Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions
Abstract
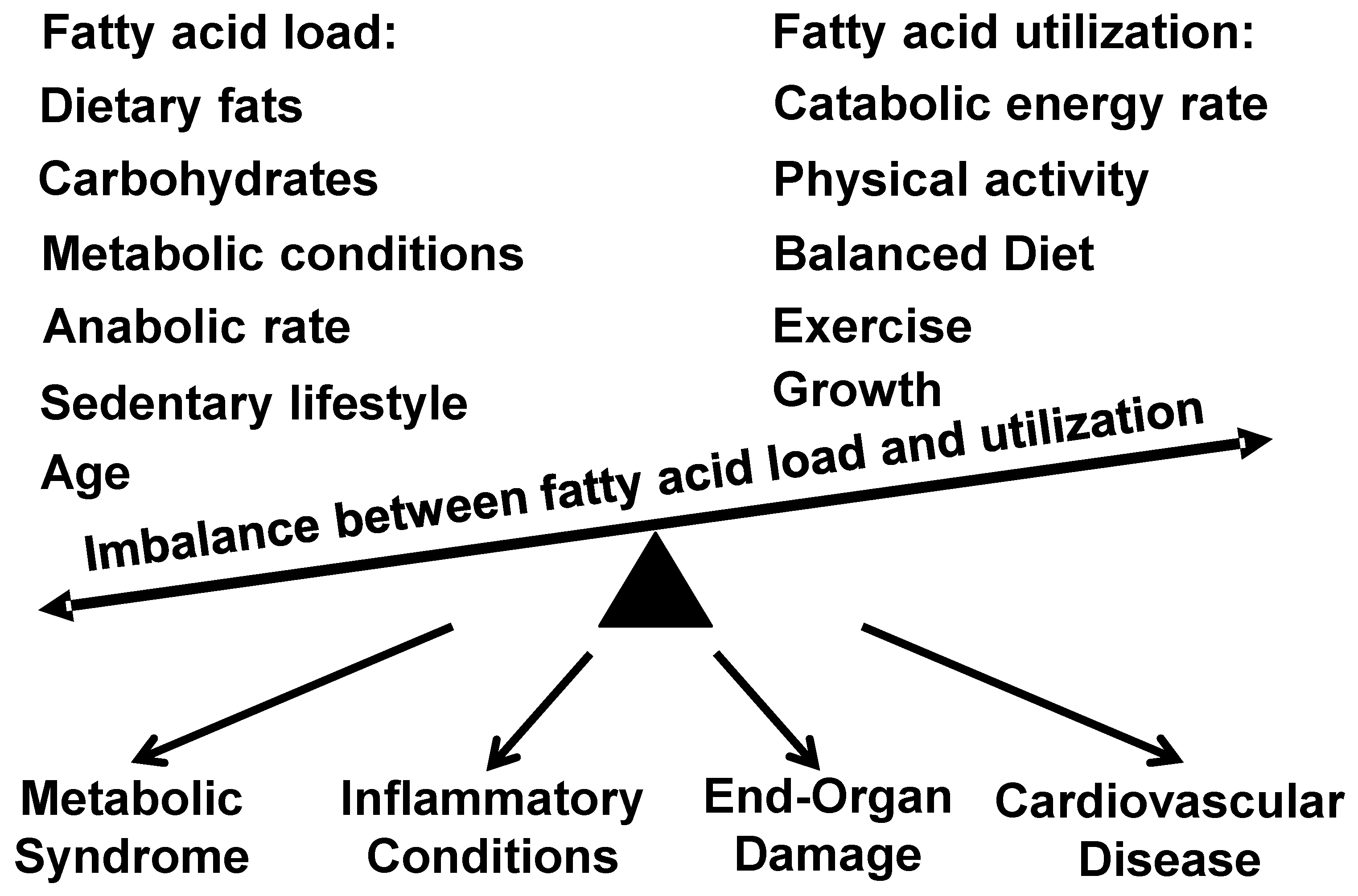
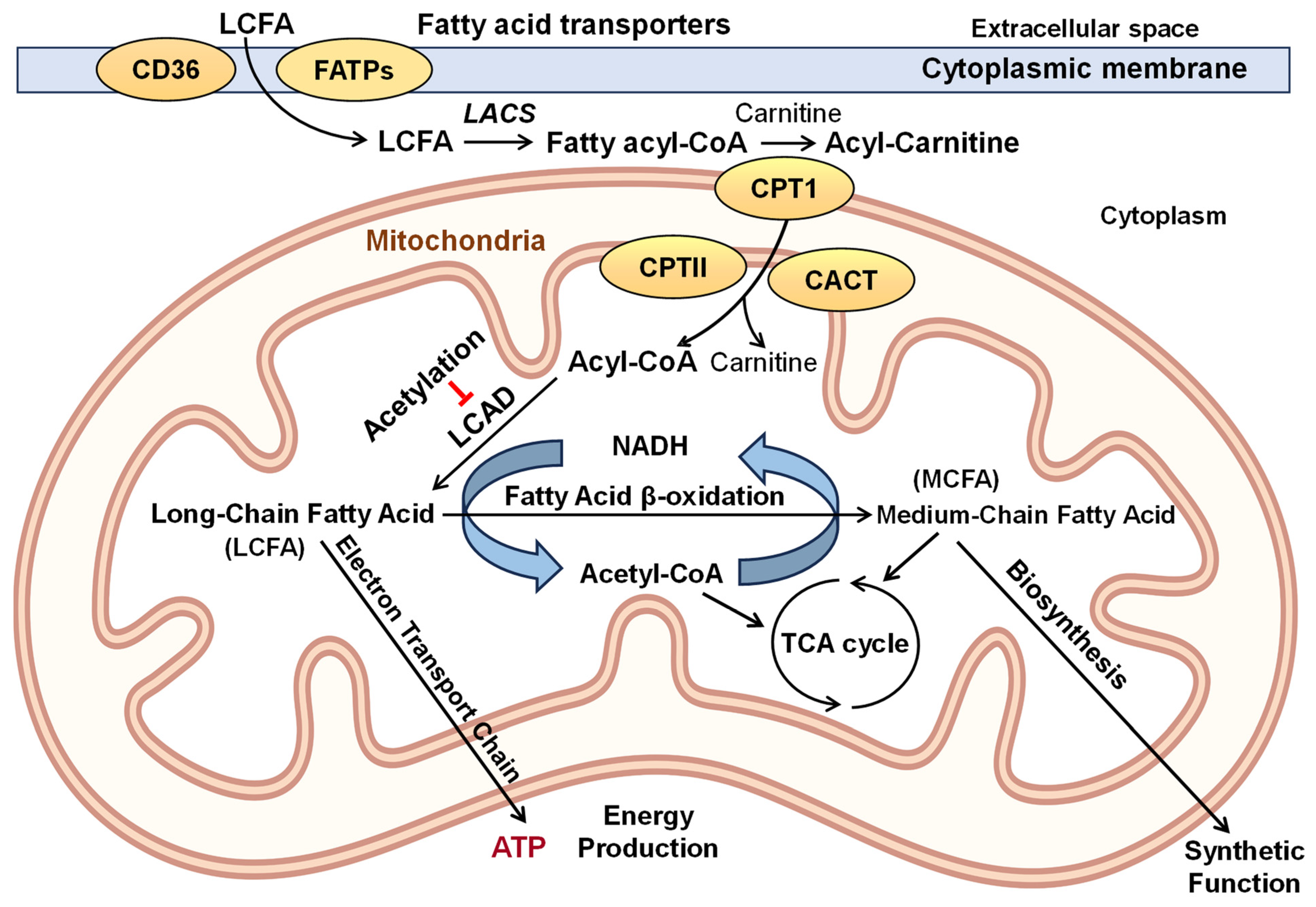
1. Introduction
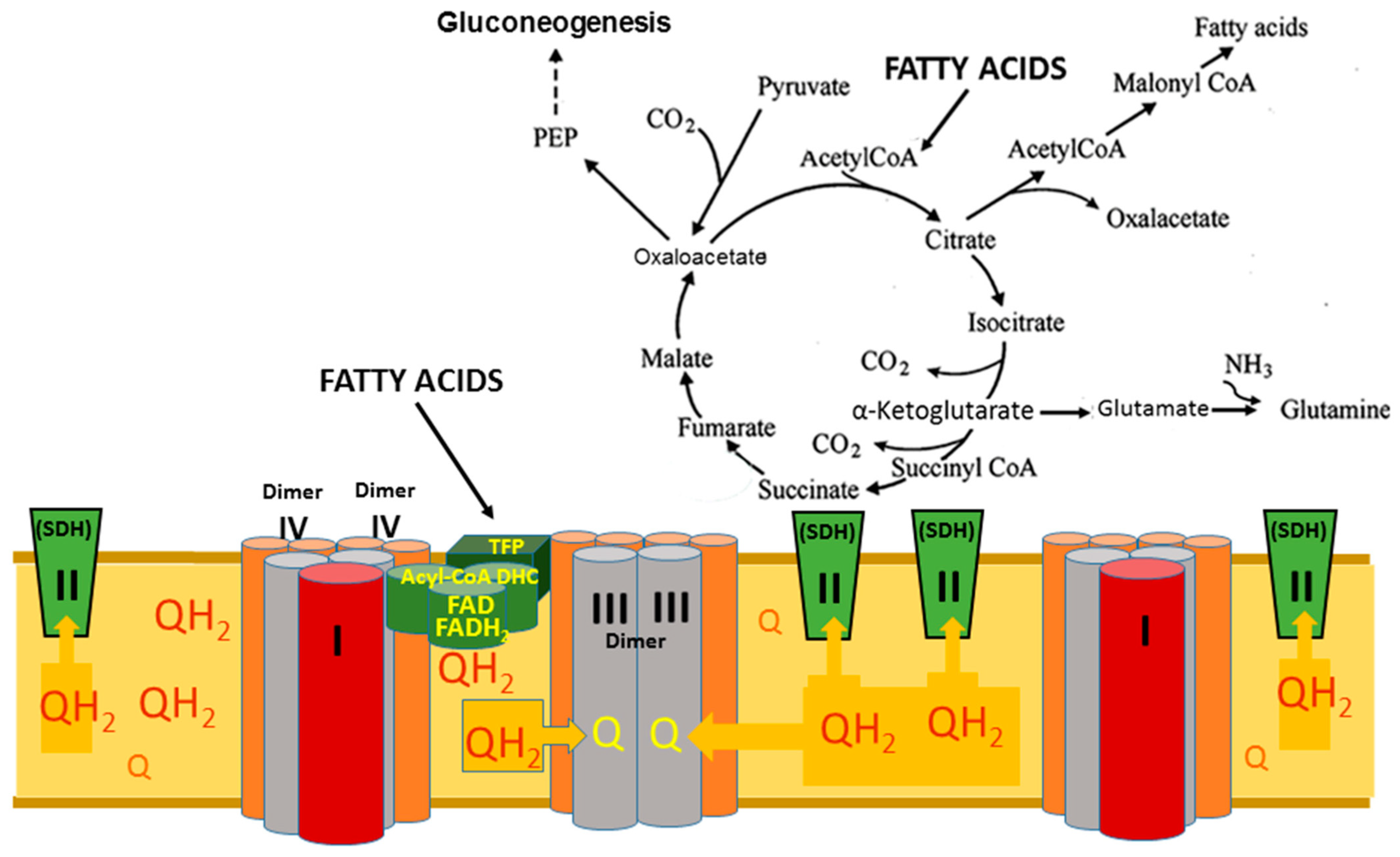
2. Heart
2.1. Fatty Acid Oxidation Supporting Normal Cardiac Function
2.2. Impaired Fatty Acid Oxidation in Cardiac Dysfunction
2.3. Targeting Fatty Acid Oxidation in Cardiac Dysfunction
3. Kidney
3.1. Essential Role of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Kidney Function
3.2. Impaired Fatty Acid Oxidation in Kidney Dysfunction
3.3. Targeting Fatty Acid Oxidation in Kidney Dysfunction
4. Skeletal Muscle
Essential Role of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscle Function
5. Endothelial Cells and Vascular Function
5.1. Fatty Acid Oxidation in Endothelial Cells
5.2. Impaired Fatty Acid Oxidation in Endothelial Dysfunction
5.3. Targeting Fatty Acid Oxidation in Endothelial Dysfunction
6. Epithelial Cells
6.1. Fatty Acid Oxidation in Epithelial Cell Function
6.2. Impaired Fatty Acid Oxidation in Epithelial Dysfunction
6.3. Targeting Fatty Acid Oxidation in Epithelial Dysfunction
7. Discussion and Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heindel, J.J.; Blumberg, B.; Cave, M.; Machtinger, R.; Mantovani, A.; Mendez, M.A.; Nadal, A.; Palanza, P.; Panzica, G.; Sargis, R.; et al. Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Yusuf, S. Emerging epidemic of cardiovascular disease in developing countries. Circulation 1998, 97, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Murray, C.J.L.; Roth, G.A.; Global Burden of Cardiovascular, D.; Risks, C. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks, 1990–2022. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2350–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Despres, J.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Origin of mitochondria by intracellular enslavement of a photosynthetic purple bacterium. Proc. R. Soc. 2006, 273, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, H.M.; Neuspiel, M.; Wasiak, S. Mitochondria: More than just a powerhouse. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R551–R560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Clardy, J.; Xavier, R.J. Gut microbiome lipid metabolism and its impact on host physiology. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Moore, B.N.; Pluznick, J.L. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptors and Blood Pressure Regulation: Council on Hypertension Mid-Career Award for Research Excellence 2021. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoor, V.; Strassheim, D.; Sullivan, T.; Verin, A.; Umapathy, N.S.; Dempsey, E.C.; Frank, D.N.; Stenmark, K.R.; Gerasimovskaya, E. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate Attenuates Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling and Inflammation in Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Vacca, M.; De Angelis, M.; Farella, I.; Lanza, E.; Khalil, M.; Wang, D.Q.; Sperandio, M.; Di Ciaula, A. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, E.; Gharagozlian, S.; Valeur, J.; Aas, A.M. Short-chain fatty acids as a link between diet and cardiometabolic risk: A narrative review. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, J.T.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Biochemistry, Fatty Acid Oxidation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556002/ (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Demarquoy, J.; Le Borgne, F. Crosstalk between mitochondria and peroxisomes. