Characterization of High and Low IFNG-Expressing Subgroups in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
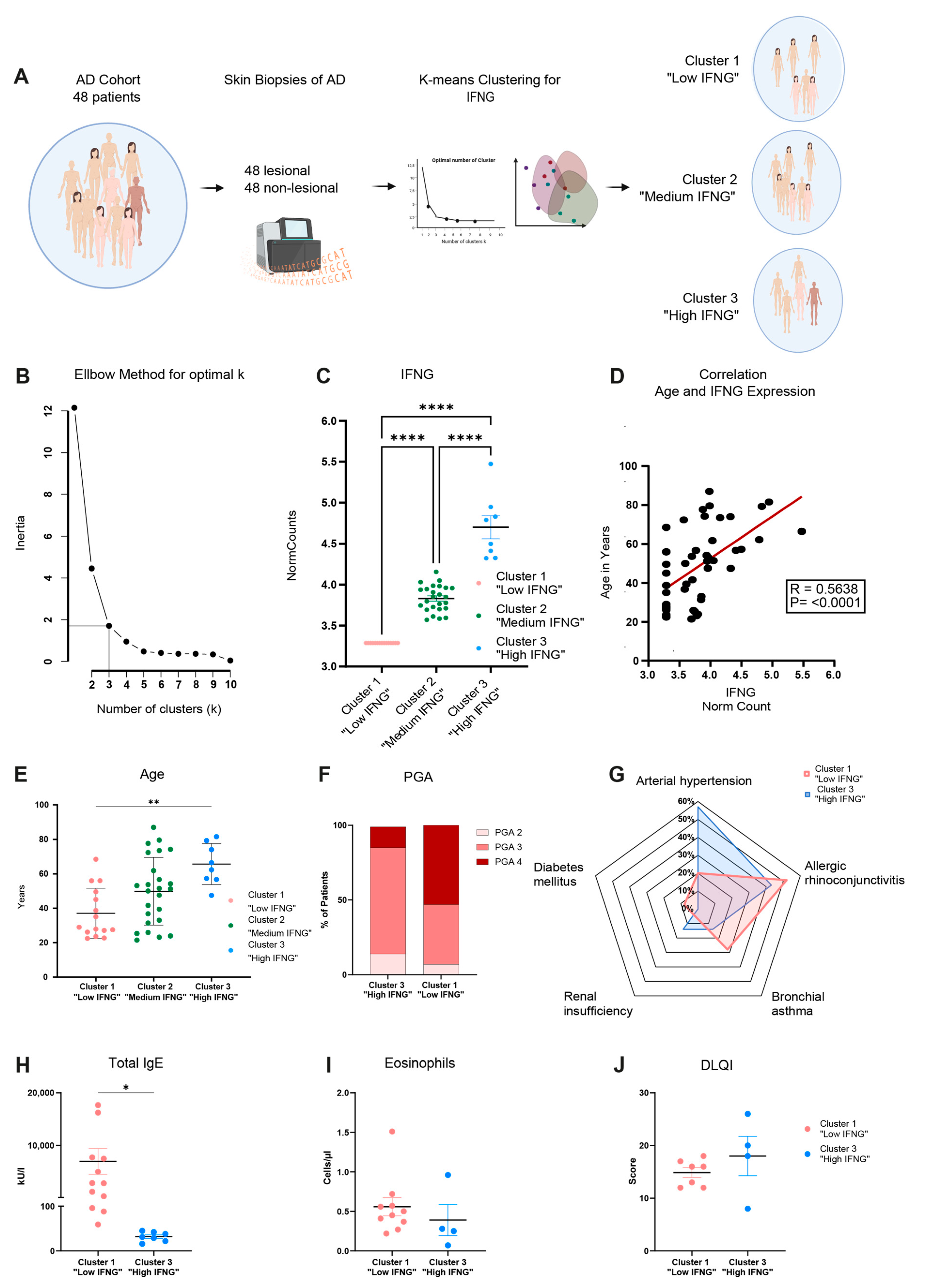
2.1. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals High, Medium and Low IFNG Subgroups of AD Correlating with Patients’ Ages
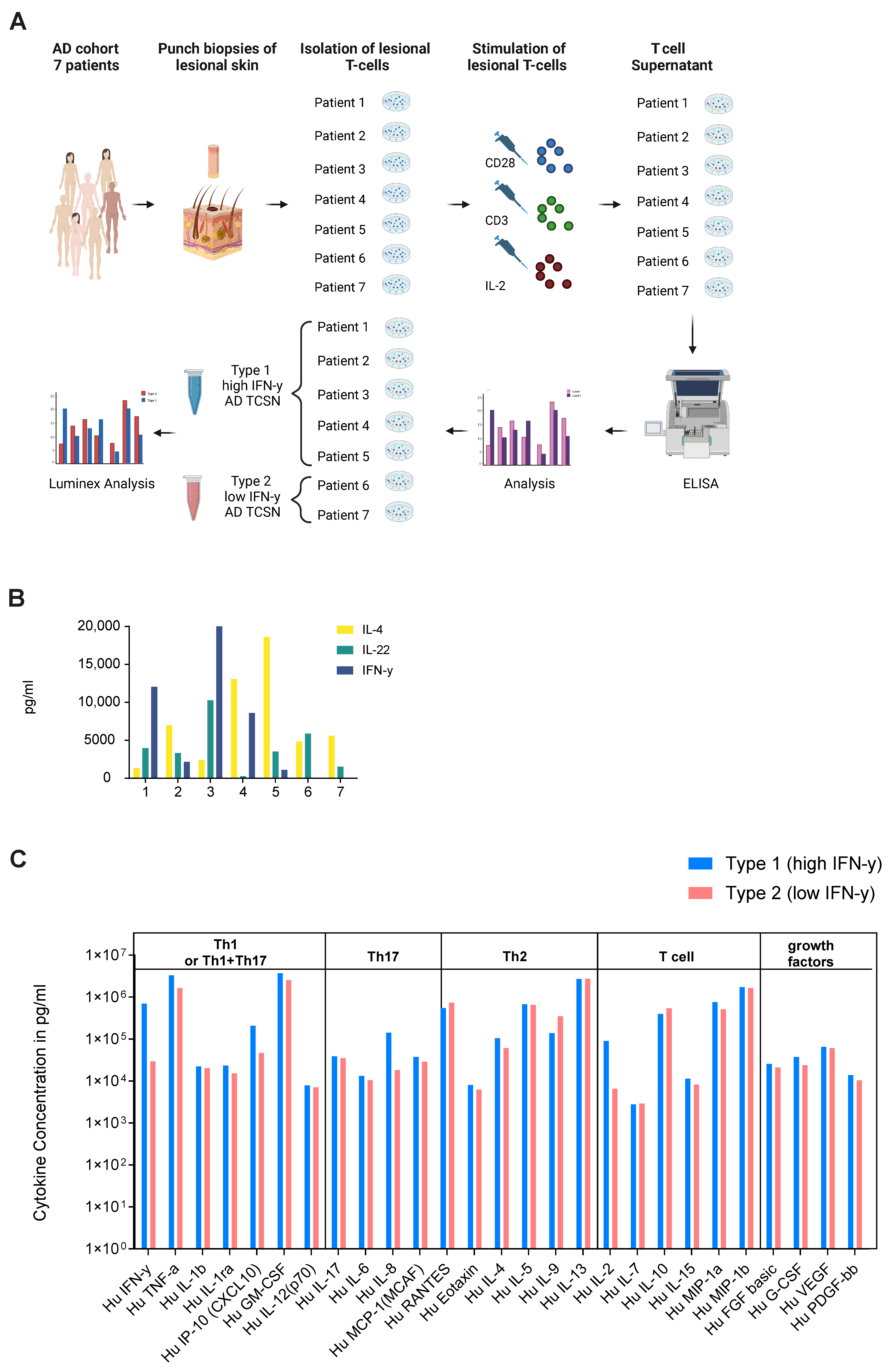
2.2. Ex Vivo Secretome Analysis of Lesional T Cells of AD Patients Confirms High and Low IFN-γ Subgroups
2.3. Low and High IFNG AD Subgroups Show Distinct Molecular Pathways with a Strong Activation of Type 1 Immunity in the High IFNG Group

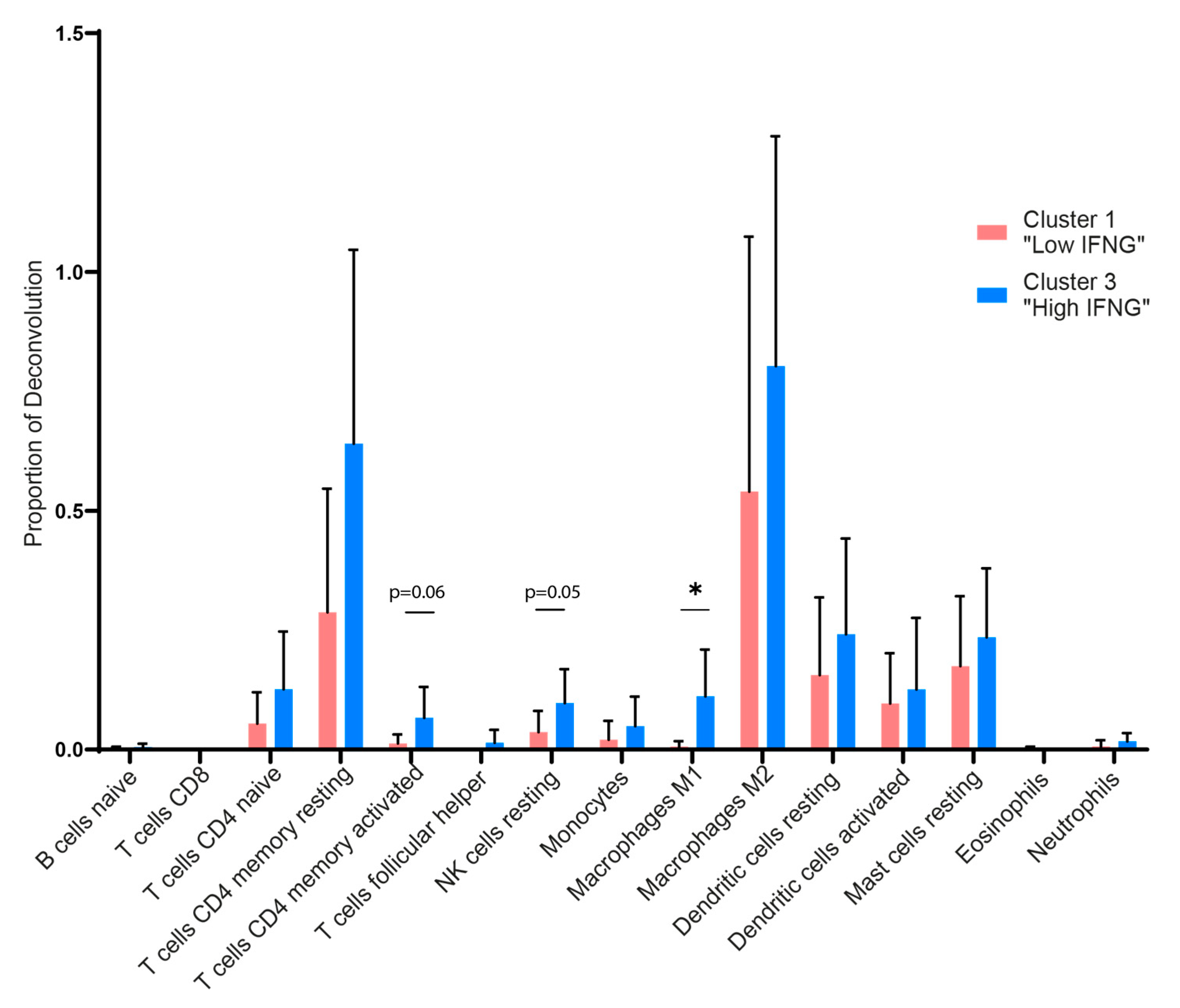
2.4. Digital Cytometry Reveals Higher Amounts of M1 Macrophages, NK Cells and CD4 Memory T Cells in the High IFNG AD Subgroup
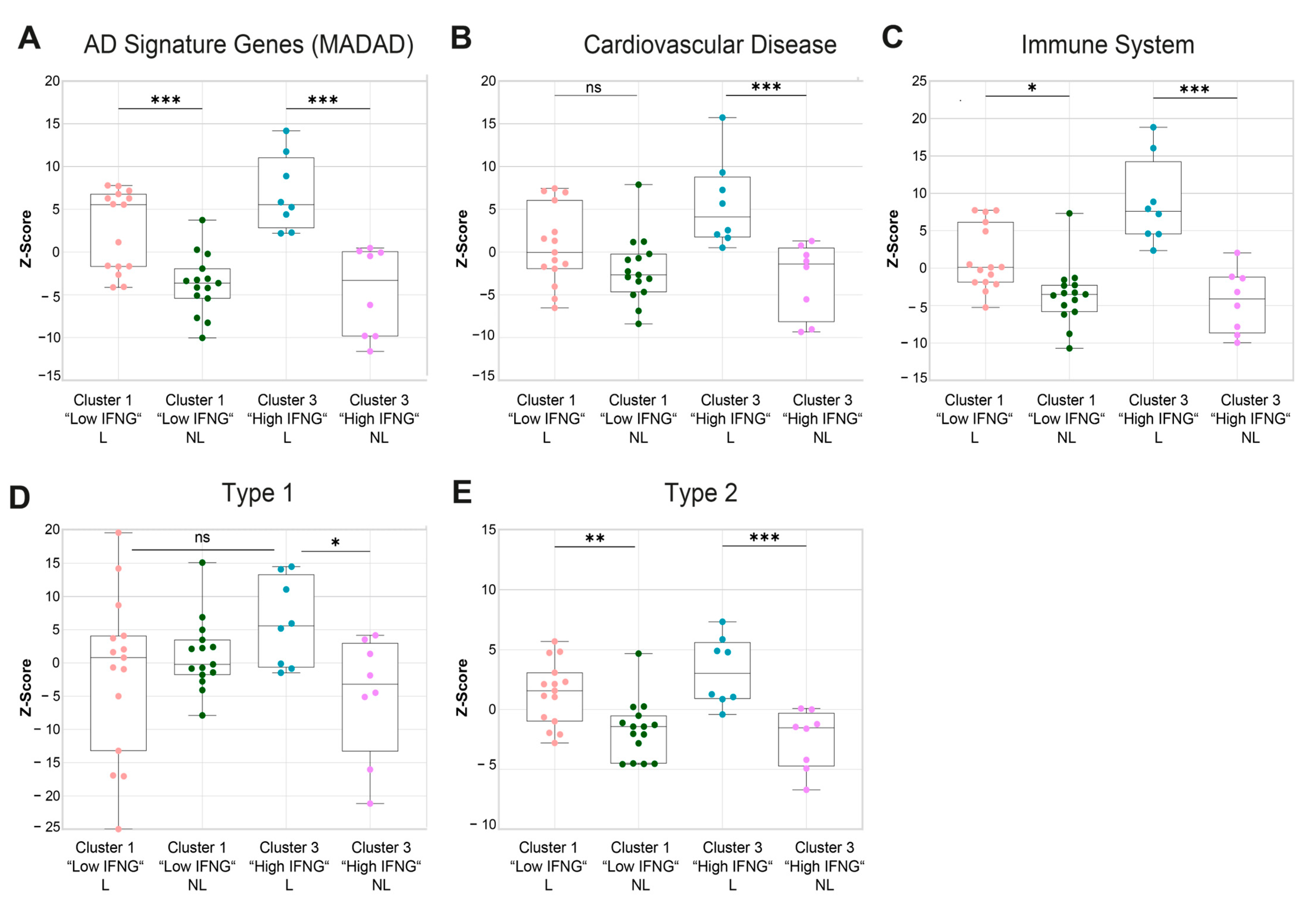
2.5. Gene Set Variation Analysis Shows a Higher Cardiovascular Risk, a More Pronounced Activation of the Immune System and a Higher Enrichment of Type 1-Associated Genes in the High IFNG AD Subgroup
2.6. High and Low IFNG AD Subgroups Share a Strong Common Core Signature with Dupilumab Response Genes

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Cohort
4.2. RNAseq Library Preparation, Sequencing, Mapping and Quantification
4.3. Cluster Analysis (Elbow Method, K-Mean Clustering) and RNAseq Analysis
4.4. Digital Cytometry/Deconvolution—CIBERSORTx
4.5. Gene Set Variation Analysis
4.6. Inform Algorithms and Comparison with Dupilumab Signature
4.7. Visualization
4.8. Analysis of the Secretome of Lesional T Cells
4.9. Language Editing
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bieber, T.; Paller, A.S.; Kabashima, K.; Feely, M.; Rueda, M.J.; Ross Terres, J.A.; Wollenberg, A. Atopic dermatitis: Pathomechanisms and lessons learned from novel systemic therapeutic options. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1432–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowicki, T.; He, H.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis endotypes and implications for targeted therapeutics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Lacour, J.-P.; Spelman, L.; Galimberti, R.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Bissonnette, R.; King, B.A.; Thyssen, J.P.; Silverberg, J.I.; Bieber, T.; et al. Baricitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and inadequate response to topical corticosteroids: Results from two randomized monotherapy phase III trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Bieber, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Beck, L.A.; Blauvelt, A.; Cork, M.J.; Silverberg, J.I.; Deleuran, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Lacour, J.