Electrophysiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in U251 Human Glioblastoma Cells: Possible Implications in Gliomagenesis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
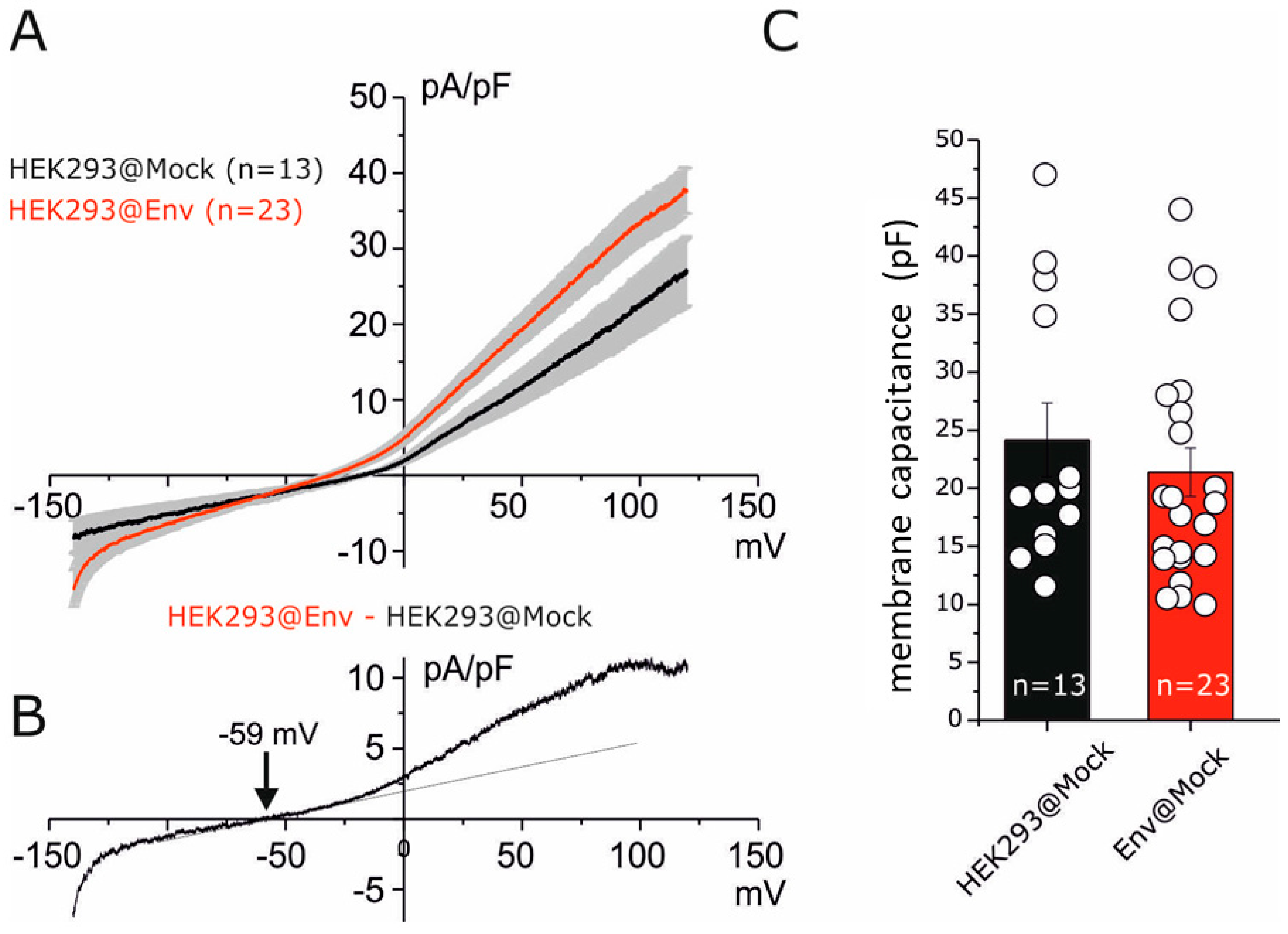
2.1. Electrophysiological Impact of E Protein Transfection in HEK293 Cells
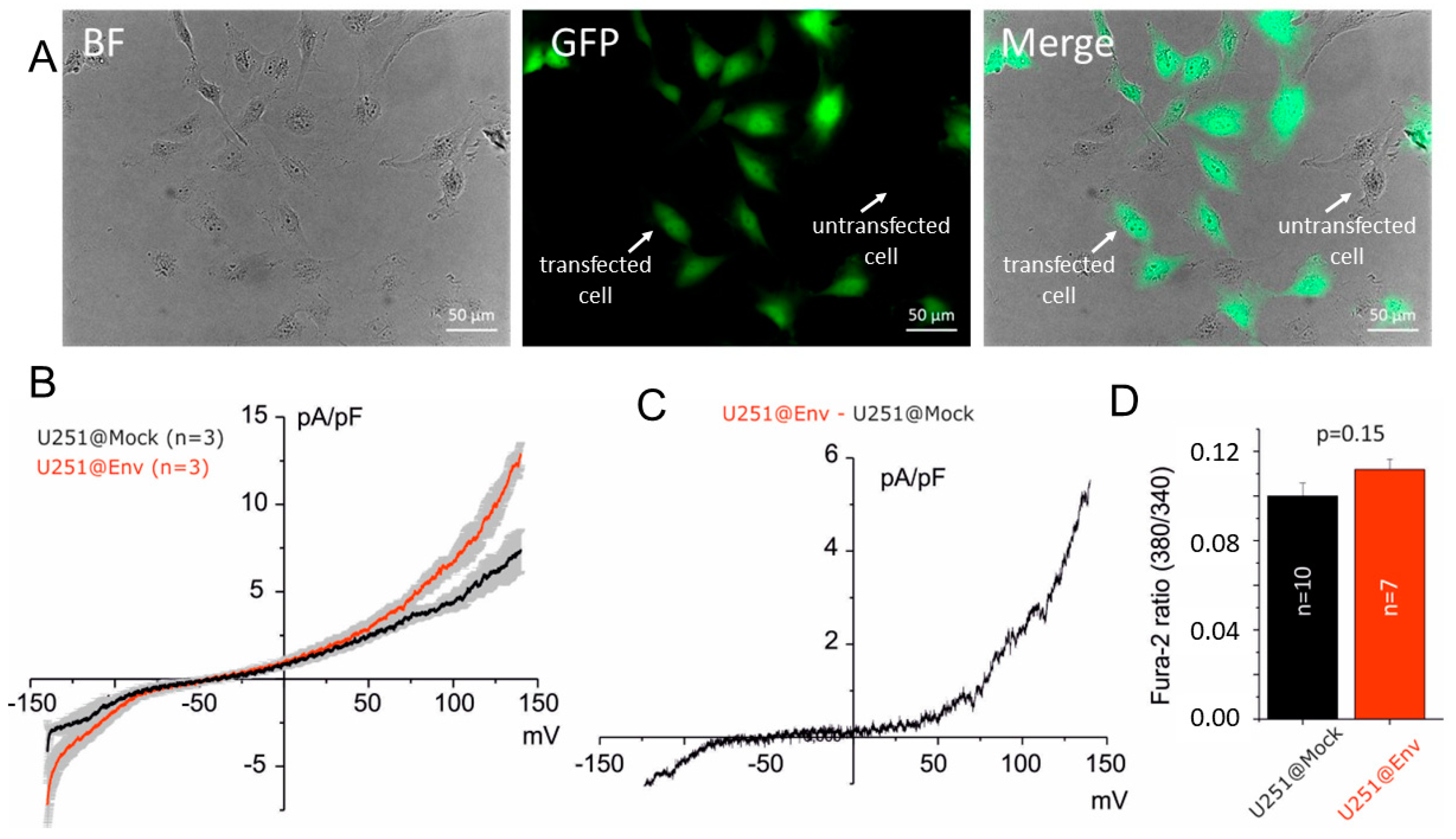
2.2. Electrophysiological Impact of E Protein Transfection in Human U251 Glioblastoma Cells
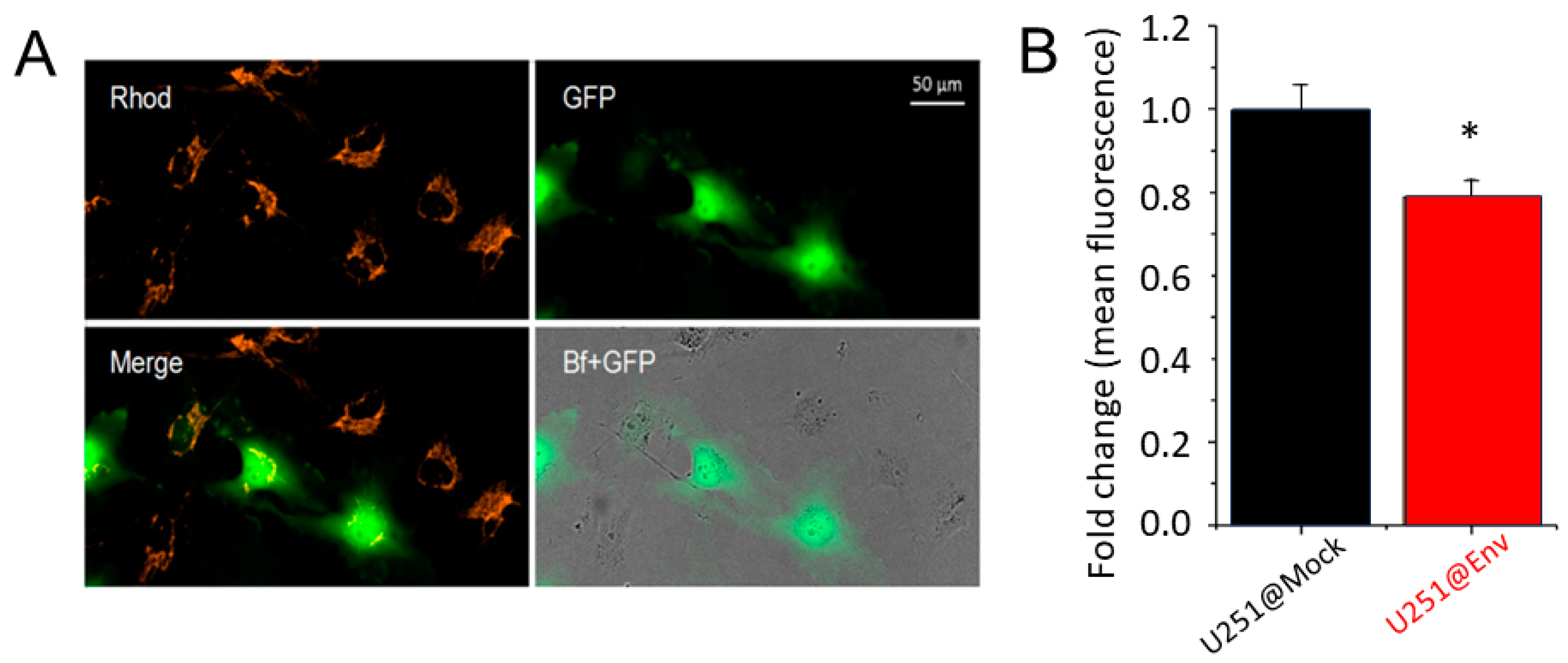
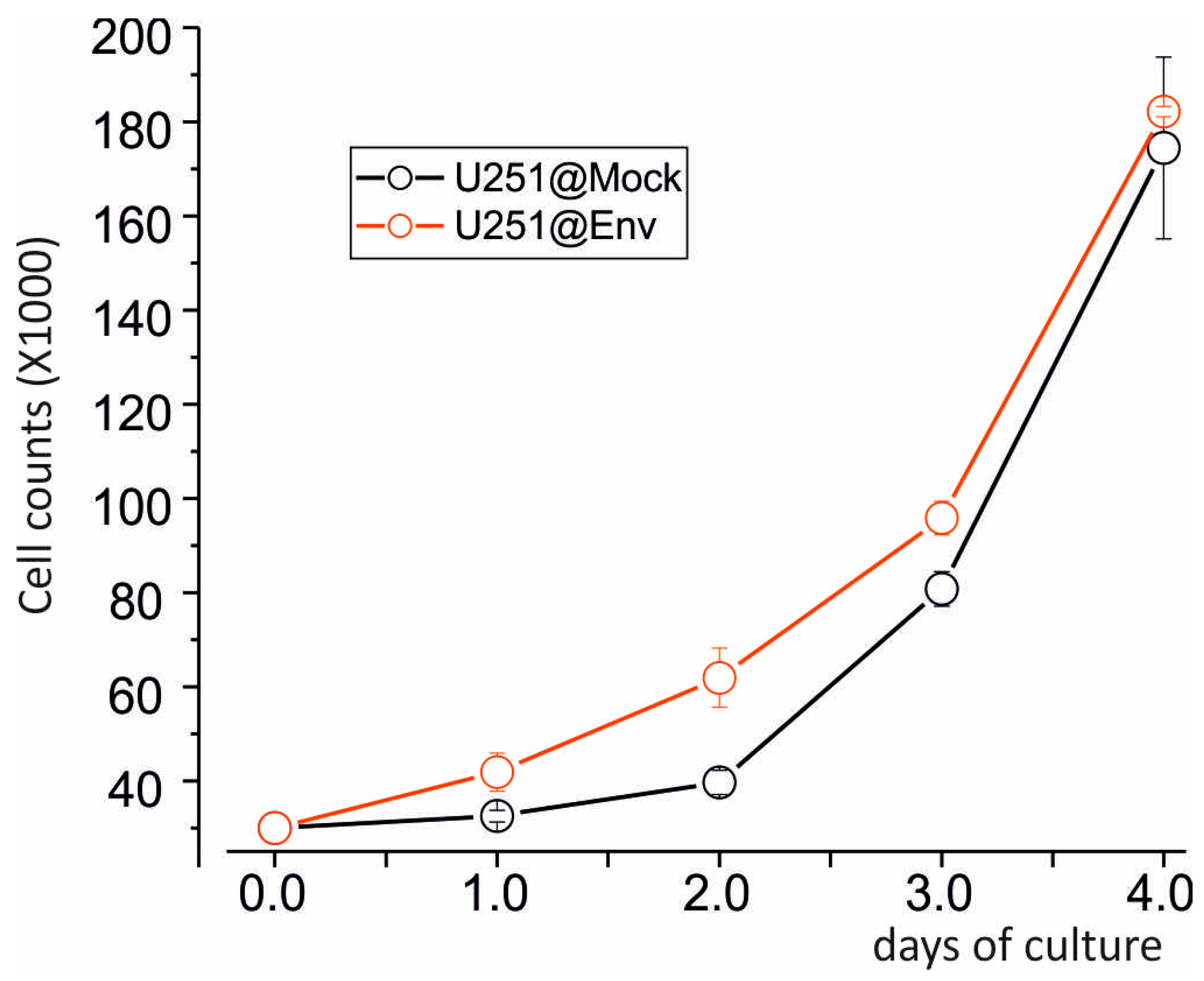
2.3. E Protein Expression Induces Mitochondria Depolarization and Promotes U251 Cell Growth
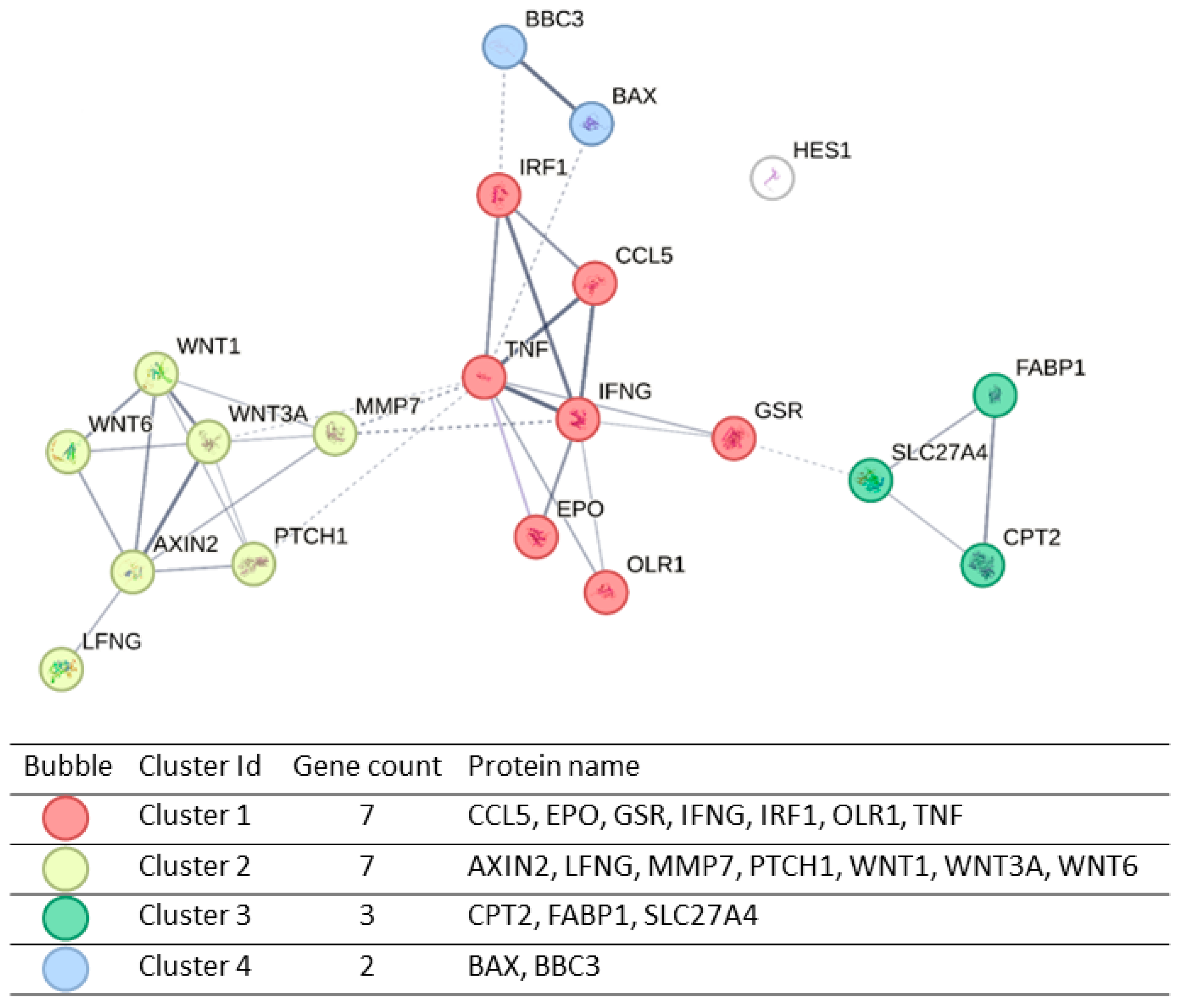
2.4. Transcriptional Effects of E Protein Expression in U251 Glioblastoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
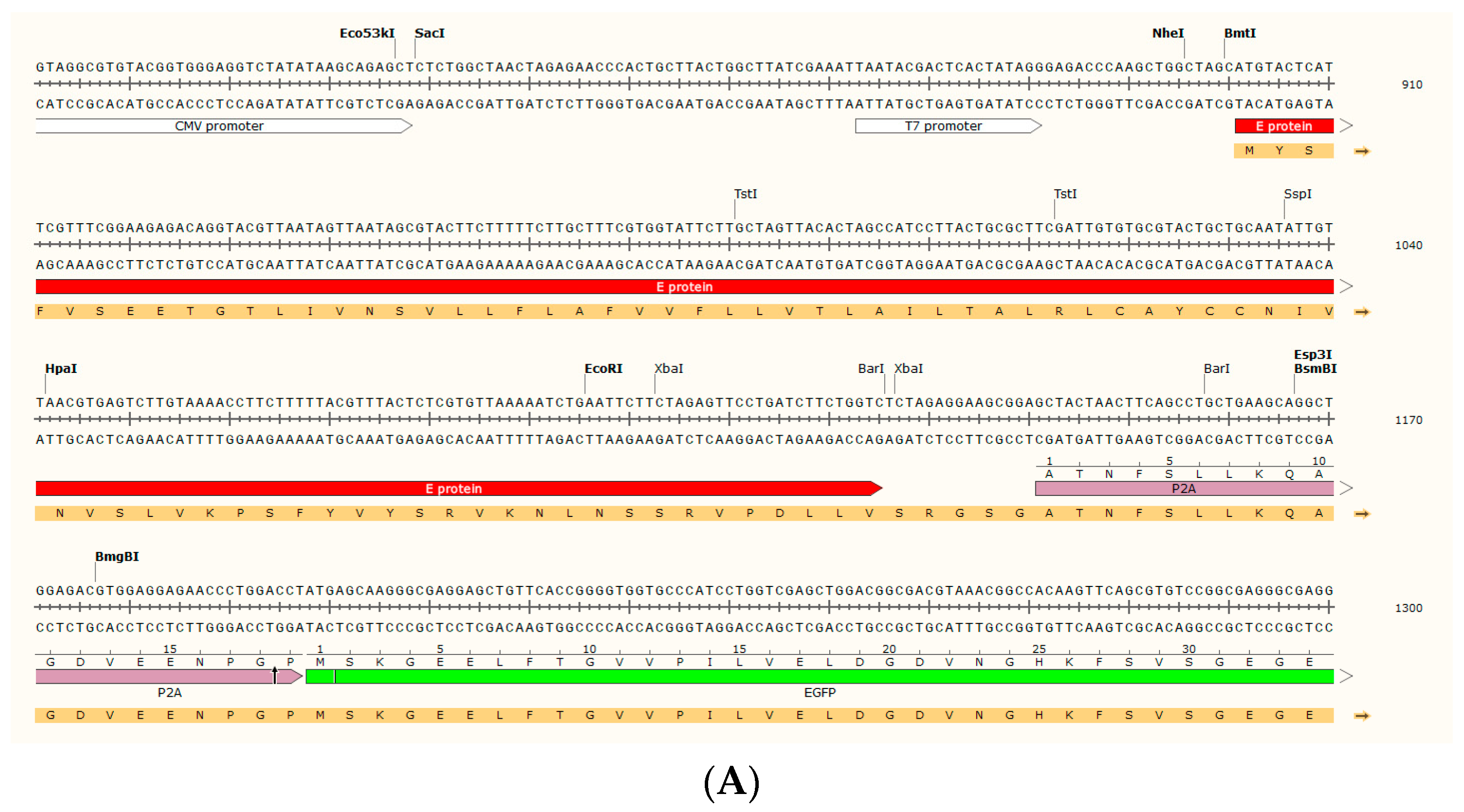
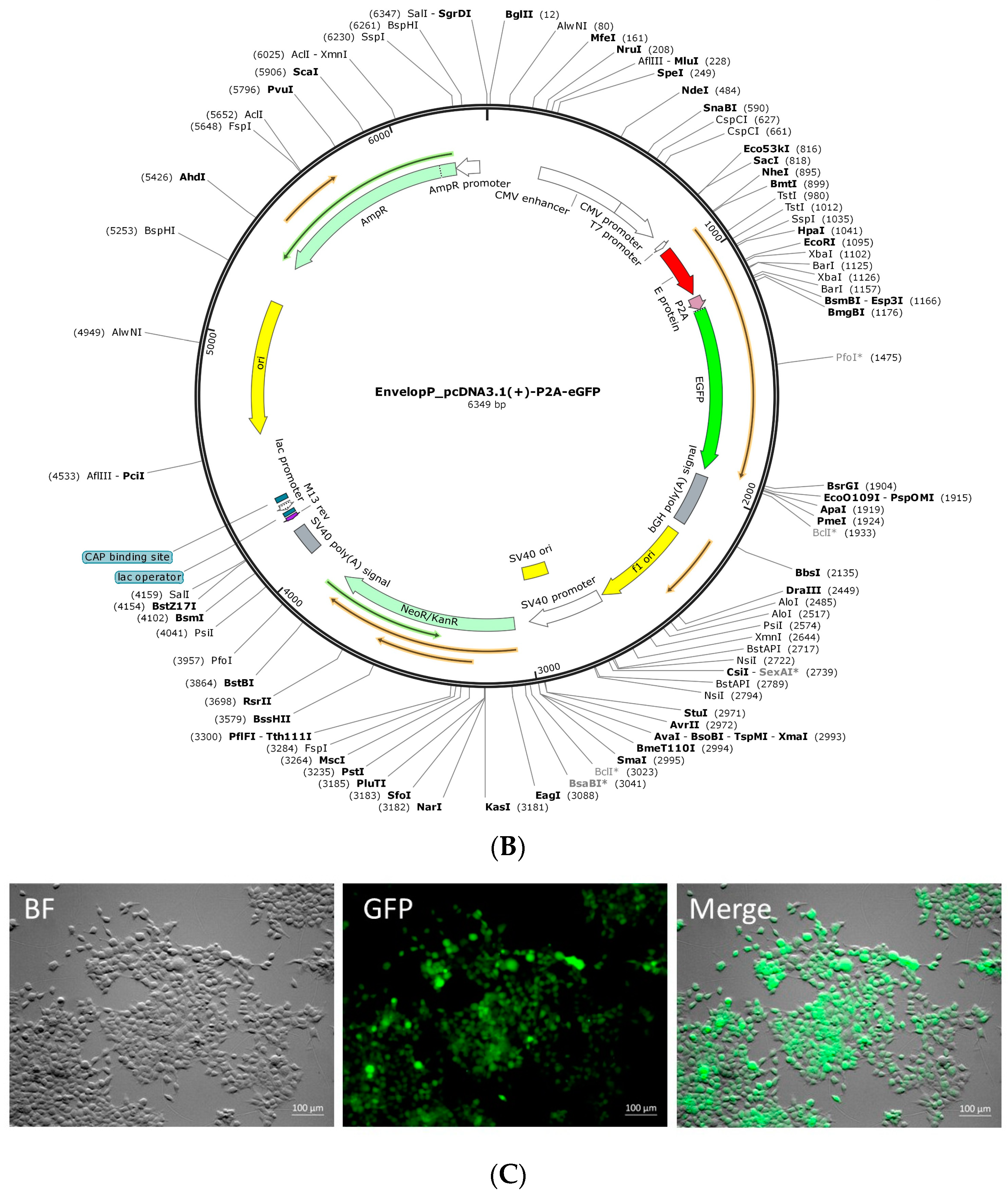
4.1. Mock_pcDNA3.1(+)-P2A-eGFP Plasmid Construction
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Stable Transfections
4.4. PCR and rtPCR
4.5. Patch Clamp Recordings
4.6. Calcium Measurement Assay
4.7. ΔΨm Estimation
4.8. Growth Curve Assessment
4.9. Gene Ontology and Protein Interaction Network Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. COVID-19 2024. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Babalola, B.A.; Akinsuyi, O.S.; Folajimi, E.O.; Olujimi, F.; Otunba, A.A.; Chikere, B.; Adewumagun, I.A.; Adetobi, T.E. Exploring the Future of SARS-CoV-2 Treatment after the First Two Years of the Pandemic: A Comparative Study of Alternative Therapeutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.P.; Liu, S.-L. Challenges and Prospects in Developing Future SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Overcoming Original Antigenic Sin and Inducing Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhola, S.; Trisal, J.; Thakur, V.; Kaur, P.; Kulshrestha, S.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kumar, P. Neurological Toll of COVID-19. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-García, J.C.; Reinoso-Cobo, A.; Piqueras-Sola, B.; Cortés-Martín, J.; Menor-Rodríguez, M.J.; Alabau-Dasi, R.; Rodríguez-Blanque, R. Long COVID and Physical Therapy: A Systematic Review. Diseases 2023, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-Month Neurological and Psychiatric Outcomes in 236 379 Survivors of COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Xie, H.; Mou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Peng, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhong, M.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, Z.; et al. COVID−19 Hospitalization Increases the Risk of Developing Glioblastoma: A Bidirectional Mendelian-Randomization Study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1185466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, O.A.; Ivanova, O.N.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Yusubalieva, G.M.; Baklaushev, V.P.; Yanvarev, D.V.; Kechko, O.I.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Fedorov, V.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Establishes a Productive Infection in Hepatoma and Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Lines. Cancers 2023, 15, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Liang, L.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, K. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Evidence of Endothelial Dysfunction in the Brains of COVID-19 Patients with Implications for Glioblastoma Progression. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalpoor, H.; Akbari, A.; Nabi-Afjadi, M. Ephrin (Eph) Receptor and Downstream Signaling Pathways: A Promising Potential Targeted Therapy for COVID-19 and Associated Cancers and Diseases. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Yuen, T.T.-T.; Shuai, H.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Tsang, J.O.