The Effects of Sevoflurane and Aβ Interaction on CA1 Dendritic Spine Dynamics and MEGF10-Related Astrocytic Synapse Engulfment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Sevoflurane and Its Interaction with Aβ Isoforms on DSD
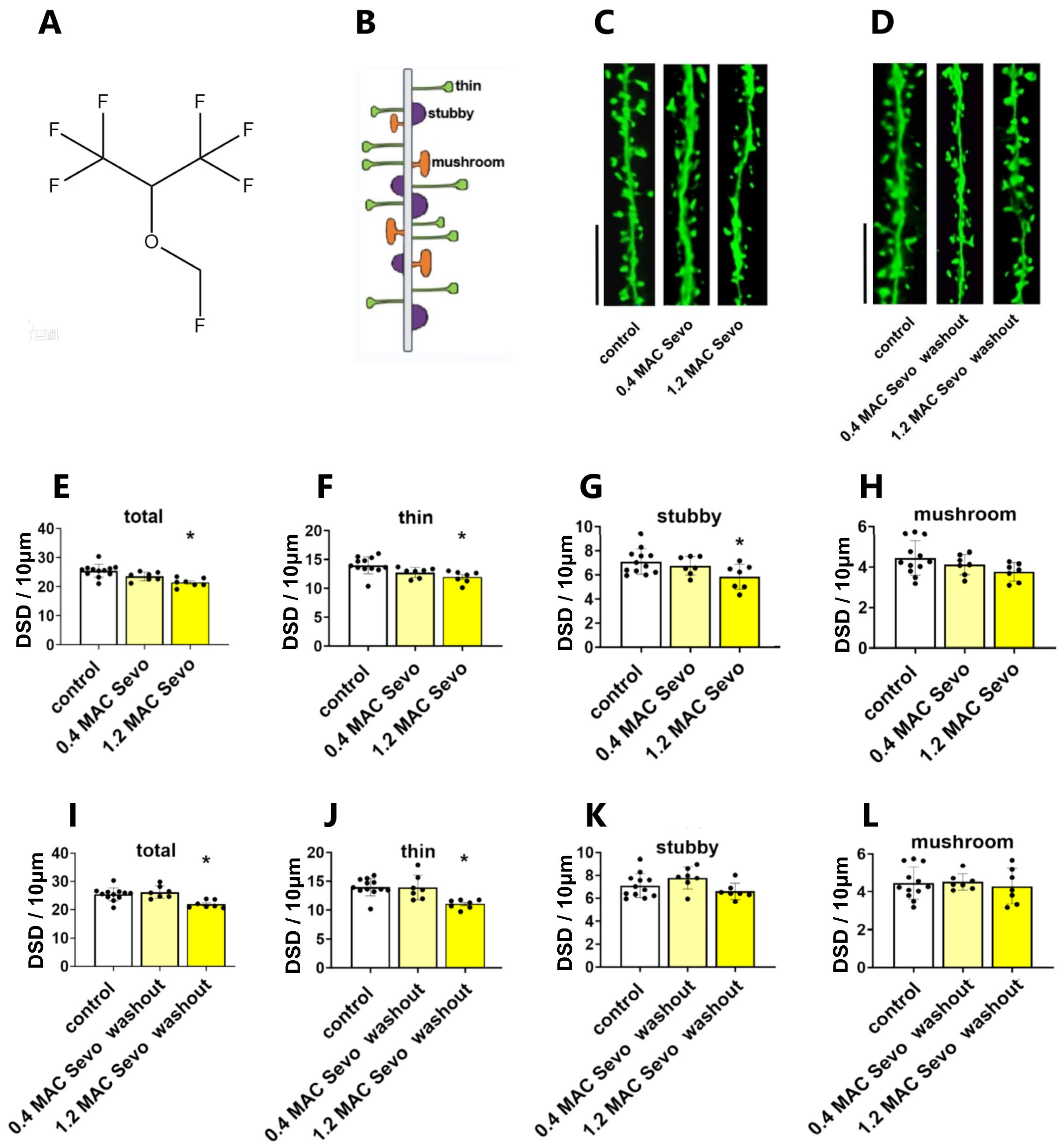
2.1.1. Sevoflurane at 0.4/1.2 MAC Decreases DSD
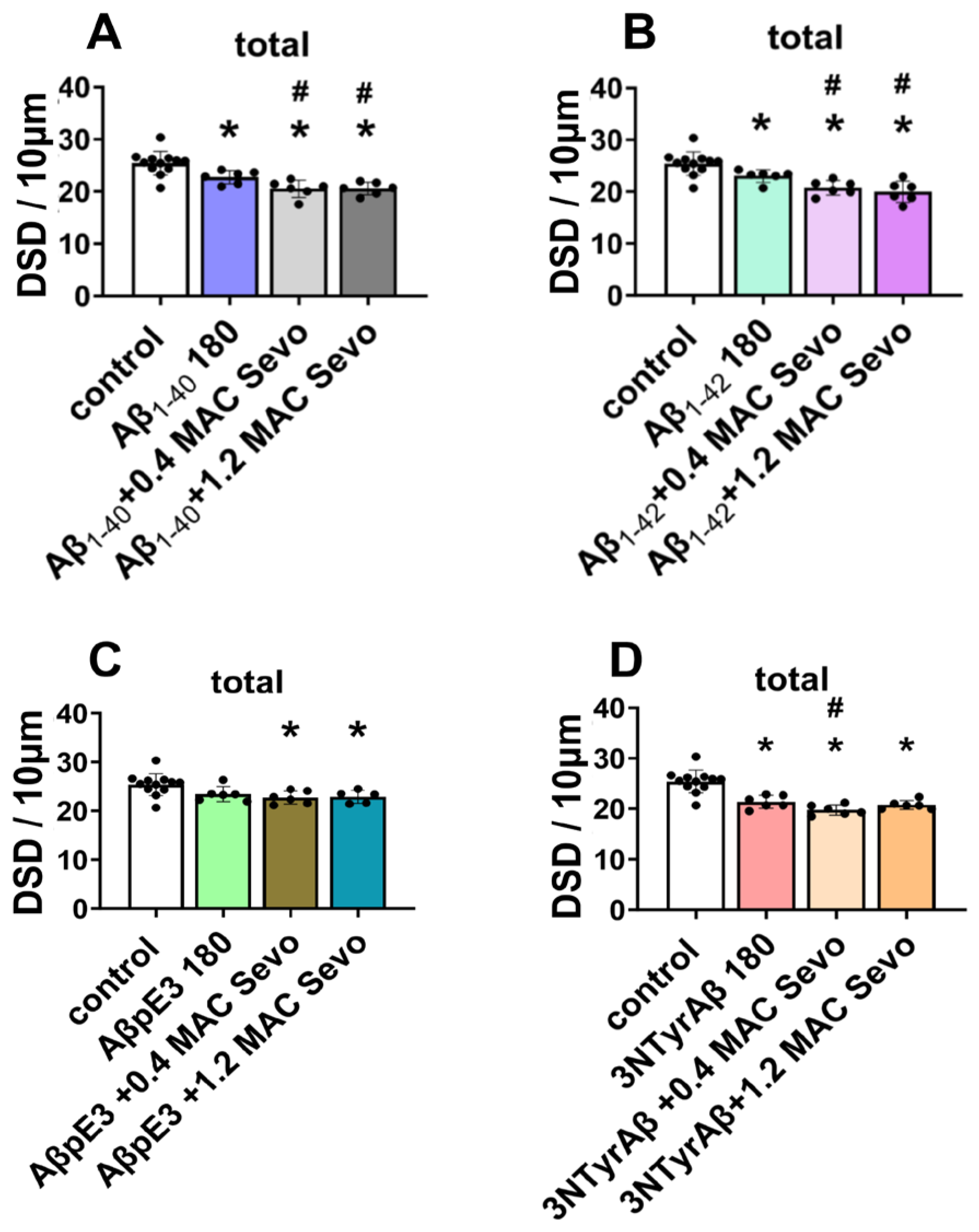
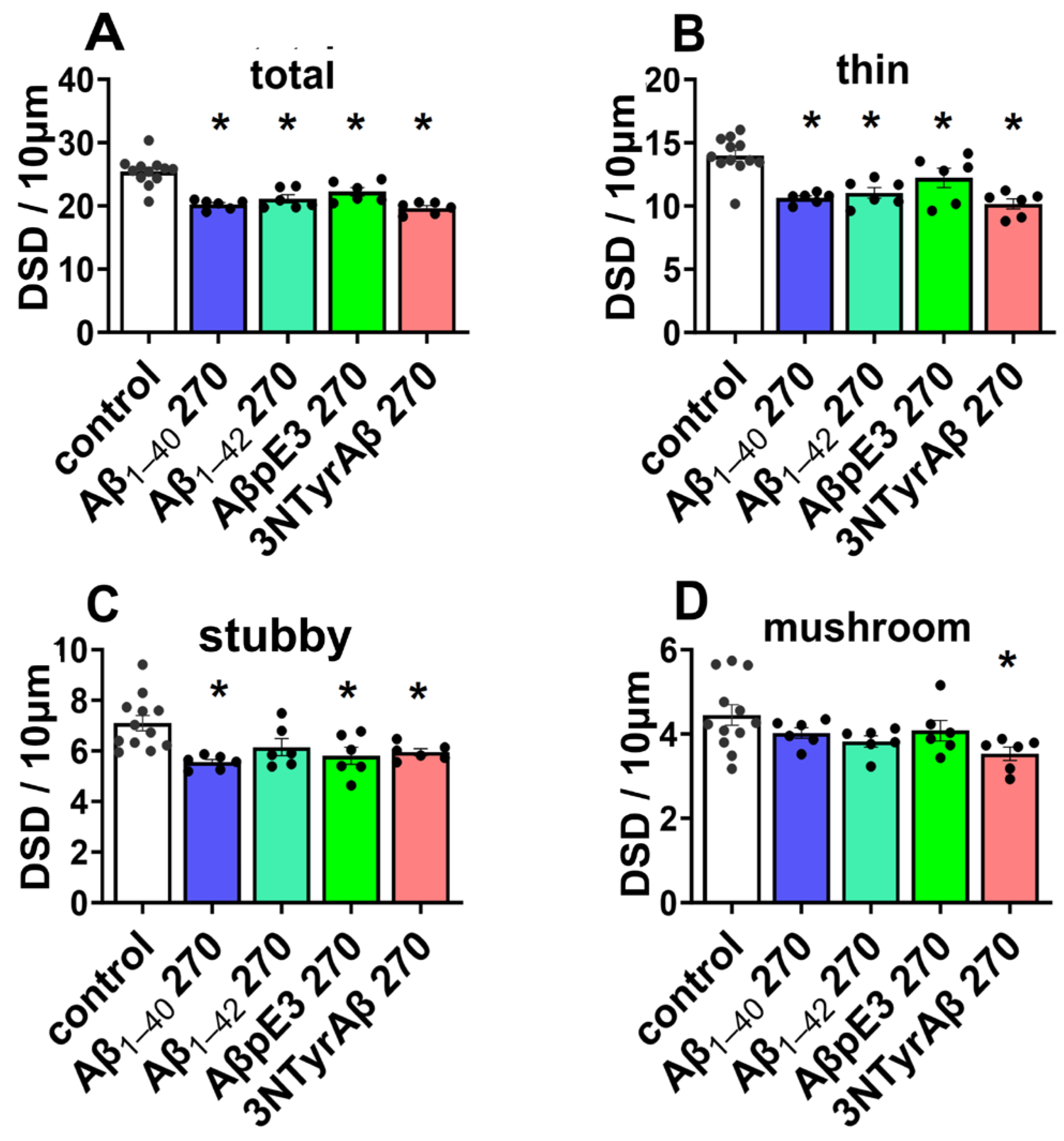
2.1.2. Effects of Aβ Pre-Treatment 90 min + Sevoflurane 90 min on DSD
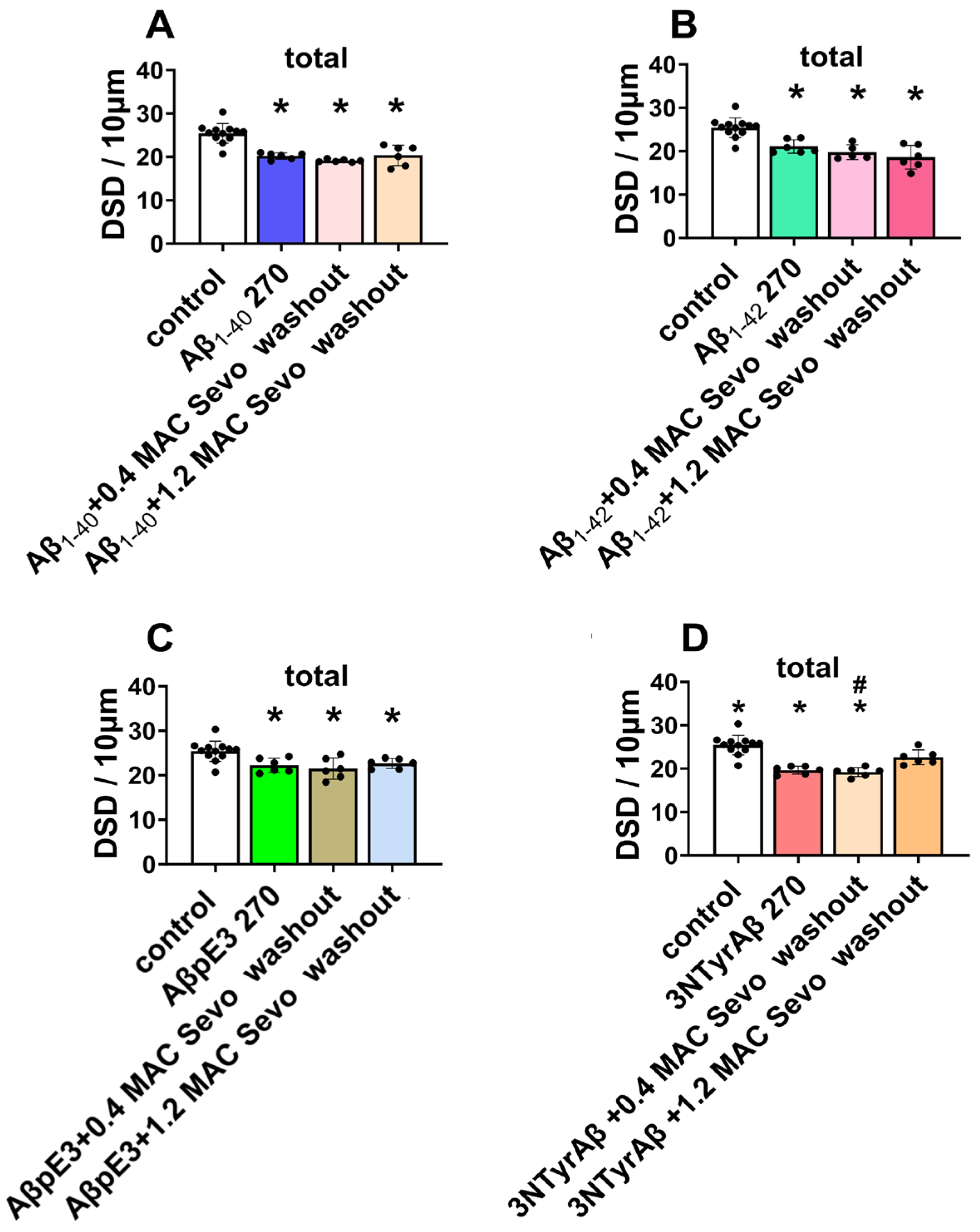
2.1.3. Effects of Sevoflurane Removal for 90 min on DSD
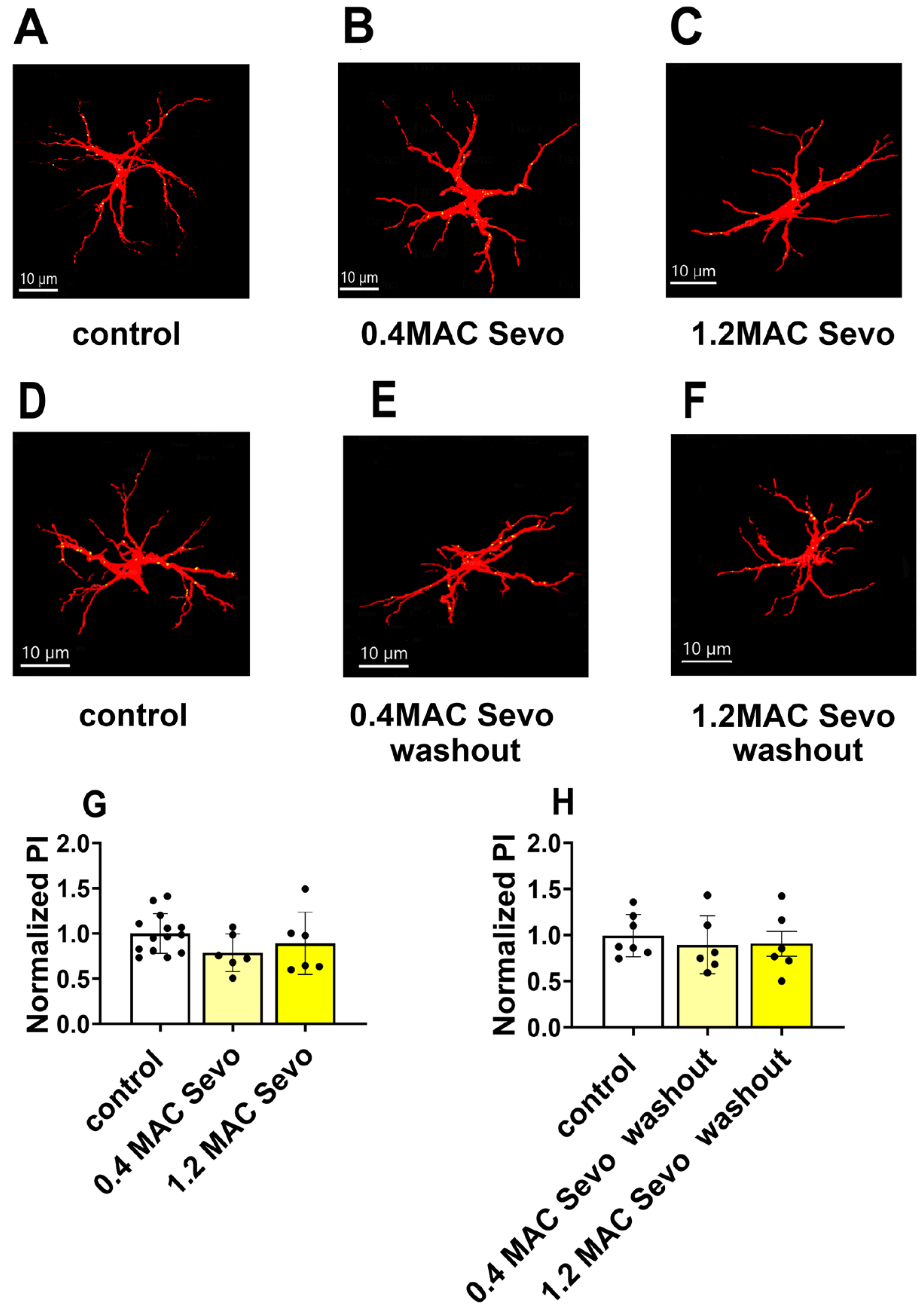
2.2. Effects of Sevoflurane and Its Interaction with Aβ on Astrocyte-Mediated Synaptic Engulfment
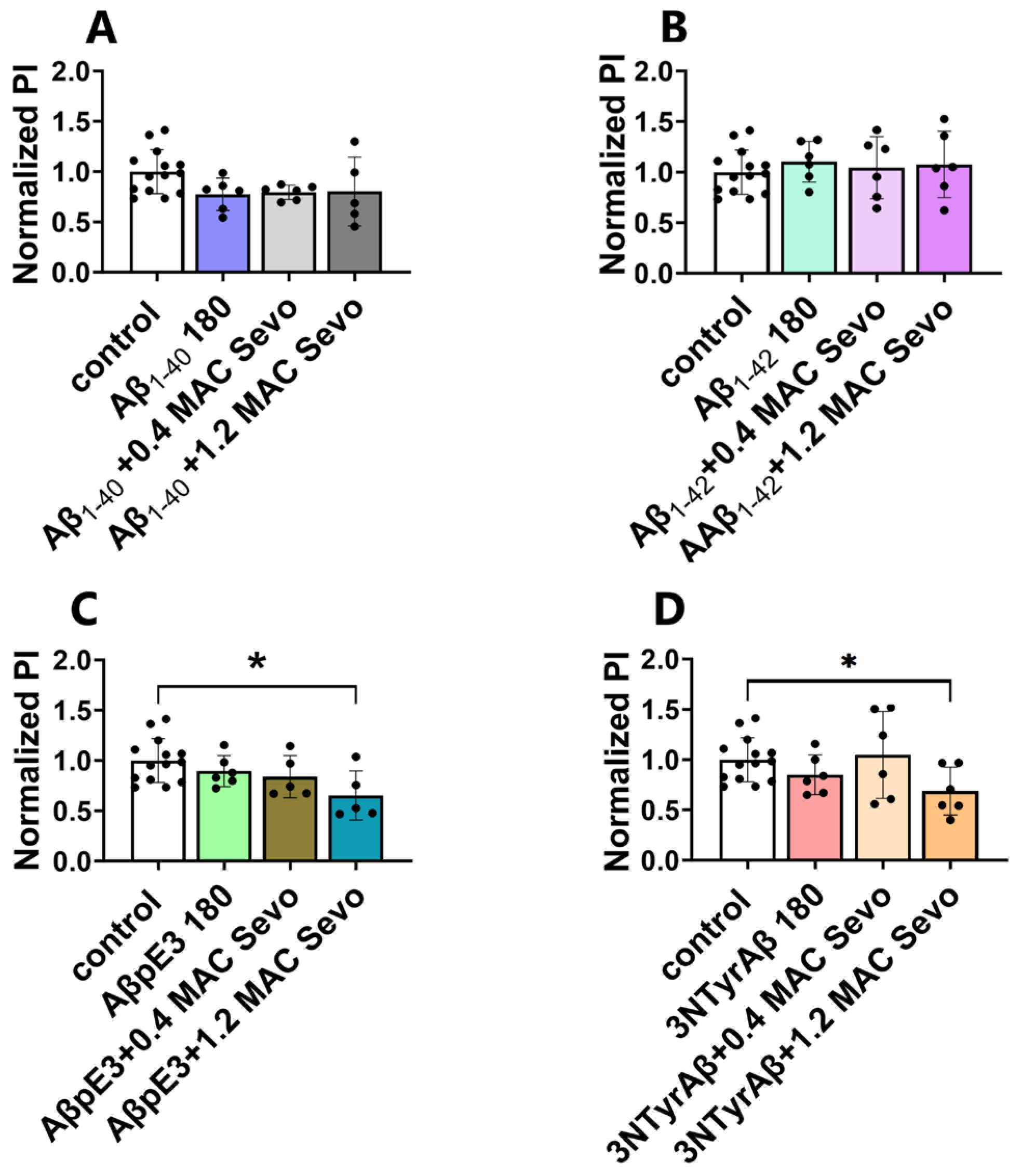
2.2.1. Effects of Aβ Pre-Treatment 90 min + Sevoflurane 90 min on Astrocyte-Mediated Synaptic Engulfment
2.2.2. 1.2 MAC Sevoflurane Decreases Astrocyte-Mediated Synaptic Engulfment in Acute Hippocampal Brain Slices Pretreated with AβpE3/3NTyrAβ
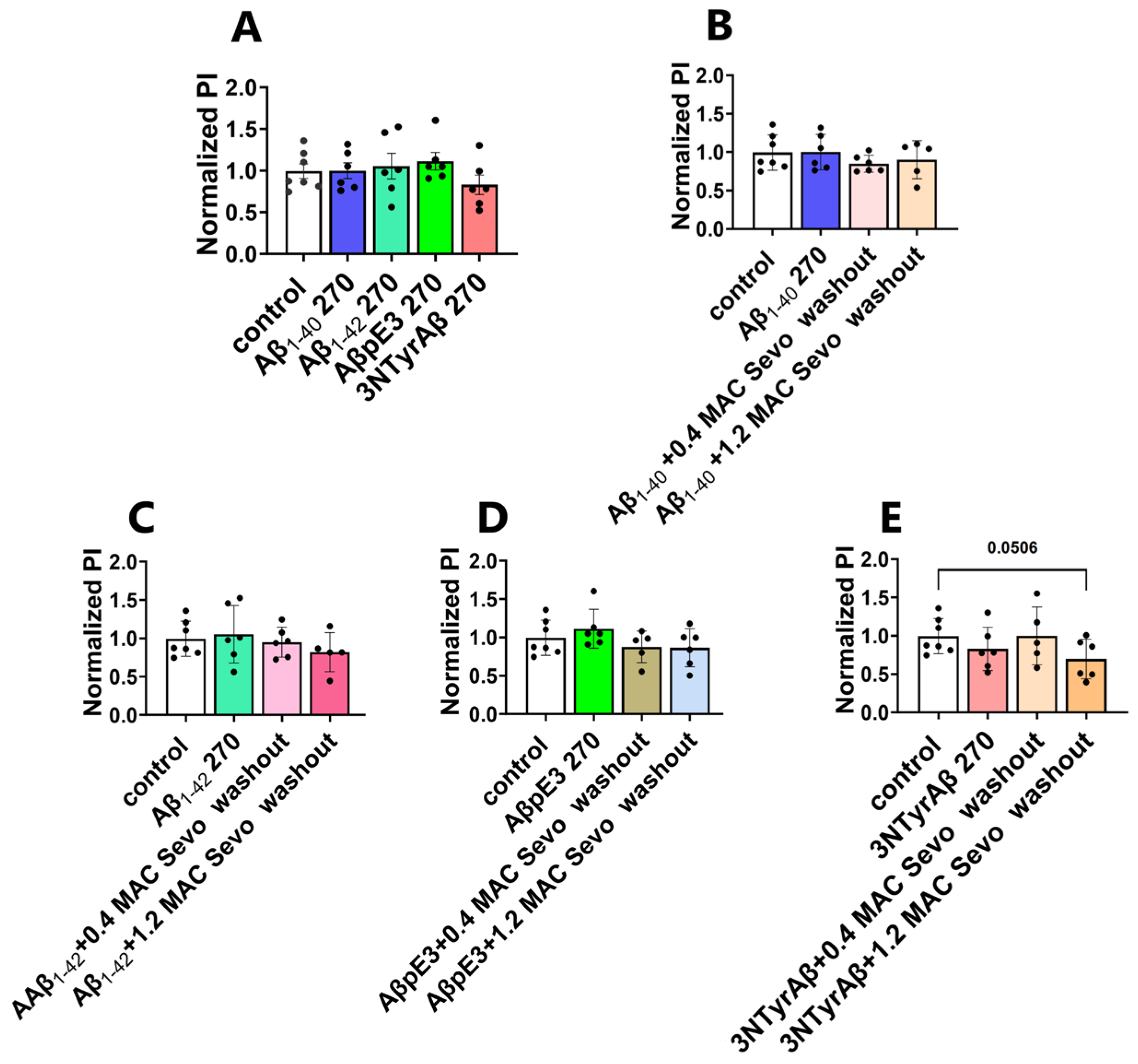
2.2.3. Removal of 1.2 MAC Sevoflurane Decreases Astrocyte-Mediated Synaptic Engulfment in Acute Hippocampal Brain Slices Pretreated Only with 3NTyrAβ
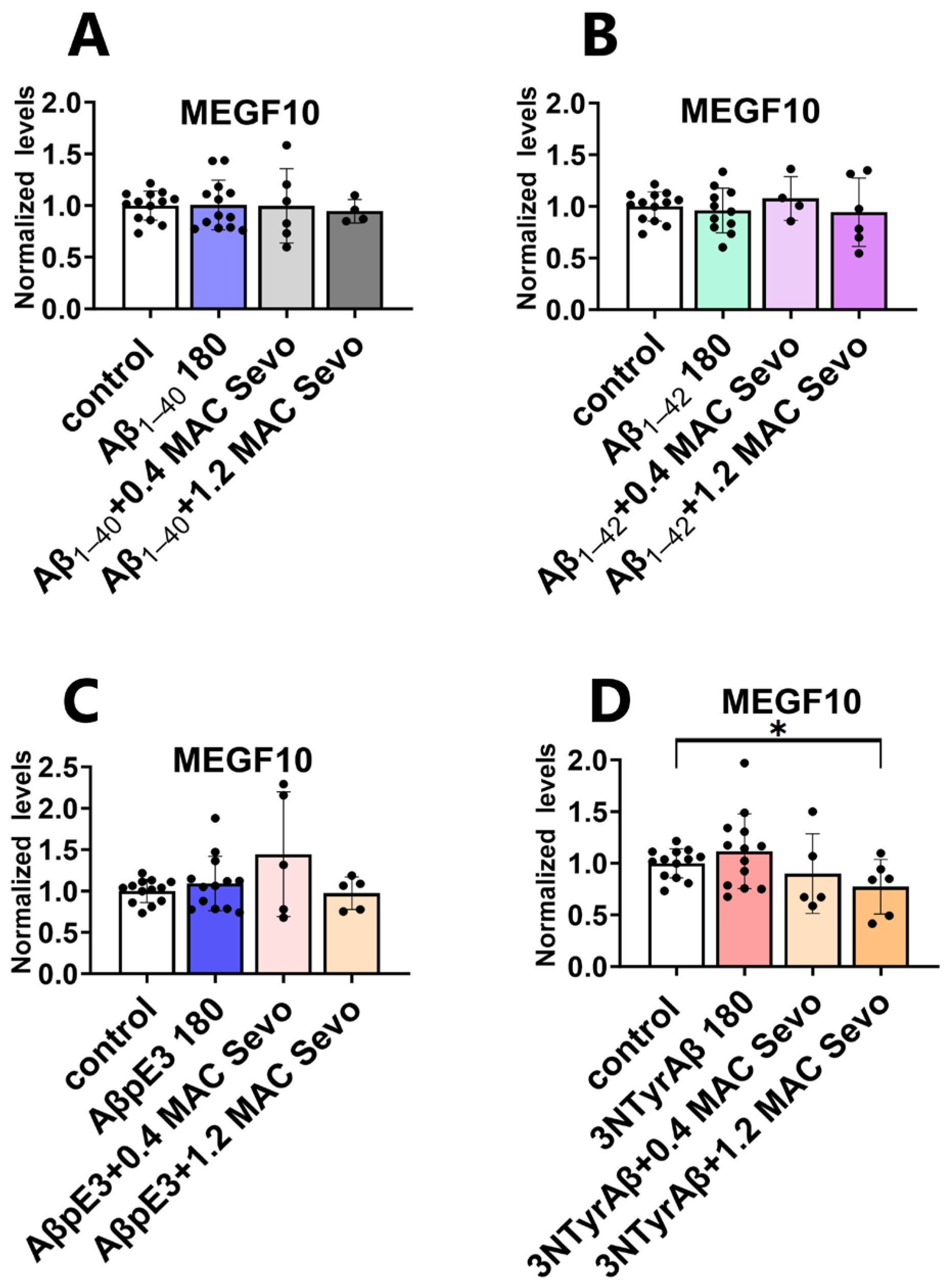
2.3. Effects of Sevoflurane and Its Interaction with 3NTyrAβ on the Expression of MEGF10
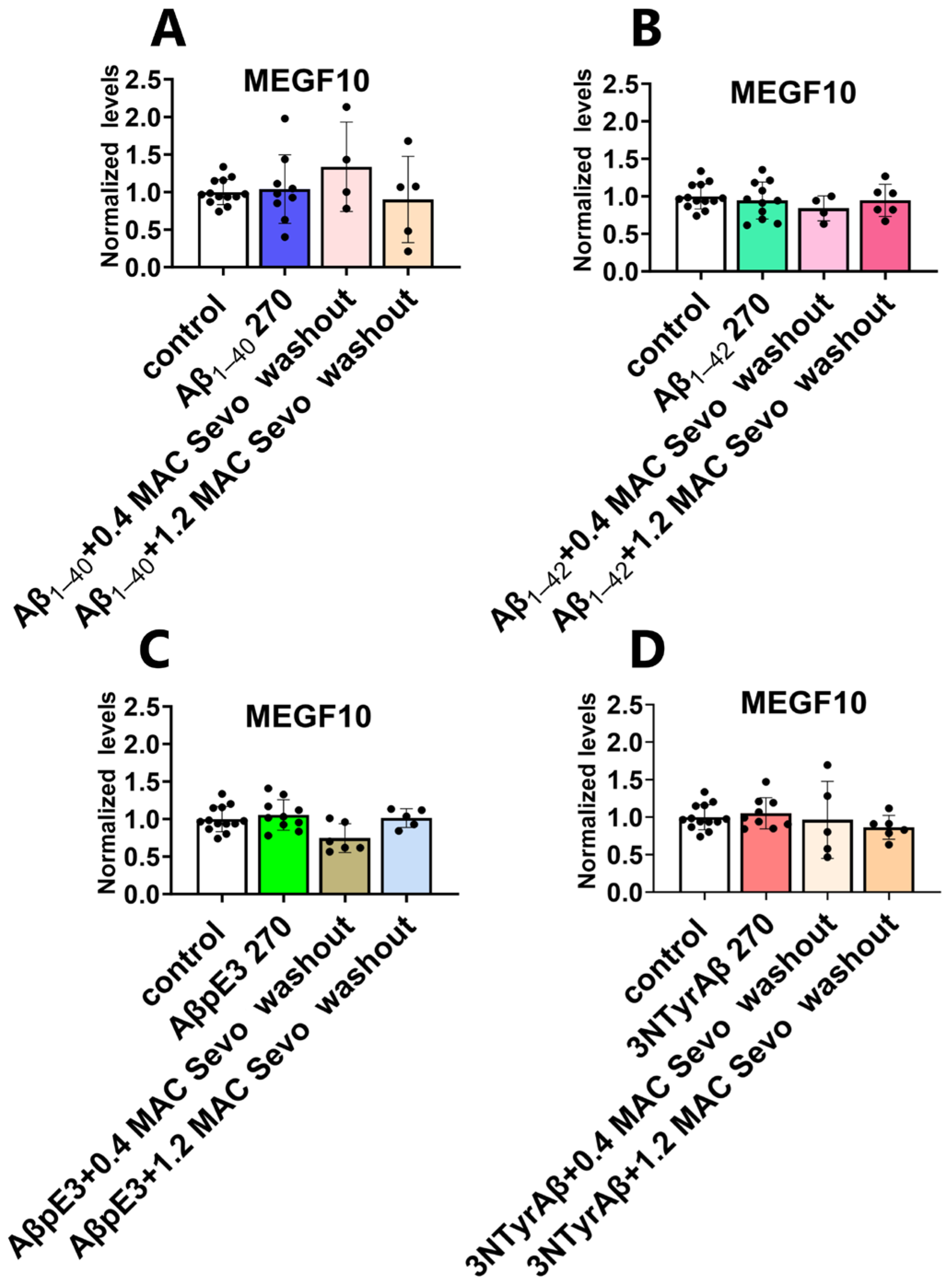
2.3.1. Neither 0.4 MAC nor 1.2 MAC Sevoflurane Affects the MEGF10 Expressions
2.3.2. The Downregulation of MEGF10 Expression by Co-Application of 1.2 MAC Sevoflurane with 3NTyrAβ Is Diminished after the Removal of Sevoflurane
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Preparation of Acute Hippocampal Brain Slices
4.3. Aβ Preparation and Incubation
4.4. Sevoflurane Application
4.5. Experiment Schedule and Workflow
4.6. Analysis of Dendritic Spines
4.7. Immunofluorescence and Colocalization Analysis
4.7.1. Immunofluorescence Staining and Image Acquisition
4.7.2. Quantitative Analysis of Astrocyte-Mediated Synaptic Engulfment
4.8. Western Blotting
4.8.1. Sample Preparation
4.8.2. Preparation of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.8.3. Electrophoresis and Transferring
4.8.4. Blocking and Antibody Incubation
4.8.5. Analysis of Western Blots
