In Vitro Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia Employing Magnetite Gamma-Cyclodextrin Nanobioconjugates for Human Squamous Skin Carcinoma Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nanobioconjugates Characterization
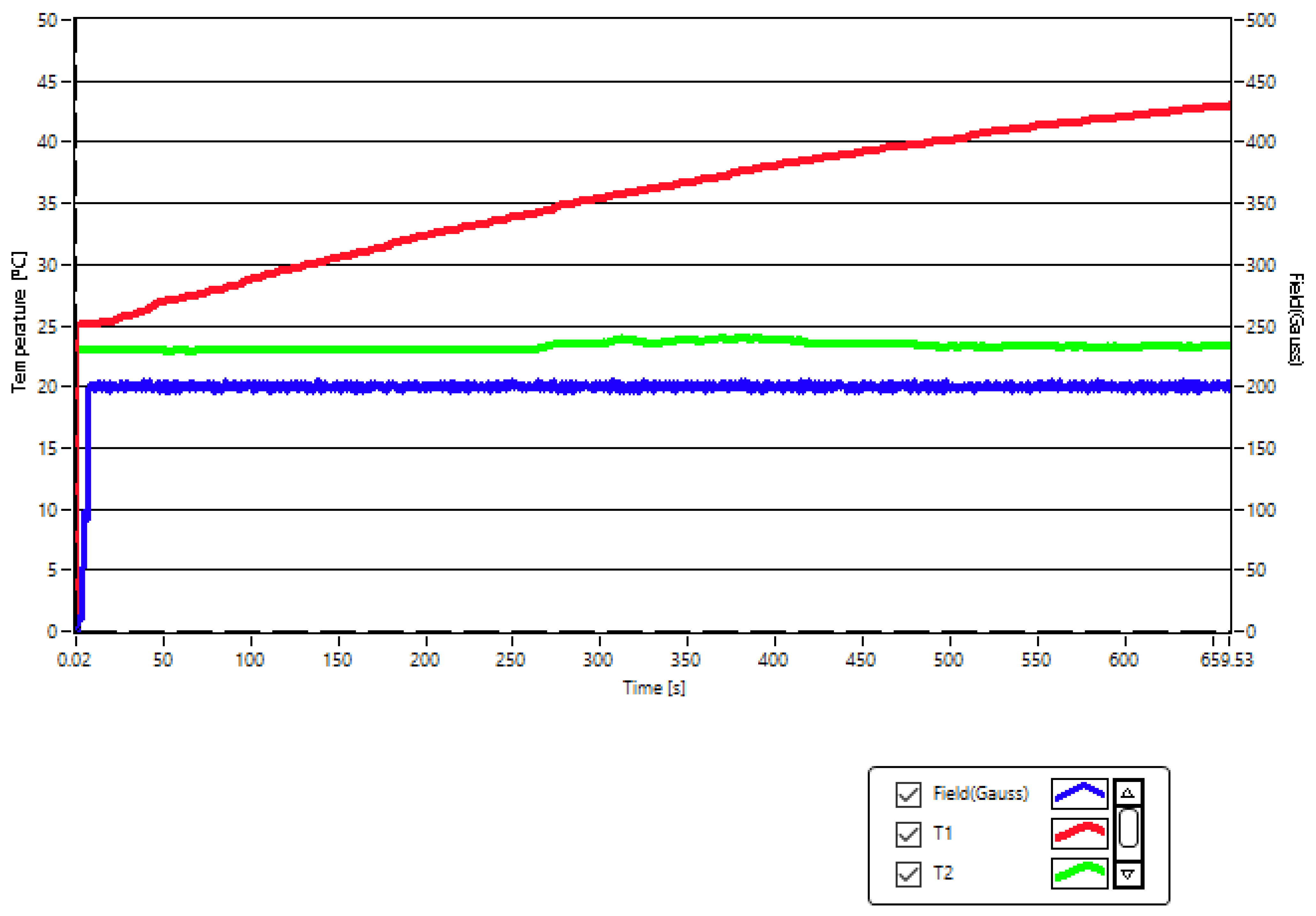
2.2. Experimental Conditios in SPMHT with Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs) Nanobioconjugates: Reaching the Required Temperature for Cancer Cell Therapy
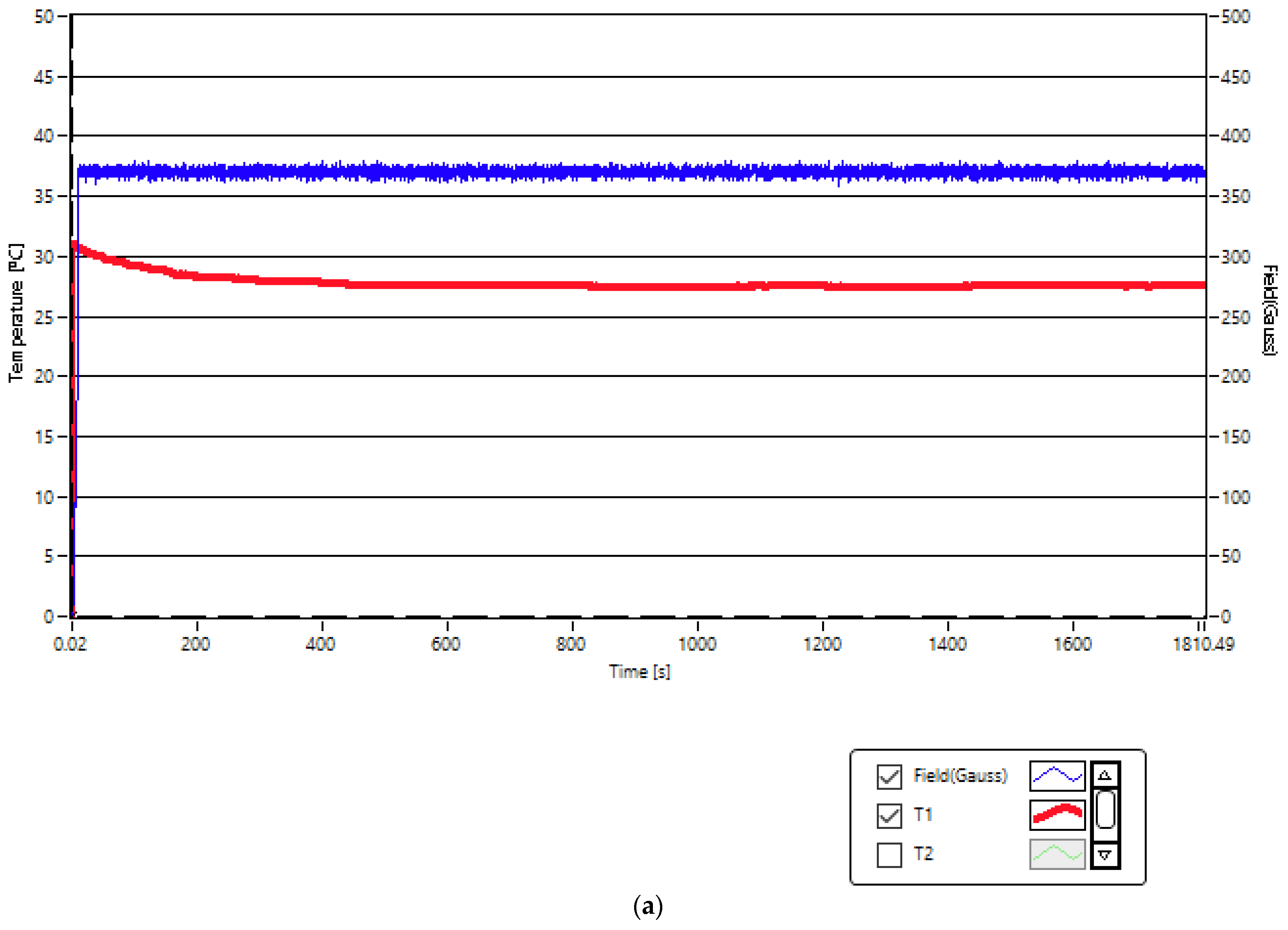
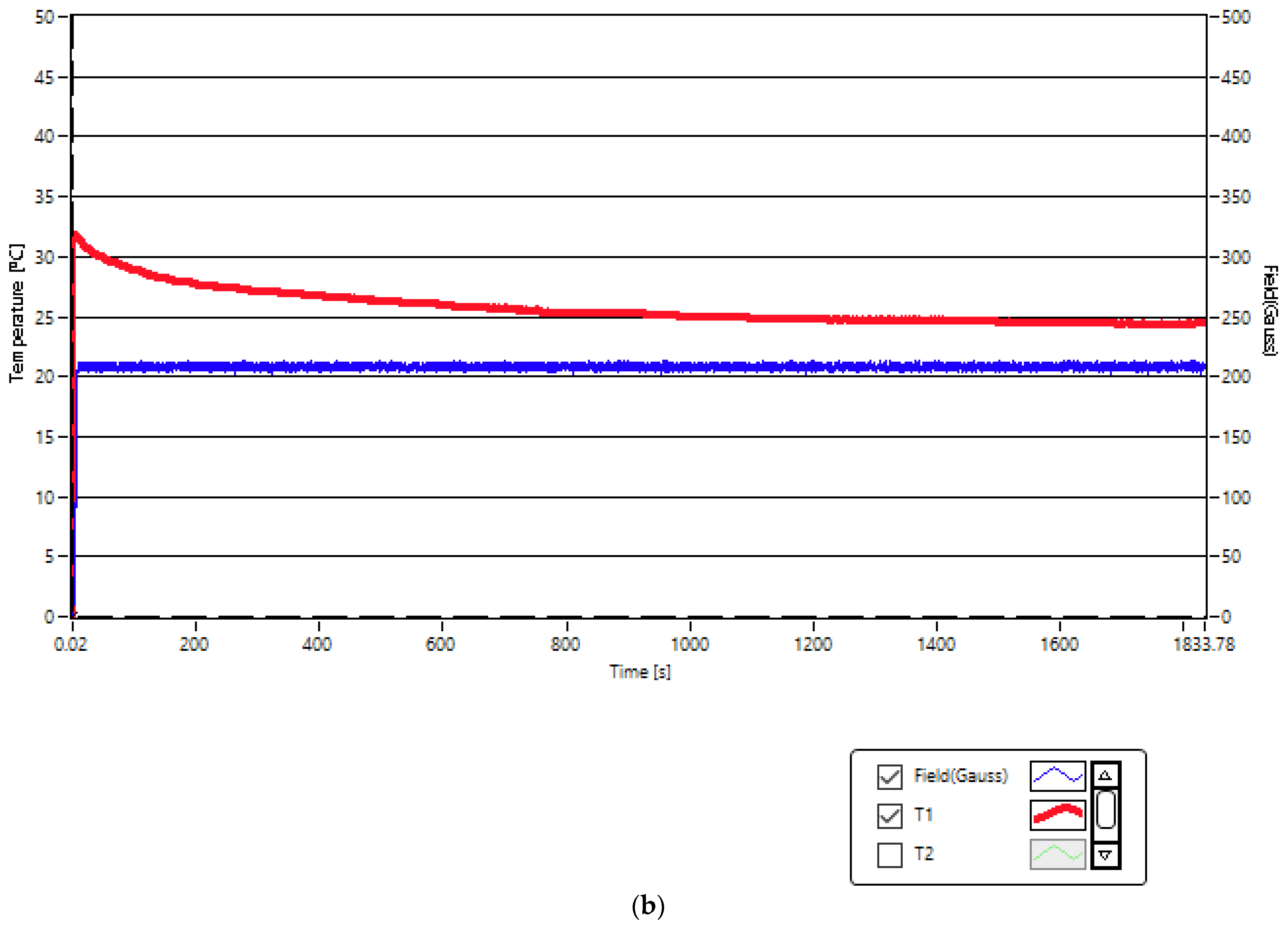
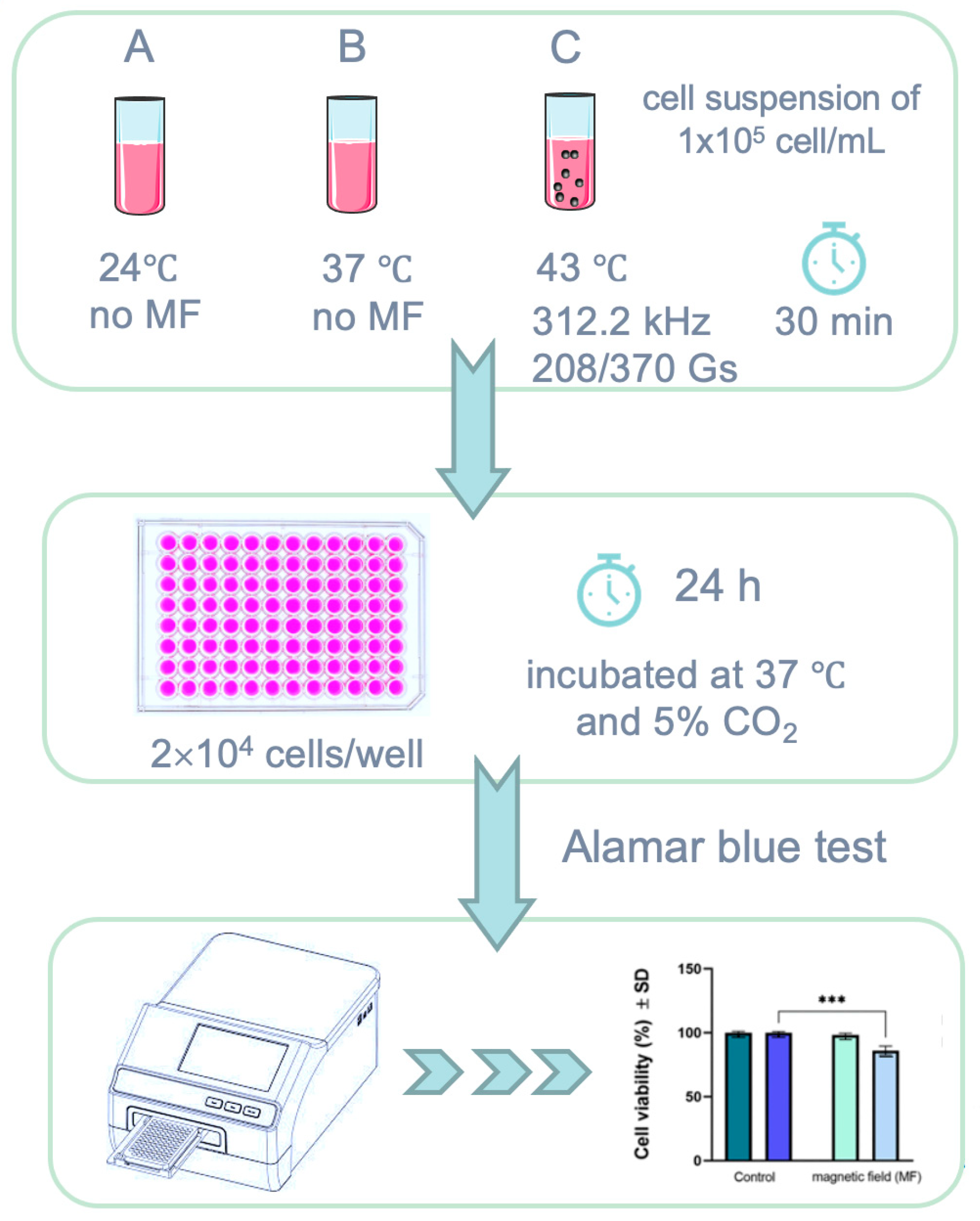
2.3. Squamous Skin Carcinoma (A431) Cells Viability above the Known Biological Magnetic Field Limit
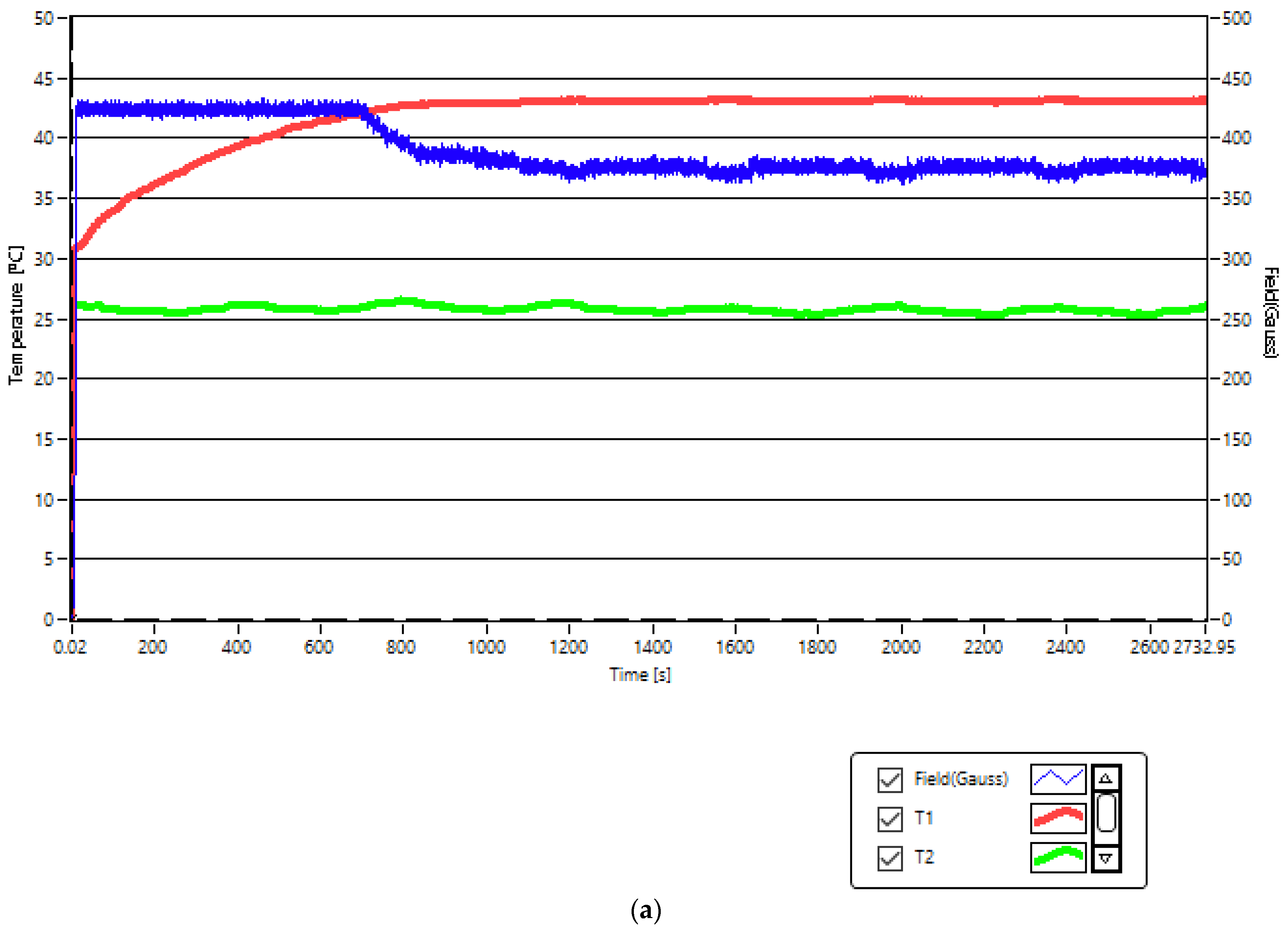
2.4. In Vitro Squamous Skin Carcinoma Cells Therapy by Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia with Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs) Nanobioconjugates
2.5. Biological Impact of Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs) Nanobioconjugates under SPMHT Conditions on A431 Cell Viability
2.6. SPMHT Limitations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The Human Epidermoid Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line
3.2. Nanobioconjugates Used in SPMHT for Cancer Therapy
3.3. In Vitro SPMHT Experiment
3.4. Alamar Blue Colorimetric Test
3.5. Representation and Statistical Evaluation of Experimental Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilger, I. In vivo applications of magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caizer, C. Magnetic/Superparamagnetic hyperthermia as an effective noninvasive alternative method for therapy of malignant tumors. In Nanotheranostics: Applications and Limitations; Rai, M., Jamil, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 297–335. [Google Scholar]
- Beola, L.; Asín, L.; Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Fernández-Afonso, Y.; Fratila, R.M.M.; Serantes, D.; Ruta, S.; Chantrell, R.W.