-L.; Huang, X.; et al. Comparative Tropism, Replication Kinetics, and Cell Damage Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with Implications for Clinical Manifestations, Transmissibility, and Laboratory Studies of COVID-19: An Observational Study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e14–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielarz, V.; Willemart, K.; Avalosse, N.; De Swert, K.; Lotfi, R.; Lejeune, N.; Poulain, F.; Ninanne, N.; Gilloteaux, J.; Gillet, N.; et al. Susceptibility of Neuroblastoma and Glioblastoma Cell Lines to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Brain Res. 2021, 1758, 147344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Meade, P.; Watanabe, F.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Rafferty, S.B.; Moniz-Garcia, D.; Schiapparelli, P.V.; Jentoft, M.E.; Imitola, J.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. SARS-CoV2 Entry Factors Are Expressed in Primary Human Glioblastoma and Recapitulated in Cerebral Organoid Models. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 161, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.G.; Mukhtar, T.; Eze, U.C.; Simoneau, C.R.; Ross, J.; Parikshak, N.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Koontz, M.; Velmeshev, D.; et al. Tropism of SARS-CoV-2 for Human Cortical Astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122236119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus Envelope Protein: Current Knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, V.S.; McKay, M.J.; Shcherbakov, A.A.; Dregni, A.J.; Kolocouris, A.; Hong, M. Structure and Drug Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein Transmembrane Domain in Lipid Bilayers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Usera, F.; Enjuanes, L. Coronavirus Virulence Genes with Main Focus on SARS-CoV Envelope Gene. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, E.; Vallese, F.; Hartel, A.J.W.; Morgenstern, T.J.; Kanner, S.A.; Rauh, O.; Giamogante, F.; Barazzuol, L.; Shepard, K.L.; Colecraft, H.M.; et al. Perturbation of the Host Cell Ca2+ Homeostasis and ER-Mitochondria Contact Sites by the SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins E and M. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenaghan, C.; Hanson, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Nichols, C.G. Coronavirus Proteins as Ion Channels: Current and Potential Research. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 573339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Garcia, D.; Bekdash, R.; Abbott, G.W.; Yazawa, M.; Harrison, N.L. The Envelope Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Increases Intra-Golgi pH and Forms a Cation Channel That Is Regulated by pH. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 2851–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.R.; Alameh, M.; Ollivier, B.; Montnach, J.; Bidère, N.; Souazé, F.; Escriou, N.; Charpentier, F.; Baró, I.; De Waard, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 E and 3a Proteins Are Inducers of Pannexin Currents. Cells 2023, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcuri, C.; Fioretti, B.; Bianchi, R.; Mecca, C.; Tubaro, C.; Beccari, T.; Franciolini, F.; Giambanco, I.; Donato, R. Microglia-Glioma Cross-Talk: A Two Way Approach to New Strategies against Glioma. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 268–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, P.; Mangino, G.; Fioretti, B.; Catacuzzeno, L.; Puca, R.; Ponti, D.; Miscusi, M.; Franciolini, F.; Ragona, G.; Calogero, A. The Inhibition of KCa3.1 Channels Activity Reduces Cell Motility in Glioblastoma Derived Cancer Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catacuzzeno, L.; Fioretti, B.; Franciolini, F. Expression and Role of the Intermediate-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel KCa3.1 in Glioblastoma. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 421564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragonese, F.; Monarca, L.; Bastioli, F.; Arcuri, C.; Mancinelli, L.; Fioretti, B. Silver Ions Promote Blebs Growth in U251 Glioblastoma Cell by Activating Nonselective Cationic Currents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliakopanou, A.; Antonopoulos, I.; Darzenta, N.; Serifi, I.; Simos, Y.V.; Katsenos, A.P.; Bellos, S.; Alexiou, G.A.