Molecular Mechanisms of Fetal and Neonatal Lupus: A Narrative Review of an Autoimmune Disease Transferal across the Placenta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanisms
2.1. Placenta: Immunological Interface and IgG Transfer
2.2. Autoantibodies Anti-SSA/Ro and Anti-SSB/La and Their Association with Autoimmune Diseases
2.3. Fetal Antigens and Immune Complex Formation
2.4. Apoptosis, Cardiac Damage, and Tissue Remodeling
3. Congenital Heart Block and Other Complications
3.1. Overview
3.2. Pathogenesis
3.3. Clinical Presentation
3.4. Diagnosis
3.5. Prognosis for Infants with Maternal Anti-RO/SSA Antibodies
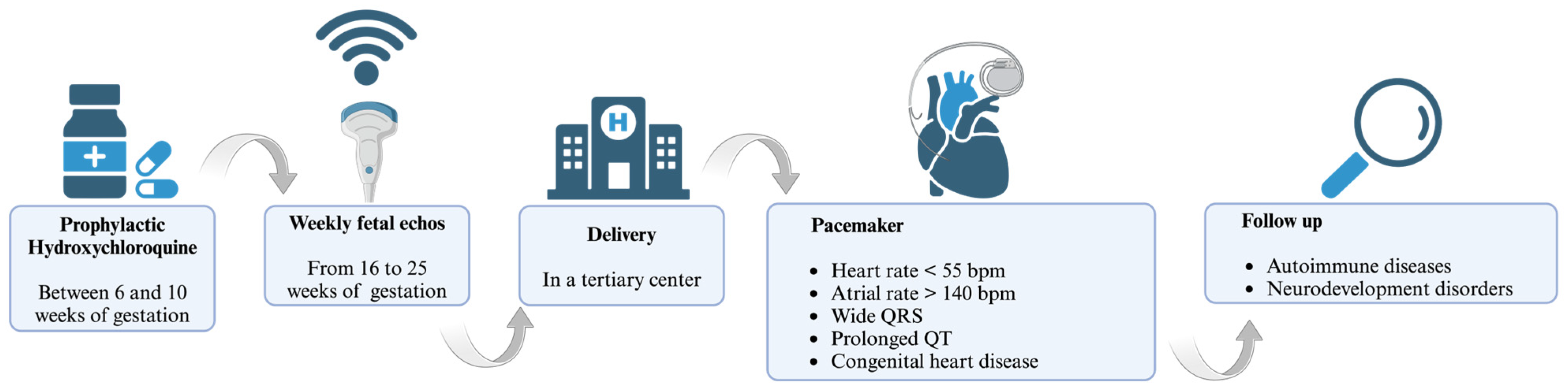
3.6. Management
4. Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCuistion, C.H.; Schoch, E.P. Possible discoid lupus erythematosus in newborn infant. Report of a case with subsequent development of acute systemic lupus erythematosus in mother. Arch. Dermatol. 1983, 119, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, G.R. Congenital, Acute Lupus Erythematosus Associated with Subendocardial Fibroelastosis: Report of a Case. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1957, 28, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, P.G.; Jones, C.A. The development of the immune system during pregnancy and early life. Allergy 2000, 55, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang Hoftman, A.; Hernandez, M.I.; Lee, K.-W.; Stiehm, E.R. Newborn Illnesses Caused by Transplacental Antibodies. Adv. Pediatr. 2008, 55, 271–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucato, A.; Cimaz, R.; Stramba-Badiale, M. Neonatal Lupus. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 23, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, P.; Quinello, C.; Silveira-Lessa, A.L.; Zago, C.A.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M. IgG Placental Transfer in Healthy and Pathological Pregnancies. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 985646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, N.A.; Lozano, A.; Marini, V.; Saranz, R.J.; Blumberg, R.S.; Baker, K.; Agresta, M.F.; Ponzio, M.F. Expression of FcRn receptor in placental tissue and its relationship with IgG levels in term and preterm newborns. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 80, e12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos Gutierrez, A.S.; Figueras, F.; Morales-Prieto, D.M.; Schleußner, E.; Espinosa, G.; Baños, N. Placental damage in pregnancies with systemic lupus erythematosus: A narrative review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoni, F.; Lava, S.A.G.; Fossali, E.F.; Cavalli, R.; Simonetti, G.D.; Bianchetti, M.G.; Bozzini, M.A.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Neonatal Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeggi, E.; Laskin, C.; Hamilton, R.; Kingdom, J.; Silverman, E. The Importance of the Level of Maternal Anti-Ro/SSA Antibodies as a Prognostic Marker of the Development of Cardiac Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryka-Marton, M.; Szukiewicz, D.; Teliga-Czajkowska, J.; Olesinska, M. An Overview of Neonatal Lupus with Anti-Ro Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Smith, J.D.; Shi, H.; Yang, D.D.; Flavell, R.A.; Wolin, S.L. The Ro Autoantigen Binds Misfolded U2 Small Nuclear RNAs and Assists Mammalian Cell Survival after UV Irradiation. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Izmirly, P.M.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Buyon, J.P.; Khamashta, M.A. The clinical spectrum of autoimmune congenital heart block. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucato, A.; Frassi, M.; Franceschini, F.; Cimaz, R.; Faden, D.; Pisoni, M.P.; Muscarà, M.; Vignati, G.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Catelli, L.; et al. Risk of congenital complete heart block in newborns of mothers with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies detected by counterimmunoelectrophoresis: A prospective study of 100 women. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleicher, N.; Elkayam, U. Preventing congenital neonatal heart block in offspring of mothers with anti-SSA/Ro and SSB/La antibodies: A review of published literature and registered clinical trials. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Carús, M.-E.; Askanase, A.D.; Clancy, R.M.; Di Donato, F.; Chou, T.-M.; Libera, M.R.; Chan, E.K.L.; Buyon, J.P. Anti-SSA/Ro and Anti-SSB/La Autoantibodies Bind the Surface of Apoptotic Fetal Cardiocytes and Promote Secretion of TNF-α by Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5345–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyon, J.P.; Clancy, R.M. From antibody insult to fibrosis in neonatal lupus—The heart of the matter. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; He, Y. Autoimmune congenital heart block: A case report and review of the literature related to pathogenesis and pregnancy management. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, P.; Sallé, L.; Lezoualc’h, F.; Mialet, J.; Gastineau, M.; Briand, J.-P.; Isenberg, D.A.; Fournié, G.J.; Argibay, J.; Fischmeister, R.; et al. Anti-SSA/Ro52 autoantibodies blocking the cardiac 5-HT4serotoninergic receptor could explain neonatal lupus congenital heart block. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Tunaoðlu, F.S.; Karaaðaç, A.T. Neonatal Congenital Heart Block. Indian Pediatr. 2013, 50, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Song, X.; Xiong, Y.; Ren, T.; Chang, X.; Wu, J.; Cao, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, M. Maternal and infant outcomes of pregnancy associated with anti-SSA/RO antibodies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2023, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyon, J.P.; Hiebert, R.; Copel, J.; Craft, J.; Friedman, D.; Katholi, M.; Lee, L.A.; Provost, T.T.; Reichlin, M.; Rider, L.; et al. Autoimmune-associated congenital heart block: Demographics, mortality, morbidity and recurrence rates obtained from a national neonatal lupus registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprasad, N.; Johnson, F.; Venugopal, K. Congenital complete heart block and maternal connective tissue disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 112, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.M.; Rupel, A.; Buyon, J.P. Epidemiology, etiology, detection, and treatment of autoantibody-associated congenital heart block in neonatal lupus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frassi, M.; Brucato, A.; Cavazzana, I.; Franceschini, F.; Faden, D.; Motta, M.; Doria, A.; Cimaz, R.; Pisoni, M.P.; Muscarà, M.; et al. Neonatal lupus: Clinical features and risk of congenital cardiac heart block in newborns from mothers with anti Ro/SSA antibodies. Reumatismo 2001, 53, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucato, A.; Franceschini, F.; Gasparini, M.; De Juli, E.; Ferraro, G.; Quinzanini, M.; Vignati, G.; Bortolon, C.; Ghessi, A.; Pozzoli, R. Isolated congenital complete heart block: Longterm outcome of mothers, maternal antibody specificity and immunogenetic background. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen, H.; Kurki, P.; Kaaja, R.; Heikkilä, R.; Immonen, I.; Chan, E.K.; Wallgren, E.; Friman, C. Isolated congenital heart block. Long-term outcome of mothers and characterization of the immune response to SS-A/Ro and to SS-B/La. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucato, A.; Grava, C.; Bortolati, M.; Ikeda, K.; Milanesi, O.; Cimaz, R.; Ramoni, V.; Vignati, G.; Martinelli, S.; Sadou, Y.; et al. Congenital heart block not associated with anti-Ro/La antibodies: Comparison with anti-Ro/La-positive cases. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Killen, S.A.S.; Buyon, J.P.; Friedman, D.M. Discordant spectrum of cardiac manifestations of neonatal lupus in twins. Lupus 2012, 21, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasburger, J.F.; Wacker-Gussmann, A. Congenital Heart Block in Subsequent Pregnancies of SSA/Ro-Positive Mothers: Cutting Recurrence in Half. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Izmirly, P.M.; Han, S.W.; Briassouli, P.; Rivera, T.L.; Zhong, H.; Friedman, D.M.; Clancy, R.M.; Buyon, J.P. Serum Biomarkers of Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cardiac Function in Facilitating Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Anti-SSA/Ro-Associated Cardiac Neonatal Lupus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruteau, A.-E.; Pass, R.H.; Thambo, J.-B.; Behaghel, A.; Le Pennec, S.; Perdreau, E.; Combes, N.; Liberman, L.; McLeod, C.J. Congenital and childhood atrioventricular blocks: Pathophysiology and contemporary management. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Gordon, P.; Rosenthal, E.; Simpson, J.; Miller, O.; Sharland, G. Isolated Complete Heart Block in the Fetus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izmirly, P.; Saxena, A.; Buyon, J.P. Progress in the pathogenesis and treatment of cardiac manifestations of neonatal lupus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.A. Congenital heart block: Current thoughts on management, morphologic spectrum, and role of intervention. Cardiol. Young 2014, 24 (Suppl. 2), 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Izmirly, P.M.; Mendez, B.; Buyon, J.P.; Friedman, D.M. Prevention and treatment in utero of autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, M.K.; Merchant, K.; Chan, C.J.; Choo, J.T.L.; Gopagondanahalli, K.R.; Zhang, D.Z.; Tan, T.H.; Sundararaghavan, S. Endocardial Fibroelastosis as an Independent Predictor of Atrioventricular Valve Rupture in Maternal Autoimmune Antibody Exposed Fetus: A Systematic Review with Clinicopathologic Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, R.M.; Neufing, P.J.; Zheng, P.; O’Mahony, M.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Gordon, T.P.; Buyon, J.P. Impaired clearance of apoptotic cardiocytes is linked to anti-SSA/Ro and -SSB/La antibodies in the pathogenesis of congenital heart block. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyon, J.P.; Clancy, R.M. Dying right to live longer: Positing apoptosis as a link between maternal autoantibodies and congenital heart block. Lupus 2008, 17, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, R.M.; Alvarez, D.; Komissarova, E.; Barrat, F.J.; Swartz, J.; Buyon, J.P. Ro60-associated single-stranded RNA links inflammation with fetal cardiac fibrosis via ligation of TLRs: A novel pathway to autoimmune-associated heart block. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnabi, E.; Qu, Y.; Wadgaonkar, R.; Mancarella, S.; Yue, Y.; Chahine, M.; Clancy, R.M.; Buyon, J.P.; Boutjdir, M. Congenital heart block: Identification of autoantibody binding site on the extracellular loop (domain I, S5-S6) of alpha(1D) L-type Ca channel. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutjdir, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Tseng, C.E.; El-Sherif, N.; Buyon, J.P. Serum and immunoglobulin G from the mother of a child with congenital heart block induce conduction abnormalities and inhibit L-type calcium channels in a rat heart model. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Amoura, Z.; Piette, J.C. Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibody-mediated congenital heart block. Lupus 2005, 14, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nield, L.E.; Silverman, E.D.; Taylor, G.P.; Smallhorn, J.F.; Mullen, J.B.M.; Silverman, N.H.; Finley, J.P.; Law, Y.M.; Human, D.G.; Seaward, P.G.; et al. Maternal anti-Ro and anti-La antibody-associated endocardial fibroelastosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R.M.; Markham, A.J.; Jackson, T.; Rasmussen, S.E.; Blumenberg, M.; Buyon, J.P. Cardiac fibroblast transcriptome analyses support a role for interferogenic, profibrotic, and inflammatory genes in anti-SSA/Ro-associated congenital heart block. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 313, H631–H640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R.M.; Backer, C.B.; Yin, X.; Kapur, R.P.; Molad, Y.; Buyon, J.P. Cytokine polymorphisms and histologic expression in autopsy studies: Contribution of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta 1 to the pathogenesis of autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, F.; Cavazzana, I. Anti-Ro/SSA and La/SSB antibodies. Autoimmunity 2005, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonsson, S.; Dörner, T.; Theander, E.; Bremme, K.; Larsson, P.