Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
TSLP Inflammation-Related Diseases and Tezepelumab
2. Methods
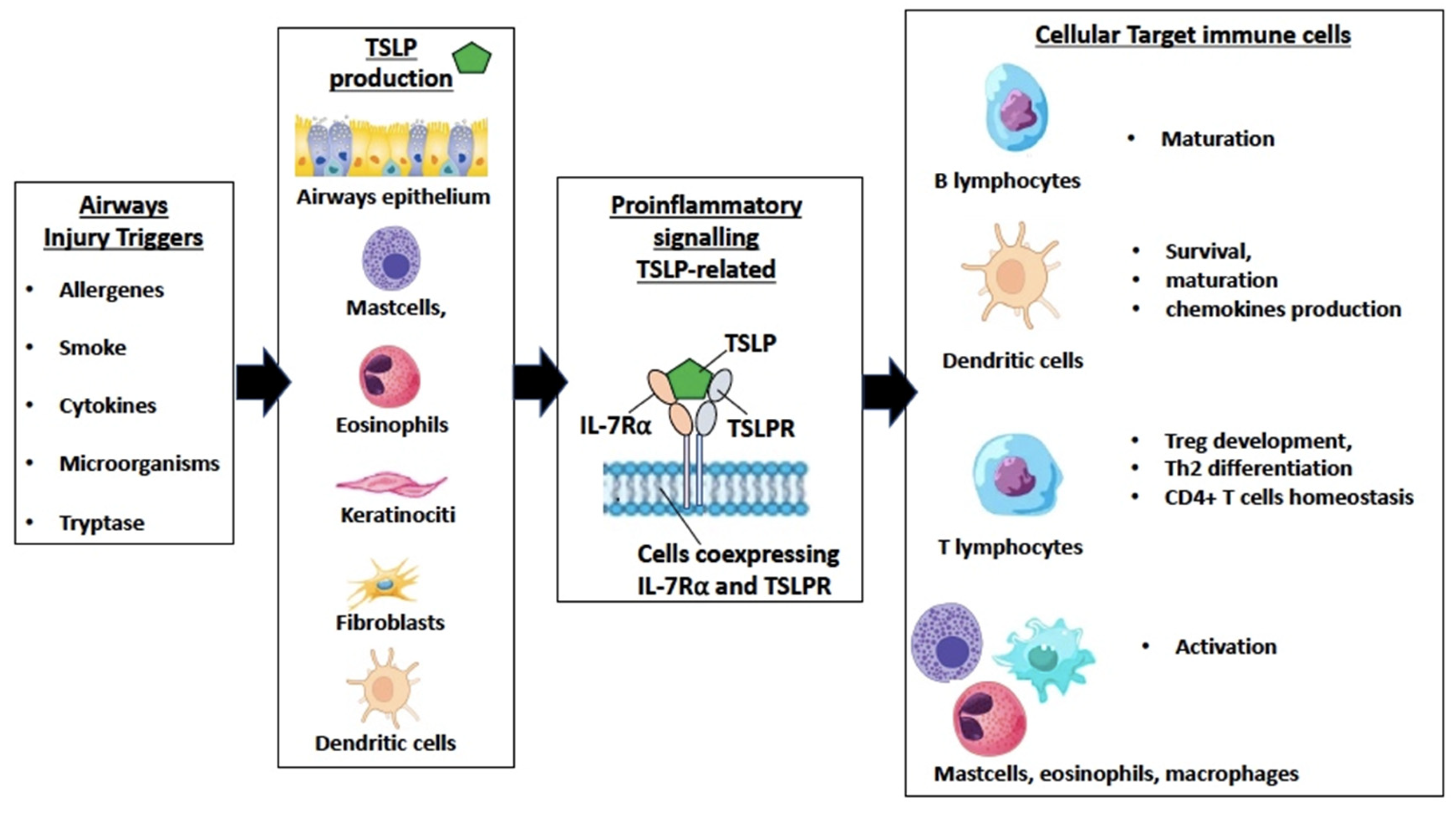
3. TSLP in Epithelium-Driven Airways Inflammation
3.1. TSLP, Alarmins, and Epithelium
3.2. TSLP Production and Airway Remodeling
3.3. TSLP in Asthma and COPD
3.4. TSLP in CRSwNP
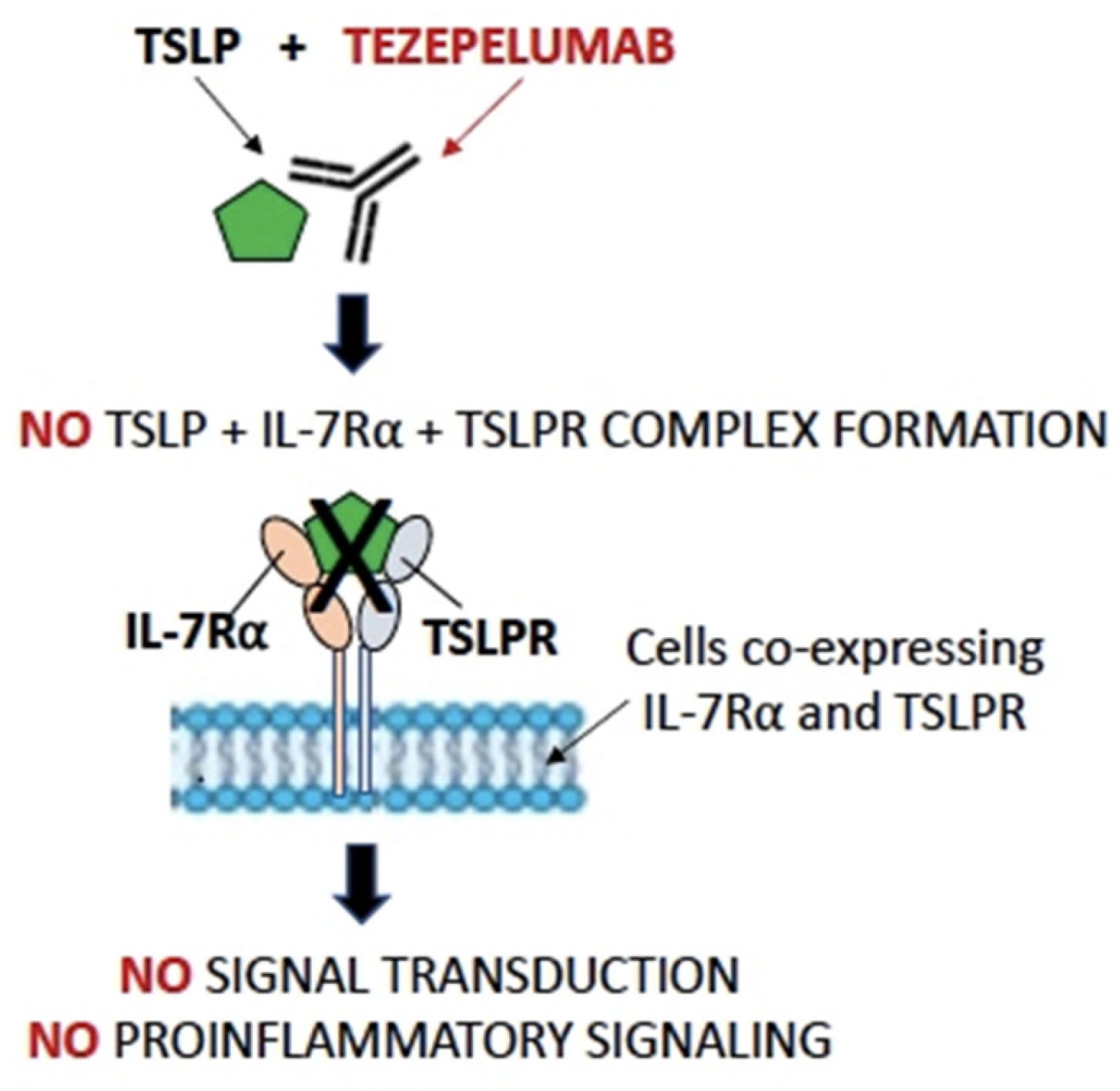
4. Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases
4.1. Tezepelumab in Asthma
4.2. Tezepelumab in CRSwNP
4.3. Tezepelumab in COPD
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenfeder, S.; Umland, S.P.; Cuss, F.M.; Chapman, R.W.; Egan, R.W. Th2 Cytokines and Asthma—The Role of Interleukin-5 in Allergic Eosinophilic Disease. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Stewart, K.; Misirovs, R.; Lipworth, B.J. Targeting Downstream Type 2 Cytokines or Upstream Epithelial Alarmins for Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canè, L.; Poto, R.; Palestra, F.; Pirozzi, M.; Parashuraman, S.; Iacobucci, I.; Ferrara, A.L.; La Rocca, A.; Mercadante, E.; Pucci, P.; et al. TSLP is localized in and released from human lung macrophages activated by T2-high and T2-low stimuli: Relevance in asthma and COPD. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, L.J.; Chandra, R.K.; Li, P.; Turner, J.H. Role of Tissue Eosinophils in Chronic Rhinosinusitis–Associated Olfactory Loss. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Bu, X.; Luan, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Distinct Type 2-High Inflammation Associated Molecular Signatures of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps with Comorbid Asthma. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, K.; Bachert, C.; Konge, L.; Thomsen, S.F.; Pedersen, A.E.; Poulsen, S.S.; Martin-Bertelsen, T.; Winther, O.; Backer, V.; Von Buchwald, C. Airway Inflammation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Asthma: The United Airways Concept Further Supported. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, G.; Sfriso, P.; Marioni, G. Role of Blood Inflammatory Cells in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019, 139, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzecry, V.; Pravettoni, V.; Segatto, G.; Marzano, A.; Ferrucci, S. Type 2-Driven Inflammation—Atopic Dermatitis, Asthma, and Hypereosinophilia—Successfully Treated with Dupilumab. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, E.B.; Cyr, S.L.; Arima, K.; McDonald, R.A.; Levit, N.A.; Nestle, F.O. Current and Emerging Strategies to Inhibit Type 2 Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Williams, D.E.; Morrissey, P.J.; Garka, K.; Foxworthe, D.; Price, V.; Friend, S.L.; Farr, A.; Bedell, M.A.; Jenkins, N.A.; et al. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a novel murine lymphoid growth factor. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentmeier, H.; Drexler, H.G.; Fleckenstein, D.; Zaborski, M.; Armstrong, A.; Sims, J.E.; Lyman, S.D. Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Varricchi, G.; Pecoraro, A.; Marone, G.