Expression of MicroRNAs in Adults with Celiac Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Celiac Disease
3. MicroRNA
4. Evaluation of miRNA in Tissue Samples from Individuals with CD
5. Evaluation of Circulating miRNAs in Patients with CD
6. Final Considerations and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebwohl, B.; Murray, J.A.; Verdú, E.F.; Crowe, S.E.; Dennis, M.; Fasano, A.; Green, P.H.R.; Guandalini, S.; Khosla, C. Gluten introduction, breastfeeding, and celiac disease: Back to the drawing board. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felli, C.; Baldassarre, A.; Masotti, A. Intestinal and circulating MicroRNAs in coeliac disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, A.; Sarshar, M.; Felli, C.; Bruno, S.P.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Ferretti, F.; Masotti, A.; Baldassarre, A. Biomarkers to monitor adherence to gluten-free diet by celiac disease patients: Gluten immunogenic peptides and urinary miRNAs. Foods 2022, 11, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Semrad, C.; Kelly, C.P.; Greer, K.B.; Limketkai, B.N.; Lebwohl, B. American College of Gastroenterology guidelines update: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, M.L.; Anderson, R.P.; Gibson, P.R. Systematic review: The evidence base for long-term management of coeliac disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 1042–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Pérez-Bravo, F.; Gaudioso, G.; Vaira, V.; Roncoroni, L.; Elli, L.; Monguzzi, E.; Araya, M. A miRNA-based blood and mucosal approach for detecting and monitoring celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsa, E.M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Budisan, L.; Braicu, C.; Para, I.; Tantau, A.I.; Orasan, O.H.; Ciobanu, L.; Pop, T.A.; Filip, G.A.; et al. Expression of selected genes and circulating microRNAs in patients with celiac disease. Medicina 2022, 58, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafari, M.; Asri, N.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Forouzesh, F.; Ehsani-Ardakani, M.J.; Jahani-Sherafat, S.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Aghdaei, H.A. Elevated interleukin-17A levels despite reduced microRNA-326 gene expression in celiac disease patients under gluten-free diet. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 60, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.L.; de Almeida, R.C.; Modderman, R.; Stachurska, A.; Dekens, J.; Barisani, D.; Meijer, C.R.; Roca, M.; Martinez-Ojinaga, E.; Shamir, R.