Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
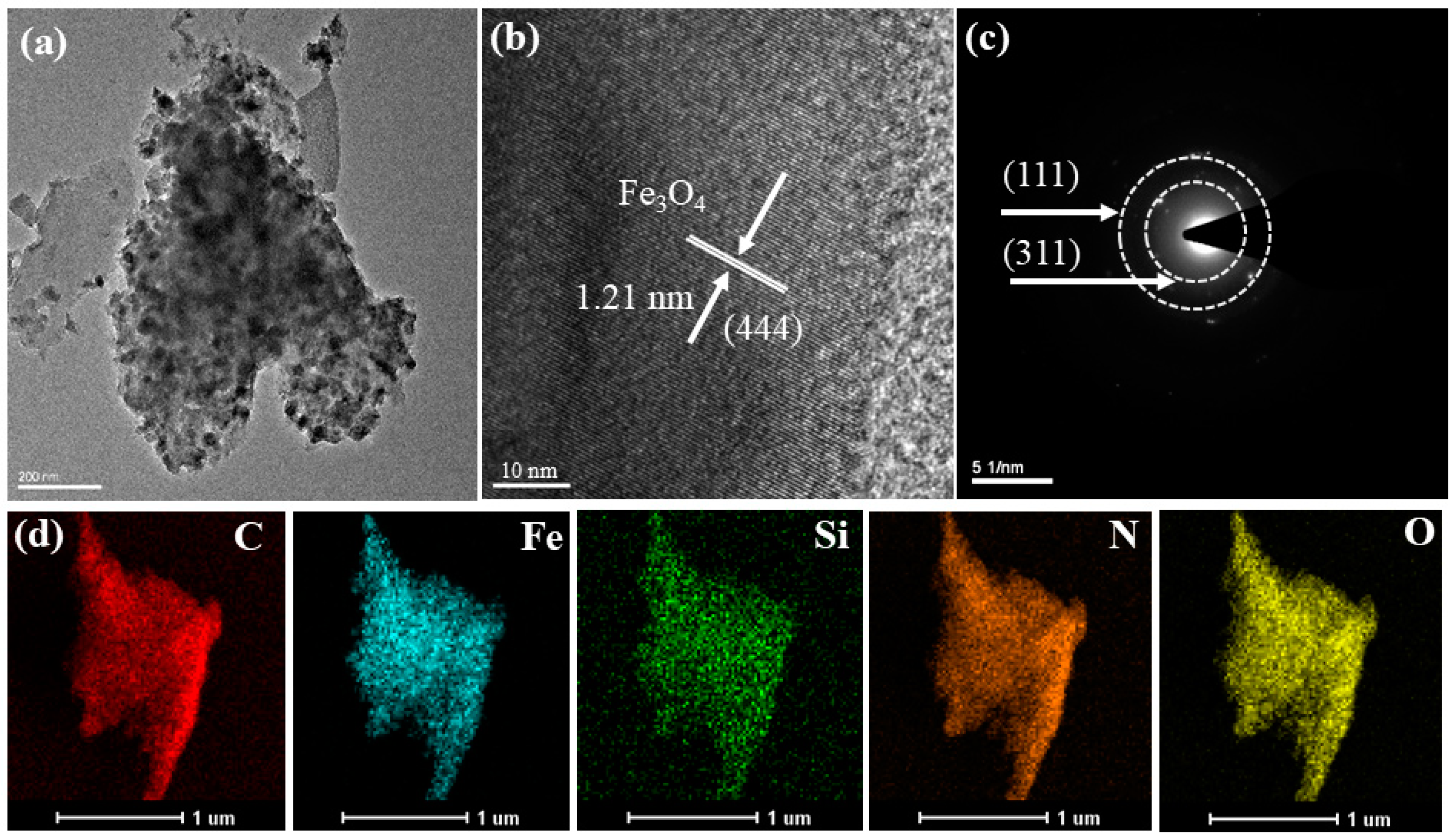
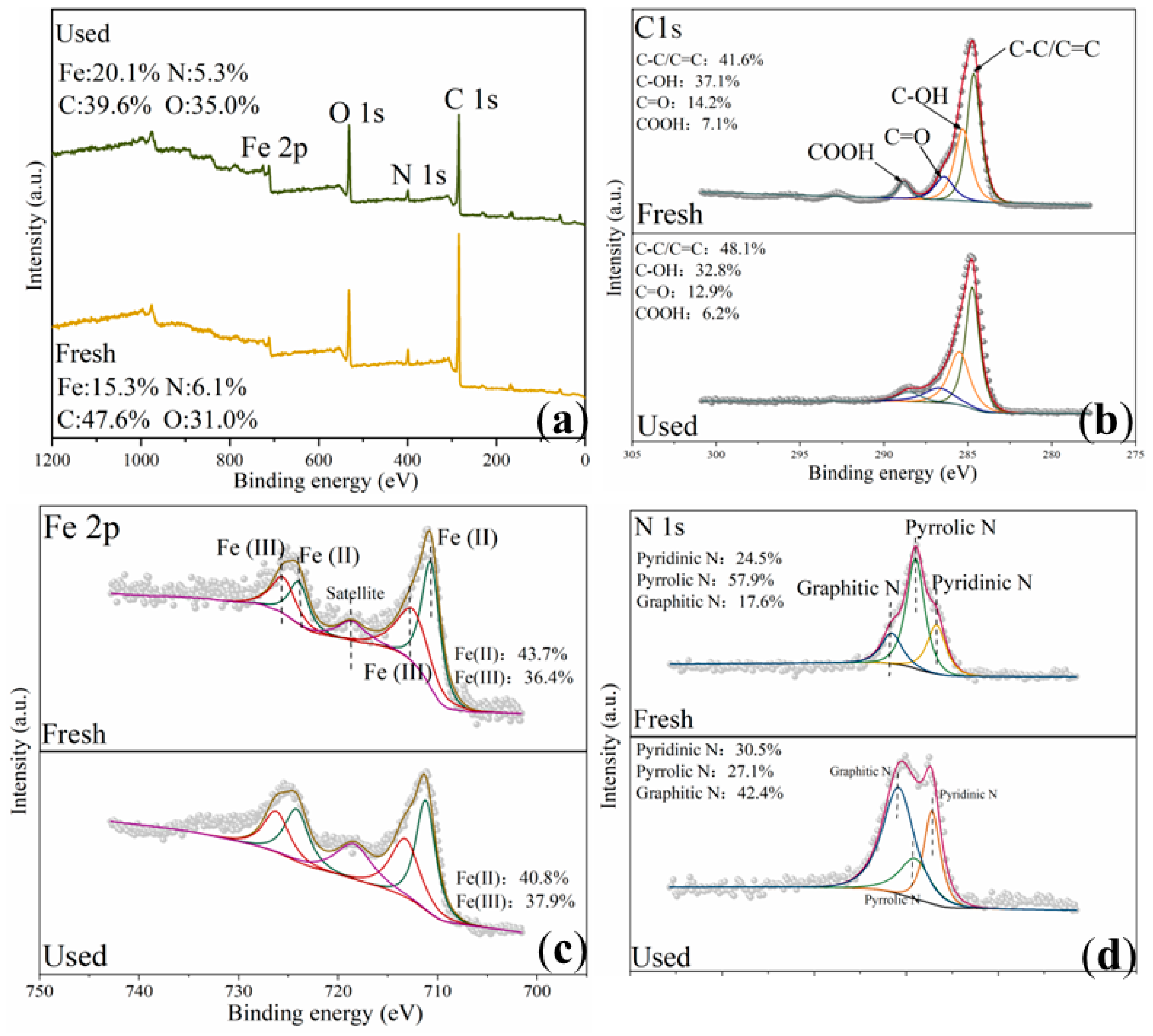
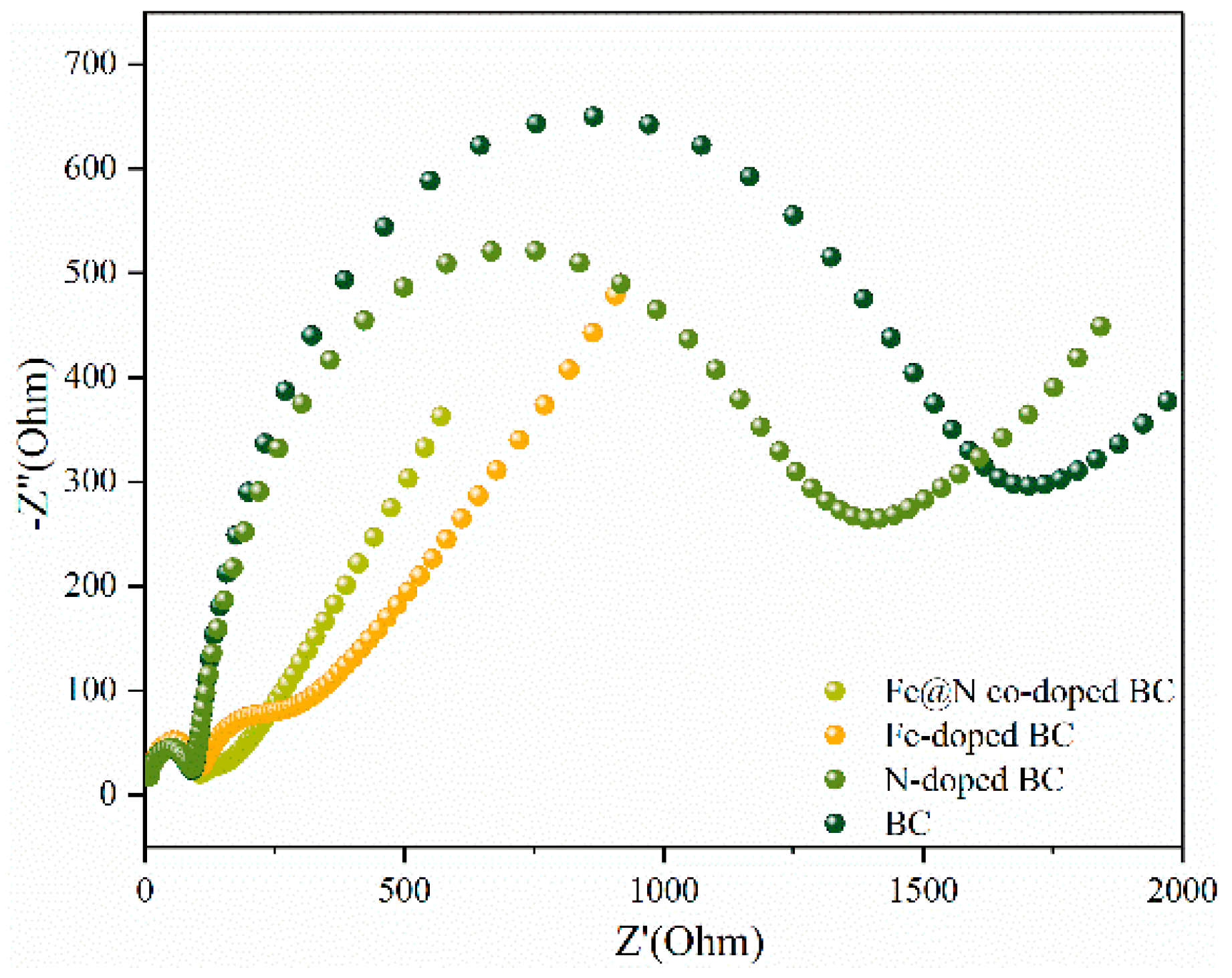
2.1. Characterization
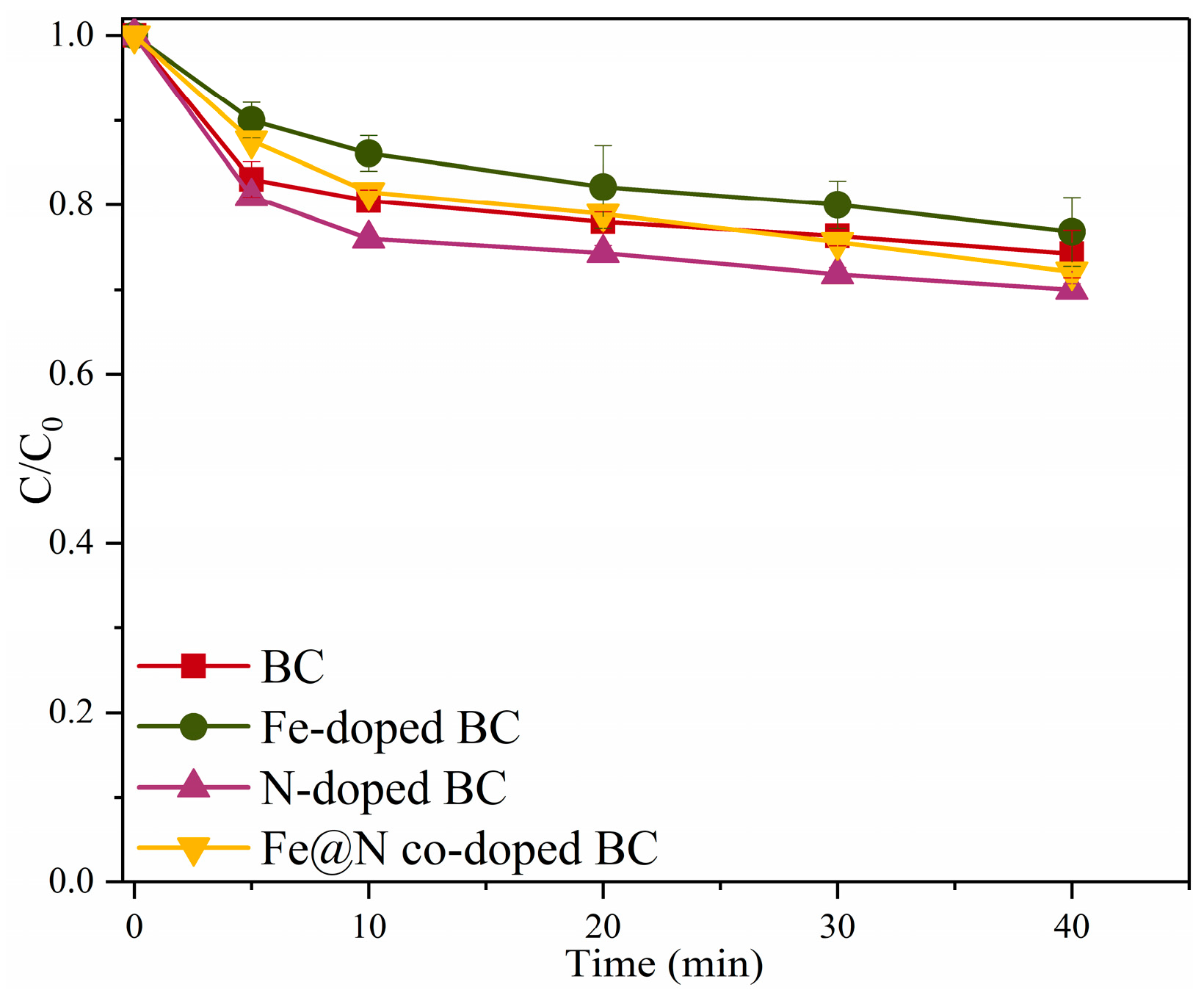
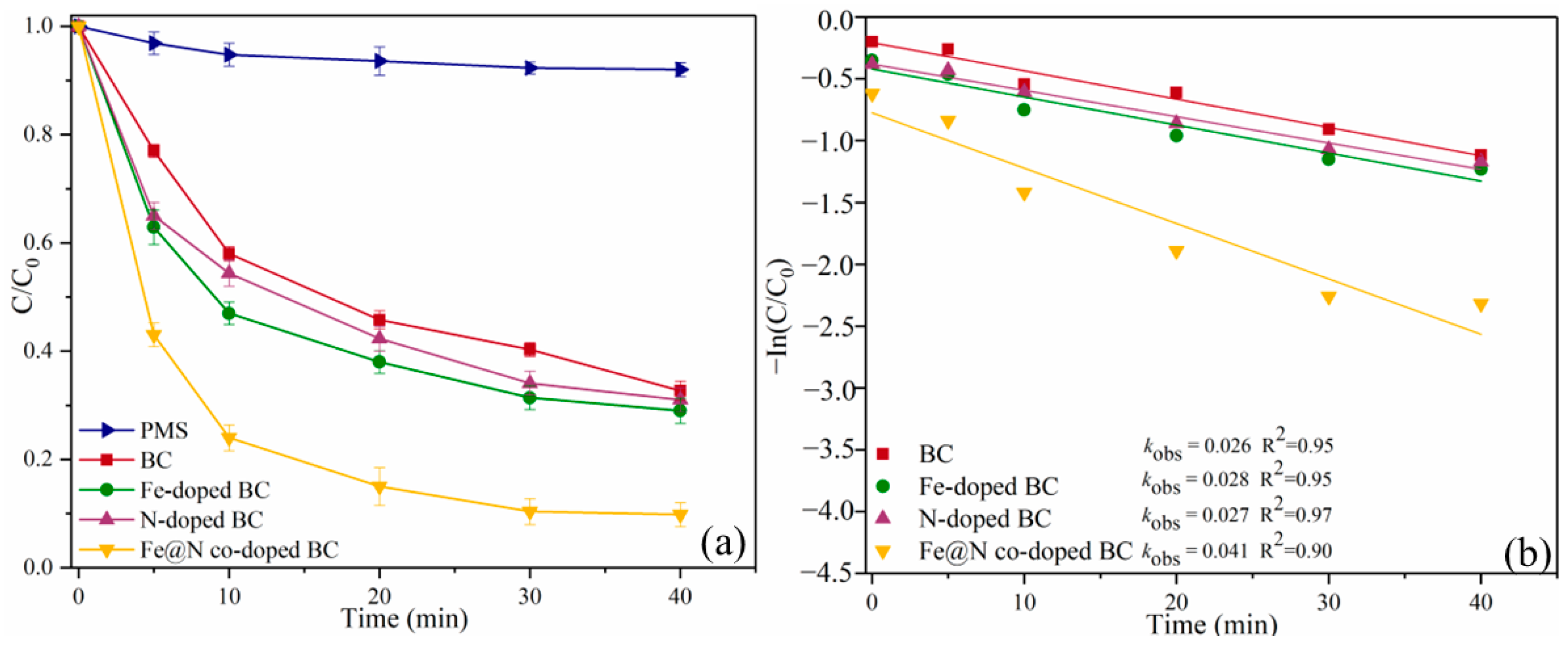
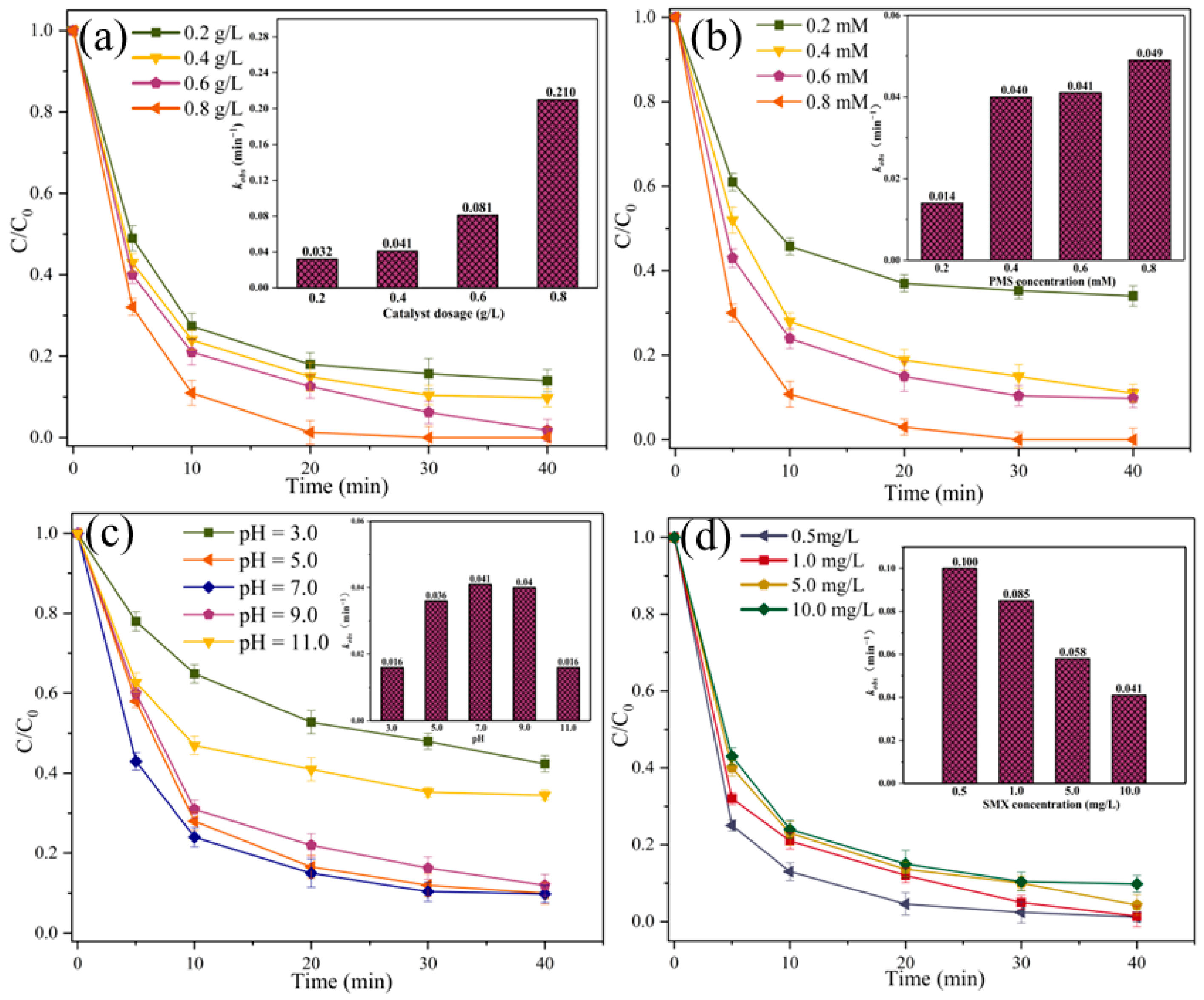
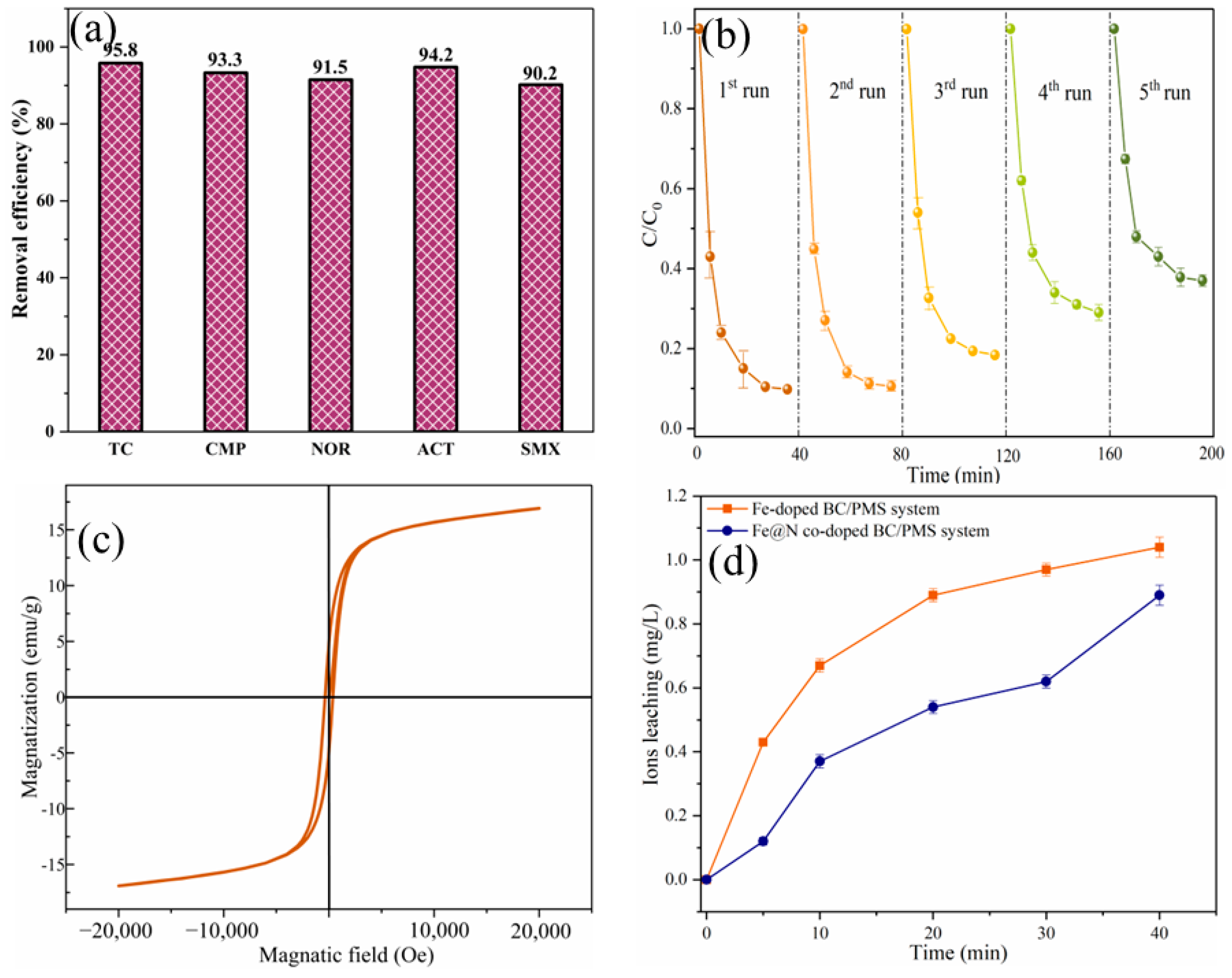
2.2. Catalytic Oxidation of SMX
2.3. Mechanism Discussion
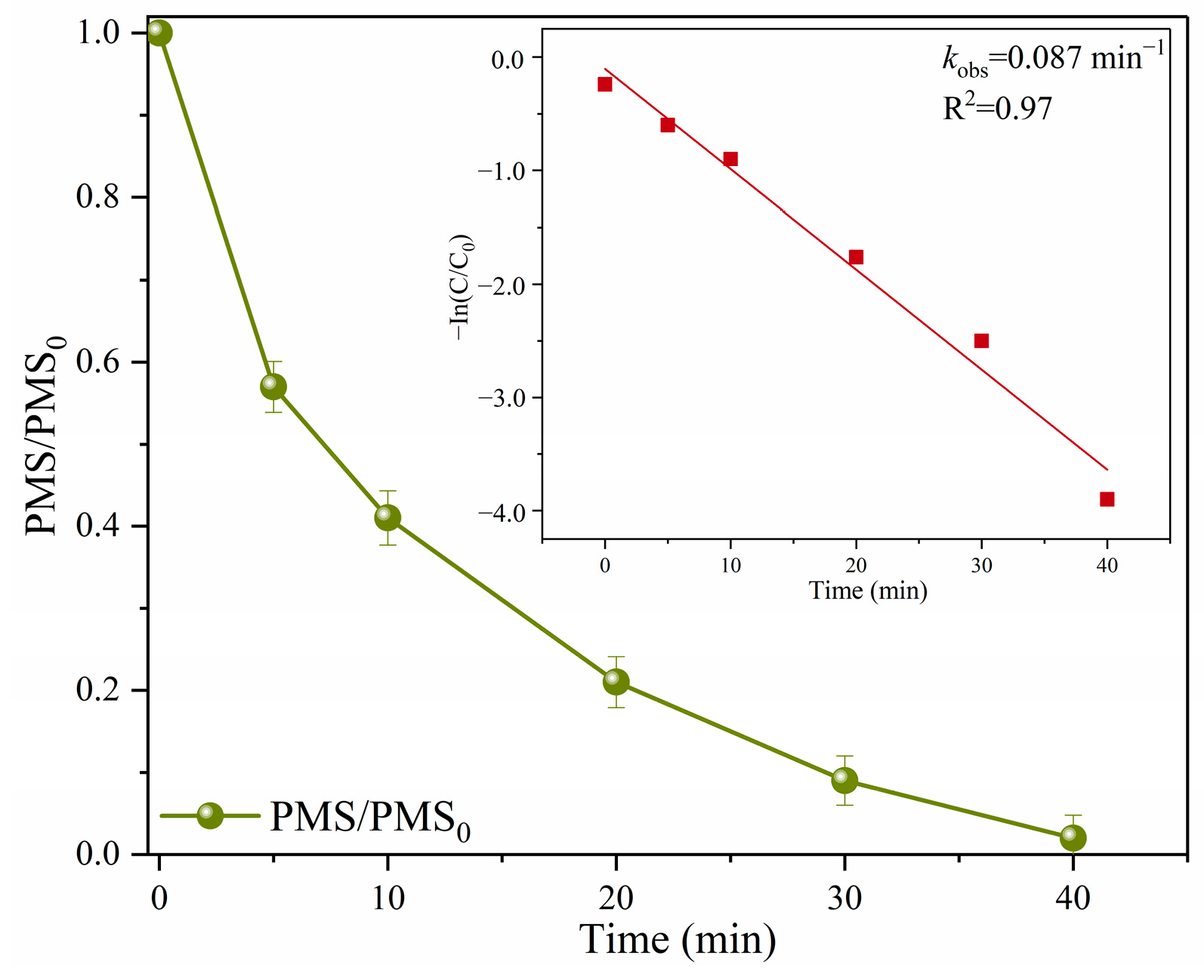
2.3.1. Identification of ROS
2.3.2. Reaction Mechanism
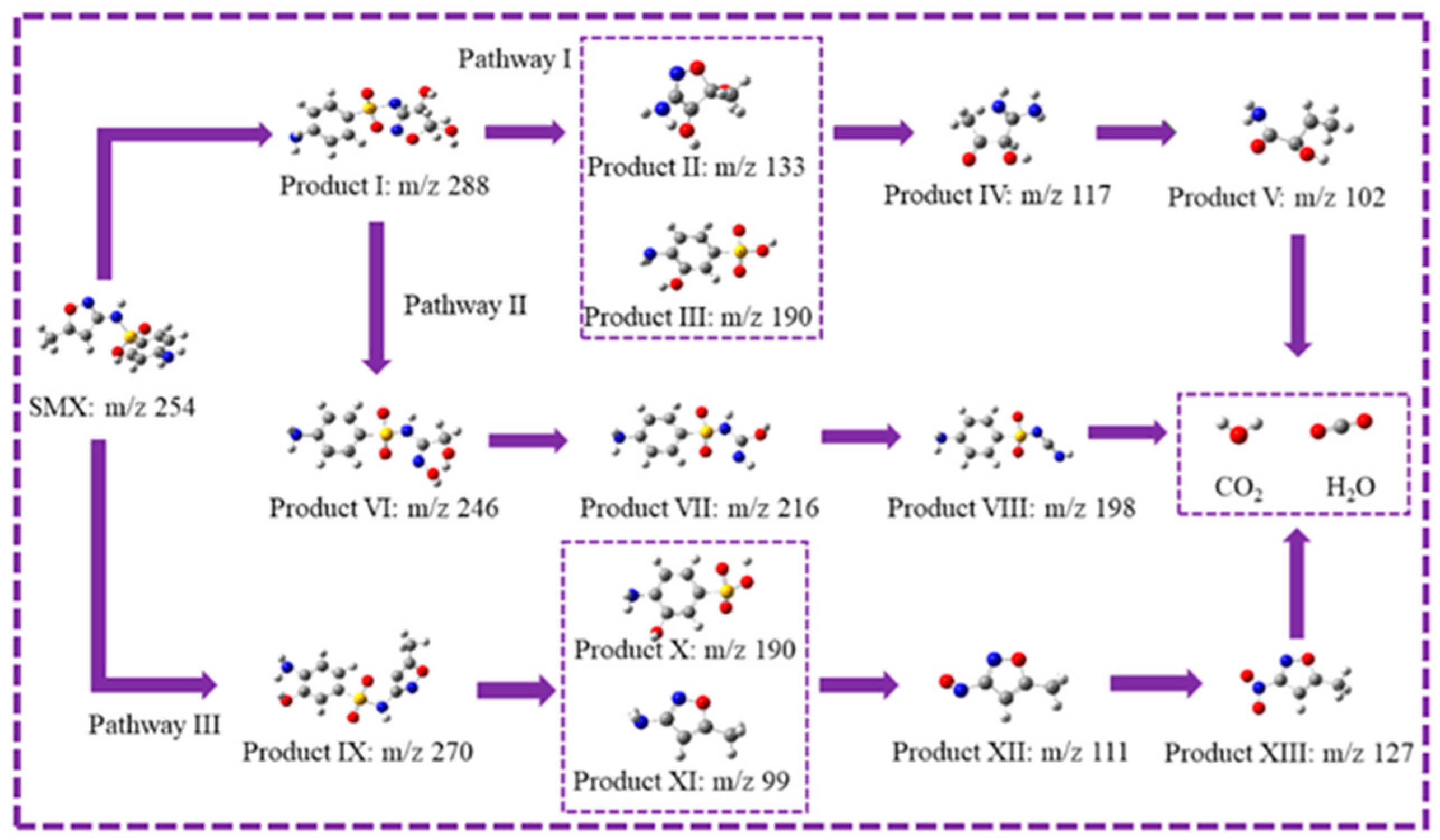
2.4. Degradation Pathways of SMX
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Catalysts
3.2. Reaction Procedures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Yin, R.; Zheng, H.; Feng, X.; Che, D.; Ren, N. Hydroxyl radical dominated degradation of aquatic sulfamethoxazole by Fe(0)/bisulfite/O2: Kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways. Water Res. 2018, 138, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, B.; Chen, X.; Song, L. Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole through peroxymonosulfate activated with expanded graphite loaded CoFe2O4 particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ding, H.