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 367–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutskits, L.; Xie, Z. Lasting impact of general anaesthesia on the brain: Mechanisms and relevance. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Pradhan, A.K.; Ziegon, L.; Schlegel, M.; Rammes, G. Beta-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein-Cleaving Enzyme Inhibition Partly Restores Sevoflurane-Induced Deficits on Synaptic Plasticity and Spine Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, D.P.; Wesnes, K.; Ballard, C.G. Subtle attentional deficits in the absence of dementia are associated with an increased risk of post-operative delirium. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2007, 23, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, Y.; Zac, L.; Refaeli, E.; Ben-Yishai, S.; Zegerman, A.; Cohen, B.; Matot, I. Preoperative Cognitive Impairment and Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Surgical Patients—A Retrospective Large Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. 2022, 278, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagna, J.A.; Miller, K.W.; Forman, S.A. Mechanisms of Actions of inhaled anesthetics. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strum, D.P.; Eger, E.I., 2nd. Partition coefficients for sevoflurane in human blood, saline, and olive oil. Anesth. Analg. 1987, 66, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Anesthetic sevoflurane causes neurotoxicity differently in neonatal naive and Alzheimer disease transgenic mice. Anesthesiology 2010, 112, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Moir, R.D.; Xia, W.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Culley, D.J.; Crosby, G.; Tanzi, R.E.; Xie, Z. The Common Inhalational Anesthetic Sevoflurane Induces Apoptosis and Increases Amyloid Protein Levels. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Liu, L.D.; Dong, Y.X.; Zhao, P.; Guo, S.B. Sevoflurane Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment Induced by Abeta (1-40) in Rats through Initiating Neurotoxicity, Neuroinflammation, and Neuronal Apoptosis in Rat Hippocampus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3802324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, H. Effect