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers for celiac disease development. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, C.; Baldassarre, A.; Uva, P.; Alisi, A.; Cangelosi, D.; Ancinelli, M.; Caruso, M.; Paolini, A.; Montano, A.; Silano, M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers of paediatric celiac disease and adherence to gluten-free diet. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, E.; Sargolzaei, J.; Tavakoli, T.; Rezaei, Z. microRNAs: Novel markers in diagnostics and therapeutics of celiac disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Lenti, M.V.; Giuffrida, P.; Vanoli, A.; Corazza, G.R. New insights into immune mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán-Gamboa, K.A.; Araya-Quezada, M.; Pérez-Bravo, F. MicroRNAs: An epigenetic tool to study celiac disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2014, 106, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebwohl, B.; Rubio-Tapia, A. Epidemiology, presentation, and diagnosis of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domsa, E.M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Para, I.; Munteanu, L.; Matei, D.; Andreica, V. Celiac disease: A multi-faceted medical condition. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global prevalence of celiac disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumara, M.; Nootigattu, V.K.T.; Sandhu, B.K. Ninety percent of celiac disease is being missed. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 45, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaño-Ponce, I.; Gutierrez-Achury, J.; Costa, A.F.; Deelen, P.; Kurilshikov, A.; Zorro, M.M.; Platteel, M.; van der Graaf, A.; Sugai, E.; Moreno, M.L.; et al. Immunochip meta-analysis in European and Argentinian populations identifies two novel genetic loci associated with celiac disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trynka, G.; Hunt, K.A.; Bockett, N.A.; Romanos, J.; Mistry, V.; Szperl, A.; Bakker, S.F.; Bardella, M.T.; Bhaw-Rosun, L.; Castillejo, G.; et al. Dense genotyping identifies and localizes multiple common and rare variant association signals in celiac disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, L.; Romino, R.; Coto, I.; Di Cosmo, N.; Percopo, S.; Maglio, M.; Paparo, F.; Gasperi, V.; Limongelli, M.G.; Cotichini, R.; et