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V.; et al. The intracellular number of magnetic nanoparticles modulates the apoptotic death pathway after magnetic hyperthermia treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43474–43487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Parekh, K.; Jain, N. In vitro hyperthermic effect of magnetic fluid on cervical and breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; de la Fuente, J.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Beyond traditional hyperthermia. in vivo cancer treatment with magnetic-responsive mesoporous silica nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocke, N.; Sethi, P.; Jyoti, A.; Chan, R.; Arnold, S.; Hilt, Z.; Upreti, M. Toxicity evaluation of magnetic hyperthermia induced by remote actuation of magnetic nanoparticles in 3D micrometastasic tumor tissue analogs for triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Ng, C.T.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Yang, H.T.; Zhao, L.Y.; Peng, E.; Lv, Y.B.; Xiao, W.; Fang, J.; Yi, J.B.; et al. Synthesis of ferromagnetic Fe0.6Mn0.4O nanofl owers as a new class of magnetic theranostic platform for in vivo T1-T2 Dual-Mode magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazeau, F.; Lévy, M.; Wilhelm, C. Optimizing magnetic nanoparticle design for nanothermotherapy. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosensweig, R. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Thiesen, B.; Wust, P.; Jordan, A. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia for prostate cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2010, 26, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Andujar, C.; Ortega, D.; Southern, P.; Nesbitt, S.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Pankhurst, Q. Real-time tracking of delayed-onset cellular apoptosis induced by intracellular magnetic hyperthermia. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Campos, I.; Asín, L.; Torres, T.E.; Marquina, C.; Tres, A.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. Cell death induced by the application of alternating magnetic fields to nanoparticle-loaded dendritic cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 205101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiesen, B.; Jordan, A. Clinical applications of magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2008, 24, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, I.; Armanetti, P.; Locatelli, E.; Flori, A.; Maturi, M.; Del Turco, S.; Menichetti, L.; Franchini, M.C. Smart assembly of Mn-ferrites/silica core–shell with fluorescein and gold nanorods: Robust and stable nanomicelles for in vivo triple modality imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2993–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caizer, C.; Hrianca, I. Dynamic magnetization of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles isolated in an SiO2 amorphous matrix. Eur. Phys. J. B 2003, 31, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, A.; Gorgo, S.; Rado, A.; Bajdak-Rusinek, K. Magnetite nanoparticles in magnetic hyperthermia and cancer therapies: Challenges and perspectives. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustini, A.; Petryk, A.; Cassim, S.; Tate, J.; Baker, I.; Hoopes, J. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano LIFE 2010, 01, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Application of nanomaterials in biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.L. Special Issue: Application of Nanomaterials in Biomedical Imaging and Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergt, R.; Dutz, S. Magnetic particle hyperthermia—Biophysical limitations of a visionary tumour therapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caizer, C.; Caizer, I.S.; Racoviceanu, R.; Watz, C.G.; Mioc, M.; Dehelean, C.A.; Bratu, T.; Soica, C. Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs) Biocompatible ferrimagnetic nanoparticles for increasing the efficacy in superparamagnetic hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T. Cancer hyperthermia using magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, K.; Bouras, A.; Bozec, D.; Ivkov, R.; Hadjipanayis, C. Magnetic hyperthermia therapy for the treatment of glioblastoma: A review of the therapy’s history, efficacy and application in humans. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchêne, D. Cyclodextrins and their inclusion complexes. In Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Ito, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Kawamura, T.; Shimada, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Saida, T.; Honda, H. Intratumoral injection of immature dendritic cells enhances antitumor effect of hyperthermia using magnetic nanoparticles. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Ito, A.; Nakahara, Y.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Futakuchi, M.; Shirai, T.; Tozawa, K.; Kohri, K. Complete regression of experimental prostate cancer in nude mice by repeated hyperthermia using magnetite cationic liposomes and a newly developed solenoid containing a ferrite core. Prostate 2006, 66, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caizer, C.; Caizer-Gaitan, I.S.; Watz, C.G.; Dehelean, C.A.; Bratu, T.; Soica, C. High efficacy on the death of breast cancer cells using spmht with magnetite cyclodextrins nanobioconjugates. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kakimi, K.; Nakayama, E.; Jimbow, K. Antitumor immunity by magnetic nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, G.; Sudame, A.; Bhati, P.; Chakrabarty, A.; Maity, D. Systematic investigations on heating effects of carboxyl-amine functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) based ferrofluids for in vitro cancer hyperthermia therapy. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Kichkailo, A.S. Aptamers increase biocompatibility and reduce the toxicity of magnetic nanoparticles used in biomedicine. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NanoTherm®Therapy, MagForce Nanomedicine, Germany. Available online: https://magforce.de/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Alphandéry, E.; Chebbi, I.; Guyot, F.; Durand-Dubief, M. Use of bacterial magnetosomes in the magnetic hyperthermia treatment of tumours: A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Reviewed and Confirmed in 2017, Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO Catalogue, Edition 3. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36406.html (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Legge, C.; Colley, H.; Lawson, M.; Rawlings, A. Targeted magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia for the treatment of oral cancer. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2019, 48, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Ru, L.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X. CD44-Targeted magnetic nanoparticles kill head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells in an alternating magnetic field. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7549–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneet, K.; De, T.; Rangarajan, A.; Jain, S. Magnetic nanofibers based bandage for skin cancer treatment: A non-invasive hyperthermia therapy. Cancer Rep. 2020, 3, e1281.38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, G.; Ravagli, C.; Mazzantini, F.; Loudos, G.; Adan, J.; Masa, M.; Psimadas, D.; Fragogeorgi, E.A.; Locatelli, E.; Innocenti, C.; et al. In vivo anticancer evaluation of the hyperthermic efficacy of anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted PEG-based nanocarrier containing magnetic nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3037–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, M.; Gneveckow, U.; Thiesen, B.; Taymoorian, K.; Cho, C.H.; Waldofner, N.; Scholz, R.; Jordan, A.; Loening, S.A.; Wust, P. Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic nanoparticles: Feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional temperature distribution. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Hauff, K.; Rothe, R.; Scholz, R.; Gneveckow, U.; Wust, P.; Thiesen, B.; Feussner, A.; Deimling, A.; Waldoefner, N.; Felix, R.; et al. Intracranial thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy: Results of a feasibility study on patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2007, 81, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, B.; Rivera, D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Brown, C.; Young, T.; Williams, T.; Huq, S.; Mattioli, M.; Bouras, A.; Hadjpanayis, C.G. Magnetic hyperthermia therapy for high grade glioma: A state-of-the-art review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Gazeau, F.; Wilhelm, C. Intracellular heating of living cells through Néel relaxation of magnetic nanoparticles. Eur. Biophys. J. 2008, 37, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, W.C. Arrhenius relationships from the molecule and cell to the clinic. Int. J. Hyperth. 