of the inhaled anesthetics isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane on the neuropathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Culley, D.J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Moir, R.D.; Frosch, M.P.; Crosby, G.; Tanzi, R.E. The common inhalation anesthetic isoflurane induces caspase activation and increases amyloid beta-protein level in vivo. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Freche, H.; Brouillette, J.; Fernandez-Gomez, F.J.; Patin, P.; Caillierez, R.; Zommer, N.; Sergeant, N.; Buée-Scherrer, V.; Lebuffe, G.; Blum, D.; et al. Tau phosphorylation and sevoflurane anesthesia: An association to postoperative cognitive impairment. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Ran, K.; Liu, J.P. Delayed preconditioning by sevoflurane elicits changes in the mitochondrial proteome in ischemia-reperfused rat hearts. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Ramos, V.; Mesa Suárez, P.; Santotoribio, J.D.; González García, M.Á.; Muñoz Hoyos, A. Neuroprotective effect of sevoflurane in general anaesthesia. Med. Clínica (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 148, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karran, E.; Mercken, M.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: An appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, C.; Sander, A.; Wang, X.X.; Buerge, M.; Jungwirth, B.; Borgstedt, L.; Kreuzer, M.; Kopp, C.; Schorpp, K.; Hadian, K.; et al. Inhalational Anesthetics Do Not Deteriorate Amyloid-β-Derived Pathophysiology in Alzheimer’s Disease: Investigations on the Molecular, Neuronal, and Behavioral Level. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 84, 1193–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, H.; Takio, K.; Ogawara, M.; Selkoe, D.J. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17082–17086. [Google Scholar]
- Kummer, M.P.; Heneka, M.T. Truncated and modified amyloid-beta species. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.L.; Le, K.X.; Cynis, H.; Ekpo, E.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Palmour, R.M.; Ervin, F.R.; Snigdha, S.; Cotman, C.W.; Saido, T.C.; et al. Pyroglutamate-3 amyloid-beta deposition in the brains of humans, non-human primates, canines, and Alzheimer disease-like transgenic mouse models. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Jawhar, S.; Wirths, O.; Bayer, T.A. Pyroglutamate Amyloid-β (Aβ): A Hatchet Man in Alzheimer Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38825–38832. [Google Scholar]