al. The first large population based twin study of coeliac disease. Gut 2002, 50, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, K.A.; van Heel, D.A. Recent advances in coeliac disease genetics. Gut 2009, 58, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchetti, L.; Calcagno, G.; Ferrajolo, A.; Sarrantonio, C.; Troncone, R.; Micillo, M.; Auricchio, S.; Salvatore, F. Discrimination between celiac and other gastrointestinal disorders in childhood by rapid human lymphocyte antigen typing. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44 Pt 1 Pt 1, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagnoff, M.F. Celiac disease: Pathogenesis of a model immunogenetic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vader, L.; Stepniak, D.T.; Bunnik, E.M.; Kooy, Y.M.; De Haan, W.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Van Veelen, P.A.; Koning, F. Characterization of cereal toxicity for celiac disease patients based on protein homology in grains. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausch, F.; Shan, L.; Santiago, N.A.; Gray, G.M.; Khosla, C. Intestinal digestive resistance of immunodominant gliadin peptides. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G996–G1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Molberg, Ø.; Parrot, I.; Hausch, F.; Filiz, F.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Structural basis for gluten intolerance in celiac sprue. Science 2002, 297, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Qiao, S.-W.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Molberg, Ø.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Identification and analysis of multivalent proteolytically resistant peptides from gluten: Implications for celiac sprue. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, M.; Abed, J.; Lebreton, C.; Cerf-Bensussan, N. Intestinal permeability in coeliac disease: Insight into mechanisms and relevance to pathogenesis. Gut 2012, 61, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Vanoli, A.; Giuffrida, P.; Luinetti, O.; Solcia, E.; Corazza, G.R. The function of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysiak-Budnik, T.; Moura, I.C.; Arcos-Fajardo, M.; Lebreton, C.; Ménard, S.; Candalh, C.; Ben-Khalifa, K.; Dugave, C.; Tamouza, H.; van Niel, G.; et al. Secretory IgA mediates retrotranscytosis of intact gliadin peptides via the transferrin receptor in celiac disease. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Corazza, G.R. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiner, M. Small intestinal biopsy: Diagnostic and research value. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1959, 52, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, M.N. Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. A molecular and immunobiologic approach to the spectrum of gluten sensitivity (“celiac sprue”). Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 330–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazza, G.R.; Villanacci, V.; Zambelli, C.; Milione, M.; Luinetti, O.; Vindigni, C.; Chioda, C.; Albarello, L.; Bartolini, D.; Donato, F. Comparison of the interobserver reproducibility with different histologic criteria used in celiac disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Kurppa, K.; Mearin, M.L.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; et al. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Card, T.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Swift, G.L.; Nasr, I.; Sanders, D.S.; Ciacci, C. Support for patients with celiac disease: A literature review. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, D.A.; Edwards-George, J.; Dennis, M.; Schuppan, D.; Cook, F.; Franko, D.L.; Blom-Hoffman, J.; Kelly, C.P. Factors that influence adherence to a gluten-free diet in adults with celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukkola, A.; Mäki, M.; Kurppa, K.; Collin, P.; Huhtala, H.; Kekkonen, L.; Kaukinen, K. Patients’ experiences and perceptions of living with coeliac disease—Implications for optimizing care. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2012, 21, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Cassani, F.; Pappas, G.; Muratori, L.; Agostinelli, D.; Veronesi, L.; Bortolotti, R.; Petrolini, N.; Bianchi, F.B.; et al. Anti-actin IgA antibodies in severe coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 137, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granito, A.; Zauli, D.; Muratori, P.; Muratori, L.; Grassi, A.; Bortolotti, R.; Petrolini, N.; Veronesi, L.; Gionchetti, P.; Bianchi, F.B.; et al. Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae and perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in coeliac disease before and after gluten-free diet. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, S.; Comani, G.B.; Elli, L.; Vanessi, S.; Ballarini, E.; Nicolini, G.; Rusconi, M.; Castoldi, M.; Meneveri, R.