microRNAs as New Biomolecular Markers to Estimate Time since Death: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
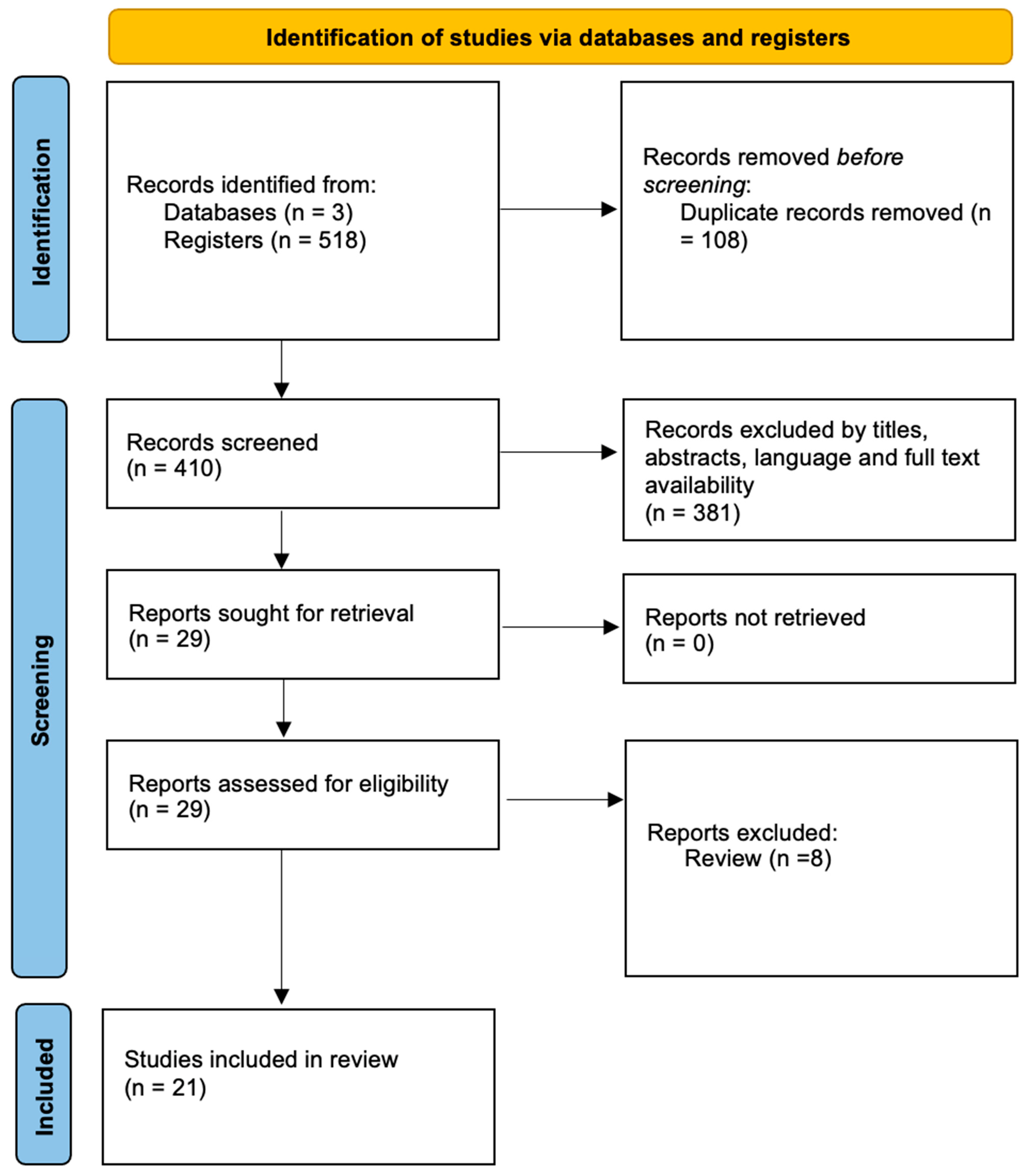
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Risk of Bias
3.2. miRNA and PMI Estimation
3.2.1. miRNA Expression Patterns Assessed within PMI of 72 h
3.2.2. miRNA Expression Patterns Assessed within PMI of 7 Days
3.2.3. miRNA Expression Patterns Assessed within PMI over 7 Days
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Evidence on microRNAs in PMI Estimation
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrestha, R.; Kanchan, T.; Krishan, K. Methods of Estimation of Time Since Death; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Babapulle, C.J.; Jayasundera, N.P. Cellular changes and time since death. Med. Sci. Law 1993, 33, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplace, K.; Baccino, E.; Peyron, P.A. Estimation of the time since death based on body cooling: A comparative study of four temperature-based methods. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriki, S.; Iino, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Fukazawa, Y.; Inai, K.; Sakai, T.; Kimura, H. Pathological analysis of cadavers for educational dissection by using postmortem imaging. Pathol. Int. 2019, 69, 580–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, T.M.; Omran, B.H.F.; El Deib, M.M.; El-Sharkawy, N.I.; Metwally, M.M.M.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M. Early postmortem biochemical, histological, and immunohistochemical alterations in skeletal muscles of rats exposed to boldenone undecylenate: Forensic implication. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2021, 83, 102248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aquila, M.; De Matteis, A.; Scatena, A.; Costantino, A.; Camporeale, M.C.; De Filippis, A. Estimation of the time of death: Where we are now? La Clinica Terapeutica 2021, 172, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.H.; Ehrett, C.; Weisensee, K.; Tica, C. Commentary on: Megyesi MS, Nawrocki SP, Haskell NH. Using accumulated degree-days to estimate the postmortem interval from decomposed human remains. J. Forensic Sci. 2023, 50, 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Otatsume, M.; Shinkawa, N.; Tachibana, M.; Kuroki, H.; Ro, A.; Sonoda, A.; Kakizaki, E.; Yukawa, N. Technical note: Excel spreadsheet calculation of the Henssge equation as an aid to estimating postmortem interval. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2023, 101, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, A.; Myburgh, J.; Steyn, M.; Becker, P.J. The effect of body size on the rate of decomposition in a temperate region of South Africa. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, M.J.; Finaughty, D.A.; Friedling, L.J.; Gibbon, V.E. The effect of clothing on decomposition and vertebrate scavengers in cooler months of the temperate southwestern Cape, South Africa. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 309, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzo, P.; Scrivano, S.; Sanavio, M.; Caenazzo, L. The Role of DNA Degradation in the Estimation of Post-Mortem Interval: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiese, A.; Scatena, A.; Costantino, A.; Di Paolo, M.; La Russa, R.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. MicroRNAs as Useful Tools to Estimate Time Since Death. A Systematic Review of Current Literature. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianci, V.; Forzese, E.; Sapienza, D.; Cianci, A.; Ieni, A.; Germanà, A.; Guerrera, M.C.; Omero, F.; Speranza, D.; Cracò, A.; et al. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Post-Mortem Assessment: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, M.; Cocimano, G.; Roccuzzo, S.; Russo, I.; Piombino-Mascali, D.; Márquez-Grant, N.; Zammit, C.; Esposito, M.; Sessa, F. New Trends in Immunohistochemical Methods to Estimate the Time since Death: A Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissenberger, J.; Amendt, J.; Klampfer, J.; Thuemmel, L.; Jakob, L.; Monticelli, F.C.; Steinbacher, P.; Pittner, S. Morphological changes and protein degradation during the decomposition process of pig cadavers placed outdoors or in tents-a pilot study. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2023, 20, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locci, E.; Stocchero, M.; Gottardo, R.; Chighine, A.; De-Giorgio, F.; Ferino, G.; Nioi, M.; Demontis, R.; Tagliaro, F.; D’aloja, E. PMI estimation through metabolomics and potassium analysis on animal vitreous humour. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2023, 137, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; He, F.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, L. Correlative analysis on the relationship between PMI and DNA degradation of cell nucleus in human different tissues. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2005, 25, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Pittner, S.; Gotsmy, W.; Zissler, A.; Ehrenfellner, B.; Baumgartner, D.; Schrüfer, A.; Steinbacher, P.; Monticelli, F. Intra- and intermuscular variations of postmortem protein degradation for PMI estimation. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2020, 134, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, S.; Purohit, P.; Mishra, R.; Gupta, V.; Setia, P. The Impact of RNA Stability and Degradation in Different Tissues to the Determination of Post-Mortem Interval: A Systematic Review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2023, 349, 111772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaribu, R.S.; Auerkari, E.I.; Suhartono, A.W.; Auerkari, P. A Small RNA, microRNA as a Potential Biomolecular Marker to Estimate Post Mortem Interval in Forensic Science: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2023, 137, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Luo, M. miRNA-103-3p-Hlf Regulates Apoptosis and Autophagy by Targeting Hepatic Leukaemia Factor in Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 3038–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, J.; Dheda, K.; Bustin, S.; Zumla, A. Real-time RT-PCR Normalisation: Strategies and Considerations. Genes Immun. 2005, 6, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozera, B.; Rapacz, M. Reference Genes in Real-Time PCR. J. Appl. Genet. 2013, 54, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guénin, S.; Mauriat, M.; Pelloux, J.; Van Wuytswinkel, O.; Bellini, C.; Gutierrez, L. Normalization of qRT-PCR Data: The Necessity of Adopting a Systematic, Experimental Conditions-Specific, Validation of References. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chervoneva, I.; Li, Y.; Schulz, S.; Croker, S.; Wilson, C.; Waldman, S.A.; Hyslop, T. Selection of Optimal Reference Genes for Normalization in Quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivano, S.; Sanavio, M.; Tozzo, P.; Caenazzo, L. Analysis of RNA in the Estimation of Post-Mortem Interval: A Review of Current Evidence. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019, 133, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odriozola, A.; Riancho, J.A.; de la Vega, R.; Agudo, G.; García-Blanco, A.; de Cos, E.; Fernández, F.; Sañudo, C.; Zarrabeitia, M.T. miRNA analysis in vitreous humor to determine the time of death: A proof-of-concept pilot study. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, D.; Kaul, D. AATF RNome has the potential to define post mortem interval. