Tofacitinib Regulates Endostatin via Effects on CD147 and Cathepsin S
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
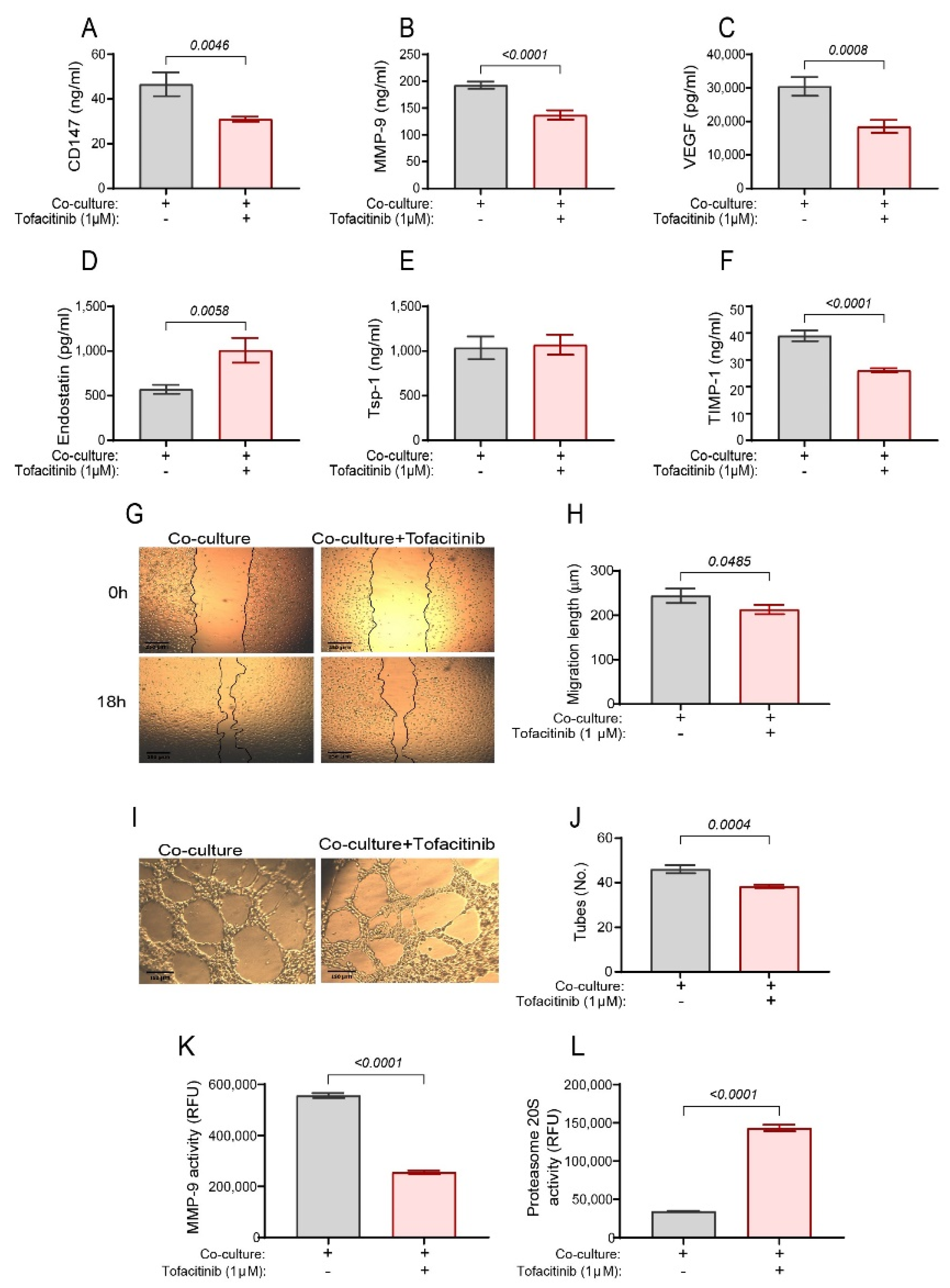
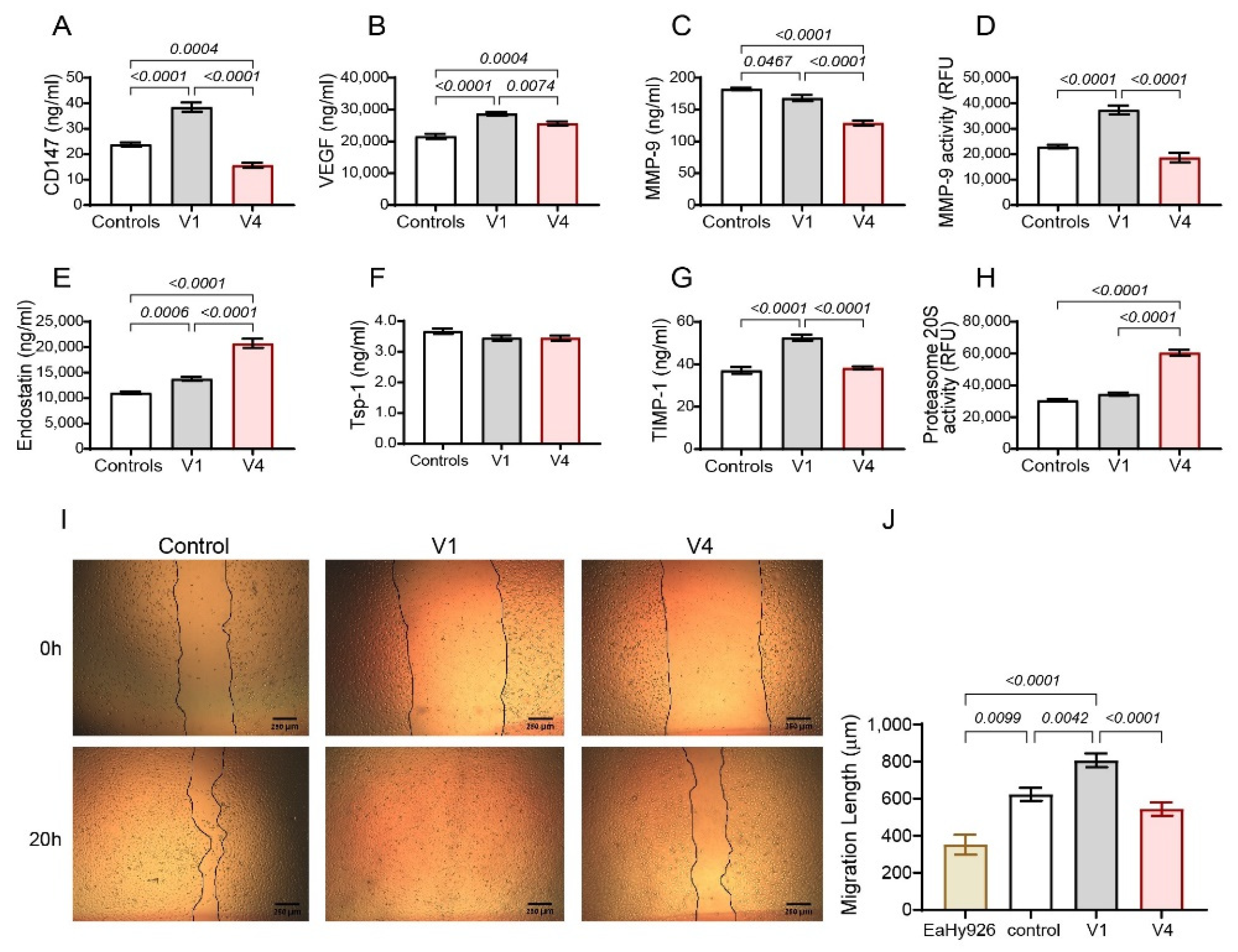
2.1. Tofacitinib Inhibits Angiogenesis in the Co-Culture and Oppositely Regulates MMP-9 and Proteasome 20S Activities
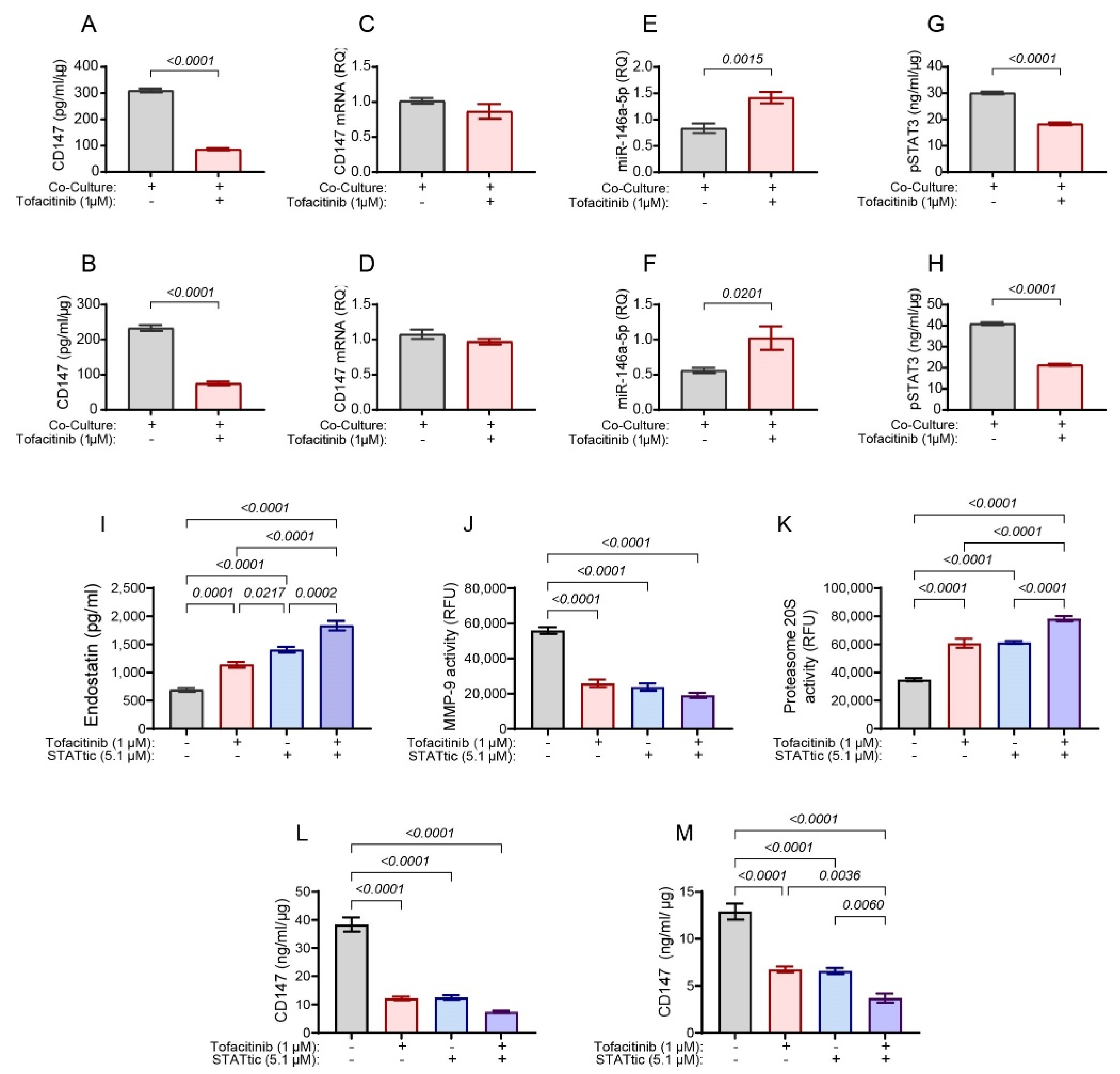
2.2. The Effects of Tofacitinib on Endostatin Are Partly Mediated by CD147
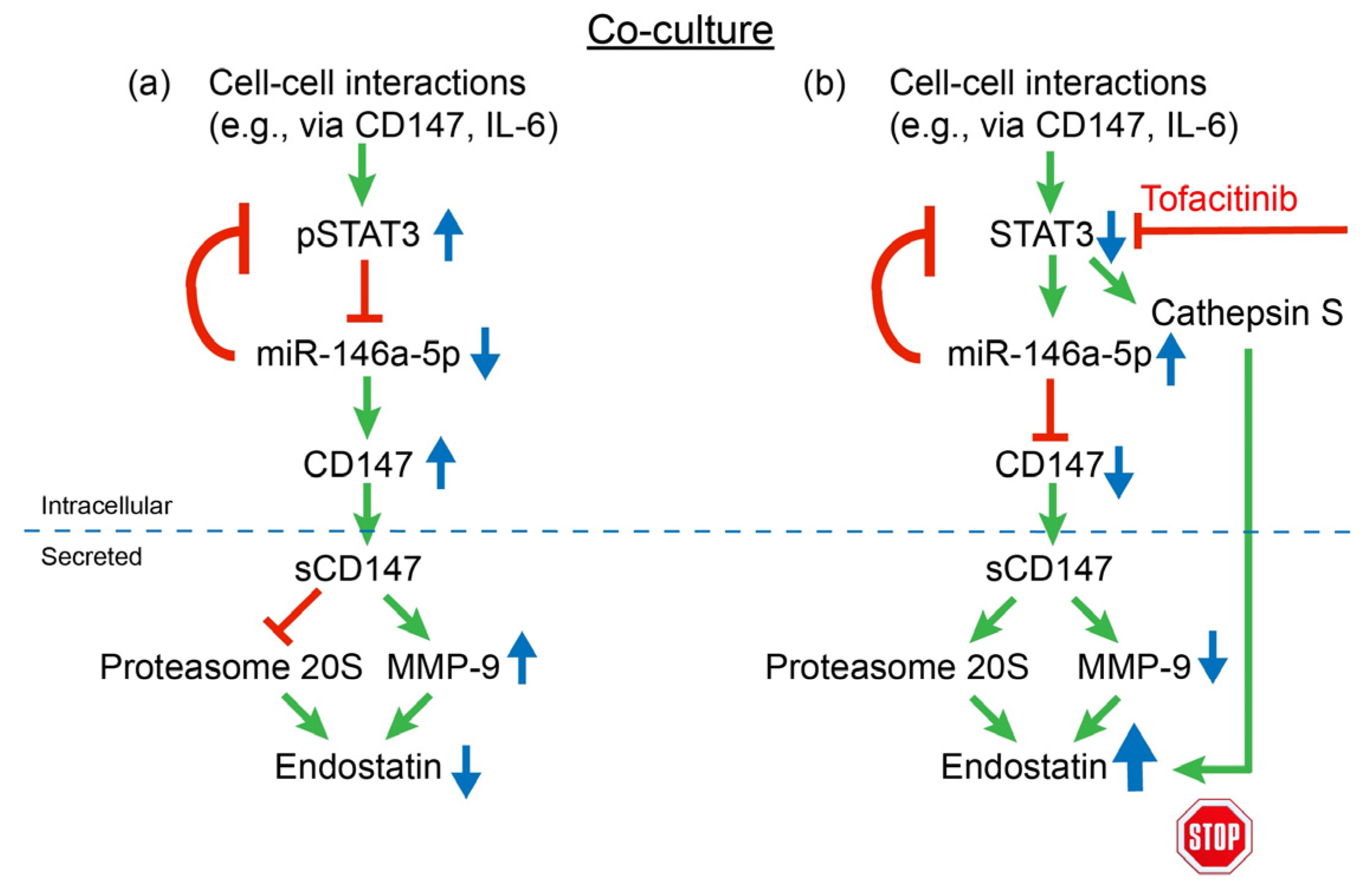
2.3. Tofacitinib Inhibits CD147 Expression through STAT3 and miR-146a-5p
2.4. Tofacitinib Reveals the Activity of Another Protease That Cleaves Endostatin
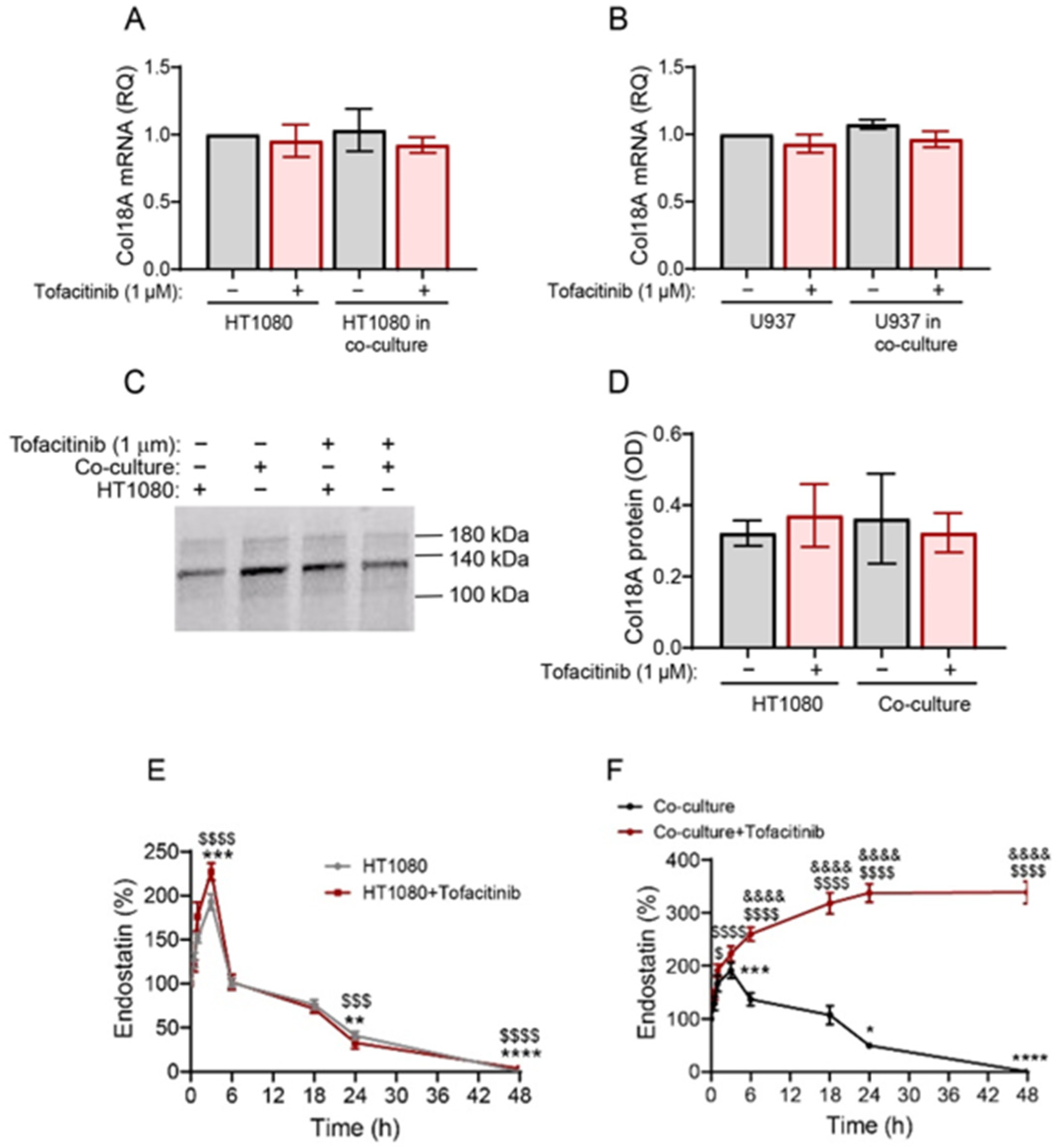
2.5. Tofacitinib Does Not Affect Col18A Transcription or Deposition but Inhibits the Degradation of Endostatin in Co-Cultures
2.6. Cathepsin S Degrades Endostatin and Tofacitinib Inhibits This Degradation and Extends the Half-Life of Endostatin
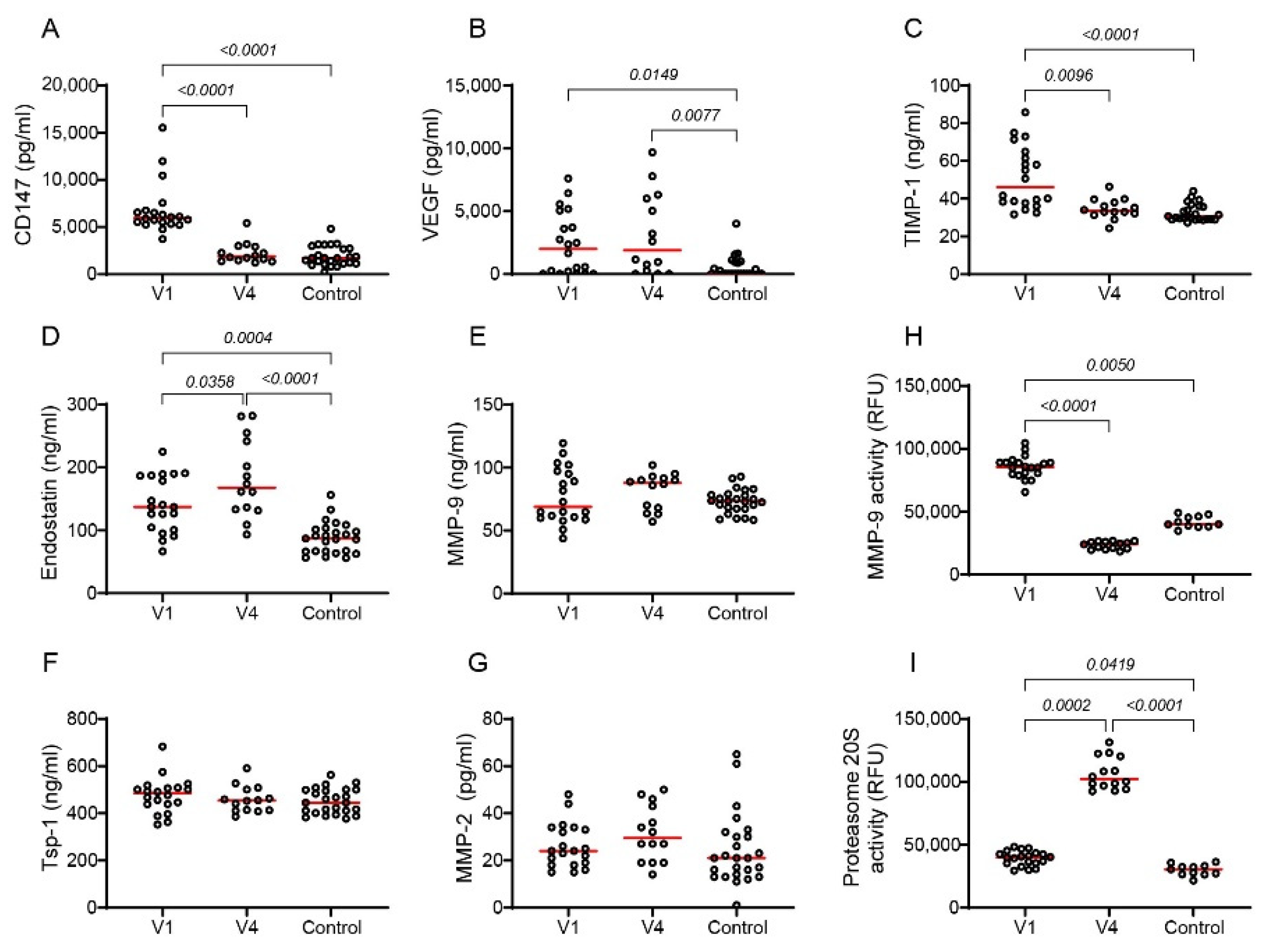
2.7. Tofacitinib Reduces Angiogenesis in RA Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultured Cells
4.2. Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.3. Reducing CD147 Expression by siRNA
4.4. Wound Assay
4.5. Tube Formation Assay
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Proteome Profiler Human Protease Array
4.9. MMP-9 Activity Assay
4.10. Proteasome 20S Activity Assay
4.11. Cathepsin S Activity Assay
4.12. Preparation of the De-Cellulararized Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
4.13. Study Population
4.14. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, H.E.; Chen, Z.; Volin, M.V.; Ravella, S.; Virupannavar, S.; Shahrara, S. The Pathogenic Role of Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, A.; Allanore, Y.; Avouac, J. Targeting synovial neoangiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Bertassoni, L.E.; Tayebi, L. Biological Aspects in Controlling Angiogenesis: Current Progress; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 79, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Hwang, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Pyun, B.