Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
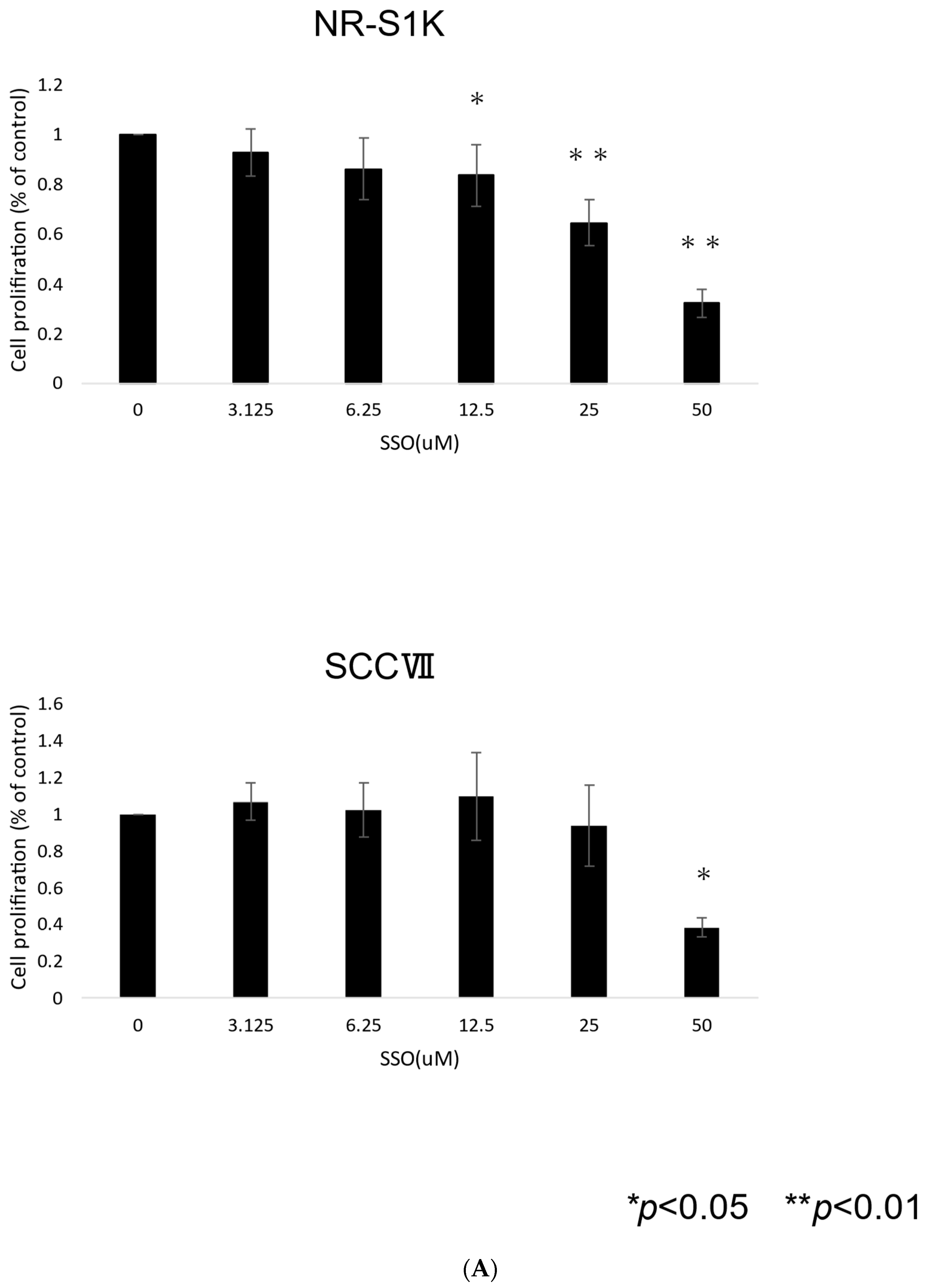
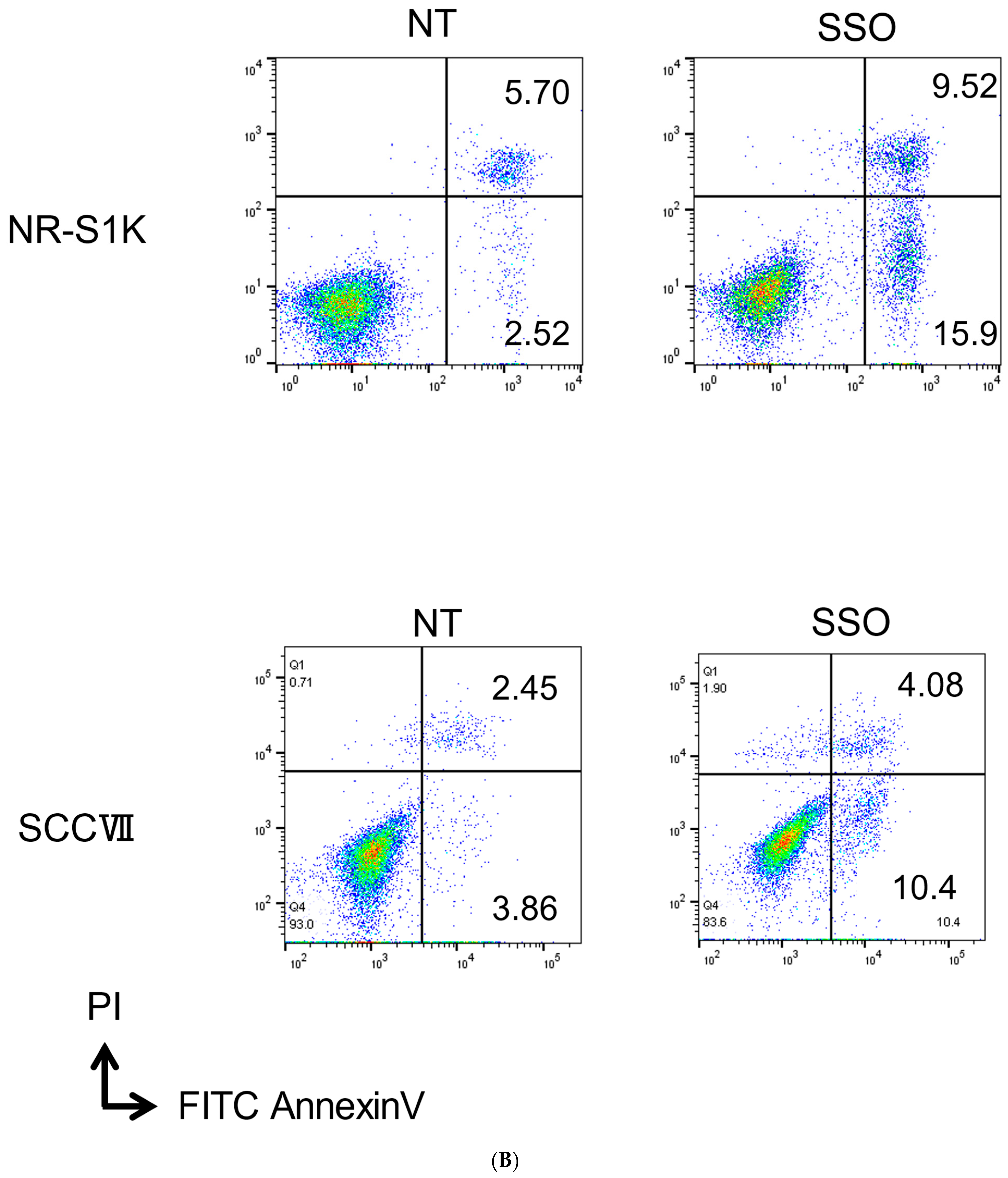
2.1. The Selective Inhibition of the CD36-Exerted Inhibitory Effect on the Proliferation of OSCCs, Accompanied by Increased Apoptotic Cell Death
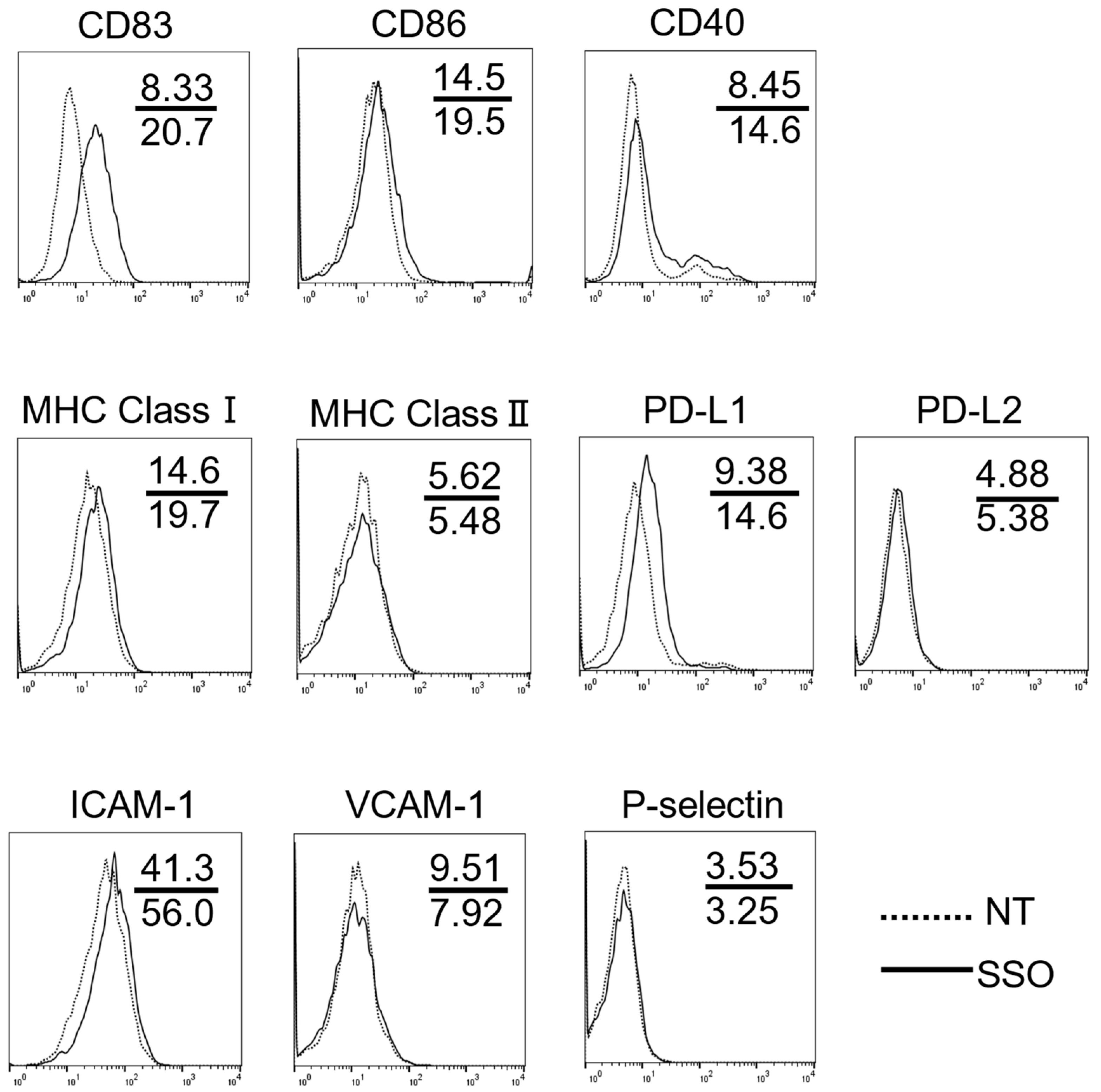
2.2. The Selective Inhibition of CD36-Altered Surface Antigen Expression in OSCCs
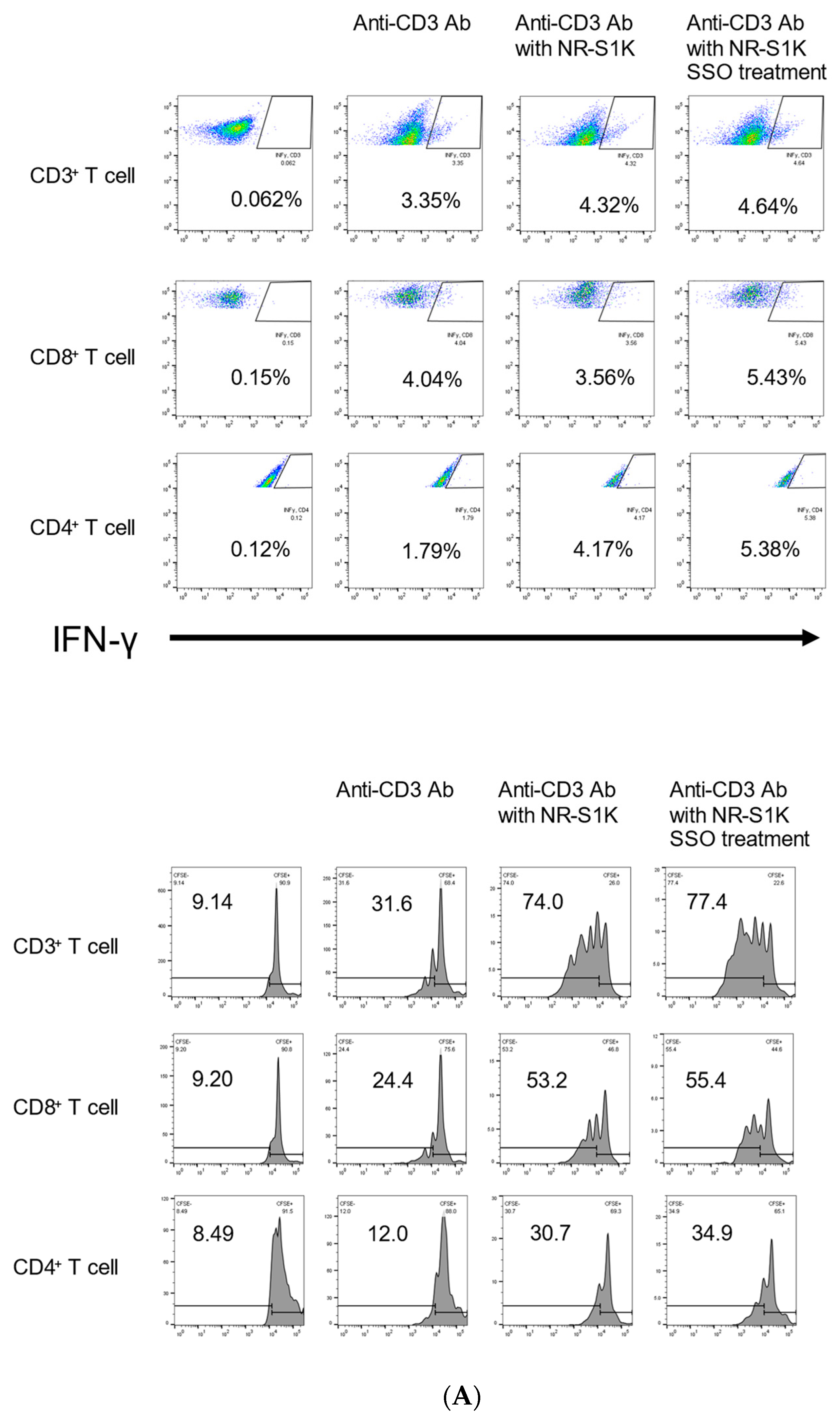
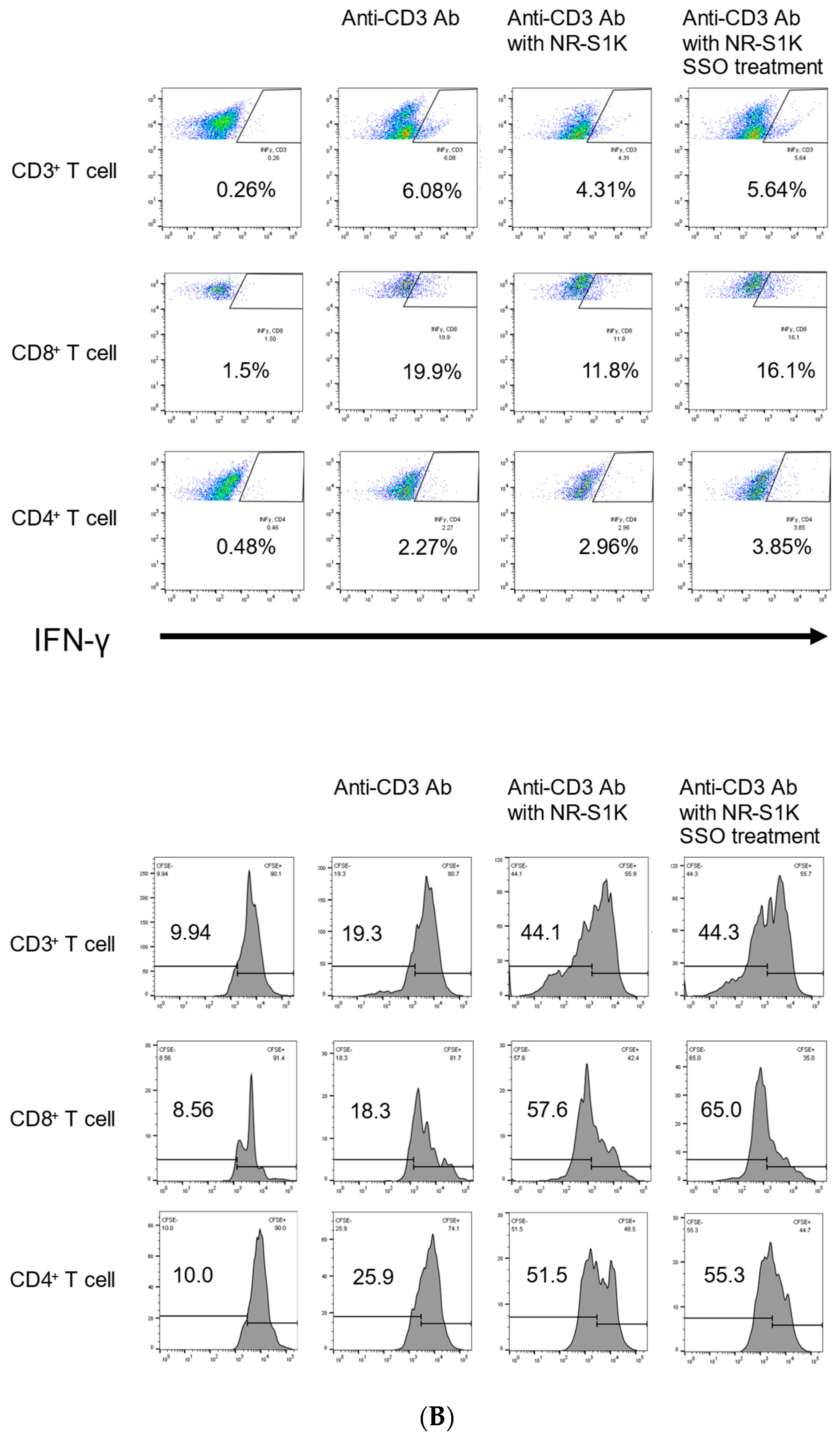
2.3. The Selective Inhibition of CD36-Induced Phenotype Alteration of OSCCs That Facilitate T Cell Responses
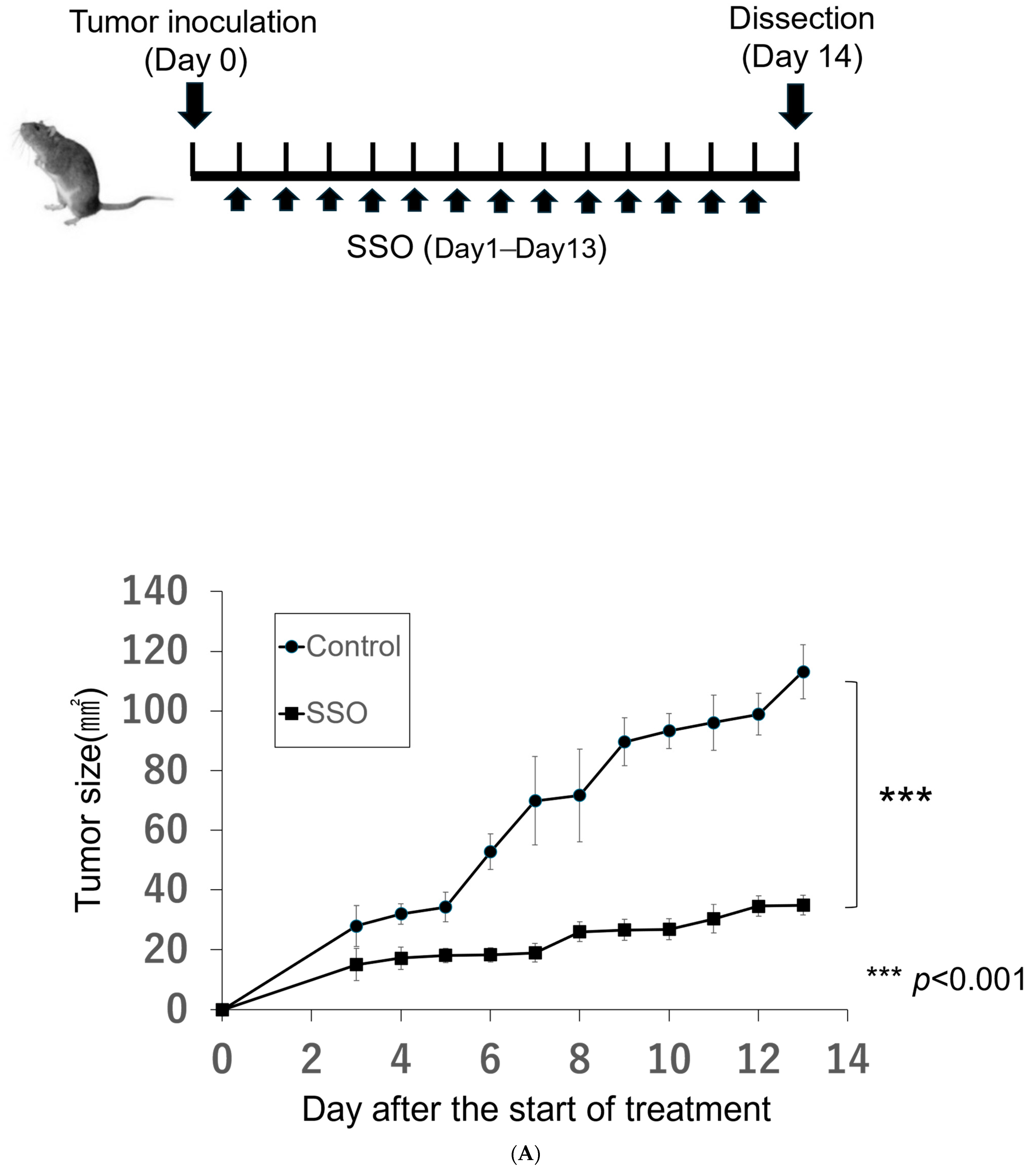
2.4. The Selective Inhibition of CD36-Exerted Antitumor Effects against an In Vivo Mouse Oral Cancer Model
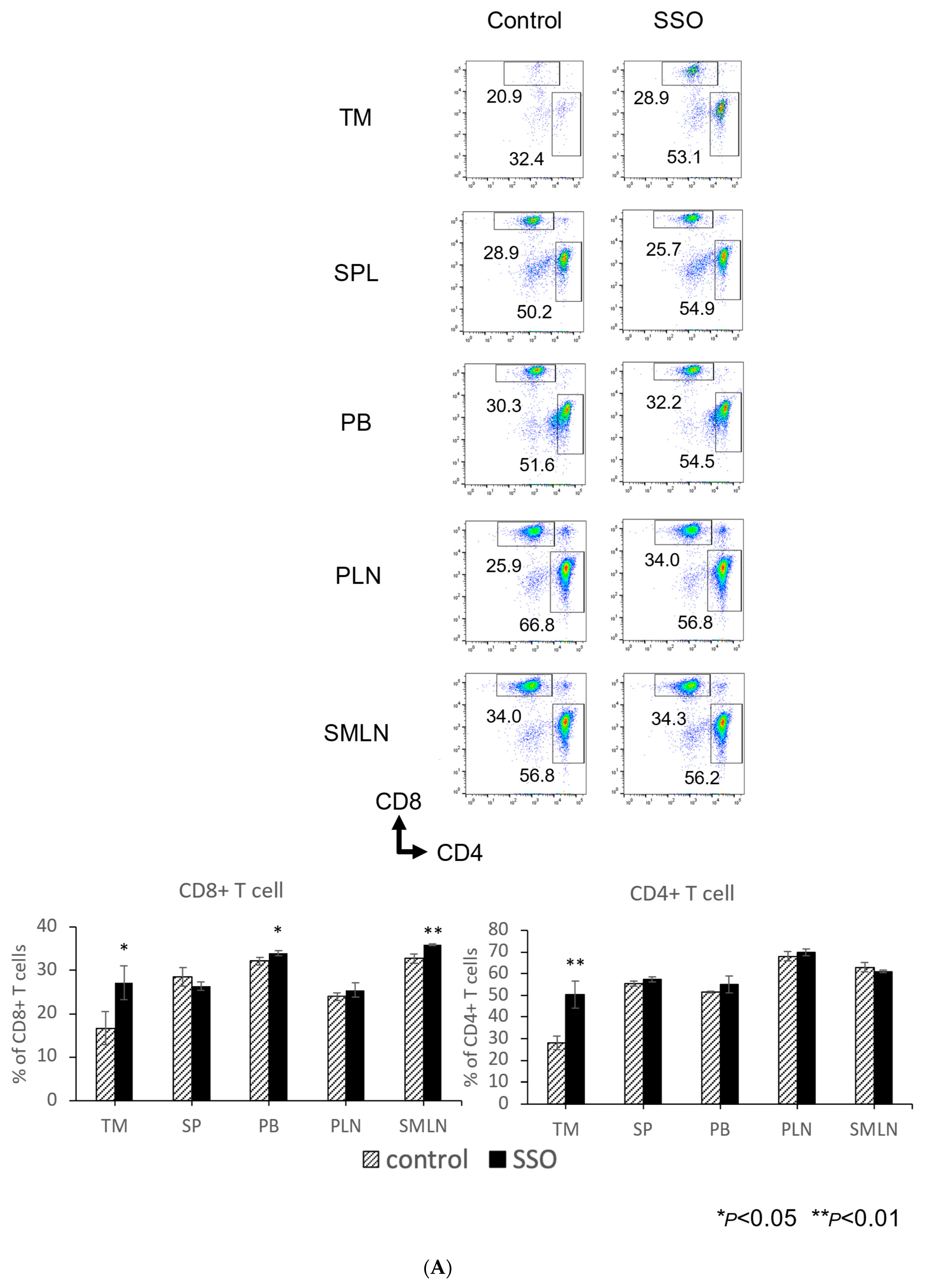
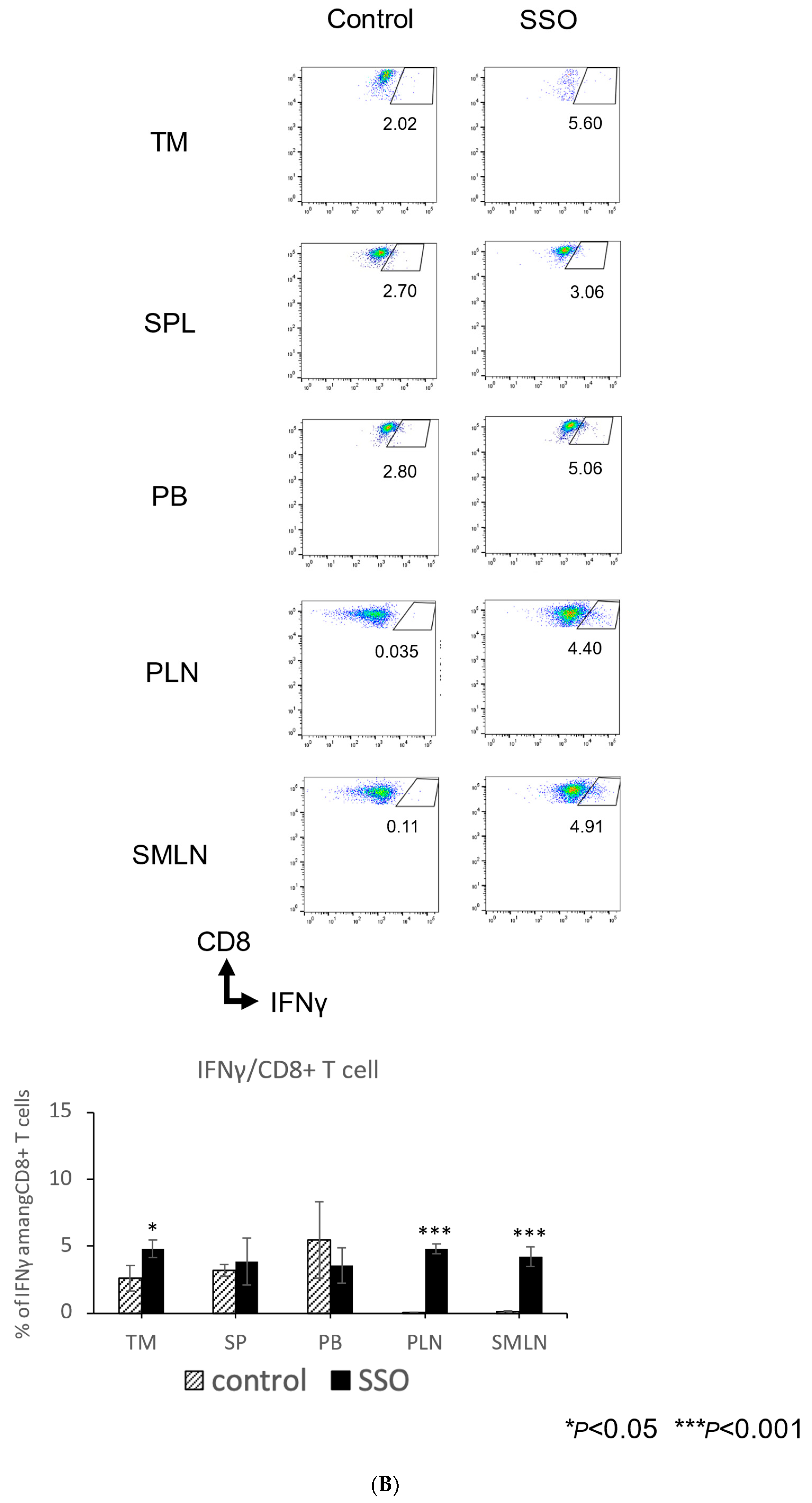
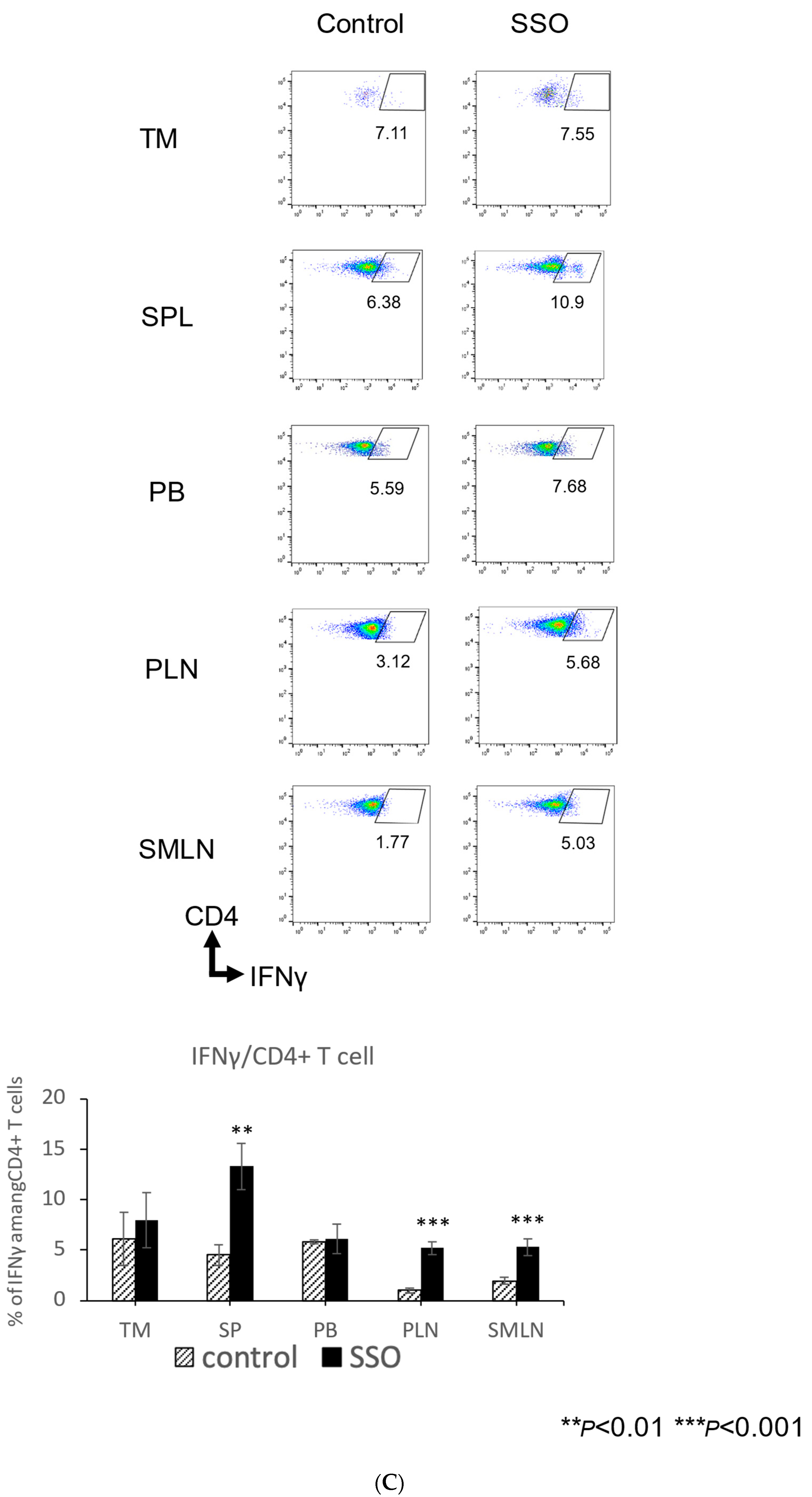
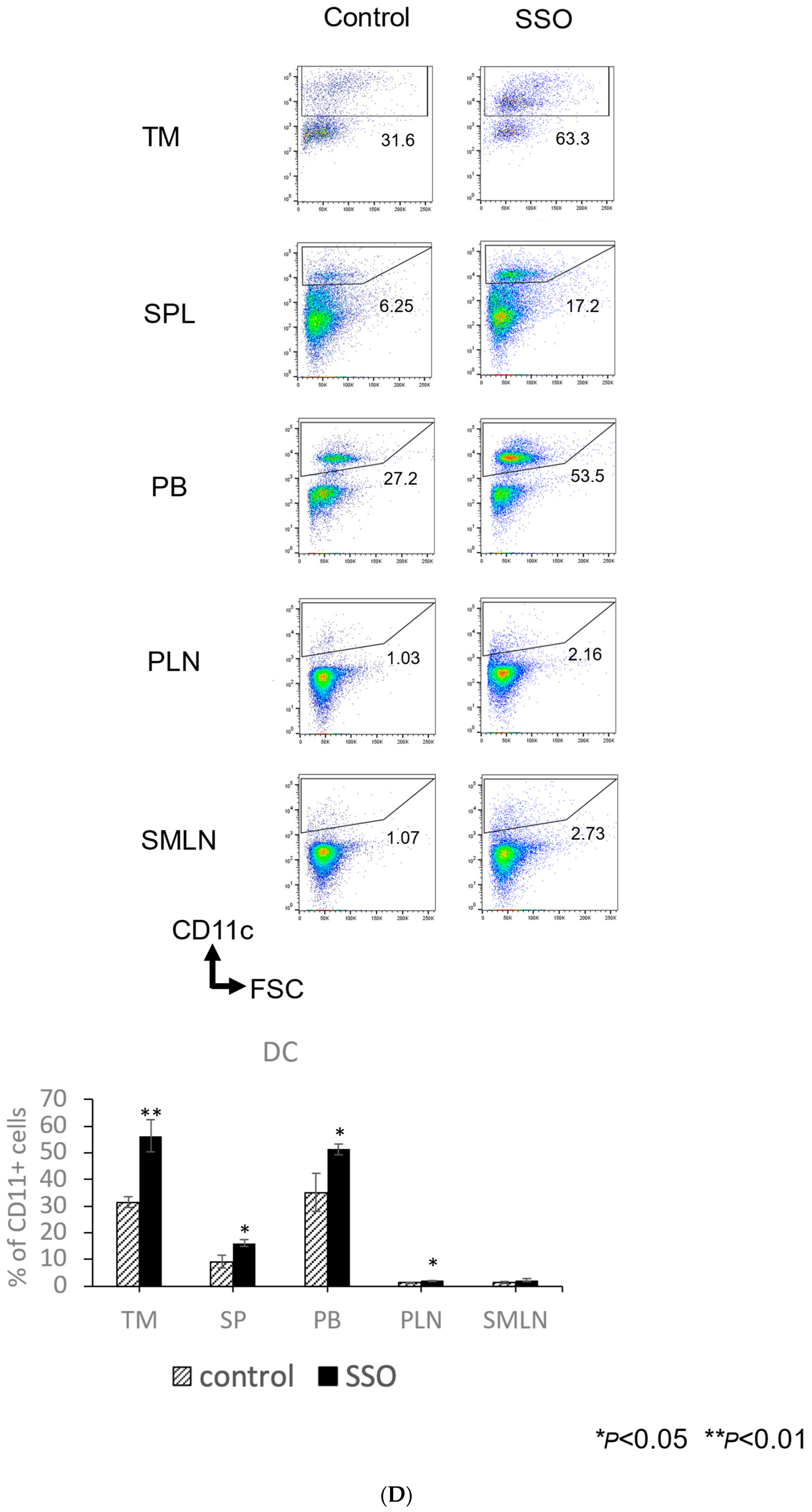
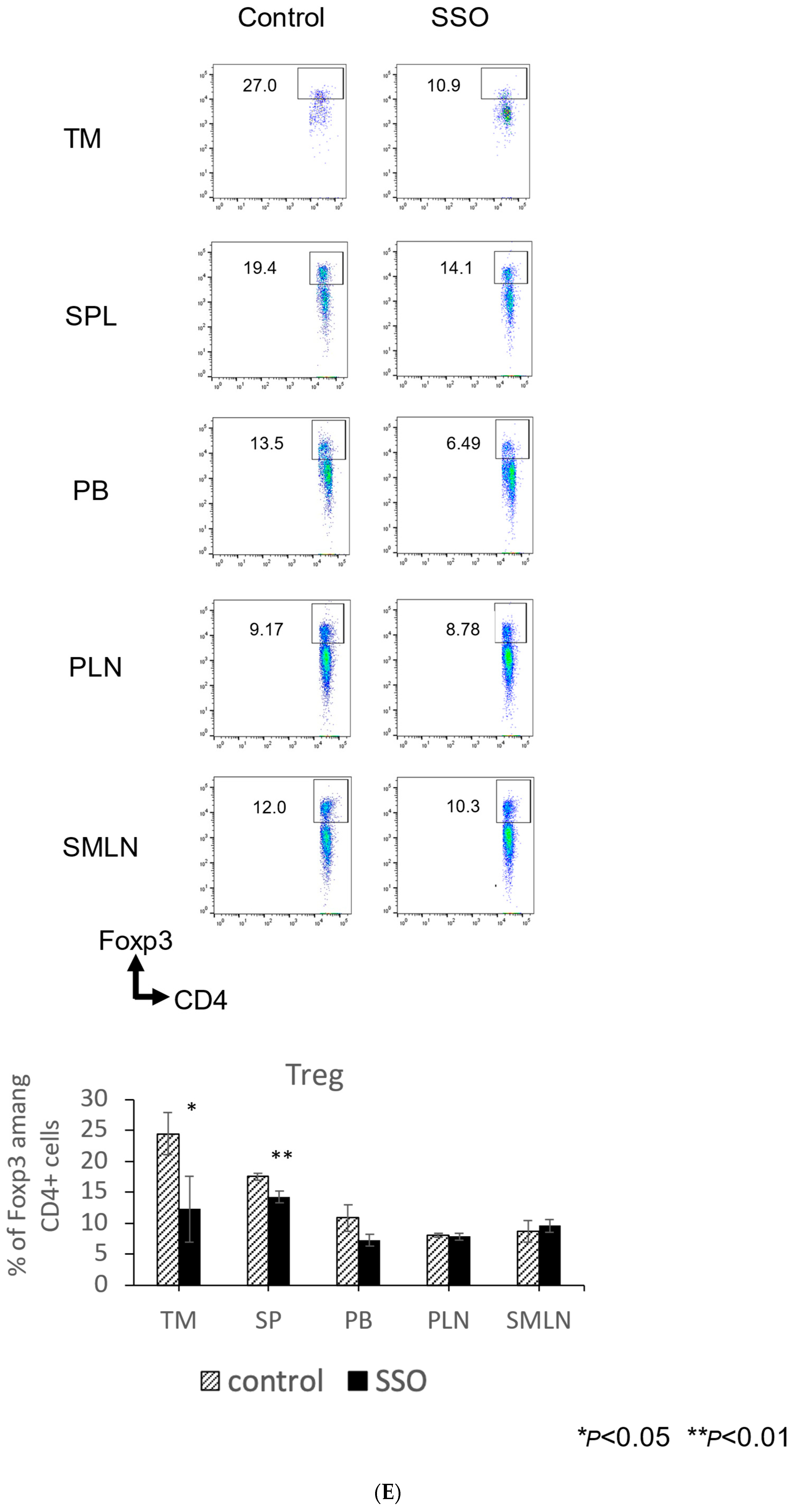
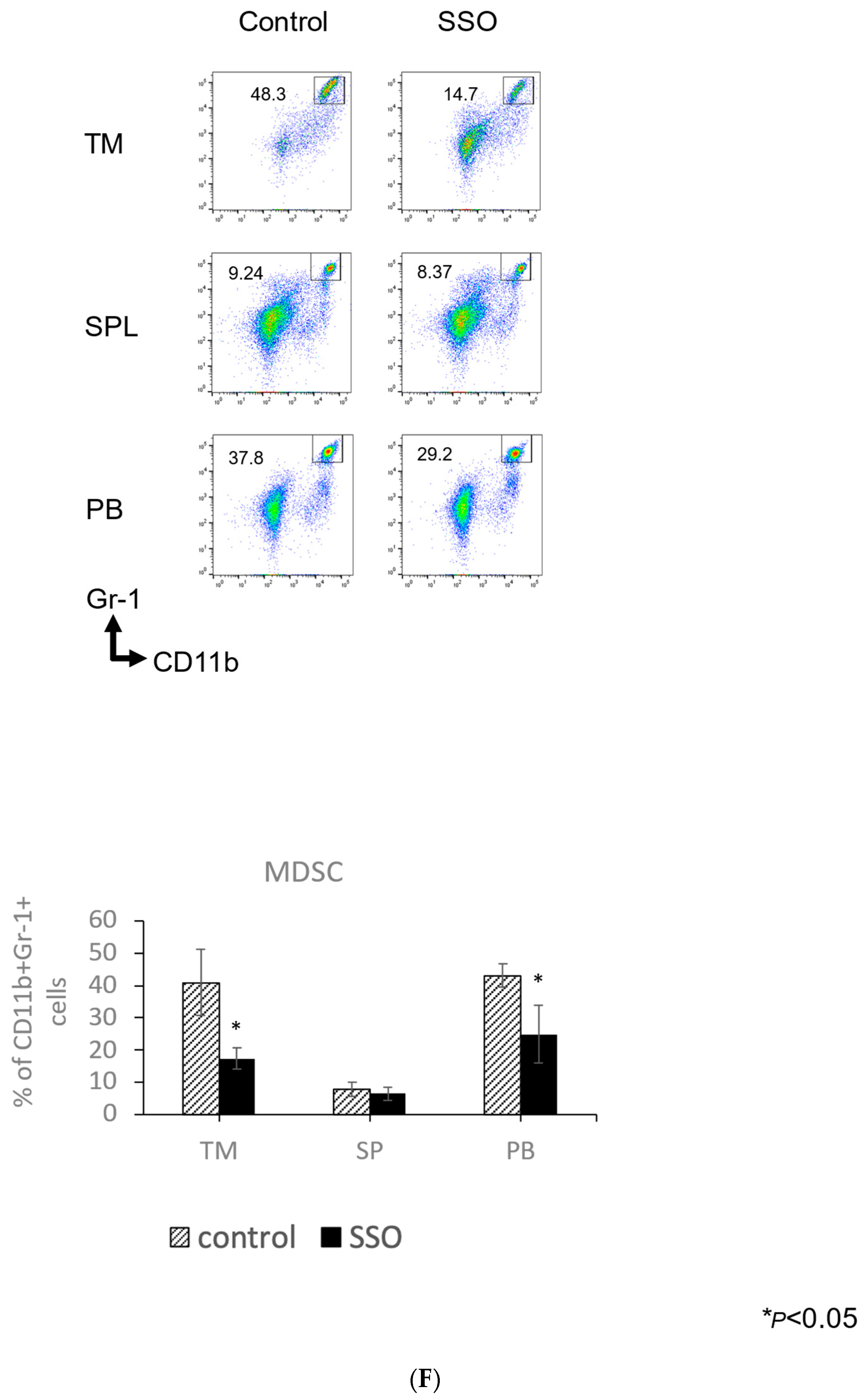
2.5. The In Vivo Administration of CD36 Inhibitor and the Modulated Distribution of Immune Cell Populations in a Mouse OSCC Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice and Cell Lines
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.3. Assessment of Cellular Apoptosis
4.4. Assessment of Phenotypic Alteration of Cells
4.5. Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR) and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
4.6. In Vivo SSO Treatment
4.7. Antibodies and Reagents
