Machine Learning-Based Etiologic Subtyping of Ischemic Stroke Using Circulating Exosomal microRNAs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Three Stroke Subtypes
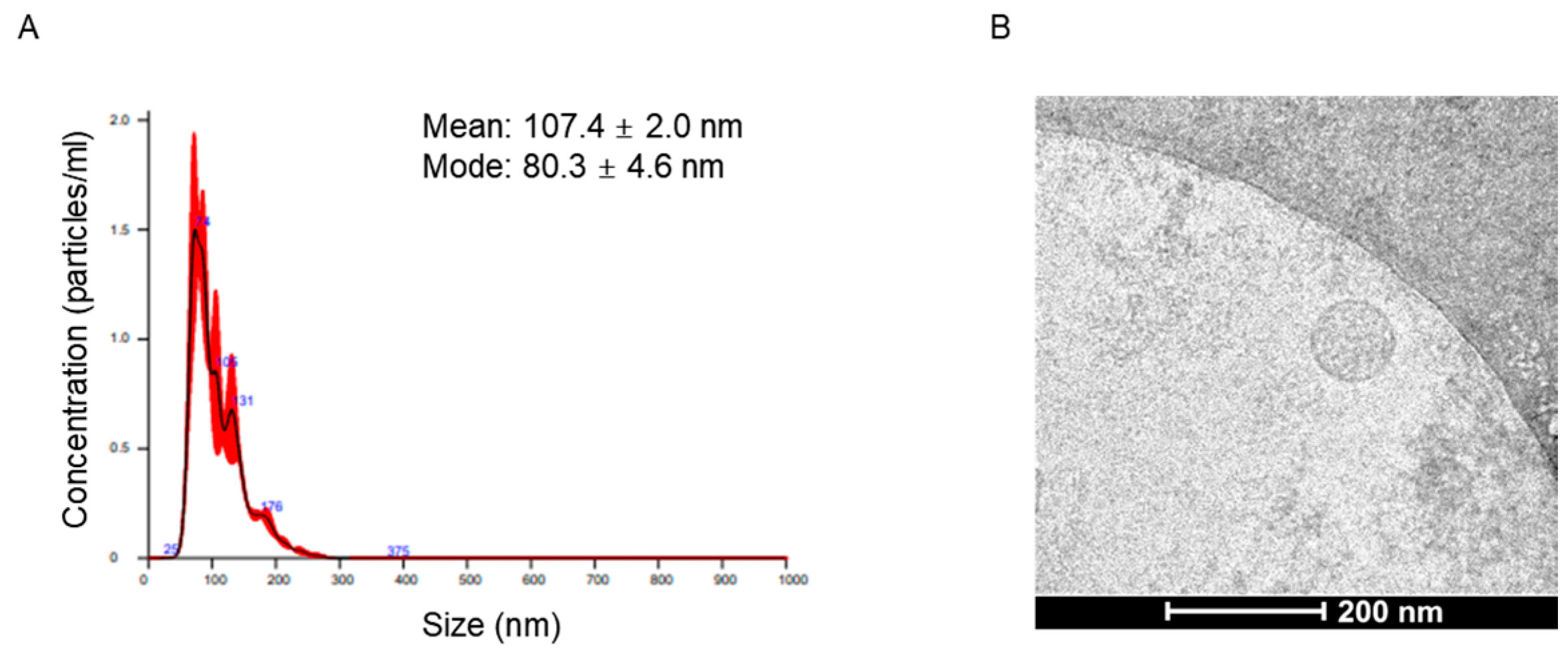
2.2. Characteristics of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles
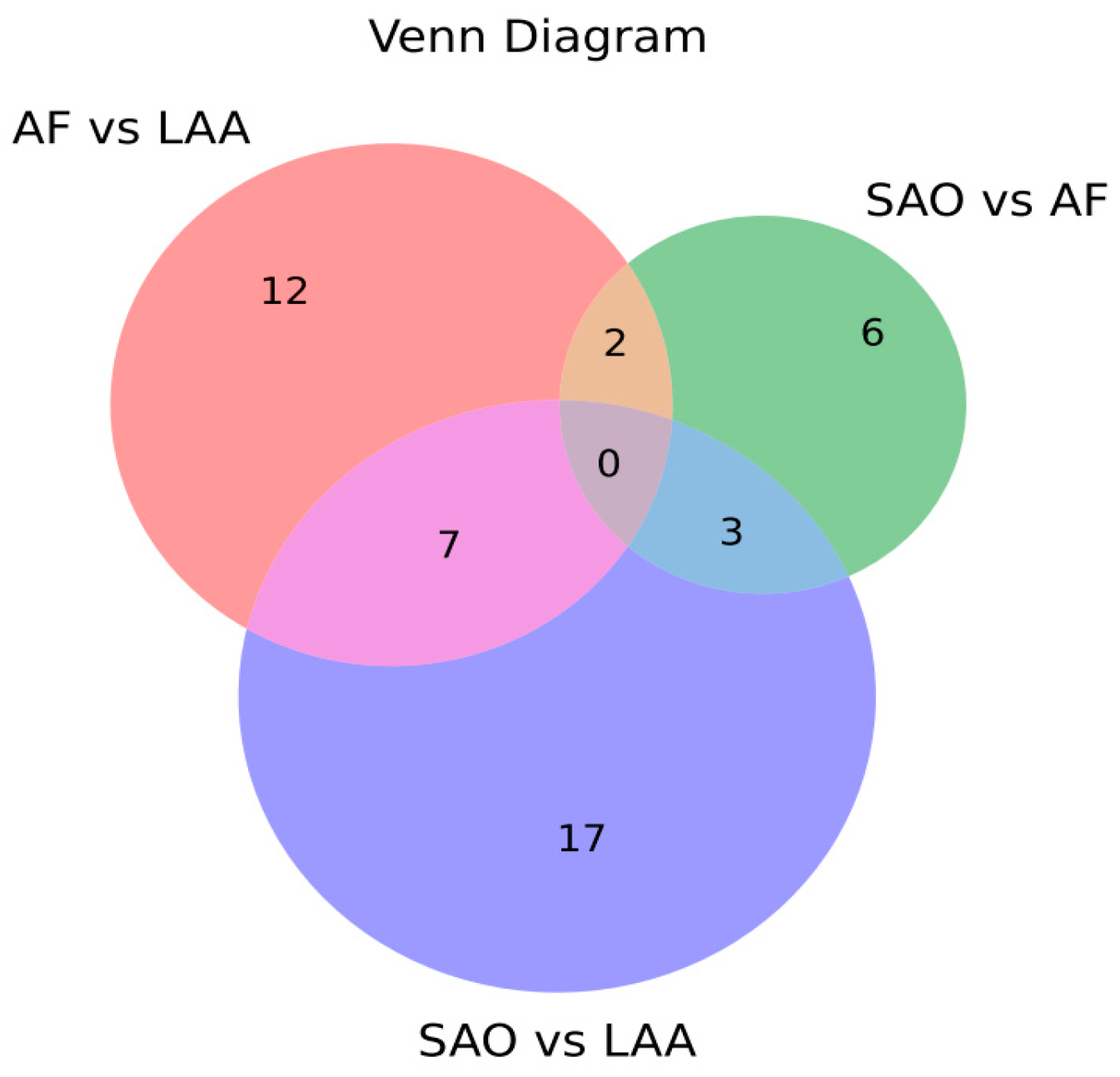
2.3. Comparison of miRNA Profiling of sEV-Derived miRNAs among Stroke Subtypes
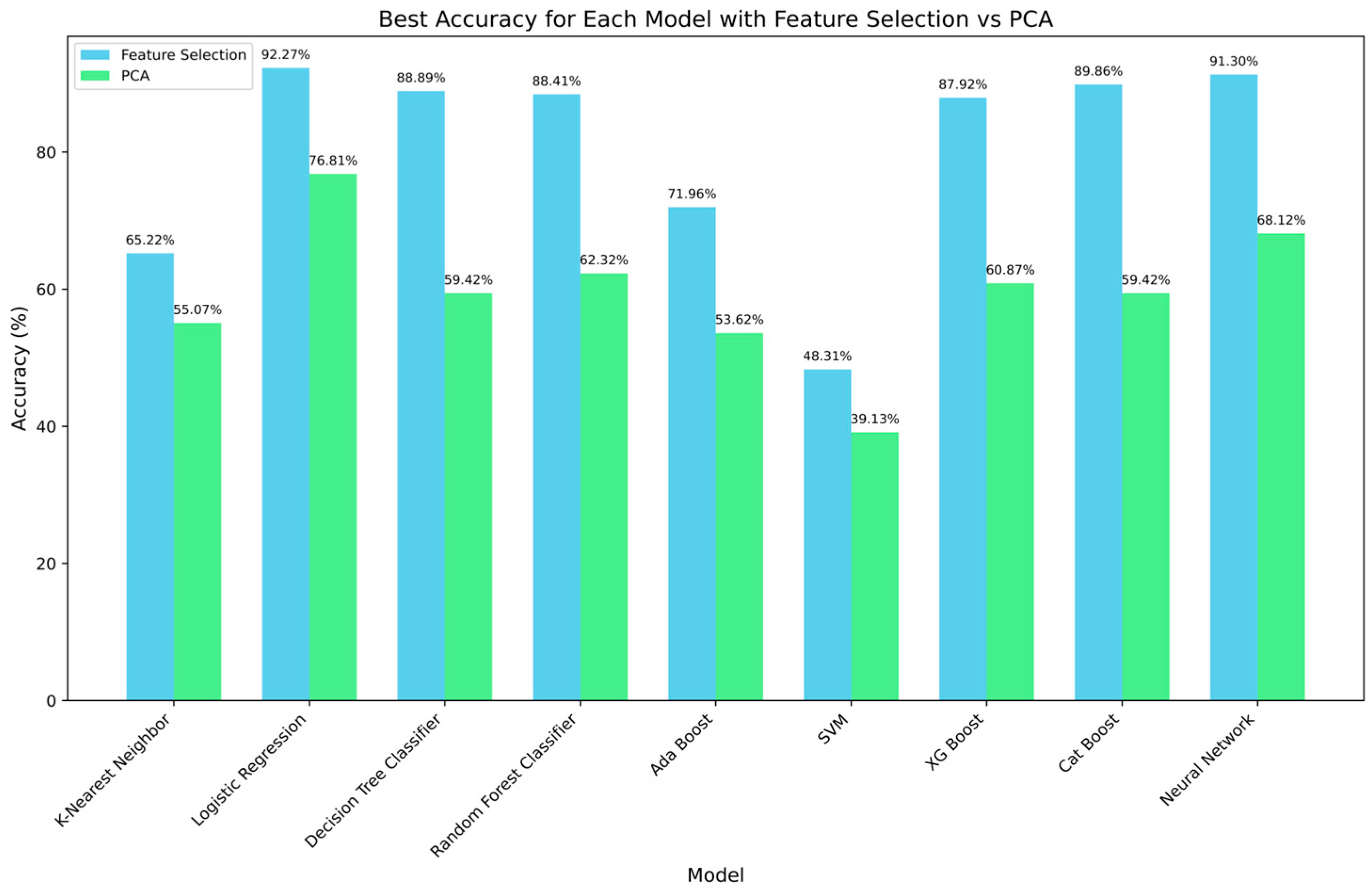
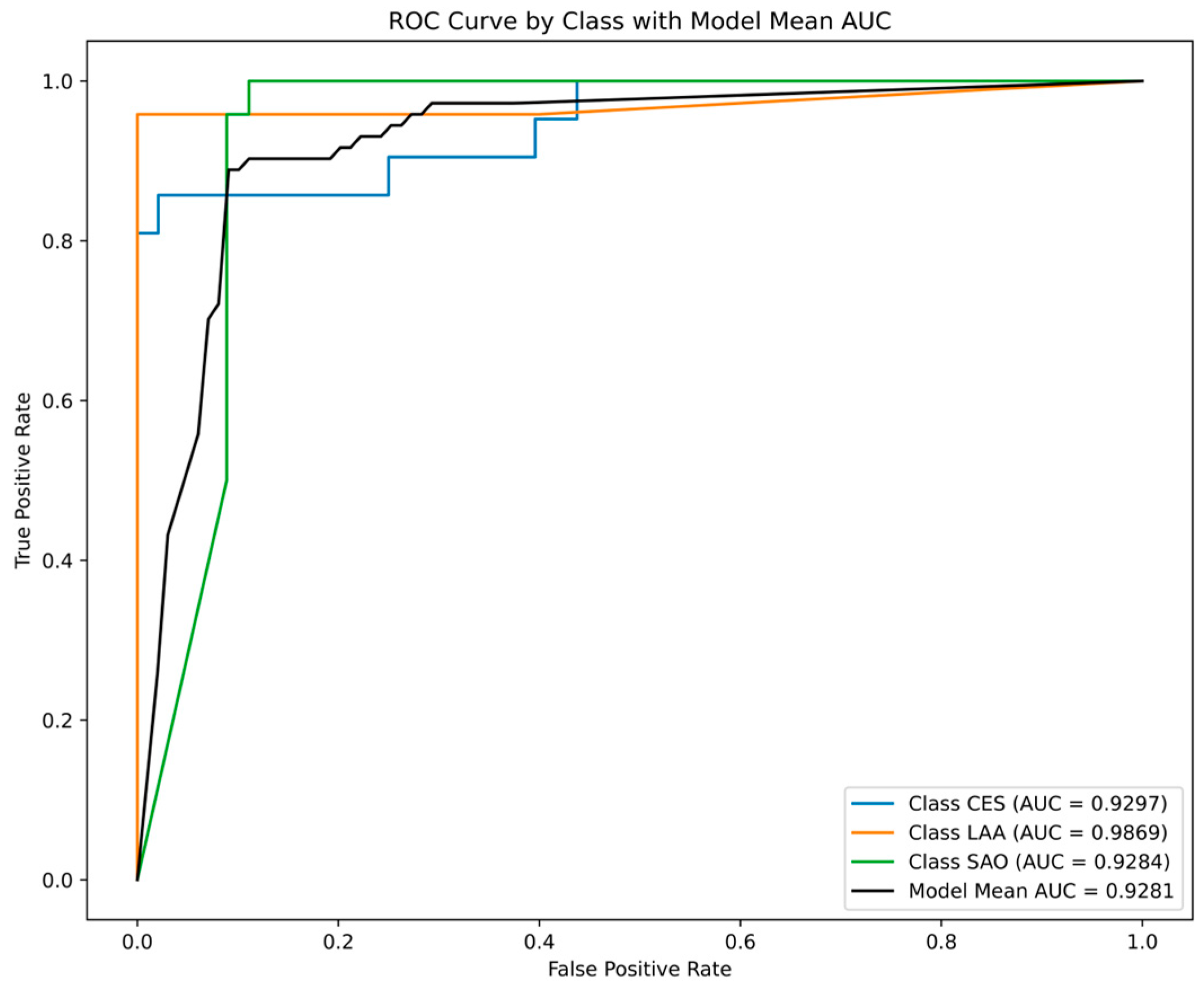
2.3.1. Performance Comparisons of ML Models
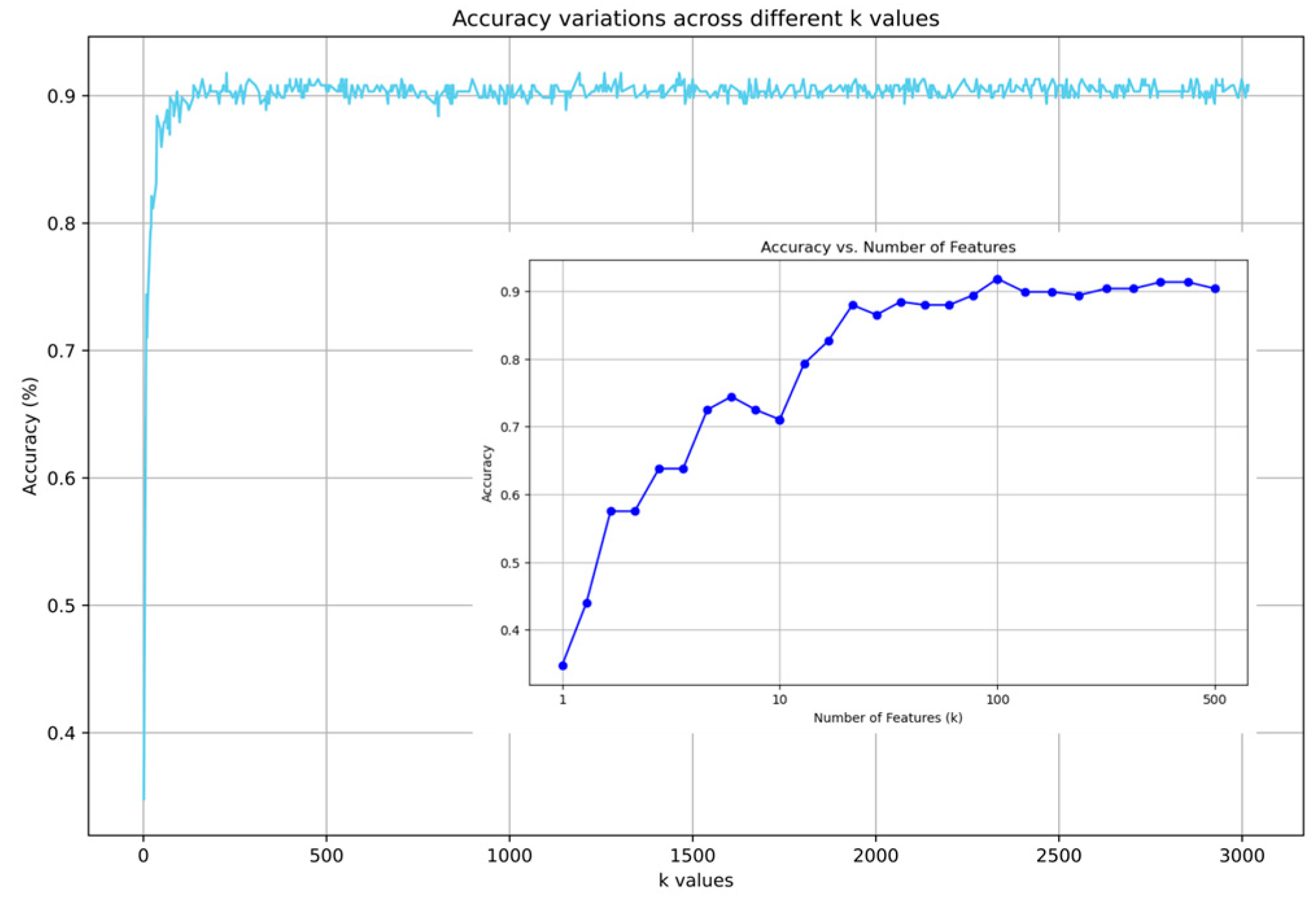
2.3.2. Impact of Feature Selection
2.3.3. Impact of Clinical Information on EV-microRNA Prediction Models
2.4. Underlying Mechanisms of EV-miRNAs for Each Stroke Subtype
2.4.1. Feature Importance Analysis
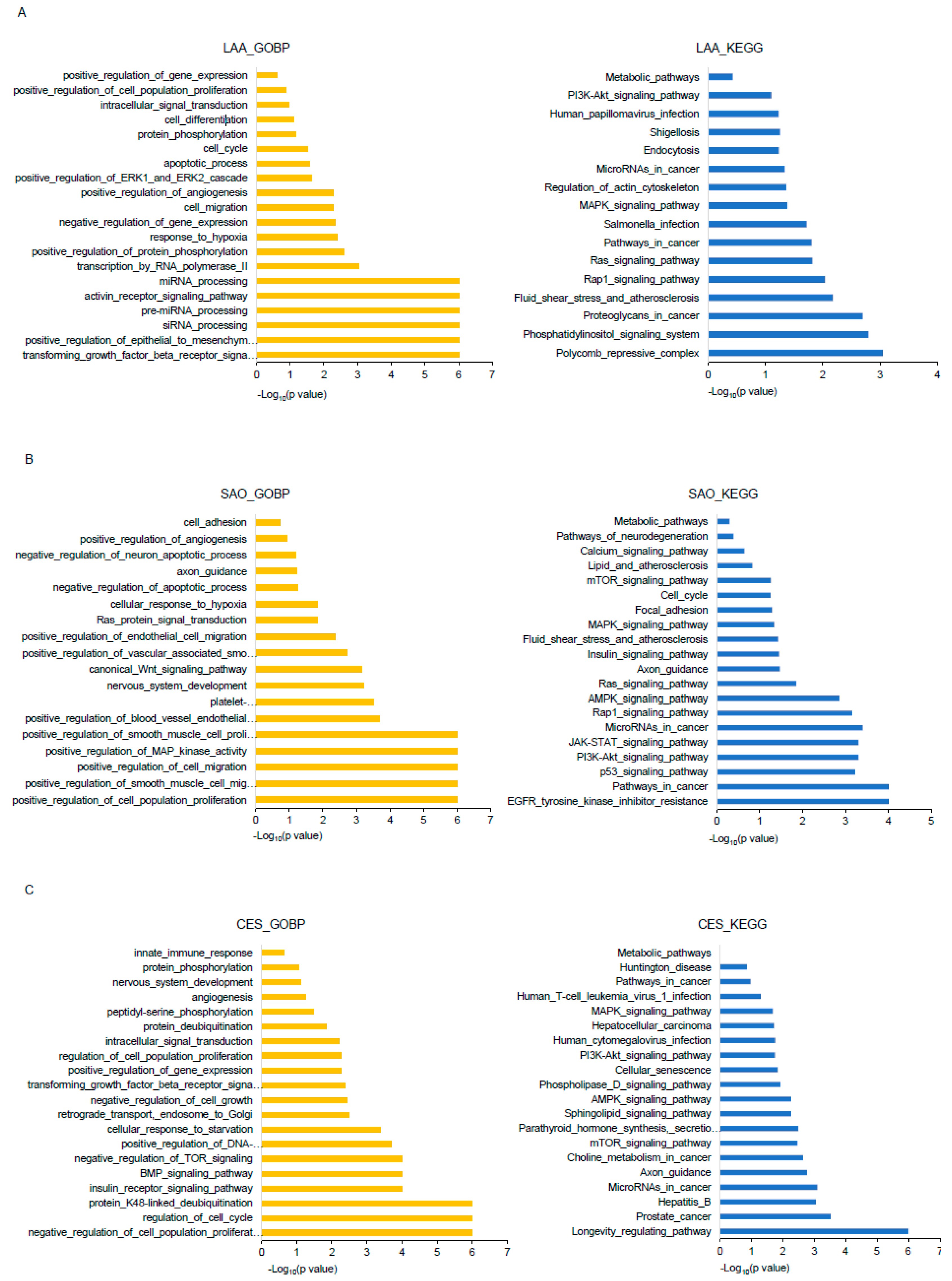
2.4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection
4.2. Isolation and Characterization of EVs
4.3. RNA Isolation
4.4. miRNA Profiling
4.5. Data Analysis Step
4.6. Bioinformatics Analysis of miRNAs