2009, 25, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rhoon, G.C. Is CEM43 still a relevant thermal dose parameter for hyperthermia treatment monitoring? Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Jangam, A.A.; Yung Shen, J.L.; Ahmad, A.; Arepally, N.; Carlton, H.; Ivkov, R.; Attaluri, A. Design of a temperature-feedback controlled automated magnetic hyperthermia therapy device. Front. Therm. Eng. 2023, 3, 1131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, D. Evolution of magnetic hyperthermia for glioblastoma multiforme therapy. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farcas, C.G.; Dehelean, C.; Pinzaru, I.A.; Mioc, M.; Socoliuc, V.; Moaca, E.A.; Avram, S.; Ghiulai, R.; Coricovac, D.; Pavel, I.; et al. Thermosensitive betulinic acid-loaded magnetoliposomes: A promising antitumor potential for highly aggressive human breast adenocarcinoma cells under hyperthermic conditions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8175–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, P.T.; Le, T.T.H.; Bui, T.Q.; Pham, H.N.; Ho, A.S.; Nguyen, L. Doxorubicin release by magnetic inductive heating and in vivo hyperthermia-chemotherapy combined cancer treatment of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 5404–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, R.M.; Raman, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Slominski, A.T. How cancer hijacks the body’s homeostasis through the neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

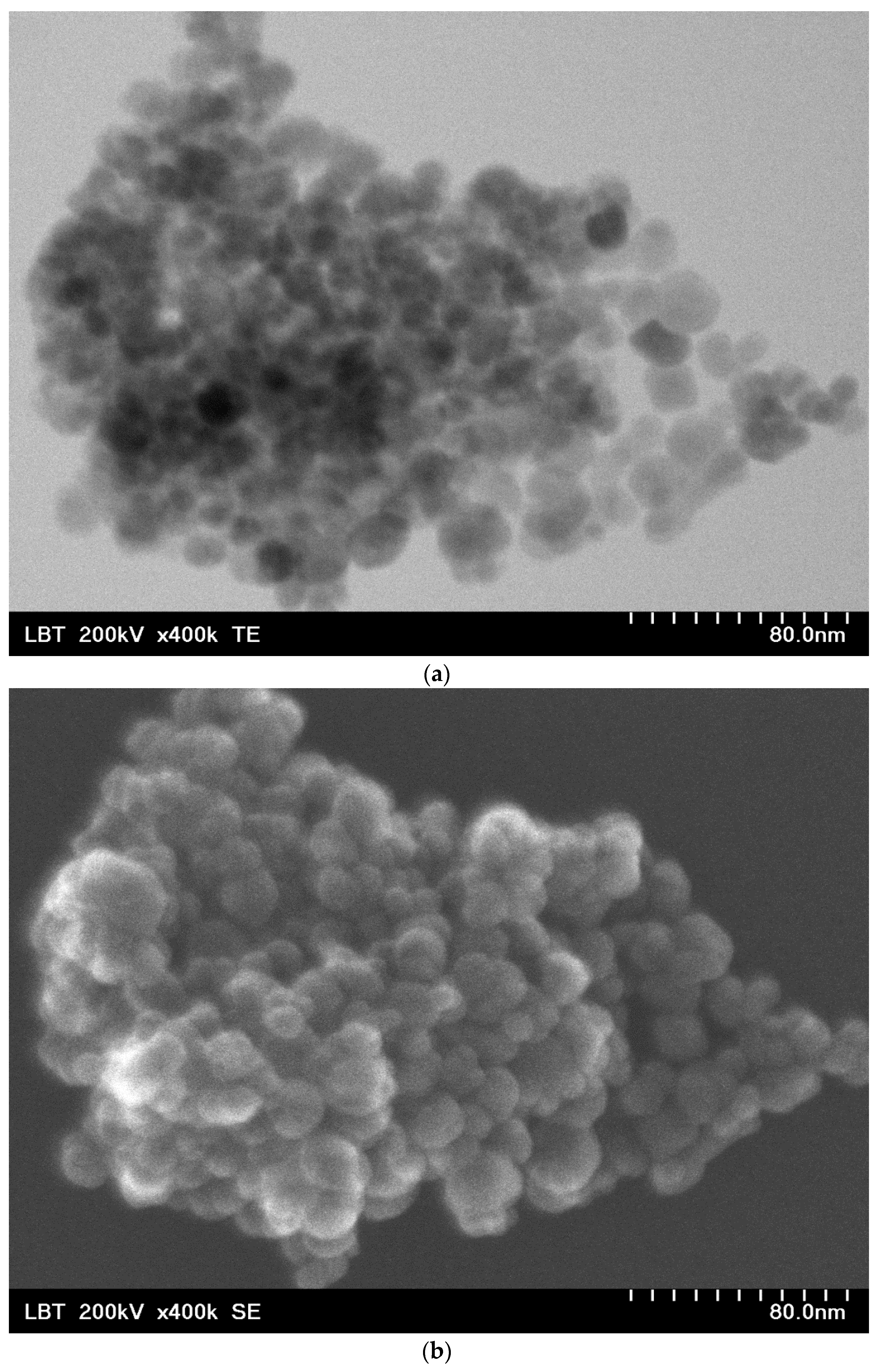
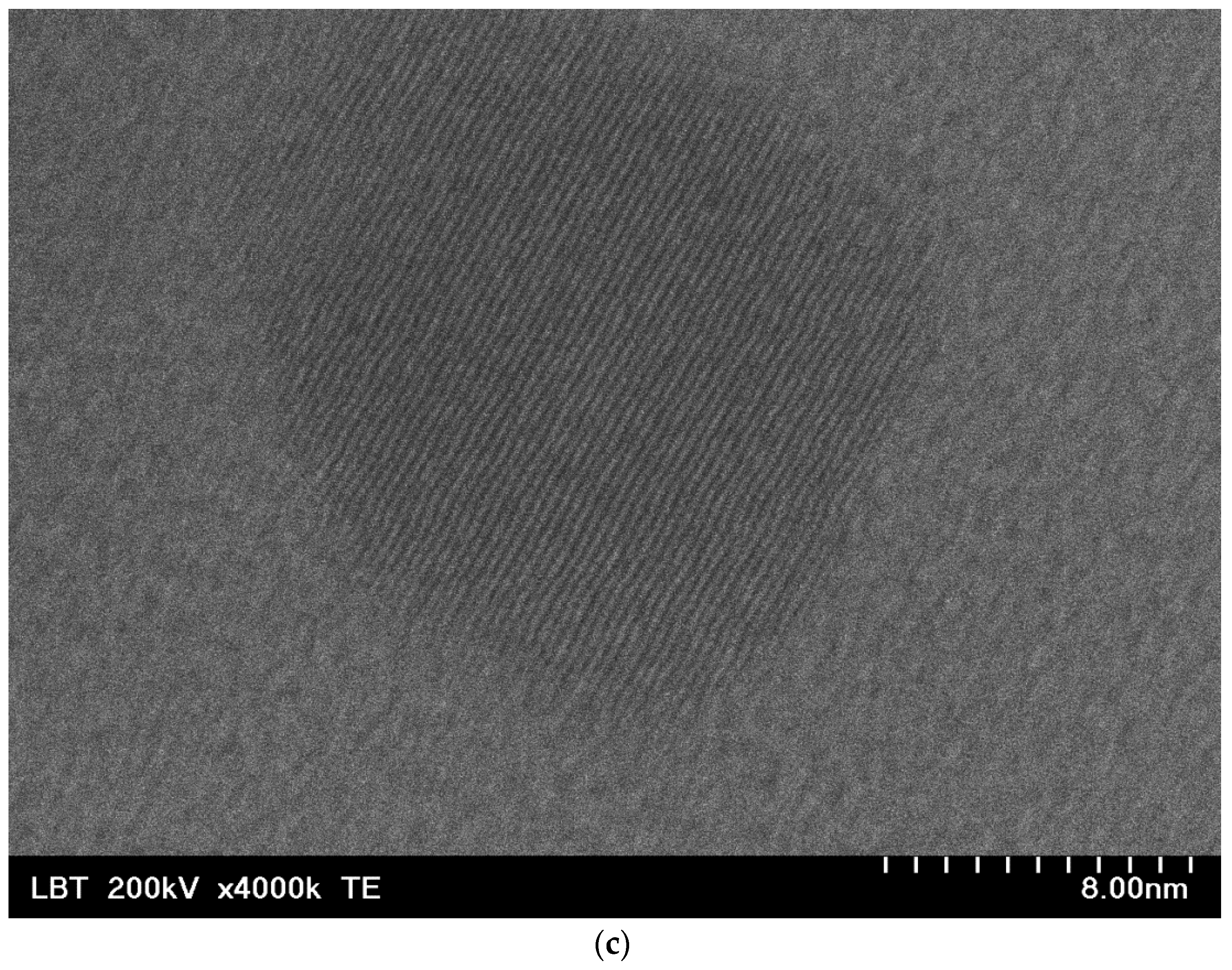
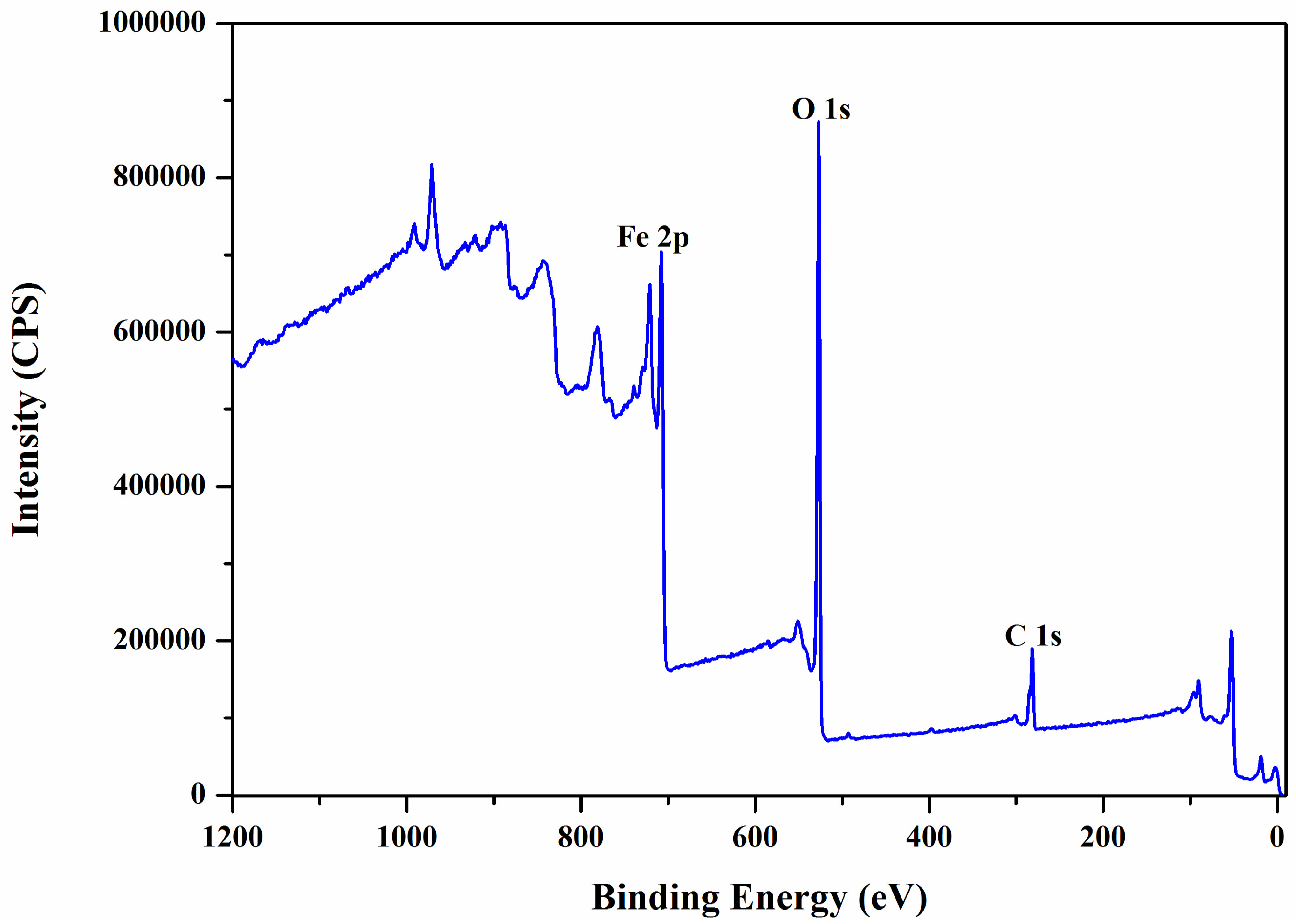
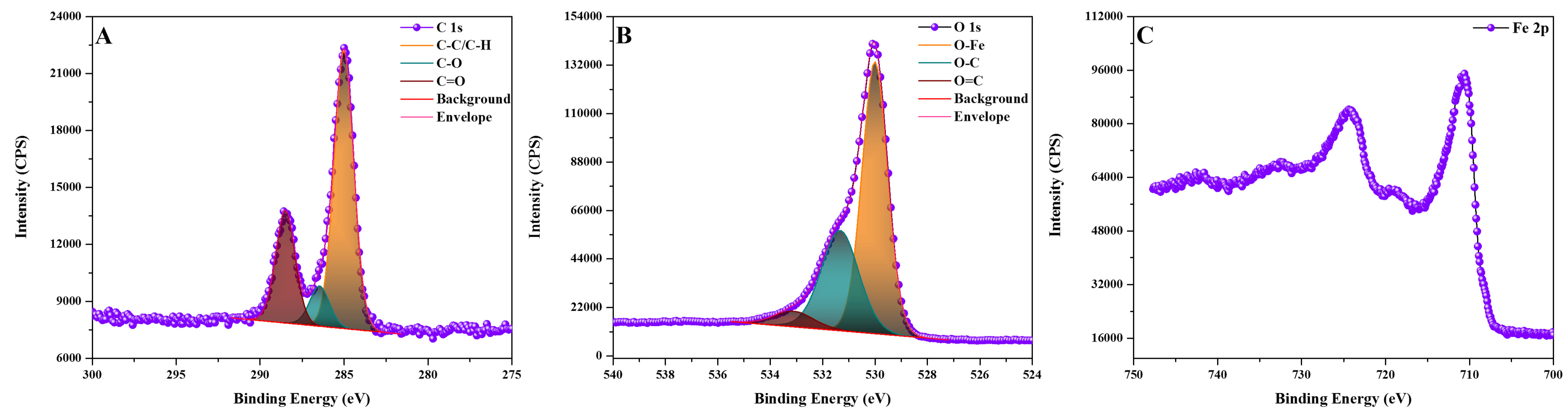



| Atomic Concentration [%] | Mass Concentration [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| Fe 2p | 27.57 | 58.93 |
| O 1s | 50.99 | 31.22 |
| C 1s | 21.44 | 9.85 |
| Binding Energy [eV] | Relative Atomic Concentration [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| C-C/C-H | * 285 | 64.54 |