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, S.T.; Gho, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.G. Endostatin blocks vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling via direct interaction with KDR/Flk-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27872–27879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, P.R.; Lawler, J. Molecular basis for the regulation of angiogenesis by thrombospondin-1 and -2. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, A.C.; Griffioen, A.W. Pathological angiogenesis: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 313–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, G.D.; Toole, B.P. How, with whom and when: An overview of CD147-mediated regulatory networks influencing matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Yao, H.; Chen, L.N.; Jia, J.F.; Wang, L.; Dai, J.Y.; Zheng, Z.H.; Chen, Z.N.; Zhu, P. CD147 induces angiogenesis through a vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α-mediated pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Lu, N.; Shi, Z.G.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, Z.N. CD147 overexpression on synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis enhances matrix metalloproteinase production and invasiveness of synoviocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, F.; Quemener, C.; Kellouche, S.; Naïmi, B.; Podgorniak, M.P.; Millot, G.; Gabison, E.E.; Calvo, F.; Dosquet, C.; Lebbé, C.; et al. EMMPRIN promotes angiogenesis through hypoxia-inducible factor-2α-mediated regulation of soluble VEGF isoforms and their receptor VEGFR-2. Blood 2009, 114, 5547–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisman, D.; Safieh, M.; Simanovich, E.; Feld, J.; Kinarty, A.; Zisman, L.; Gazitt, T.; Haddad, A.; Elias, M.; Rosner, I.; et al. Tocilizumab (TCZ) Decreases Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through Its Regulatory Effect on miR-146a-5p and EMMPRIN/CD147. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 739592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahat, M.A.; Safieh, M.; Simanovich, E.; Pasand, E.; Gazitt, T.; Haddad, A.; Elias, M.; Zisman, D. The role of EMMPRIN/CD147 in regulating angiogenesis in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, A.; Yang, J.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Chang, J.H.; Azar, D.T. Endostatin’s emerging roles in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, disease, and clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 2422–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Javier, J.A.D.; Chang, G.Y.; Oliveira, H.B.; Azar, D.T. Functional characterization of neostatins, the MMP-derived, enzymatic cleavage products of type XVIII collagen. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3601–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss-Pistilli, M.L.V.; Schuppan, D.; Barroso, M.M.S.; Assunção-Miranda, I.; Farias, S.; Lery, L.; Bauer, M.; Juliano, L.; Juliano, M.A.; Coelho-Sampaio, T. An extracellular proteasome releases endostatin from human collagen XVIII. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterstrom, U.K.; Felbor, U.; Fukai, N.; Olsen, B.R. Collagen XVIII/endostatin structure and functional role in angiogenesis. Cell Struct. Funct. 2000, 25, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillard, F.; Saidi, A.; Burden, R.E.; Scott, C.J.; Gillet, L.; Lecaille, F.; Lalmanach, G. Cysteine cathepsins S and L modulate anti-angiogenic activities of human endostatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37158–37167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Theocharis, A.D.; Piperigkou, Z.; Manou, D.; Passi, A.; Skandalis, S.S.; Vynios, D.H.; Orian-Rousseau, V.