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, C.; Deng, H. Thiourea-assisted one-step fabrication of a novel nitrogen and sulfur co-doped biochar from nanocellulose as metal-free catalyst for efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Fu, B.; Sun, Y.; Jin, P.; Bai, X.; Jin, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Nie, S. Degradation of organic pollutants by Fe/N co-doped biochar via peroxymonosulfate activation: Synthesis, performance, mechanism and its potential for practical application. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, B.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by biochar-based catalysts and applications in the degradation of organic contaminants: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cui, K.; Li, C.X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by biochar-based nanohybrids for the degradation of pharmaceutical and personal care products in aquatic environments. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Si, H.; Cao, C.; Ni, S.-Q. Sulfate radicals based heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate system catalyzed by CuO-Fe3O4-Biochar nanocomposite for bisphenol A degradation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, R.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.; Sillanpää, M. A review on persulfates activation by functional biochar for organic contaminants removal: Synthesis, characterizations, radical determination, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Lu, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; et al. Metal-free carbon materials for persulfate-based advanced oxidation process: Microstructure, property and tailoring. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 111, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, M.; Cao, Q.; Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Meng, F. The superoxide radicals’ production via persulfate activated with CuFe2O4@Biochar composites to promote the redox pairs cycling for efficient degradation of o-nitrochlorobenzene in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, M.; Cui, K.; Cui, M.; Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X. Enhanced norfloxacin degradation by iron and nitrogen co-doped biochar: Revealing the radical and nonradical co-dominant mechanism of persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived biochar for the degradation of triclosan in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cao, X.; Masek, O.; Zimmerman, A. Heterogeneity of biochar properties as a function of feedstock sources and production temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 256–257, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Bin, Q.; Shen, Y.; Huang, J.; He, D.; Chen, W. In-situ formed N-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes encapsulated with Fe nanoparticles supported by biochar as highly efficient catalyst for activation of persulfate (PS) toward degradation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, W.; Hou, Z. Synthesis of graphene encapsulated Fe3C in carbon nanotubes from biomass and its catalysis application. Carbon. 