Proteomic Analysis of Human Macrophages Overexpressing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
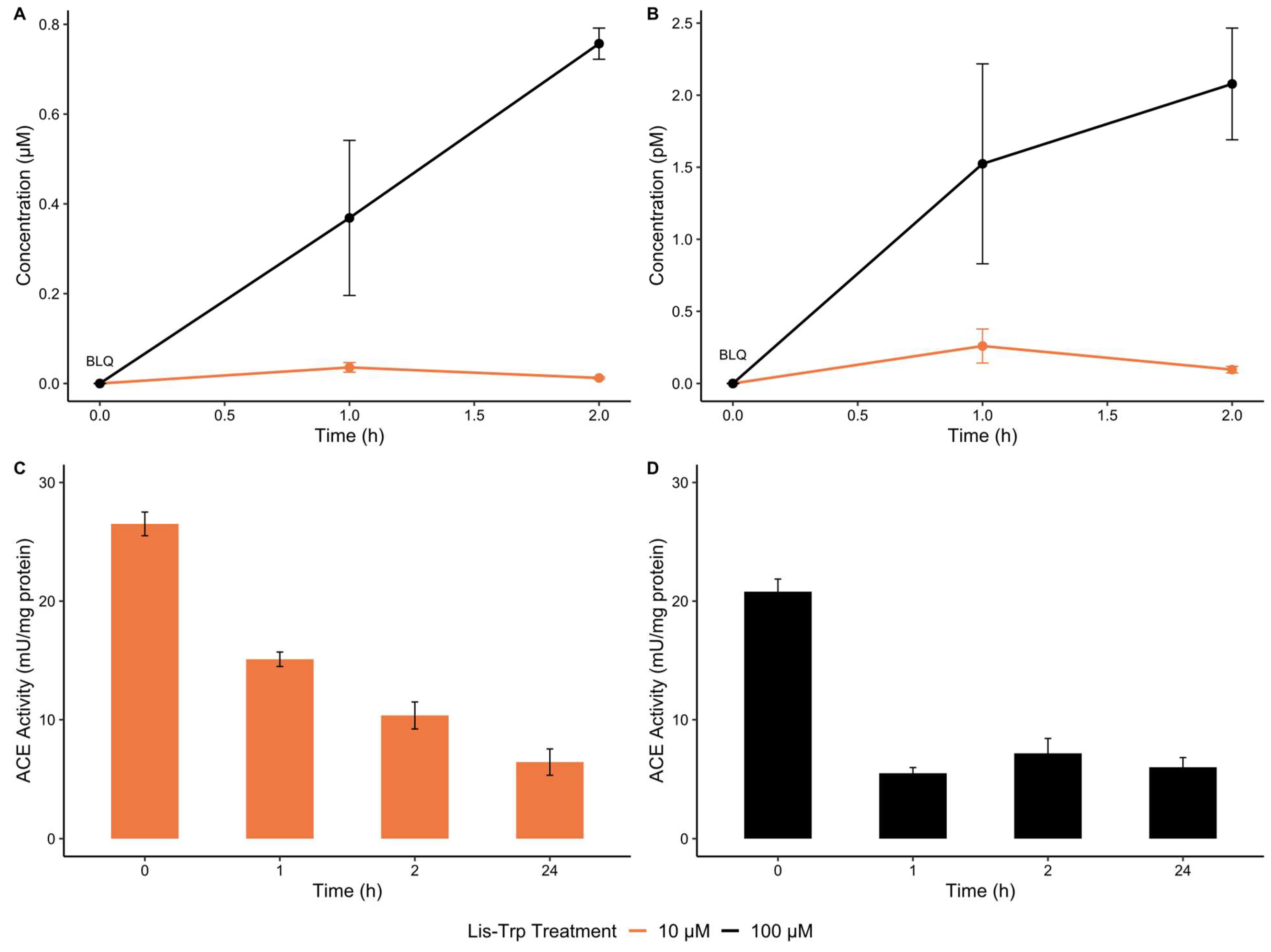
2.1. Intracellular Uptake of ACE C-Domain Inhibitor, Lisinopril–Tryptophan, by Human THP-1 Macrophages
2.2. Assessment of ACE +/+ THP-1 Macrophage Proteome
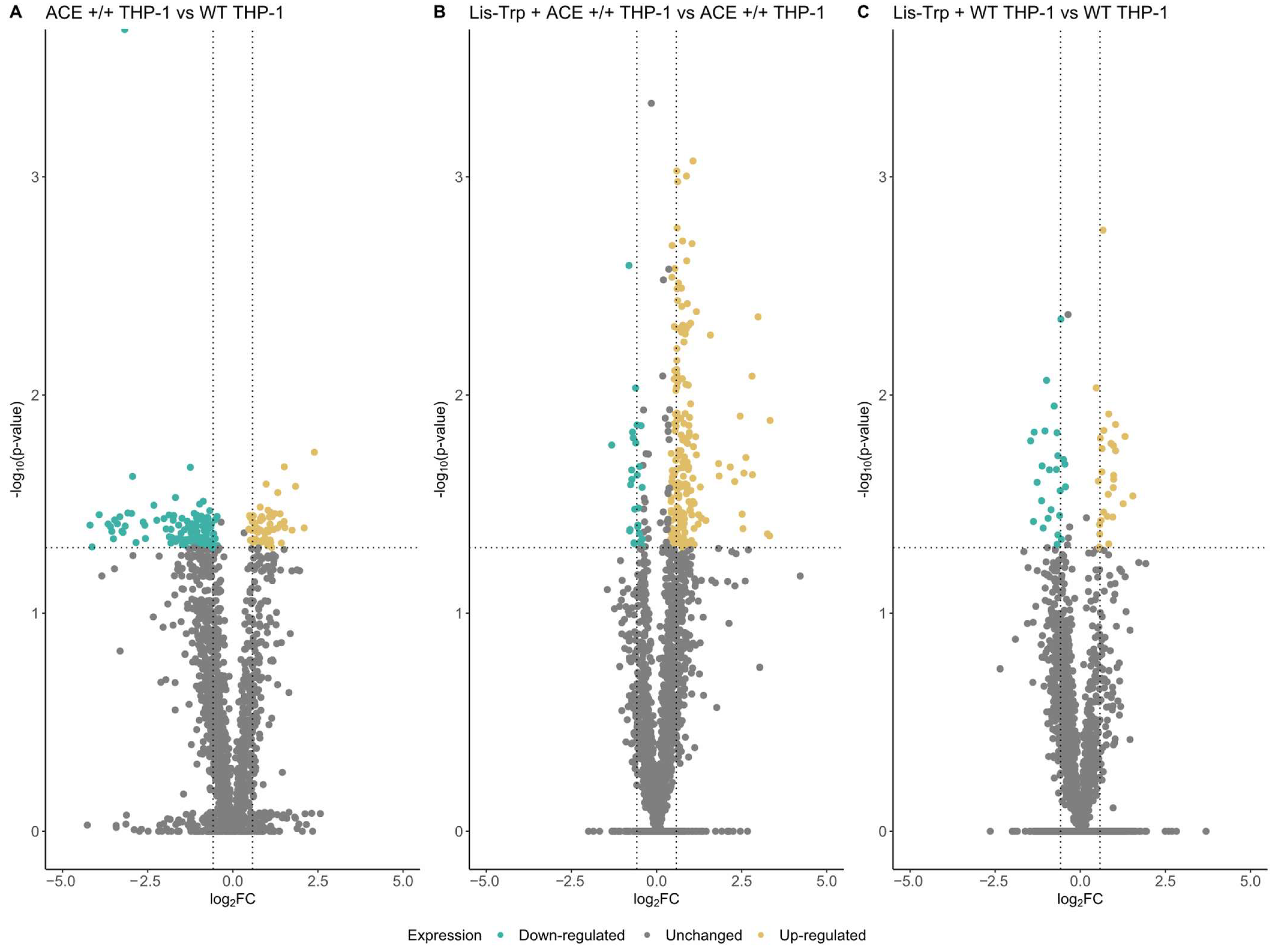
2.2.1. Differential Expression Analysis
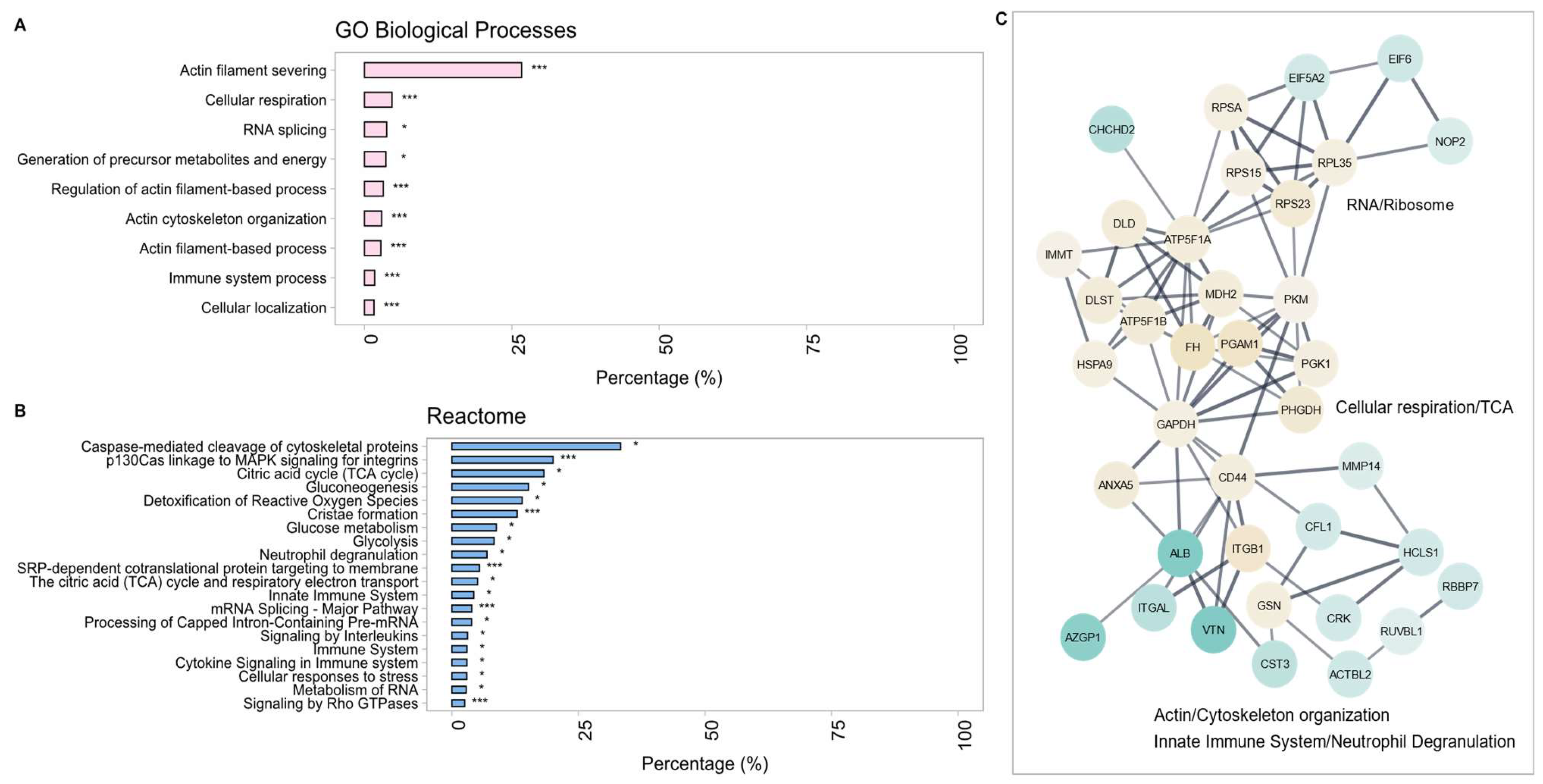
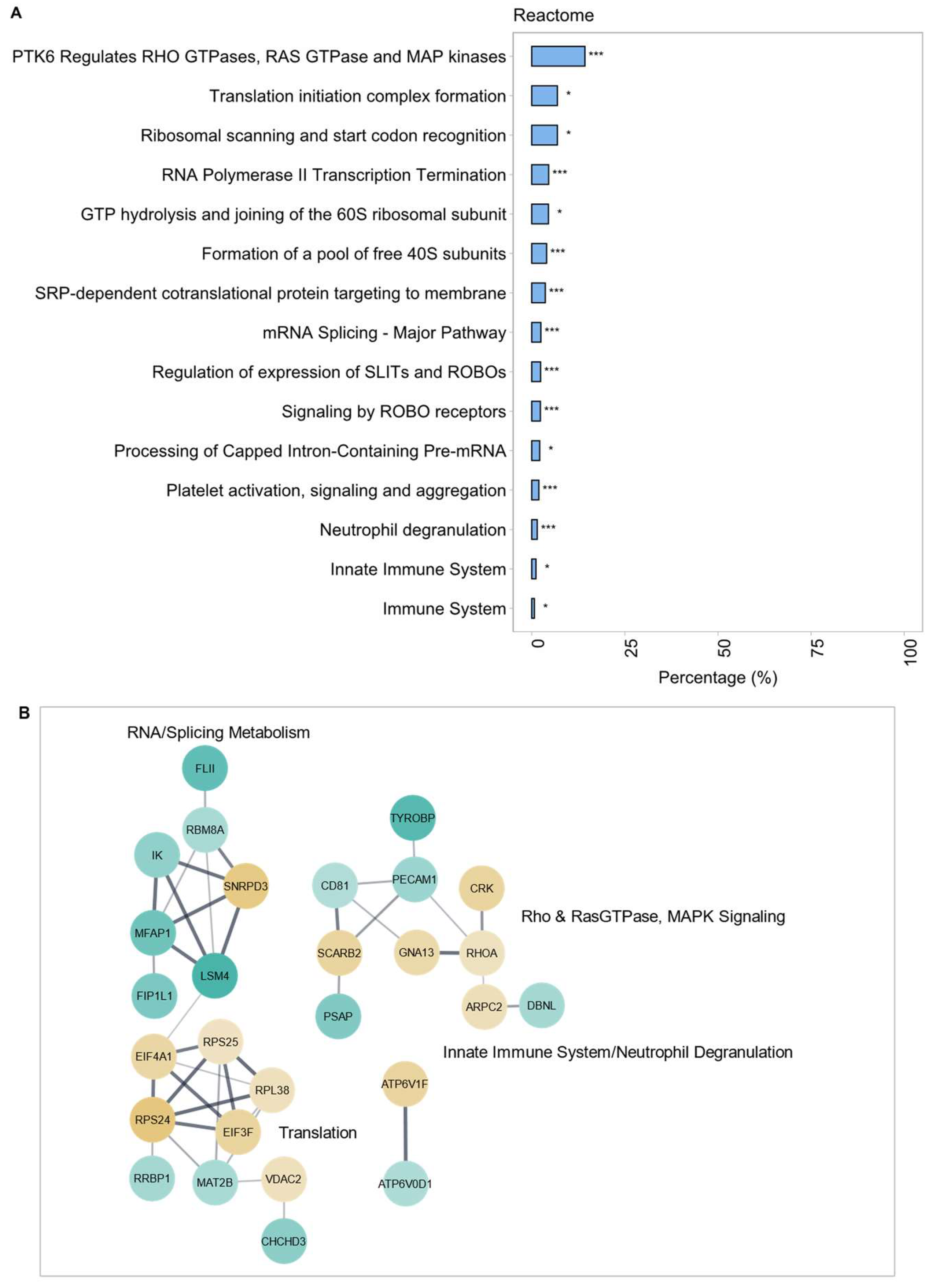
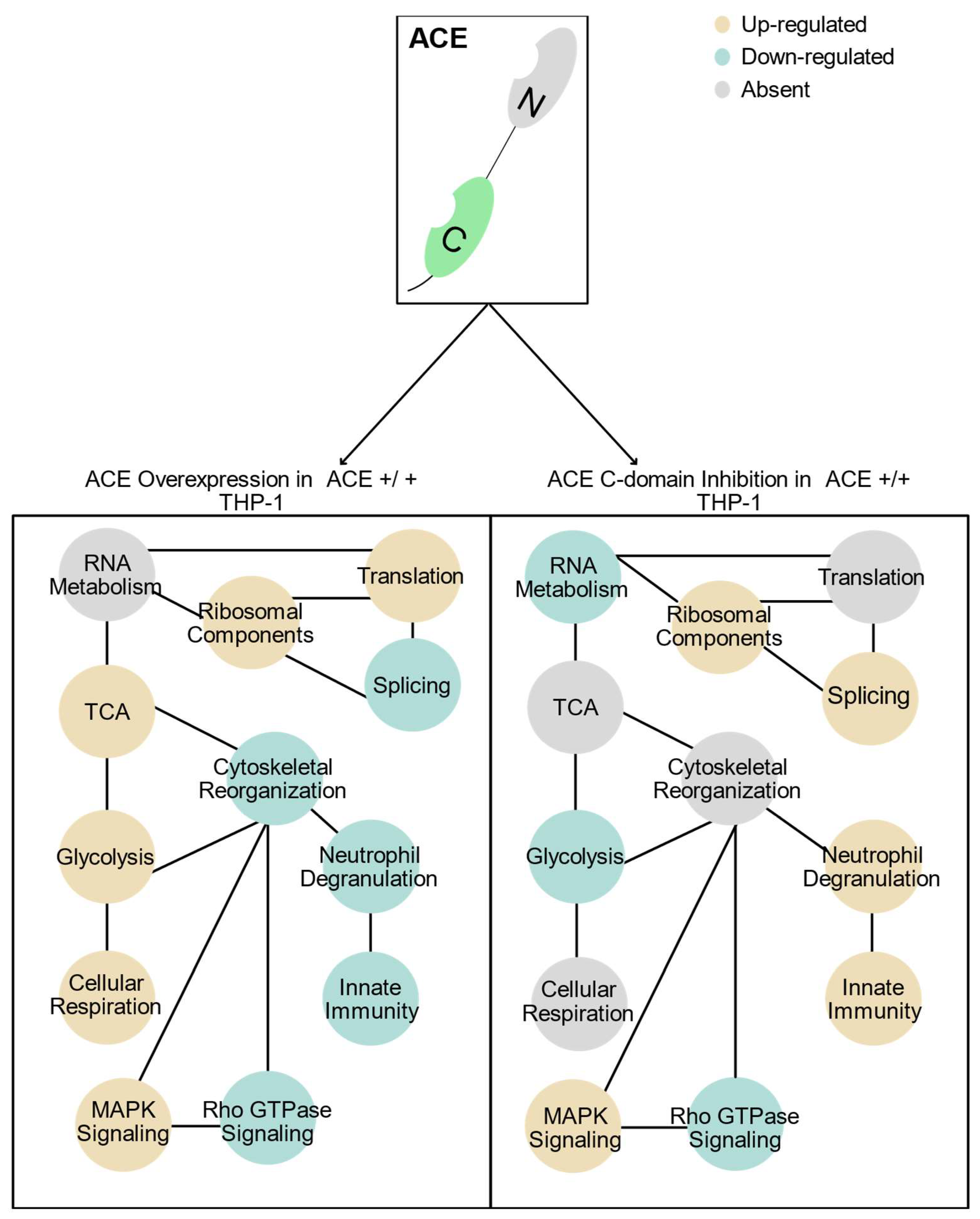
2.2.2. Gene Ontology (GO) Term Enrichment Analysis and Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture Conditions
THP-1 Differentiation into Macrophages
4.2. Lisinopril–Tryptophan Uptake Assessment
4.2.1. Lisinopril–Tryptophan Treatment and Cell Lysis
4.2.2. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Intracellular Lisinopril–Tryptophan
Sample Preparation and Extraction
Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis
4.3. ACE Activity
4.4. Global Proteome Analysis via Triple Time-of-Flight (TOF) Mass Spectrometry
4.4.1. Macrophage Treatment for Proteomic Analysis
Sample Preparation
In-Solution Digestion
Desalting
4.4.2. Triple Time-of-Flight (TOF) Sequential Window Acquisition of all Theoretical Mass Spectra (SWATH®) Mass Spectrometry
4.4.3. Data Processing and Clean-Up
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Functional Enrichment and Network Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skeggs, L.T.; Kahn, J.R.; Shumway, N.P. The preparation and function of the hypertensin-converting enzyme. J. Exp. Med. 1956, 103, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.R.W.; Riordan, J.F. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: New Concepts Concerning Its Biological Role. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbe, L.; Sturrock, E.D. Interacting cogs in the machinery of the renin angiotensin system. Biophys. Rev. 2019, 11, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyer, G.; Yates, C.J.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE): Structure, biological roles, and molecular basis for chloride ion dependence. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturrock, E.D.; Natesh, R.; van Rooyen, J.M.; Acharya, K.R. Structure of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbe, L.; Cozier, G.E.; Oosthuizen, D.; Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D. ACE2 and ACE: Structure-based insights into mechanism, regulation and receptor recognition by SARS-CoV. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozier, G.E.; Lubbe, L.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. ACE-domain selectivity extends beyond direct interacting residues at the active site. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 1241–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbe, L.; Sewell, B.T.; Woodward, J.D.; Sturrock, E.D. Cryo-EM reveals mechanisms of angiotensin I-converting enzyme allostery and dimerization. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D. Crystal structure of the human enzyme–lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 1429, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, D.; Luft, F.C.; Bader, M.; Ganten, D.