-P.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Dupilumab versus Placebo in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Källström, E.; Roscher, I.; Andreasson, A.; Bäck, O.; van Hage-Hamsten, M. Decreased frequency of intracellular IFN-gamma producing T cells in whole blood preparations from patients with atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, M.R.; Hofer, M.F.; Gately, M.; Trumble, A.; Leung, D.Y. Down-regulating effects of IL-4 and IL-10 on the IFN-gamma response in atopic dermatitis. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 6174–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jujo, K.; Renz, H.; Abe, J.; Gelfand, E.W.; Leung, D.Y. Decreased interferon gamma and increased interleukin-4 production in atopic dermatitis promotes IgE synthesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1992, 90, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Schneider, L.C.; Leung, D.Y.; Ellis, C.N.; Jaffe, H.S.; Izu, A.E.; Bucalo, L.R.; Hirabayashi, S.E.; Tofte, S.J.; Cantu-Gonzales, G.; et al. Recombinant interferon gamma therapy for atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993, 28, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, S.R.; Hanifin, J.M.; Hamilton, T.; Tofte, S.J.; Cooper, K.D. Long-term effectiveness and safety of recombinant human interferon gamma therapy for atopic dermatitis despite unchanged serum IgE levels. Arch. Dermatol. 1998, 134, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.T.; Stevens, S.R. Atopic dermatitis: The role of recombinant interferon-gamma therapy. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Katayama, I. Gamma-interferon therapy for severe cases of atopic dermatitis of the adult type. J. Dermatol. 1995, 22, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, K.; Leung, D.Y.M. Recent considerations in the use of recombinant interferon gamma for biological therapy of atopic dermatitis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M. Viruses and interferon: A fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kak, G.; Raza, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ): Exploring its implications in infectious diseases. Biomol. Concepts 2018, 9, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruner, S.; Liebenthal, C.; Heusser, C.; Brinkmann, V.; Zwirner, A.; Reinicke, C.; Harnack, K.; Sönnichsen, N.; Volk, H.D. The influence of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 on IgE production in B lymphocytes of patients with atopic dermatitis. A possible criterion for selection of patients for interferon therapy. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1991, 71, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Hama, K.; Furue, M.; Ishibashi, Y. Production of IL-4, IL-2, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1992, 3, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, H.; Jujo, K.; Bradley, K.L.; Domenico, J.; Gelfand, E.W.; Leung, D.Y. Enhanced IL-4 production and IL-4 receptor expression in atopic dermatitis and their modulation by interferon-gamma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 99, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bravo, M.; La Minguito de Escalera, M.; Domínguez, P.M.; González-Cintado, L.; del Fresno, C.; Martín, P.; Del Martínez Hoyo, G.; Ardavín, C. IL-4 blocks TH1-polarizing/inflammatory cytokine gene expression during monocyte-derived dendritic cell differentiation through histone hypoacetylation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, A.; Akdis, M.; Kleemann, D.; Altznauer, F.; Simon, H.U.; Graeve, T.; Noll, M.; Bröcker, E.B.; Blaser, K.; Akdis, C.A. T cell-mediated Fas-induced keratinocyte apoptosis plays a key pathogenetic role in eczematous dermatitis. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, Y.; Takagi, N.; Nagata, H.; Inoue, S. Interferon-γ downregulates tight junction function, which is rescued by interleukin-17A. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoh, H.; Ishitsuka, A.; Fujine, E.; Matsuhaba, S.; Nakamura, M.; Ito, H.; Inagaki, N.; Banno, Y.; Seishima, M. IFN-γ Reduces Epidermal Barrier Function by Affecting Fatty Acid Composition of Ceramide in a Mouse Atopic Dermatitis Model. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 3030268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Corinti, S.; La Placa, M.; Didona, B.; Girolomoni, G. Interferon-gamma promotes exaggerated cytokine production in keratinocytes cultured from patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Gao, P.-S.; Grigoryev, D.N.; Rafaels, N.M.; Streib, J.E.; Howell, M.D.; Taylor, P.A.; Boguniewicz, M.; Canniff, J.; Armstrong, B.; et al. Human atopic dermatitis complicated by eczema herpeticum is associated with abnormalities in IFN-γ response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traidl, S.; Roesner, L.; Zeitvogel, J.; Werfel, T. Eczema herpeticum in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewe, M.; Gyufko, K.; Schöpf, E.; Krutmann, J. Lesional expression of interferon-gamma in atopic eczema. Lancet 1994, 343, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittler, J.K.