| C-O | 286.5 | 9.32 |
| C=O | 288.5 | 26.14 |
| O-Fe | 530 | 61.26 |
| O-C | 531.3 | 33.26 |
| O=C | 533.1 | 5.48 |
| No. | Magnetic Field Amplitude (G) | Magnetic Field Frequency (kHz) | Magnetic Nanoparticle Concentrations (mg/mL) | Duration of Application of Magnetic Field (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 208 | 312.4 | 5 | 30 |
| 2 | 370 | 312.4 | 1 | 30 |
| Magnetic Field Amplitude (G) | 208(±1) | 370(±1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability (%) ± SD | Standard conditions (37 °C) | 100 ± 1.03 | 100 ± 0.92 |
| Post-exposure to magnetic field | 98.3 ± 1.44 | 86 ± 3.52 | |
| Sample/ Concentration | Cell Viability (%) ± SD A431 Cells after SPMHT (43(±0.1) °C for 30 min) | Cell Viability (%) ± SD A431 Control Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs)/ 1 mg/mL | 54.04 ± 3.91 | 100 ± 0.71 |
| Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs)/ 5 mg/mL | 42.01 ± 2.68 | |
| Fe3O4-PAA–(HP-γ-CDs)/ 10 mg/mL | 17.2 ± 4.45 |
| NPs Type, Size | Biocompatibility, NP Concentration | Tumor Type | In Vitro (Cell Line) | In Vivo (Mouse Model) | Magnetic Field | Frequency | Therapy Temperature | Therapy Duration | Viability/Inhibition Cell/Tumor Volume | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4; 8–12 nm | Coating with an amine-terminated silica shell of 6 nm, and functionalized with αvβ6 antibodies | Squamous carcinoma | VB6 cells line | - | 9.7 mT | 174 kHz | Hyperthermia temperature | 10 min. | ~50% viability at 24 h; ~25% viability at 48 h; | [35] |
| Fe3O4 | CD44 antibody (CD44-Fe3O4: 100 nm); 0.4 mg/mL | Squamous carcinoma | - | BALB/c nude mice (male) | Current of 50 A in the induction coil | 237 kHz | 43 °C | 30 min. | ~33% inhibition | [36] |
| Fe3O4 in fibrous mat. (PCL); 50–100 nm | Polycaprolactone (PCL) fibrous bandage (10 mg) | Skin cancer | Cervical cancer HeLa cell lines (variant of Dox-resistant HeLa cells) | - | 3.6 kA/m | 236 kHz | 45 °C | 10 min. | ~50% viability at 2 h | [37] |