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Emergence and evolution of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azushima, K.; Morisawa, N.; Tamura, K.; Nishiyama, A. Recent Research Advances in Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Receptors. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, M. Tissue Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Systems: Targets for Pharmacological Therapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacurari, M.; Kafoury, R.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Ndebele, K. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in vascular inflammation and remodeling. Int. J. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 689360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Shibata, T.; Giani, J.F.; Rader, F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Diverse biological functions of the renin-angiotensin system. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 44, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiras, L.C.; Cao, D.; Saito, S.; Peng, Z.; Bernstein, E.A.; Shen, J.Z.Y.; Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Giani, J.F.; Khan, Z.; et al. Overexpression of ACE in Myeloid Cells Increases Immune Effectiveness and Leads to a New Way of Considering Inflammation in Acute and Chronic Diseases. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z.; Giani, J.F.; Cao, D.-Y.; Bernstein, E.A.; Shen, X.Z. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.-Y.; Saito, S.; Veiras, L.C.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Bernstein, E.A.; Giani, J.F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme in myeloid cell immune responses. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Veiras, L.; Ahmed, F.; Shibata, T.; Bernstein, E.A.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Giani, J.F.; Khan, Z.; Bernstein, K.E. The non-cardiovascular actions of ACE. Peptides 2022, 152, 170769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semis, M.; Gugiu, G.B.; Bernstein, E.A.; Bernstein, K.E.; Kalkum, M. The Plethora of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Processed Peptides in Mouse Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6440–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Ertoy, D.; E Bernstein, K. Insights derived from ACE knockout mice. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2000, 1, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Cao, D.-Y.; Giani, J.F.; Bernstein, E.A.; Veiras, L.C.; Fuchs, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Kalkum, M.; Liu, G.Y.; et al. Overexpression of the C-domain of angiotensin-converting enzyme reduces melanoma growth by stimulating M1 macrophage polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, J.F.; Veiras, L.C.; Shen, J.Z.; Bernstein, E.A.; Cao, D.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Khan, Z.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Bernstein, K.E. Novel roles of the renal angiotensin-converting enzyme. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 529, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Shen, X.Z.; Bernstein, E.A.; Giani, J.F.; Eriguchi, M.; Zhao, T.V.