida, S. Influence of oestrogen on satellite cells and myonuclear domain size in skeletal muscles following resistance exercise. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.; Petersen, M.C.; Abudukadier, A.; Moreira, G.V.; Jurczak, M.J.; Friedman, G.; Haqq, C.M.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Anti-myostatin antibody increases muscle mass and strength and improves insulin sensitivity in old mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2212–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Cao, W.; Zhao, T.; Yu, K.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Fan, X.; Ta, D. Weight-bearing exercise prevents skeletal muscle atrophy in ovariectomized rats. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 77, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartolahti, E.; Lonnroos, E.; Hartikainen, S.; Hakkinen, A. Long-term strength and balance training in prevention of decline in muscle strength and mobility in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, I.; Krause Neto, W.; Dos Santos Portella Amorim, L.; Moraes Munhoz Ortiz, V.; Lopes Geraldo, V.; Henrique da Silva Ferreira, G.; Chagas Caperuto, E.; Florencio Gama, E. Muscle hypertrophy and ladder-based resistance training for rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.F.; Stotzer, U.S.; Domingos, M.M.; Deminice, R.; Shiguemoto, G.E.; Tomaz, L.M.; Sousa, N.M.; Ferreira, F.C.; Leite, R.D.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; et al. Effects of ovariectomy and resistance training on oxidative stress markers in the rat liver. Clinics 2013, 68, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, L.; Harnden, K.; Banerjee, R.; Real, B.; Marinou, K.; Karpe, F.; Fielding, B.A. Lower resting and total energy expenditure in postmenopausal compared with premenopausal women matched for abdominal obesity. J. Nutr. Sci. 2014, 3, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporez, J.P.; Akamine, E.H.; Davel, A.P.; Franci, C.R.; Rossoni, L.V.; Carvalho, C.R. Dehydroepiandrosterone protects against oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction in ovariectomized rats. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraca, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of exercise training on weight loss, body composition changes, and weight maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity: An overview of 12 systematic reviews and 149 studies. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S4), e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pighon, A.; Paquette, A.; Barsalani, R.; Chapados, N.A.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Yasari, S.; Prud’homme, D.; Lavoie, J.M. Resistance training attenuates fat mass regain after weight loss in ovariectomized rats. Maturitas 2009, 64, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masanova, V.; Krivosikova, Z.; Ursinyova, M.; Uhnakova, I.; Kebis, A.; Kramarova, P.; Wsolova, L.; Gajdos, M. Effects of Ovariectomy and Exercise Training on Mineral Status in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Rat Model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.S.R.; Fonseca, G.; Ottone, N.; Silva, P.A.; Antonaccio, R.F.; Silva, G.; Rocha, M.; Coimbra, C.C.; Esteves, E.A.; Mang, Z.A.; et al. Strength training improves insulin resistance and differently affects mitochondria in skeletal muscle and visceral adipose tissue in high-fat fed mice. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, T.A.; de Lima Junior, E.A.; Teixeira, A.A.; Biondo, L.A.; da Rocha, L.A.F.; Valadao, I.C.; Silveira, L.S.; Cabral-Santos, C.; de Souza, C.O.; Rosa Neto, J.C. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-alpha signaling in obese mice. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest, C.P.; Johannsen, N.M.; Swift, D.L.; Gillison, F.B.; Mikus, C.R.; Lucia, A.; Kramer, K.; Lavie, C.J.; Church, T.S. Aerobic and strength training in concomitant metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargeant, J.A.; Gray, L.J.; Bodicoat, D.H.; Willis, S.A.; Stensel, D.J.; Nimmo, M.A.; Aithal, G.P.; King, J.A. The effect of exercise training on intrahepatic triglyceride and hepatic insulin sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corriveau, P.; Paquette, A.; Brochu, M.; Prud’homme, D.