| Fe3O4 in fibrous mat. (PCL); 50–100 nm | Polycaprolactone (PCL) fibrous bandage (10 mg) | Skin cancer | - | BALB/c mice (female) | 3.6 kA/m | 236 kHz | 45 °C | 15 min. according to therapy plan: 1z, 1z, 1z, 2z, 2z (z-day) | ~7% decreases volume tumor at 24 h; ~82% decreases volume tumor at 2z; Complete tumor regression after 30 days of the treatment | [37] |
| Fe3O4; ~12 nm | 1-PNP-hEGFR; 4.53 mg/mL | Squamous carcinoma | - | Epidermoid cancer in an A431 tumor-bearing mouse | 25 kA/m | 173 kHz | Hyperthermia temperature | 30 min. | ~60% decreases in tumor volume | [38] |
| Fe3O4; ~16 nm | Coated with PAA-(HP-γ-CDs); 10 mg/mL | Squamous carcinoma | A431 cells line | - | 13.37 kA/m | 312.4 kHz | 43 °C | 30 min. | 17.2% viability at 24 h | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caizer-Gaitan, I.-S.; Watz, C.-G.; Caizer, C.; Dehelean, C.-A.; Bratu, T.; Crainiceanu, Z.; Coroaba, A.; Pinteala, M.; Soica, C.-M. In Vitro Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia Employing Magnetite Gamma-Cyclodextrin Nanobioconjugates for Human Squamous Skin Carcinoma Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158380
Caizer-Gaitan I-S, Watz C-G, Caizer C, Dehelean C-A, Bratu T, Crainiceanu Z, Coroaba A, Pinteala M, Soica C-M. In Vitro Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia Employing Magnetite Gamma-Cyclodextrin Nanobioconjugates for Human Squamous Skin Carcinoma Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158380
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaizer-Gaitan, Isabela-Simona, Claudia-Geanina Watz, Costica Caizer, Cristina-Adriana Dehelean, Tiberiu Bratu, Zorin Crainiceanu, Adina Coroaba, Mariana Pinteala, and Codruta-Marinela Soica. 2024. "In Vitro Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia Employing Magnetite Gamma-Cyclodextrin Nanobioconjugates for Human Squamous Skin Carcinoma Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158380
APA StyleCaizer-Gaitan, I.-S., Watz, C.-G., Caizer, C., Dehelean, C.-A., Bratu, T., Crainiceanu, Z., Coroaba, A., Pinteala, M., & Soica, C.-M. (2024). In Vitro Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia Employing Magnetite Gamma-Cyclodextrin Nanobioconjugates for Human Squamous Skin Carcinoma Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158380










