Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Aromatic Compounds
Abstract
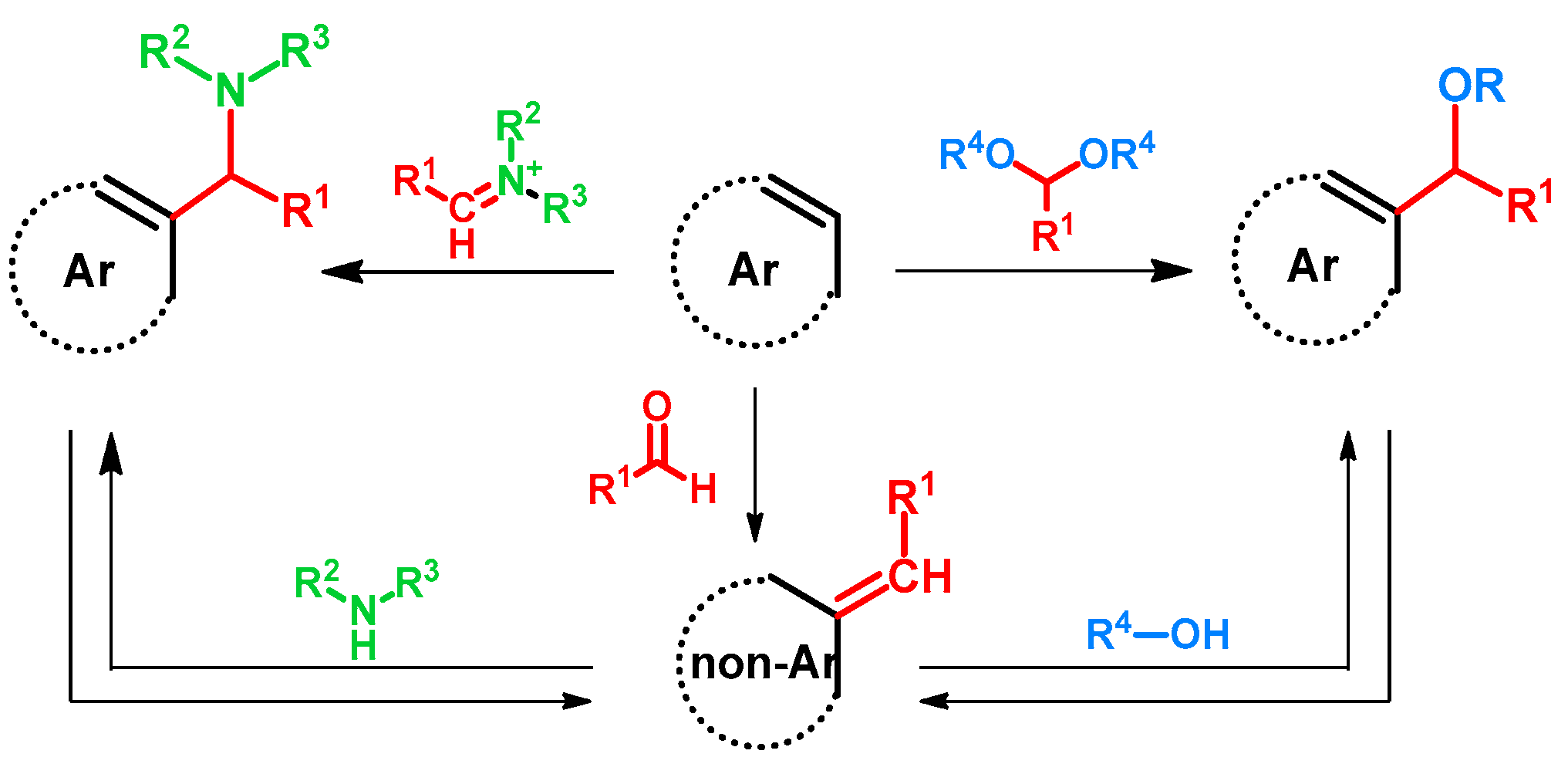
:1. Introduction
2. Hydroxy- and Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Arenes: Direct and Catalytic Methods
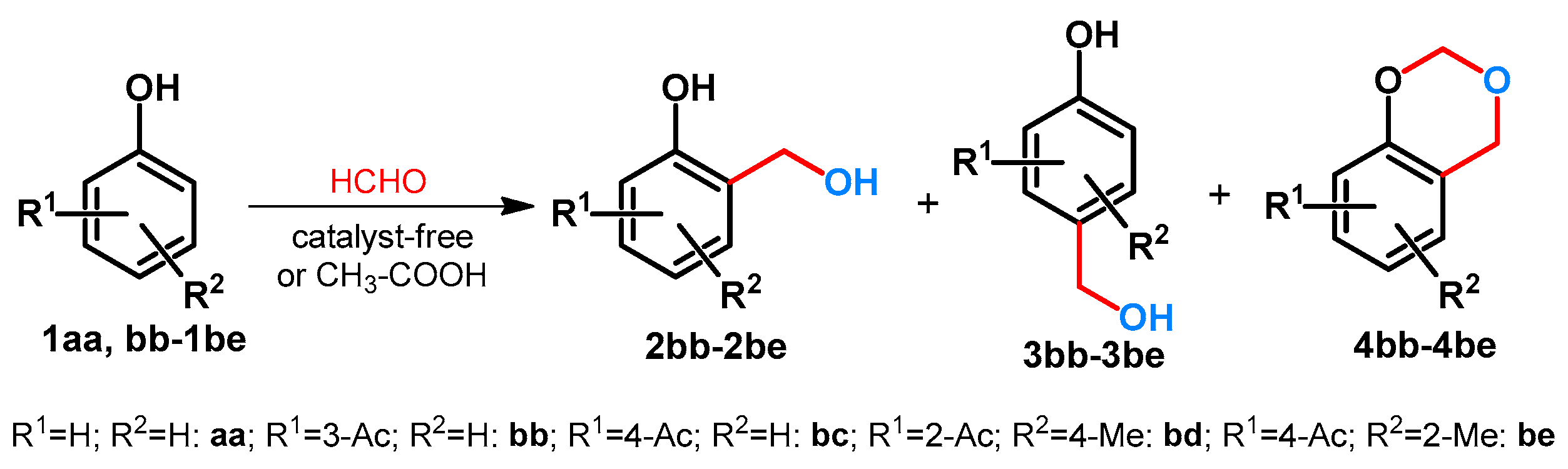
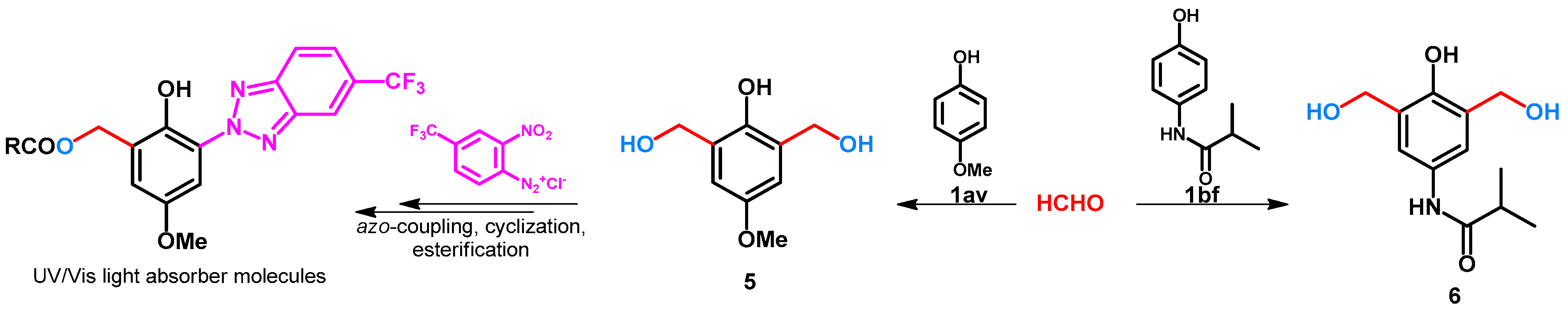
2.1. Hydroxy- and Alkoxymethylation of Monocylic Arenes
2.2. Hydroxy- and Alkoxymethylation of Phenol-Fused Carbocycles
2.3. Hydroxy- and Alkoxymethylation of N-heterocycles
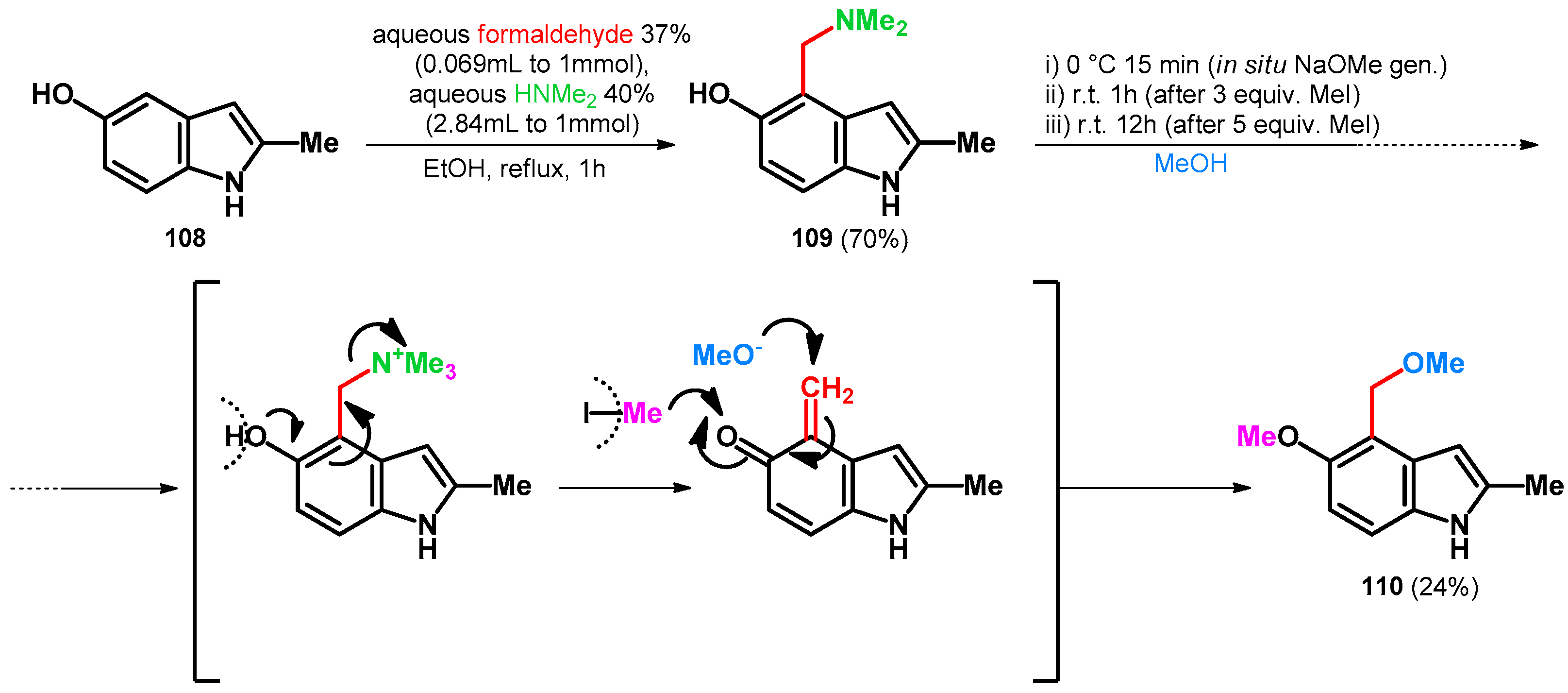
2.3.1. Hydroxy- and Alkoxymethylation of Indoles
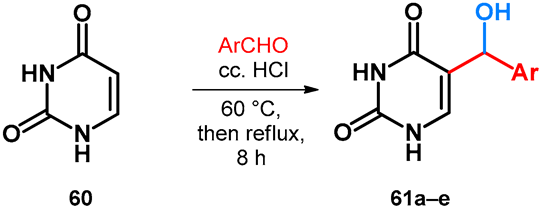
2.3.2. Hydroxy- and Alkoxymethylation of Uracil
3. Hydroxy- and Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Arenes via Aminoalkyl Intermediates
3.1. Transformations of Phenolic Mannich Bases
3.2. Transformations of Semi-Synthetic Phenols and N-heterocycles
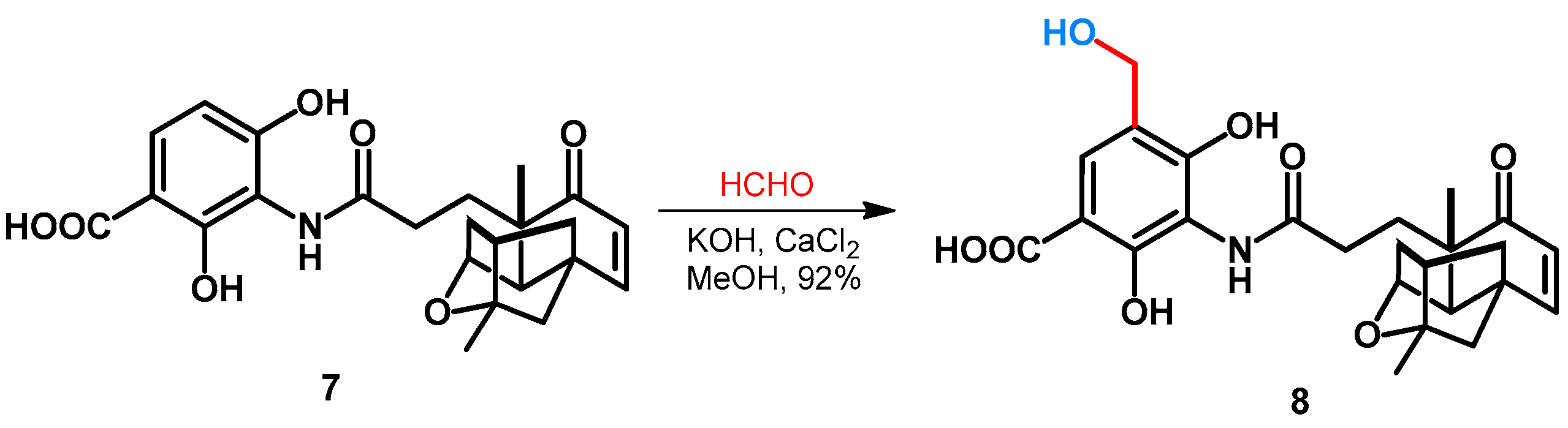
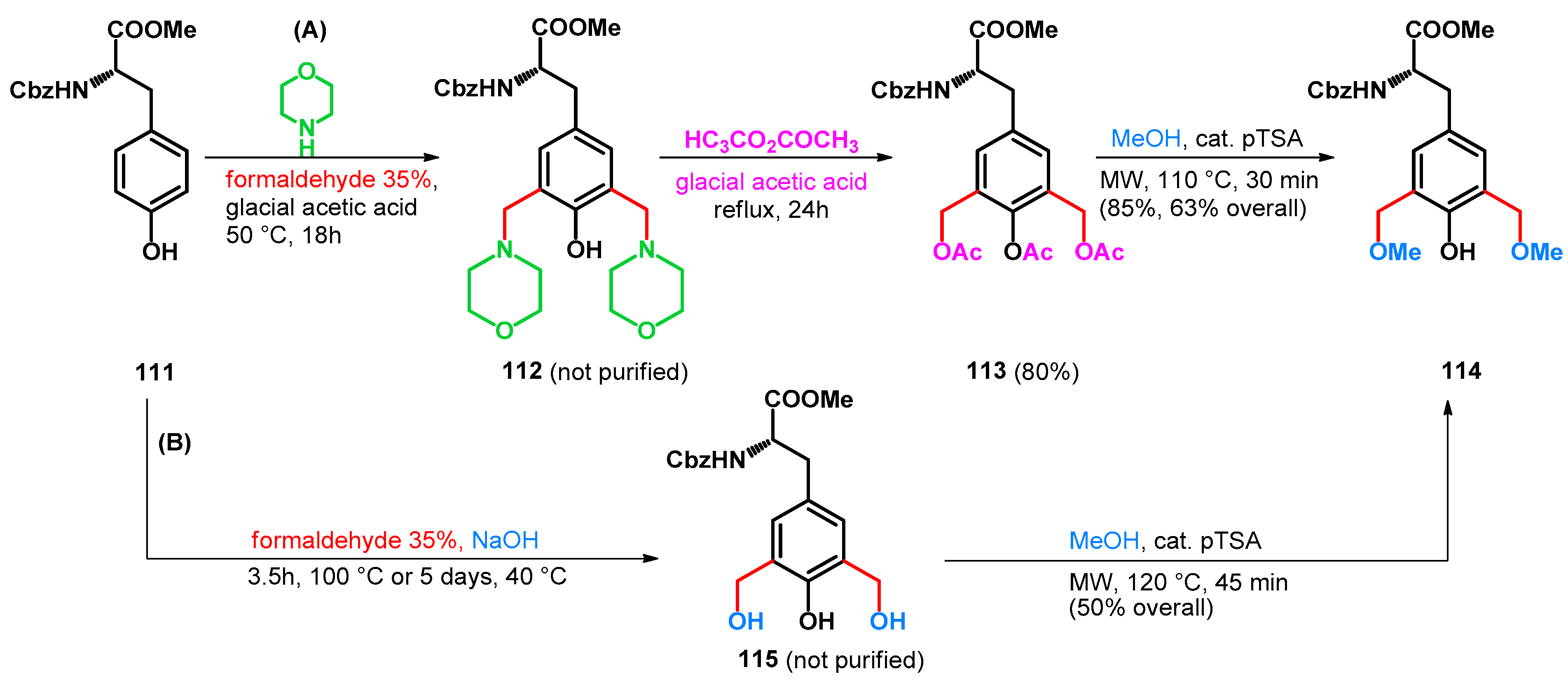
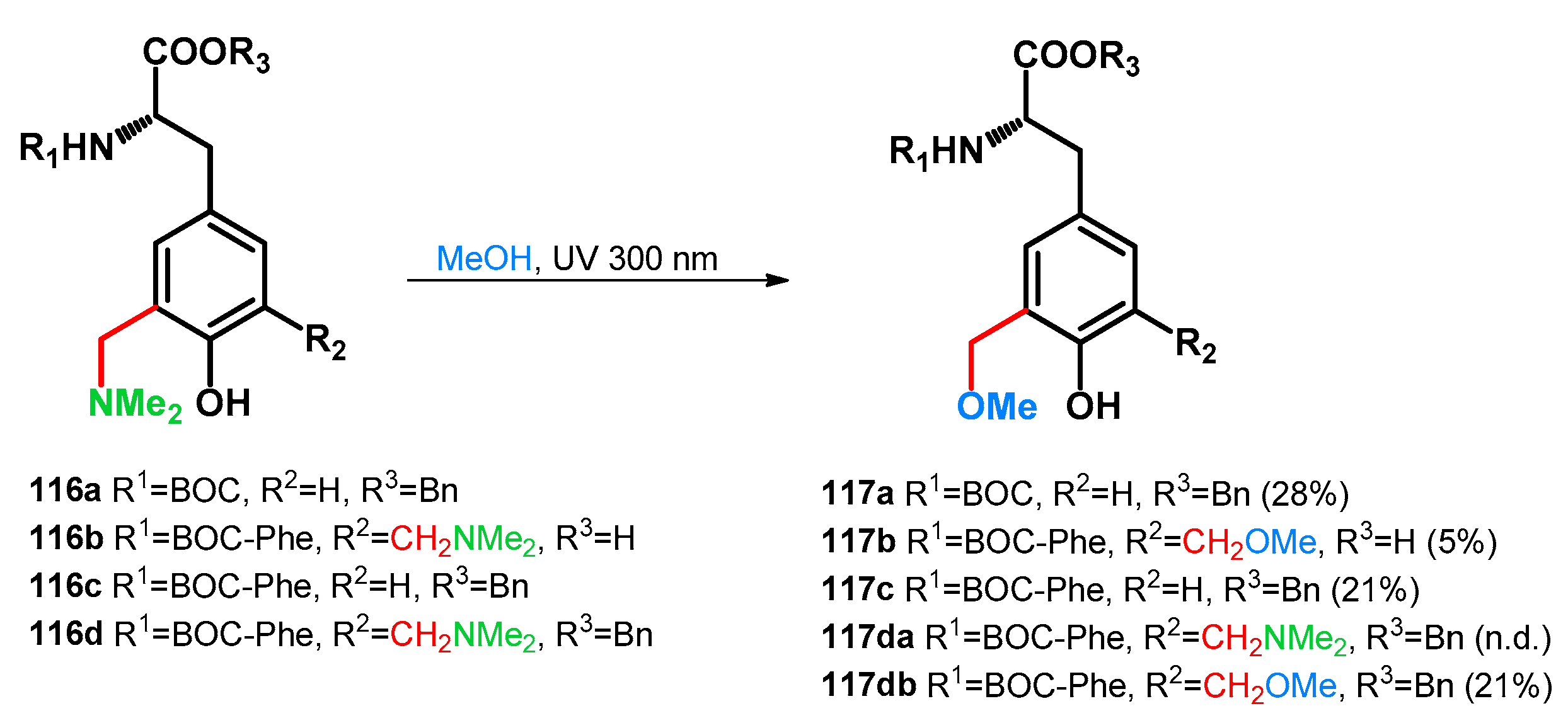
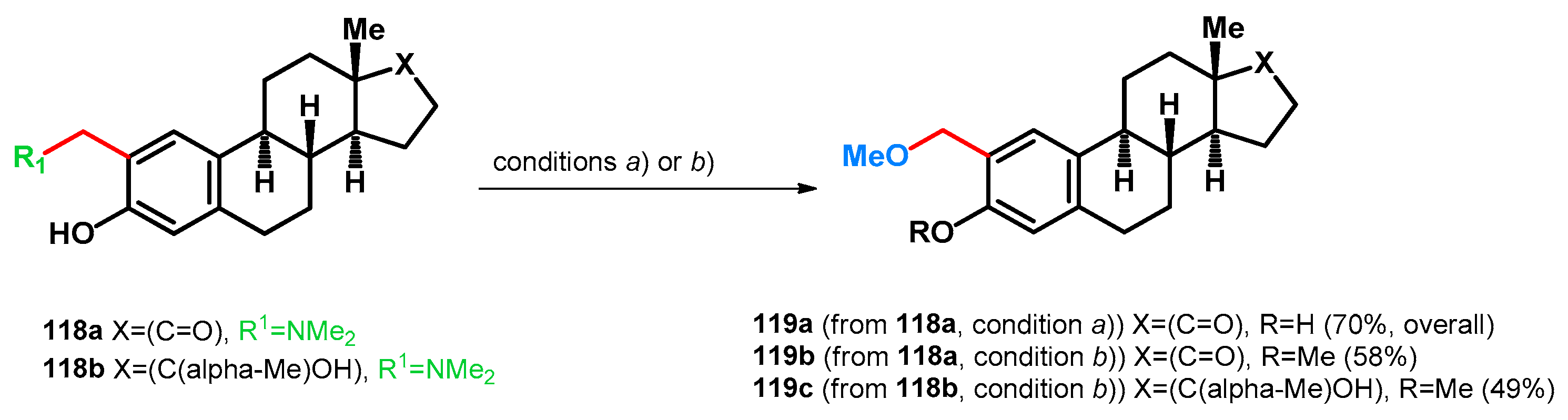
3.2.1. Transformations of Phenol-Fused Molecules
3.2.2. Transformations of N-heterocycles
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAM | bisarylmethylene |
| BINOL | 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol |
| BDMS | bromodimethylsulfonium bromide |
| BODIPY | dipyrrometheneboron difluoride |
| BPR | boron-modified phenolic resin |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| EDG | electron donating group |
| MOM | methoxymethyl |
| MPM | p-methoxybenzyl |
| PPTS | pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate |
| pTSA | p-toluenesulfonic acid |
| QM | quinone methide |
| (R)-TRIP | (R)-3,3′-bis(2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl)-1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-diyl hydrogenphosphate |
| TBSO | tert-butyl-dimethylsilyloxy |
| TRIS | tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, tromethamine |
References
- Barta, P.; Fülöp, F.; Szatmári, I. Mannich Base-Connected Syntheses Mediated by Ortho-Quinone Methides. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardellicchio, C.; Capozzi, M.A.M.; Naso, F. The Betti Base: The Awakening of a Sleeping Beauty. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, M.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Du, G. Mechanism of Base-Catalyzed Resorcinol-Formaldehyde and Phenol-Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Condensation Reactions: A Theoretical Study. Polymers 2017, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, C.; Yin, X.; Cui, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y. Directed C3-Alkoxymethylation of Indole via Three-Component Cascade Reaction. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossy, J.; Lutz, F.; Alauze, V.; Meyer, C. Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions by Using Bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide. Synlett 2002, 2002, 0045–0048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Da, C.-S. Direct Asymmetric Friedel–Crafts Reaction of Naphthols with Acetals Catalyzed by Chiral Brønsted Acids. Synlett 2015, 27, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerth, H.M.; Leonard, N.M.; Mohan, R.S. Synthesis of Homoallyl Ethers via Allylation of Acetals in Ionic Liquids Catalyzed by Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, P.; Srinivas, H.D.; Watson, M.P. Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective Additions to Oxocarbenium Ions: Alkynylation of Isochroman Acetals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17142–17145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, I.; Fülöp, F. Simple Access to Pentacyclic Oxazinoisoquinolines via an Unexpected Transformation of Aminomethylnaphthols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4440–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csütörtöki, R.; Szatmári, I.; Koch, A.; Heydenreich, M.; Kleinpeter, E.; Fülöp, F. Synthesis and Conformational Analysis of New Naphth[1,2-e][1,3]Oxazino[3,4-c]Quinazoline Derivatives. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 8564–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csütörtöki, R.; Szatmári, I.; Koch, A.; Heydenreich, M.; Kleinpeter, E.; Fülöp, F. Syntheses and Conformational Analyses of New Naphth[1,2-e][1,3]Oxazino[3,2-c]Quinazolin-13-Ones. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 4600–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, I.; Barta, P.; Csámpai, A.; Fülöp, F. Synthesis and Detailed Conformational Analysis of New Naphthoxazino[2,3-a]Benz[c]Azepine and Naphthoxazino[2,3-a]Thieno[3,2-c]Pyridine Derivatives. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 4790–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, I.; Barta, P.; Tóth, G.; Balázs, A.; Halász, J.; Fülöp, F. Synthesis and Conformational Behaviour of Enantiomeric Naphthoxazinoquinoxalinone Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5537–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, I.; Belasri, K.; Heydenreich, M.; Koch, A.; Kleinpeter, E.; Fülöp, F. Ortho-Quinone Methide Driven Synthesis of New O, N- or N,N-Heterocycles. ChemistryOpen 2019, 8, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedűs, D.; Szemerédi, N.; Spengler, G.; Szatmári, I. Application of Partially Aromatic Ortho-Quionone-Methides for the Synthesis of Novel Naphthoxazines with Improved Antibacterial Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 237, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Komeyama, K.; Yoshida, H.; Takaki, K. Convenient Synthesis of 2-Amino-4 H -chromenes from Photochemically Generated o-Quinone Methides and Malononitrile. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2015, 52, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, A.S.; Kekhvaeva, A.E.; Chalikidi, P.N.; Abaev, V.T.; Trushkov, I.V.; Uchuskin, M.G. A Simple Synthesis of Densely Substituted Benzofurans by Domino Reaction of 2-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohols with 2-Substituted Furans. Synthesis 2019, 51, 3747–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkushev, A.A.; Strel’nikov, V.N.; Uchuskin, M.G.; Trushkov, I.V. A Simple Synthesis of Benzofurans by Acid-Catalyzed Domino Reaction of Salicyl Alcohols with N-Tosylfurfurylamine. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 6523–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yeo, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, S. P-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Inhibits Four Obesity-related Enzymes in Vitro. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami Vetha, B.S.; Adam, A.G.; Aileru, A. Redox Responsive Copolyoxalate Smart Polymers for Inflammation and Other Aging-Associated Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, B.; Riem-Ha, H.; Hesse, M. Synthesis of Two Metabolites of the Antiarrythmicum Amiodarone. Helv. Chim. Acta 2002, 85, 2990–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozumi, T.; Komiyama, M. Quantitative Analysis on Ortho-Directing Activities of Divalent Metal Salts in Hydroxymethylation of Phenol by Formaldehyde. J. Mol. Catal. 1991, 69, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Jeong, J.-H. A Convergent Synthetic Study of Biologically Active Benzofuran Derivatives. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Novel Cardanol-Containing Boron-Modified Phenolic Resin Composites: Non-Isothermal Curing Kinetics, Thermal Properties, and Ablation Mechanism. High Perform. Polym. 2017, 29, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, P. Research Progress in Boron-Modified Phenolic Resin and Its Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, G.; Casnati, G.; Puglia, G.; Sartori, G. Selective Reactions between Phenols and Formaldehyde. A Superior Synthesis of Salicyl Alcohols. Synthesis 1980, 1980, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-J.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Wu, Q.-X.; Wang, R.; Dai, C.-Y.; Shen, Z.-L.; Xie, C.-L.; Wu, Y.-C. Water-Promoted Ortho-Selective Monohydroxymethylation of Phenols in the NaBO2 System. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 3100–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavani, F.; Pozzo, L.D.; Maselli, L.; Mezzogori, R. Hydroxymethylation of 2-Methoxyphenol Catalyzed by H-Mordenite: Analysis of the Reaction Scheme. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2002, 142, 565–572, ISBN 978-0-444-51174-4. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, J.; Borthakur, N.; Goswami, A. A Water Based Method for Hydroxymethylation of Phenols and Phenolic Ketones. J. Chem. Res. 2003, 2003, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, W.R. UV/Visible Light Absorbers for Ophthalmic Lens Materials. U.S. Patent 2010113641A1, 6 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Adegawa, Y. Chemical Amplification Type Negative-Working Resist Composition for Electron Beams or X-rays. Patent EP1109066A1, 20 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, K.; Deng, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, X.; Shen, B.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Semisynthesis and Biological Evaluation of Platensimycin Analogues with Varying Aminobenzoic Acids. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12625–12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.H.C. 3-Chloromethyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoic acid. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 1981, 13, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohda, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Tamegai, T.; Hirose, N. New Bronchodilators. Synthesis and Bronchodilating Activity of Some 3-(Alkoxymethy1)-a-(N-Substituted Aminomethy1)-4-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohols. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 3, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranathan, K.P.; Mandiyan, V.; Ekkati, A.R.; Bae, J.H.; Schlessinger, J.; Jorgensen, W.L. Discovery of Novel Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Kinase Inhibitors by Structure-Based Virtual Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Robertson, A.D.; Kenche, V.; Thompson, P.; Prabaharan, H.; Anderson, K.; Abbott, B.; Goncalves, I.; Nesbitt, W.; Shoenwaelder, S.; et al. Inhibition of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Beta. Patent WO2004016607A1, 26 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.K.; Williams, H.W.R.; Tardiff, S.; Dufresne, C.; Scheigetz, J.; Bélanger, P.C. Ortho-Specific Alkylation of Phenols via 1,3,2-Benzodioxaborins. Can. J. Chem. 1989, 67, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, F.J.; Aguilar, I.; Zamora, R. Model Studies on the Effect of Aldehyde Structure on Their Selective Trapping by Phenolic Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, F.; Cadraghi, G.; Casnati, G.; Sartori, G.; Fava, G.G.; Belicchi, M.F. Asymmetric Electrophilic Substitution on Phenols. 1. Enantioselective Ortho-Hydroxyalkylation Mediated by Chiral Alkoxyaluminum Chlorides. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 5018–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, P.G. Ytterbium(III) Trifluoromethanesulfonate Catalyzed Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution with Glyoxalate and Lipase-Mediated Product Resolution: A Convenient Route to Optically Active Aromatic r-Hydroxy Esters. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 4732–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesbach, U.; Mueller, U.; Puetter, H.; Quaiser, C.; Winsel, H. Electrochemical Method for Producing Benzaldehyde Dimethyl Acetylene. Patent WO2009059944A1, 14 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Griesbach, U.; Mueller, U.; Ebel, K.; Botzem, J.; Yilmaz, B.; Stock, C. Method for the Regioselective Alkoxyalkylation of Substituted Benzenes. Patent WO2009059941A1, 14 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kito, T.; Yoshinaga, K.; Ohkami, S.; Ikeda, K.; Yamaye, M. Precursors in the Alkylation of 2-Naphthol with Benzyl Alcohol in the Presence of a Base. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 4628–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshiour, S.; Shaabani, A.; Pedarpour, M.; Sarvary, A. An oxy-Michael addition: 2,5-dihydroxy1,4-benzoquinone-assisted synthesis of 1-[ethoxy(phenyl)methyl]-2-naphthol and 5-[ethoxy(phenyl)methyl]-6-hydroxyquinoline derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 40, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, E.; Bose, G.; Khan, A.T. An Expedient and Efficient Method for the Cleavage of Dithioacetals to the Corresponding Carbonyl Compounds Using Organic Ammonium Tribromide (OATB). Synlett 2001, 6, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, E.; Sahu, P.R.; Khan, A.T. A Useful and Catalytic Method for Protection of Carbonyl Compounds into the Corresponding 1,3-Oxathiolanes and Deprotection to the Parent Carbonyl Compounds. Synlett 2002, 3, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Basha, R.S.; Dar, A.A.; Das, D.K.; Khan, A.T. A Direct Approach for the Expedient Synthesis of Unsymmetrical Ethers by Employing Bromodimethylsulfonium Bromide (BDMS) Mediated C-S Bond Cleavage of Naphthalene-2-Ol Sulfides. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79759–79764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csütörtöki, R.; Szatmári, I.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Fülöp, F. Synthesis of Hydroxynaphthyl-Substituted α-Amino Acid Derivatives via a Modified Mannich Reaction. Synlett 2011, 2011, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaye, M.; Okano, H.; Motoyanagi, Y.; Cho (Toh), N.; Yoshinaga, T.; Tsuru, T.; Mukae, K. Novel α-Hydroxy- α-(2-Hydroxy-1-Naphthyl)Acetic Acid and Its Derivatives. Preparation and Optical Resolution. Synthesis 2004, 3, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuisen, E.J.; Weatherhead, J.G. Indoline Derivatives. Patent WO2018020357A1, 1 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. 6,8-Dimethylol Chrysin and 6,8-Dimethylol Ether Chrysin, Method for Preparing Same and Pharmaceutical Use. Patent CN101307043A, 19 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.B.; Haseltine, J.N.; Visncik, M. Tremorgenic Indole Alkaloid Studies 6. Preparation of an Advanced Intermediate for the Synthesis of Penitrem D. Synthesis of an Indole-Oxocane. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 2431–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Kanoh, N.; Ishiyama, H.; Hartz, R.A. Total Synthesis of (−)-Penitrem D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11254–11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J.; Venables, B.; Guernon, J.; Chen, J.; Sit, S.-Y.; Rajamani, R.; Knox, R.J.; Matchett, M.; Pieschl, R.L.; Herrington, J.; et al. Discovery of New Indole-Based Acylsulfonamide Nav1.7 Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zha, D.; Cui, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Shi, J.; Han, B. Friedel–Crafts Reaction of Indoles for (3-Indolyl)Methyl Ethers under Basic Condition: Application in Unsymmetrical Bis(Indolyl)Methanes. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, C.; Cho, D.; Baik, M.-H.; Hong, S. Site-Selective 1,1-Difunctionalization of Unactivated Alkenes Enabled by Cationic Palladium Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10045–10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, M.H.; Ramana, C.V. Facile Synthesis of the Spiro-Pyridoindolone Scaffold via a Gold-Catalysed Intramolecular Alkynol Cyclisation/Hydroindolylation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.L.; Pridgen, L.N. An Acid-Catalyzed Hydroxyalkylation of Uracil: A Facile Synthesis of 5-(Arylhydroxymethyl)Uracils. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 2592–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spáčilová, L.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; Křupková, S.; Hradil, P.; Hlaváč, J. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity of Various 5-[Alkoxy-(4-Nitro-Phenyl)-Methyl]-Uracils in Their Racemic Form. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6647–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batinac, S.; Sermek, D.M.; Cetina, M.; Pavelić, K.; Mintas, M.; Raić-Malić, S. Synthesis of the novel bicyclicoxepino-pyrimidine and fluorinated pyrrolidinopyrimidines. Heterocycles 2004, 63, 2523–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M.D.; Chuaqui, C.; Malona, J.; McDonald, J.J.; Ni, Y.; Niu, D.; Petter, R.C.; Singh, J. MK2 Inhibitors and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 20160075720A1, 17 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, P.D.; Rafsanjani, H.S.; Rand, L. Reaction of Phenolic Mannich Base Methiodides and Oxides with Various Nucleophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 3364–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, E.; Zanaletti, R.; Freccero, M.; Mella, M. Alkylation of Amino Acids and Glutathione in Water by o -Quinone Methide. Reactivity and Selectivity. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, H.J.; Michel, K. Bestrahlung von 2-Morpholinomethyl-phenol in Isopropanol 5. Mitt.: Zur Photochemie der 2-Aminomethyl-phenole. Arch. Pharm. 1971, 304, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, K.; Higashida, N. Highly Efficient Photochemical Generation of O-Quinone Methide from Mannich Bases of Phenol Derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5005–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloredo-Mels, S.; Doria, F.; Verga, D.; Freccero, M. Photogenerated Quinone Methides as Useful Intermediates in the Synthesis of Chiral BINOL Ligands. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinert, E.E.; Dondi, R.; Colloredo-Melz, S.; Frankenfield, K.N.; Mitchell, C.H.; Freccero, M.; Rokita, S.E. Substituents on Quinone Methides Strongly Modulate Formation and Stability of Their Nucleophilic Adducts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11940–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škalamera, Đ.; Bohne, C.; Landgraf, S.; Basarić, N. Photodeamination Reaction Mechanism in Aminomethyl p -Cresol Derivatives: Different Reactivity of Amines and Ammonium Salts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 10817–10828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, F.; Lena, A.; Bargiggia, R.; Freccero, M. Conjugation, Substituent, and Solvent Effects on the Photogeneration of Quinone Methides. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlatić, K.; Antol, I.; Uzelac, L.; Mikecin Dražić, A.-M.; Kralj, M.; Bohne, C.; Basarić, N. Labeling of Proteins by BODIPY-Quinone Methides Utilizing Anti-Kasha Photochemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashibara, T.; Sato, J.; Torihara, M. Process for Producing Chroman-Carboxylic Acid. Patent EP1184378A1, 6 March 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, H.; He, S.; Yan, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, S.; Niu, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; et al. Macromolecular Hindered Phenol Antioxidant and Preparation Method and Application Thereof. Patent CN113512232A, 19 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kunita, K.; Aoshima, K.; Nakamura, I.; Nakamura, T. Negative Working Image Recording Material. Patent EP0874282A1, 28 October 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Okumuto, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Niina, N. Benzotriazole Derivative. Patent JP2015151369A, 24 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crisp, G.T.; Turner, P.D. Preparation of Functionalised Aryl Alkynes as Precursors to Extended Cyclophanes. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, H. Novel Alkoxymethyl-Substituted Bisphenol Compound. Patent JP2018115120A, 26 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nummelin, S.; Falabu, D.; Shivanyuk, A.; Rissanen, K. Alkoxy-, Acyloxy-, and Bromomethylation of Resorcinarenes. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 2869–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, M.; Iwanek, W. Synthesis of Alkoxymethyl Derivatives of Resorcinarene via the Mannich Reaction Catalysed with Iminodiacetic Acid. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 1508–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M.; Pedrycz, A.; Gawdzik, B.; Wzorek, A. Preparation of Partially Functionalised Resorcinarene Derivatives. Supramol. Chem. 2013, 25, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Kaneko, K.; Endoh, M.; Uchida, H.; Hoshino, O. A Novel Ring Cleavage and Recyclization of N-Cyanomethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolinium Methioidides: A Biomimetic Synthesis of Libetamine. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 10189–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.C.; Johnson, R.K.; Hecht, S.M.; Kingsbury, W.D.; Holden, K.G. Water Soluble Camptothecin Analogs. Patent EP0321122A2, 21 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bracher, F.; Tremmel, T. From Lead to Drug Utilizing a Mannich Reaction: The Topotecan Story. Arch. Pharm. 2017, 349, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Q. The Solvolysis of Topotecan in Alcohols and Acetic Anhydride. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2324–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Meng, G.; Liu, Z.; Dong, M.; Li, Y.; Ju, D.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of Novel 10-Hydroxycamptothecin Derivatives Utilizing Topotecan Hydrochloride as Ortho-Quinonemethide Precursor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, J.A.; Sperry, J. Synthesis of Three Tricholoma-Derived Indoles via an Ortho-Quinone Methide. Arkivoc 2018, 2018, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.A.; Johnson, W.O. Position Selective Mannich Reactions of Some 5- and 6-Hydroxyindoles. Tetrahedron 1970, 26, 3685–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bew, S.P.; Hughes, D.L.; Sharma, S.V. Acid-Catalyzed Synthesis of Methylene-Bridged (S)-Tyrosine−Phenol Dimers. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7881–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husak, A.; Noichl, B.P.; Šumanovac Ramljak, T.; Sohora, M.; Škalamera, Đ.; Budiša, N.; Basarić, N. Photochemical Formation of Quinone Methides from Peptides Containing Modified Tyrosine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 10894–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, M.; Peters, R.H.; Chao, W.-R.; Shigeno, K. Estrone Sulfamate Inhibitors of Estrone Sulfatase, and Associated Pharmaceutical Compositions and Methods of Use. Patent WO1999033858A2, 8 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Kawase, K. 2-Methoxymethyl-17alpha-Substituted Estradiol-3-Methyl Ethers and Their Preparation. U.S. Patent 3132162A, 5 May 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Jia, J.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Song, J.; Yao, B.; Liang, J.; Chang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.X.; et al. Flavone Derivatives, Preparation Method and Application Thereof. Patent CN108017608B, 17 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lőrincz, E.B.; Tóth, G.; Spolárics, J.; Herczeg, M.; Hodek, J.; Zupkó, I.; Minorics, R.; Ádám, D.; Oláh, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; et al. Mannich-Type Modifications of (−)-Cannabidiol and (−)-Cannabigerol Leading to New, Bioactive Derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19618–19637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csuvik, O.; Szatmári, I. Synthesis of Bioactive Aminomethylated 8-Hydroxyquinolines via the Modified Mannich Reaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mészáros, J.P.; Poljarević, J.M.; Szatmári, I.; Csuvik, O.; Fülöp, F.; Szoboszlai, N.; Spengler, G.; Enyedy, É.A. An 8-Hydroxyquinoline–Proline Hybrid with Multidrug Resistance Reversal Activity and the Solution Chemistry of Its Half-Sandwich Organometallic Ru and Rh Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 7977–7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, V.F.S.; Palkó, R.; Tóth, S.; Szabó, M.J.; Sessler, J.; Dormán, G.; Enyedy, É.A.; Soós, T.; Szatmári, I.; Szakács, G. Structure–Activity Relationships of 8-Hydroxyquinoline-Derived Mannich Bases with Tertiary Amines Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 7729–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Chui, C.H.; Chan, S.W.; Kok, S.H.L.; Chan, D.; Tsoi, M.Y.T.; Leung, P.H.M.; Lam, A.K.Y.; Chan, A.S.C.; Lam, K.H.; et al. Synthesis of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Derivatives as Novel Antitumor Agents. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. 8-Hydroxyquinoline: A Privileged Structure with a Broad-Ranging Pharmacological Potential. Med. Chem. Commun. 2015, 6, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, Y.; Chou, Y.; Wu, I. Dibromomethane as One-Carbon Source in Organic Synthesis: The Mannich Base Formation from the Reaction of Phenolic Compounds with a Preheated Mixture of Dibromomethane and Diethylamine. Synth. Commun. 2004, 34, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
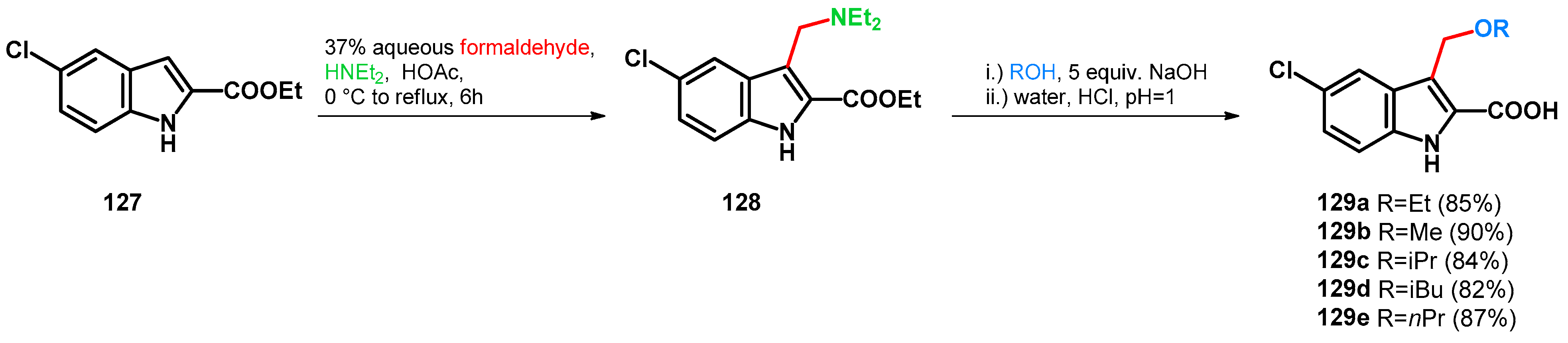
- Abdelrahman, M.H.; Aboraia, A.S.; Youssif, B.G.M.; Elsadek, B.E.M. Design, Synthesis and Pharmacophoric Model Building of New 3-alkoxymethyl/3-phenyl Indole-2-carboxamides with Potential Antiproliferative Activity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.A.M.; Shaker, M.E.; Alzarea, S.I.; Hendawy, O.M.; Mohamed, F.A.M.; Gouda, A.M.; Ali, A.T.; Morcoss, M.M.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Trembleau, L.; et al. Optimization and SAR Investigation of Novel 2,3-Dihydropyrazino[1,2-a]Indole-1,4-Dione Derivatives as EGFR and BRAFV600E Dual Inhibitors with Potent Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 120, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, M.; Das, C.; Deka, B.; Saikia, P.; Baruah, P. Hydrogen-Bond-Catalyzed Arylation of 3-(Aminoalkyl)Indoles via C–N Bond Cleavage with Thiourea under Microwave Irradiation: An Approach to 3-(α,α-Diarylmethyl)Indoles. Synlett 2016, 27, 2788–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Lőrinczi, B.; Szatmári, I. C–3 Alkoxymethylation of 4-Oxo-1,4-Dihydroquinoline 2-Carboxylic Acid Esters via Organic Additives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zádori, D.; Veres, G.; Szalárdy, L.; Klivényi, P.