Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
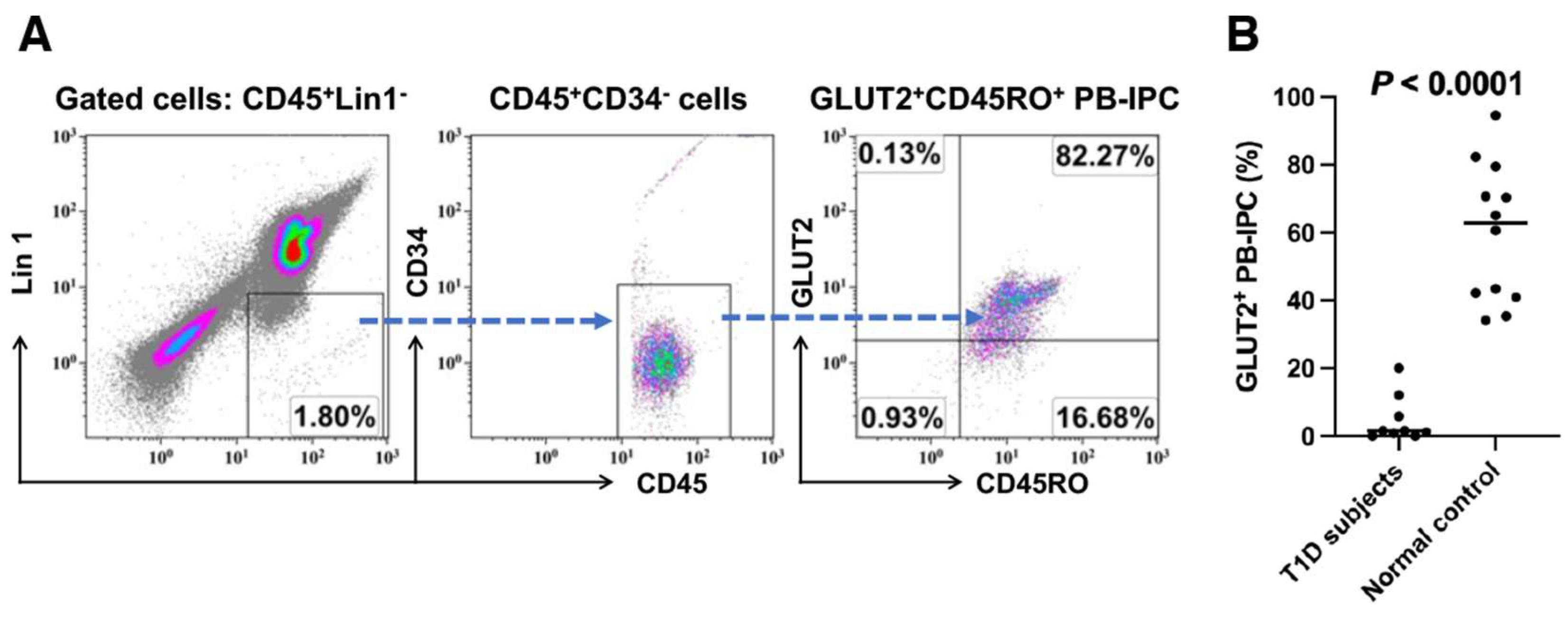
2.1. Low Expression of GLUT2 on Recent Onset T1D Patient-Derived PB-IPC
2.2. Upregulate the Expression of GLUT2 on Recent Onset T1D Patient-Derived PB-IPC
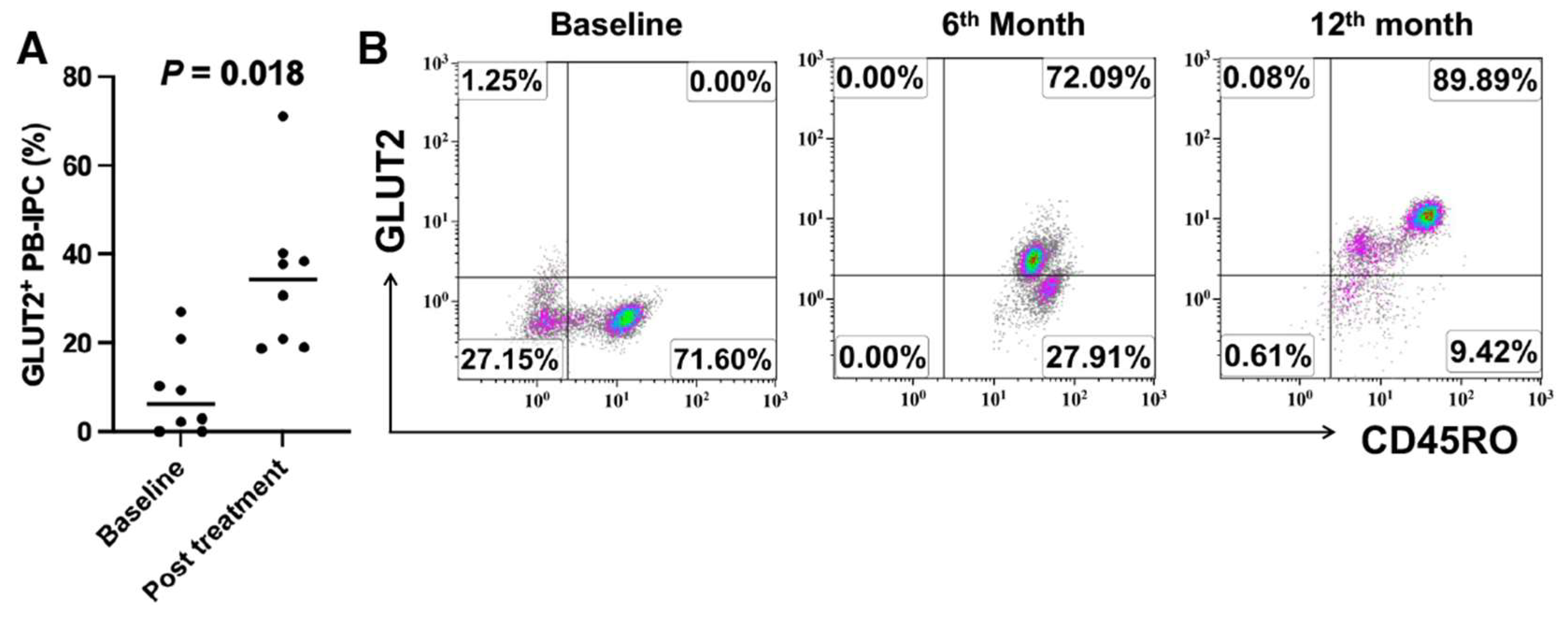
2.3. Upregulate the Expression of GLUT2 on Longstanding T1D Patient-Derived PB-IPC after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy
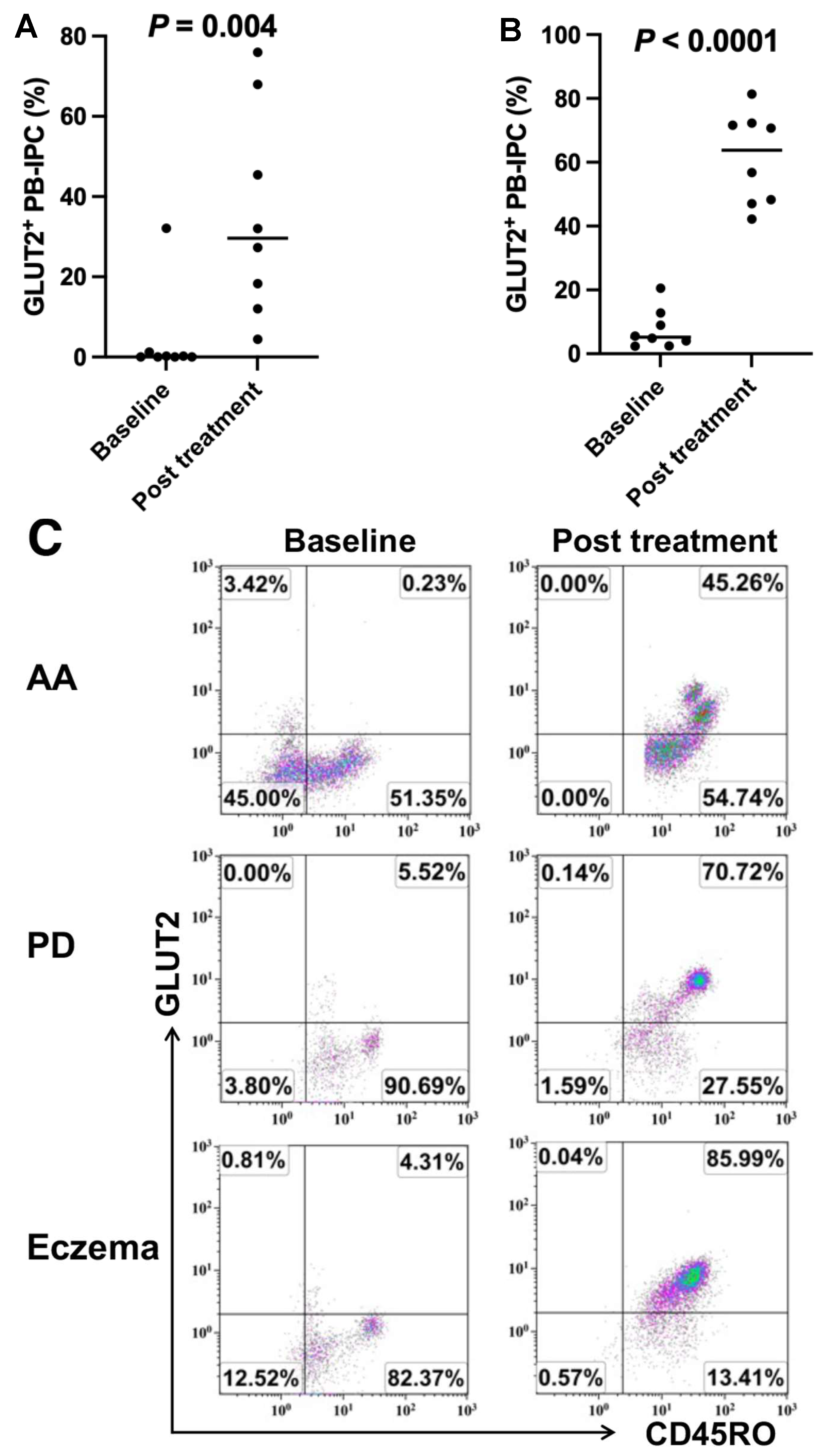
2.4. Increase in the Expression of GLUT2 on PB-IPC in Patients with Other Autoimmune- or Inflammation-Associated Diseases after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy
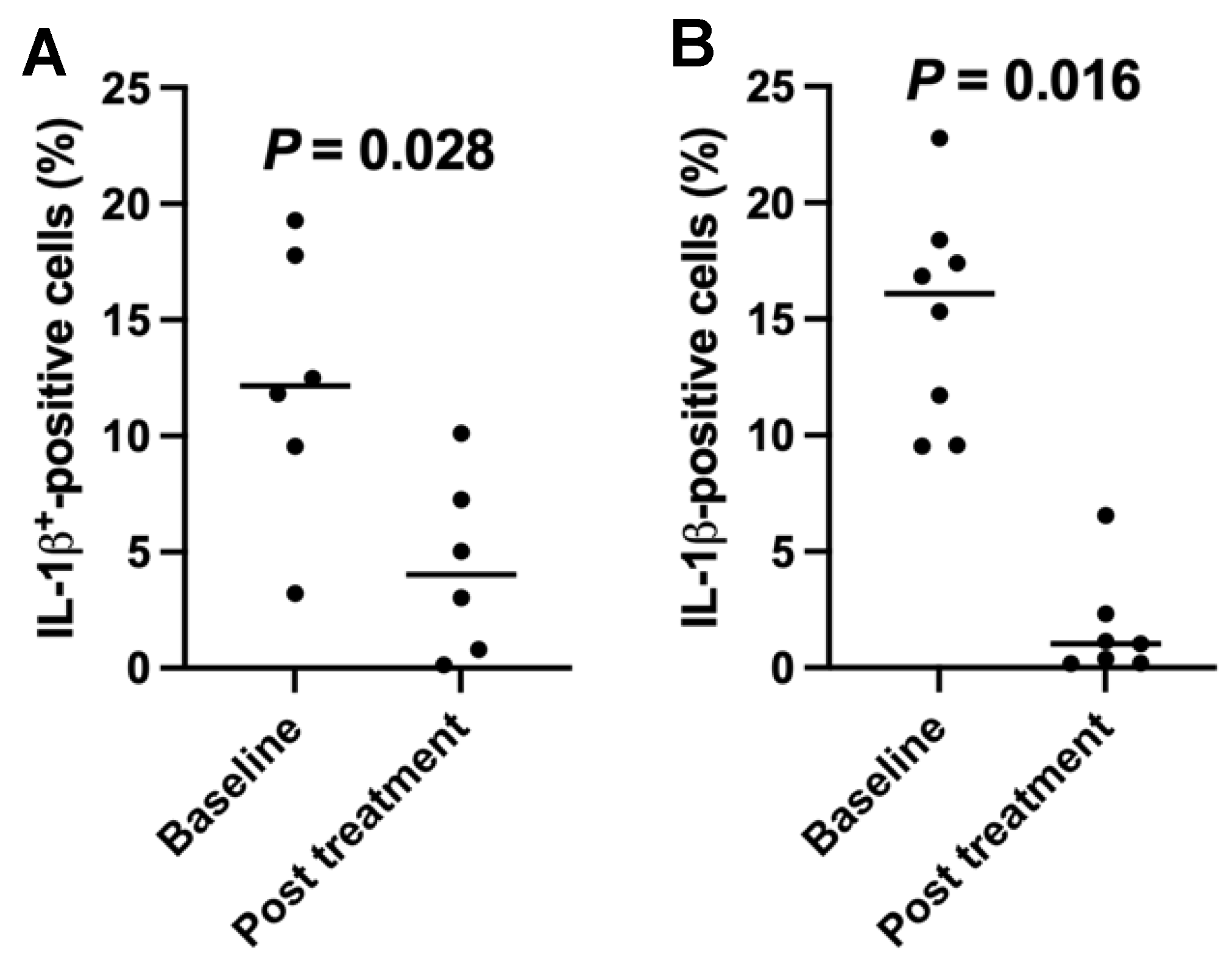
2.5. Downregulation of the Percentages of Inflamatory Interleukin (IL)1-β-Positive Cells in T1D Subjects after the SCE Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Culture of CB-SC and Co-Culture of CB-SC with Patients’ PBMC
4.3. Flow Cytometry
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | alopecia areata |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CB-SC | cord blood-derived stem cells |
| CD | cluster differentiation |
| ES | embryonic stem cells |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GLUT2 | glucose transporter 2 |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| iPS | induced pluripotent stem cells |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| PB-IPC | peripheral blood insulin-producing cells |
| PBMC | peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| SCE | stem cell educator |
| T1D | type 1 diabetes |
References
- Rahmati, M.; Keshvari, M.; Mirnasuri, S.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Il Shin, J.; Smith, L. The global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of pediatric new-onset type 1 diabetes and ketoacidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5112–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Khunti, K. COVID-19 and Diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, D.; Empringham, J.; Pechlivanoglou, P.; Uleryk, E.M.; Cohen, E.; Shulman, R. Incidence of Diabetes in Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2321281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, L. COVID-19 and Type 1 Diabetes. Pediatr. Ann. 2024, 53, e244–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.Z. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou-Marketou, N.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes: A review of early natural history, pathogenesis, and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.V.; Kuffova, L.; Delibegovic, M. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haji, M.; Erqou, S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Type 1 diabetes and risk of heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluestone, J.A.; Herold, K.; Eisenbarth, G. Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes. Nature 2010, 464, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Scholten, B.J.; Kreiner, F.F.; Gough, S.C.L.; von Herrath, M. Current and future therapies for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzin-Frankel, J. Trying to reset the clock on type 1 diabetes. Science 2011, 333, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, J.F. Anti-CD3 antibodies for type 1 diabetes: Beyond expectations. Lancet 2011, 378, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, M.J.; Atkinson, M.A.; Schatz, D.A. Efforts to prevent and halt autoimmune beta cell destruction. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. 2010, 39, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herold, K.C.; Vignali, D.A.; Cooke, A.; Bluestone, J.A. Type 1 diabetes: Translating mechanistic observations into effective clinical outcomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, E.; Hebrok, M. Stem Cell-Based Clinical Trials for Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 631463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, M.J.; Hilkens, C.M.U.; Martinez-Caceres, E.M. Challenges in tolerogenic dendritic cell therapy for autoimmune diseases: The route of administration. Immunother. Adv. 2023, 3, ltad012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Ye, M.; Hu, C.; Yin, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Reversal of type 1 diabetes via islet beta cell regeneration following immune modulation by cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Knight, C.M.; Jiang, Z.; Delgado, E.; Van Hoven, A.M.; Ghanny, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yu, H.; Hu, W.; et al. Stem Cell Educator therapy in type 1 diabetes: From the bench to clinical trials. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, E.; Perez-Basterrechea, M.; Suarez-Alvarez, B.; Zhou, H.; Revuelta, E.M.; Garcia-Gala, J.M.; Perez, S.; Alvarez-Viejo, M.; Menendez, E.; Lopez-Larrea, C.; et al. Modulation of Autoimmune T-Cell Memory by Stem Cell Educator Therapy: Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 2024–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Ye, M.; Hu, C.; Zhou, H.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Targeting insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes via immune modulation of cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (CB-SCs) in stem cell educator therapy: Phase I/II clinical trial. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients following Stem Cell Educator therapy. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lazzarini, P.; Wang, Y.; Di, A.; Chen, M. A unique human blood-derived cell population displays high potential for producing insulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Hu, W.; Song, X.; Zhao, Y. Generation of Multipotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Peripheral Blood Following the Treatment with Platelet-Derived Mitochondria. Cells 2020, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Hu, W.; Song, X.; Descalzi-Montoya, D.; Yang, Z.; Korngold, R.; Zhao, Y. Generation of Hematopoietic-Like Stem Cells from Adult Human Peripheral Blood Following Treatment with Platelet-Derived Mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B. GLUT2 in pancreatic and extra-pancreatic gluco-detection (review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2001, 18, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Xue, J.; Li, P.; Fu, X. The role of GLUT2 in glucose metabolism in multiple organs and tissues. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 6963–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szablewski, L. Glucose Transporters in Brain: In Health and in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 55, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellett, G.L.; Brot-Laroche, E. Apical GLUT2: A major pathway of intestinal sugar absorption. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3056–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, E. Anti-Islet Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgjerd, E.P. Type 1 Diabetes-related Autoantibodies in Different Forms of Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2019, 15, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliuca, F.W.; Millman, J.R.; Gurtler, M.; Segel, M.; Van, D.A.; Ryu, J.H.; Peterson, Q.P.; Greiner, D.; Melton, D.A. Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell 2014, 159, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, A.; Faust, A.L.; Bushnell, H.L.; Engquist, E.N.; Kenty, J.H.; Harb, G.; Poh, Y.C.; Sintov, E.; Gurtler, M.; Pagliuca, F.W.; et al. Charting cellular identity during human in vitro beta-cell differentiation. Nature 2019, 569, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, E.; Martinson, L.A.; Kadoya, K.; Bang, A.G.; Kelly, O.G.; Eliazer, S.; Young, H.; Richardson, M.; Smart, N.G.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, T.; Guo, M.; Ji, J.; Meng, X.; Fu, T.; Nie, T.; Wei, T.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, W.; et al. Treating a type 2 diabetic patient with impaired pancreatic islet function by personalized endoderm stem cell-derived islet tissue. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogrebe, N.J.; Ishahak, M.; Millman, J.R. Developments in stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy for treating type 1 diabetes. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, A.; Nostro, M.C.; Sneddon, J.B. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived insulin-producing cells: A regenerative medicine perspective. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.N.; Westenskow, P.D.; Todorova, D.; Hu, Z.; Lin, T.; Rong, Z.; Kim, J.; He, J.; Wang, M.; et al. Humanized Mice Reveal Differential Immunogenicity of Cells Derived from Autologous Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Vuononvirta, J.; Fanti, S.; Bonacina, F.; D’Amati, A.; Wang, G.; Poobalasingam, T.; Fankhaenel, M.; Lucchesi, D.; Coleby, R.; et al. The glucose transporter 2 regulates CD8(+) T cell function via environment sensing. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1969–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, C. Mechanisms of interleukin-1beta release. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginhoux, F.; Jung, S. Monocytes and macrophages: Developmental pathways and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissmann, F.; Manz, M.G.; Jung, S.; Sieweke, M.H.; Merad, M.; Ley, K. Development of monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Science 2010, 327, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitina, E.; Larionova, I.; Choinzonov, E.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Monocytes and Macrophages as Viral Targets and Reservoirs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, L.; Gini, E.; Baci, D.; Tremolati, M.; Fanuli, M.; Bassani, B.; Farronato, G.; Bruno, A.; Mortara, L. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8917804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.A.; Devitt, A.; Johnson, J.R. Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, B.; Suri, A.; Miller, M.J.; Unanue, E.R. Dendritic cells in islets of Langerhans constitutively present beta cell-derived peptides bound to their class II MHC molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6121–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, B.; Carrero, J.A.; Ferris, S.T.; Sojka, D.K.; Moore, L.; Epelman, S.; Murphy, K.M.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Randolph, G.J.; Unanue, E.R. The pancreas anatomy conditions the origin and properties of resident macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.A.; McCarthy, D.P.; Ferris, S.T.; Wan, X.; Hu, H.; Zinselmeyer, B.H.; Vomund, A.N.; Unanue, E.R. Resident macrophages of pancreatic islets have a seminal role in the initiation of autoimmune diabetes of NOD mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E10418–E10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinselmeyer, B.H.; Vomund, A.N.; Saunders, B.T.; Johnson, M.W.; Carrero, J.A.; Unanue, E.R. The resident macrophages in murine pancreatic islets are constantly probing their local environment, capturing beta cell granules and blood particles. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Veysman, B. Revisiting the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes: Importance of Neural Input to Pancreatic Islets and the Therapeutic Capability of Stem Cell Educator (TM) Therapy to Restore Their Integrity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, N.; Kurata, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, S.; Masumoto, J. The role of interleukin-1 in general pathology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Pickersgill, L.; Donath, M.Y. Blockade of interleukin 1 in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maedler, K.; Sergeev, P.; Ris, F.; Oberholzer, J.; Joller-Jemelka, H.I.; Spinas, G.A.; Kaiser, N.; Halban, P.A.; Donath, M.Y. Glucose-induced beta cell production of IL-1beta contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Veysman, B.; Antolijao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Papagni, Y.; Wang, H.; Ross, R.; Tibbot, T.; Povrzenic, D.; Fox, R. Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158337
Zhao Y, Veysman B, Antolijao K, Zhao Y, Papagni Y, Wang H, Ross R, Tibbot T, Povrzenic D, Fox R. Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158337
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yong, Boris Veysman, Kristine Antolijao, Yelu Zhao, Yldalina Papagni, Honglan Wang, Robin Ross, Terri Tibbot, Darinka Povrzenic, and Richard Fox. 2024. "Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158337
APA StyleZhao, Y., Veysman, B., Antolijao, K., Zhao, Y., Papagni, Y., Wang, H., Ross, R., Tibbot, T., Povrzenic, D., & Fox, R. (2024). Increase in the Expression of Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) on the Peripheral Blood Insulin-Producing Cells (PB-IPC) in Type 1 Diabetic Patients after Receiving Stem Cell Educator Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158337