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynberg, A.; Demaison, L. Fatty Acid Oxidation in the Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1996, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Bi, X. Integrated Control of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Heart Failure. Metabolites 2023, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockley, J. Long-chain fatty acid oxidation disorders and current management strategies. Am. J. Manag. Care 2020, 26, S147–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschey, M.D.; Shimazu, T.; Goetzman, E.; Jing, E.; Schwer, B.; Lombard, D.B.; Grueter, C.A.; Harris, C.; Biddinger, S.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; et al. SIRT3 regulates mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation by reversible enzyme deacetylation. Nature 2010, 464, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.V.; Mayorov, V.I.; Dikalova, A.E.; Dikalov, S.I. Long-Chain and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids in Energy Metabolism of Murine Kidney Mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.V.; Dikalov, S.I. Cardiolipin, Perhydroxyl Radicals and Lipid Peroxidation in Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1323028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.D.; Hill, K.E.; Burk, R.F.; Nammour, T.M.; Badr, K.F.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd. A series of prostaglandin F2-like compounds are produced in vivo in humans by a non-cyclooxygenase, free radical-catalyzed mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9383–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.J., 2nd; Fessel, J.P. The biochemistry of the isoprostane, neuroprostane, and isofuran pathways of lipid peroxidation. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2004, 128, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradies, G.; Petrosillo, G.; Paradies, V.; Ruggiero, F.M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging: Role of oxidative stress and cardiolipin. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja, G. The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 127, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, H.B.; Annapure, U.S. Triglycerides of medium-chain fatty acids: A concise review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.G.; Zhou, D.D.; Wu, S.X.; Huang, S.Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Yang, Z.J.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.N.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Health Benefits and Side Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Ussher, J.R.; Folmes, C.D.; Jaswal, J.S.; Stanley, W.C. Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 207–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromhout, D. Epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases in Europe. Public Health Nutr. 2001, 4, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Kennedy, E.; Barrier, P.; Danford, D.; Ernst, N.D.; Grundy, S.M.; Leveille, G.A.; Van Horn, L.; Williams, C.L.; Booth, S.L. Dietary fat consumption and health. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, S3–S19, Discussion S19–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.C.; Avula, U.M.R.; Wan, E.Y.; Reyes, M.V.; Lakkadi, K.R.; Subramanyam, P.; Nakanishi, K.; Homma, S.; Muchir, A.; Pajvani, U.B.; et al. Dietary Saturated Fat Promotes Arrhythmia by Activating NOX2 (NADPH Oxidase 2). Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, A.O.; Koh, W.P.; Yuan, J.M.; Gross, M.D.; Pereira, M.A. Western-style fast food intake and cardiometabolic risk in an Eastern country. Circulation 2012, 126, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suarez, V.J.; Beltran-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Florez, L.; Martin-Rodriguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, S.E.; Orr, E.; Boyer, B.B.; Thompson, B. Culturally adapting an evidence-based intervention to promote a healthy diet and lifestyle for Yup’ik Alaska native communities. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2023, 82, 2159888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaei, F.; Shakiba, M.; Saneifard, H.; Vahidshahi, K.; Alaei, M. Defects in Very Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Presenting as Different Types of Cardiomyopathy. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2022, 2022, 5529355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, N.; Bross, P.; Andresen, B.S. Genetic defects in fatty acid beta-oxidation and acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. Molecular pathogenesis and genotype-phenotype relationships. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.J.; Burton, B.K. Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Long-chain Fatty-acid Oxidation Disorders: A Review. touchREV Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Cheng, E.; Zhi, S.; Kong, L.; Yao, H.W.; Li, J. Cigarette Smoke Reduces Fatty Acid Catabolism, Leading to Apoptosis in Lung Endothelial Cells: Implication for Pathogenesis of COPD. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.K.; Jolly, S.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Fox, K.A.; Anand, S.S.; Yusuf, S. Association of diet, exercise, and smoking modification with risk of early cardiovascular events after acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2010, 121, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillmore, N.; Mori, J.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation alterations in heart failure, ischaemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, R.A.; Mulrooney, D.A.; Rhea, I.B.; Yu, C.; Johnson, J.N.; Chow, E.J.; Ehrhardt, M.J.; Hudson, M.M.; Ness, K.K.; Armstrong, G.T.; et al. Modifiable Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Survivors of Childhood Cancer: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol 2024, 6, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dludla, P.V.; Ziqubu, K.; Mabhida, S.E.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Hanser, S.; Nkambule, B.B.; Basson, A.K.; Pheiffer, C.; Tiano, L.; Kengne, A.P. Dietary Supplements Potentially Target Plasma Glutathione Levels to Improve Cardiometabolic Health in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukino-Iwashita, M.; Nagatomo, Y.; Kawai, A.; Taruoka, A.; Yumita, Y.; Kagami, K.; Yasuda, R.; Toya, T.; Ikegami, Y.; Masaki, N.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Gut-Heart Axis: Their Role in the Pathology of Heart Failure. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppert, J.; Lehrke, M.; Marx, N.; Jankowski, J.; Noels, H. Lipoproteins and lipids in cardiovascular disease: From mechanistic insights to therapeutic targeting. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Tian, R.; Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1487–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Xu, R.; Li, N.; Wang, F.; Han, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D. Energy metabolism disorders and potential therapeutic drugs in heart failure. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.R.; Quaggin, S.E.; Hoenig, M.P.; Dworkin, L.D. The glomerulus: The sphere of influence. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guder, W.G.; Ross, B.D. Enzyme distribution along the nephron. Kidney Int. 1984, 26, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.I.; Balaban, R.S.; Barrett, L.; Mandel, L.J. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity and Na+- and K+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase-mediated ion transport in the intact renal cell. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 10319–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nourbakhsh, N.; Pham, H.; Tham, R.; Zuckerman, J.E.; Singh, P. Evolution of altered tubular metabolism and mitochondrial function in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. 2020, 319, F229–F244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Zondler, L.; Ludwig, N.; Kardell, M.; Luneburg, C.; Henke, K.; Mersmann, S.; Margraf, A.; Spieker, T.; Tekath, T.; et al. Glutamine prevents acute kidney injury by modulating oxidative stress and apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e163161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.V. The Structure of the Cardiac Mitochondria Respirasome Is Adapted for the beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Spitzer, J.J. Metabolism of Free Fatty Acids by Myocardium and Kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 1964, 206, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.; Mayorov, V.I.; Dikalov, S. Metabolic Syndrome and beta-Oxidation of Long-Chain Fatty Acids in the Brain, Heart, and Kidney Mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Chouchani, E.T. Why succinate? Physiological regulation by a mitochondrial coenzyme Q sentinel. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, P.M.; Robben, J.H. Succinate receptors in the kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.M.; Hirayama, B.A.; Loo, D.F. Active sugar transport in health and disease. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Moran, A. Heterogeneity of sodium-dependent D-glucose transport sites along the proximal tubule: Evidence from vesicle studies. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 242, F406–F414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Moran, A. Further studies of proximal tubular brush border membrane D-glucose transport heterogeneity. J. Membr. Biol. 1982, 70, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Kanai, Y.; Wells, R.G.; Hediger, M.A. The high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter. Re-evaluation of function and distribution of expression. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 12032–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewin, L.S. Sugar or Fat? Renal Tubular Metabolism Reviewed in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.L.; Anderson, W.P.; O’Connor, P.M.; Evans, R.G. Evidence that renal arterial-venous oxygen shunting contributes to dynamic regulation of renal oxygenation. Am. J. Physiol. 2007, 292, F1726–F1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, J.F.; Chan, M.K.; El-Nahas, M.; Varghese, Z. Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet 1982, 2, 1309–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.Z.