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Glutamatergic Dysfunctioning in Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Therapeutic Targets. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zádori, D.; Nyiri, G.; Szőnyi, A.; Szatmári, I.; Fülöp, F.; Toldi, J.; Freund, T.F.; Vécsei, L.; Klivényi, P. Neuroprotective Effects of a Novel Kynurenic Acid Analogue in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Huntington’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rózsa, É.; Robotka, H.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J. The Janus-Face Kynurenic Acid. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, K.; Robotka, H.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondria, Metabolic Disturbances, Oxidative Stress and the Kynurenine System, with Focus on Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 257, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigler, G.; Szénási, G.; Simó, A.; Lévay, G.; Hársing, L.G.; Sas, K.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J. Neuroprotective Effect of L-Kynurenine Sulfate Administered before Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice and Global Cerebral Ischemia in Gerbils. Eur. J. Pharm. 2007, 564, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, C.; Shepard, P.D.; Bari, F.; Schwarcz, R. Cortical Spreading Depression Augments Kynurenate Levels and Reduces Malonate Toxicity in the Rat Cortex. Brain Res. 2004, 1002, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wielosz, M.; Turski, W.A.; Urbañska, E.M. Endogenous level of kynurenic acid and activities of kynurenine aminotransferases following transient global ischemia in the gerbil hippocampus. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 443–447. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, L.K.; Linderholm, K.R.; Engberg, G.; Paulson, L.; Blennow, K.; Lindström, L.H.; Nordin, C.; Karanti, A.; Persson, P.; Erhardt, S. Elevated Levels of Kynurenic Acid in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Male Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fejes, A.; Párdutz, A.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Kynurenine Metabolites and Migraine: Experimental Studies and Therapeutic Perspectives. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, K.; Plangár, I.; Tuka, B.; Gellért, L.; Varga, D.; Demeter, I.; Farkas, T.; Kis, Z.; Marosi, M.; Zádori, D.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Effects of Some Kynurenic Acid Analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7590–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiszlavicz, Z.; Németh, B.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Tápai, K.; Ocsovszky, I.; Mándi, Y. Different Inhibitory Effects of Kynurenic Acid and a Novel Kynurenic Acid Analogue on Tumour Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) Production by Mononuclear Cells, HMGB1 Production by Monocytes and HNP1-3 Secretion by Neutrophils. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 383, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellért, L.; Fuzik, J.; Göblös, A.; Sárközi, K.; Marosi, M.; Kis, Z.; Farkas, T.; Szatmári, I.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; et al. Neuroprotection with a New Kynurenic Acid Analog in the Four-Vessel Occlusion Model of Ischemia. Eur. J. Pharm. 2011, 667, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marosi, M.; Nagy, D.; Farkas, T.; Kis, Z.; Rózsa, É.; Robotka, H.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Toldi, J. A Novel Kynurenic Acid Analogue: A Comparison with Kynurenic Acid. An in Vitro Electrophysiological Study. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vámos, E.; Párdutz, Á.; Varga, H.; Bohár, Z.; Tajti, J.; Fülöp, F.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. L-Kynurenine Combined with Probenecid and the Novel Synthetic Kynurenic Acid Derivative Attenuate Nitroglycerin-Induced nNOS in the Rat Caudal Trigeminal Nucleus. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lőrinczi, B.; Csámpai, A.; Fülöp, F.; Szatmári, I. Synthesis of New C-3 Substituted Kynurenic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

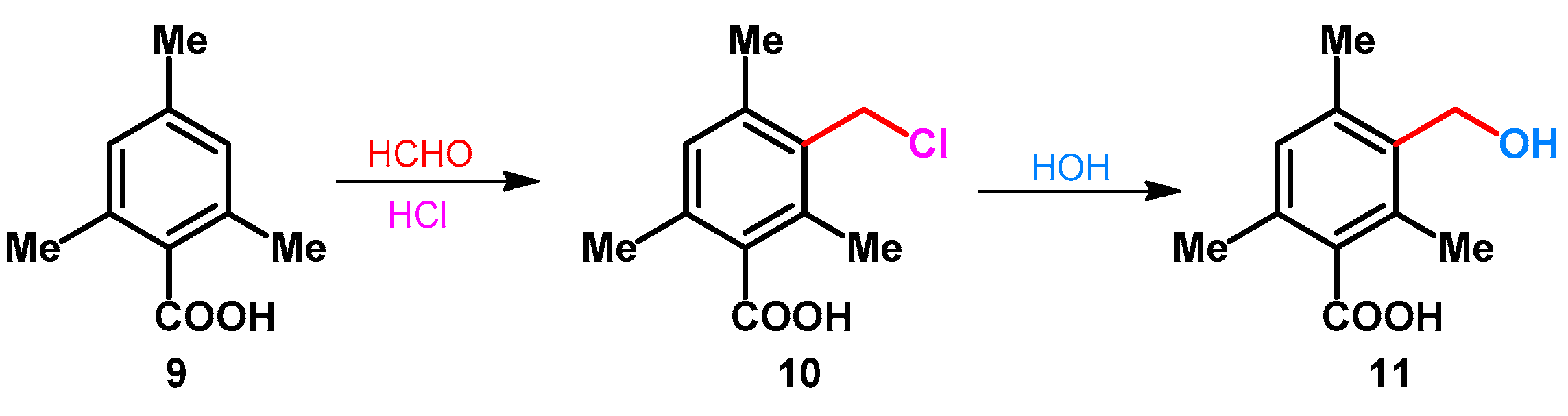

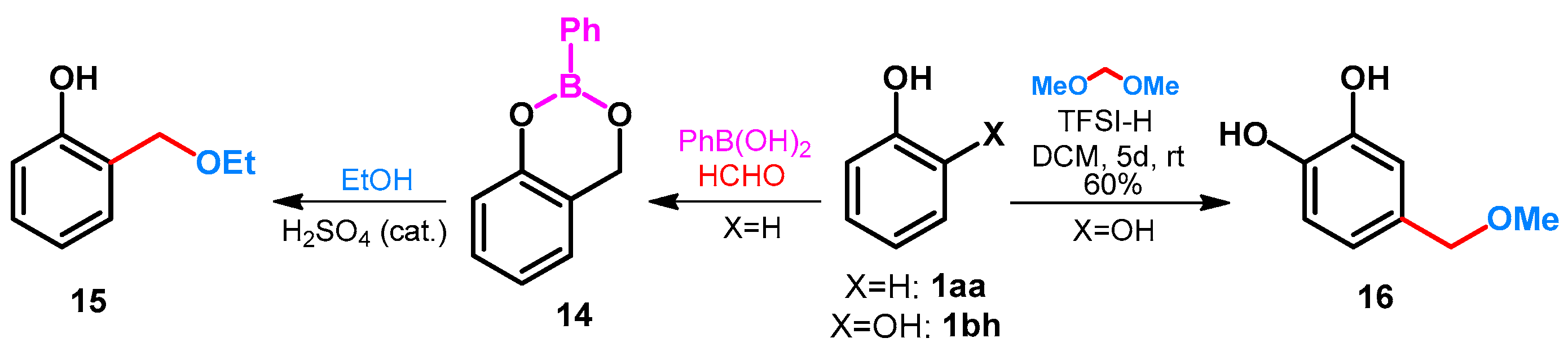
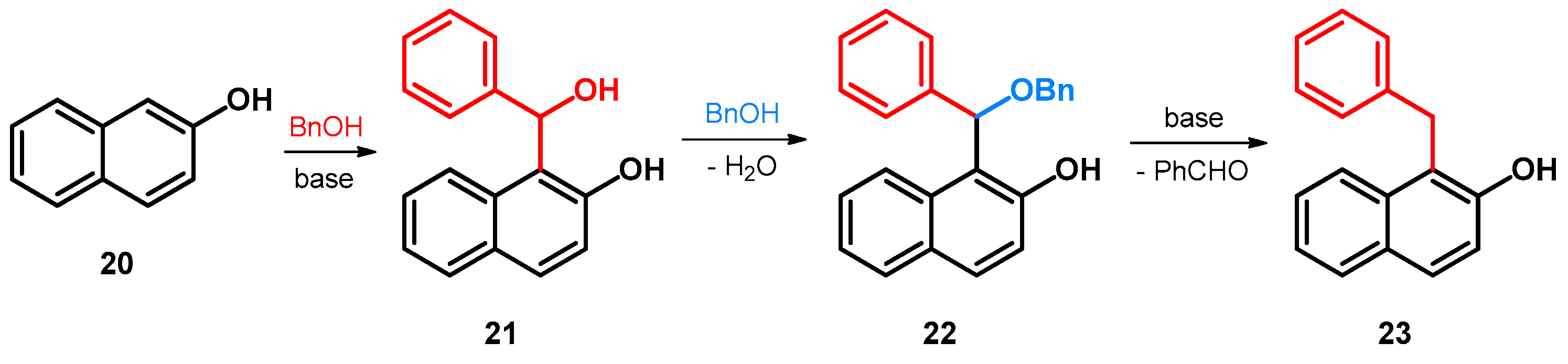


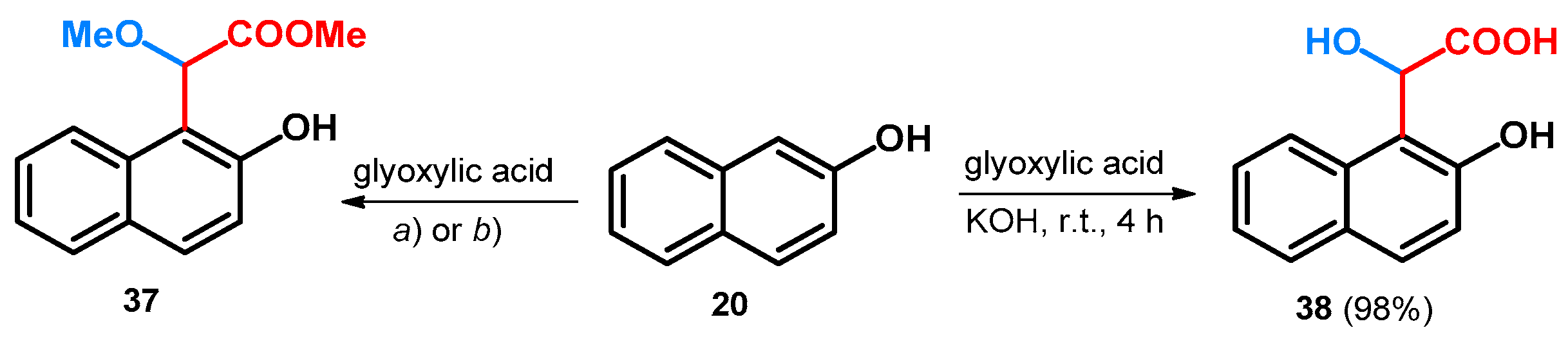

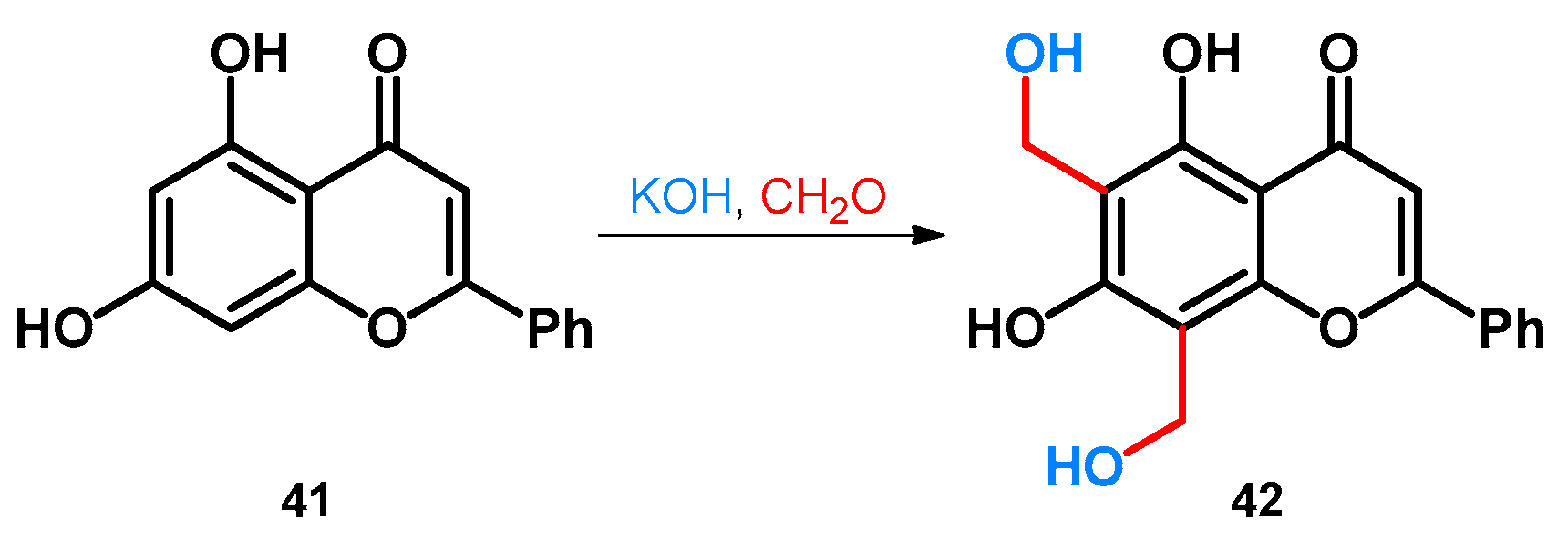
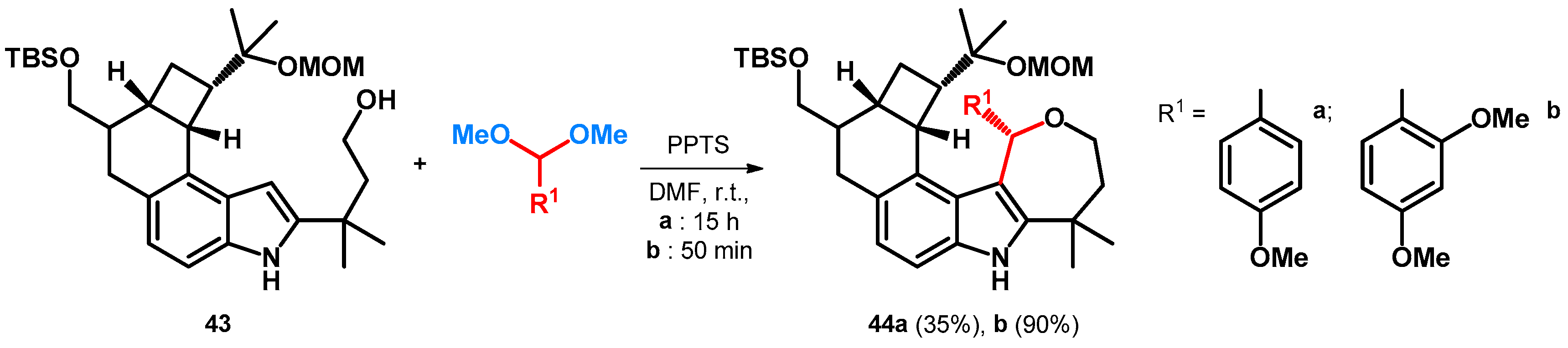

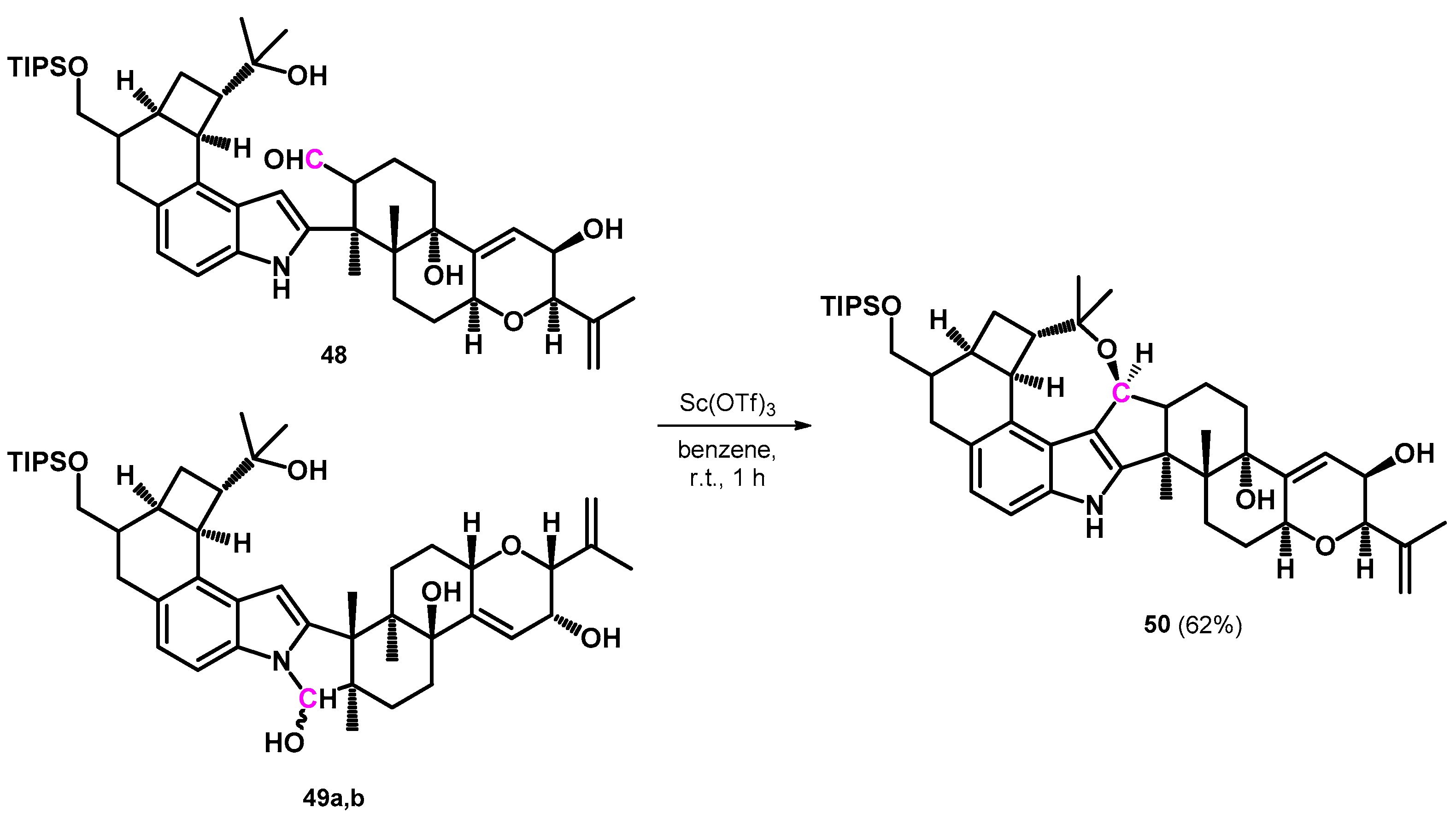
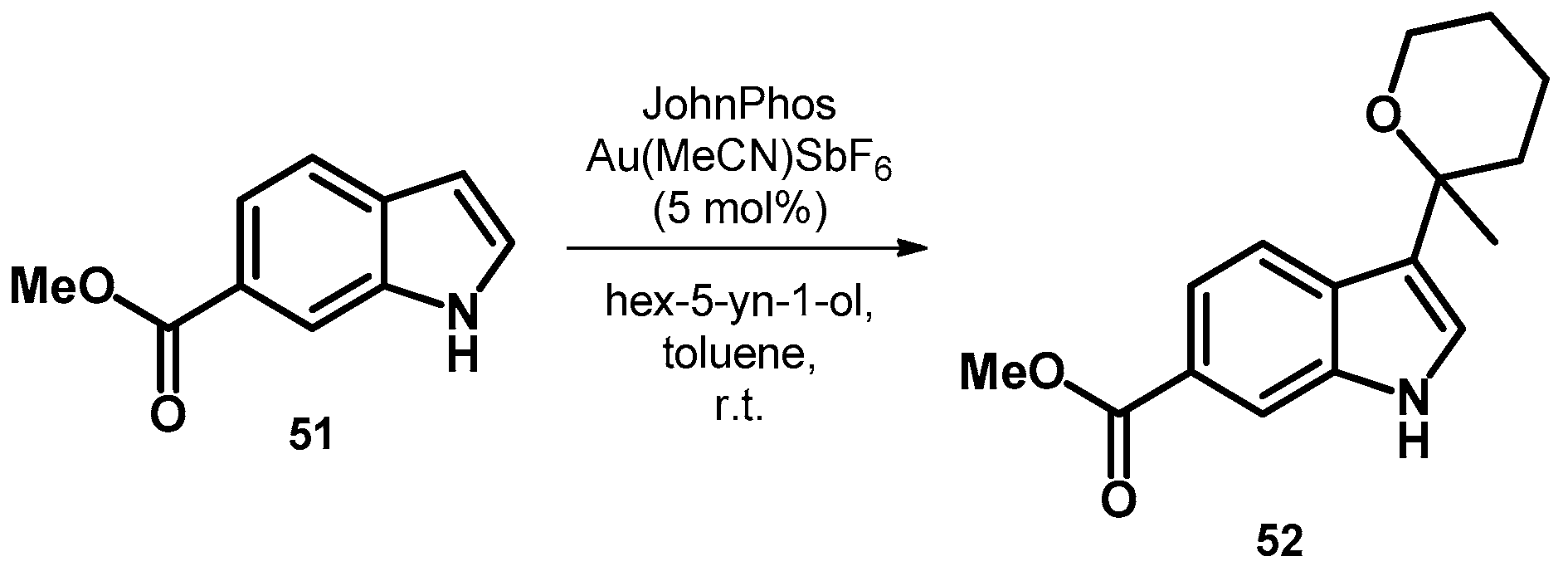


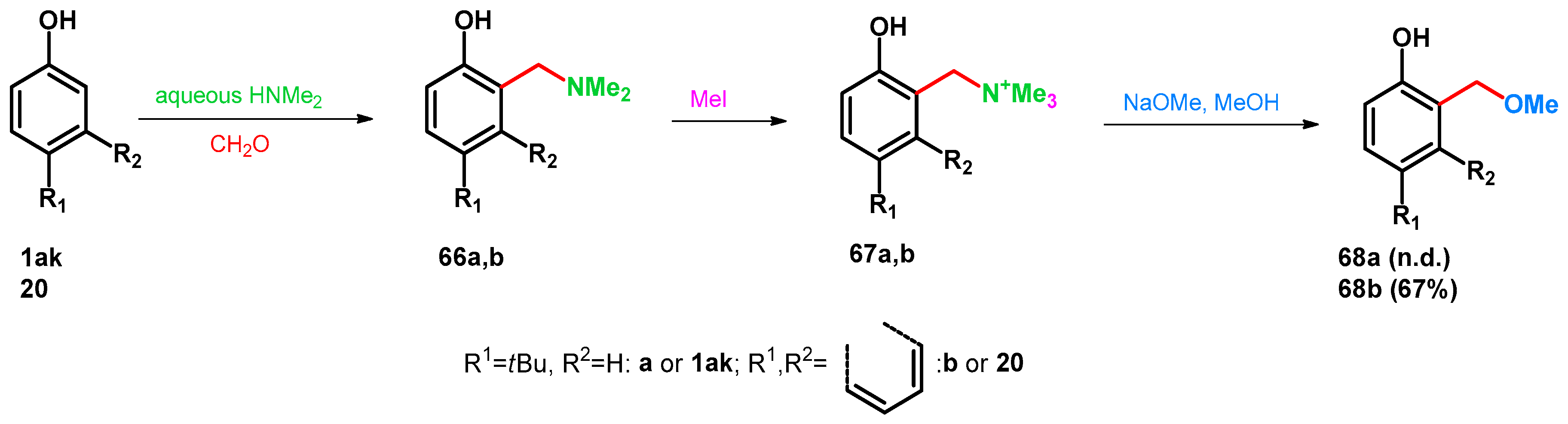
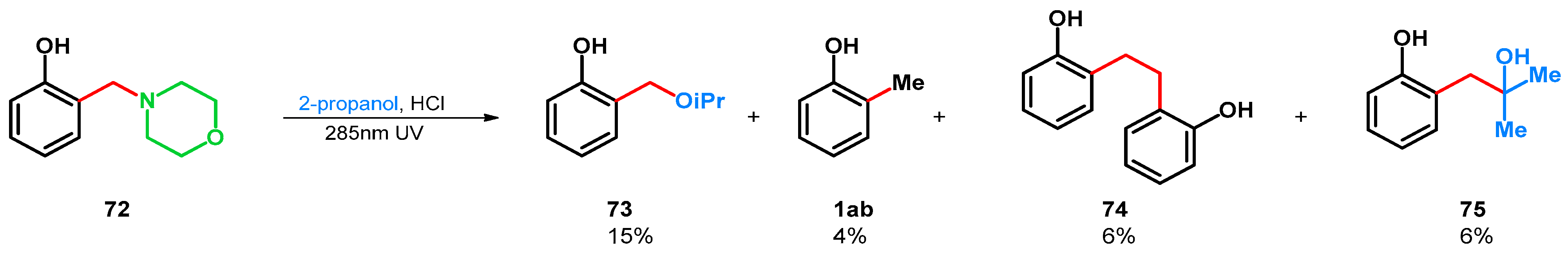
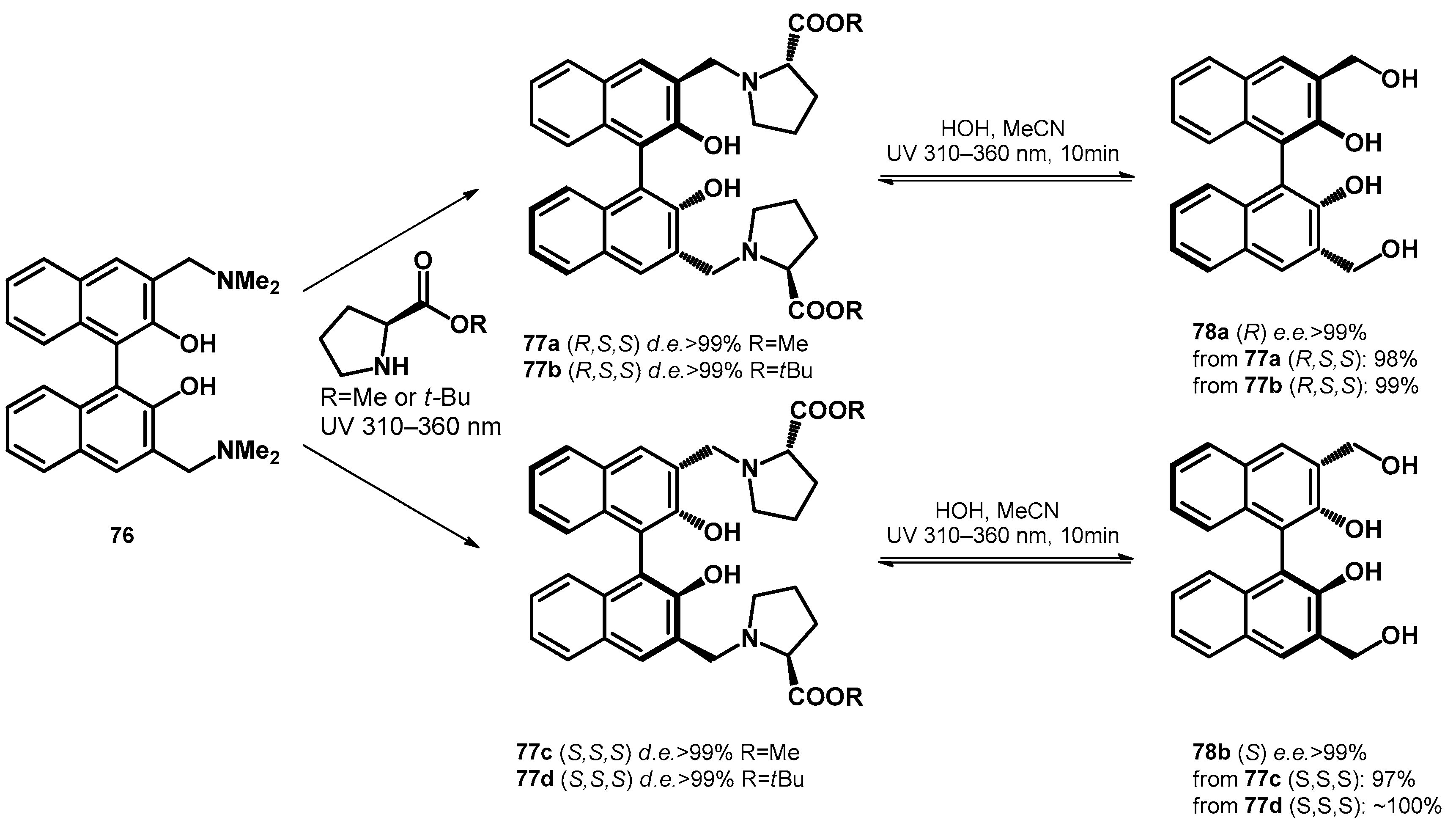
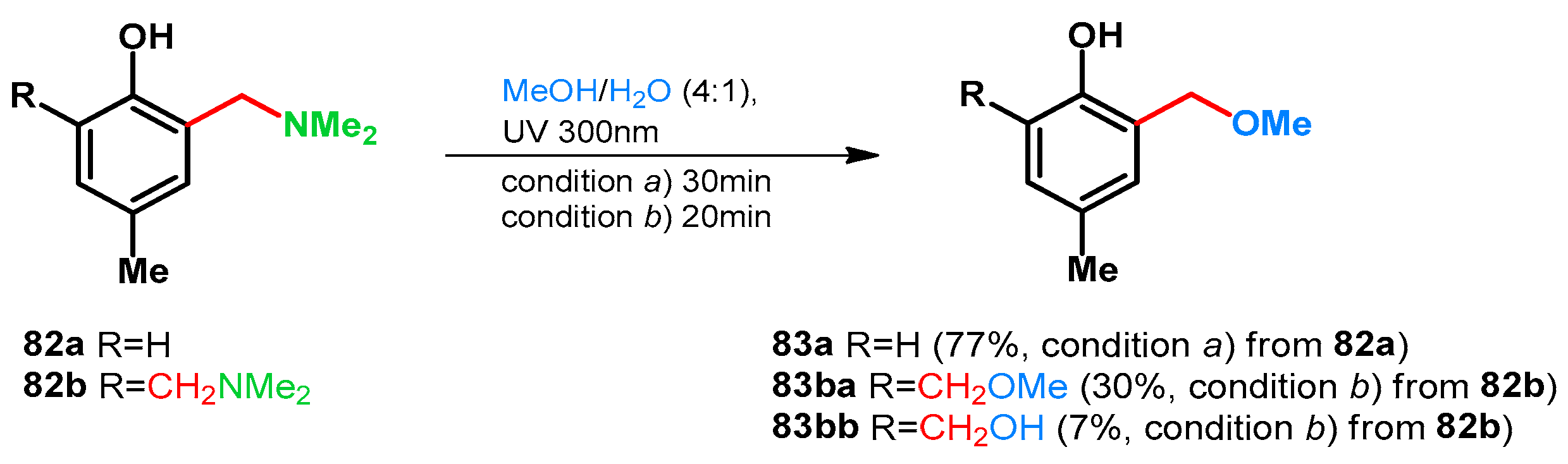
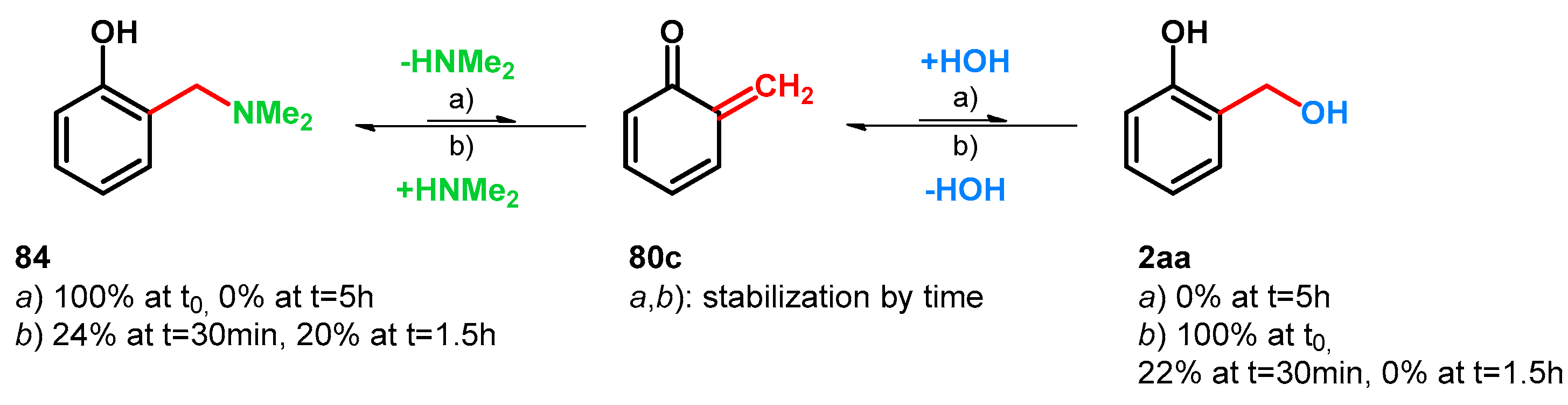


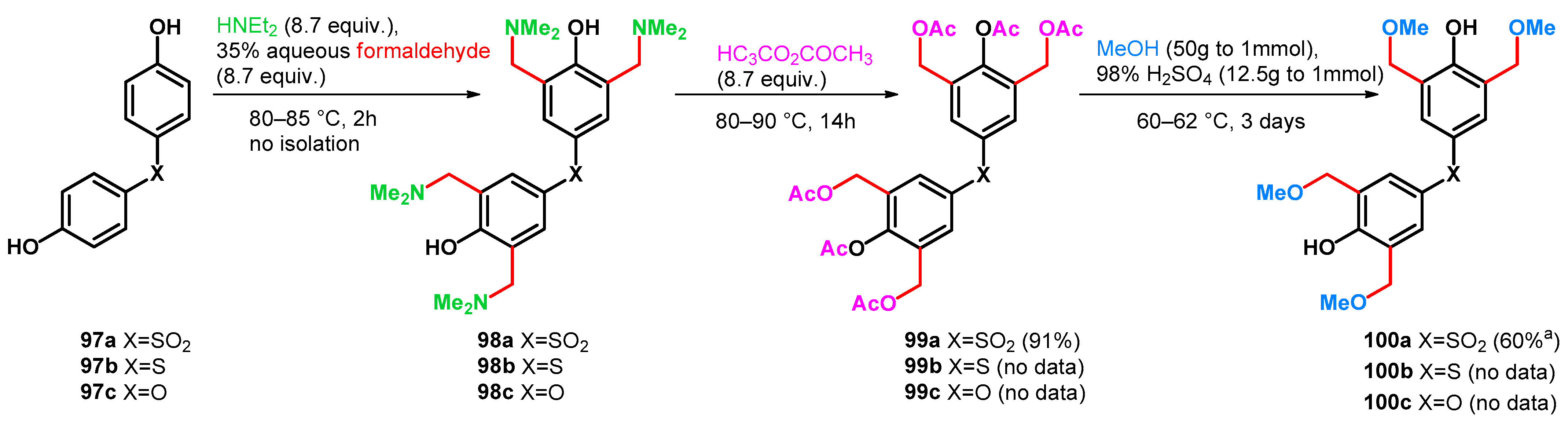
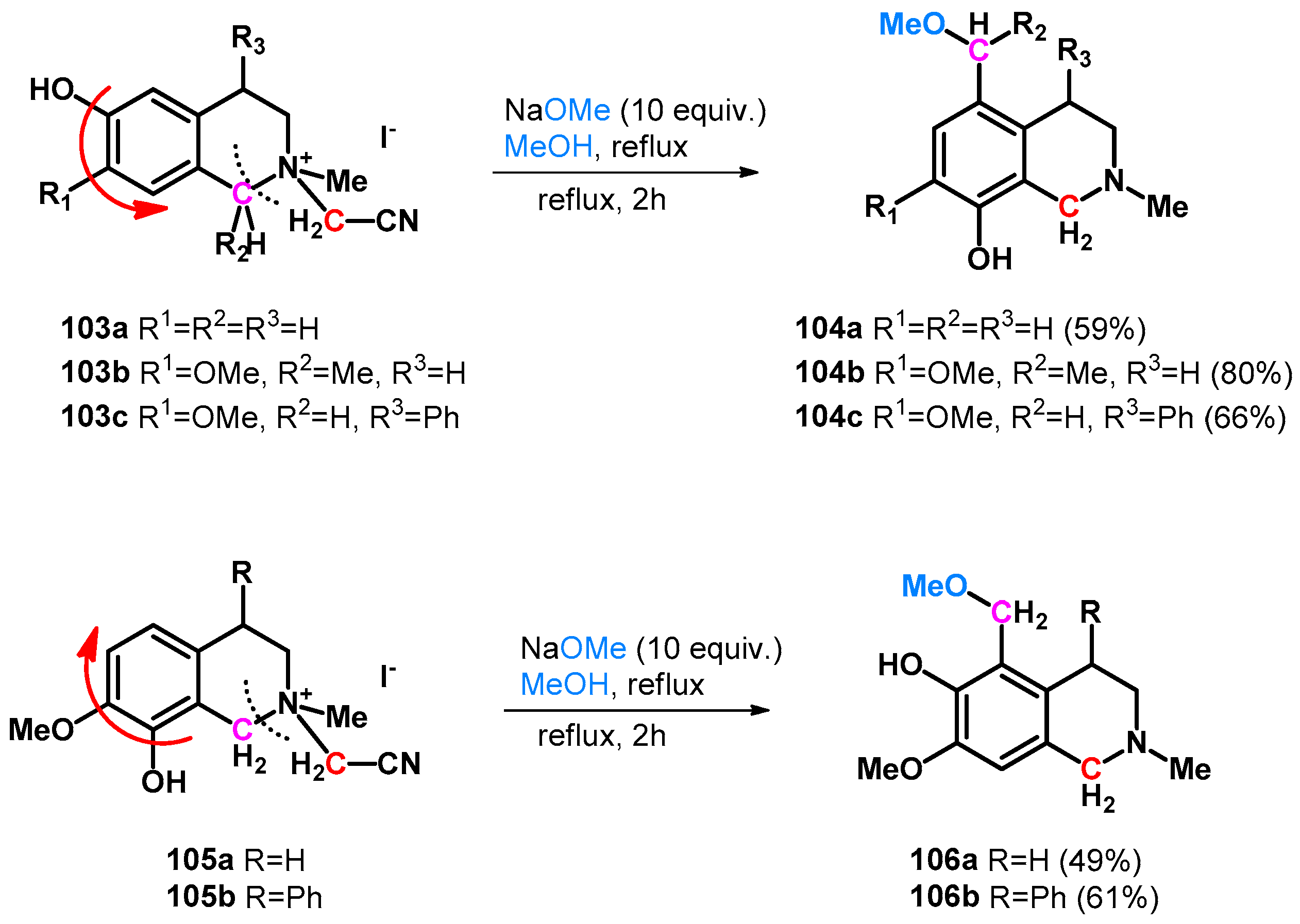
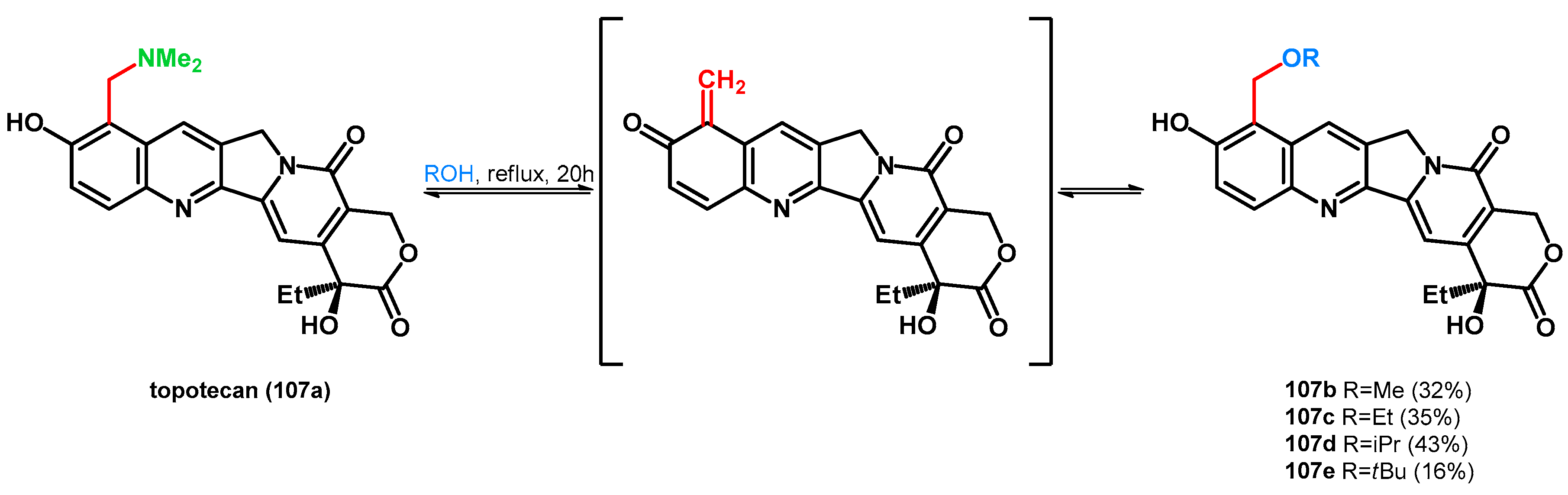


 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Product | Conditions | Yield | Reference |
| 1 | H | H | H | H | 2aa | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 66 | [26] |
| 2 | H | H | H | H | 2aa | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 93 | [27] |
| 3 | Me | H | H | H | 2ab | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 77 | [26] |
| 4 | Me | H | H | H | 2ab | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 87 | [27] |
| 5 | H | H | Me | H | 2ac | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 92 | [26] |
| 6 | H | H | Me | H | 2ac | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 90 | [27] |
| 7 | H | H | i-Bu | H | 2ad | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 85 | [26] |
| 8 | Ph | H | H | H | 2ae | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 65 | [26] |
| 9 | cyclohexyl | H | H | H | 2af | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 85 | [26] |
| 10 | Me | H | Me | H | 2ag | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 92 | [26] |
| 11 | H | Me | Me | H | 2ah | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 95 | [26] |
| 12 | t-Bu | H | H | Me | 2ai | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 95 | [26] |
| 13 | H | H | Ph | H | 2aj | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 95 | [27] |
| 14 | H | H | t-Bu | H | 2ak | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 86 | [27] |
| 15 | H | H | Et | H | 2al | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 89 | [27] |
| 16 | F | H | H | H | 2am | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 85 | [27] |
