Repurposing Anticancer Drugs Targeting the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Respiratory Virus Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Roles of the MAPK/ERK Pathway in Viral Infections
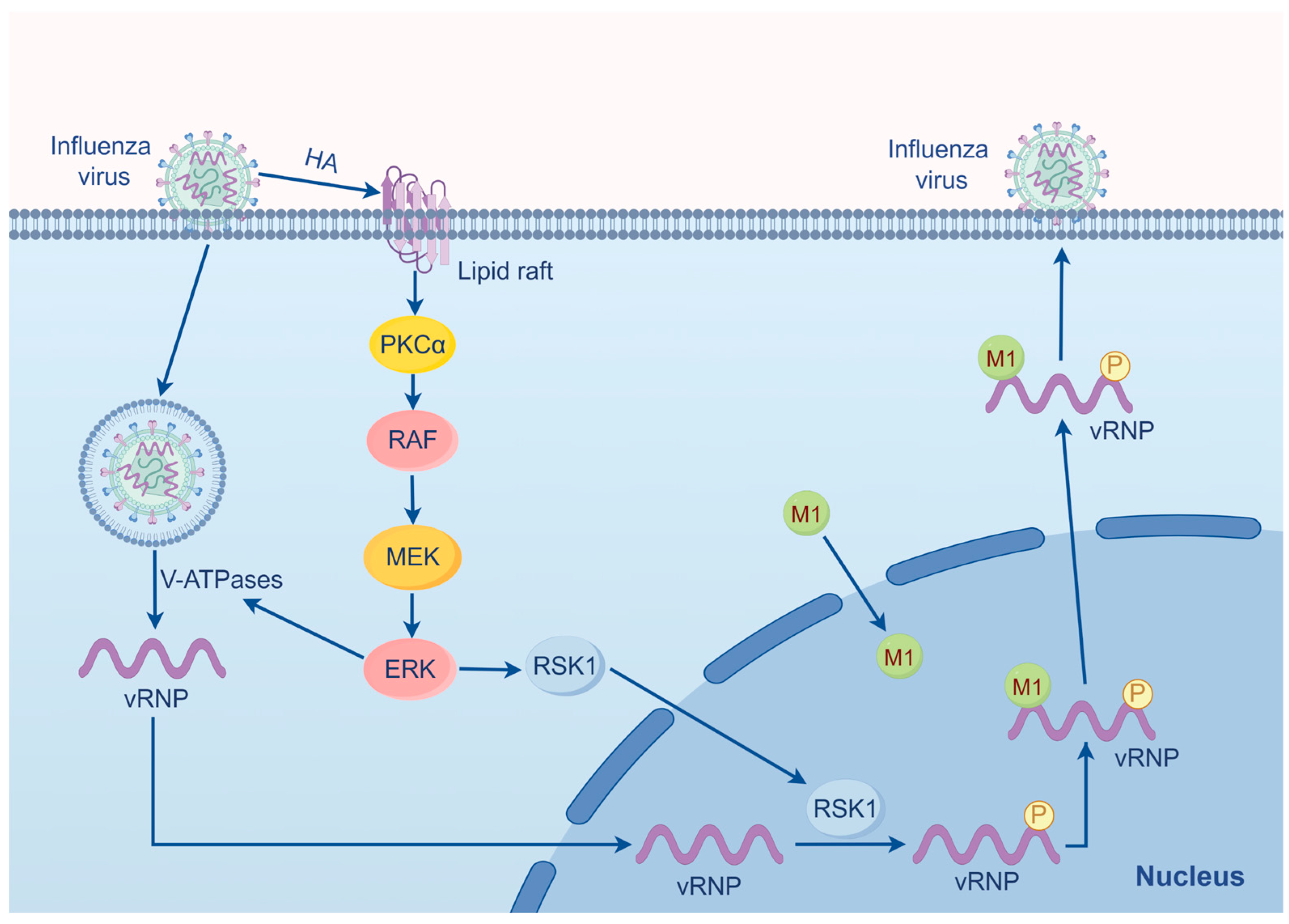
2.1. Influenza Virus
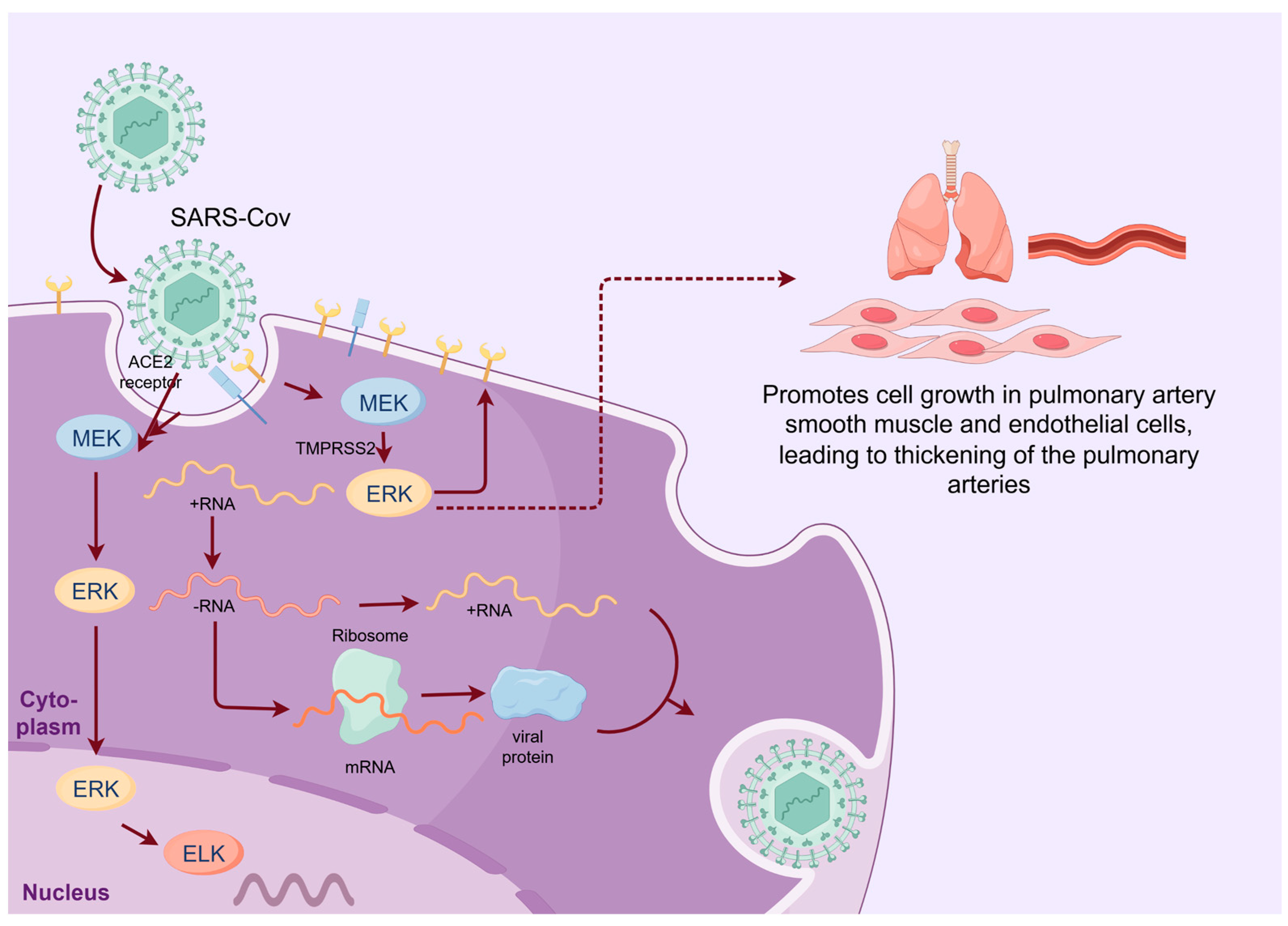
2.2. SARS-CoV-2
3. The MEK/ERK Pathway Serves as a Novel Antiviral Target
4. The Clinical Development of MEK Inhibitors for Antivirus
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subbarao, K.; Mahanty, S. Respiratory Virus Infections: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 52, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, N.H.L. Transmissibility and transmission of respiratory viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and Influenza A Respiratory Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 552909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacova, I.; De Boeck, I.; Bron, P.A.; Delputte, P.; Lebeer, S. Topical Microbial Therapeutics against Respiratory Viral Infections. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, M.; Hugentobler, W.J.; Iwasaki, A. Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020, 7, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huntington, K.; Zhang, S.; Carlsen, L.; So, E.Y.; Parker, C.; Sahin, I.; Safran, H.; Kamle, S.; Lee, C.M.; et al. MEK inhibitors reduce cellular expression of ACE2. pERK, pRb while stimulating NK-mediated cytotoxicity and attenuating inflammatory cytokines relevant to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4201–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, S.; Pirzadeh, M.; Carver, K.Y.; Deng, J.C. Respiratory Viral Infection-Induced Microbiome Alterations and Secondary Bacterial Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, H.T.; Higham, S.L.; Moffatt, M.F.; Cox, M.J.; Tregoning, J.S. Respiratory Viral Infection Alters the Gut Microbiota by Inducing Inappetence. mBio 2020, 11, e03236-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillóniz, C.; Pericàs, J.M.; Rojas, J.R.; Torres, A. Severe Infections Due to Respiratory Viruses. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 43, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, S.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O. MEK inhibitors as novel host-targeted antivirals with a dual-benefit mode of action against hyperinflammatory respiratory viral diseases. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2023, 59, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleschka, S.; Wolff, T.; Ehrhardt, C.; Hobom, G.; Planz, O.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Influenza virus propagation is impaired by inhibition of the Raf/MEK/ERK signalling cascade. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacqué, J.M.; Mann, A.; Enslen, H.; Sharova, N.; Brichacek, B.; Davis, R.J.; Stevenson, M. Modulation of HIV-1 infectivity by MAPK. a virion-associated kinase. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuvanshi, R.; Bharate, S.B. Recent Developments in the Use of Kinase Inhibitors for Management of Viral Infections. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 893–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivacqua, R.; Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Raimondi, M.V.; Romeo, I.; Alcaro, S.; Andrei, G.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A. Insight into non-nucleoside triazole-based systems as viral polymerases inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Yin, Q.; Snell, A.H.; Wan, L. RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer evolution and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.K.; Becker, A.; Park, J.I. Growth Inhibitory Signaling of the Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eblen, S.T. Extracellular-Regulated Kinases: Signaling From Ras to ERK Substrates to Control Biological Outcomes. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 138, 99–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.G. Regulation of TGF-β Signal Transduction. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 874065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Acevedo, L.A.; Marmorstein, R. The MEK/ERK Network as a Therapeutic Target in Human Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Flaherty, K.T.; Robert, C.; Arance, A.; de Groot, J.W.B.; Garbe, C.; Gogas, H.J.; Gutzmer, R.; Krajsová, I.; Liszkay, G.; et al. COLUMBUS 5-Year Update: A Randomized. Open-Label, Phase III Trial of Encorafenib Plus Binimetinib Versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib in Patients with BRAF V600-Mutant Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Chik, K.K.; Chan, J.F.; Cai, J.P.; Cao, H.; Tsang, J.O.; Zou, Z.; Hung, Y.P.; Tang, K.; Jia, L.; et al. Vemurafenib Inhibits Enterovirus A71 Genome Replication and Virus Assembly. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A.; Wen, X.; Ou, X.; Mao, S.; Gao, Q.; Sun, D.; Jia, R.; Yang, Q.; et al. Enterovirus Replication Organelles and Inhibitors of Their Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, S.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Horng, J.T. Phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK in an early entry step of enterovirus 71. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, G.; Qiu, F.; Ren, F.; Lin, B.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Q.; Huang, C. PLX8394. a RAF inhibitor, inhibits enterovirus 71 replication by blocking RAF/MEK/ERK signaling. Virol. Sin. 2023, 38, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieske, N.V.; Tonby, K.; Kvale, D.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Tasken, K. Targeting Tuberculosis and HIV Infection-Specific Regulatory T Cells with MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Meng, C.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; Qiu, X.; Liu, W.; Ding, C.; Ying, L. Upregulation of DUSP6 impairs infectious bronchitis virus replication by negatively regulating ERK pathway and promoting apoptosis. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Kapoor, A.; He, R.; Venkatadri, R.; Forman, M.; Posner, G.H.; Arav-Boger, R. In vitro combination of anti-cytomegalovirus compounds acting through different targets: Role of the slope parameter and insights into mechanisms of Action. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonjardim, C.A. Viral exploitation of the MEK/ERK pathway—A tale of vaccinia virus and other viruses. Virology 2017, 507, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, E.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Structure and Function of the Influenza Virus Transcription and Replication Machinery. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a038398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.J.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Peiris, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnell, J.R.; Chou, J.J. Structure and mechanism of the M2 proton channel of influenza A virus. Nature 2008, 451, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cady, S.D.; Luo, W.; Hu, F.; Hong, M. Structure and function of the influenza A M2 proton channel. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7356–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmapalan, D. Influenza. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, S.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O.; Wolff, T. Ringing the alarm bells: Signalling and apoptosis in influenza virus infected cells. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, A.; Boff, L.; Anhlan, D.; Krischuns, T.; Brunotte, L.; Schuberth, C.; Wedlich-Soldner, R.; Drexler, H.; Ludwig, S. Dissecting the mechanism of signaling-triggered nuclear export of newly synthesized influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16557–16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjuki, H.; Gornitzky, A.; Marathe, B.M.; Ilyushina, N.A.; Aldridge, J.R.; Desai, G.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Influenza A virus-induced early activation of ERK and PI3K mediates V-ATPase-dependent intracellular pH change required for fusion. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S.; Wolff, T.; Ehrhardt, C.; Wurzer, W.J.; Reinhardt, J.; Planz, O.; Pleschka, S. MEK inhibition impairs influenza B virus propagation without emergence of resistant variants. FEBS Lett. 2004, 561, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjuki, H.; Alam, M.I.; Ehrhardt, C.; Wagner, R.; Planz, O.; Klenk, H.D.; Ludwig, S.; Pleschka, S. Membrane accumulation of influenza A virus hemagglutinin triggers nuclear export of the viral genome via protein kinase Calpha-mediated activation of ERK signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16707–16715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjuki, H.; Yen, H.L.; Franks, J.; Webster, R.G.; Pleschka, S.; Hoffmann, E. Higher polymerase activity of a human influenza virus enhances activation of the hemagglutinin-induced Raf/MEK/ERK signal cascade. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vrijens, P.; Noppen, S.; Boogaerts, T.; Vanstreels, E.; Ronca, R.; Chiodelli, P.; Laporte, M.; Vanderlinden, E.; Liekens, S.; Stevaert, A.; et al. Influenza virus entry via the GM3 ganglioside-mediated platelet-derived growth factor receptor β signalling pathway. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keck, F.; Ataey, P.; Amaya, M.; Bailey, C.; Narayanan, A. Phosphorylation of Single Stranded RNA Virus Proteins and Potential for Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Viruses 2015, 7, 5257–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M.; Pashapour, S. SARS-CoV-2 and the Possible Role of Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway in Viral Survival: Is This a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for COVID-19? Pharmacology 2021, 106, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- V’Kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, H.; Ebensperger, M.; Schönsiegel, A.; Hamza, H.; Koch-Heier, J.; Schreiber, A.; Ludwig, S.; Schindler, M.; Planz, O. Influenza A virus replication has a stronger dependency on Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway activity than SARS-CoV-2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1264983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, A.; Viemann, D.; Schöning, J.; Schloer, S.; Mecate Zambrano, A.; Brunotte, L.; Faist, A.; Schöfbänker, M.; Hrincius, E.; Hoffmann, H.; et al. The MEK1/2-inhibitor ATR-002 efficiently blocks SARS-CoV-2 propagation and alleviates pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Nikolaienko, S.I.; Dibrova, V.A.; Dibrova, Y.V.; Vasylyk, V.M.; Novikov, M.Y.; Shults, N.V.; Gychka, S.G. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cell signaling in lung vascular cells. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2021, 137, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Gu, C.; Yue, Y.; Wu, K.K.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y. Spike protein of SARS-CoV stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent protein kinase C pathways. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, C. Porcine deltacoronavirus activates the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway to promote its replication. Virus Res. 2020, 283, 197961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtita, S.; Belhassan, A.; Aouidate, A.; Belaidi, S.; Bouachrine, M.; Lakhlifi, T. Discovery of Potent SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors from Approved Antiviral Drugs via Docking and Virtual Screening. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2021, 24, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayachi, F.; Lima, E.C.; Sakly, A.; Mejri, H.; Ben Lamine, A. Modeling of adsorption isotherms of reactive red RR-120 on spirulina platensis by statistical physics formalism involving interaction effect between adsorbate molecules. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 141, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dochi, T.; Akita, A.; Kishimoto, N.; Takamune, N.; Misumi, S. Trametinib suppresses HIV-1 replication by interfering with the disassembly of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid core. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.; Vijay, S.; McNevin, J.; McElrath, M.J.; Holland, E.C.; Gujral, T.S. Machine learning identifies molecular regulators and therapeutics for targeting SARS-CoV2-induced cytokine release. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021, 17, e10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haasbach, E.; Müller, C.; Ehrhardt, C.; Schreiber, A.; Pleschka, S.; Ludwig, S.; Planz, O. The MEK-inhibitor CI-1040 displays a broad anti-influenza virus activity in vitro and provides a prolonged treatment window compared to standard of care in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2017, 142, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchhagen, C.; Jarick, M.; Mewis, C.; Hertlein, T.; Niemann, S.; Ohlsen, K.; Peters, G.; Planz, O.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. Metabolic conversion of CI-1040 turns a cellular MEK-inhibitor into an antibacterial compound. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haasbach, E.; Hartmayer, C.; Planz, O. Combination of MEK inhibitors and oseltamivir leads to synergistic antiviral effects after influenza A virus infection in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Klemsz, M.J.; Kacena, M.A.; Sandusky, G.; Zhang, X.; Kaplan, M.H. Inhibition of MEK signaling prevents SARS-CoV2-induced lung damage and improves the survival of infected mice. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 6097–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Dong, X.; Xiao, X.; Xiang, Z.; Lei, X.; Wang, J. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis of responses to enterovirus A71 infection reveals novel targets for antiviral and viral replication. Antivir. Res. 2023, 220, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.G.; Liu, X.J.; Guo, Y.L.; Chen, C.L. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain promotes IL-6 and IL-8 release via ATP/P2Y(2) and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in human bronchial epithelia. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 167, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Wakita, T.; Shimizu, H. Cellular kinase inhibitors that suppress enterovirus replication have a conserved target in viral protein 3A similar to that of enviroxime. J. Gen Virol. 2009, 90, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglino, P.; Fava, P.; Brizio, M.; Marra, E.; Rubatto, M.; Merli, M.; Tonella, L.; Ribero, S.; Fierro, M.T. Anti-BRAF/anti-MEK targeted therapies for metastatic melanoma patients during the COVID-19 outbreak: Experience from an Italian skin cancer unit. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 17, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, A.; Ambrosy, B.; Planz, O.; Schloer, S.; Rescher, U.; Ludwig, S. The MEK1/2 Inhibitor ATR-002 (Zapnometinib) Synergistically Potentiates the Antiviral Effect of Direct-Acting Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, K.E.; Carlsen, L.; So, E.Y.; Piesche, M.; Liang, O.; El-Deiry, W.S. Integrin/TGF-beta1 Inhibitor GLPG-0187 Blocks SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Pseudovirus Infection of Airway Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Which Could Attenuate Disease Severity. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.F.; Sebolt-Leopold, J.; Meyer, M.B. CI-1040 (PD184352). a targeted signal transduction inhibitor of MEK (MAPKK). Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, P.M.; Adjei, A.A.; Varterasian, M.; Gadgeel, S.; Reid, J.; Mitchell, D.Y.; Hanson, L.; DeLuca, P.; Bruzek, L.; Piens, J.; et al. Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of the oral MEK inhibitor CI-1040 in patients with advanced malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5281–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Agarwal, S. Direct Targeting of the Raf-MEK-ERK Signaling Cascade Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6508–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.P.; Reddy, H.; Caivano, M.; Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laure, M.; Hamza, H.; Koch-Heier, J.; Quernheim, M.; Müller, C.; Schreiber, A.; Müller, G.; Pleschka, S.; Ludwig, S.; Planz, O. Antiviral efficacy against influenza virus and pharmacokinetic analysis of a novel MEK-inhibitor. ATR-002, in cell culture and in the mouse model. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füll, Y.; Wallasch, C.; Hilton, A.; Planz, O. Pharmacokinetics. absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of the MEK inhibitor zapnometinib in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1050193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch-Heier, J.; Schönsiegel, A.; Waidele, L.M.; Volk, J.; Füll, Y.; Wallasch, C.; Canisius, S.; Burnet, M.; Planz, O. Pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics and Antiviral Efficacy of the MEK Inhibitor Zapnometinib in Animal Models and in Humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 893635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, G.; Stenglein, S.; Prozesky, H.; Manudhane, G.; Sandulescu, O.; Bauer, M.; Overend, T.; Koch, W.; Neuschwander, D.; Planz, O.; et al. Efficacy and safety of zapnometinib in hospitalised adult patients with COVID-19 (RESPIRE): A randomised. double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, proof-of-concept, phase 2 trial. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 65, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Rodner, F.; Oberberg, N.; Anhlan, D.; Bletz, S.; Mellmann, A.; Planz, O.; Ludwig, S. The host-targeted antiviral drug Zapnometinib exhibits a high barrier to the development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance. Antivir. Res. 2024, 225, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | MEK Inhibitors | Structure | Anticancer | Antivirus (Preclinical) | References for Virus Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trametinib | 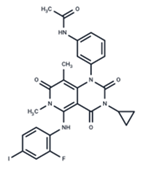 | FDA approved | SARS-CoV-2 Influenza B HIV | [52,53,54] |