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F. An update on the lipid nephrotoxicity hypothesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombijn, J.M.; Hooft, L.; Jun, M.; Webster, A.C.; Bots, M.L.; Verhaar, M.C.; Vernooij, R.W. Antioxidants for adults with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 11, CD008176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Herrera, A.; Ramirez-Camacho, I.; Zazueta, C.; Tapia, E.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Altered proximal tubule fatty acid utilization, mitophagy, fission and supercomplexes arrangement in experimental Fanconi syndrome are ameliorated by sulforaphane-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 153, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelani, H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chang, D.; Nammi, S. Chronic treatment of curcumin improves hepatic lipid metabolism and alleviates the renal damage in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonn, E.; Bosch, J.; Yusuf, S.; Sheridan, P.; Pogue, J.; Arnold, J.M.; Ross, C.; Arnold, A.; Sleight, P.; Probstfield, J.; et al. Effects of long-term vitamin E supplementation on cardiovascular events and cancer: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2005, 293, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalova, A.; Mayorov, V.; Xiao, L.; Panov, A.; Amarnath, V.; Zagol-Ikapitte, I.; Vergeade, A.; Ao, M.; Yermalitsky, V.; Nazarewicz, R.R.; et al. Mitochondrial Isolevuglandins Contribute to Vascular Oxidative Stress and Mitochondria-Targeted Scavenger of Isolevuglandins Reduces Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Hypertension. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukund, K.; Subramaniam, S. Skeletal muscle: A review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2020, 12, e1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.; Orynbayeva, Z.; Vavilin, V.; Lyakhovich, V. Fatty acids in energy metabolism of the central nervous system. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 472459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A. Synergistic Oxidation of Fatty Acids, Glucose and Amino Acids Metabolites by Isolated Rat Heart Mitochondria. EC Cardiol. 2018, 5, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- Koves, T.R.; Noland, R.C.; Bates, A.L.; Henes, S.T.; Muoio, D.M.; Cortright, R.N. Subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar mitochondria play distinct roles in regulating skeletal muscle fatty acid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 288, C1074–C1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.D. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevoshchikova, I.V.; Quinlan, C.L.; Orr, A.L.; Gerencser, A.A.; Brand, M.D. Sites of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production during fatty acid oxidation in rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 61, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, C.L.; Perevoshchikova, I.V.; Hey-Mogensen, M.; Orr, A.L.; Brand, M.D. Sites of reactive oxygen species generation by mitochondria oxidizing different substrates. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mohsen, A.W.; Mihalik, S.J.; Goetzman, E.S.; Vockley, J. Evidence for physical association of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29834–29841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A.; Arevalo, J.A.; Osmond, A.D.; Leija, R.G.; Curl, C.C.; Tovar, A.P. Lactate in contemporary biology: A phoenix risen. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1229–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchin, A.; Kalucka, J.; Dubois, C.; Carmeliet, P. How Endothelial Cells Adapt Their Metabolism to Form Vessels in Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Gifford, J.R.; Andtbacka, R.H.; Trinity, J.D.; Hyngstrom, J.R.; Garten, R.S.; Diakos, N.A.; Ives, S.J.; Dela, F.; Larsen, S.; et al. Cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle mitochondrial respiration: Are all mitochondria created equal? Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H346–H352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Kawagishi, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wells, Q.S.; Edmunds, L.R.; Fergusson, M.M.; Yu, Z.X.; Rovira, I.I.; Brittain, E.L.; et al. A Metabolic Basis for Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 689–698 e687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Lee, M.D.; Buckley, C.; Zhang, X.; McCarron, J.G. Mitochondrial ATP Production is Required for Endothelial Cell Control of Vascular Tone. Function 2023, 4, zqac063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamuri, S.S.; Sure, V.N.; Kolli, L.; Evans, W.R.; Sperling, J.A.; Bix, G.J.; Wang, X.; Atochin, D.N.; Murfee, W.L.; Mostany, R.; et al. Aging related impairment of brain microvascular bioenergetics involves oxidative phosphorylation and glycolytic pathways. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2022, 42, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.L. Pyruvate Kinase and Warburg Metabolism in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Uncoupled Glycolysis and the Cancer-Like Phenotype of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circulation 2017, 136, 2486–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimoto, K.; Okuno, K.; Kuroda, R.; Shanas, N.; Cicalese, S.M.; Eguchi, K.; Elliott, K.J.; Kawai, T.; Corbett, C.B.; Peluzzo, A.M.; et al. Glucose consumption of vascular cell types in culture: Toward optimization of experimental conditions. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2022, 322, C73–C85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oller, J.; Gabande-Rodriguez, E.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, M.J.; Desdin-Mico, G.; Aranda, J.F.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.; Ballesteros-Martinez, C.; Blanco, E.M.; Roldan-Montero, R.; Acuna, P.; et al. Extracellular Tuning of Mitochondrial Respiration Leads to Aortic Aneurysm. Circulation 2021, 143, 2091–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Yucel, N.; Kim, B.; Arany, Z. Local Mitochondrial ATP Production Regulates Endothelial Fatty Acid Uptake and Transport. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 309–319 e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabowski, D.S.; Cohen, K.E.; Abu-Hatoum, O.; Gutterman, D.D.; Freed, J.K. Crossing signals: Bioactive lipids in the microvasculature. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H1185–H1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenon, S.M.; Aguado-Zuniga, J.; Hatton, J.P.; Owens, C.D.; Conte, M.S.; Hughes-Fulford, M. Effects of fatty acids on endothelial cells: Inflammation and monocyte adhesion. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 177, e35–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Peng, Y.; Hang, W.; Nie, J.; Zhou, N.; Wang, D.W. The role of CD36 in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yang, W.Q.; Luo, W.W.; Zhang, L.L.; Mai, Y.