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Lavoie, J.M. Resistance training prevents liver fat accumulation in ovariectomized rats. Maturitas 2008, 59, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporez, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Faarkrog, K.; Chukijrungroat, N.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanism by which arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 ablation causes insulin resistance in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E11285–E11292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporez, J.P.G.; Kanda, S.; Petersen, M.C.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Samuel, V.T.; Bhanot, S.; Petersen, K.F.; Jurczak, M.J.; Shulman, G.I. ApoA5 knockdown improves whole-body insulin sensitivity in high-fat-fed mice by reducing ectopic lipid content. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulizi, A.; Camporez, J.P.; Zhang, D.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I.; Vatner, D.F. Ectopic lipid deposition mediates insulin resistance in adipose specific 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 transgenic mice. Metabolism 2019, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporez, J.P.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Petersen, M.C.; Pesta, D.; Guigni, B.A.; Serr, J.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; Samuel, V.T.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Madiraju, A.K.; Gassaway, B.M.; Marcel, M.; Nasiri, A.R.; Butrico, G.; Marcucci, M.J.; Zhang, D.; Abulizi, A.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Insulin receptor Thr1160 phosphorylation mediates lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, M.M.; Rodrigues, M.F.; Stotzer, U.S.; Bertucci, D.R.; Souza, M.V.; Marine, D.A.; Gatto Cdo, V.; de Araujo, H.S.; de Andrade Perez, S.E. Resistance training restores the gene expression of molecules related to fat oxidation and lipogenesis in the liver of ovariectomized rats. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.A.; Pinho, C.A.; Rocha, L.G.; Tuon, T.; Silveira, P.C.; Pinho, R.A. Effect of different models of physical exercise on oxidative stress markers in mouse liver. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, J.D.M.; Aidar, F.J.; de Matos, D.G.; de Oliveira, J.U.; Júnior, A.S.S.; Dos Santos, J.L.; Marçal, A.C.; de Araújo, S.S. The 6-week Effects of HIIT on Biomarkers of Tissue and Oxidative Damage in Wistar Rats Previously Supplemented with Pyridoxine. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 14, 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger, T.A., Jr.; Farrar, R.P. Physiological hypertrophy of the FHL muscle following 8 weeks of progressive resistance exercise in the rat. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronczek, G.A.; Soares, G.M.; de Barros, J.F.; Vettorazzi, J.F.; Kurauti, M.A.; Marconato-Junior, E.; Zangerolamo, L.; Marmentini, C.; Boschero, A.C.; Costa-Junior, J.M. Resistance exercise training improves glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin secretion in C57BL/6 mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, T.F.; Marques, S.O.; Pieri, B.L.; de Souza, D.R.; Araujo, L.V.; Nesi, R.T.; Scheffer, D.L.; Comin, V.H.; Pinho, R.A.; Muller, A.P.; et al. Responses of skeletal muscle hypertrophy in Wistar rats to different resistance exercise models. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Week | Intensity (% Maximal Load) | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60% | 3/12 |
| 2 | 80% | 4/8 |
| 3–4 | 100% | 5/6 |
| 5–6 | 120% | 6/5 |
| 7–8 | 140% | 6/4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, J.D.M.; Silva, J.F.T.; Alves, E.d.S.; Cruz, A.G.; Santos, A.R.M.; Camargo, F.N.; Talarico, C.H.Z.; Silva, C.A.A.; Camporez, J.P. Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105066
Santos JDM, Silva JFT, Alves EdS, Cruz AG, Santos ARM, Camargo FN, Talarico CHZ, Silva CAA, Camporez JP. Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Jessica D. M., José F. T. Silva, Ester dos S. Alves, Alessandra G. Cruz, Anne R. M. Santos, Felipe N. Camargo, Carlos H. Z. Talarico, Carlos A. A. Silva, and João Paulo Camporez. 2024. "Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105066
APA StyleSantos, J. D. M., Silva, J. F. T., Alves, E. d. S., Cruz, A. G., Santos, A. R. M., Camargo, F. N., Talarico, C. H. Z., Silva, C. A. A., & Camporez, J. P. (2024). Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105066