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; et al. miRNAs affect the expression of innate and adaptive immunity proteins in celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K. Micro-RNA in disease and gene therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 8, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaira, V.; Roncoroni, L.; Barisani, D.; Gaudioso, G.; Bosari, S.; Bulfamante, G.; Doneda, L.; Conte, D.; Tomba, C.; Bardella, M.T.; et al. microRNA profiles in coeliac patients distinguish different clinical phenotypes and are modulated by gliadin peptides in primary duodenal fibroblasts. Clin. Sci. 2013, 126, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, E.; Neveu, B.; Kostantin, E.; Tsongalis, G.J.; De Guire, V. How close are miRNAs from clinical practice? A perspective on the diagnostic and therapeutic market. EJIFCC 2019, 30, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Pelizzaro, F.; Cardin, R.; Sarasini, G.; Minotto, M.; Carlotto, C.; Fassan, M.; Palo, M.; Farinati, F.; Zingone, F. Crosstalk between microRNAs and oxidative stress in coeliac disease. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2024, 9, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

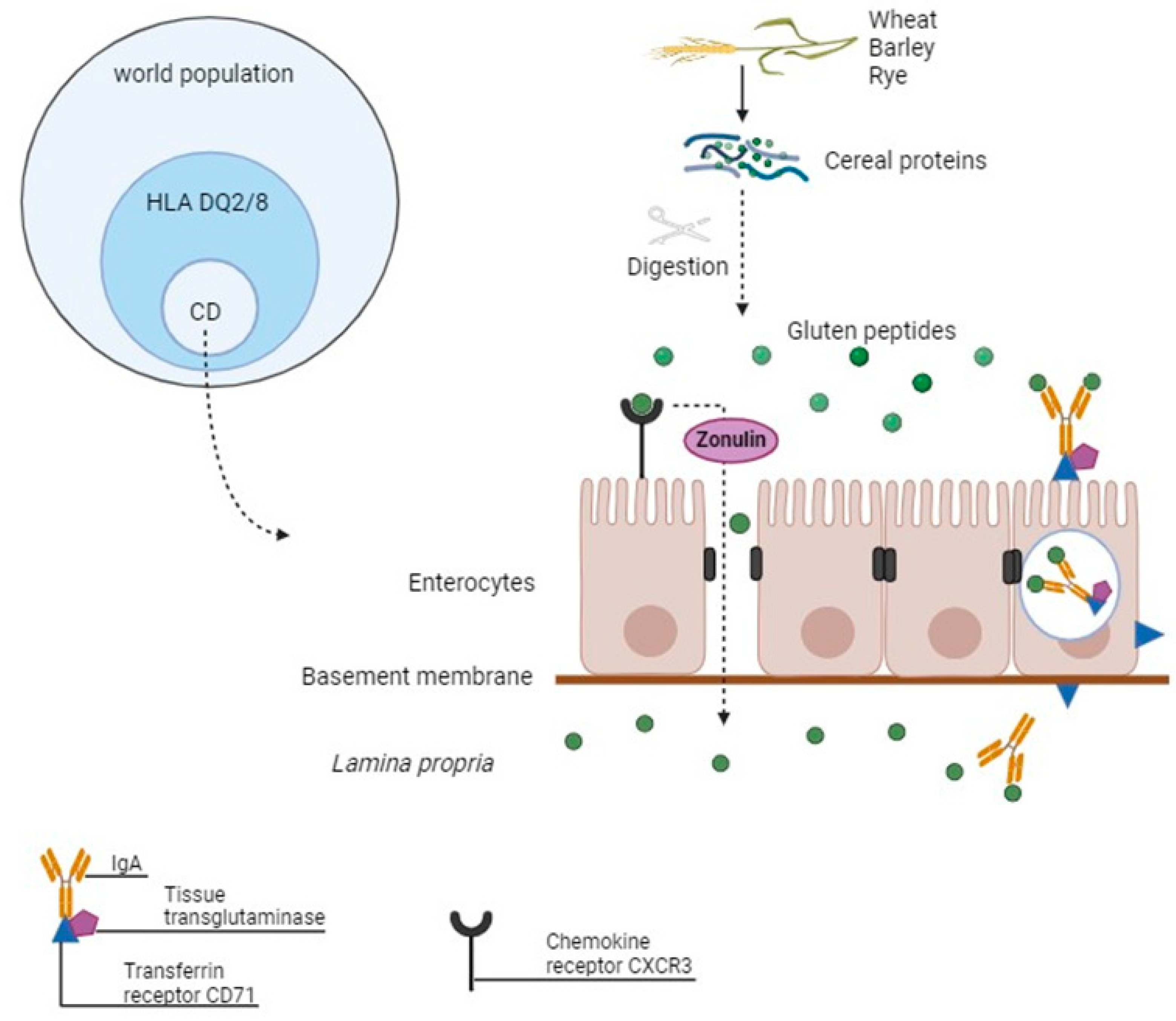
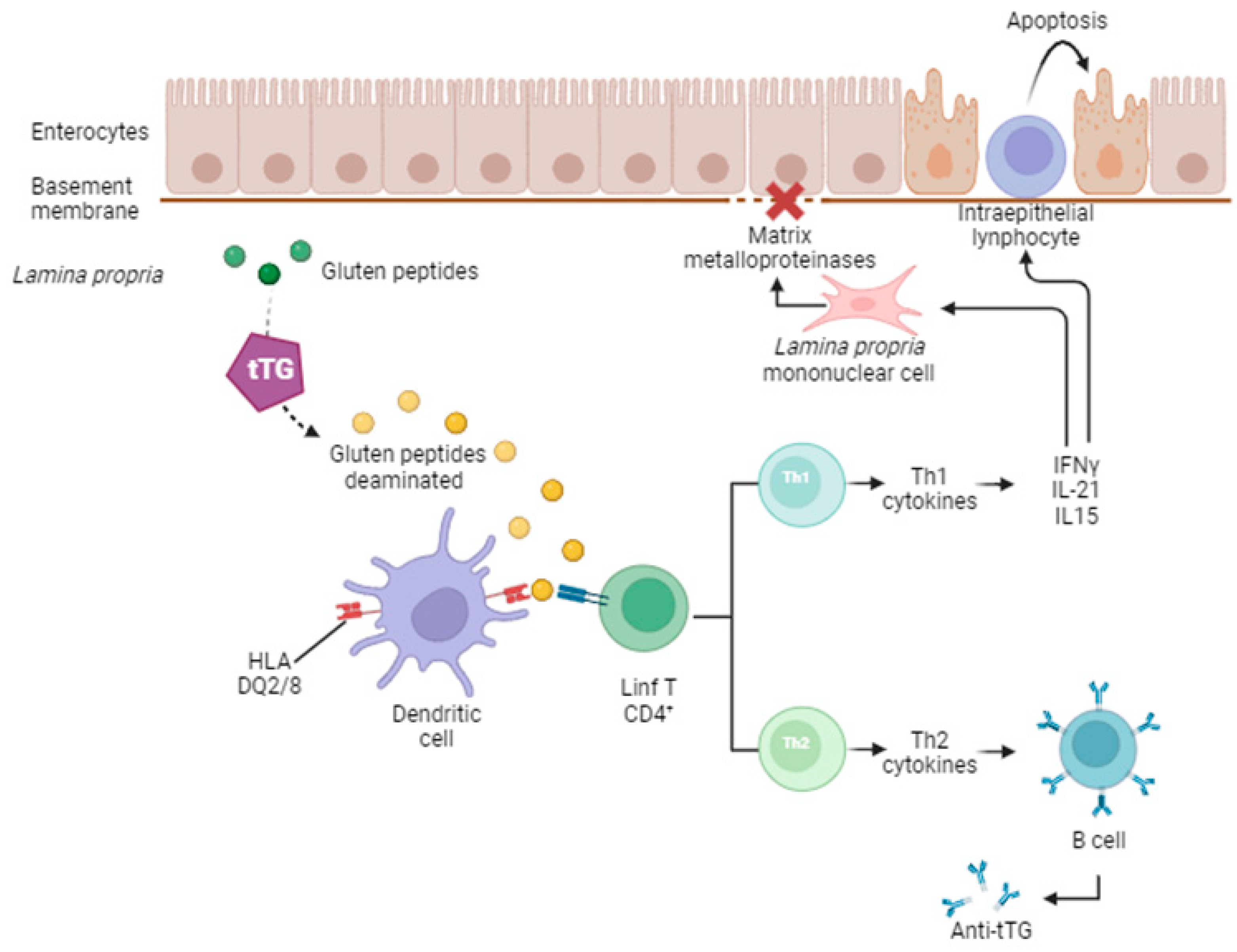
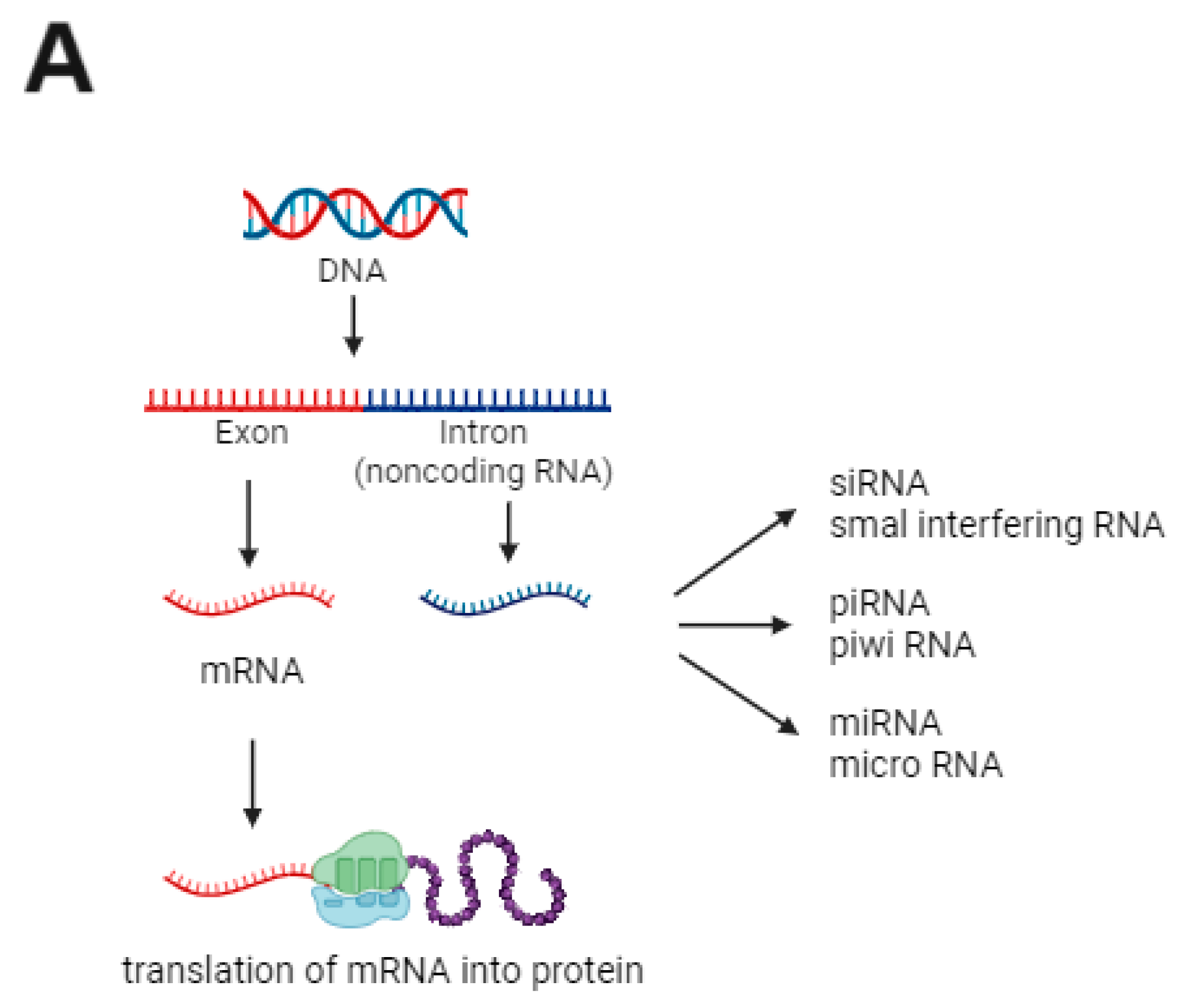

| Included Studies | Population (Number) | Material | Increased (↑) miRNAs | Decreased (↓) miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magni et al., 2014 [43] | 31 individuals for miRNA expression: (2 groups): - 21: Active CD (9 Marsh 3A-B + 12 Marsh 3C) - 10: control group AND 14 individuals for in vitro gliadin exposure for 4 and 24 h and fibroblast culture analysis (2 groups): - 9: Remission CD on GFD - 5: control group Both before and after stimulation for 4 and 24 h | Intestinal mucosa | No significant changes | Control vs. active CD: ↓ miR-192-5p ↓ miR-31-5p ↓ miR-338-3p ↓ miR-197 AND Remission CD on GFD fibroblast before vs. after gliadin exposure: ↓ miR-192-5p |
| Vaira et al., 2014 [45] | 64 individuals (5 groups): - 12: “classical” CD - 11: “anemia” CD - 18: GFD normal mucosa - 11: GFD atrophic mucosa - 12: healthy controls 6 patients from the CD group + 4 from the control group were tested “in vitro” before and after gliadin exposure | Intestinal mucosa and fibroblast culture | Control vs. “classical” CD: ↑ miR-551b-5p ↑ miR-1290 