| 2 | Cobimetinib | 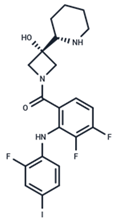 | FDA approved | COVID-19 cytokine release | [55] |
| 3 | CI-1040 | 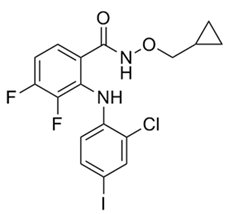 | Phase II | Influenza | [56,57] |
| 4 | PD0325901 |  | Phase II | Influenza A | [58] |
| 5 | Selumetinib | 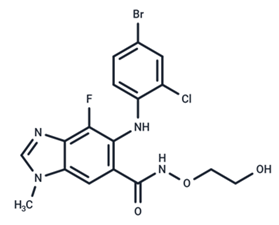 | Phase III | SARS-CoV-2 | [59] |
| 6 | MEK162 | 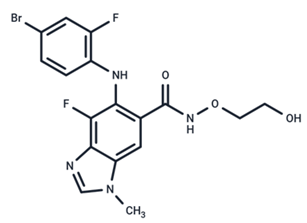 | Phase III | No data | |
| 7 | AZD8330 | 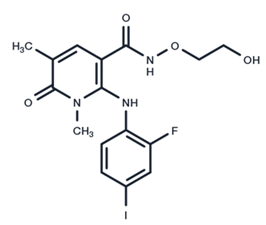 | Phase I | Influenza A | [58] |
| 8 | TAK-733 | 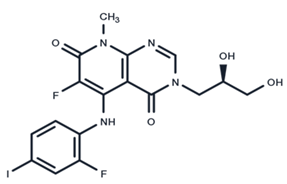 | Phase I | No data | |
| 9 | GDC-0623 | 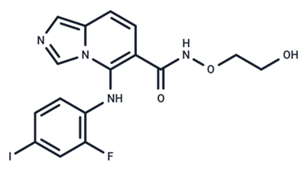 | Phase I | No data | |
| 10 | Refametinib | 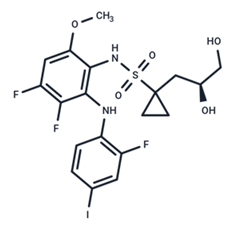 | Phase II | No data | |
| 11 | Pimasertib | 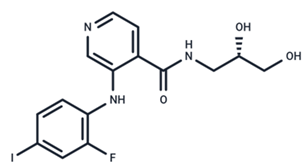 | Phase II | Enteroviurs-A71 | [60] |
| 12 | RO4987655 | 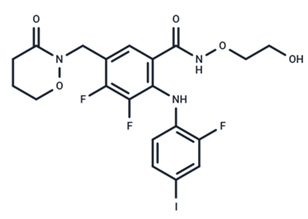 | Phase I | No data | |
| 13 | RO5126766 | 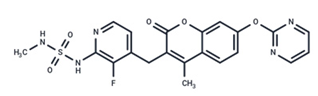 | Phase I | No data | |
| 14 | HL-085 | 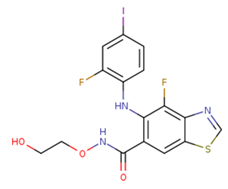 | Phase I | No data | |
| 15 | CInQ-03 | 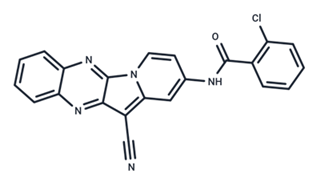 | Preclinical | No data | |
| 16 | G-573 | 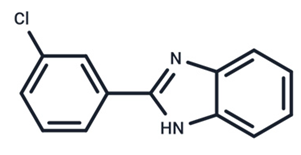 | Preclinical | No data | |
| 17 | PD184161 | 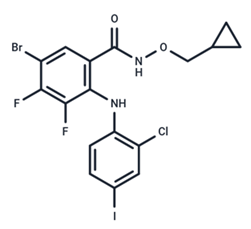 | Preclinical | No data | |
| 18 | PD318088 | 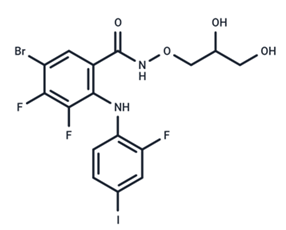 | Preclinical | No data | |
| 19 | PD98059 | 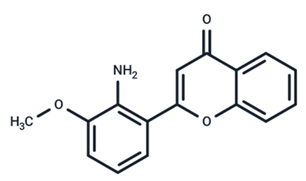 | Preclinical | SARS-CoV-2 | [61] |
| 20 | RO5068760 |  | Preclinical | No data | |
| 21 | U0126 | 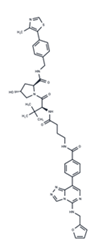 | Preclinical | Influenza | [39] |
| 22 | SL327 | 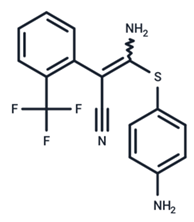 | Preclinical | Enterovirus | [62] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Luo, Z. Repurposing Anticancer Drugs Targeting the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Respiratory Virus Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136946
Liu Y, Luo Z. Repurposing Anticancer Drugs Targeting the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Respiratory Virus Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136946
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuchen, and Zhijun Luo. 2024. "Repurposing Anticancer Drugs Targeting the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Respiratory Virus Infections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136946
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Luo, Z. (2024). Repurposing Anticancer Drugs Targeting the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Respiratory Virus Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136946