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 247, e21–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.H.; Li, Z.H.; Tuo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, K.; Bian, J.; Ma, J.L.; Chen, L. Correlation between RNA Degradation Patterns of Rat’s Brain and Early PMI at Different Temperatures. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 32, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, Y.H.; Ma, K.J.; Li, Z.H.; Sun, Y.F.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, L.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Zhao, Q.R.; Yang, T. Correlation between RNA Expression Level and Early PMI in Human Brain Tissue. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 32, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.F.; Ali, M.M.; Basyouni, H.; Rashed, L.A.; Amer, E.A.E.; Abd, E.-K.D. Histological and miRNAs postmortem changes in incisional wound. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Lv, Y.; Tao, L.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Ma, K.; Shi, Q.; Xiao, B.; et al. Identification of the miRNA-3185/CYP4A11 axis in cardiac tissue as a biomarker for mechanical asphyxia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 311, 110293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rivera, V.; Cárdenas-Monroy, C.A.; Millan-Catalan, O.; González-Corona, J.; Huerta-Pacheco, N.S.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.; Villavicencio-Queijeiro, A.; Pedraza-Lara, C.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Bravo-Gómez, M.E.; et al. Dysregulation of miR-381-3p and miR-23b-3p in skeletal muscle could be a possible estimator of early post-mortem interval in rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshanfar, A.; Kian, M.; Dehghan, Z.; Valizadeh, A.; Moayedi, J. Comparison of the Effects of Two Methods of Euthanasia on Post Mortem Changes in Rats: Histopathological and Molecular Findings. Comp. Clin. Path. 2022, 31, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardado-Estrada, M.; Cárdenas-Monroy, C.A.; Martínez-Rivera, V.; Cortez, F.; Pedraza-Lara, C.; Millan-Catalan, O.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. A miRNome analysis at the early postmortem interval. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C.; Ma, K.J.; Lv, Y.H.; Zhang, P.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, D.; Chen, L. Postmortem interval determination using 18S-rRNA and microRNA. Sci. Justice 2014, 54, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Lü, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Ma, K.J.; Chen, L. Correlation between Five RNA Markers of Rat’s Skin and PMI at Different Temperatures. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014, 30, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Pan, H.; Zeng, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, A.; Jiang, J.; Ma, K.; Chen, L. Exploration of the R Code-Based Mathematical Model for PMI Estimation Using Profiling of RNA Degradation in Rat Brain Tissue at Different Temperatures. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2015, 11, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.C.; Xue, A.M.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, K.J.; Chen, L. RNA degradation as described by a mathematical model for postmortem interval determination. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2016, 44, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Pan, H.; Zeng, Y.; Tao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.C.; Ma, K.J.; Chen, L. Estimation of the Human Postmortem Interval Using an Established Rat Mathematical Model and Multi-RNA Markers. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2017, 13, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jang, S.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Na, J.Y. Difference in microRNA Levels in the Post-Mortem Blood from Different Sampling Sites: A Proof of Concept. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2021, 78, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.H.; Ma, K.J.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Zhang, P.; Shen, Y.W.; Jiang, N.; Ma, D.; Chen, L. A Time Course Study Demonstrating mRNA, microRNA, 18S rRNA, and U6 snRNA Changes to Estimate PMI in Deceased Rat’s Spleen. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Du, T.; Shao, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, Y. Evaluating the potential of housekeeping genes, rRNAs, snRNAs, microRNAs and circRNAs as reference genes for the estimation of PMI. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2018, 14, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Du, T.; Ye, X.; Shao, C.; Xie, J.; Shen, Y. Using miRNAs and circRNAs to estimate PMI in advanced stage. Leg. Med. 2019, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehhi, S.; Haddrill, P.R. Estimating time since deposition using quantification of RNA degradation in body fluid-specific markers. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 298, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, J.Y. Estimation of the post-mortem interval using microRNA in the bones. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2020, 75, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Ali, W.; Sandhu, S.; Mishra, S.; Singh, U.S.; Verma, A.K.; Singh, M.; Ahmad, M.K.; Kumari, S. Post-Mortem Interval Estimation Using miRNAs of Road Traffic Accident Cases: A Forensic Molecular Approach. Sci. Justice 2023, 63, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y. Research Progress of DNA-Based Technologies for Postmortem Interval Estimation. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 38, 747–753. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlow, N.; Mills, D.; Byrd, J.; Warren, M.; Long, M.T. Review of the Current and Potential Use of Biological and Molecular Methods for the Estimation of the Postmortem Interval in Animals and Humans. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2023, 35, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, A.; Singh, S.P.; Singh, P.; Gupta, O.P.; Manas, A.; Gupta, S. Role of Molecular Techniques in PMI Estimation: An Update. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2021, 83, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, S.A.; Brill, L.B., 2nd; Bennett, J.P., Jr. Stability of Gene Expression in Postmortem Brain Revealed by cDNA Gene Array Analysis. Brain Res. 2002, 942, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panovska-Griffiths, J.; Kerr, C.C.; Waites, W.; Stuart, R.M. Mathematical Modeling as a Tool for Policy Decision Making: Applications to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Handb. Stat. 2021, 44, 291–326. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio-Silva, F.; Magalhães, T.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Silvestre, R. Profiling of RNA degradation for estimation of post mortem [corrected] interval. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Elfenbein, S.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, M.; Qiu, C.; Ding, Y.; Lu, J. Characterization of the Mammalian miRNA Turnover Landscape. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2326–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, N. miR-142-3p modulates the circadian clock through targeting Bmal1. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 9589–9597. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.; Han, D.H.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Park, J.W.; Jeong, H. Circadian Regulation of microRNA Expression in Murine and Human Tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13853–13858. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, L.B.; Lund, A.H. miR-21 and Programmed Cell Death. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Raver-Shapira, N.; Marciano, E.; Meiri, E.; Spector, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Moskovits, N.; Bentwich, Z.; Avniel, A.; Yakhini, Z.; Oren, M. Transcriptional Activation of miR-34a Contributes to p53-Mediated Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.B.; Xue, L.; Yang, J.; Ma, A.H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, M.; Qin, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, X.; deVere White, R.W. An Androgen-Regulated miRNA Suppresses Bak1 Expression and Induces Androgen-Independent Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19983–19988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianci, V.; Mondello, C.; Sapienza, D.; Guerrera, M.C.; Cianci, A.; Cracò, A.; Omero, F.; Gioffrè, V.; Gualniera, P.; Asmundo, A.; et al. Potential Role of mRNA in Estimating Postmortem Interval: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Ma, K.; Xiao, B.; Fei, G.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, L.; et al. Model for the prediction of mechanical asphyxia as the cause of death based on four biological indexes in human cardiac tissue. Sci. Justice 2021, 61, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, C.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Amendt, J.; Wang, J. Dynamics of Insects, Micro-organisms and Muscle mRNA on Pig Carcasses and Their Significances in Estimating PMI. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 329, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors | Year | mRNA | Sample | Tissue | Sample Number | Temperature | PMI—Time Frame Assessed | PMI Significance | PMI Epicrisis | Reference—Control Genes/RNA/DNA—No | Statistical Analysis | Estimated Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odriozola A. [27] | 2013 | miR-34c | Dead human | Vitreous humor | 34 | N.R. * | Up to 24 h | at least up to 24 h | decrease as PMI increase | miR-222 | Two-tailed Student’s t test | N.R. * |
| miR-222 | stable up to 24 h | |||||||||||
| miR-888 | ||||||||||||
| miR-484 | downregulated | |||||||||||
| miR-142-5p | upregulated (* if death occured during night) | |||||||||||
| miR-541 | ||||||||||||
| Sharma et al. [28] | 2015 | miR-2909 | Mice | Heart, lungs, brain, spleen, liver, pancreas and kidneys | 9 | 25 °C | 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h, 72 h | up to 48 h | stable up to 48 if sacrificed at 8:00 pm; stable up to 12 h if sacrificed at 12:00 p.m. | N.U. * | SPSS window v.19 and ANOVA | N.R. * |
| Lu Y.H. [29] | 2016 | miR-9 and miR-125b | Rat | Brain | 222 | 5, 15, 25, 35 °C | 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24 h | miRNA-9 and miRNA-125b remain stable up to 24 | stable up to 24 h | 5S rRNA, miR-9, miR-125b | Regression analysis by SPSS software 8 (v.19) | Average error rate: 14.1% (β-actin) and 22.2% (GAPDH) |
| Lu Y.H. [30] | 2016 | miR-9 and miR-125b | Dead human | Brain | 12 | N.R. * | from 4.3 to 22.5 h | miRNA-9, miRNA-125b suitable as internal reference markers | stable up to 24 h | 5S rRNA, miR-9, miR-125b | Quadratic regression (R software v.19) | Error rate: 24.6% (β-actin) and 41.0% (GAPDH) |
| Ibrahim S.F. [31] | 2019 | miR-205 miR-21 | Rats | Skin | 18 | N.R. * | 0, 24, 48 h | N.S.S. * | marked increase at 24 h and strong decrease at 48 h | N.R. * | Pearson correlation test | N.R. * |
| Han L. et al. [32] | 2020 | miR-3185 | Dead human | Heart | 51 | from 5 °C to 40 °C | from 1.5 h to 30.5 h | N.S.S. * | upregulated in mechanical asphyxia death compared with other death | β-actin mRNA | t-test; Mann-Whitney tests | N.R. * |
| Martinez-Rivera V. [33] | 2021 | miR-144-3p; | Rats | Skeletal muscle | 25 | 25 °C | 0, 3, 6, 12, 24 h | N.S.S. * | decreased at 0–6 h | * To normalize the expression of EPC1: ACTB gene (Rn00667869_m1) | Non-parametric Kruskal Wallis; Mann U Whitney test; Pearson’s Chi-squared test; Cochran-Armitage test; Spearman Rho | N.R. * |