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Isoforms, Inflammatory Disorders, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianferoni, A.; Spergel, J. The importance of TSLP in allergic disease and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, I.; Bahmer, T.; Braido, F.; Cosío, B.G.; Humbert, M.; Idzko, M.; Adamek, L. Severe T2-High Asthma in the Biologics Era: European Experts’ Opinion. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnes, J.R.; Molfino, N.A.; Colice, G.; Martin, U.; Corren, J.; Menzies-Gow, A. Targeting TSLP in Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, S.M. Tezepelumab: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves Maintenance Treatment for Severe Asthma | FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-maintenance-treatment-severe-asthma (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Tezspire | European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tezspire (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Kurihara, M.; Kabata, H.; Irie, M.; Fukunaga, K. Current Summary of Clinical Studies on Anti-TSLP Antibody, Tezepelumab, in Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, C.; Colantuono, S.; Ciasca, G.; Basile, U.; Di Santo, R.; Bagnasco, D.; Passalacqua, G.; Caminati, M.; Michele, S.; Senna, G.; et al. Different aspects of severe asthma in real life: Role of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins and correlation to comorbidities and disease severity. Allergy 2023, 78, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Comeau, M.R.; Jessup, H.K.; Yoon, B.R.; Brewer, A.; Chartier, S.; Paquette, N.; Ziegler, S.F.; Sarfati, M.; Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, K.; Peelman, F.; Braun, H.; Lopez, J.; Van Rompaey, D.; Dansercoer, A.; Vandenberghe, I.; Pauwels, K.; Tavernier, J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Structure and antagonism of the receptor complex mediated by human TSLP in allergy and asthma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata, H.; Flamar, A.L.; Mahlakõiv, T.; Moriyama, S.; Rodewald, H.R.; Ziegler, S.F.; Artis, D. Targeted deletion of the TSLP receptor reveals cellular mechanisms that promote type 2 airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.H.; Park, C.O.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, Y.S.; Bae, B.G.; Noh, J.Y.; Lee, K.H. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-activated invariant natural killer T cells trigger an innate allergic immune response in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 290–299.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattarini, L.; Trichot, C.; Bogiatzi, S.; Grandclaudon, M.; Meller, S.; Keuylian, Z.; Durand, M.; Volpe, E.; Madonna, S.; Cavani, A.; et al. TSLP-Activated Dendritic Cells Induce Human T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation through OX40-Ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1529–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Duramad, O.; Hori, T.; Delespesse, G.J.; Watanabe, N.; Qin, F.X.F.; Yao, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.J. TSLP-Activated Dendritic Cells Induce an Inflammatory T Helper Type 2 Cell Response through OX40 Ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherzad, A.