Control vs. “anemia” CD: ↑ miR-551b-5p ↑ miR-1290 “Classical” vs. “anemia” CD: ↑ miR-638 GFD atrophic mucosa vs. GFD normal mucosa ↑ miR-551a | Control vs. “classical” CD: ↓ miR-31-5p ↓ miR-192-3p Control vs. “anemia” CD: ↓ miR-31-5p ↓ miR-192-3p “Classical” vs. “anemia” CD: ↓ miR-194-5p ↓ miR-551b-5p Control vs. active CD and Control vs. GFD atrophic mucosa: ↓ miR-192-3p ↓ miR-551a |
| Included Studies | Population (Number) | Material | Increased (↑) miRNAs | Decreased (↓) miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bascuñán et al., 2020 [7] | 30 individuals (3 groups): - 10: CD at diagnosis - 10: GFD -10: control group | Plasma, PBMCs, monocytes (and intestinal mucosa) | CD at diagnosis vs. control and GFD vs. control: in monocytes↑ miR-146a; ↑ miR-155; ↑ miR-21. in PBMCs ↑ miR-155. in plasma ↑ miR-155; ↑ miR-21; ↑ miR-125bCD at diagnosis and GFD before and after in vitro gliadin stimulation. in PBMCs and monocytes ↑ miR-146a; ↑ miR-155. only in PBMCs ↑ miR-21. | No significant changes |
| Domsa et al., 2022 [8] | 58 individuals (3 groups): - 15: CD at diagnosis - 33: GFD - 10: control group | Blood | CD at diagnosis vs. control: ↑ miR-194-5p (very close to the significant value p = 0.0510) GFD vs. control: ↑ miR-194-5p (close to the significant value p = 0.0671) | No significant changes |
| Nafari et al., 2022 [9] | 80 individuals (2 groups): - 40: GFD - 40: control group | Blood | No significant changes | GFD vs. controls ↓ miR-326 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rigo, F.F.; Oliveira, E.C.S.d.; Quaglio, A.E.V.; Moutinho, B.D.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Expression of MicroRNAs in Adults with Celiac Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179412
Rigo FF, Oliveira ECSd, Quaglio AEV, Moutinho BD, Di Stasi LC, Sassaki LY. Expression of MicroRNAs in Adults with Celiac Disease: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRigo, Francielen Furieri, Ellen Cristina Souza de Oliveira, Ana Elisa Valencise Quaglio, Bruna Damásio Moutinho, Luiz Claudio Di Stasi, and Ligia Yukie Sassaki. 2024. "Expression of MicroRNAs in Adults with Celiac Disease: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179412
APA StyleRigo, F. F., Oliveira, E. C. S. d., Quaglio, A. E. V., Moutinho, B. D., Di Stasi, L. C., & Sassaki, L. Y. (2024). Expression of MicroRNAs in Adults with Celiac Disease: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179412