- Kummer, M.P.; Hermes, M.; Delekarte, A.; Hammerschmidt, T.; Kumar, S.; Terwel, D.; Walter, J.; Pape, H.C.; Konig, S.; Roeber, S.; et al. Nitration of tyrosine 10 critically enhances amyloid beta aggregation and plaque formation. Neuron 2011, 71, 833–844. [Google Scholar]
- Rammes, G.; Seeser, F.; Mattusch, K.; Zhu, K.; Haas, L.; Kummer, M.; Heneka, M.; Herms, J.; Parsons, C.G. The NMDA receptor antagonist Radiprodil reverses the synaptotoxic effects of different amyloid-beta (Abeta) species on long-term potentiation (LTP). Neuropharmacology 2018, 140, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheva, K.D.; Weinberg, R.J.; Smith, S.J. A synapse census for the ages. Science 2020, 369, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, J.C.; Grienberger, C. Synaptic Plasticity Forms and Functions. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, C.D.; Olive, M.F. Structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines—Root or result of behavior? Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Bestard-Lorigados, I.; Song, W. The synapse as a treatment avenue for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, T. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granak, S.; Hoschl, C.; Ovsepian, S.V. Dendritic spine remodeling and plasticity under general anesthesia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2021, 226, 2001–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite synapses: Glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, G.; Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Tripartite synapses: Astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.S.; Allen, N.J.; Eroglu, C. Astrocytes Control Synapse Formation, Function, and Elimination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attardo, A.; Fitzgerald, J.E.; Schnitzer, M.J. Impermanence of dendritic spines in live adult CA1 hippocampus. Nature 2015, 523, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.S.; Clarke, L.E.; Wang, G.X.; Stafford, B.K.; Sher, A.; Chakraborty, C.; Joung, J.; Foo, L.C.; Thompson, A.; Chen, C.; et al. Astrocytes mediate synapse elimination through MEGF10 and MERTK pathways. Nature 2013, 504, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Wan, Z.; Gu, F.; Ma, L.; Leng, Y. Hippocampal astrocyte dysfunction contributes to etomidate-induced long-lasting synaptic inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, K.; Miao, H.; Li, T. The Role of Astrocytes in the Mechanism of Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, D.; Bickler, P.E.; Crosby, G.J.; Culley, D.J.; Eckenhoff, M.F.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Hogan, K.J.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Palotas, A.; Perouansky, M.; et al. Consensus statement: First International Workshop on Anesthetics and Alzheimer’s disease. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Liang, G.; Wu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Joseph, D.J.; Inan, S.; Wei, H. Dual Effects of Isoflurane on Proliferation, Differentiation, and Survival in Human Neuroprogenitor Cells. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Inan, S. Dual effects of neuroprotection and neurotoxicity by general anesthetics: Role of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; McAuliffe, S.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ichinose, F.; Yue, Y.; Xie, Z. The potential dual effects of anesthetic isoflurane on Aβ-induced apoptosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Hu, J.; Ma, D. Postoperative delirium: Perioperative assessment, risk reduction, and management. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseneder, R.; Kratzer, S.; von Meyer, L.; Eder, M.; Kochs, E.; Rammes, G. Isoflurane and sevoflurane dose-dependently impair hippocampal long-term potentiation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 623, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wong, J.K.Y.; Zhu, K.; Noakes, P.G.; Rammes, G. The Anaesthetics Isoflurane and Xenon Reverse the Synaptotoxic Effects of Abeta(1-42) on Megf10-Dependent Astrocytic Synapse Elimination and Spine Density in Ex Vivo Hippocampal Brain Slices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, K.; Cardoso, C.; de Chevigny, A. Dendritic Spine Plasticity: Function and Mechanisms. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2020, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Homma, K.J.; Poo, M.M. Shrinkage of dendritic spines associated with long-term depression of hippocampal synapses. Neuron 2004, 44, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, H.; Sheng, M. Dentritic spines: Structure, dynamics and regulation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Ou, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C. The Effects of General Anesthetics on Synaptic Transmission. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 936–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platholi, J.; Hemmings, H.C. Effects of General Anesthetics on Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.C.; Pan, A.; Li, L.; Sedensky, M.; Morgan, P. Neurotoxicity of anesthetics: Mechanisms and meaning from mouse intervention studies. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 71, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Noh, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Mun, J.Y.; Park, H.; Chung, W.S. Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis. Nature 2021, 590, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.K.; Shi, Q.; Tartler, K.J.; Rammes, G. Quantification of astrocytic synaptic pruning in mouse hippocampal slices in response to ex vivo Aβ treatment via colocalization analysis with C1q. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarovic, N.; Nicholls, F.; Rettich, A.; Kronen, P.; Haessig, M.; Jirkof, P.; Arras, M. Isoflurane and sevoflurane provide equally effective anaesthesia in laboratory mice. Lab. Anim. 2010, 44, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.M.; Jensen, F.E.; Tsao, B. Three-dimensional structure of dendritic spines and synapses in rat hippocampus (CA1) at postnatal day 15 and adult ages: Implications for the maturation of synaptic physiology and long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 2685–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.K.; Neumüller, T.; Klug, C.; Fuchs, S.; Schlegel, M.; Ballmann, M.; Tartler, K.J.; Pianos, A.; Garcia, M.S.; Liere, P.; et al. Chronic administration of XBD173 ameliorates cognitive deficits and neuropathology via 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