| 17 | H | H | F | H | 2an | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 90 | [27] |
| 18 | F | F | H | H | 2ao | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 90 | [27] |
| 19 | F | H | H | F | 2ap | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 92 | [27] |
| 20 | H | H | Cl | H | 2aq | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 80 | [27] |
| 21 | H | H | Cl | H | 2aq | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 67 | [26] |
| 22 | H | Cl | H | H | 2ar | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 90 | [27] |
| 23 | H | H | Br | H | 2as | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 69 | [26] |
| 24 | H | H | Br | H | 2as | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 83 | [27] |
| 25 | H | Br | H | H | 2at | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 91 | [27] |
| 26 | H | H | I | H | 2au | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 70 | [26] |
| 27 | H | H | OMe | H | 2av | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 66 | [26] |
| 28 | H | H | OMe | H | 2av | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 90 | [27] |
| 29 | OMe | H | H | H | 2aw | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 88 | [27] |
| 30 | OMe | H | H | H | 2ax | H-mordenite, 80 °C, water/methanol | 70 | [28] |
| 31 | H | H | OBn | H | 2ay | NaBO2, H2O, 40 °C | 83 | [27] |
| 32 | H | H | OH | H | 2az | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 59 | [26] |
| 33 | i-pentyl | H | OH | H | 2ba | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 61 | [26] |
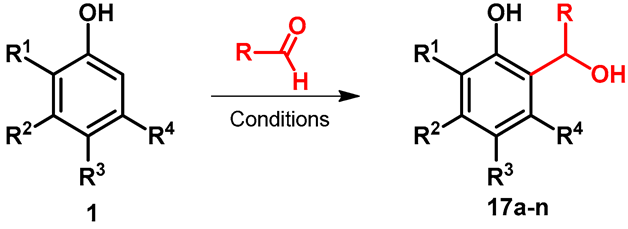 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Product | Conditions | Yield | Reference |
| 1 | Bu | Me | OH | H | H | 17a | DME/xylene, 135 °C | 66 | [38] |
| 2 | -CCl3 | H | H | H | H | 17b | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 96 | [39] |
| 3 | -CCl3 | H | H | Me | H | 17c | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 97 | [39] |
| 4 | -CCl3 | H | H | t-Bu | H | 17d | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 97 | [39] |
| 5 | -CCl3 | Me | H | H | H | 17e | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 65 | [39] |
| 6 | -CCl3 | i-Pr | H | H | H | 17f | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 78 | [39] |
| 7 | -CCl3 | t-Bu | H | H | H | 17g | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 53 | [39] |
| 8 | -CCl3 | Me | H | H | Me | 17h | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 55 | [39] |
| 9 | -CCl3 | Br | H | H | H | 17i | Toluene, 4 h, 15 °C | 51 | [39] |
| 10 | -COOEt | H | H | t-Bu | H | 17j | Yb(OTf)3/CH2Cl2, 10 h, rt | 88 | [40] |
| 11 | -COOEt | H | t-Bu | H | H | 17k | Yb(OTf)3/CH2Cl2, 10 h, rt | 90 | [40] |
| 12 | -COOEt | H | H | OH | H | 17l | Yb(OTf)3/CH2Cl2, 10 h, rt | 80 | [40] |
| 13 | -COOEt | H | Et2N | H | H | 17m | Yb(OTf)3/CH2Cl2, 10 h, rt | 68 | [40] |
| 14 | -COOEt | H | H | F | H | 17n | Yb(OTf)3/CH2Cl2, 10 h, rt | 81 | [40] |
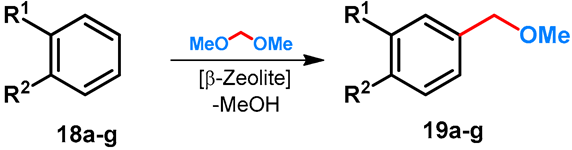 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | Product | Conditions | Conversion | Reference |
| 1 | H | i-Pr | 19a | 17 h, 80–90 °C | 12 | [41] |
| 2 | H | i-Pr | 19a | 54 h, 120 °C | 46 | [42] |
| 3 | H | i-Bu | 19b | 65 h, 75 °C | 25 | [42] |
| 4 | H | t-Bu | 19c | 90 h, 70 °C | 24 | [42] |
| 5 | H | OMe | 19d | 6 h, 95 °C | 24 | [42] |
| 6 | OMe | OH | 19e | 3 h, 95 °C | 15 | [42] |
| 7 | OMe | OMe | 19f | 64 h, 95 °C | 25 | [42] |
| 8 | H | OH | 19g | 6 h, 95 °C | 24 | [42] |
| X | R2 | Compound | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH (24a) | p-NO2C6H4 (25a) | 26a | 86 |
| CH (24a) | m-NO2C6H4 (25b) | 26b | 82 |
| CH (24a) | o-NO2C6H4 (25c) | 26c | 82 |
| CH (24a) | p-MeC6H4 (25d) | 26d | 79 |
| CH (24a) | p-(O-CH2-Ph)C6H4 (25e) | 26e | 81 |
| CH (24a) | p-OMeC6H4 (25f) | 26f | 63 |
| CH (24a) | 2-naphthyl (25g) | 26g | 61 |
| N (24b) | p-BrC6H4 (25h) | 26h | 73 |
| N (24b) | Ph (25i) | 26i | 71 |
| N (24b) | p-OMeC6H4 (25j) | 26j | 72 |
| Entry | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst (27, mol%) | 5 | 25 | 50 | 750 | 100 | 150 |
| Yield of 28f (%) | Trace | 21 | 42 | 63 | 86 | 87 |
| 24 | R2 | Product | Yield (%) | ee (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-naphthol (24a) | Ph (28a) | 30a | 64 | 68 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | o-MeC6H4 (28b) | 30b | 58 | 55 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | m-MeC6H4 (28c) | 30c | 61 | 71 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | p-MeC6H4 (28d) | 30d | 54 | 63 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | m-MeOC6H4 (28e) | 30e | 68 | 63 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | o-ClC6H4 (28f) | 30f | 42 | 40 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | p-ClC6H4 (28g) | 30g | 55 | 58 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | p-BrC6H4 (28h) | 30h | 51 | 33 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | p-FC6H4 (28i) | 30i | 46 | 50 |
| 2-naphthol (24a) | 2-naphthyl (28j) | 30g | 44 | 66 |
| 6-bromo-2-naphthol (24c) | Ph (28a) | 30j | 57 | 57 |
| 6-bromo-2-naphthol (24c) | m-MeC6H4 (28c) | 30k | 58 | 66 |
| 6-bromo-2-naphthol (24c) | m-MeOC6H4 (28e) | 30l | 54 | 66 |
| 1-naphthol (24c) | Ph (28a) | 30m | 72 | 20 |
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | Product | Yield (%) | Method |
| Ph | Et | 32a | 94 | (a) |
| Ph | Me | 32b | 90 | |
| Ph | n-Pr | 32c | 92 | |
| Ph | i-Pr | 32d | 82 | |
| Ph | n-Bu | 32e | 88 | |
| Ph | Bn | 32f | 84 | |
| Ph | CH2CH=CH2 | 32g | 82 | |
| Ph | CH2C≡CH | 32h | 80 | |
| Ph | (CH2)3CH=CH2 | 32i | 84 | |
| Ph | (CH2)4Ph | 32j | 88 | |
| Ph | (CH2)2OH | 32k | 81 | |
| Ph | (CH2)8OH | 32l | 82 | |
| p-NO2-Ph | Me | 32m | 94 | |
| p-NO2-Ph | n-Bu | 32n | 88 | |
| p-F-Ph | Et | 32o | 94 | |
| p-Br-Ph | Me | 32p | 92 | |
| 2-C10H7 | Me | 32q | 88 | |
| p-Me-Ph | Et | 32r | 90 | |
| Ph | H | 32s | 84 | (b) |
| p-NO2-Ph | H | 32t | 88 | |
| p-F-Ph | H | 32u | 86 | |
| p-Cl-Ph | H | 32v | 84 | |
| p-Me-Ph | H | 32w | 82 | |
 | |||||||||
| Products of synthesis route a | |||||||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | Yield (%) | R1 | R2 | R3 | Yield (%) | ||
| H | H | Me | 54aa | 89 | 6-Br | H | Me | 54ap | 80 |
| 2-Ph | H | Me | 54ab | 90 | 7-NO2 | H | Me | 54aq | 92 |
| 4-F | H | Me | 54ac | 88 | H | Ph | Me | 54ar | 79 |
| 4-Cl | H | Me | 54ad | 82 | H | C5H4N | Me | 54as | 89 |
| 4-OMe | H | Me | 54ae | 82 | H | o-NO2C6H4 | Me | 54at | 88 |
| 4-OCH2Ph | H | Me | 54af | 84 | H | o-MeC6H4 | Me | 54au | 87 |
| 5-Me | H | Me | 54ag | 85 | H | m- MeC6H4 | Me | 54av | 96 |
