Kynurenine Pathway after Kidney Transplantation: Friend or Foe?
Abstract
1. Introduction
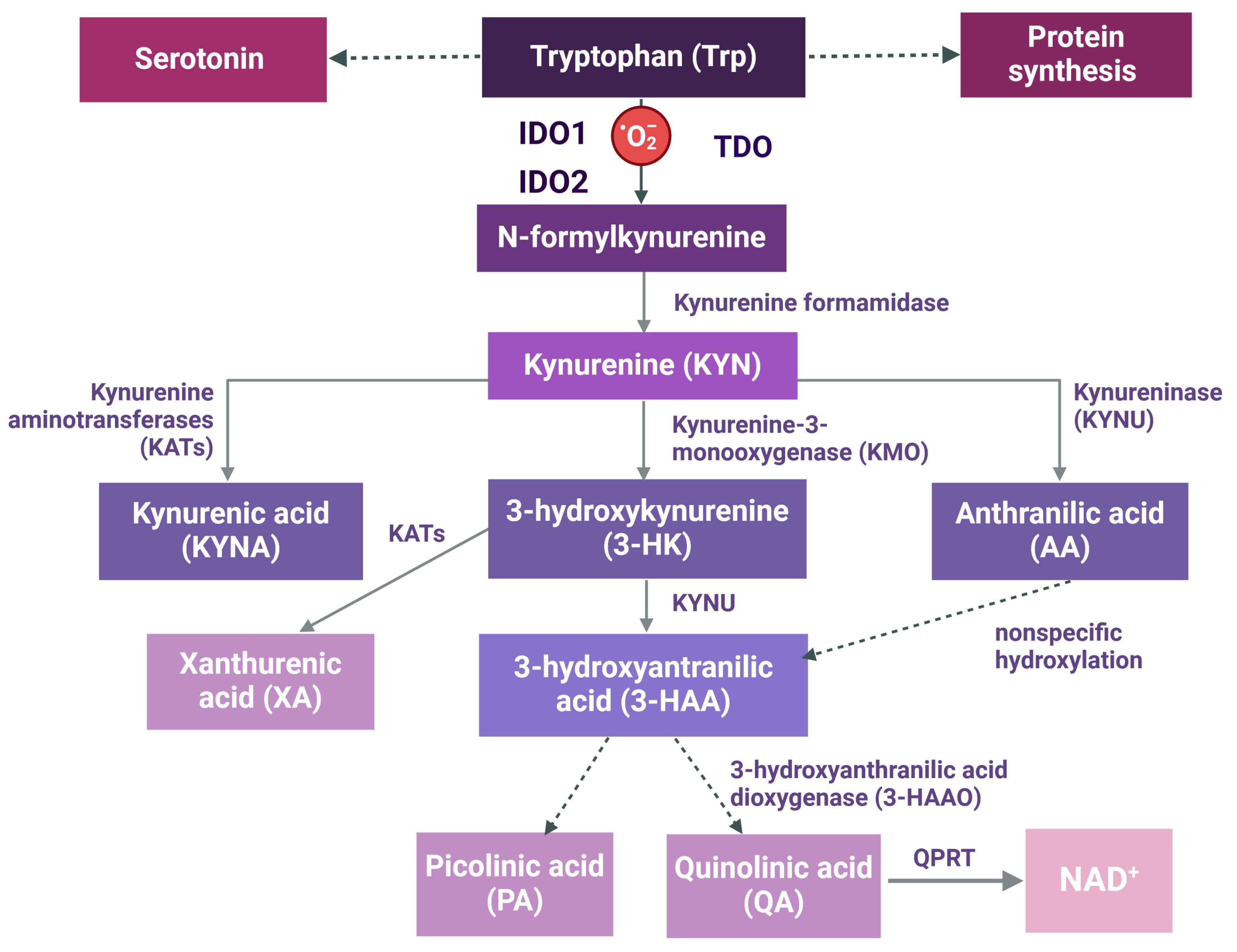
2. The Kynurenine (KYN) Pathway
3. Immune Function in Kidney Transplantation and the Kynurenine Pathway
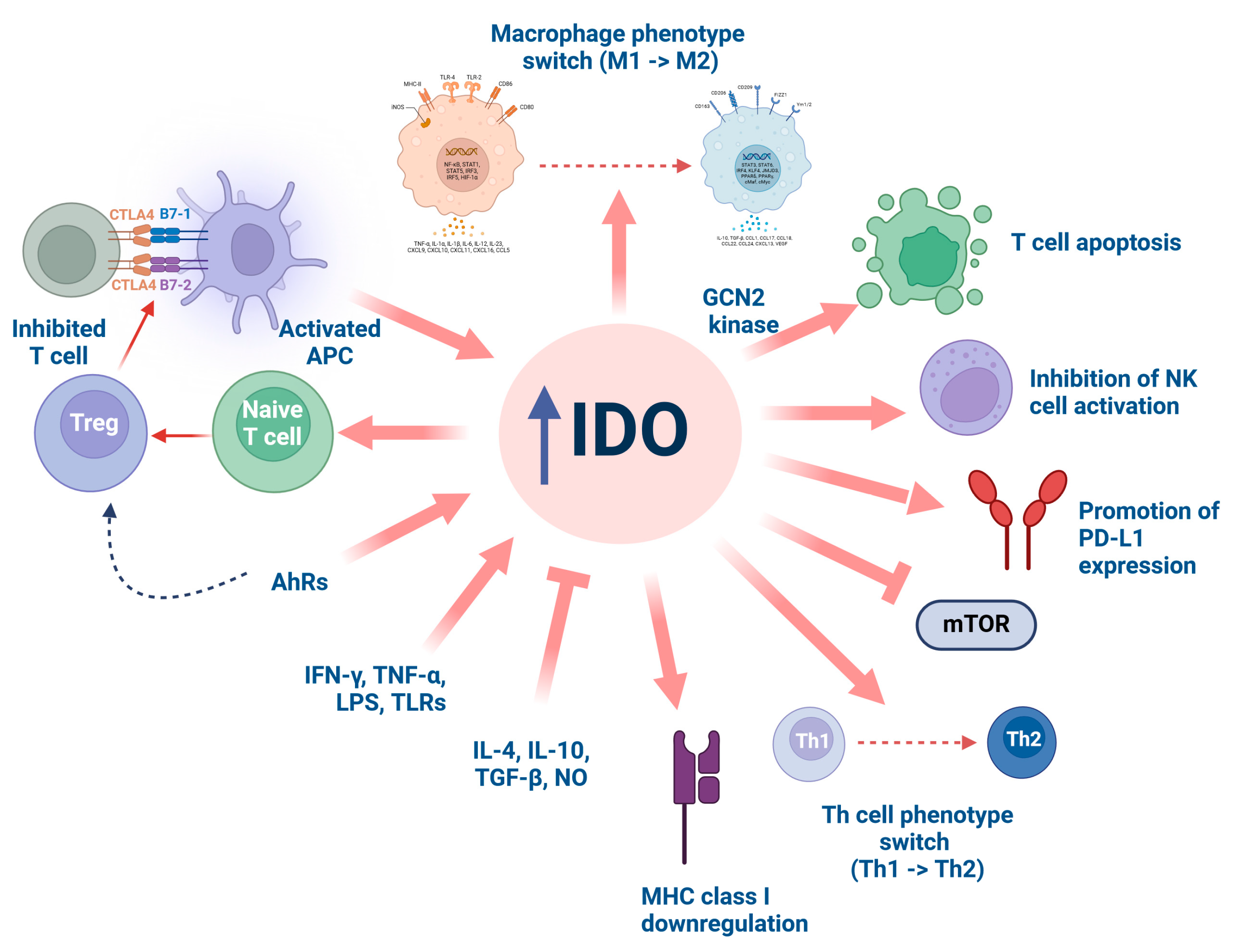
3.1. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO)
3.2. Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase (KMO)
3.3. Kynurenic Acid (KYNA)
4. Infections
5. Malignancies
6. Cardiovascular Risk
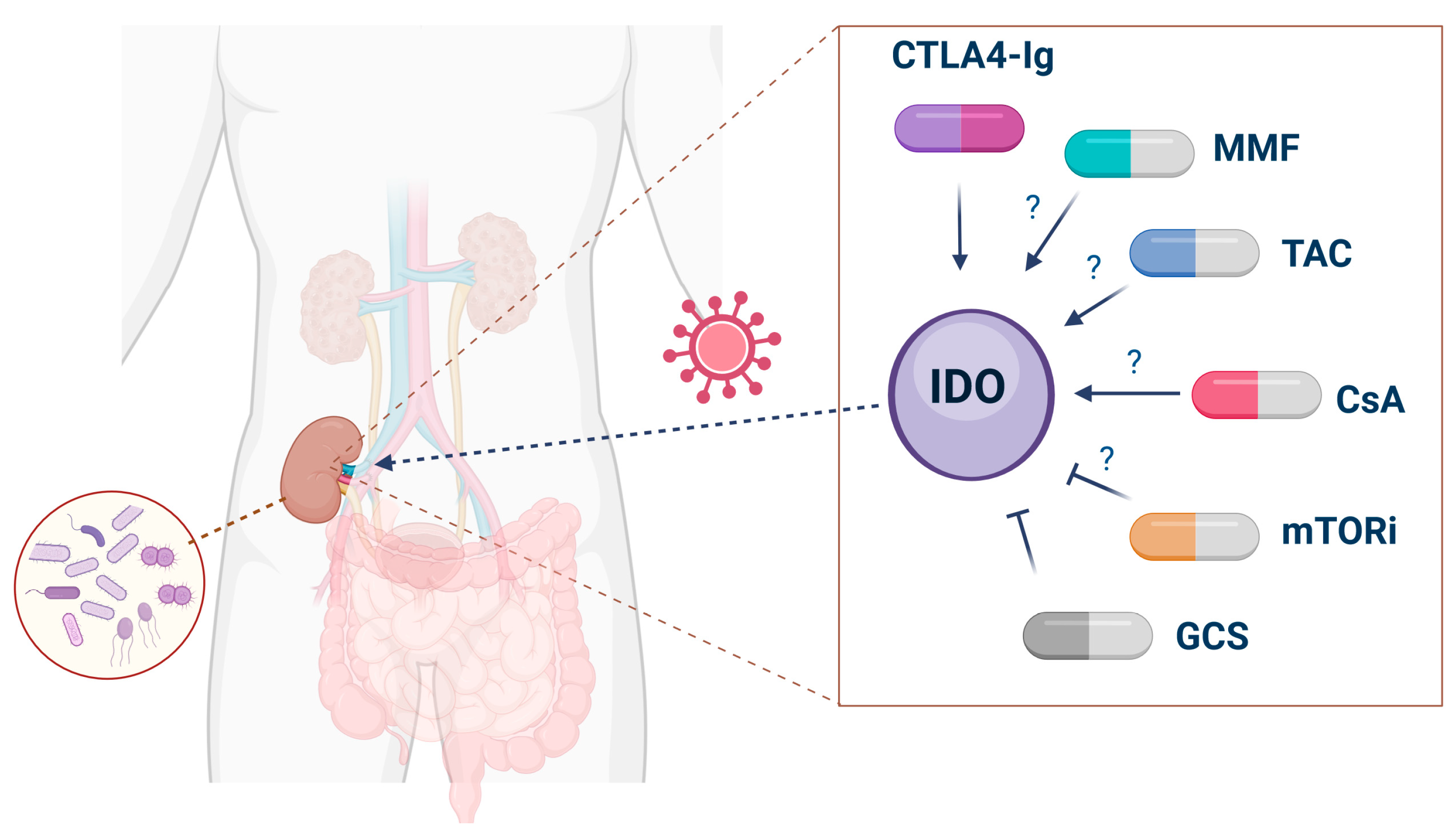
7. Pharmacological Interventions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1-MT | 1-methyltryptophan |
| 3-HAA | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid |
| 3-HAAO | 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase |
| 3-HK | 3-hydroxykynurenine |
| AA | anthranilic acid |
| AAV | ANCA-associated vasculitis |
| ABMR | antibody-mediated rejection |
| AdCTLA4Ig | adenovirus-mediated CTLA4Ig |
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| AMPA | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| ANCA | antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| AR | acute rejection |
| BKV | polyomavirus BK |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CTLA4 | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| CTLA4-Ig | CTLA4 fusion protein |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| CsA | cyclosporine |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemofiltration |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| dd-cfDNA | donor-derived cell-free DNA |
| ESKD | end stage kidney disease |
| GCN2 | general control non-derepressible 2 |
| GCS | glucocorticosteroids |
| GLU | glutamate |
| GPR35 | G protein-coupled receptor 35 |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HMGB1 | high mobility group box protein 1 |
| hsCRP | high-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| HTK | histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate |
| IDO | indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase |
| IDO1 | indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 |
| IDO2 | indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 2 |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| IL | interleukin |
| KAT | kynurenine aminotransferase |
| KMO | kynurenine 3-monooxygenase |
| KRT | kidney replacement therapy |
| KYN | kynurenine |
| KYNA | kynurenic acid |
| KYNU | kynureninase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MHC | mean histocompatibility complex |
| MMF | mycophenolate mofetil |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| mTORi | mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor |
| NAD+ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NAMPT | nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase |
| N-formyl-KYN | N-formyl-kynurenine |
| NK | natural killer |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| PA | picolinic acid |
| PD-1 | programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| QA | quinolinic acid |
| QPRT | quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| sTNF-1 | soluble TNF-receptor-1 |
| TAC | tacrolimus |
| TCR | T cell mediated rejection |
| TDO | tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| Th | T helper cell |
| TLR | toll like receptor |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TPE | therapeutic plasma exchange |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| Trp | tryptophan |
| TSG-6 | TNF-stimulated gene 6 |
| XA | xanthurenic acid |
References
- Jager, K.J.; Kovesdy, C.; Langham, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Jha, V.; Zoccali, C. A Single Number for Advocacy and Communication-Worldwide More than 850 Million Individuals Have Kidney Diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting Life Expectancy, Years of Life Lost, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 250 Causes of Death: Reference and Alternative Scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 Countries and Territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, M.; Caskey, F.J.; Evans, M.; Torino, C.; Szymczak, M.; Drechsler, C.; Pippias, M.; de Rooij, E.; Porto, G.; Stel, V.S.; et al. The Impact of Gender on the Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Older Adults with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Steingroever, J.; Lee, K.H.; Oh, J.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, J.; Larkins, N.G.; Schaefer, F.; Hong, S.H.; Jeong, G.H.; et al. Clinical Interventions and All-Cause Mortality of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Umbrella Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, J.S.; Joshi, M.; Yan, G.; Norris, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Yuan, C.M.; Nee, R. Global Epidemiology of End-Stage Kidney Disease and Disparities in Kidney Replacement Therapy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stel, V.S.; Jager, K.J.; Ortiz, A. Sixty Years of European Renal Association (ERA) Registry Data on Kidney Disease: Visualizing Differences in Clinical Practice. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, 39, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerstra, B.A.; Boenink, R.; Astley, M.E.; Bonthuis, M.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Arribas Monzón, F.; Åsberg, A.; Beckerman, P.; Bell, S.; Cases Amenós, A.; et al. The ERA Registry Annual Report 2021: A Summary. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, V.S.; Boenink, R.; Astley, M.E.; Boerstra, B.A.; Radunovic, D.; Skrunes, R.; Ruiz San Millán, J.C.; Slon Roblero, M.F.; Bell, S.; Ucio Mingo, P.; et al. A Comparison of the Epidemiology of Kidney Replacement Therapy between Europe and the United States: 2021 Data of the ERA Registry and the USRDS. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, gfae040, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Bucay, A.; Gordon, C.E.; Francis, J.M. Non-Immunological Complications Following Kidney Transplantation. F1000Research 2019, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkies, K.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Kowalczyk, A.; Lizakowski, S.; Małyszko, J. Malignancies in Adult Kidney Transplant Candidates and Recipients: Current Status. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Tripepi, G.; Stel, V.; Fu, E.L.; Mallamaci, F.; Dekker, F.; Jager, K.J. Biomarkers in Clinical Epidemiology Studies. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Athreya, A.; Kataria, A. Biomarkers in Kidney Transplantation: A Rapidly Evolving Landscape. Transplantation 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Sellares, J.; Tinel, C.; Anglicheau, D.; Bestard, O.; Friedewald, J.J. European Society of Organ Transplantation Consensus Statement on Testing for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Kidney Allograft Rejection. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulpaite, R.; Miknevicius, P.; Leber, B.; Strupas, K.; Stiegler, P.; Schemmer, P. Tryptophan Metabolism via Kynurenine Pathway: Role in Solid Organ Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Floc’h, N.; Otten, W.; Merlot, E. Tryptophan Metabolism, from Nutrition to Potential Therapeutic Applications. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, H.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Role of Kynurenines in the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2005, 2, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Oxidative Stress during Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, N.-A.; Roudsari, N.M.; Shayan, M.; Niazi Shahraki, F.; Hosseini, Y.; Momtaz, S.; Abdolghaffari, A.H. IDO/Kynurenine; Novel Insight for Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Cytokine 2023, 166, 156206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenines as a Novel Target for the Treatment of Malignancies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrocka, I.; Załuska, W. Kynurenine Pathway in Kidney Diseases. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Kalaska, B.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine Pathway in Chronic Kidney Disease: What’s Old, What’s New, and What’s Next? Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 117864692095488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunis, C.J.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Wareham, N.J.; Murphy, A.J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Hazen, S.L.; Hanssen, N.M.J. Tryptophan Metabolites and Incident Cardiovascular Disease: The EPIC-Norfolk Prospective Population Study. Atherosclerosis 2023, 387, 117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Xie, C.; Shi, J. The Role of the Kynurenine Pathway in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1406856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiluk, M.; Lewkowicz, J.; Kowalska, I.; Pawlak, D.; Łagoda, K.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A. Alterations of the Kynurenine Pathway in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes are Associated with Metabolic Control of Diabetes. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2023, 133, 16581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozieł, K.; Urbanska, E.M. Kynurenine Pathway in Diabetes Mellitus—Novel Pharmacological Target? Cells 2023, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainz, U.; Jürgens, B.; Heitger, A. The Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in Transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2007, 20, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Correia, M.A. Heme: A Regulator of Rat Hepatic Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 377, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Cetina Biefer, H.; Vasudevan, A.; Elkhal, A. Aspects of Tryptophan and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide in Immunity: A New Twist in an Old Tale. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 117864691771349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, W.E.; Mehler, A.H. The Adaptive Increase of the Tryptophan Peroxidase-Oxidase System of Liver. Science 1951, 113, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, W.E.; Auerbach, V.H. The Hormonal Control of Tryptophan Peroxidase in the Rat. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 214, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, G.; Feigelson, P. Purification and Properties of Rat Liver Tryptophan Oxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 5327–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, J.M.; Borden, E.C.; Sondel, P.M.; Byrne, G.I. Interferon-Induced Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity in Human Mononuclear Phagocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1989, 45, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwu, P.; Du, M.X.; Lapointe, R.; Do, M.; Taylor, M.W.; Young, H.A. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Production by Human Dendritic Cells Results in the Inhibition of T Cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 3596–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, R.; Imanishi, J.; Oku, T.; Kishida, T.; Hayaishi, O. Induction of Pulmonary Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase by Interferon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, T.A.; Carlin, J.M. Transcriptional Activation of Indoleamine Dioxygenase by Interleukin 1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Interferon-Treated Epithelial Cells. Cytokine 2000, 12, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallarino, F.; Pallotta, M.T.; Matino, D.; Gargaro, M.; Orabona, C.; Vacca, C.; Mondanelli, G.; Allegrucci, M.; Boon, L.; Romani, R.; et al. LPS-Conditioned Dendritic Cells Confer Endotoxin Tolerance Contingent on Tryptophan Catabolism. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Stocker, R. Redox Reactions Related to Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Tryptophan Metabolism along the Kynurenine Pathway. Redox Rep. 1999, 4, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, O.; Yoshida, R.; Kido, R.; Hayaishi, O. Tryptophan Degradation in Mice Initiated by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3648–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Tryptophan Availability for Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism across the Life Span: Control Mechanisms and Focus on Aging, Exercise, Diet and Nutritional Supplements. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, E.; Øverli, Ø.; Winberg, S. Tryptophan Metabolic Pathways and Brain Serotonergic Activity: A Comparative Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, R.; Duhadaway, J.B.; Kamasani, U.; Laury-Kleintop, L.; Muller, A.J.; Prendergast, G.C. Novel Tryptophan Catabolic Enzyme IDO2 is the Preferred Biochemical Target of the Antitumor Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitory Compound D-1-Methyl-Tryptophan. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7082–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, H.J.; Yuasa, H.J.; Austin, C.J.D.; Weiser, S.; Hunt, N.H. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-2; a New Enzyme in the Kynurenine Pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.; Liu, A. What is the Tryptophan Kynurenine Pathway and Why is It Important to Neurotherapeutics? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, S.; Peterhans, E.; Stocker, R. Antioxidant Activities of Some Tryptophan Metabolites: Possible Implication for Inflammatory Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2506–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. 3-Hydroxykynurenine, an Endogenous Oxidative Stress Generator, Causes Neuronal Cell Death with Apoptotic Features and Region Selectivity. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, L.E.; Leopold, M.C.; Huang, X.; Atwood, C.S.; Saunders, A.J.; Hartshorn, M.; Lim, J.T.; Faget, K.Y.; Muffat, J.A.; Scarpa, R.C.; et al. 3-Hydroxykynurenine and 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid Generate Hydrogen Peroxide and Promote Alpha-Crystallin Cross-Linking by Metal Ion Reduction. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 7266–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.S.; Junior, O.V.R.; Dos Santos, T.M.; Silveira, J.S.; Deniz, B.F.; Alves, V.S.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Savio, L.E.B.; Wyse, A.T.S. Effect of Quinolinic Acid on Behavior, Morphology, and Expression of Inflammatory/Oxidative Status in Rats’ Striatum: Is Coenzyme Q10 a Good Protector? Neurotox. Res. 2023, 41, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Katsuki, H. Hydrogen Peroxide-Mediated Neuronal Cell Death Induced by an Endogenous Neurotoxin, 3-Hydroxykynurenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganong, A.H.; Cotman, C.W. Kynurenic Acid and Quinolinic Acid Act at N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors in the Rat Hippocampus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1986, 236, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, P.J.; Grossman, C.J.; Hayes, A.G. Kynurenate and FG9041 Have Both Competitive and Non-Competitive Antagonist Actions at Excitatory Amino Acid Receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 151, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapiuk, A.; Urbanska, E.M. Kynurenic Acid in Neurodegenerative Disorders-Unique Neuroprotection or Double-Edged Sword? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, C.; Owe-Larsson, M.; Urbanska, E.M. New Perspective on Anorexia Nervosa: Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway Hypothesis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamos, E.; Pardutz, A.; Klivenyi, P.; Toldi, J.; Vecsei, L. The Role of Kynurenines in Disorders of the Central Nervous System: Possibilities for Neuroprotection. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 283, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, T.W.; Williams, R.O. Tryptophan Metabolism as a “reflex” Feature of Neuroimmune Communication: Sensor and Effector Functions for the Indoleamine-2, 3-Dioxygenase Kynurenine Pathway. J. Neurochem. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenic Acid as an Antagonist of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Brain: Facts and Challenges. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Murray, I.A.; Schroeder, J.C.; Flaveny, C.A.; Lahoti, T.S.; Laurenzana, E.M.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Perdew, G.H. Kynurenic Acid is a Potent Endogenous Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand That Synergistically Induces Interleukin-6 in the Presence of Inflammatory Signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic Acid as a Ligand for Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, K.; Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Roberts, A.I.; Li, F.; Han, Y.; Rabson, A.B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Kynurenic Acid, an IDO Metabolite, Controls TSG-6-Mediated Immunosuppression of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirthgen, E.; Hoeflich, A.; Rebl, A.; Günther, J. Kynurenic Acid: The Janus-Faced Role of an Immunomodulatory Tryptophan Metabolite and Its Link to Pathological Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, B.; Melhem, H.; Niess, J.H. GPR35 in Intestinal Diseases: From Risk Gene to Function. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, P.; Owe-Larsson, M.; Urbańska, E.M. Microbiota, Tryptophan and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors as the Target Triad in Parkinson’s Disease—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.; Hess, M.; Weimer, B.C. Microbial-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites and Their Role in Neurological Disease: Anthranilic Acid and Anthranilic Acid Derivatives. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schefold, J.C.; Zeden, J.P.; Fotopoulou, C.; Von Haehling, S.; Pschowski, R.; Hasper, D.; Volk, H.D.; Schuett, C.; Reinke, P. Increased Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) Activity and Elevated Serum Levels of Tryptophan Catabolites in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Possible Link between Chronic Inflammation and Uraemic Symptoms. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, K.; Kowalewska, A.; Pawlak, D.; Mysliwiec, M. Kynurenine and Its Metabolites—Kynurenic Acid and Anthranilic Acid are Associated with Soluble Endothelial Adhesion Molecules and Oxidative Status in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 338, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, K.; Myśliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine Pathway—A New Link between Endothelial Dysfunction and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Adv. Med. Sci. 2010, 55, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, N.; McKercher, C.; Nichols, D.S.; Davies, N.; Shellie, R.A.; Hilder, E.F.; Jose, M.D. Tryptophan Metabolism, Its Relation to Inflammation and Stress Markers and Association with Psychological and Cognitive Functioning: Tasmanian Chronic Kidney Disease Pilot Study. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konje, V.C.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Bellovich, K.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Gipson, D.S.; Afshinnia, F.; Mathew, A.V. Michigan Kidney Translational Core CPROBE Investigator Group Tryptophan Levels Associate with Incident Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, T.; VanDerWoude, E.; Han, Y.; Byun, J.; Konje, V.C.; Gillespie, B.W.; Saran, R.; Mathew, A.V. Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites Predict Subclinical Atherosclerotic Disease and New Cardiovascular Events in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1952–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Zheng, J.; Shi, H.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Prediction Model for Early-Stage CKD Using the Naples Prognostic Score and Plasma Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretschneider, H.J. Survival Time and Recuperative Time of The Heart in Normothermia and Hypothermia. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Kreislaufforsch. 1964, 30, 11–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Mangino, M.J. Preservation Methods for Kidney and Liver. Organogenesis 2009, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, A.; Brockmann, J.G.; Becker, F. HTK-N: Modified Histidine-Tryptophan-Ketoglutarate Solution-A Promising New Tool in Solid Organ Preservation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Robertson, L.; Gallinetti, J.; Mejia, P.; Vose, S.; Charlip, A.; Chu, T.; Mitchell, J.R. Surgical Stress Resistance Induced by Single Amino Acid Deprivation Requires Gcn2 in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 118ra11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougeray, S.; Mami, I.; Bertho, G.; Beaune, P.; Thervet, E.; Pallet, N. Tryptophan Depletion and the Kinase GCN2 Mediate IFN-γ-Induced Autophagy. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2954–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, T.; Pissas, G.; Sounidaki, M.; Antoniadis, N.; Antoniadi, G.; Liakopoulos, V.; Stefanidis, I. Preconditioning of Primary Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells without Tryptophan Increases Survival under Hypoxia by Inducing Autophagy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Alexander, M.P.; Schinstock, C. Challenges and Opportunities for Designing Clinical Trials for Antibody Mediated Rejection. Front. Transpl. 2024, 3, 1389005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, D.H.; Zhou, M.; Attwood, J.T.; Bondarev, I.; Conway, S.J.; Marshall, B.; Brown, C.; Mellor, A.L. Prevention of Allogeneic Fetal Rejection by Tryptophan Catabolism. Science 1998, 281, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohib, K.; Guan, Q.; Diao, H.; Du, C.; Jevnikar, A.M. Proapoptotic Activity of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Expressed in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 293, F801-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.-B.; Luo, G.-H.; Bao, D.-S.; Chen, A.-J.; Zhuang, Y.-X.; Guo, Y.-N.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, Z.-P.; Lu, Y.-P.; et al. Impact of Immunosuppressive Agents on the Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase, Heme Oxygenase-1 and Interleukin-7 in Mesangial Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, S.H.; Heidt, S.; Krop, J.; IJsselsteijn, M.E.; Eggermont, J.; Kers, J.; Reinders, M.E.J.; Koning, F.; van Kooten, C. IDO+ Endothelial Cells in Glomeruli of Kidney Transplantation Patients with Glomerulitis. Transpl. Direct 2024, 10, e1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrincova-Yaghi, D.; Seelen, M.A.; Kema, I.P.; Deelman, L.E.; Van Der Heuvel, M.C.; Breukelman, H.; Van Den Eynde, B.J.; Henning, R.H.; Van Goor, H.; Sandovici, M. Early Posttransplant Tryptophan Metabolism Predicts Long-Term Outcome of Human Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2015, 99, e97–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, T.; Gusella, G.L.; Brooks, A.; Longo, D.L.; Varesio, L. Interleukin-4 Inhibits Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Expression in Human Monocytes. Blood 1994, 83, 1408–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, C.R.; González, R.G.; Kniep, E.; Roch, S.; Däubener, W. Cytokine Mediated Regulation of Interferon-Gamma-Induced IDO Activation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 467, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Mohr, D.; Stocker, R. Nitric Oxide Inhibits Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity in Interferon-Gamma Primed Mononuclear Phagocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14457–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.K.; Park, H.J.; Macleod, M.; Chandler, P.; Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L. Tryptophan Deprivation Sensitizes Activated T Cells to Apoptosis Prior to Cell Division. Immunology 2002, 107, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallarino, F.; Grohmann, U.; Vacca, C.; Bianchi, R.; Orabona, C.; Spreca, A.; Fioretti, M.C.; Puccetti, P. T Cell Apoptosis by Tryptophan Catabolism. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurawaki, S.; Nakashima, A.; Ishiuchi, N.; Kanai, R.; Maeda, S.; Sasaki, K.; Masaki, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pretreated with Interferon-Gamma Attenuate Renal Fibrosis by Enhancing Regulatory T Cell Induction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, D.H.; Sharma, M.D.; Mellor, A.L. Ligation of B7-1/B7-2 by Human CD4+ T Cells Triggers Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity in Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4100–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Wang, H.-S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K.-F.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, G.; Cai, S.-H.; Du, J. The Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) in Immune Tolerance: Focus on Macrophage Polarization of THP-1 Cells. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 289, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, S.; Goto, S.; Tahara, K.; Sasaki, A.; Kawano, K.; Kitano, S. Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase Suppresses NK Cell Activity and Accelerates Tumor Growth. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2003, 3, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tredget, E.E.; Ghahary, A. Cell Surface Expression of MHC Class I Antigen is Suppressed in Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Genetically Modified Keratinocytes: Implications in Allogeneic Skin Substitute Engraftment. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frumento, G.; Rotondo, R.; Tonetti, M.; Damonte, G.; Benatti, U.; Ferrara, G.B. Tryptophan-Derived Catabolites are Responsible for Inhibition of T and Natural Killer Cell Proliferation Induced by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, L.M.F.; Peng, W.; Mandik-Nayak, L. Impact of IDO1 and IDO2 on the B Cell Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 886225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, R.; Rust, S.; Duhadaway, J.B.; Mautino, M.R.; Munn, D.H.; Vahanian, N.N.; Link, C.J.; Prendergast, G.C. IDO Inhibits a Tryptophan Sufficiency Signal That Stimulates MTOR: A Novel IDO Effector Pathway Targeted by D-1-Methyl-Tryptophan. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.F.A.; Goth, S.R.; Dong, B.; Pessah, I.N.; Matsumura, F. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Mediates Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An Interaction between Kynurenine and the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Can Generate Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, M.T.; Orabona, C.; Volpi, C.; Vacca, C.; Belladonna, M.L.; Bianchi, R.; Servillo, G.; Brunacci, C.; Calvitti, M.; Bicciato, S.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase is a Signaling Protein in Long-Term Tolerance by Dendritic Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myśliwiec, P.; Myśliwiec, H.; Pawlak, D.; Dadan, J.; Buczko, W.; Pawlak, K. Tryptophan and Its Metabolites in Renal Allograft Recipients. Przegl. Lek. 2009, 66, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Te Linde, E.; van Roij, C.J.M.; Meijers, B.K.I.; De Loor, H.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Wetzels, J.F.M. Cognitive Function and Uremic Toxins after Kidney Transplantation: An Exploratory Study. Kidney360 2020, 1, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, L.V.; Minović, I.; Franssen, C.F.M.; van Faassen, M.; Sanders, J.-S.F.; Berger, S.P.; Navis, G.; Kema, I.P.; Bakker, S.J.L. The Tryptophan/Kynurenine Pathway, Systemic Inflammation, and Long-Term Outcome after Kidney Transplantation. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F475–F486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.W.; Russell, P.M.; Kinzler, G.J.; Reckard, C.R.; Flanigan, R.C.; Thompson, K.D.; Bermes, E.W. Oxidative Tryptophan Metabolism in Renal Allograft Recipients: Increased Kynurenine Synthesis is Associated with Inflammation and OKT3 Therapy. Cytokine 1992, 4, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandacher, G.; Cakar, F.; Winkler, C.; Schneeberger, S.; Obrist, P.; Bösmüller, C.; Werner-Felmayer, G.; Werner, E.R.; Bonatti, H.; Margreiter, R.; et al. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Kidney Allograft Rejection through IDO Metabolism Evaluation. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieseg, S.P.; Baxter-Parker, G.; Lindsay, A. Neopterin, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress: What Could We Be Missing? Antioxidants 2018, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahdou, I.; Sadeghi, M.; Daniel, V.; Schenk, M.; Renner, F.; Weimer, R.; Löb, S.; Schmidt, J.; Mehrabi, A.; Schnitzler, P.; et al. Increased Pretransplantation Plasma Kynurenine Levels Do Not Protect from but Predict Acute Kidney Allograft Rejection. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśnicki, K.; Donizy, P.; Kuriata-Kordek, M.; Uchmanowicz, I.; Zachciał, J.; Hałoń, A.; Janczak, D.; Banasik, M. Interstitial Foci Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1: A Potential Biomarker for Kidney Transplant Rejection. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaden, J.; Abendroth, D.; Völp, A.; Marzinzig, M. Dynamics and Diagnostic Relevance of Kynurenine Serum Level after Kidney Transplantation. Ann. Transpl. 2015, 20, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Gupta, S.; Al Khasawneh, E.; Haafiz, A.; Shuster, J.J.; Theriaque, D.W.; Shahlaee, A.H.; Garrett, T.J. Immune Biomarker Panel Monitoring Utilizing IDO Enzyme Activity and CD4 ATP Levels: Prediction of Acute Rejection vs. Viral Replication Events. Pediatr. Transpl. 2011, 15, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Al Khasawneh, E.; Gupta, S.; Shuster, J.J.; Theriaque, D.W.; Shahlaee, A.H.; Garrett, T.J. Verification of Association of Elevated Serum Ido Enzyme Activity with Acute Rejection and Low Cd4-Atp Levels with Infection. Transplantation 2013, 96, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, R.; Merchen, T.D.; Fang, X.; Wang, Y. Protective Role of Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase in Allograft Rejection and Tubular Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korstanje, R.; Deutsch, K.; Bolanos-Palmieri, P.; Hanke, N.; Schroder, P.; Staggs, L.; Bräsen, J.H.; Roberts, I.S.D.; Sheehan, S.; Savage, H.; et al. Loss of Kynurenine 3-Mono-Oxygenase Causes Proteinuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Chavez, J.A.; D’Aquino, K.E.; Meng, R.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Pocai, A.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.-J. Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase Limits de Novo NAD+ Synthesis through Dietary Tryptophan in Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cell Models. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C1423–C1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaher, S.S.; Germain, C.; Fu, H.; Larkin, D.F.P.; George, A.J.T. 3-Hydroxykynurenine Suppresses CD4+ T-Cell Proliferation, Induces T-Regulatory-Cell Development, and Prolongs Corneal Allograft Survival. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Merchen, T.D.; Fang, X.; Lassiter, R.; Ho, C.-S.; Jajosky, R.; Kleven, D.; Thompson, T.; Mohamed, E.; Yu, M.; et al. Regulation of Indoleamine 2,3 Dioxygenase and Its Role in a Porcine Model of Acute Kidney Allograft Rejection. J. Investig. Med. 2018, 66, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, H.; Sakai, T.; Kuwahara, Y.; Ito, M.; Tsuritani, K.; Hirasawa, Y.; Nagamatsu, T. Effects of Kynurenine Metabolites on Mesangial Cell Proliferation and Gene Expression. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 87, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Huang, G.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Suppression of Experimental Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis by Tryptophan. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Xie, R.; He, H.; Xie, Q.; Zhao, X.; Kang, G.; Cheng, C.; Yin, W.; Cong, J.; Li, J.; et al. Kynurenic Acid Ameliorates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Blocking Calcium Mobilization via GPR35. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1019365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.P.; Singh, U.P.; Singh, B.; Price, R.L.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Leads to Reciprocal Epigenetic Regulation of FoxP3 and IL-17 Expression and Amelioration of Experimental Colitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi Elizei, S.; Poormasjedi-Meibod, M.-S.; Wang, X.; Kheirandish, M.; Ghahary, A. Kynurenic Acid Downregulates IL-17/1L-23 Axis in Vitro. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 431, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallarini, S.; Magliulo, L.; Paoletti, T.; de Lalla, C.; Lombardi, G. Expression of Functional GPR35 in Human INKT Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblad, S.S.; Mydel, P.; Hellvard, A.; Jonsson, I.-M.; Bokarewa, M.I. The N-Methyl-d-Aspartic Acid Receptor Antagonist Memantine Ameliorates and Delays the Development of Arthritis by Enhancing Regulatory T Cells. Neurosignals 2012, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiszlavicz, Z.; Németh, B.; Fülöp, F.; Vécsei, L.; Tápai, K.; Ocsovszky, I.; Mándi, Y. Different Inhibitory Effects of Kynurenic Acid and a Novel Kynurenic Acid Analogue on Tumour Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) Production by Mononuclear Cells, HMGB1 Production by Monocytes and HNP1-3 Secretion by Neutrophils. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 383, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchowska, E.; Luchowski, P.; Wielosz, M.; Turski, W.A.; Urbanska, E.M. FK506 Attenuates 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium- and 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Evoked Inhibition of Kynurenic Acid Synthesis in Rat Cortical Slices. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2003, 63, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, A.M.; Reynolds, D.J.; Harper, A.; Devitt, A.; Pearce, J.H. Low-Nutrient Induction of Abnormal Chlamydial Development: A Novel Component of Chlamydial Pathogenesis? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1993, 106, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Xu, L.; Tao, J.; Cui, D.; Liu, T.F. Tryptophan Catabolism via the Kynurenine Pathway Regulates Infection and Inflammation: From Mechanisms to Biomarkers and Therapies. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, A.; Krupa, M.M.; Pawlak, K. Kynurenine Pathway-An Underestimated Factor Modulating Innate Immunity in Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury? Cells 2022, 11, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, W.; Kocki, T.; Pilat, J.; Parada-Turska, J.; Malbrain, M.L.N.G. Changes in Plasma Kynurenic Acid Concentration in Septic Shock Patients Undergoing Continuous Veno-Venous Haemofiltration. Inflammation 2014, 37, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadeghi, M.; Lahdou, I.; Daniel, V.; Schnitzler, P.; Fusch, G.; Schefold, J.C.; Zeier, M.; Iancu, M.; Opelz, G.; Terness, P. Strong Association of Phenylalanine and Tryptophan Metabolites with Activated Cytomegalovirus Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monjaras-Avila, C.U.; Lorenzo-Leal, A.C.; Luque-Badillo, A.C.; D’Costa, N.; Chavez-Muñoz, C.; Bach, H. The Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zam, W.; Ali, L. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Cancer. Curr. Rev. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 17, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobi-McCloud, A.; Muthuswamy, R.; Battaglia, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Putluri, V.; Singh, P.K.; Qian, F.; Huang, R.-Y.; et al. IDO1 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Induces PD-1 in T Cells via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, L.S.; Floyd, J.L.; Kuo, L.-W.; Post, M.D.; Bickerdike, M.; O’Neill, K.; Sompel, K.; Jordan, K.R.; Corr, B.R.; Marjon, N.; et al. Targeting Tryptophan Catabolism in Ovarian Cancer to Attenuate Macrophage Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, B.; Zeng, R.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhong, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, L.; et al. Increased Coexpression of PD-L1 and IDO1 is Associated with Poor Overall Survival in Patients with NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löb, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Zieker, D.; Brücher, B.L.D.M.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Opelz, G.; Terness, P. IDO1 and IDO2 are Expressed in Human Tumors: Levo- but Not Dextro-1-Methyl Tryptophan Inhibits Tryptophan Catabolism. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, G.; Rutigliano, M.; Ferro, M.; Giglio, A.; Intini, A.; Triggiano, F.; Palazzo, S.; Gigante, M.; Castellano, G.; Ranieri, E.; et al. Activation of the Kynurenine Pathway Predicts Poor Outcome in Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 461.e15–461.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornigold, N.; Dunn, K.R.; Craven, R.A.; Zougman, A.; Trainor, S.; Shreeve, R.; Brown, J.; Sewell, H.; Shires, M.; Knowles, M.; et al. Dysregulation at Multiple Points of the Kynurenine Pathway is a Ubiquitous Feature of Renal Cancer: Implications for Tumour Immune Evasion. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Tryptophan Metabolism and Disposition in Cancer Biology and Immunotherapy. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20221682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.E.; Sharif, T.; Martell, E.; Dai, C.; Kim, Y.; Lee, P.W.K.; Gujar, S.A. NAD+ Salvage Pathway in Cancer Metabolism and Therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 114, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, M.; Takahara, K.; Zennami, K.; Nagakawa, T.; Maeda, Y.; Shiogama, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Muto, Y.; Nukaya, T.; Takenaka, M.; et al. Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase in Tumor Cells is Associated with Resistance to Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-H.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, A.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Chen, H.-Z.; Jin, J.-M.; Luan, X. Targeting Metabolism to Enhance Immunotherapy within Tumor Microenvironment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, Y.; Nozawa, H.; Sonoda, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Emoto, S.; Murono, K.; Sasaki, K.; Ishihara, S. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitor Suppresses Colon Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 3337–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Bai, L.; Tong, R.; Yang, H.; Zhong, L. Targeting Indoleamine Dioxygenase and Tryptophan Dioxygenase in Cancer Immunotherapy: Clinical Progress and Challenges. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 2639–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.A.; Sordillo, P.P. Suppression of Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase as a Treatment for Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 5275–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Letelier, R.A.; Dou, R.; Vykoukal, J.; Sater, A.H.A.; Ostrin, E.; Hanash, S.; Fahrmann, J.F. The Kynurenine Pathway Presents Multi-Faceted Metabolic Vulnerabilities in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1256769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerhaeghe, T.; Murakami, N.; Le Moine, A.; Brouard, S.; Sprangers, B.; Degauque, N. Fine-Tuning Tumor- and Allo-Immunity: Advances in the Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Deneka-Hannemann, S.; Jarosz, B.; Zgrajka, W.; Stoma, F.; Trojanowski, T.; Turski, W.A.; Rzeski, W. Kynurenic Acid Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Human Glioblastoma T98G Cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Turski, W.A.; Rajtar, G. Kynurenic Acid Inhibits Colon Cancer Proliferation in Vitro: Effects on Signaling Pathways. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Zurawska, M.; Kiś, J.; Starownik, R.; Zgrajka, W.; Bar, K.; Turski, W.A.; Rzeski, W. Kynurenic Acid in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma: Its Antiproliferative and Antimigrative Action on Caki-2 Cells. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, K.; Wnorowski, A.; Turski, W.A.; Plech, T. Kynurenic Acid and Cancer: Facts and Controversies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 77, 1531–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsik, D.L.; Chen, J.-K.; Bollag, W.B.; Isales, C.M. Chronic Infusion of the Tryptophan Metabolite, Kynurenine Increases Mean Arterial Pressure in Male Sprague Dawley Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2024, 327, F199–F207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.W. Increased Tryptophan Catabolism Provides Predictive Value to Chronic Heart Failure Patients with Low-Grade Inflammation. Inflammation 2024. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáspár, R.; Halmi, D.; Demján, V.; Berkecz, R.; Pipicz, M.; Csont, T. Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 768560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiewicz, M.; Moniuszko, M.; Pawlak, D.; Knapp, M.; Rusak, M.; Kazimierczyk, R.; Musial, W.J.; Dabrowska, M.; Kaminski, K.A. Activity of the Kynurenine Pathway and Its Interplay with Immunity in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Heart 2016, 102, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryc, J.; Naumnik, B. Thrombolome and Its Emerging Role in Chronic Kidney Diseases. Toxins 2021, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Chamieh, C.; Larabi, I.A.; Alencar De Pinho, N.; Lambert, O.; Combe, C.; Fouque, D.; Frimat, L.; Jacquelinet, C.; Laville, M.; Laville, S.; et al. Study of the Association between Serum Levels of Kynurenine and Cardiovascular Outcomes and Overall Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, K.; Tankiewicz, J.; Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Tissue Factor/Its Pathway Inhibitor System and Kynurenines in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients on Conservative Treatment. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Hypercoagulability is Independently Associated with Kynurenine Pathway Activation in Dialysed Uraemic Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, K.; Domaniewski, T.; Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenines and Oxidative Status are Independently Associated with Thrombomodulin and von Willebrand Factor Levels in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Thromb. Res. 2009, 124, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wejksza, K.; Rzeski, W.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic Acid Protects against the Homocysteine-Induced Impairment of Endothelial Cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Hyperhomocysteinemia and the Presence of Cardiovascular Disease are Associated with Kynurenic Acid Levels and Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients Undergoing Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapolski, T.; Kamińska, A.; Kocki, T.; Wysokiński, A.; Urbanska, E.M. Aortic Stiffness-Is Kynurenic Acid a Novel Marker? Cross-Sectional Study in Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafa, O.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Ortiz, A.; Dounousi, E.; Ekart, R.; Ferro, C.J.; Mark, P.B.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Del Vecchio, L.; Mallamaci, F. Sex Disparities in Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamerith, G.; Mildner, F.; Merkel, P.A.; Harris, K.; Cooney, L.; Lim, N.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; et al. Association of Baseline Soluble Immune Checkpoints with the Risk of Relapse in PR3-ANCA Vasculitis Following Induction of Remission. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroecksnadel, S.; Sucher, R.; Kurz, K.; Fuchs, D.; Brandacher, G. Influence of Immunosuppressive Agents on Tryptophan Degradation and Neopterin Production in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Transpl. Immunol. 