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. A serologic marker for fetal risk of congenital heart block. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, A.; Sonesson, S.-E.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Molecular mechanisms of congenital heart block. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 325, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonello, M.; Ruffatti, A.; Favaro, M.; Tison, T.; Del Ross, T.; Calligaro, A.; Hoxha, A.; Mattia, E.; Punzi, L. Maternal autoantibody profiles at risk for autoimmune congenital heart block: A prospective study in high-risk patients. Lupus Sci. Med. 2016, 3, e000129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.H.; Clancy, R.M.; Lee, K.H.; Saxena, A.; Izmirly, P.M.; Buyon, J.P. Umbilical cord blood levels of maternal antibodies reactive with p200 and full-length Ro 52 in the assessment of risk for cardiac manifestations of neonatal lupus. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R.M.; Halushka, M.; Rasmussen, S.E.; Lhakhang, T.; Chang, M.; Buyon, J.P. Siglec-1 Macrophages and the Contribution of IFN to the Development of Autoimmune Congenital Heart Block. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandberg, L.; Ambrosi, A.; Espinosa, A.; Ottosson, L.; Eloranta, M.-L.; Zhou, W.; Elfving, A.; Greenfield, E.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Interferon-alpha induces up-regulation and nuclear translocation of the Ro52 autoantigen as detected by a panel of novel Ro52-specific monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisney, A.R.; Szelinski, F.; Reiter, K.; Burmester, G.R.; Rose, T.; Dörner, T. High maternal expression of SIGLEC1 on monocytes as a surrogate marker of a type I interferon signature is a risk factor for the development of autoimmune congenital heart block. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, M.; Thorlacius, G.E.; Ivanchenko, M.; Ottosson, V.; Kyriakidis, N.; Lagnefeldt, L.; Tingström, J.; Sirsjö, A.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Aronsson, E.; et al. Type I IFN system activation in newborns exposed to Ro/SSA and La/SSB autoantibodies in utero. RMD Open 2020, 6, e000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornaun, H.; Oztarhan, K.; Ocak, Z.; Ekiz, A.; Ulucan, K.; Buyukkale, G.; Gedikbasi, A. Contribution of TGFB1 and TNF-α genes in one of twin pregnancies with congenital complete heart block phenotype. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 210, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, L.; Izmirly, P.; Buyon, J.P.; Phoon, C.K.L. Autoimmune Congenital Complete Heart Block: How Late Can It Occur? Am. J. Perinatol. Rep. 2023, 13, e29–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Morel, N.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Levesque, K.; Maltret, A.; Khamashta, M.; Brucato, A. Routine repeated echocardiographic monitoring of fetuses exposed to maternal anti-SSA antibodies: Time to question the dogma. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e187–e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinski, M.; Cuneo, B.F. Novel approaches to the surveillance and management of fetuses at risk for anti-Ro/SSA mediated atrioventricular block. Semin. Perinatol. 2022, 46, 151585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P.A. Congenital heart block: Clinical features and therapeutic approaches. Lupus 2007, 16, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Gitelman, M.S. Neonatal Lupus: What We Have Learned and Current Approaches to Care. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caluwé, E.; Van De Bruaene, A.; Willems, R.; Troost, E.; Gewillig, M.; Rega, F.; Budts, W. Long-Term Follow-Up of Children with Heart Block Born from Mothers with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective Study from the Database Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease in University Hospitals Leuven. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2016, 39, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Frias, J.; Badri, T. Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cimaz, R.; Spence, D.L.; Hornberger, L.; Silverman, E.D. Incidence and spectrum of neonatal lupus erythematosus: A prospective study of infants born to mothers with anti-Ro autoantibodies. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppa, A.A.; Riccardi, R.; Frezza, S.; Gallini, F.; Luciano, R.M.P.; Alighieri, G.; Romagnoli, C.; De Carolis, S. Neonatal lupus: Follow-up in infants with anti -SSA/Ro antibodies and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carolis, S.; Garufi, C.; Garufi, E.; De Carolis, M.P.; Botta, A.; Tabacco, S.; Salvi, S. Autoimmune Congenital Heart Block: A Review of Biomarkers and Management of Pregnancy. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 607515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howley, L.W.; Eyerly-Webb, S.A.; Killen, S.A.S.; Paul, E.; Krishnan, A.; Gropler, M.R.F.; Drewes, B.; Dion, E.; Lund, A.; Buyon, J.P.; et al. Variation in prenatal surveillance and management of anti-SSA/Ro autoantibody positive pregnancies. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2024, 37, 2323623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuneo, B.F.; Sonesson, S.-E.; Levasseur, S.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; Krishnan, A.; Donofrio, M.T.; Raboisson, M.-J.; Hornberger, L.K.; Van Eerden, P.; Sinkovskaya, E.; et al. Home Monitoring for Fetal Heart Rhythm During Anti-Ro Pregnancies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdulska, J.M.; Rudnicka, L.; Szykut-Badaczewska, A.; Mehrholz, D.; Nowicki, R.J.; Barańska-Rybak, W.; Wilkowska, A. Neonatal lupus erythematosus—Practical guidelines. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rein, A.J.J.T.; Mevorach, D.; Perles, Z.; Gavri, S.; Nadjari, M.; Nir, A.; Elchalal, U. Early diagnosis and treatment of atrioventricular block in the fetus exposed to maternal anti-SSA/Ro-SSB/La antibodies: A prospective, observational, fetal kinetocardiogram-based study. Circulation 2009, 119, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, H.; Sonesson, S.-E.; Sharland, G.; Granath, F.; Simpson, J.M.; Carvalho, J.S.; Jicinska, H.; Tomek, V.; Dangel, J.; Zielinsky, P.; et al. Isolated atrioventricular block in the fetus: A retrospective, multinational, multicenter study of 175 patients. Circulation 2011, 124, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Lee, L.A.; Askanase, A.D.; Katholi, M.; Buyon, J.P. Long-term followup of children with neonatal lupus and their unaffected siblings. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasef, N.; Hafez, M.; Bark, A. Neonatal lupus erythematosus. J. Neonatol. Clin. Pediatr. 2014, 1, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Silka, M.J.; Shah, M.J.; Silva, J.N.A.; Balaji, S.; Beach, C.M.; Benjamin, M.N.; Berul, C.I.; Cannon, B.; Cecchin, F.; Cohen, M.I.; et al. 2021 PACES expert consensus statement on the indications and management of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices in pediatric patients: Executive summary. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2022, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, S.; Rauniyar, S.P.G.; Gyawali, B.; Bhusal, T.; Basnet, S. Neonatal lupus erythematosus manifested as a complete heart block: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Du, L.; Pan, J.; Zheng, J.; Chen, A.; Chen, L. A 10-year retrospective study of neonatal lupus erythematous in China. Asian Pac. J. Allergy 2016, 34, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Amoura, Z.; Villain, E.; Cohen, L.; Piette, J.C. Anti-SSA/Ro antibodies and the heart: More than complete congenital heart block? A review of electrocardiographic and myocardial abnormalities and of treatment options. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Østensen, M.; Khamashta, M.; Lockshin, M.; Parke, A.; Brucato, A.; Carp, H.; Doria, A.; Rai, R.; Meroni, P.; Cetin, I.; et al. Anti-in-flammatory and immunosuppressive drugs and reproduction. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.M.; Llanos, C.; Izmirly, P.M.; Brock, B.; Byron, J.; Copel, J.; Cummiskey, K.; Dooley, M.A.; Foley, J.; Graves, C.; et al. Evaluation of fetuses in a study of intravenous immunoglobulin as preventive therapy for congenital heart block: Results of a multicenter, prospective, open-label clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routsias, J.G.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Friedman, D.M.; Llanos, C.; Clancy, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Buyon, J.; Tzioufas, A.G. Association of the idiotype:antiidiotype antibody ratio with the efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for the prevention of recurrent autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2783–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoni, C.N.; Brucato, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Espinosa, G.; Cervera, R.; Belmonte-Serrano, M.; Sánchez-Román, J.; García-Hernández, F.G.; Tincani, A.; Bertero, M.T.; et al. Failure of intravenous immunoglobulin to prevent congenital heart block: Findings of a multicenter, prospective, observational study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clowse, M.E.B.; Eudy, A.M.; Kiernan, E.; Williams, M.R.; Bermas, B.; Chakravarty, E.; Sammaritano, L.R.; Chambers, C.D.; Buyon, J. The prevention, screening and treatment of congenital heart block from neonatal lupus: A survey of provider practices. Rheumatology 2018, 57, v9–v17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R.M.; Markham, A.J.; Reed, J.H.; Blumenberg, M.; Halushka, M.K.; Buyon, J.P. Targeting downstream transcription factors and epigenetic modifications following toll-like receptor 7/8 ligation to forestall tissue injury in anti-Ro60 associated heart block. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 67, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izmirly, P.M.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Pisoni, C.N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Kim, M.Y.; Saxena, A.; Friedman, D.; Llanos, C.; Piette, J.C.; Buyon, J.P. Maternal use of hydroxychloroquine is associated with a reduced risk of recurrent anti-SSA/Ro-antibody-associated cardiac manifestations of neonatal lupus. Circulation 2012, 126, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, T.; Kondo, Y.; Tsuboi, H.; Noma, H.; Tabuchi, D.; Sugita, T.; Okamoto, S.; Terasaki, T.; Shimizu, M.; Honda, F.; et al. QTc interval prolongation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with hydroxychloroquine. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, B.H. Pregnancy in Women With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Messages for the Clinician. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamashta, M.A.; Mackworth-Young, C. Antiphospholipid (Hughes’) syndrome. BMJ 1997, 314, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Petri, M. Pregnancy in SLE. Baillieres Clin. Rheumatol. 1998, 12, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clowse, M.E.B.; Jamison, M.; Myers, E.; James, A.H. A national study of the complications of lupus in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 199, 127.e1–127.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, J.; Smyth, A.; Tower, C.; Helbert, M.; Venning, M.; Garovic, V. Maternal deaths in women with lupus nephritis: A review of published evidence. Lupus 2012, 21, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, H.O.; Ahmed, S.R.; Alzolibani, A.; Kamal, M.M.; Mostafa, M.S.; Gamal, R.M.; Atallah, D.A.A.; Abd-El-Aall, D.-E.M. Does cutaneous lupus erythematosus have more favorable pregnancy outcomes than systemic disease? A two-center study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 92, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, N. New-onset systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, E.; Clowse, M.E.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus and pregnancy outcomes: An update and review of the literature. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojan, G.; Baer, A.N. Flares of systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy and the puerperium: Prevention, diagnosis and management. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 8, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Lai, K.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, K. Systemic lupus erythematosus and risk of preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Lupus 2017, 26, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hirankarn, N.; et al. Meta-analysis followed by replication identifies loci in or near CDKN1B, TET3, CD80, DRAM1, and ARID5B as associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Asians. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Ponticelli, C. Pregnancy after lupus nephritis. Lupus 2005, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerman, R.S.; Ramsey, R.D.; Kao, L.W.; Bringman, J.J.; Bush, A.J.; Wan, J.Y. Hypertensive disease in pregnancies complicated by systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, J.F.; Arkema, E.V.; Nguyen, C.; Svenungsson, E.; Wikström, A.; Palmsten, K.; Salmon, J.E. Early-onset Preeclampsia in Lupus Pregnancy. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2017, 31, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.; Oliveira, G.H.M.; Lahr, B.D.; Bailey, K.R.; Norby, S.M.; Garovic, V.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Pregnancy Outcomes in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2010, 5, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, C.A.M.; Di Michele, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Rossi, A.; Malova, M.; Benders, M.; van den Hoogen, A.; Dudink, J. Neurodevelopmental consequences of preterm punctate white matter lesions: A systematic review. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaritano, L.R.; Bermas, B.L.; Chakravarty, E.E.; Chambers, C.; Clowse, M.E.B.; Lockshin, M.D.; Marder, W.; Guyatt, G.; Branch, D.W.; Buyon, J.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Reproductive Health in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 529–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lateef, A.; Petri, M. Management of pregnancy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoli, L.; Bertsias, G.K.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Brown, S.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Doria, A.; Fischer-Betz, R.; Forger, F.; Moraes-Fontes, M.F.; et al. EULAR recommendations for women’s health and the management of family planning, assisted reproduction, pregnancy and menopause in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and/or antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Ludovico, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Mainieri, F.; Di Michele, S.; Girlando, V.; Ciarelli, F.; La Bella, S.; Chiarelli, F.; Attanasi, M.; Mauro, A.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Fetal and Neonatal Lupus: A Narrative Review of an Autoimmune Disease Transferal across the Placenta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105224
Di Ludovico A, Rinaldi M, Mainieri F, Di Michele S, Girlando V, Ciarelli F, La Bella S, Chiarelli F, Attanasi M, Mauro A, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Fetal and Neonatal Lupus: A Narrative Review of an Autoimmune Disease Transferal across the Placenta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105224
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Ludovico, Armando, Marta Rinaldi, Francesca Mainieri, Stefano Di Michele, Virginia Girlando, Francesca Ciarelli, Saverio La Bella, Francesco Chiarelli, Marina Attanasi, Angela Mauro, and et al. 2024. "Molecular Mechanisms of Fetal and Neonatal Lupus: A Narrative Review of an Autoimmune Disease Transferal across the Placenta" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105224
APA StyleDi Ludovico, A., Rinaldi, M., Mainieri, F., Di Michele, S., Girlando, V., Ciarelli, F., La Bella, S., Chiarelli, F., Attanasi, M., Mauro, A., Bizzi, E., Brucato, A., & Breda, L. (2024). Molecular Mechanisms of Fetal and Neonatal Lupus: A Narrative Review of an Autoimmune Disease Transferal across the Placenta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105224