| miR-23b-3p; | 24 h | significantly down-regulated at 3 to 24 h | ||||||||||
| miR-381-3p | 0, 3, 12, 24 h | significantly down-regulated in the first 3 h and upregulated at 6 to 24 h | ||||||||||
| Derakhshanfar A. [34] | 2022 | miR-122 | Rats | Liver and kidney | 10 | 25 °C | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24, 48 h | N.S.S. * | upregulated at 4, 10, and 24 h; downregulated at 6, 8, and 48 h | miR-16, miR 221, Let-7a, U6 snRNA | Graph Pad Prism8.0 and SPSS 17.0 software | N.R. * |
| Guardado-Estrada M. [35] | 2023 | 1218 miRNAs, of whom156 downregulated (84) or upregulated (72) at 24 h | Rats | Skeletal muscle | 9 | 22 °C | 0, 24 h | N.R. * | miR-139-5p most significant downregulated, rno-miR-92b-5p most significant upregulated | Affymetrix Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC) SoftwareTM 4.0 | Robust Multi-chip Analysis (RMA) | N.R. * |
| Authors | Year | mRNA | Sample | Tissue | Sample Number | Temperature | PMI—Time Frame Assessed | PMI Significance | PMI Epicrisis | Reference–Control Genes/RNA/DNA—No | Statistical Analysis | Estimated Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wen-Can L. [36] | 2014 | miR-1, miR-143, miR-208, 18S rRNA | Rats (Sprague-Dawley) | Heart | 6 | 25 °C | 1, 3, 6, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, and 168 h, up to 7 days | up to 168 h | miR-1 has a stable expression along the studied PMI; 18S rRNA gradually increased in the early stage and peaked at around 96 h | miR-1 | Variance and linear regression | N.R. * |
| Pan H. [37] | 2014 | miR-203 | Rat | Skin | 18 | 4, 15, 35 °C | From 0 to 120 h | N.R. * | remain stable up to 120 h | miR-203 | Regression analysis (GraphPad) | N.R. * |
| Ma J. [38] | 2015 | miR-9, miR-125b (Other RNAs: β-actin, GAPDH and RPS29 mRNA, 5S and 18S rRNA, U6 snRNA and Let-7a) | Rats (Sprague-Dawley) | Brain | 270 | 4, 15, 25, 35 °C | 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 h | N.R. * | miR-9, miR-125b remain stable up to up to 144 days | miR-9, miR-125b | Bivariate cubic curve and quadratic regression | Mean error rate 4.8% Ranging from 30% (30 h at 20 °C) to 43% (10 h at 30 °C) |
| 36 | 10, 20, 30 °C | 10, 30, 50, 100 h | ||||||||||
| Lv Y. [39] | 2016 | miR-195, miR-200c (lung); miR-1, miR-206, (skeletal muscle) | Rats | Lungs and skeletal muscle | 216 | 10, 20, 30 °C | 0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144 h | Up to 144 h | Stable up to 144 h, then decreased | b-actin and GAPDH, 18S rRNA, RPS29 mRNA | Linear, quadratic, and cubic regression, △Ct method | 7.4% |
| 15 | 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 °C | 10, 60, 110 h | ||||||||||
| Dead human | 12.5% | |||||||||||
| 12 | ambient temperature of the crime scene before being transferred to freezer or autopsy | ariable from 7 to 73 h | ||||||||||
| Lv Y. [40] | 2017 | miR-1, miR-133a, miR-122, miR-9, miR-125b | Dead human; rats Sprague-Dawley | Human heart (Apex Cordis), liver (right lobe), and brain (frontal cortex) | Thirteen dead human (seven males, six females); 36 rats | 4 °C, 15 °C, 25 °C, 35 °C | From 6–71 h up to 5 days | Up to 71 h | Stable up to 5 days | β-actin, GAPDH, RPS29 mRNA | Linear, quadratic, and cubic regression (R software v. 2.3), ΔCt method | Mean estimated error: 5.06 (human); 2.89 (rat) |
| Kim S-Y. [41] | 2021 | miR-16, miR-208b, let-7e, miR-1 | Dead human | Venous blood from three different sites (external iliac vein, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus) | 28 (17 male, 11 female) | N.R. * | From 16 to 86 h | N.S.S. * | Variable in relation to the sampling site | Ce_miR-39_1 | ΔCt method, Spearson’s correlation, and Tukey’s analysis | N.R. * |