 : significant increase,
: significant increase,  : significant decrease,
: significant decrease,  : a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 was used to represent statistical significance.
: a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 was used to represent statistical significance.
 : significant increase,
: significant increase,  : significant decrease,
: significant decrease,  : a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 was used to represent statistical significance.
: a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 was used to represent statistical significance.| DSD | Aβ1-40 | Aβ1-42 | AβpE3 | 3NTyrAβ | Compared to? | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | ||
| 0.4 MAC Sevo |  |  | — |  |  | — |  | — | — |  |  | — | control |
| p = 0.0008 | 0.035 | 0.156 | 0.0006 | 0.040 | 0.768 | 0.012 | 0.154 | 0.610 | <0.0001 | 0.014 | 0.082 | ||
| — |  | — | — |  | — | — |  | — | — | — | — | Aβ 180 min | |
| 0.542 | 0.041 | 0.809 | 0.976 | 0.007 | 0.987 | 0.714 | 0.040 | 0.974 | 0.960 | 0.115 | 0.677 | ||
| 1.2 MAC Sevo |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | — |  |  |  |  | control |
| 0.0002 | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.027 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.035 | 0.160 | 0.051 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.009 | ||
| — |  |  | — |  | — | — |  |  |  |  | — | Aβ 180 min | |
| 0.885 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.698 | 0.005 | 0.150 | 0.783 | 0.035 | 0.055 | 0.033 | 0.044 | 0.074 | ||
 : significant increase,
: significant increase,  : significant decrease,
: significant decrease,  : a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 represents statistical significance.
: a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 represents statistical significance.
 : significant increase,
: significant increase,  : significant decrease,
: significant decrease,  : a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 represents statistical significance.