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Liu, S.T.; Jiang, L.J.; Liu, P.Q.; Li, Z.M. Disturbance of Fatty Acid Metabolism Promoted Vascular Endothelial Cell Senescence via Acetyl-CoA-Induced Protein Acetylation Modification. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1198607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, M.D.; Marciano, D.P.; Fu, P.; Franco, M.C.; Unwalla, H.; Tieu, K.; Fineman, J.R.; Wang, T.; Black, S.M. Metabolic reprogramming, oxidative stress, and pulmonary hypertension. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zeng, H.; Chen, S.T.; Roman, R.J.; Aschner, J.L.; Didion, S.; Chen, J.X. Endothelial specific SIRT3 deletion impairs glycolysis and angiogenesis and causes diastolic dysfunction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 112, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, T.; Huang, C.; Sun, M.; Shen, W. Sirtuin 3 governs autophagy-dependent glycolysis during Angiotensin II-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 16645–16661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, C.A.; Mathieu, B.; Joudiou, N.; Zampieri, L.X.; Brusa, D.; Sonveaux, P.; Feron, O.; Gallez, B. Targeting Endothelial Cell Metabolism by Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase and Glutaminase-1. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoors, S.; De Bock, K.; Cantelmo, A.R.; Georgiadou, M.; Ghesquiere, B.; Cauwenberghs, S.; Kuchnio, A.; Wong, B.W.; Quaegebeur, A.; Goveia, J.; et al. Partial and transient reduction of glycolysis by PFKFB3 blockade reduces pathological angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Dai, Z. Fatty Acid Metabolism in Endothelial Cell. Genes 2022, 13, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henninger, C.; Clouet, P.; Cao Danh, H.; Pascal, M.; Bezard, J. Effects of fenofibrate treatment on fatty acid oxidation in liver mitochondria of obese Zucker rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 3231–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, E.; Moschetta, A.; Haller, D. Mitochondrial function—Gatekeeper of intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurn, H.; Daly, D.T. Histology, Epithelial Cell. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559063/ (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Kang, J.X.; Man, S.F.; Brown, N.E.; Labrecque, P.A.; Garg, M.L.; Clandinin, M.T. Essential fatty acid metabolism in cultured human airway epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1128, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Tang, B. Crosstalk Between the Gut Microbiota and Epithelial Cells Under Physiological and Infectious Conditions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 832672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Nigam, S.K. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation in the reassembly of occludin and other tight junction proteins. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, F737–F750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerbette, T.; Rioux, V.; Bostoen, M.; Ciesielski, V.; Coppens-Exandier, H.; Buraud, M.; Lan, A.; Boudry, G. Saturated fatty acids differently affect mitochondrial function and the intestinal epithelial barrier depending on their chain length in the in vitro model of IPEC-J2 enterocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1266842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotta, S.; Villa, M.; Major, J.; Finsterbusch, K.; Llorian, M.; Carmeliet, P.; Buescher, J.; Wack, A. Repair of airway epithelia requires metabolic rewiring towards fatty acid oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Ma, J.; Lu, R.