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ay, H.; Furie, K.L.; Singhal, A.; Smith, W.S.; Sorensen, A.G.; Koroshetz, W.J. An evidence-based causative classification system for acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, e364–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, D.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Di Mascio, M.T.; Vinisko, R.; Bath, P.M.; Group, P.R.S. Types of stroke recurrence in patients with ischemic stroke: A substudy from the PRoFESS trial. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2014, 9, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzelins, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Sobolevska, K.; Abols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Santare, D.; Rudnickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.A.; Kim, I.S. Emerging Prospects of Exosomes for Cancer Treatment: From Conventional Therapy to Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2002440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kralingen, J.C.; McFall, A.; Ord, E.N.J.; Coyle, T.F.; Bissett, M.; McClure, J.D.; McCabe, C.; Macrae, I.M.; Dawson, J.; Work, L.M. Altered Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Expression in Ischemic Stroke and Small Vessel Disease. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Alonso-Lopez, E.; Perez-Mato, M.; Laso-Garcia, F.; Gomez-de Frutos, M.C.; Diekhorst, L.; Garcia-Bermejo, M.L.; Conde-Moreno, E.; Fuentes, B.; de Lecinana, M.A.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Proteins and MicroRNA Profiles in Subcortical and Cortical-Subcortical Ischaemic Stroke. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Oh, M.J.; Yoo, J.; Oh, G.S.; Chung, J.W.; Seo, W.K.; Kim, G.M.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, S.W.; et al. Circulating Extracellular-Vesicle-Incorporated MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Cancer. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K.; Gordillo, G.M.; Khanna, S.; Roy, S. Micromanaging vascular biology: Tiny microRNAs play big band. J. Vasc. Res. 2009, 46, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Qi, G.X.; Liu, M.X.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, J.H.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, S. Deep Learning Promotes Profiling of Multiple miRNAs in Single Extracellular Vesicles for Cancer Diagnosis. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quer, G.; Arnaout, R.; Henne, M.; Arnaout, R. Machine Learning and the Future of Cardiovascular Care: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsat, M.S.; Ferme, E.; Camara, J. Machine Learning for Brain Stroke: A Review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, J.; Di, S.; Nelson, W. Opening the Black Box: The Promise and Limitations of Explainable Machine Learning in Cardiology. Can. J. Cardiol. 2022, 38, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeys, Y.; Inza, I.; Larranaga, P. A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2507–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, O.Y.; Park, K.M.; Jeong, D.S. Occurrence of Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants: Causes and Prevention Strategies. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Chauhan, G.; Traylor, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Okada, Y.; Mishra, A.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Giese, A.K.; van der Laan, S.W.; Gretarsdottir, S.; et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Markus, H.S. Stroke Genetics: Discovery, Insight Into Mechanisms, and Clinical Perspectives. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit, S.L.; Weng, L.C.; McArdle, P.F.; Trinquart, L.; Choi, S.H.; Mitchell, B.D.; Rosand, J.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Benjamin, E.J.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Atrial fibrillation genetic risk differentiates cardioembolic stroke from other stroke subtypes. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, D.; Kirchner, B.; Hermann, S.; Marte, M.; Wurmser, C.; Brandes, F.; Kotschote, S.; Bonin, M.; Steinlein, O.K.; Pfaffl, M.W.; et al. Evaluation of serum extracellular vesicle isolation methods for profiling miRNAs by next-generation sequencing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1481321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Revull, M.; Martinez-Gonzalez, B.; Quer, J.; Esteban, J.I.; Nunez-Moreno, G.; Minguez, P.; Burgui, I.; Ramos-Ruiz, R.; Soria, M.E.; Rico, A.; et al. Comparison of Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Methods for miRNA Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zieren, R.C.; Horie, K.; Kim, C.J.; Mallick, E.; Jing, Y.; Feng, M.; Kuczler, M.D.; Green, J.; Amend, S.R.