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Fuchs, S.; Liu, G.Y.; Bernstein, K.E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme enhances the oxidative response and bactericidal activity of neutrophils. Blood 2017, 130, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z.; Giani, J.F.; Zhao, T.; Eriguchi, M.; Bernstein, E.A.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Shen, X.Z. Overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme in myelomonocytic cells enhances the immune response. F1000Research 2016, 5, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwan-Duodu, D.; Weiss, D.; Peng, Z.; Veiras, L.C.; Cao, D.-Y.; Saito, S.; Khan, Z.; Bernstein, E.A.; Giani, J.F.; Taylor, W.R.; et al. Overexpression of myeloid angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) reduces atherosclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 520, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Saito, S.; Xu, L.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Ahmed, F.; Jovanovic, P.; Shibata, T.; Che, M.; Bernstein, E.A.; et al. Myeloid cell ACE shapes cellular metabolism and function in PCSK-9 induced atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1278383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Khan, Z.; Li, X.; Saito, S.; Bernstein, E.A.; Victor, A.R.; Ahmed, F.; Hoshi, A.O.; Veiras, L.C.; Shibata, T.; et al. Macrophage angiotensin-converting enzyme reduces atherosclerosis by increasing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and fundamentally changing lipid metabolism. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 1825–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.Z.; Li, P.; Weiss, D.; Fuchs, S.; Xiao, H.D.; Adams, J.A.; Williams, I.R.; Capecchi, M.R.; Taylor, W.R.; Bernstein, K.E. Mice with enhanced macrophage angiotensin-converting enzyme are resistant to melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Salumbides, B.; Koronyo, Y.; Sheyn, J.; Pelissier, L.; Yu, J.; Bernstein, E.; Shen, X.; Fuchs, D.; Pham, M.; et al. P3-348: Targeted high-expression of ACE to myelomonocytic cells diminishes Alzheimer’s-like pathology and restores memory and learning in mouse models. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, P579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Shah, K.; Koronyo, Y.; Bernstein, E.; Giani, J.F.; Janjulia, T.; Black, K.L.; Shi, P.D.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Fuchs, S.; et al. ACE overexpression in myelomonocytic cells: Effect on a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, M.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Amyloid β-protein is degraded by cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37644–37650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmuth, K.M.; Masuyer, G.; Douglas, R.G.; Schwager, S.L.; Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D. Kinetic and structural characterization of amyloid-β peptide hydrolysis by human angiotensin-1-converting enzyme. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwan-Duodu, D.; Datta, V.; Shen, X.Z.; Goodridge, H.S.; Bernstein, E.A.; Fuchs, S.; Liu, G.Y.; Bernstein, K.E. Bernstein, Angiotensin-converting enzyme overexpression in mouse myelomonocytic cells augments resistance to Listeria and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39051–39060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.