: a decrease with significance very close to 0.05; —: no change. Aβ 180 min: Aβ incubated for 180 min. Sevo: sevoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 represents statistical significance.| DSD | Aβ1-40 | Aβ1-42 | AβpE3 | 3NTyrAβ | Compared to? | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | Thin | Stubby | Mushroom | ||
| 0.4 MAC Sevo washout |  |  |  |  |  | — |  |  | — |  |  | — | control |
| p < 0.0001 | 0.003 | 0.053 | 0.0005 | 0.025 | 0.105 | 0.037 | 0.003 | 0.146 | <0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.062 | ||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Aβ 270 min | |
| 0.618 | 0.994 | 0.347 | 0.629 | 0.672 | 0.887 | 0.995 | 0.637 | 0.758 | 1.000 | 0.185 | 0.755 | ||
| 1.2 MAC Sevo washout |  |  | — |  |  |  |  | — |  | — |  |  | control |
| 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.110 | <0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.052 | 0.028 | 0.776 | 0.023 | 0.403 | 0.033 | 0.015 | ||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — |  | — |  | — | — | Aβ 270 min | |
| 0.656 | 0.806 | 0.193 | 0.296 | 0.156 | 0.804 | 0.997 | 0.035 | 0.082 | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.844 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Pradhan, A.K.; Fenzl, T.; Rammes, G. The Effects of Sevoflurane and Aβ Interaction on CA1 Dendritic Spine Dynamics and MEGF10-Related Astrocytic Synapse Engulfment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137393
Shi Q, Wang X, Pradhan AK, Fenzl T, Rammes G. The Effects of Sevoflurane and Aβ Interaction on CA1 Dendritic Spine Dynamics and MEGF10-Related Astrocytic Synapse Engulfment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137393
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qinfang, Xingxing Wang, Arpit Kumar Pradhan, Thomas Fenzl, and Gerhard Rammes. 2024. "The Effects of Sevoflurane and Aβ Interaction on CA1 Dendritic Spine Dynamics and MEGF10-Related Astrocytic Synapse Engulfment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137393
APA StyleShi, Q., Wang, X., Pradhan, A. K., Fenzl, T., & Rammes, G. (2024). The Effects of Sevoflurane and Aβ Interaction on CA1 Dendritic Spine Dynamics and MEGF10-Related Astrocytic Synapse Engulfment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137393