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Leonardos, I.; et al. Glioblastoma Research on Zebrafish Xenograft Models: A Systematic Review. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratto, D.; Ferrari, B.; Roda, E.; Brandalise, F.; Siciliani, S.; De Luca, F.; Priori, E.C.; Di Iorio, C.; Cobelli, F.; Veneroni, P.; et al. Squaring the Circle: A New Study of Inward and Outward-Rectifying Potassium Currents in U251 GBM Cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglioti, C.; Palazzetti, F.; Monarca, L.; Lobello, R.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Iannitti, R.G.; Russo, R.; Ragonese, F.; Pennetta, C.; De Luca, A.; et al. LY294002 Inhibits Intermediate Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium (KCa3.1) Current in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 790922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullaev, I.F.; Rudkouskaya, A.; Mongin, A.A.; Kuo, Y.-H. Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels BK and IK1 Are Functionally Expressed in Human Gliomas but Do Not Regulate Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-R.; Li, L.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Shin, B.A.; Choi, S.-Y. High Cleavage Efficiency of a 2A Peptide Derived from Porcine Teschovirus-1 in Human Cell Lines, Zebrafish and Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Sun, X.; Cao, K.; Wang, R. Endogenous Kv Channels in Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK-293) Cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2002, 238, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretti, B.; Catacuzzeno, L.; Sforna, L.; Aiello, F.; Pagani, F.; Ragozzino, D.; Castigli, E.; Franciolini, F. Histamine Hyperpolarizes Human Glioblastoma Cells by Activating the Intermediate-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C102–C110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragonese, F.; Monarca, L.; De Luca, A.; Mancinelli, L.; Mariani, M.; Corbucci, C.; Gerli, S.; Iannitti, R.G.; Leonardi, L.; Fioretti, B. Resveratrol Depolarizes the Membrane Potential in Human Granulosa Cells and