2016, 99, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O. Effects of thermal modification of a biochar on persulfate activation and mechanisms of catalytic degradation of a pharmaceutical. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, H. Persulfate activation with sawdust biochar in aqueous solution by enhanced electron donor-transfer effect. Sci. Total Env. 2019, 690, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Removal of sulfamethoxazole from water via activation of persulfate by Fe3C@NCNTs including mechanism of radical and nonradical process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, M.; Su, X.; Sun, J. High-efficiency degradation of organic pollutants with Fe, N co-doped biochar catalysts via persulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Luo, Z.; Du, S.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic MgFe(2)O(4)/biochar derived from pomelo peel as a persulfate activator for levofloxacin degradation: Effects and mechanistic consideration. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, X.; Xie, M.; Kong, L.; Natarajan, V.; Ma, L.; Zhan, J. The magnetic biochar derived from banana peels as a persulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, F.; Liang, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Beiyuan, J.; et al. Magnetic bimetallic Fe, Ce-embedded N-enriched porous biochar for peroxymonosulfate activation in metronidazole degradation: Applications, mechanism insight and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, R.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, M.; Cao, X.; Zeng, G. Singlet oxygen-dominated activation of peroxymonosulfate by passion fruit shell derived biochar for catalytic degradation of tetracycline through a non-radical oxidation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, G.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Panda manure biochar-based green catalyst to remove organic pollutants by activating peroxymonosulfate: Important role of non-free radical pathways. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Peng, F. Highly efficient and acid-corrosion resistant nitrogen doped magnetic carbon nanotubes for the hexavalent chromium removal with subsequent reutilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, T.; Su, R.; Luo, J. Activated peroxymonosulfate with ferric chloride-modified biochar to degrade bisphenol A: Characteristics, influencing factors, reaction mechanism and reuse performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Yan, J.