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of methods for small extracellular vesicles separation from human plasma, urine and cell culture medium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, D.E.; Tahir, M.; Faheem, M.; Alves, W.; Correa, B.L.; Andrade, G.R.; Larsen, M.R.; Oliveira, G.P., Jr.; Pereira, R.W. Comparison of Four Purification Methods on Serum Extracellular Vesicle Recovery, Size Distribution, and Proteomics. Proteomes 2023, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bengio, S.; Hardt, M.; Recht, B.; Vynyals, O. Understanding deep learning (still) requires rethinking. Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, E.H.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Seo, W.K.; Kim, G.M.; Bang, O.Y. Luminal and Wall Changes in Intracranial Arterial Lesions for Predicting Stroke Occurrence. Stroke 2020, 51, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, J.G.; Ko, Y.; Hong, K.S.; Park, J.M.; Kang, K.; Park, T.H.; Park, S.S.; Lee, K.B.; et al. Moderate alcohol intake reduces risk of ischemic stroke in Korea. Neurology 2015, 85, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, S.L.; Widen, S.G.; Prough, D.S.; Hellmich, H.L. Principal component analysis of blood microRNA datasets facilitates diagnosis of diverse diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.M.; Atomi, W.H.; Rehman, M.Z. The Effect of Data Pre-processing on Optimized Training of Artificial Neural Networks. Procedia Technol. 