Promotes Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 115, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Gu, H.; Li, L.; Wu, T.; Xie, W.; Li, M.; Zhao, N. TNIP1-Mediated TNF-α/NF-κB Signalling Cascade Sustains Glioma Cell Proliferation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, S. Graph Clustering Via a Discrete Uncoupling Process. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2008, 30, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Babenko, V.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Balakireva, A.V.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, C.A.; Asuthkar, S.; Guda, M.R.; Tsung, A.J.; Velpula, K.K. Cancer Stem Cell Molecular Reprogramming of the Warburg Effect in Glioblastomas: A New Target Gleaned from an Old Concept. CNS Oncol. 2016, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, B.K.; Seethamraju, H.; Dhody, K.; Corley, M.J.; Kazempour, K.; Lalezari, J.P.; Pang, A.P.; Sugai, C.; Francisco, E.B.; Pise, A.; et al. Disruption of the CCL5/RANTES-CCR5 Pathway Restores Immune Homeostasis and Reduces Plasma Viral Load in Critical COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yağcı, S.; Serin, E.; Acicbe, Ö.; Zeren, M.İ.; Odabaşı, M.S. The Relationship between Serum Erythropoietin, Hepcidin, and Haptoglobin Levels with Disease Severity and Other Biochemical Values in Patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43 (Suppl. S1), 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, J.K.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Metabolic Messengers: Tumour Necrosis Factor. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Jyotaki, M.; Kim, A.; Chai, J.; Simon, N.; Zhou, M.; Bachmanov, A.A.; Huang, L.; Wang, H. Regulation of Bitter Taste Responses by Tumor Necrosis Factor. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, J.; Olsen, H.; Sørensen, N.; Thrasivoulou, C.; Ahmed, A. Wnts Control Membrane Potential in Mammalian Cancer Cells. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5899–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefani, D.; Rizzuto, R.; Pozzan, T. Enjoy the Trip: Calcium in Mitochondria Back and Forth. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcom, E.F.; Nath, A.; Power, C. Acute and Chronic Neurological Disorders in COVID-19: Potential Mechanisms of Disease. Brain 2021, 144, 3576–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, A.F.; Lin, B.C.; Piggott, B.J. Ion Channels in Gliomas-From Molecular Basis to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfroni, G.; Ragonese, F.; Monarca, L.; Astolfi, A.; Mancinelli, L.; Iannitti, R.G.; Bastioli, F.; Barreca, M.L.; Cecchetti, V.; Fioretti, B. New Insights on KCa3.1 Channel Modulation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING V10: Protein-Protein Interaction Networks, Integrated over the Tree of Life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
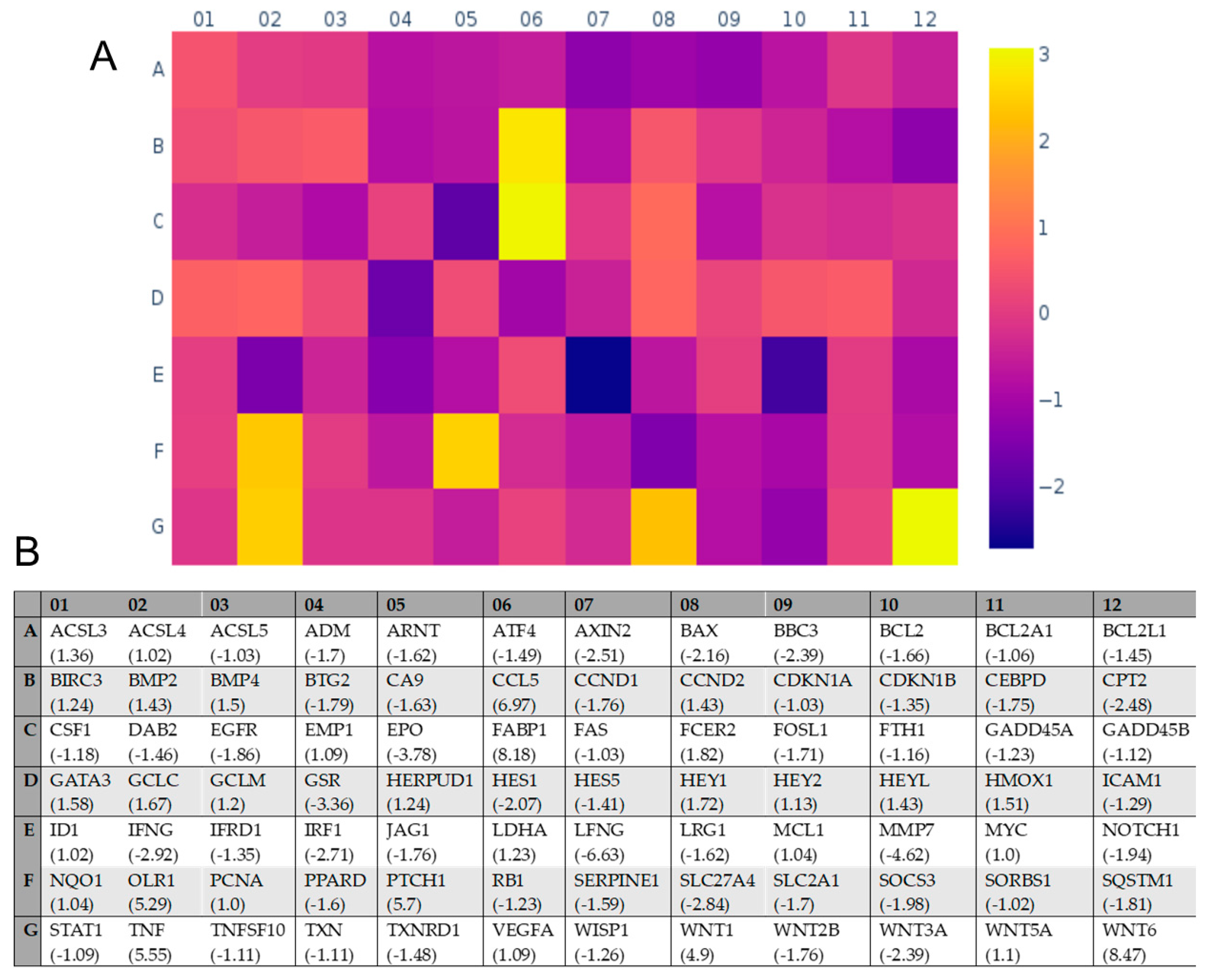
| Gene Name 1 | Mock Average ΔCT 2 | U251@Env Average ΔCT 2 | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| LFNG | 8.50 | 11.23 | −6.63 |
| MMP7 | 8.26 | 10.47 | −4.62 |
| EPO | 11.58 | 13.50 | −3.78 |
| GSR | 8.74 | 10.49 | −3.36 |
| IFNG | 10.72 | 12.27 | −2.92 |
| SLC27A4 | 5.73 | 7.24 | −2.84 |
| IRF1 | 5.72 | 7.16 | −2.71 |
| AXIN2 | 10.73 | 12.06 | −2.51 |
| CPT2 | 9.25 | 10.56 | −2.48 |
| BBC3 | 9.23 | 10.49 | −2.39 |
| WNT3A | 12.78 | 14.04 | −2.39 |
| BAX | 3.34 | 4.45 | −2.16 |
| HES1 | 3.79 | 4.84 | −2.07 |
| WNT1 | 15.12 | 18.83 | 4.90 |
| OLR1 | 15.12 | 12.72 | 5.29 |
| TNF | 15.12 | 12.65 | 5.55 |
| PTCH1 | 14.87 | 12.36 | 5.70 |
| CCL5 | 15.12 | 12.32 | 6.97 |
| FABP1 | 15.12 | 12.09 | 8.18 |
| WNT6 | 15.12 | 12.04 | 8.47 |
| PANTHER Pathways | # 1 | # 2 | Expected 3 | Fold Enrichment 4 | Raw p Value 5 | FDR 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WNT signaling pathway | 309 | 6 | 0.32 | 19.04 | 4.88 × 10−7 | 7.86 × 10−5 |
| Alzheimer disease-presenilin pathway | 126 | 4 | 0.13 | 31.13 | 7.38 × 10−6 | 3.96 × 10−4 |
| Cadherin signaling pathway | 164 | 3 | 0.17 | 17.94 | 5.94 × 10−4 | 2.39 × 10−2 |
| Notch signaling pathway | 44 | 2 | 0.04 | 44.57 | 9.13 × 10−4 | 2.94 × 10−2 |