| 5-OMe | H | Me | 54ah | 81 | H | p- MeC6H4 | Me | 54aw | 82 |
| 5-NO2 | H | Me | 54ai | 65 | H | m-CHOC6H4 | Me | 54ax | 96 |
| 5-F | H | Me | 54aj | 88 | H | m-OMeC6H4 | Me | 54ay | 79 |
| 5-Cl | H | Me | 54ak | 85 | H | p-PhC6H4 | Me | 54az | 72 |
| 5-Br | H | Me | 54al | 83 | H | p-CNC6H4 | Me | 54ba | 89 |
| 6-COOCH3 | H | Me | 54am | 57 | H | 2,4-Cl2C6H3 | Me | 54ca | 98 |
| 6-F | H | Me | 54an | 81 | H | CH3CH3C6H3 | Me | 54da | 84 |
| 6-Cl | H | Me | 54ao | 80 | H | H | CH2CF3 | 54ea | 83 |
| Products of synthesis route b | |||||||||
| R1 | R2 | R3 | Yield (%) | R1 | R2 | R3 | Yield (%) | ||
| H | p-CF3C6H4 | Me | 54fa | 98 | 4-Me | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54pa | 89 |
| H | Ph | Me | 54ga | 96 | 5-Me | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54qa | 92 |
| H | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54ha | 96 | 6-Me | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54ea | 94 |
| H | p-ClC6H4 | Me | 54ia | 95 | 7-Me | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54sa | 93 |
| H | p-FC6H4 | Me | 54ja | 97 | 5-Cl | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54ta | 96 |
| H | o-ClC6H4 | Me | 54ka | 96 | 5-Br | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54ua | 98 |
| H | 3,4-Cl2C6H4 | Me | 54la | 50 | 5-OMe | p-CF3C6H4 | Me | 54va | 96 |
| H | p-NO2C6H4 | Me | 54ma | 65 | 5-CN | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54wa | 42 |
| 2-Me | p-BrC6H4 | Me | 54na | 96 | 5-CN | p-CF3C6H4 | Me | 54xa | 56 |
| 2-Me | p-ClC6H4 | Me | 54oa | 93 | |||||
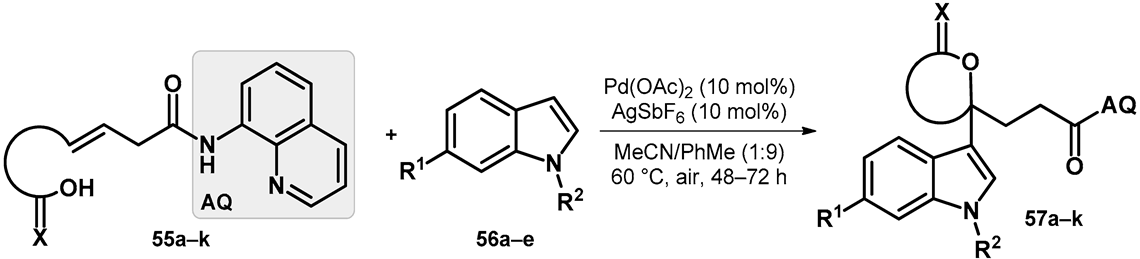 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
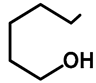
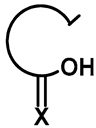 | R1 | R2 | Compound | Yield (%) |  | R1 | R2 | Compound | Yield (%) |
 | Me | H | 57a | 55 | 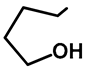 | H | F | 57g | 46 |
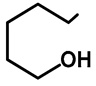 | H | H | 57b | 47 | 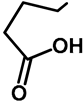 | Me | H | 57h | 56 a |
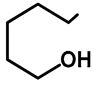 | H | OMe | 57c | 56 | 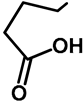 | H | H | 57i | 54 a |
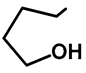 | Me | H | 57d | 58 |  | H | OMe | 57j | 56 a |
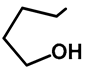 | Me | OMe | 57e | 58 |  | Me | H | 57k | 36 |
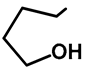 | H | H | 57f | 56 | |||||
| Reaction Scheme | R1 | R2 | Compound | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 5-OMe | H | 59a | 74 |
| 5-Me | H | 59b | 80 | |
| 5-F | H | 59c | 86 | |
| 5-Cl | H | 59d | 66 | |
| 5-Br | H | 59e | 73 | |
| 5-I | H | 59f | 77 | |
| 6-F | H | 59g | 90 | |
| 6-Cl | H | 59h | 90 | |
| 6-Br | H | 59i | 76 | |
| 4-Br | H | 59j | 59 | |
| 7-Me | H | 59k | 76 | |
| H | 2-Me | 59l | 75 |
 | |||||
| Ar | 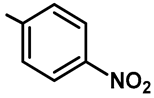 |  | 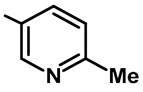 | 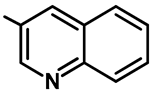 | 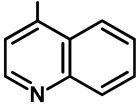 |
| Yield (%) | 74 | 66 | 70 | 64 | 82 |
| Compound | 61a | 61b | 61c | 61d | 61e |
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Condition | NH2R | Yield (%) | Maximal Yield (%) of 2aa |
| 70a | a (pH = 7, 12 h) | glycine | 27 | 70 |
| b (pH = 7, 2 h) | 25 | 75 | ||
| 70b | a (pH = 6, 15 h) | serine | 60 | 36 |
| b (pH = 7, 2 h) | 9 | – | ||
| 70c,d | a (pH = 5.0, 1 h) | lysine | c: 10 (on ω-NH2), d: 30 (on α-NH2) | 39 |
| b (pH = 12, 2 h) | c: 16 (on ω-NH2), d: 64 (on α-NH2) | – | ||
| 70e, 71a | a (1 h) | tyrosine | e: max. 64 (pH = 10) 71a: max. 18 (pH = 12) | max. 32 (pH = 7) |
| 71b | a (pH = 7, 0.5 h) | glutathione (on thiol) | 84 | – |
| b (pH = 7, 2 h) | 86 | 12 | ||
 | ||||||
| (a) incubation at 100 °C, (b) laser flash photolysis, 266 nm | ||||||
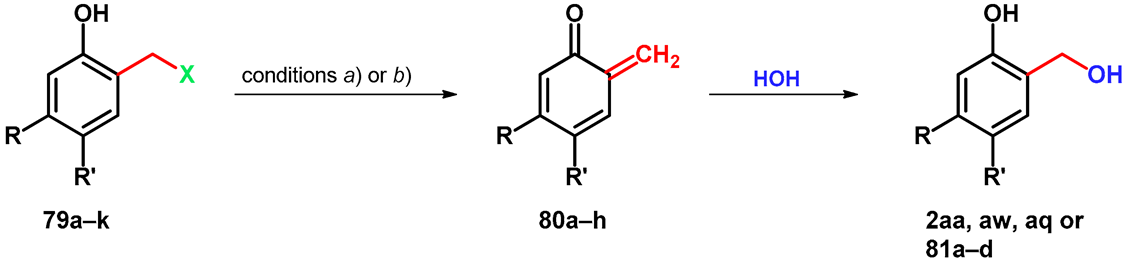
| Mannich Base | X | R | R’ | Conditions | oQM | o-HO-benzylalcohol |
| 79a | 4-morpholinyl | -COOMe | -H | a | 80a | 81a |
| 79b | 4-morpholinyl | -H | -COOMe | a | 80b | 81b |
| 79c | 4-morpholinyl | -H | -H | a | 80c | 2aa |
| 79d | 4-morpholinyl | -H | -OMe | a | 80d | 2aw |
| 79e | 4-morpholinyl | -OMe | -H | a | 80e | 81c |
| 79f | -N+Me3 | -H | -H | b | 80c | 2aa |
| 79g | -N+Me3 | -H | -COOMe | b | 80b | 81b |
| 79h | -N+Me3 | -H | -OMe | b | 80d | 2aw |
| 79i | -N+Me3 | -H | -Cl | b | 80f | 2aq |
| 79j | -N+Me3 | -H | -CN | b | 80g | 81d |
| 79k | -N+Me3 | -H | -CN | b | 80h | 81e |
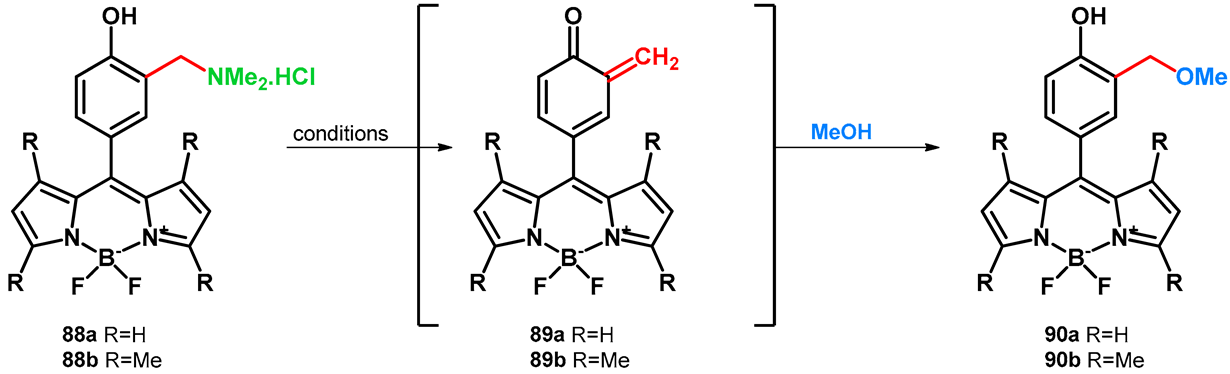 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unisolated yields of compounds 89a,b and conditions | |||||
| # | Solvent | Wavelength of irradiation | |||
| 254 nm | 300 nm | 350 nm | visible, cool white | ||
| 90a | MeOH | decomposed | 2 | no reaction | |
| MeOH/HOH 1:1, pH = 7 | 68 (16 h) | 42 (16 h) | 2 (16 h) | <1 (16 h) | |
| MeOH/HOH 1:1, pH = 9 | decomposed | 52 (16 h) | 8 (16 h) | <1 (16 h) | |
| 90b | MeOH | 30 (9 h) | 12 (12 h) | 1 (16 h) | no reaction |
| MeOH/HOH 1:1, pH = 7 | 100 (2 h) | 100 (6 h) | 21 (16 h) | 2 (16 h) | |
| MeOH/HOH 1:1, pH = 9 | 94 (4 h) | 100 (6 h) | 19 (16 h) | 2 (16 h) | |
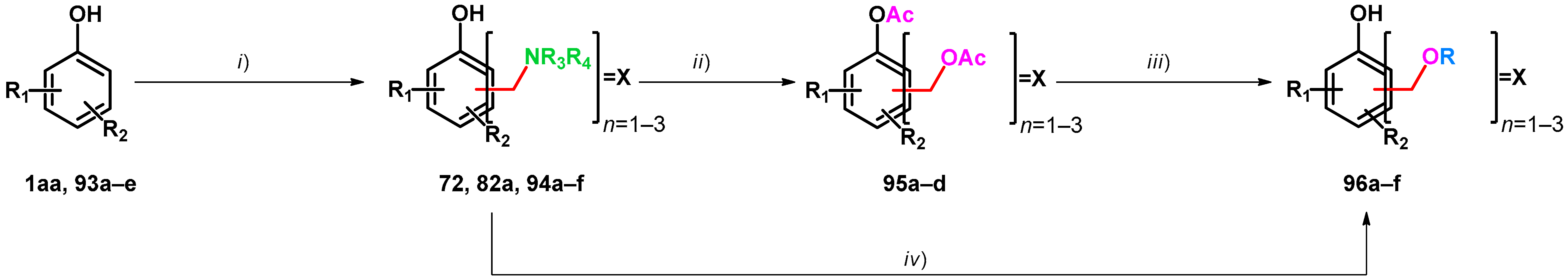 | ||||||||
| Compound | Condition (i) | Compound | Condition (ii) | Compound | Condition (iii) | Compound | Ref. | |
| 1aa: R1 = R2 = H | 10 equiv. 40% formaldehyde in water, 10 equiv. 50% aqueous Me2NH, 40 °C, 6 h | 82a: 2,4,6-X X = CH2NMe2, R1 = R2 = H | 10 equiv. Ac2O, 100 °C, 4 h | 95a: 2,4,6-X X = CH2OAc, R1 = R2 = H | 10. equiv. K2CO3, EtOH, 80 °C, 2 h | 96a: 2,4,6-X X = CH2OEt | [73] | |
| 2.0 equiv. 38% formaldehyde in water, 0.98 equiv. morpholine, 50 °C, 15 h | 72: 2,6-X X= morpholino-methyl, R1 = R2 = H (20%) | Ac2O, reflux | 95b: 2,6-X X = CH2OAc, R1 = R2 = H (57%) | From this step, divergent reaction routes were applied | [75] | |||
| 93a: R1 = 4-Br, R2 = H | 2.2 equiv. 38% formaldehyde in water, 2.2 equiv. morpholine, 80 °C, 6 h, in HOAc | 94a: 2,6-X X = morpholino-methyl, R1 = 4-Br, R2 = H (82%) | Ac2O (2.2 mL to 1 mol) and HOAc (0.15 to 1 mmol), reflux, 24 h | 95c: 2,6-X X = CH2OAc R1 = 4-Br, R2 = H (64%) | [75] | |||
| 94b was synthesized via different reaction route | 94b: 2,6-X X= morpholino-methyl, R1 = 4-phenylethynyl | Ac2O (11 mL to 1 mmol), HOAc (0.45 to 1 mmol), reflux, 14 h | 95d: 2,6-X X = CH2OAc, R1 = 4-phenyl ethynyl, R2 = H (75%) | 5M H2SO4 in THF, reflux | 96b: 2,6-X X = CH2OH, R1 = 4-phenyl ethynyl, R2 = H (48%) | [75] | ||
| Compound | Condition (i) | Compound | Condition (iv) | Compound | Ref. | |||