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gulewicz, K.J.; Wang, C.Q.F.; Mitsui, H.; Cardinale, I.; de Guzman Strong, C.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Progressive activation of T(H)2/T(H)22 cytokines and selective epidermal proteins characterizes acute and chronic atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, D.A.; Malajian, D.; Krueger, J.G.; Workman, C.T.; Wang, T.; Tian, S.; Litman, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Suárez-Fariñas, M. Meta-analysis derived atopic dermatitis (MADAD) transcriptome defines a robust AD signature highlighting the involvement of atherosclerosis and lipid metabolism pathways. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; He, H.; Malik, K.; Wen, H.-C.; Gonzalez, J.; Chan, T.C.-C.; Estrada, Y.; Zheng, X.; Khattri, S.; et al. The atopic dermatitis blood signature is characterized by increases in inflammatory and cardiovascular risk proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, A.B.; Zhou, L.; Diaz, A.; Ungar, B.; Dan, J.; He, H.; Estrada, Y.D.; Xu, H.; Fernandes, M.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; et al. The proteomic skin profile of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis patients shows an inflammatory signature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, R.; Choi, S.; Zhou, L.; Pavel, A.; Estrada, Y.D.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Increased cardiovascular and atherosclerosis markers in blood of older patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esaki, H.; Ewald, D.A.; Ungar, B.; Rozenblit, M.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Estrada, Y.D.; Peng, X.; Mitsui, H.; Litman, T.; et al. Identification of novel immune and barrier genes in atopic dermatitis by means of laser capture microdissection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäbitz, A.; Hillig, C.; Mubarak, M.; Jargosch, M.; Farnoud, A.; Scala, E.; Kurzen, N.; Pilz, A.C.; Bhalla, N.; Thomas, J.; et al. Spatial transcriptomics landscape of lesions from non-communicable inflammatory skin diseases. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Ungar, B.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Ardeleanu, M.; Esaki, H.; Suprun, M.; Estrada, Y.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Dupilumab progressively improves systemic and cutaneous abnormalities in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwah, V.S.; Kinaret, P.A.S.; Serra, A.; Scala, G.; Lauerma, A.; Fortino, V.; Greco, D. INfORM: Inference of NetwOrk Response Modules. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2136–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fania, L.; Moretta, G.; Antonelli, F.; Scala, E.; Abeni, D.; Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S. Multiple Roles for Cytokines in Atopic Dermatitis: From Pathogenic Mediators to Endotype-Specific Biomarkers to Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, T.; Skabytska, Y.; Kaesler, S.; Volz, T. Regulation of T Cell Immunity in Atopic Dermatitis by Microbes: The Yin and Yang of Cutaneous Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyerich, K.; Novak, N. Immunology of atopic eczema: Overcoming the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Allergy 2013, 68, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facheris, P.; Da Rosa, J.C.; Pagan, A.D.; Angelov, M.; Del Duca, E.; Rabinowitz, G.; Gómez-Arias, P.J.; Rothenberg-Lausell, C.; Estrada, Y.D.; Bose, S.; et al. Age of onset defines two distinct profiles of atopic dermatitis in adults. Allergy 2023, 78, 2202–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Stölzl, D.; Wehkamp, U.; Sun, J.; Gerdes, S.; Sarkar, M.K.; Hübenthal, M.; Zeng, C.; Uppala, R.; et al. Progression of acute-to-chronic atopic dermatitis is associated with quantitative rather than qualitative changes in cytokine responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimkhani, C.; Silverberg, J.I.; Dellavalle, R.P. Defining intrinsic vs. extrinsic atopic dermatitis. Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ishida, K.; Mukumoto, S.; Yamada, Y.; Imokawa, G.; Kabashima, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Bito, T.; Nakamura, M.; Ogasawara, K.; et al. Comparison of skin barrier function and sensory nerve electric current perception threshold between IgE-high extrinsic and IgE-normal intrinsic types of atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Stasikowska-Kanicka, O.; Wągrowska-Danilewicz, M.; Hawro, M.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M.; Hawro, T. Clinically uninvolved but not healthy-The skin of patients with atopic dermatitis is primed for itch and inflammation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Del Duca, E.; Arents, B.; Bissonnette, R.; Drucker, A.M.; Flohr, C.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Hijnen, D.; Kabashima, K.; Leshem, Y.A.; et al. Treat-to-target in dermatology: A scoping review and International Eczema Council survey on the approach in atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Suryawanshi, H.; Morozov, P.; Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Del Duca, E.; Kim, H.J.; Kameyama, N.; Estrada, Y.; Der, E.