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Schmelzer, C.E.H.; et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6850–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahat, M.M.; Sabtan, H.; Simanovich, E.; Haddad, A.; Gazitt, T.; Feld, J.; Slobodin, G.; Kibari, A.; Elias, M.; Zisman, D.; et al. Soluble CD147 regulates endostatin via its effects on the activities of MMP-9 and secreted proteasome 20S. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1319939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornez, I.; Yajnanarayana, S.P.; Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D. JAK/STAT disruption induces immuno-deficiency: Rationale for the development of JAK inhibitors as immunosuppressive drugs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 451, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malemud, C.J. The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2018, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadina, M.; Johnson, C.; Schwartz, D.; Bonelli, M.; Hasni, S.; Kanno, Y.; Changelian, P.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Translational and clinical advances in JAK-STAT biology: The present and future of jakinibs. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; McGarry, T.; Orr, C.; McCormick, J.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Tofacitinib regulates synovial inflammation in psoriatic arthritis, inhibiting STAT activation and induction of negative feedback inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, C.H. STAT3: A critical transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling suppresses pathogenic immune responses in medium and large vessel vasculitis. Circulation 2018, 137, 1934–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, G.; Czókolyová, M.; Hamar, A.; Pusztai, A.; Tajti, G.; Katkó, M.; Végh, E.; Petho, Z.; Bodnár, N.; Horváth, Á.; et al. Effects of 1-year tofacitinib therapy on angiogenic biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, SI304–SI312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Panzera, N.; Grazia, N.; Di Vito Nolfi, M.; Di Francesco, B.; Navarini, L.; Maurizi, A.; Rucci, N.; et al. Blocking Jak/STAT signalling using tofacitinib inhibits angiogenesis in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanovich, E.; Brod, V.; Rahat, M.M.; Rahat, M.A. Function of miR-146a-5p in Tumor Cells As a Regulatory Switch between Cell Death and Angiogenesis: Macrophage Therapy Revisited. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.; van Riel, P.L.C. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, S93–S99. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, S. Tofacitinib: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traves, P.G.; Murray, B.; Campigotto, F.; Galien, R.; Meng, A.; Di Paolo, J.A. JAK selectivity and the implications for clinical inhibition of pharmacodynamic cytokine signalling by filgotinib, upadacitinib, tofacitinib and baricitinib. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Kesavan, P.; Nakada, M.T.; Yan, L. Tumor-stroma interaction: Positive feedback regulation of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) expression and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent generation of soluble EMMPRIN. Mol. Cancer Res. 2004, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J. Cluster of differentiation 147 is a key molecule during hepatocellular carcinoma cell-hepatic stellate cell cross-talk in the rat liver. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Lilly, B. Fibroblasts potentiate blood vessel formation partially through secreted factor TIMP-1. Angiogenesis 2008, 11, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojiani, M.V.; Ghoshal-Gupta, S.; Kutiyanawalla, A.; Mathur, S.; Rojiani, A.M. TIMP-1 overexpression in lung carcinoma enhances tumor kinetics and angiogenesis in brain metastasis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.-X.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.-N. microRNA-146a inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating VEGF through dual pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutti, N.; Huber, O.; Friedrich, K. CD147 (EMMPRIN) controls malignant properties of breast cancer cells by interdependent signaling of Wnt and JAK/STAT pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 451, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emori, T.; Kasahara, M.; Sugahara, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Ito, H.; Narumiya, S.; Higashi, Y.; Fujii, Y. Role of JAK-STAT signaling in the pathogenic behavior of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Effect of the novel JAK inhibitor peficitinib. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 882, 173238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Z.; Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z. MiR-146a is directly regulated by STAT3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involved in anti-tumor immune suppression. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, E.A.; Steinle, J.J. miR-146a suppresses STAT3/VEGF pathways and reduces apoptosis through IL-6 signaling in primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in high glucose conditions. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xue, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, D.; Yu, C.; Peng, J. STAT3-activated lncRNA XIST accelerates the inflammatory response and apoptosis of LPS-induced acute lung injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6550–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.L.Y.; Cheung, B.K.W.; Li, J.C.B.; Lau, A.S.Y. A role for STAT3 and cathepsin S in IL-10 down-regulation of IFN-γ-induced MHC class II molecule on primary human blood macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Control | RA Group | p Value | Non-Responding * | Responding * | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 25 | 20 | - | 3 | 11 | |
| Sex: Female (%) | 19 (95%) | 17 (85%) | ns | 3 (100%) | 10 (91%) | ns |
| Age (years) ± SD | 51.44 ± 2.10 | 65.1 ± 6.05 | 0.0007 | 80 ± 3.8 | 63.91 ± 3.7 | 0.0385 |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) ± SD | 26.56 ± 1.19 | 27.5 ± 1.09 | ns | 25.13 ± 2.5 | 27.47 ± 1.5 | ns |
| Disease duration (years) ± SD | - | 9.9 ± 1.9 | - | 22.0 ± 9.0 | 8.2 ± 2.01 | ns |
| Tobacco use (%) | 3 (15%) | 4 (20%) | ns | 0 (0%) | 2 (18.2%) | ns |
| Alcohol use (%) | 7 (35%) | 0 (0%) | 0.0123 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ns |
| RF factor (%) | 0 (0%) | 17 (40%) | 0.0017 | 1 (33.3%) | 3 (27.3%) | ns |
| CRP ± SD | - | 1.534 ± 0.33 | - | 0.29 ± 0.26 | 1.53 ± 0.43 | 0.0385 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension (%) | - | 10 (50%) | - | 2 (66.6%) | 7 (63.6%) | ns |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | - | 5 (25%) | - | 1 (33.3%) | 3 (27.3%) | ns |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | - | 4 (20%) | - | 0 (0%) | 3 (27.3%) | ns |
| Medication (at baseline) | ||||||
| Methotrexate (MTX) | - | 20 (100%) | - | 3 (100%) | 11 (100%) | ns |
| Leflunomide (LEF) | - | 1 (5%) | - | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) | ns |
| Sulfasalazine (SSZ) | - | 1 (5%) | - | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) | ns |
| Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil-PLQ) | - | 3 (15%) | - | 0 (0%) | 3 (27.3%) | ns |
| Corticosteroid (%) | - | 3 (15%) | - | 0 (0%) | 2 (18.2%) | ns |
| Spearman r | 95% CI | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endostatin | −0.1499 | −0.469 to 0.203 | ns |
| MMP-9 | −0.0871 | −0.423 to 0.268 | ns |
| TIMP-1 | 0.6159 | 0.342 to 0.793 | 0.0001 |
| CRP | 0.7482 | 0.492 to 0.885 | <0.0001 |
| TJC | 0.4659 | 0.136 to 0.703 | 0.0063 |
| SJC | 0.6656 | 0.409 to 0.825 | <0.0001 |
| CDAI | 0.5259 | 0.186 to 0.753 | 0.0034 |
| DAS28 | 0.5805 | 0.246 to 0.791 | 0.0015 |
| MMP-9 activity | 0.6529 | 0.395 to 0.815 | <0.0001 |
| Proteasome 20S activity | −0.6196 | −0.796 to −0.347 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zisman, D.; Sabtan, H.; Rahat, M.M.; Simanovich, E.; Haddad, A.; Gazitt, T.; Feld, J.; Slobodin, G.; Kibari, A.; Elias, M.; et al. Tofacitinib Regulates Endostatin via Effects on CD147 and Cathepsin S. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137267
Zisman D, Sabtan H, Rahat MM, Simanovich E, Haddad A, Gazitt T, Feld J, Slobodin G, Kibari A, Elias M, et al. Tofacitinib Regulates Endostatin via Effects on CD147 and Cathepsin S. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137267
Chicago/Turabian StyleZisman, Devy, Hala Sabtan, Maya M. Rahat, Elina Simanovich, Amir Haddad, Tal Gazitt, Joy Feld, Gleb Slobodin, Adi Kibari, Muna Elias, and et al. 2024. "Tofacitinib Regulates Endostatin via Effects on CD147 and Cathepsin S" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137267
APA StyleZisman, D., Sabtan, H., Rahat, M. M., Simanovich, E., Haddad, A., Gazitt, T., Feld, J., Slobodin, G., Kibari, A., Elias, M., & Rahat, M. A. (2024). Tofacitinib Regulates Endostatin via Effects on CD147 and Cathepsin S. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137267





_Amit_Rahat.jpg)