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Chai, B.; Wang, C.; Song, G. Built-in electric field mediated peroxymonosulfate activation over biochar supported-Co3O4 catalyst for tetracycline hydrochloride degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Nengzi, L.-C.; Gou, J.; Li, B.; Cheng, X. Activation of persulfate by a novel magnetic CuFe2O4/Bi2O3 composite for lomefloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Nasir Khan, M.A.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Singlet oxygen-dominated non-radical oxidation process for efficient degradation of bisphenol A under high salinity condition. Water Res. 2019, 148, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, G.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Garces, H.F.; Yan, K. Fabrication of ultrathin lily-like NiCo2O4 nanosheets via mooring NiCo bimetallic oxide on waste biomass-derived carbon for highly efficient removal of phenolic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 136066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fang, S. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co, S co-doped bamboo biochar for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Insights into the role of S. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cui, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, M.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Removal of chlorophenols in the aquatic environment by activation of peroxymonosulfate with nMnOx@Biochar hybrid composites: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Nie, G.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. The Intrinsic Nature of Persulfate Activation and N-Doping in Carbocatalysis. Env. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6438–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, C.; Mao, Q.; Wang, C.; Yan, J. Nonradicals induced degradation of organic pollutants by peroxydisulfate (PDS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Recent advances and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzaz, A.A.; Matei Ghimbeu, C.; Jellai, S.; El-Bassi, L.; Jeguirim, M. Olive Mill by-Products Thermochemical Conversion via Hydrothermal Carbonization and Slow Pyrolysis: Detailed Comparison between the Generated Hydrochars and Biochars Characteristics. Processes 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Ao, Z.; Pu, S.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. Core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@Zn/Co-ZIFs to activate peroxymonosulfate for highly efficient degradation of carbamazepine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 277, 119136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, M.; Kang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Li, S. Peroxymonosulfate activation by cobalt particles embedded into biochar for levofloxacin degradation: Efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ge, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, C.; Akram, M.