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of human skin identifies novel fibroblast subpopulation and enrichment of immune subsets in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, Y. Extrinsic and intrinsic types of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-J.; Song, M.-G.; Sung, W.-T.; Lee, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, E.-S.; Yang, J.-M. Comparison of transepidermal water loss, capacitance and pH values in the skin between intrinsic and extrinsic atopic dermatitis patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2003, 18, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danastas, K.; Miranda-Saksena, M.; Cunningham, A.L. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Interactions with the Interferon System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, P.Y.; Leung, D.Y.M. The infectious aspects of atopic dermatitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2010, 30, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegräber, M.; Worm, M.; Werfel, T.; Svensson, A.; Novak, N.; Simon, D.; Darsow, U.; Augustin, M.; Wollenberg, A. Recurrent eczema herpeticum—A retrospective European multicenter study evaluating the clinical characteristics of eczema herpeticum cases in atopic dermatitis patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymański, U.; Cios, A.; Ciepielak, M.; Stankiewicz, W. Cytokines and apoptosis in atopic dermatitis. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. Immunological differences between intrinsic and extrinsic types of atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasraie, S.; Werfel, T. Role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 942375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, S.; Lou, Z.; Gao, J. The macrophage polarization in inflammatory dermatosis and its potential drug candidates. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, T.; Waisman, A.; Ranjan, R.; Roes, J.; Krieg, T.; Müller, W.; Roers, A.; Eming, S.A. Differential roles of macrophages in diverse phases of skin repair. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3964–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.P.; Hogaboam, C.M. Macrophages in allergic asthma: Fine-tuning their pro- and anti-inflammatory actions for disease resolution. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiekens, R.C.; Thepen, T.; Oosting, A.J.; Bihari, I.C.