| Apoptosis signaling pathway | 119 | 2 | 0.12 | 16.48 | 6.47 × 10−3 | 1.74 × 10−1 |
| CCKR signaling map | 172 | 2 | 0.18 | 11.40 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 2.64 × 10−1 |
| Angiogenesis | 171 | 2 | 0.17 | 11.47 | 1.30 × 10−2 | 2.99 × 10−1 |
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | 20 | 1 | 0.02 | 49.03 | 2.02 × 10−2 | 3.62 × 10−1 |
| Interferon-gamma signaling pathway | 30 | 1 | 0.03 | 32.69 | 3.02 × 10−2 | 4.42 × 10−1 |
| Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | 262 | 2 | 0.27 | 7.49 | 2.89 × 10−2 | 4.65 × 10−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monarca, L.; Ragonese, F.; Biagini, A.; Sabbatini, P.; Pacini, M.; Zucchi, A.; Spaccapelo, R.; Ferrari, P.; Nicolini, A.; Fioretti, B. Electrophysiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in U251 Human Glioblastoma Cells: Possible Implications in Gliomagenesis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126669
Monarca L, Ragonese F, Biagini A, Sabbatini P, Pacini M, Zucchi A, Spaccapelo R, Ferrari P, Nicolini A, Fioretti B. Electrophysiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in U251 Human Glioblastoma Cells: Possible Implications in Gliomagenesis? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126669
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonarca, Lorenzo, Francesco Ragonese, Andrea Biagini, Paola Sabbatini, Matteo Pacini, Alessandro Zucchi, Roberta Spaccapelo, Paola Ferrari, Andrea Nicolini, and Bernard Fioretti. 2024. "Electrophysiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in U251 Human Glioblastoma Cells: Possible Implications in Gliomagenesis?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126669
APA StyleMonarca, L., Ragonese, F., Biagini, A., Sabbatini, P., Pacini, M., Zucchi, A., Spaccapelo, R., Ferrari, P., Nicolini, A., & Fioretti, B. (2024). Electrophysiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein in U251 Human Glioblastoma Cells: Possible Implications in Gliomagenesis? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126669








