Phenotypic Variability in Novel Doublecortin Gene Variants Associated with Subcortical Band Heterotopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Electroclinical and Neuroimaging Data
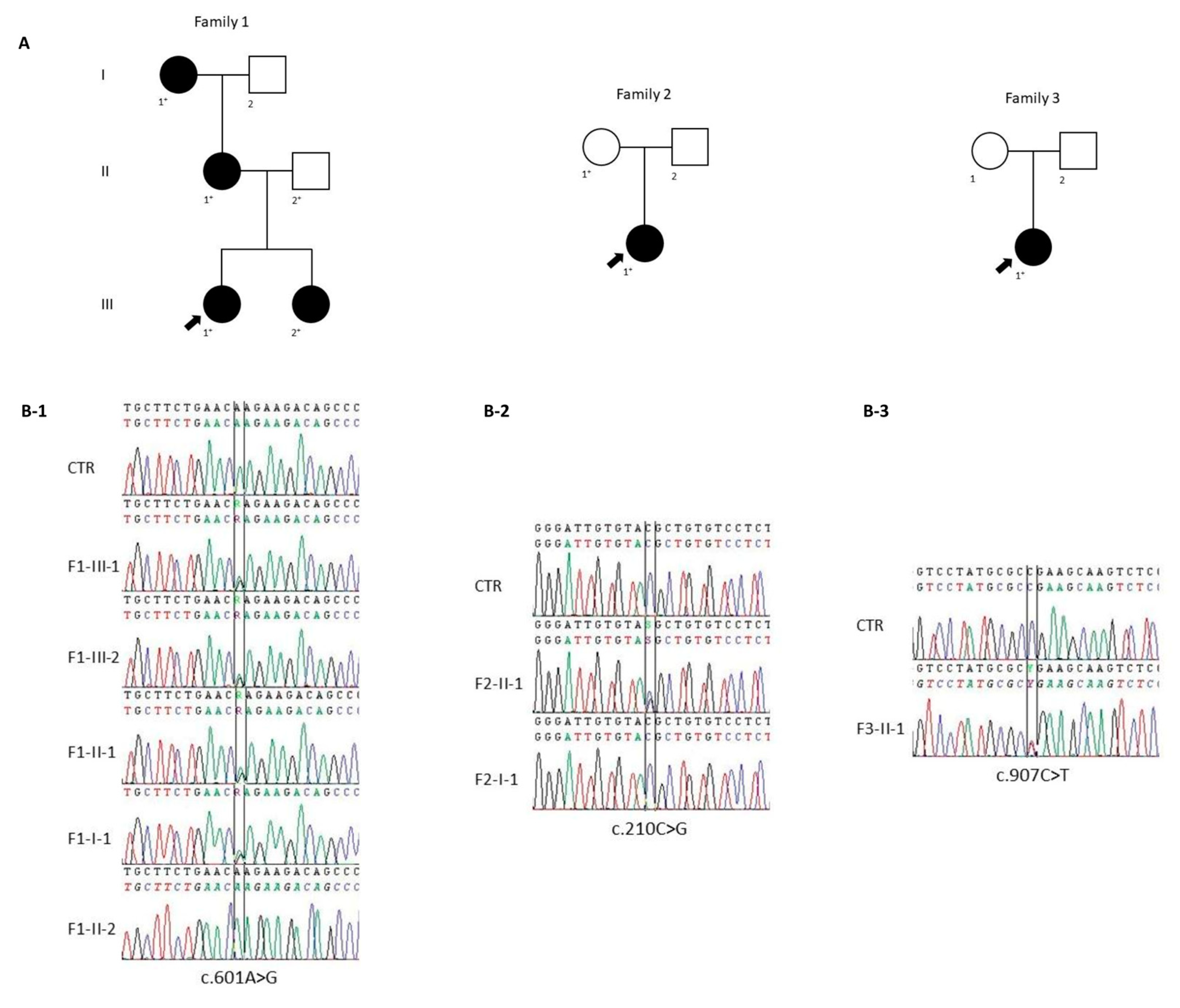
2.1.1. Family 1
2.1.2. Family 2
2.1.3. Family 3
2.2. Genetic Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cohort Description
4.2. Next-Generation Sequencing
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. Sanger Sequencing
4.5. Predictive Tools
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francis, F.; Koulakoff, A.; Boucher, D.; Chafey, P.; Schaar, B.; Vinet, M.-C.; Friocourt, G.; McDonnell, N.; Reiner, O.; Kahn, A.; et al. Doublecortin Is a Developmentally Regulated, Microtubule-Associated Protein Expressed in Migrating and Differentiating Neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Ramos, R.L.; Ackman, J.B.; Thomas, A.M.; Lee, R.V.; LoTurco, J.J. RNAi reveals doublecortin is required for radial migration in rat neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahi-Buisson, N.; Souville, I.; Fourniol, F.J.; Toussaint, A.; Moores, C.A.; Houdusse, A.; Lemaitre, J.Y.; Poirier, K.; Khalaf-Nazzal, R.; Hully, M.; et al. New insights into genotype–phenotype correlations for the doublecortin-related lissencephaly spectrum. Brain 2013, 136, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, J.G.; Lin, P.T.; Flanagan, L.A.; Walsh, C.A. Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.R.; Cheng, J.F.; Liu, Y.T.; Hsu, T.R.; Lin, K.M.; Chen, C.; Lin, C.L.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, J.W. Novel lissencephaly-associated DCX variants in the C-terminal DCX domain affect microtubule binding and dynamics. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, M.; Geraldo, A.F.; Utz, N.; Tortora, D.; Pogledic, I.; Klonowski, W.; Triulzi, F.; Arrigoni, F.; Mankad, K.; Leventer, R.J.; et al. Definitions and classification of malformations of cortical development: Practical guidelines. Brain 2020, 143, 2874–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrini, E.; Conti, V.; Dobyns, W.B.; Guerrini, R. Genetic Basis of Brain Malformations. Mol. Syndromol. 2016, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermoyal, J.-C.; Hardy, D.; Goirand-Lopez, L.; Vinck, A.; Silvagnoli, L.; Fortoul, A.; Francis, F.; Cappello, S.; Bureau, I.; Represa, A.; et al. Grey matter heterotopia subtypes show specific morpho-electric signatures and network dynamics. Brain 2023, 147, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leventer, R.J. Genotype-phenotype correlation in lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia: The key questions answered. J. Child. Neurol. 2005, 20, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, N.; Chiari, S.; Mirzaa, G.M.; Aldinger, K.; Parrini, E.; Olds, C.; Barkovich, A.J.; Guerrini, R.; Dobyns, W.B. Lissencephaly: Expanded imaging and clinical classification. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.; Dobyns, W.B.; Di Donato, N. Lissencephaly: Update on diagnostics and clinical management. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 35, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, B.S.; Archer, J.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Caciagli, L.; Cendes, F.; Chinvarun, Y.; Concha, L.; Federico, P.; Gaillard, W.; Kobayashi, E.; et al. ILAE neuroimaging task force highlight: Subcortical laminar heterotopia. Epileptic Disord. 2024, 26, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, P.-L.; Souville, I.; Boddaert, N.; Elie, C.; Pinard, J.M.; Plouin, P.; Moutard, M.L.; Portes, V.D.; Van Esch, H.; Joriot, S.; et al. The location of DCX mutations predicts malformation severity in X-linked lissencephaly. Neurogenetics 2008, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Liu, N.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, B.; Song, F.; Dong, R.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. DCX variants in two unrelated Chinese families with subcortical band heterotopia: Two case reports and review of literature. Heliyon 2023, 14, e22323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.H.; Kuo, P.W.; Myers, C.T.; Li, S.W.; Lin, W.C.; Fu, T.