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Knol, E.F. Heterogeneity within tissue-specific macrophage and dendritic cell populations during cutaneous inflammation in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 145, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, C.; Zhou, W.; Ma, X.; Pu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lv, F. TRPA1 deficiency alleviates inflammation of atopic dermatitis by reducing macrophage infiltration. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelato, F.; Mastorino, L.; Stepkina, E.; Cavaliere, G.; Ribero, S.; Quaglino, P.; Ortoncelli, M. Is Dupilumab as Effective in Intrinsic Atopic Dermatitis as It Is in Extrinsic Atopic Dermatitis? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and Cancer Risk with Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascott, A.; Mulick, A.; Yu, A.M.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Schmidt, M.; Abuabara, K.; Smeeth, L.; Roberts, A.; Langan, S.M. Atopic eczema and major cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based studies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, A.M.; Harvey, P.J. Atopic dermatitis and cardiovascular disease: What are the clinical implications? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1736–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverwood, R.J.; Forbes, H.J.; Abuabara, K.; Ascott, A.; Schmidt, M.; Schmidt, S.A.J.; Smeeth, L.; Langan, S.M. Severe and predominantly active atopic eczema in adulthood and long term risk of cardiovascular disease: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2018, 361, k1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, J.P.; Maqsood, M.H.; Gelfand, J.M.; Weber, B.N.; Bangalore, S.; Lo Sicco, K.I.; Garshick, M.S. Cardiovascular and Venous Thromboembolic Risk With JAK Inhibitors in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, R.; Garzorz-Stark, N.; Lauffer, F.; Jargosch, M.; Pilz, C.; Roenneberg, S.; Schäbitz, A.; Böhner, A.; Seiringer, P.; Thomas, J.; et al. Integration of phenomics and transcriptomics data to reveal drivers of inflammatory processes in the skin. bioRxiv 2020. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Steen, C.B.; Liu, C.L.; Gentles, A.J.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Scherer, F.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Esfahani, M.S.; Luca, B.A.; Steiner, D.; et al. Determining cell type abundance and expression from bulk tissues with digital cytometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Olesen, C.M.; Pavel, A.B.; Clausen, M.