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, G.D.; Wynder, E.L. Etiological and preventive implications in alcohol carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1979, 39 Pt 2, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blot, W.L.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Winn, D.M.; Austin, D.F.; Greenberg, R.S.; Preston-Martin, S.; Bernstein, L.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Stemhagen, A.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 3282–3287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Wyk, C.W.; Stander, I.; Padayachee, A.; Grobler-Rabie, A.F. The areca nut chewing habit and oral squamous cell carcinoma in South African Indians. A retrospective study. S. Afr. Med. J. 1993, 83, 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Sturgis, E.M.; Cinciripini, P.M. Trends in head and neck cancer incidence in relation to smoking prevalence: An emerging epidemic of human papillomavirus-associated cancers? Cancer 2007, 110, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Gupta, S.; Weiss, J.; Gluck, I.; Eder, J.P.; Burtness, B.; Tahara, M.; Keam, B.; Kang, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Pooled analyses after long-term follow-up in KEYNOTE-012. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Abumrad, N.A. Cellular fatty acid uptake: A pathway under construction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choromańska, B.; Myśliwiec, P.; Choromańska, K.; Dadan, J.; Chabowski, A. The role of CD36 receptor in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Kuda, O.; Samovski, D. Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, R.; et al. CD36 palmitoylation disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.W.