| 93b: R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = Me | 50% aqueous Me2NH, paraformaldehyde | 94c: 2-X = CH2NMe2, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = Me | cat. KOH, 5 equiv. paraformaldehyde ethylene glycol, 150 °C, 24 h | 96c: 2-X = CH2O(CH2)2OH, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = Me | [74] | |||
| 93c: R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = t-Bu | 94d: 2-X = CH2NMe2, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = t-Bu | 96d: 2-X = CH2O(CH2)2OH, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = t-Bu | [74] | |||||
| 93d: R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2-hydroxy)ethyl | 94e: 2-X = CH2NMe2, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2-hydroxy)ethyl | 96e: 2-X = CH2O(CH2)2OH, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2-hydroxy)ethyl | [74] | |||||
| 93e: R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2,2,4,4-tetramethyl)butyl | 94f: 2-X = CH2NMe2, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2,2,4,4-tetramethyl)butyl | 96f: 2-X = CH2O(CH2)2OH, R1 = 2-(2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl), R2 = 1-(2,2,4,4-tetramethyl)butyl | [74] | |||||
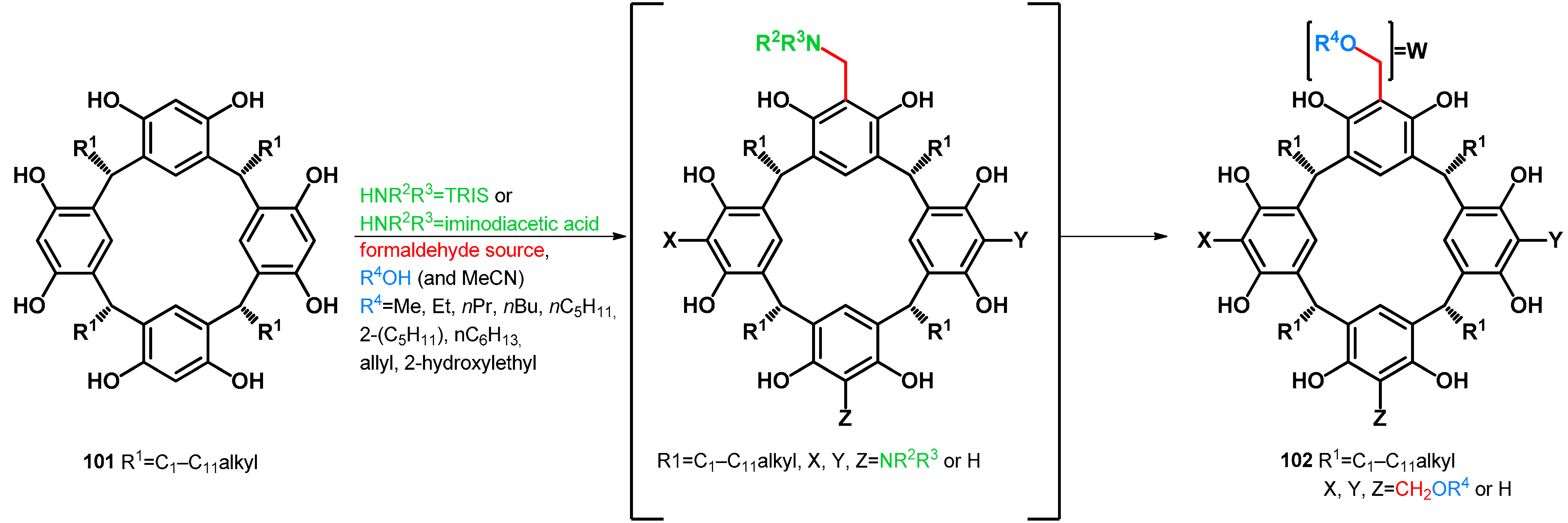 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Condition | 102 | Ref. |
| a: R1 = Et | 20 equiv. aqueous formaldehyde 37%, HOAc (0.1 mL to 1 mmol), EtOH (10 mL to 1 mmol), 9 equiv. NHR2R3 = TRIS, 1 h R.T., 1–2 h reflux | a: R1 = Et, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (55%) | [77] |
| b: R1 = C5H11 | b: R1 = C5H11, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (42–69%) a | [77] | |
| c: R1 = C11H23 | c: R1 = C11H23, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (42–69%) a | [77] | |
| d: R1 = i-Bu | 5 equiv. aqueous formaldehyde 37%, cat. NHR2R3 = iminodiacetic acid (in water) (9.4 mol%), R4OH as solvent, reflux, 12 h | d: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OMe (79%) | [78] |
| e: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (66%) | [78] | ||
| f: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OnPr (64%) | [78] | ||
| g: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OnBu (46%) | [78] | ||
| h: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OnPe (40%) | [78] | ||
| i: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OnHx (28%) | [78] | ||
| 2 equiv. aqueous formaldehyde 37%, cat. NHR2R3 = iminodiacetic acid (10% m/m), R4OH as solvent, reflux (reaction times separately assigned) | j: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = H, W = CH2OMe (34%, 4 h) | [79] | |
| k: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = H, W = CH2OEt (39%, 135 min) | [79] | ||
| l: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = H, W = CH2OnPr (39%, 90 min) | [79] | ||
| m: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = H, W = CH2OAllyl (43%, 90 min) | [79] | ||
| n: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = Z = H, W = CH2O(2-hydroxyethyl) (37%, 30 min) | [79] | ||
| o: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = H, X = W = CH2OnPr (14%, 160 min) | [79] | ||
| p: R1 = i-Bu, X = Y = H, Z = W = CH2OnPr (24%, 160 min) | [79] | ||
| q: R1 = i-Bu, X = H, Y = Z = W = CH2OnPr (29%, 180 min) | [79] | ||
| r: R1 = i-Bu, X = H, Y = Z = W = CH2OAllyl (30%, 180 min) | [79] | ||
| e: R1 = nC11H23 | 5 equiv. aqueous formaldehyde 37%, cat. NHR2R3 = iminodiacetic acid (in water) (9.4 mol%), R4OH as solvent, reflux, 4 h | s: R1 = nC11H23, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (42%) | [78] |
| f: R1 = Me | t: R1 = Me, X = Y = Z = W = CH2OEt (65%) | [78] | |
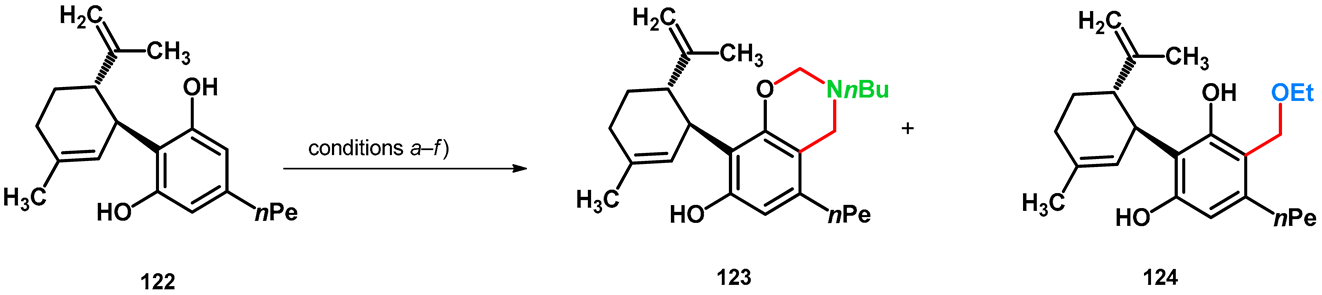 | |||
| conditions | 123 (%) | 124 (%) | |
| (a) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, 3.0 equiv. NH2nBu, MeOH, room temperature, 7 days | 89 | – |
| (b) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, 3.0 equiv. NH2nBu, EtOH, reflux, 20 h | 64 | 21 |
| (c) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, 3.0 equiv. NH2nBu, EtOH, reflux, 6 h then 45 °C, 18 h overnight | ~100 | 0 |
| (d) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, 3.0 equiv. NH2nBu, 1,4-dioxane, reflux, 6 h then 50 °C, 18 h overnight | 60 | – |
| (e) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, 3.0 equiv. NEt3, EtOH, reflux, 2 days (reflux, 6 h then 45 °C, 16 h overnight) | – | 30 |
| (f) | 3.0 equiv. 36% aqueous formaldehyde, EtOH, 3 days (reflux, 6 h then 45 °C, 16 h overnight) | – | 0 a |
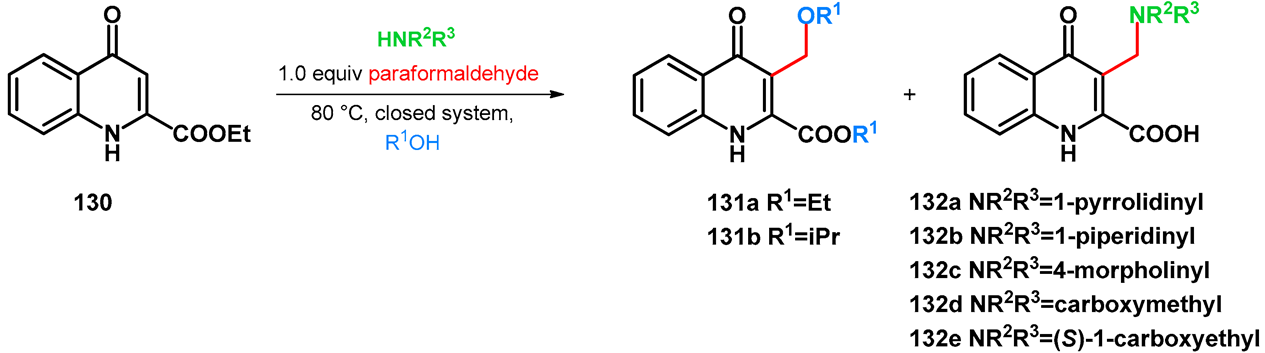 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Conversion, Reaction Time (and Isolated Yield) | |||
| HNR2R3 | Equivalence | R1OH | 131 | 132 |
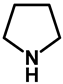 | 1.0 | Ethanol | 0% | a: 75% (60 h) |
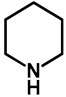 | 1.0 | Ethanol | 0% | b: 98% (60 h) |
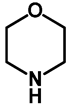 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 4% (8 h) | c: 92% (60 h) |
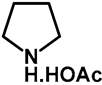 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 3% (1–3 h) | a: 56% (28 h) |
 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 5% (1–5 h) | b: 34% (20 h) |
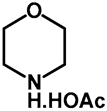 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 20% (9 h) | c: 60% (9 h) |
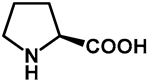 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 5% (6 h) | 0% |
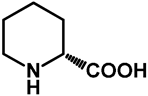 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 15% (22 h) | 0% |
 | 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 15% (60 h) | 0% |
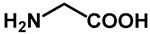 | 1.0 | Ethanol | 0% | d: isolated 44% (88 h) |
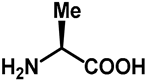 | 1.0 | Ethanol | 0% | e: isolated 9% (95 h) |
 | 0.1 | Ethanol | a: 6% (24 h) | 0% |
| 0.5 | Ethanol | a: 39% (40 h, isolated 33%) | 0% | |
| 1.0 | Ethanol | a: 25% (22 h) | 0% | |
| 2.0 | Ethanol | a: 48% (40 h) | 0% | |
| 0.5 | 2-Propanol | b: 21% (26 h, isolated 16%) | 0% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simon, P.; Lőrinczi, B.; Szatmári, I. Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Aromatic Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136966
Simon P, Lőrinczi B, Szatmári I. Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Aromatic Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136966
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimon, Péter, Bálint Lőrinczi, and István Szatmári. 2024. "Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Aromatic Compounds" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136966
APA StyleSimon, P., Lőrinczi, B., & Szatmári, I. (2024). Alkoxyalkylation of Electron-Rich Aromatic Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136966