-L.; Wu, J.; Estrada, Y.; Zhang, N.; Agner, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Tape-Strip Proteomic Profiling of Atopic Dermatitis on Dupilumab Identifies Minimally Invasive Biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möbus, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Harder, I.; Boraczynski, N.; Szymczak, S.; Hübenthal, M.; Stölzl, D.; Gerdes, S.; Kleinheinz, A.; Abraham, S.; et al. Blood transcriptome profiling identifies 2 candidate endotypes of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauffer, F.; Jargosch, M.; Krause, L.; Garzorz-Stark, N.; Franz, R.; Roenneberg, S.; Böhner, A.; Mueller, N.S.; Theis, F.J.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; et al. Type I Immune Response Induces Keratinocyte Necroptosis and Is Associated with Interface Dermatitis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyerich, K.; Pennino, D.; Scarponi, C.; Foerster, S.; Nasorri, F.; Behrendt, H.; Ring, J.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Albanesi, C.; Cavani, A. IL-17 in atopic eczema: Linking allergen-specific adaptive and microbial-triggered innate immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 59–66.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavazais, S.; Jargosch, M.; Dupont, S.; Labéguère, F.; Menet, C.; Jagerschmidt, C.; Ohm, F.; Kupcsik, L.; Parent, I.; Cottereaux, C.; et al. IRAK4 inhibition dampens pathogenic processes driving inflammatory skin diseases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabj3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wasserer, S.; Jargosch, M.; Mayer, K.E.; Eigemann, J.; Raunegger, T.; Aydin, G.; Eyerich, S.; Biedermann, T.; Eyerich, K.; Lauffer, F. Characterization of High and Low IFNG-Expressing Subgroups in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116158
Wasserer S, Jargosch M, Mayer KE, Eigemann J, Raunegger T, Aydin G, Eyerich S, Biedermann T, Eyerich K, Lauffer F. Characterization of High and Low IFNG-Expressing Subgroups in Atopic Dermatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116158
Chicago/Turabian StyleWasserer, Sophia, Manja Jargosch, Kristine E. Mayer, Jessica Eigemann, Theresa Raunegger, Görkem Aydin, Stefanie Eyerich, Tilo Biedermann, Kilian Eyerich, and Felix Lauffer. 2024. "Characterization of High and Low IFNG-Expressing Subgroups in Atopic Dermatitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116158
APA StyleWasserer, S., Jargosch, M., Mayer, K. E., Eigemann, J., Raunegger, T., Aydin, G., Eyerich, S., Biedermann, T., Eyerich, K., & Lauffer, F. (2024). Characterization of High and Low IFNG-Expressing Subgroups in Atopic Dermatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 6158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116158