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S.; Head, R.; Surgery, N.; Maximilian, J. Current Understanding of Nasal Epithelial Cell Mis-Differentiation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal, R.G.; Randell, S.H.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Voynow, J.; Sunday, M.E. Airway Epithelial Cells: Current Concepts and Challenges. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, E.E.; Kashyap, M.; Leonard, W.J. TSLP: A Key Regulator of Asthma Pathogenesis. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2012, 9, e83–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsbjerg, C.M.; Sverrild, A.; Lloyd, C.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Bel, E.H. Anti-Alarmins in Asthma: Targeting the Airway Epithelium with next-Generation Biologics. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata, H.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S. The Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (ILC2) Regulatory Network and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 286, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Testino, E.; Nicola, S.; Melissari, L.; Russo, M.; Canevari, R.F.; Brussino, L.; Passalacqua, G. Specific Therapy for T2 Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakos, E.; Papadopoulos, N.G. IL-25: The Missing Link between Allergy, Viral Infection, and Asthma? Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 256fs38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickel, E.A.; Siegel, L.A.; Yoon, B.-R.P.; Rottman, J.B.; Kugler, D.G.; Swart, D.A.; Anders, P.M.; Tocker, J.E.; Comeau, M.R.; Budelsky, A.L. Identification of Functional Roles for Both IL-17RB and IL-17A in Mediating IL-25-Induced Activities. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4299–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Peng, N.; Tang, Y.; Yu, N.; Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Ciccia, F.; Lu, L. Roles of IL-25 in Type 2 Inflammation and Autoimmune Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Liao, S.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.Y. Role of IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP in Triggering United Airway Diseases toward Type 2 Inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 2794–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peebles, R.S.; Aronica, M.A. Proinflammatory Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Asthma. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.F. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Allergic Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Zuo, Y.G. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Cutaneous Immune-Mediated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 698522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, J.; Watanabe, N.; Kido, M.; Saga, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Nishio, A.; Chiba, T. Human TSLP and TLR3 Ligands Promote Differentiation of Th17 Cells with a Central Memory Phenotype under Th2-polarizing Conditions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Kabata, H.; Kabashima, K.; Asano, K. Anti-TSLP Antibodies: Targeting a Master Regulator of Type 2 Immune Responses. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Yang, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.H. Role of Nasal Fibroblasts in Airway Remodeling of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: The Modulating Functions Reexamined. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paplinska-Goryca, M.; Misiukiewicz-Stepien, P.; Proboszcz, M.; Nejman-Gryz, P.; Gorska, K.; Krenke, R. The Expressions of TSLP, IL-33, and IL-17A in Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells from Asthma and COPD Patients are Related to Epithelial–Macrophage Interactions. Cells 2020, 9, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moermans, C.; Damas, K.; Guiot, J.; Njock, M.S.; Corhay, J.L.; Henket, M.; Schleich, F.; Louis, R. Sputum IL-25, IL-33 and TSLP, IL-23 and IL-36 in airway obstructive diseases. Reduced levels of IL-36 in eosinophilic phenotype. Cytokine 2021, 140, 155421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Park, H.J.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, K.S.; Yoo, K.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Rhee, C.K. Association between Serum Levels of Interleukin-25/Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and the Risk of Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejman-Gryz, P.; Górska, K.; Paplińska-Goryca, M.; Proboszcz, M.; Krenke, R. Periostin and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Potential Crosstalk in Obstructive Airway Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heerden, D.; van Binnendijk, R.S.; Tromp, S.A.M.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; van Neerven, R.J.J.; den Hartog, G. Asthma-Associated Long TSLP Inhibits the Production of IgA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-Parke, H.; Linden, D.; Mousnier, A.; Scott, I.C.; Killick, H.; Borthwick, L.A.; Fisher, A.J.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C.; Kidney, J.C. Altered Differentiation and Inflammation Profiles Contribute to Enhanced Innate Responses in Severe COPD Epithelium to Rhinovirus. Infect. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 741989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, N.; Klingler, A.I.; Tan, B.K.; Poposki, J.A.; Hulse, K.E.; Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; et al. Epithelial activators of type 2 inflammation: Elevation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin, but not IL-25 or IL-33, in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chicago, Illinois. Allergy 2018, 73, 2251–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divekar, R.; Kita, H. Recent Advances in Epithelium-Derived Cytokines (IL-33, IL-25 and TSLP) and Allergic Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, W.T.; Zhang, J.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Vliagoftis, H.