-Y.; Spivia, W.R.; Veiras, L.C.; Khan, Z.; Peng, Z.; Jones, A.E.; Bernstein, E.A.; Saito, S.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Parker, S.J.; et al. ACE overexpression in myeloid cells increases oxidative metabolism and cellular ATP. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 295, 1369–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Bhat, S.A.; Cao, D.; Saito, S.; Bernstein, E.A.; Nishi, E.; Medenilla, J.D.; Wang, E.T.; Chan, J.L.; Pisarska, M.D.; et al. Testicular ACE regulates sperm metabolism and fertilization through the transcription factor PPARγ. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.Z.; Billet, S.; Lin, C.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Chen, X.; E Lukacher, A.; E Bernstein, K. The carboxypeptidase ACE shapes the MHC class I peptide repertoire. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.Z.; Lukacher, A.E.; Billet, S.; Williams, I.R.; Bernstein, K.E. Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme changes major histocompatibility complex class I peptide presentation by modifying C termini of peptide precursors. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9957–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; E Bernstein, K.; Fang, J.; Shen, X.Z. Angiotensin-converting enzyme affects the presentation of MHC class II antigens. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Y.; Giani, J.F.; Veiras, L.C.; Bernstein, E.A.; Okwan-Duodu, D.; Ahmed, F.; Bresee, C.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Bernstein, K.E.; et al. An ACE inhibitor reduces bactericidal activity of human neutrophils in vitro and impairs mouse neutrophil activity in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Lopes, R.; Montezano, A.C.; Neves, K.B.; Harvey, A.; Rios, F.J.; Skiba, D.S.; Arendse, L.B.; Guzik, T.J.; Graham, D.; Poglitsch, M.; et al. Selective Inhibition of the C-Domain of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Combined With Inhibition of NEP (Neprilysin): A Potential New Therapy for Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 78, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denti, P.; Sharp, S.-K.; Kröger, W.L.; Schwager, S.L.; Mahajan, A.; Njoroge, M.; Gibhard, L.; Smit, I.; Chibale, K.; Wiesner, L.; et al. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of lisinopril-tryptophan, a novel C-domain ACE inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 56, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nchinda, A.T.; Chibale, K.; Redelinghuys, P.; Sturrock, E.D. Synthesis and molecular modeling of a lisinopril–tryptophan analogue inhibitor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4616–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, A.; Rakugi, H.; Ohishi, M.; Yanagitani, Y.; Takiuchi, S.; Moriguchi, K.; Fennessy, P.A.; Higaki, J.; Ogihara, T. Up-regulation of renin-angiotensin system during differentiation of monocytes to macrophages. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 537–545. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/fulltext/1999/17040/upregulation_of_renin_angiotensin_system_during.12.aspx (accessed on 5 May 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlstedt, K.; Trouvain, C.; Namgaladze, D.; Fleming, I. Adipocyte-derived lipids increase angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) expression and modulate macrophage phenotype. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohishi, M.; Ueda, M.; Rakugi, H.; Naruko, T.; Kojima, A.; Okamura, A.; Higaki, J.; Ogihara, T. Enhanced expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme is associated with progression of coronary atherosclerosis in humans. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, D.; Sturrock, E.D. Exploring the Impact of ACE Inhibition in Immunity and Disease. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2022, 2022, 9028969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha, R.; Greig, D.; Kelley, B.V.; Mamouei, Z.; Sekimura, T.; Cevallos, N.; Olson, T.; Chaudry, A.; Magyar, C.; Leisman, D.; et al. Inhibition of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Impairs Anti-staphylococcal Immune Function in a Preclinical Model of Implant Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryniarski, P.; Nazimek, K.; Marcinkiewicz, J. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Most Commonly Used Antihypertensive Drugs—Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.; Artursson, P.; Avdeef, A.; Di, L.; Ecker, G.F.; Faller, B.; Houston, J.B.; Kansy, M.; Kerns, E.H.; Krämer, S.D.; et al. Passive lipoidal diffusion and carrier-mediated cell uptake are both important mechanisms of membrane permeation in drug disposition. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeirssen, V.; Van Camp, J.; Verstraete, W. Bioavailability of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Van Bocxlaer, J.; Vermeulen, A. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling of lisinopril in children: A case story of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaites, D.T.; Cavet, M.; Hirst, B.H.; Simmons, N.L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor transport in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.I.; Amidon, G.L. Passive and carrier-mediated intestinal absorption components of two angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor prodrugs in rats: Enalapril and fosinopril. Pharm. Res. 1989, 06, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.I.; Amidon, G.L. Intestinal absorption mechanism of dipeptide angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors of the lysyl-proline type: Lisinopril and SQ 29,852. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, F.; Fang, D.; Hu, Y.; Smith, D.E.; Jiang, H. Functional and molecular expression of the proton-coupled oligopeptide transporters in spleen and macrophages from mouse and human. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwarycz, B.; Wong, E.A. Expression of the peptide transporters PepT1, PepT2, and PHT1 in the embryonic and posthatch chick. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, H.; Heinrich, M.; Birkemeyer, C.; Meixensberger, J.; Gaunitz, F. The proton-coupled oligopeptide transporters PEPT2, PHT1 and PHT2 mediate the uptake of carnosine in glioblastoma cells. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Song, F.; Yang, X.; Weng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H. Substrate Transport Properties of the Human Peptide/Histidine Transporter PHT2 in Transfected MDCK Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3416–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Hsu, P.-H.; Lin, H.-T.V. Determination of drug efflux pump efficiency in drug-resistant bacteria using MALDI-TOF MS. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Gebauer, L.; Brockmöller, J.; Dücker, C. Relationships between Inhibition, Transport and Enhanced Transport via the Organic Cation Transporter 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Aguanno, D.; Board, M.; Callaghan, R. Exploiting the metabolic energy demands of drug efflux pumps provides a strategy to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, S.S.; Cluzel, P.; Aldana, M. Adaptive resistance in bacteria requires epigenetic inheritance, genetic noise, and cost of efflux pumps. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, E.; Vergalli, J.; Conraux, L.; Taillier, C.; Vassort, A.; Pajović, J.; Réfrégiers, M.; Mourez, M.; Pagès, J.-M. Antibiotics and efflux: Combined spectrofluorimetry and mass spectrometry to evaluate the involvement of concentration and efflux activity in antibiotic intracellular accumulation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 74, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwager, S.L.; Carmona, A.K.; Sturrock, E.D. A high-throughput fluorimetric assay for angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, S.M.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Albrecht, R.F.; Kost, O.A. Simultaneous Determination of ACE Activity with 2 Substrates Provides Information on the Status of Somatic ACE and Allows Detection of Inhibitors in Human Blood. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, M.; Jassal, B.; Stephan, R.; Milacic, M.; Rothfels, K.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Griss, J.; Sevilla, C.; Matthews, L.; Gong, C.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D649–D655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Ong, F.S.; Blackwell, W.-L.B.; Shah, K.H.; Giani, J.F.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Shen, X.Z.; Fuchs, S. A modern understanding of the traditional and nontraditional biological functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 65, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalise, U.; Daseke, M.J.; Kalusche, W.J.; Konfrst, S.R.; Rodriguez-Paar, J.R.; Flynn, E.R.; Cook, L.M.; Becirovic-Agic, M.; Lindsey, M.L. Macrophages secrete murinoglobulin-1 and galectin-3 to regulate neutrophil degranulation after myocardial infarction. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichelberger, K.R.; Goldman, W.E. Manipulating neutrophil degranulation as a bacterial virulence strategy. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlikowska, B.; Stachura, A.; Gierlikowski, W.; Demkow, U. Phagocytosis, Degranulation and Extracellular Traps Release by Neutrophils—The Current Knowledge, Pharmacological Modulation and Future Prospects. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 666732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodermann, V.; Nahrendorf, M. Neutrophil–macrophage cross-talk in acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 38, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, P. Mechanisms of degranulation in neutrophils. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miselis, J.; Siminiak, T.; Wysocki, H. Evidence for stimulation of neutrophil degranulation by selected angiotensin con-verting enzyme inhibitors in vitro. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1994, 8, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wysocki, H.; Siminiak, T.; Zozulińska, D.; Wierusz-Wysocka, B. Evaluation of the effect of oral enalapril on neutrophil functions: Comparison with the in vitro effect of enalapril and enalaprilat. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clapperton, M.; McMurray, J.; Fisher, A.; Dargie, H. The effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on human neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 38, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rørvig, S.; Østergaard, O.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Borregaard, N. Proteome profiling of human neutrophil granule subsets, secretory vesicles, and cell membrane: Correlation with transcriptome profiling of neutrophil precursors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlstedt, K.; Gershome, C.; Trouvain, C.; Hofmann, W.-K.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Fleming, I. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors Modulate Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein 1 and Adiponectin Expression in Adipocytes via the ACE-Dependent Signaling Cascade. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlstedt, K.; Gershome, C.; Friedrich, M.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Fleming, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) dimerization is the initial step in the ACE inhibitor-induced ACE signaling cascade in endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.I.; Nogueira, M.D.; Campanha-Rodrigues, A.L.; Pereira, L.M.; Andrade, M.C.C.; Parreiras-E-Silva, L.T.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Mortara, R.A.; Casarini, D.E. The binding of captopril to angiotensin I-converting enzyme triggers activation of signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 315, C367–C379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eickels, M.; Grohé, C.; Löbbert, K.; Stimpel, M.; Vetter, H. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors block mitogenic signalling pathways in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1999, 359, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlstedt, K.; Brandes, R.P.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Is Involved in Outside-In Signaling in Endothelial Cells. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I. Signaling by the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomsma, F.; de Bruyn, J.H.B.; Derkx, F.H.M.; Schalekamp, M.A.D.H. Opposite Effects of Captopril on Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme ‘Activity’ and ‘Concentration’; Relation between Enzyme Inhibition and Long-Term Blood Pressure Response. Clin. Sci. 1981, 60, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, C.; Egashira, K.; Inoue, S.; Takemoto, M.; Ni, W.; Koyanagi, M.; Kitamoto, S.; Usui, M.; Kaibuchi, K.; Shimokawa, H.; et