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Li, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aziz, A.; Sherin, M.; Dalia, A. Clinical relevance of thrombospondin receptor (CD36) expression in Egyptian de novo adult acute myeloid leukemia. Egypt. J. Haematol. 2013, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.S.; Otvos, B.; Sinyuk, M.; Alvarado, A.G.; Hitomi, M.; Stoltz, K.; Wu, Q.; Flavahan, W.; Levison, B.; Johansen, M.L.; et al. Cancer stem cell-specific scavenger receptor CD36 drives glioblastoma progression. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1746–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladanyi, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kenny, H.A.; Johnson, A.; Mitra, A.K.; Sundaresan, S.; Nieman, K.M.; Pascual, G.; Benitah, S.A.; Montag, A.; et al. Adipocyte-induced CD36 expression drives ovarian cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2285–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Han, H.; Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. CD36 plays a critical role in proliferation, migration and tamoxifen-inhibited growth of ER-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.; Rychahou, P.G.; He, D.; Jafari, N.; Wang, C.; Lee, E.Y.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M.; Zaytseva, Y.Y. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase upregulates expression of CD36 to sustain proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, J.; Yeo, J.H.; Kwon, D.; Min, B.S.; Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Interaction between CD36 and FABP4 modulates adipocyte-induced fatty acid import and metabolism in breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zheng, E.; Wei, L.; Zeng, H.; Qin, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Ruan, X.Z.; et al. The fatty acid receptor CD36 promotes HCC progression through activating Src/PI3K/AKT axis-dependent aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yokobori, T.; Saito, H.; Kuriyama, K.; Kumakura, Y.; Honjo, H.; Hara, K.; Sakai, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Obinata, H.; et al. CD36 expression is associated with cancer aggressiveness and energy source in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, J.C.; Sanhueza, T.; de Porras, V.R.; Etxaniz, O.; Rodriguez, H.; Martinez-Cardús, A.; Grande, E.; Castellano, D.; Climent, M.A.; Lobato, T.; et al. Prognostic impact of CD36 immunohistochemical expression in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with cystectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, G.; Avgustinova, A.; Mejetta, S.; Martín, M.; Castellanos, A.; Attolini, C.S.; Berenguer, A.; Prats, N.; Toll, A.; Hueto, J.A.; et al. Targeting metastasis-initiating cells through the fatty acid receptor CD36. Nature 2017, 541, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Cai, X.; Long, L.; Xie, L.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, C. CD36 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in cervical cancer by interacting with TGF-β. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Wu, N.; Xu, B.; Chu, Y.; Li, X.; Su, S.; Chen, D.; Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Fatty acid-induced CD36 expression via O-GlcNAcylation drives gastric cancer