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Sokol, C.L.; Robinson, C.; Jacquet, A. Protease Allergens as Initiators–Regulators of Allergic Inflammation. Allergy 2023, 78, 1148–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M.; Sahin, M.; Yenisey, C. Increased TSLP, IL-33, IL-25, IL-19, IL 21 and Amphiregulin (AREG) Levels in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyp. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiao, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Association between Methylation in Nasal Epithelial TSLP Gene and Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, N.; Poposki, J.A.; Klingler, A.I.; Tan, B.K.; Hulse, K.E.; Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; et al. Role of RANK-L as a potential inducer of ILC2-mediated type 2 inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boita, M.; Garzaro, M.; Raimondo, L.; Riva, G.; Mazibrada, J.; Pecorari, G.; Bucca, C.; Bellone, G.; Vizio, B.; Heffler, E.; et al. Eosinophilic Inflammation of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Is Related to OX40 Ligand Expression. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottini, M.; Licini, A.; Lombardi, C.; Bagnasco, D.; Comberiati, P.; Berti, A. Small Airway Dysfunction and Poor Asthma Control: A Dangerous Liaison. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2021, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.B.; Trudo, F.; Voorham, J.; Xu, X.; Kerkhof, M.; Jie, J.L.Z.; Tran, T.N. Adverse Outcomes from Initiation of Systemic Corticosteroids for Asthma: Long-Term Observational Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corren, J.; Garcia Gil, E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Parnes, J.R.; van der Merwe, R.; Sałapa, K.; O’Quinn, S. Tezepelumab Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma in PATHWAY. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diver, S.; Khalfaoui, L.; Emson, C.; Wenzel, S.E.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wechsler, M.E.; Johnston, J.; Molfino, N.; Parnes, J.R.; Megally, A.; et al. Effect of Tezepelumab on Airway Inflammatory Cells, Remodeling, and Hyperresponsiveness in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma (CASCADE): A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Brightling, C.E.; Kuna, P.; Korn, S.; Welte, T.; Griffiths, J.M.; Sałapa, K.; Hellqvist, Å.; Almqvist, G.; et al. Evaluation of the Oral Corticosteroid-Sparing Effect of Tezepelumab in Adults with Oral Corticosteroid-Dependent Asthma (SOURCE): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Korn, S.; Corren, J.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.; Bednarczyk, A.; Ponnarambil, S.; Caveney, S.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Tezepelumab in People with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma (DESTINATION): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Extension Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.; Snidvongs, K.; Xie, M.; Banglawala, S.; Sommer, D. High tissue eosinophilia as a marker to predict recurrence for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04851964 (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Shen, S.; Xian, M.; Yan, B.; Lan, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (DUBHE): Rationale and design of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Asia Pac. Allergy 2024, 14, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04039113 (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Corren, J.