al. Important Role of Rho-kinase in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Inflammation and Remodeling Induced by Long-Term Blockade of Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Rats. Hypertension 2002, 39, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, R.; Giordani, A.S.; Lorenzo, C.A. ROCK (RhoA/Rho Kinase) Activation in Atrial Fibrillation: Molecular Pathways and Clinical Implications. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2023, 19, E171122210986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, I.; Wehinger, S.; Andrés, V.; García-García, F.J.; Fuentes, E. RhoA/rho kinase pathway activation in age-associated endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Gardete, S.; Jansen, R.S.; Shetty, A.; Dick, T.; Rhee, K.Y.; Dartois, V. Verapamil Targets Membrane Energetics in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02107-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, D.; Merkel, P.; Eggers, L.F.; Schlüter, H. Proteolytic Processing of Angiotensin-I in Human Blood Plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elased, K.M.; Cool, D.R.; Morris, M. Novel mass spectrometric methods for evaluation of plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 1 and renin activity. Hypertension 2005, 46, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demichev, V.; Messner, C.B.; Vernardis, S.I.; Lilley, K.S.; Ralser, M. DIA-NN: Neural networks and interference correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat. Methods 2019, 17, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, J.D.; Cox, J. A Network Module for the Perseus Software for Computational Proteomics Facilitates Proteome Interaction Graph Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software Environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, S. Graph Clustering Via a Discrete Uncoupling Process. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2007, 30, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Bandeira, N.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Sharma, V.; Carver, J.J.; Mendoza, L.; Kundu, D.J.; Wang, S.; Bandla, C.; Kamatchinathan, S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium at 10 years: 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D1539–D1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: A hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oosthuizen, D.; Ganief, T.A.; Bernstein, K.E.; Sturrock, E.D. Proteomic Analysis of Human Macrophages Overexpressing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137055
Oosthuizen D, Ganief TA, Bernstein KE, Sturrock ED. Proteomic Analysis of Human Macrophages Overexpressing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137055
Chicago/Turabian StyleOosthuizen, Delia, Tariq A. Ganief, Kenneth E. Bernstein, and Edward D. Sturrock. 2024. "Proteomic Analysis of Human Macrophages Overexpressing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137055
APA StyleOosthuizen, D., Ganief, T. A., Bernstein, K. E., & Sturrock, E. D. (2024). Proteomic Analysis of Human Macrophages Overexpressing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137055