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Mefford, H.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, J.W. A novel DCX missense mutation in a family with X-linked lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia syndrome inherited from a low-level somatic mosaic mother: Genetic and functional studies. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portes, V.D.; Francis, F.; Pinard, J.-M.; Desguerre, I.; Moutard, M.-L.; Snoeck, I.; Meiners, L.C.; Capron, F.; Cusmai, R.; Ricci, S.; et al. doublecortin is the major gene causing X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH). Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, R.; Parrini, E. Neuronal migration disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 38, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, A.; Cendes, F.; Theodore, W.H.; Gill, R.S.; Koepp, M.J.; Hogan, R.E.; Jackson, G.D.; Federico, P.; Labate, A.; Vaudano, A.E.; et al. Recommendations for the use of structural magnetic resonance imaging in the care of patients with epilepsy: A consensus report from the International League against Epilepsy Neuroimaging Task Force. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykamp, K.; Anderson, M.; Powers, M.; Garcia, J.; Herrera, B.; Ho, Y.-Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Patil, N.; Thusberg, J.; Westbrook, M.; et al. Sherloc: A comprehensive refinement of the ACMG–AMP variant classification criteria. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 19, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejaver, V.; Byrne, A.B.; Feng, B.J.; Pagel, K.A.; Mooney, S.D.; Karchin, R.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.; Harrison, S.M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Greenblatt, M.S.; et al. Calibration of computational tools for missense variant pathogenicity classification and ClinGen recommendations for PP3/BP4 criteria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Family | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variant type | missense | nonsense | nonsense |
| NT change | c.601A>G | c.210C>G | c.907C>T |
| AA change | p.Lys201Glu | p.Tyr70* | p.Arg303* |
| Accession no. | - | rs587783532 | rs587783592 |
| gnomAD variant frequency | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MutationTaster | disease-causing | disease-causing | disease-causing |
| PolyPhen2 | probably damaging | - | - |
| Revel | 0.916 | - | - |
| CADD-phred | 26.20 | 34.00 | 36.00 |
| MetaDome | 0.25 | - | - |
| Alpha Missense | 0.9989 | - | - |
| ACMG classification | likely pathogenic | pathogenic | pathogenic |
| ACMG criteria | PM1 + PM2 + PP1 + PP3 + PP4 | PVS1 + PM2 + PP1 | PVS1 + PM2 + PM6 + PP5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Procopio, R.; Fortunato, F.; Gagliardi, M.; Talarico, M.; Sammarra, I.; Sarubbi, M.C.; Malanga, D.; Annesi, G.; Gambardella, A. Phenotypic Variability in Novel Doublecortin Gene Variants Associated with Subcortical Band Heterotopia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105505
Procopio R, Fortunato F, Gagliardi M, Talarico M, Sammarra I, Sarubbi MC, Malanga D, Annesi G, Gambardella A. Phenotypic Variability in Novel Doublecortin Gene Variants Associated with Subcortical Band Heterotopia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105505
Chicago/Turabian StyleProcopio, Radha, Francesco Fortunato, Monica Gagliardi, Mariagrazia Talarico, Ilaria Sammarra, Maria Chiara Sarubbi, Donatella Malanga, Grazia Annesi, and Antonio Gambardella. 2024. "Phenotypic Variability in Novel Doublecortin Gene Variants Associated with Subcortical Band Heterotopia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105505
APA StyleProcopio, R., Fortunato, F., Gagliardi, M., Talarico, M., Sammarra, I., Sarubbi, M. C., Malanga, D., Annesi, G., & Gambardella, A. (2024). Phenotypic Variability in Novel Doublecortin Gene Variants Associated with Subcortical Band Heterotopia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105505