metastasis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5359–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Kinoshita, J.; Munesue, S.; Hamabe-Horiike, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Moriyama, H.; Nakamura, K.; Harada, S.; et al. Hypoxia-induced CD36 expression in gastric cancer cells promotes peritoneal metastasis via fatty acid uptake. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 30, 3125–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Tomihara, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Heshiki, W.; Moniruzzaman, R.; Sekido, K.; Tachinami, H.; Ikeda, A.; Imaue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. CD36 expression on oral squamous cell carcinoma cells correlates with enhanced proliferation and migratory activity. Oral. Dis. 2020, 26, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, S.; Tröltzsch, M.; Knösel, T.; Liokatis, P.; Kasintsova, A.; Eberl, M.; Ortner, F.; Otto, S.; Fegg, F.; Boskov, M.; et al. Fatty acid receptor CD36 functions as a surrogate parameter for lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khami, A.A.; Zheng, L.; Del Valle, L.; Hossain, F.; Wyczechowska, D.; Zabaleta, J.; Sanchez, M.D.; Dean, M.J.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Ochoa, A.C. Exogenous lipid uptake induces metabolic and functional reprogramming of tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1344804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Franco, F.; Tsui, Y.C.; Xie, X.; Trefny, M.P.; Zappasodi, R.; Mohmood, S.R.; Fernández-García, J.; Tsai, C.H.; Schulze, I.; et al. CD36-mediated metabolic Ma X, adaptation supports regulatory T cell survival and function in tumors. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, L.; Ye, L.; Su, P.; Bi, E.; Wang, Q.; Yang, M.; Qian, J.; Yi, Q. CD36-mediated ferroptosis dampens intratumoral CD8+ T cell effector function and impairs their antitumor ability. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1001–1012.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chaudhary, O.; Rodríguez-Morales, P.; Sun, X.; Chen, D.; Zappasodi, R.; Xu, Z.; Pinto, A.F.; Williams, A.; Schulze, I.; et al. Uptake of oxidized lipids by the scavenger receptor CD36 promotes lipid peroxidation and dysfunction in CD8+ T cells in tumors. Immunity 2021, 54, 1561–1577.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.S.; Lee, H.K. Autophagy protein ATG5 regulates CD36 expression and antitumour MHC class II antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Autophagy 2019, 15, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomihara, K.; Fuse, H.; Heshiki, W.; Takei, R.; Zhang, B.; Arai, N.; Nakamori, K.; Noguchi, M. Gemcitabine chemotherapy induces phenotypic alterations of tumor cells that facilitate antitumor T cell responses in a mouse model of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridel, S.J.; Axelrod, F.; Rozenkrantz, N.; Smith, J.W. Orlistat is a novel inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, E.; Schulze, A.; Zechner, R.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migita, T.; Ruiz, S.; Fornari, A.; Fiorentino, M.; Priolo, C.; Zadra, G.; Inazuka, F.; Grisanzio, C.; Palescandolo, E.; Shin, E.; et al. Fatty acid synthase: A metabolic enzyme and candidate oncogene in prostate cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, R.U.; Parker, S.J.; Eichner, L.J.; Kolar, M.J.; Wallace, M.; Brun, S.N.; Lombardo, P.S.; Van Nostrand, J.L.; Hutchins, A.; Vera, L.; et al. Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.B.; Ali, A.; Luengo, A.; Kodack, D.P.; Deik, A.; Abbott, K.L.; Bezwada, D.; Blanc, L.; Prideaux, B.; Jin, X.; et al. Fatty acid synthesis is required for breast cancer brain metastasis. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.N.; Yamazaki, M.; Maruyama, S.; Abé, T.; Haga, K.; Kawaharada, M.; Izumi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanuma, J.I. Cholesterol is a regulator of CAV1 localization and cell migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herber, D.L.; Cao, W.; Nefedova, Y.; Novitskiy, S.V.; Nagaraj, S.; Tyurin, V.A.; Corzo, A.; Cho, H.I.; Celis, E.; Lennox, B.; et al. Lipid accumulation and dendritic cell dysfunction in cancer. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Q.; Tang, Z.; Huang, R.; Qu, W.F.; Fang, Y.; Yang, R.; Tao, C.Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.L.; Sun, H.X.; et al. CD36+ cancer-associated fibroblasts provide immunosuppressive microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma via secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Jinhua, P.; Omura, K.; Azuma, M. Multipotency of CD11bhighGr-1+ immature myeloid cells accumulating in oral squamous cell carcinoma-bearing mice. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, D.; Tachinami, H.; Suzuki, N.; Yamazaki, M.; Yonesi, A.; Takaichi, M.; Imaue, S.; Yamada, S.I.; Tanuma, J.I.; Tomihara, K.; et al. PAK4 inhibition augments anti-tumour effect by immunomodulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Tomihara, K.; Heshiki, W.; Sakurai, K.; Sekido, K.; Tachinami, H.; Rohan, M.; Inoue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Noguchi, M. Astaxanthin ameliorates cisplatin-induced damage in normal human fibroblasts. Oral. Sci. Int. 2019, 16, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonesi, A.; Tomihara, K.; Takatsuka, D.; Tachinami, H.; Yamazaki, M.; Jadidi, A.R.Y.; Takaichi, M.; Imaue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Yamada, S.I.; et al. Rapamycin Induces Phenotypic Alterations in Oral Cancer Cells That May Facilitate Antitumor T Cell Responses. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaichi, M.; Tachinami, H.; Takatsuka, D.; Yonesi, A.; Sakurai, K.; Rasul, M.I.; Imaue, S.; Yamada, S.-I.; Ruslin, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179438
Takaichi M, Tachinami H, Takatsuka D, Yonesi A, Sakurai K, Rasul MI, Imaue S, Yamada S-I, Ruslin M, Yamazaki M, et al. Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179438
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaichi, Mayu, Hidetake Tachinami, Danki Takatsuka, Amirmoezz Yonesi, Kotaro Sakurai, Muhammad Irfan Rasul, Shuichi Imaue, Shin-Ichi Yamada, Muhammad Ruslin, Manabu Yamazaki, and et al. 2024. "Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179438
APA StyleTakaichi, M., Tachinami, H., Takatsuka, D., Yonesi, A., Sakurai, K., Rasul, M. I., Imaue, S., Yamada, S.-I., Ruslin, M., Yamazaki, M., Tanuma, J.-I., Noguchi, M., & Tomihara, K. (2024). Targeting CD36-Mediated Lipid Metabolism by Selective Inhibitor-Augmented Antitumor Immune Responses in Oral Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179438