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional porous graphene-like biochar derived from Enteromorpha as a persulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of graphitic N and radicals transformation. J Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





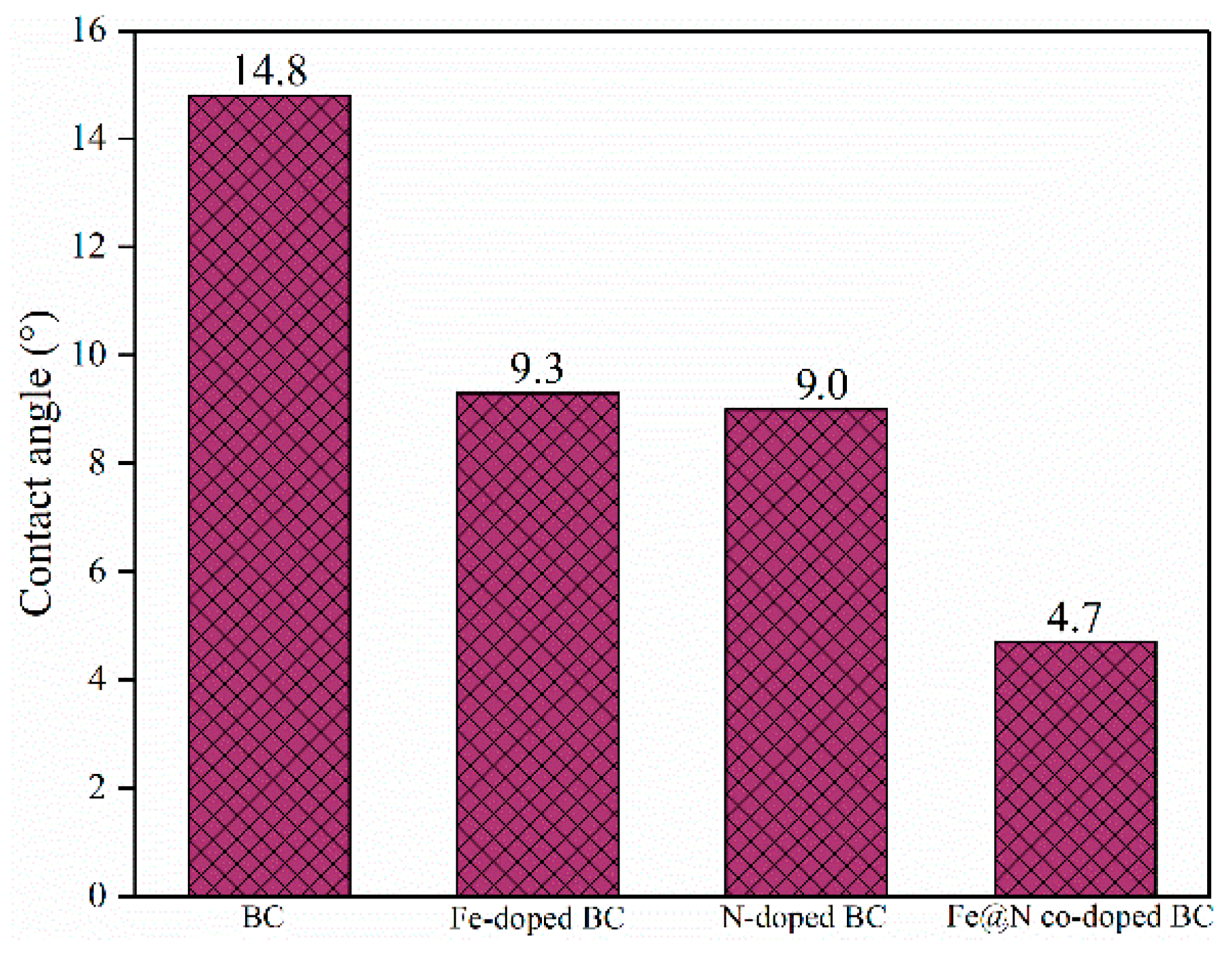

| Samples | SBET (m2/g) a | Pore Volume (cm3/g) a | Average Pore Diameter (nm) a | ID/IG b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 194.86 | 0.110 | 2.46 | 1.07 |
| Fe-doped BC | 216.38 | 0.220 | 3.64 | 0.81 |
| N-doped BC | 287.67 | 0.300 | 3.56 | 1.02 |
| Fe@N co-doped BC | 269.21 | 0.240 | 3.48 | 2.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Wang, D.; Wei, Q. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910528
Liu T, Li C, Chen X, Chen Y, Cui K, Wang D, Wei Q. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910528
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tong, Chenxuan Li, Xing Chen, Yihan Chen, Kangping Cui, Dejin Wang, and Qiang Wei. 2024. "Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910528
APA StyleLiu, T., Li, C., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Cui, K., Wang, D., & Wei, Q. (2024). Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910528