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP: From Allergy to Cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuking, M.B.; Burkhard, R. Microbial Modulation of Intestinal T Helper Cell Responses and Implications for Disease and Therapy. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.P.; Rabe, K.F.; Hanania, N.A.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Cole, J.; Bafadhel, M.; Christenson, S.A.; Papi, A.; Singh, D.; Laws, E.; et al. Dupilumab for COPD with Type 2 Inflammation Indicated by Eosinophil Counts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Boulet, L.P.; Cockcroft, D.W.; Davis, B.E.; Korn, S.; Kornmann, O.; Leigh, R.; Mayers, I.; et al. Inhaled anti-TSLP antibody fragment, ecleralimab, blocks responses to allergen in mild asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2201193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Design | Exacerbations Annualized Rate of Exacerbations/Relative Reduction vs. Placebo | OCS | FEV1 (L) (Difference vs. Placebo) | Control of Disease (Difference vs. Placebo, Evaluated with ACQ6) | Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTHMA | ||||||
| PATHWAY | 70 mg sc Q4w 210 mg sc Q4w 280 mg sc Q2w Placebo | 0.27 (0.20 to 0.36)/62 (42 to 75) 0.20 (0.14 to 0.28)/71 (54 to 82) 0.23 (0.17 to 0.32)/66 (47 to 79) 0.72 (0.61 to 0.86) | Not assessed | +0.12 (0.02 to 0.22) +0.13 (0.03 to 0.23) +0.15 (0.05 to 0.25) | −0.26 (−0.52 to 0.01) −0.29 (−0.56 to −0.01) −0.31 (−0.58 to −0.04) | Exacerbation reduction. Respiratory function improvement |
| NAVIGATOR | 210 mg sc Q4W Placebo | 0.93 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.07) 2.10 (95% CI 1.84 to 2.39) | Not assessed | +0.13 (0.08 to 0.18) | −0.33 (−0.46 to −0.20) | Exacerbation reduction. Respiratory function improvement. |
| SOURCE | 210 mg Q4W Placebo | 1.38 (0.98 to 1.95) 2.00 (1.46 to 2.74) Annualized rate of exacerbations | 1.28 (0.69–2.35) Cumulative OR | +0.26 (0.13 to 0.39) | −0.37 (0.71 to −0.02) | No differences in OCS intake. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagnasco, D.; De Ferrari, L.; Bondi, B.; Candeliere, M.G.; Mincarini, M.; Riccio, A.M.; Braido, F. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115972
Bagnasco D, De Ferrari L, Bondi B, Candeliere MG, Mincarini M, Riccio AM, Braido F. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115972
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagnasco, Diego, Laura De Ferrari, Benedetta Bondi, Maria Giulia Candeliere, Marcello Mincarini, Anna Maria Riccio, and Fulvio Braido. 2024. "Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115972
APA StyleBagnasco, D., De Ferrari, L., Bondi, B., Candeliere, M. G., Mincarini, M., Riccio, A. M., & Braido, F. (2024). Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Tezepelumab in Airway Diseases: From Physiological Role to Target Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115972





