Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rescues Cav1.2-L-Type Ca2+ Channel Decline Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids via Both Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
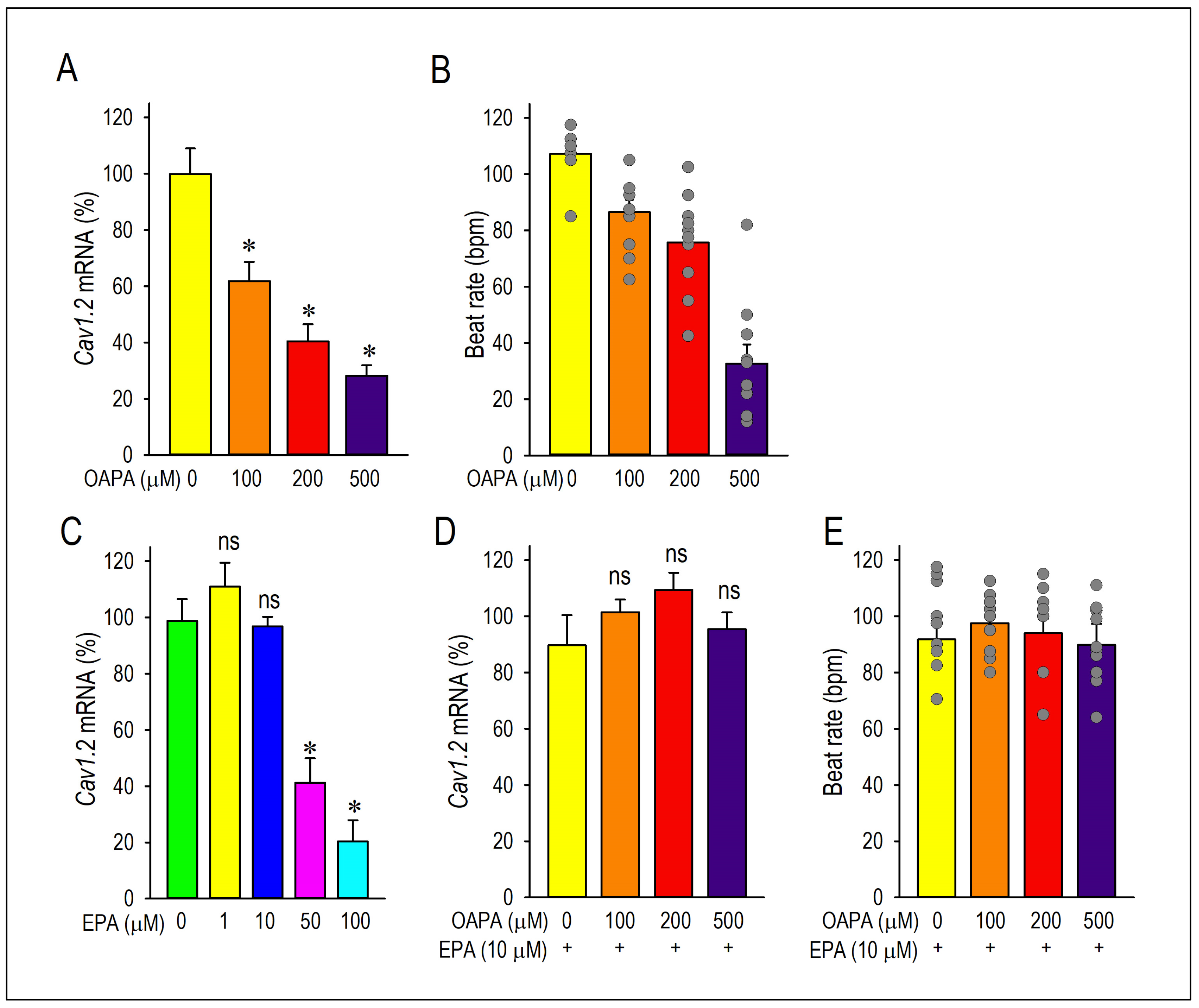
2.1. Actions of Saturated Fatty Acid on the L-Type Ca2+ Channel and the Cellular Excitability
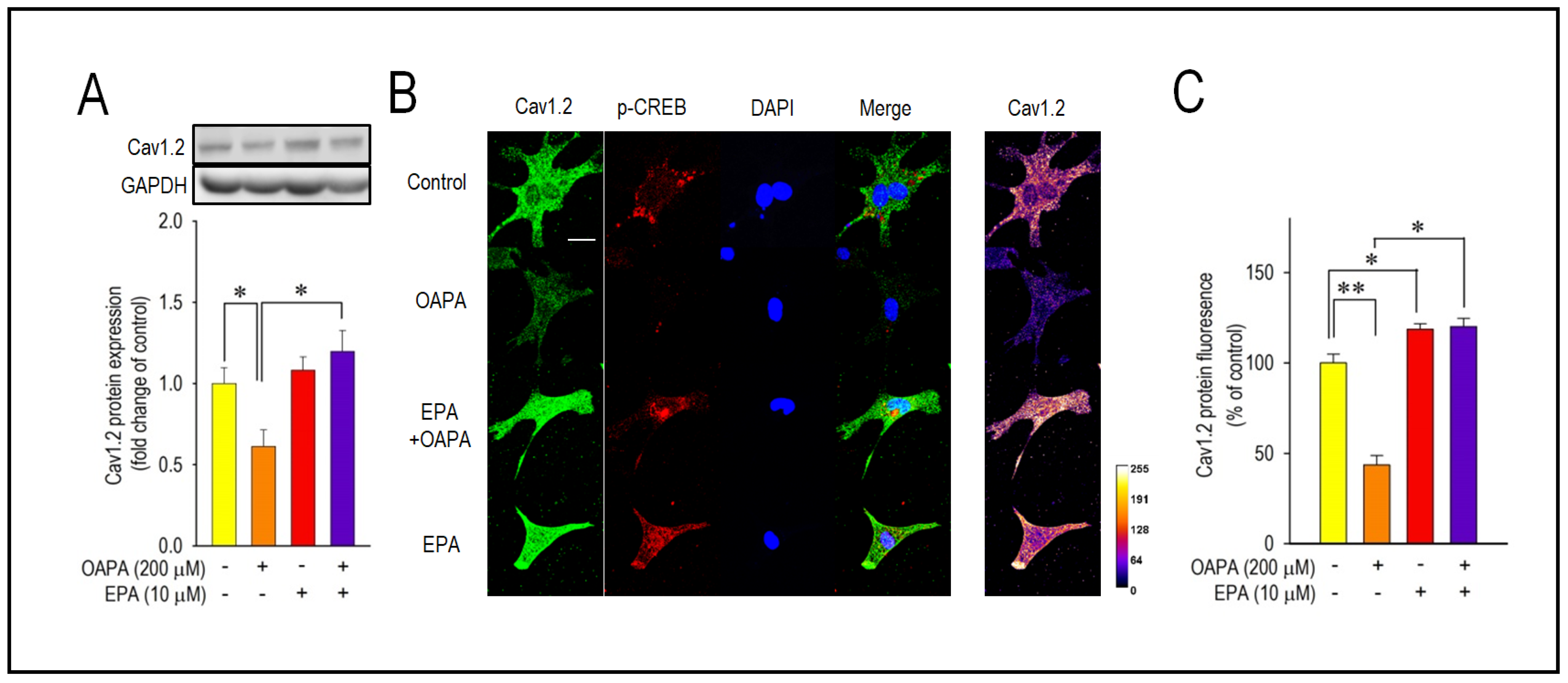
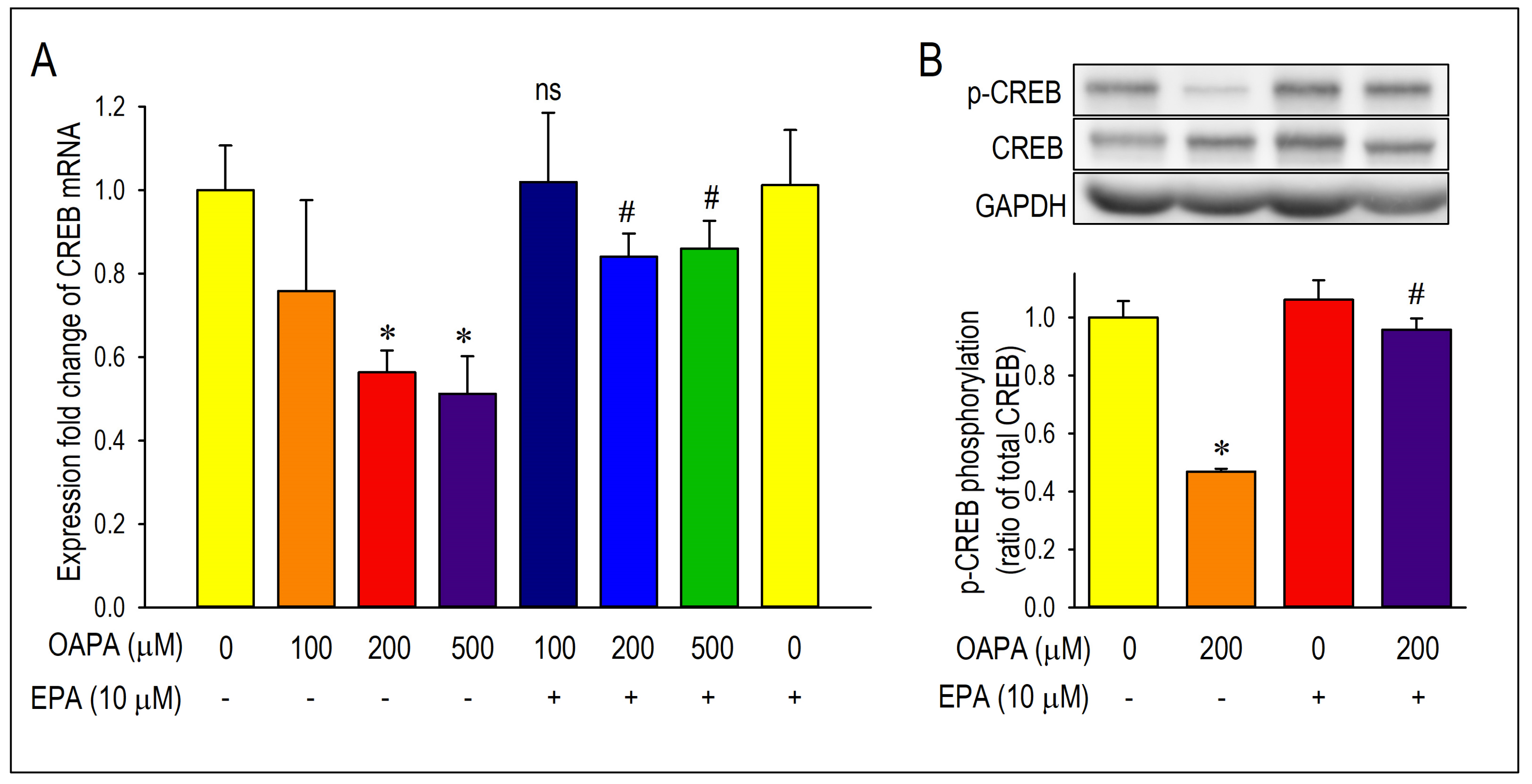
2.2. EPA Rescued OAPA-Induced Reduction in L-Type Ca2+ Channel
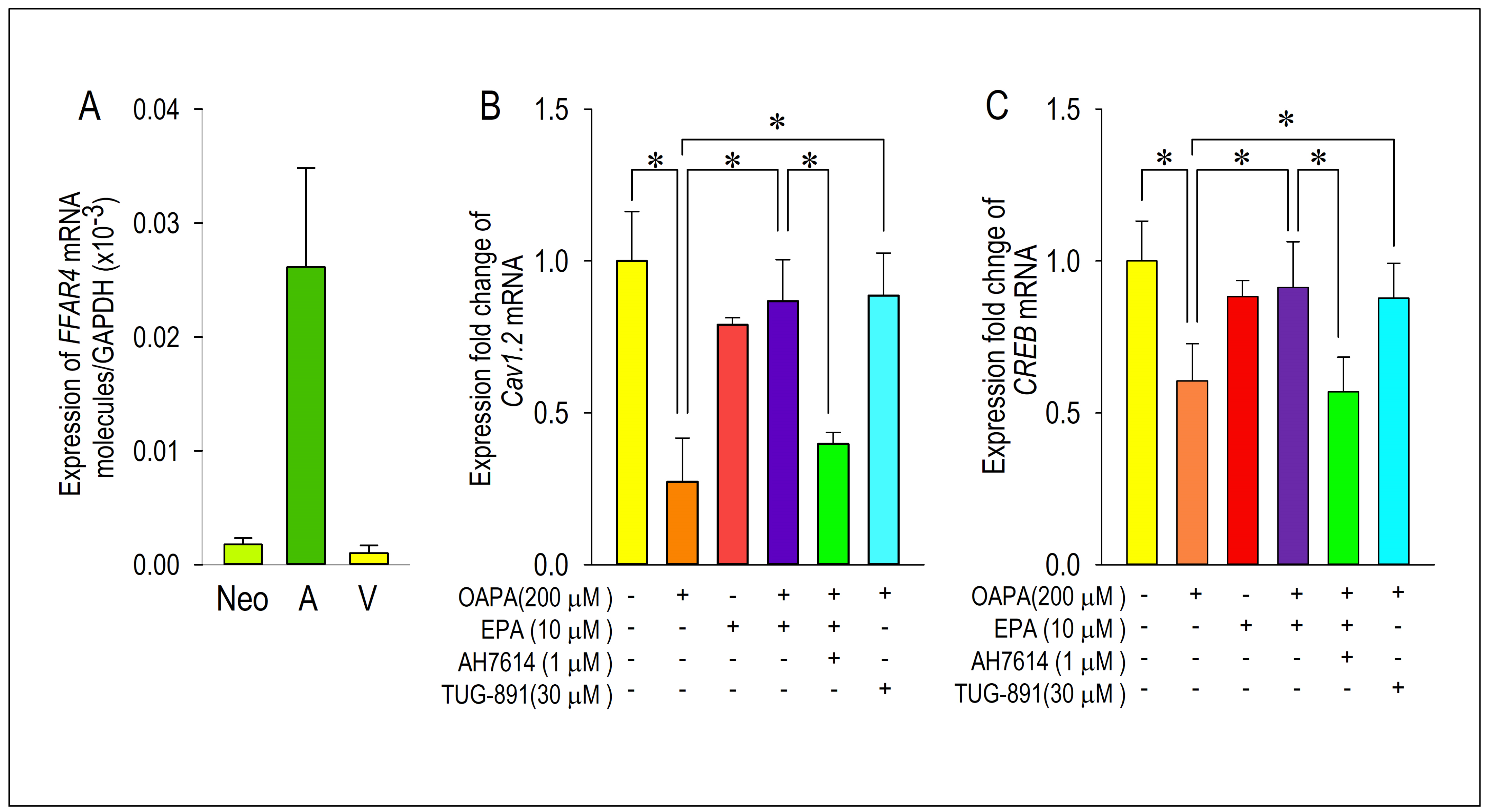
2.3. Actions of FFAR4 in Cardiomyocytes
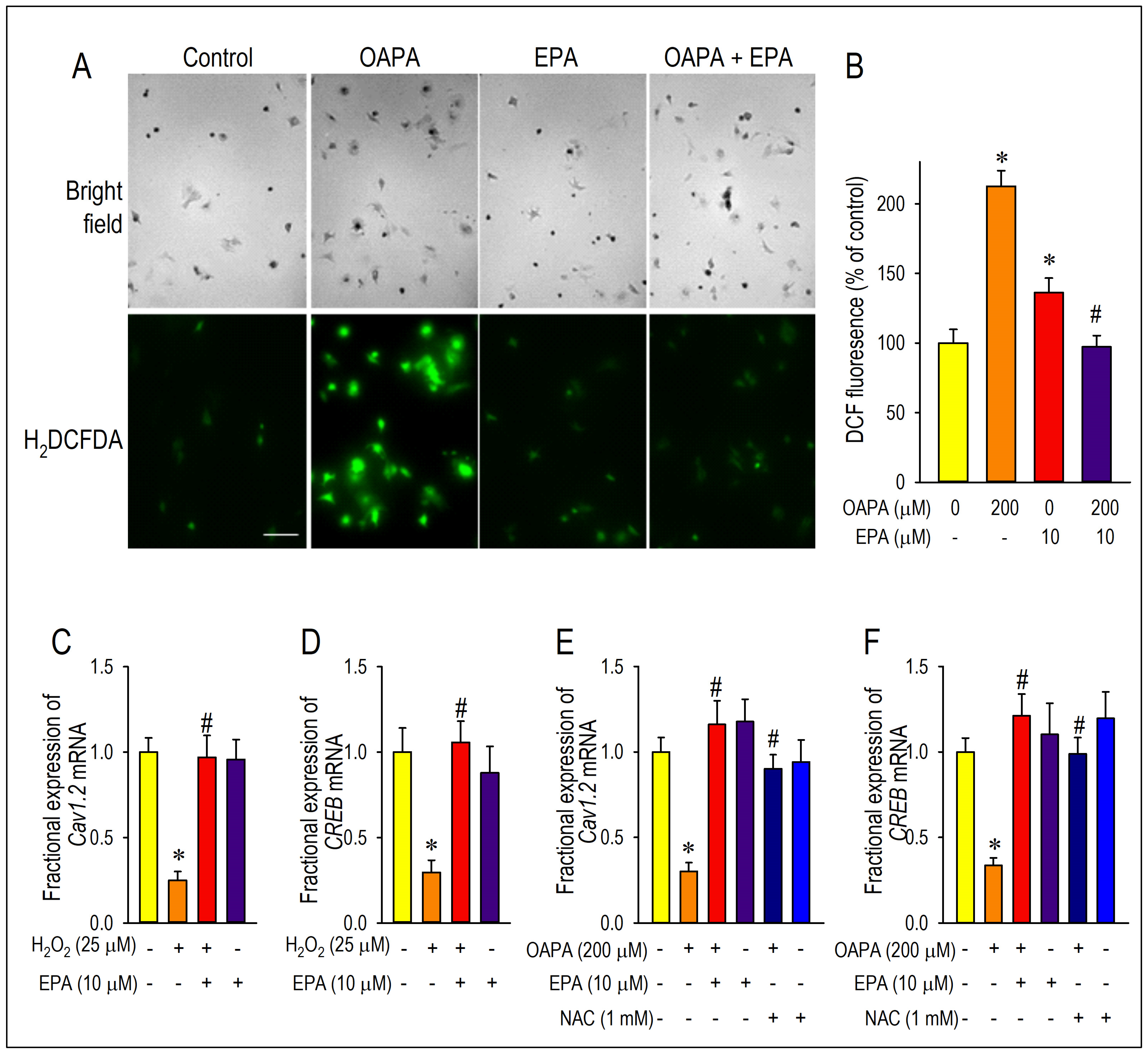
2.4. Actions of ROS for Cav1.2 Expression
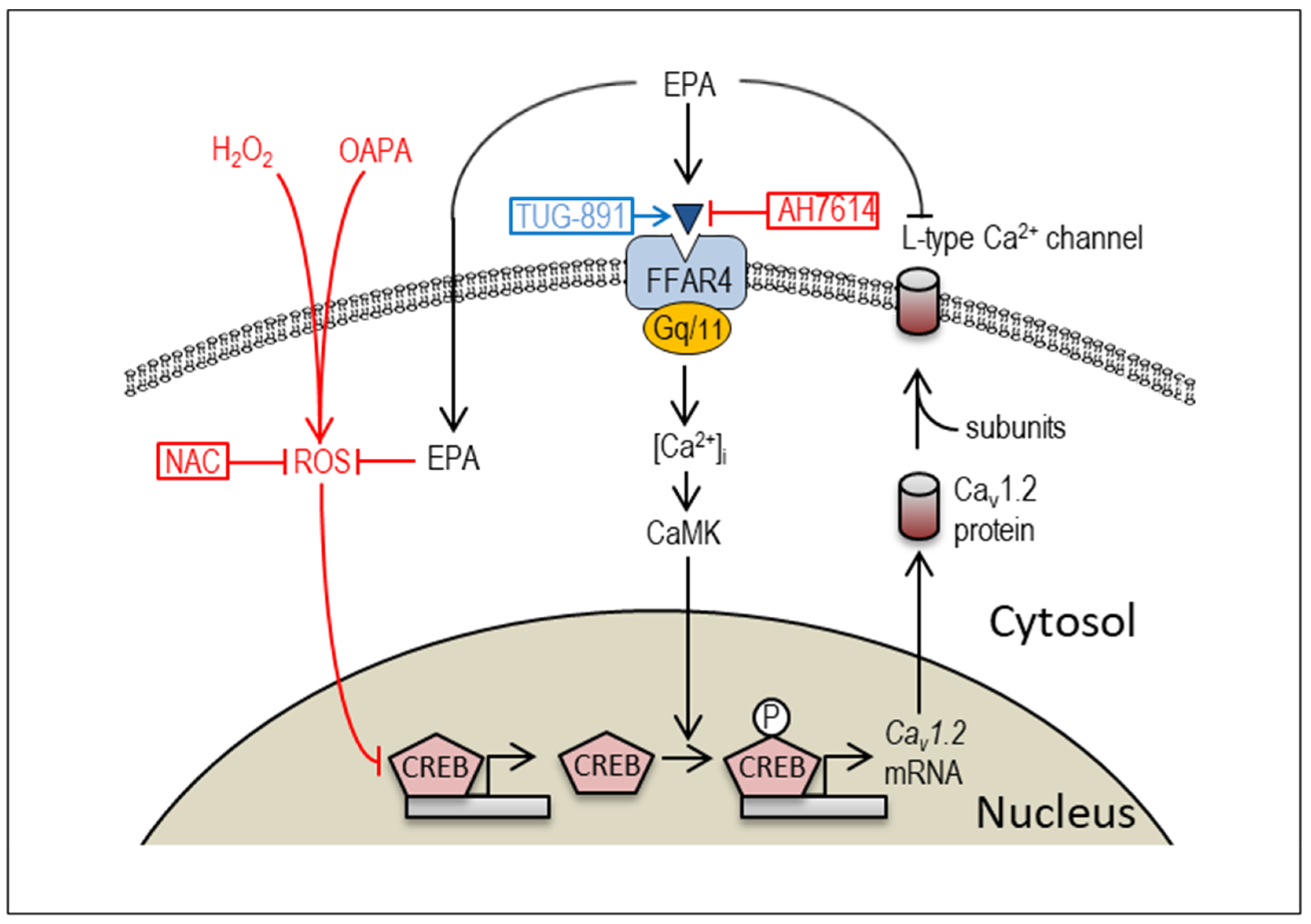
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Isolation of Neonatal Mouse Cardiomyocytes
4.3. Preparation of OAPA and Cell Culture
4.4. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Accumulation
4.5. Electrophysiological Measurements
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Immunocytochemistry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouven, X.; Charles, M.A.; Desnos, M.; Ducimetiere, P. Circulating nonesterified fatty acid level as a predictive risk factor for sudden death in the population. Circulation 2001, 104, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.F.; Kurien, V.A.; Greenwood, T.W. Relation between serum-free-fatty acids and arrhythmias and death after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 1968, 291, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiuve, S.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Sandhu, R.K.; Bernstein, A.M.; Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Albert, C.M. Dietary fat quality and risk of sudden cardiac death in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; King, I.B.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Knopp, R.H.; Mozaffarian, D.; McKnight, B.; Rea, T.D.; Rice, K.; Friedlander, Y.; Lumley, T.S.; et al. Endogenous red blood cell membrane fatty acids and sudden cardiac arrest. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Adrogue, J.V.; Golfman, L.; Uray, I.; Lemm, J.; Youker, K.; Noon, G.P.; Frazier, O.H.; Taegtmeyer, H. Intramyocardial lipid accumulation in the failing human heart resembles the lipotoxic rat heart. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.C.; Avula, U.M.R.; Wan, E.Y.; Reyes, M.V.; Lakkadi, K.R.; Subramanyam, P.; Nakanishi, K.; Homma, S.; Pajvani, U.B.; Thorp, E.B.; et al. Dietary saturated fat promotes arrhythmia by activating NOX2 (NADPH oxidase 2). Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauconnier, J.; Andersson, D.C.; Zhang, S.J.; Lanner, J.T.; Wibom, R.; Katz, A.; Bruton, J.D.; Westerblad, H. Effects of palmitate on Ca2+ handling in adult control and ob/ob cardiomyocytes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromolaran, A.S. Mechanisms of electrical remodeling in lipotoxic guinea pig heart. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 519, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, J.E.; Vork, M.M.; Roemen, T.H.; de Jong, Y.F.; Cleutjens, J.P.; van der Vusse, G.J.; van Bilsen, M. Saturated but not monounsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic cell death in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmagid, S.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Nielsen, D.E.; Badawi, A.; EI-Sohemy, A.; Mutch, D.M.; Ma, D.W.L. Comprehensive profiling of plasma fatty acid concentrations in young healthy canadean adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116195. [Google Scholar]
- Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Lipotoxicity in the heart. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetrullo, S.; D’Adamo, S.; Panichi, V.; Borzi, R.M.; Pignatti, C.; Flamigni, F. Modulation of fatty acid-related genes in the response of H9c2 cardiac cells to palmitate and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Cells 2020, 9, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, I.J.; Trent, C.M.; Schulze, P.C. Lipid metabolism and toxicity in the heart. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Cote, G.M.; Trucillo, M.P.; Pimentel, D.R.; Ido, Y.; Ruderman, N.B.; Sawyer, D.B. Oleate prevents palmitate-induced cytotoxic stress in cardiac myocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, P.K.; O’Neill, B.T.; Roberts, M.W.; Buchanan, J.; Yun, U.J.; Cooksey, R.C.; Boudina, S.; Abel, E.D. Impaired cardiac efficiency and increased fatty acid oxidation in insulin-resistant ob/ob mouse hearts. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourie, J.I. Interaction of reactive oxygen species with ion transport mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, C1–C24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Okabe, E. Superoxide anion radical-triggered Ca2+ release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum through ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Song, Y.; Daviglus, M.L.; Liu, K.; Van Horn, L.; Dyer, A.R.; Greenland, P. Accumulated evidence on fish consumption and coronary heart disease mortality: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Circulation 2004, 109, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gissi-HF, I. Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in patients with chronic heart failure (the GISSI-HF trial): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.H.; Abuissa, H.; Sastre, A.; Steinhaus, D.M.; Harris, W.S. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on resting heart rate, heart rate variability in men with healed myocardial infractions and depressed ejection fractions. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, J.C.; Macknight, A.D.C.; Rodrigo, G.C. The electrical and mechanical response of adult guinea pig and rat ventricular myocytes to ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 356, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Ma, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Josephson, M.E.; Wang, G.K.; Morgan, J.P.; Leaf, A. Potent block of inactivation-deficient Na+ channels by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C362–C370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. N-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Evidence explained and mechanisms explored. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrier, G.R.; Redondo, I.; Zhu, J.; Murphy, M.G. Differential effects of docosahezaenoic acid on contractions and L-type Ca2+ current in adult cardiac myocytes. Cardovasc. Res. 2002, 54, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallaq, H.; Smith, T.W.; Leaf, A. Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in heart cells by fish oil fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, J.; Arita, M. Cardioprotective mechanism of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Wu, J.H. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denys, A.; Hichami, A.; Khan, N.A. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid modulate MAP kinase (ERK1/ERK2) signaling in human T cells. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.Y.; Talukdar, S.; Bae, E.J.; Imamura, T.; Morinaga, H.; Fan, W.Q.; Li, P.; Lu, W.J.; Watkins, S.M.; Olefsky, J.M. GPR120 is an omega-3 fatty acid receptor mediating potent anti-inflammatory and insulin sensitizing effects. Cell 2010, 142, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, E.; Watterson, K.R.; Stocker, C.J.; Sokol, E.; Jenkins, L.; Simon, K.; Grundmann, M.; Petersen, R.K.; Wargent, E.T.; Hudson, B.D.; et al. Activity of dietary fatty acids on FFA1 and FFA4 and characterization of pinolenic acid as a dual FFA1/FFA4 agonist with potential effect against metabolic diseases. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, A.; Hirasawa, A.; Poulain-Godefroy, O.; Bonnefond, A.; Hara, T.; Yengo, L.; Kimura, I.; Leloire, A.; Liu, N.; Iida, K.; et al. Dysfunction of lipid sensor GPR120 leads to obesity in both mouse and human. Nature 2012, 483, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.A.; Harsch, B.A.; Healy, C.L.; Joshi, S.S.; Huang, S.; Walker, R.E.; Wagner, B.M.; Ernste, K.M.; Huang, W.; Block, R.C.; et al. Free fatty acid receptor 4 responds to endogenous fatty acids to protect the heart from pressure overload. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Lee, C.C.; Wu, D.Y.; Chen, S.; Lee, T.M. Differential effects of EPA and DHA on PPARγ-mediated sympathetic innervation in infarcted rat hearts by GPR120-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 103, 108950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, M.; Tahara, S.; Wang, Y.; Ono, K. Oxytocin downregulates the Cav1.2 L-type Ca2+ channel via Gi/cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway in cardiomyocytes. Membranes 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Huang, J.; Lee, B.-K.; Jung, Y.-S.; Im, E.; Koh, J.-M.; Im, D.-S. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids protect human hepatoma cells from developing steatosis through FFA4 (GPR120). BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, G.A., Jr.; Makuck, R.F.; Rivkees, S.A. Intracellular calcium plays an essential role in cardiac development. Dev. Dyn. 2003, 227, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakili, R.; Voigt, N.; Kääb, S.; Dobrev, D.; Nattel, S. Recent advances in the molecular pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2955–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachtsis, B.; Whitfield, J.; Hawley, J.A.; Hoffman, N.J. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids mitigate palmitate-induced impairments in skeletal muscle cell viability and differentiation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, C.; Bartolo, A.D.; Guzzi, R.; Crocco, M.C.; Rago, V.; Romeo, N.; Perrotta, I.; Francesco, E.M.D.; Muoio, M.G.; Granieri, M.C.; et al. Palmitate-induced cardiac lipotoxicity is relieved by the redox-active motif of SELENOT through improving mitochondrial function and regulating metabolic state. Cells 2023, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías, J.G.; Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Carrasco Loza, R.; Sepúlveda, N.; Álvarez, P.; Quezada, M.; Quiñones, J.; Molina, V.; Castillo, R.L. Polyunsaturated fatty acid induces cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion through the inhibition of NF-kappaB and induction of Nrf2. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Macias, A.; Prieto, A.; de la Cruz, A.; Gonzalez, T.; Valenzuela, C. Effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiac ion channels. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, B.M.; de la Cruz, A.; Wu, X.; Jowais, J.J.; Perez, M.E.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Liin, S.I.; Larsson, H.P. Polyunsaturated fatty acid analogues differentially affect cardiac Nav, Cav, and Kv channels through unique mechanisms. eLife 2020, 9, e51453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Wright, S.N.; Wang, G.K.; Morgan, J.P.; Leaf, A. Fatty acids suppress voltage-gated Na+ currents in HEK293t cells transfected with the alpha-subunit of the cardiac Na+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Gomez, A.M.; Morgan, J.P.; Lederer, W.J.; Leaf, A. Suppression of voltage-gated L-type Ca2+ currents by polyunsaturated fatty acids in adult and neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Smith, T.; Baumgarten, C.M.; Wood, M.A.; Tseng, G.N. Long-term fish oil supplementation induces cardiac electrical remodeling by changing channel protein expression in the rabbit model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, O.; Hei, A.G.V.; Battisha, A.; Hammad, T.; Pham, S.; Chilton, R. Cardiovascular, electrophysiologic, and hematologic effects of omega-3 fatty acids beyond reducing hypertriglyceridemia: As it pertains to the recently published REDUCE-IT trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuburaya, R.; Yasuda, S.; Ito, Y.; Shiroto, T.; Gao, J.Y.; Ito, K.; Shimokawa, H. Eicosapentaenoic acid reduces ischemic ventricular fibrillation via altering monophasic action potential in pigs. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Ruan, L.; Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and pitavastatin on electrophysiology and anticoagulant gene expression in mouse with rapid atrial pacing. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.X.; Li, Y.; Leaf, A. Regulation of sodium channel gene expression by class I antiarrhythmic drugs and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2724–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaf, A. The electrophysiological basis for the antiarrhythmic actions of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2001, 3, D98–D105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dumancas, G.G.; Kimani, M.; Purdie, N.; Reilly, L. Partial least squares (PLS1) algorithm for quantitating cholesterol and polyunsaturated fatty acids in human serum. J. Biotech Res. 2010, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- von Schacky, C. Omega-3 fatty acids: Anti-arrhythmic, pro-arrhythmic, or both? Fornt. Physiol. 2012, 3, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Shibata, R.; Tsuji, Y.; Shimano, M.; Inden, Y.; Murohara, T. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents atrial fibrillation associated with heart failure in a rabbit model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1814–H1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Geelen, A.; Brouwer, I.A.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Zock, P.L.; Katan, M.B. Effect of fish oil on heart rate in humans: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Circulation 2005, 112, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, M.; Horikawa, K.; Funaki, M. Cardiomyocytes cultured on mechanically compliant substrates, but not on conventional culture devices, exhibit prominent mitochondrial dysfunction due to reactive oxygen species and insulin resistance under high glucose. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Morishima, M.; Dan, L.; Takahashi, N.; Saikawa, T.; Nattel, S.; Ono, K. Binge alcohol exposure triggers atrial fibrillation through T-type Ca2+ channel upregulation via protein kinase C (PKC)/glycogen synthesis kinase 3β (GSK3β)/nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signaling-an experimental account of holiday heart syndrome. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Morishima, M.; Zheng, M.; Uchino, T.; Mannen, K.; Takahashi, A.; Nakaya, Y.; Komuro, I.; Ono, K. Transcription factors Csx/Nkx2.5 and GATA4 distinctly regulate expression of Ca2+ channels in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 42, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morishima, M.; Wang, P.; Horii, K.; Horikawa, K.; Ono, K. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rescues Cav1.2-L-Type Ca2+ Channel Decline Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids via Both Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147570
Morishima M, Wang P, Horii K, Horikawa K, Ono K. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rescues Cav1.2-L-Type Ca2+ Channel Decline Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids via Both Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(14):7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147570
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorishima, Masaki, Pu Wang, Kosuke Horii, Kazuki Horikawa, and Katsushige Ono. 2024. "Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rescues Cav1.2-L-Type Ca2+ Channel Decline Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids via Both Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Cardiomyocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 14: 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147570
APA StyleMorishima, M., Wang, P., Horii, K., Horikawa, K., & Ono, K. (2024). Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rescues Cav1.2-L-Type Ca2+ Channel Decline Caused by Saturated Fatty Acids via Both Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14), 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147570