| Authors | Year | mRNA | Sample | Tissue | Sample Number | Temperature | PMI—Time Frame Assessed | PMI Significance | PMI Epicrisis | Reference—Control Genes/RNA/DNA—No | Statistical Analysis | Estimated Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lv. Y. [42] | 2014 | miR-125b and miR-143 (Other RNAs: β-actin, GAPDH1 and 2 mRNA, ACTB1 and 2,18S rRNA, U6 snRNA) | Rats (18) | Spleen | 6 | 4, 25 °C | 0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 h | At 25 °C, miR-125b and miR-143 stable up to 44 h; at 4 °C, miR-125b and miR-143 stable up to 312 h | miR-125b Ct values fluctuated slightly within 36 h and then increased slowly at 25 °C; the same trend has been observed within 144 h at 4 °C | miR-125b and miR-143 for GAPDH1 and 2, ACTB1 and 2, U6, and 18S rRNA | Linear, quadratic, cubic, reciprocal, exponential, and logarithmic regression (GraphPad v5.0) | <10% at 25 °C and <20% at 4 °C |
| 6 | 0, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, 168, 192, 216, 240, 264, 288, and 312 h | |||||||||||
| 3 | 0, 5, 55 and 105 h | |||||||||||
| 3 | 0, 20, 100, 180, and 260 h | |||||||||||
| Tu C. [43] | 2018 | miR-122, miR133a (and Gapdh, Rps18, β-actin, 5S, 18S, U6, circ-AFF1, LC-Ogdh, LC-LRP6) | Mice BALB/cc | Liver, heart, and skeletal muscle | 45 | 25 °C | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 d | Up to 7.5 days | Stable up to 8 days | geNorm and NormFinder | △Ct method | N.R. * |
| Tu C. [44] | 2019 | miR-122, miR133a | Mice BALB/cc | Liver, heart, and skeletal muscle | 15 | 25 °C | 0, 1.5, 3.5, 5.5, 7.5 days | From 0 to 6 days | Stable up to 7.5 days | geNorm and NormFinder | Linear, quadratic, and cubic regression | 0.62; 0.5 d if the data of all three tissues studied are combined together |
| Alshehhi S. [45] | 2019 | miR205 | Living human | Fresh saliva | 19 | Room temperature | 0, 7, 14, 28, 90, 180, 270, 360 days | N.R. * | Stable up to 360 days; | ACTB, 18S, U6 | Relative expression ratio | N.R. * |
| miR10b | Up to 14 days | degrades slightly up to 14 days; | ||||||||||
| Fresh ejaculated semen | ||||||||||||
| miR891a | N.R. * | remains stable up to 360 days | ||||||||||
| Na J.Y. [46] | 2020 | let-7e, miR-16 | Dead human | Patella | 71 | N.R. * | <1 month, 1 month, 3 month, 6 month, >6 month | Up to 1 month | Rapid decrease in the first month | Ce_miR-39_1 | ΔCt method, unpaired t-test | N.R. * |
| Singh P. [47] | 2023 | miRNA-195, miRNA-206, miRNA-378 | Dead human | Heart (left ventricle) | 20 | Room temperature | 12, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 168 and 196 h | From 24 to 196 h | Decrease from 24 to 196 h | miRNA-1 | Unpaired t-test | N.R. * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cianci, V.; Mondello, C.; Sapienza, D.; Guerrera, M.C.; Cianci, A.; Cracò, A.; Luppino, F.; Gioffrè, V.; Gualniera, P.; Asmundo, A.; et al. microRNAs as New Biomolecular Markers to Estimate Time since Death: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179207
Cianci V, Mondello C, Sapienza D, Guerrera MC, Cianci A, Cracò A, Luppino F, Gioffrè V, Gualniera P, Asmundo A, et al. microRNAs as New Biomolecular Markers to Estimate Time since Death: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179207
Chicago/Turabian StyleCianci, Vincenzo, Cristina Mondello, Daniela Sapienza, Maria Cristina Guerrera, Alessio Cianci, Annalisa Cracò, Francesco Luppino, Vittorio Gioffrè, Patrizia Gualniera, Alessio Asmundo, and et al. 2024. "microRNAs as New Biomolecular Markers to Estimate Time since Death: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179207
APA StyleCianci, V., Mondello, C., Sapienza, D., Guerrera, M. C., Cianci, A., Cracò, A., Luppino, F., Gioffrè, V., Gualniera, P., Asmundo, A., & Germanà, A. (2024). microRNAs as New Biomolecular Markers to Estimate Time since Death: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179207