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhao, J.F.; Kang, Y.F.; Hu, J.J.; Wang, N.; Song, J.; Zhong, J.; et al. Perturbated glucose metabolism augments epithelial cell proinflammatory function in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 991–1004 e1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucci, F.; Rumio, C. Tumor Cell Glycolysis-At the Crossroad of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Autophagy. Cells 2022, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerbette, T.; Boudry, G.; Lan, A. Mitochondrial function in intestinal epithelium homeostasis and modulation in diet-induced obesity. Mol. Metab. 2022, 63, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Ornatowski, W.; Vergne, I.; Naylor, J.; Delgado, M.; Roberts, E.; Ponpuak, M.; Master, S.; Pilli, M.; White, E.; et al. Human IRGM regulates autophagy and cell-autonomous immunity functions through mitochondria. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xie, N.; Banerjee, S.; Ge, J.; Guo, S.; Liu, G. Impairment of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Alveolar Epithelial Cells Mediates Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Console, L.; Scalise, M.; Giangregorio, N.; Tonazzi, A.; Barile, M.; Indiveri, C. The Link Between the Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Derangement and Kidney Injury. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivetti, G.; Giordano, G.; Corradi, D.; Melissari, M.; Lagrasta, C.; Gambert, S.R.; Anversa, P. Gender differences and aging: Effects on the human heart. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1995, 26, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.L.; Rennie, C.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Substrate utilization during endurance exercise in men and women after endurance training. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2001, 280, E898–E907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezek, P.; Jaburek, M.; Holendova, B.; Plecita-Hlavata, L. Fatty Acid-Stimulated Insulin Secretion vs. Lipotoxicity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, W.; Chen, Y. Editorial: The Roles of Lipids in Immunometabolism: The Crosstalk Between Lipid Metabolisms and Inflammation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 938535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahzadi, R.; Hejazi, M.S.; Molavi, O.; Pishgahzadeh, E.; Montazersaheb, S.; Jafari, S. Clinical Significance of Carnitine in the Treatment of Cancer: From Traffic to the Regulation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 9328344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dikalov, S.; Panov, A.; Dikalova, A. Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126498
Dikalov S, Panov A, Dikalova A. Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126498
Chicago/Turabian StyleDikalov, Sergey, Alexander Panov, and Anna Dikalova. 2024. "Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126498
APA StyleDikalov, S., Panov, A., & Dikalova, A. (2024). Critical Role of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Metabolism in Normal Cell Function and Pathological Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126498