2013, 11, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, H. Machine learning-based predictive modeling of depression in hypertensive populations. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Nishiyama, T.; Shimizu, K.; Kadota, K. TCC: An R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| LAA | SAO | CES | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 72.5 ± 8.5 | 67.0 ± 11.8 | 73.3 ± 10.0 | 0.077 |
| Male sex | 20 (83.3%) | 17 (70.8%) | 17 (77.3%) | 0.588 |
| Risk factor | ||||
| Hypertension | 19 (79.2%) | 19 (79.2%) | 16 (72.7%) | 0.837 |
| Diabetes | 11 (45.8%) | 9 (37.5%) | 7 (31.8%) | 0.616 |
| Dyslipidemia | 13 (54.2%) | 13 (54.2%) | 9 (40.9%) | 0.588 |
| Smoking | 0.300 | |||
| Never | 9 (37.5%) | 12 (50.0%) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| Ex smoker | 7 (29.2%) | 5 (20.8%) | 8 (36.4%) | |
| Current smoker | 8 (33.3%) | 7 (29.2%) | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Alcohol | 0.607 | |||
| None | 14 (58.3%) | 18 (75.0%) | 14 (63.6%) | |
| Light–moderate | 5 (20.9%) | 6 (25.0%) | 5 (22.6%) | |
| Heavy | 5 (20.9%) | - | 3 (13.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, J.-W.; Seo, W.-K.; Kim, G.-M.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Bang, O.Y. Machine Learning-Based Etiologic Subtyping of Ischemic Stroke Using Circulating Exosomal microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126761
Bang JH, Kim EH, Kim HJ, Chung J-W, Seo W-K, Kim G-M, Lee D-H, Kim H, Bang OY. Machine Learning-Based Etiologic Subtyping of Ischemic Stroke Using Circulating Exosomal microRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126761
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Ji Hoon, Eun Hee Kim, Hyung Jun Kim, Jong-Won Chung, Woo-Keun Seo, Gyeong-Moon Kim, Dong-Ho Lee, Heewon Kim, and Oh Young Bang. 2024. "Machine Learning-Based Etiologic Subtyping of Ischemic Stroke Using Circulating Exosomal microRNAs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126761
APA StyleBang, J. H., Kim, E. H., Kim, H. J., Chung, J.-W., Seo, W.-K., Kim, G.-M., Lee, D.-H., Kim, H., & Bang, O. Y. (2024). Machine Learning-Based Etiologic Subtyping of Ischemic Stroke Using Circulating Exosomal microRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126761