2011, 25, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.M.; Nadler, S.G.; Stetsko, D.K.; Suchard, S.J. Abatacept Modulates Human Dendritic Cell-Stimulated T-Cell Proliferation and Effector Function Independent of IDO Induction. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pree, I.; Bigenzahn, S.; Fuchs, D.; Koporc, Z.; Nierlich, P.; Winkler, C.; Brandacher, G.; Sykes, M.; Muehlbacher, F.; Langer, F.; et al. CTLA4Ig Promotes the Induction of Hematopoietic Chimerism and Tolerance Independently of Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase. Transplantation 2007, 83, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boasso, A.; Herbeuval, J.-P.; Hardy, A.W.; Winkler, C.; Shearer, G.M. Regulation of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Tryptophanyl-TRNA-Synthetase by CTLA-4-Fc in Human CD4+ T Cells. Blood 2005, 105, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, B.; Song, Y.; Yu, Z.; Guo, S. Local Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen-4 Immunoglobulin Inhibition of Rejection Response is Dependent on Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activities in the Allograft. Transpl. Proc. 2014, 46, 3637–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Lima, G.; Uribe-Uribe, N.; Avila-Casado, C.; Mancilla, E.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E.; Pérez-Garrido, J.; Pérez, M.; Cárdenas, G.; Llorente, L.; et al. High Levels of IDO-Expressing CD16+ Peripheral Cells, and Tregs in Graft Biopsies from Kidney Transplant Recipients under Belatacept Treatment. Transpl. Proc. 2010, 42, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Lima, G.; Alberú, J.; Palafox, D.; Uribe-Uribe, N.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E.; Reyes Acevedo, R.; Mondragón, G.; Chevaile, A.; Llorente, L. Infiltrating Cellular Pattern in Kidney Graft Biopsies Translates into Forkhead Box Protein 3 Up-Regulation and P16INK4α Senescence Protein down-Regulation in Patients Treated with Belatacept Compared to Cyclosporin A. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Bostock, I.C.; Lima, G.; Mancilla-Urrea, E.; Mondragón, G.; Reyes-Acevedo, R.; Chevaile, A.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E.; Llorente, L.; Alberú, J. Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Immunoregulatory as Well as Th17A and Th22 Cell Subpopulations in Kidney Transplant Recipients under Belatacept or Cyclosporine Treatment. Transpl. Immunol. 2014, 30, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Hu, L.; Tringali, E.; Senatore, M.; Talarico, R.; Di Dio, M.; Ruotolo, C.; La Manna, G.; Garofalo, C.; Zaza, G. Improving Kidney Disease Care: One Giant Leap for Nephrology. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrocka, I.; Kocki, T.; Turski, W.A. The Effect of Three Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on Kynurenic Acid Production in Rat Kidney in Vitro. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrocka, I.; Targowska-Duda, K.M.; Wnorowski, A.; Kocki, T.; Jóźwiak, K.; Turski, W.A. Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers Decrease Kynurenic Acid Production in Rat Kidney in Vitro. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrocka, I.; Załuska, W. The Influence of Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors on Kynurenic Acid Production in Rat Kidney: A Novel Path for Kidney Protection? Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrocka, I.; Kocki, T.; Urbańska, E.; Załuska, W. Effects of Fenofibrate and Gemfibrozil on Kynurenic Acid Production in Rat Kidneys In Vitro: Old Drugs, New Properties. Life 2023, 13, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, K.; Kozieł, K.; Urbańska, E.M. Novel Activity of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents Linked with Decreased Formation of Tryptophan Metabolite, Kynurenic Acid. Life 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Tabatabaei, A.; Jalili, R.B.; Khosravi-Maharlooei, M.; Hartwell, R.; Kilani, R.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ghahary, A. Immunoprotection and Functional Improvement of Allogeneic Islets in Diabetic Mice, Using a Stable Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Producing Scaffold. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavrincova-Yaghi, D.; Deelman, L.E.; van Goor, H.; Seelen, M.A.; Vavrinec, P.; Kema, I.P.; Gomolcak, P.; Benigni, A.; Henning, R.H.; Sandovici, M. Local Gene Therapy with Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Protects against Development of Transplant Vasculopathy in Chronic Kidney Transplant Dysfunction. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Montassier, E.; Chesneau, M.; Guerif, P.; Hittle, L.; Giral, M.; Bromberg, J.S.; Brouard, S. Unique and Specific Proteobacteria Diversity in Urinary Microbiota of Tolerant Kidney Transplanted Recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2020, 20, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| KYN Pathway Element | Organ or System Function Modification |
|---|---|
| Indoleamine-2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) |
|
| Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) | |
| Kynurenic acid (KYNA) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakrocka, I.; Urbańska, E.M.; Załuska, W.; Kronbichler, A. Kynurenine Pathway after Kidney Transplantation: Friend or Foe? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189940
Zakrocka I, Urbańska EM, Załuska W, Kronbichler A. Kynurenine Pathway after Kidney Transplantation: Friend or Foe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(18):9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189940
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakrocka, Izabela, Ewa M. Urbańska, Wojciech Załuska, and Andreas Kronbichler. 2024. "Kynurenine Pathway after Kidney Transplantation: Friend or Foe?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 18: 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189940
APA StyleZakrocka, I., Urbańska, E. M., Załuska, W., & Kronbichler, A. (2024). Kynurenine Pathway after Kidney Transplantation: Friend or Foe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(18), 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189940








