Unveiling the Role of Two Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Insecticide-Resistant House Flies, Musca domestica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rhodopsin-like GPCR Gene Up-Regulation in Permethrin Resistant House Fly, M. domestica
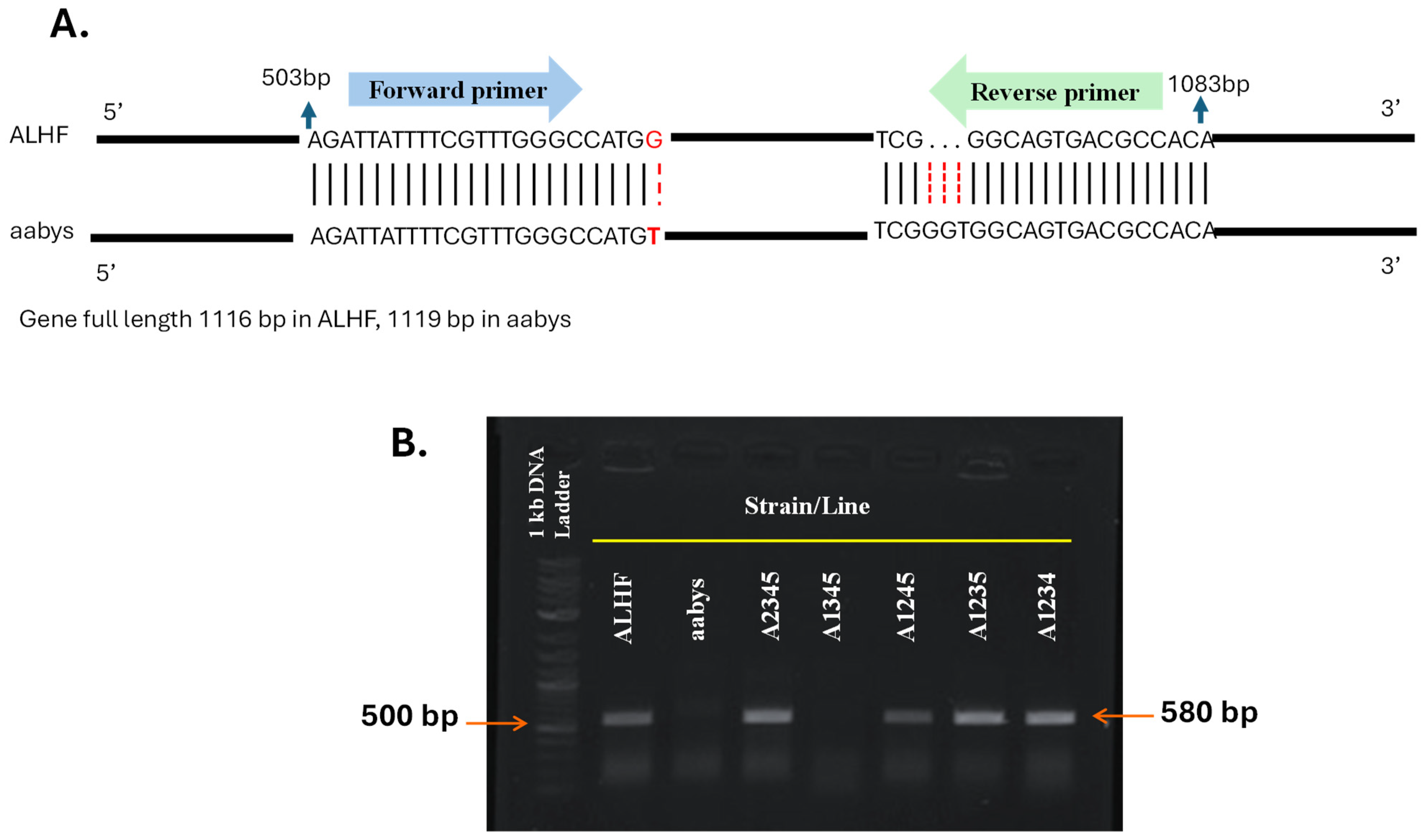
2.2. Localization and Mapping of Overexpressed GPCR Genes to the Autosomes of House Flies
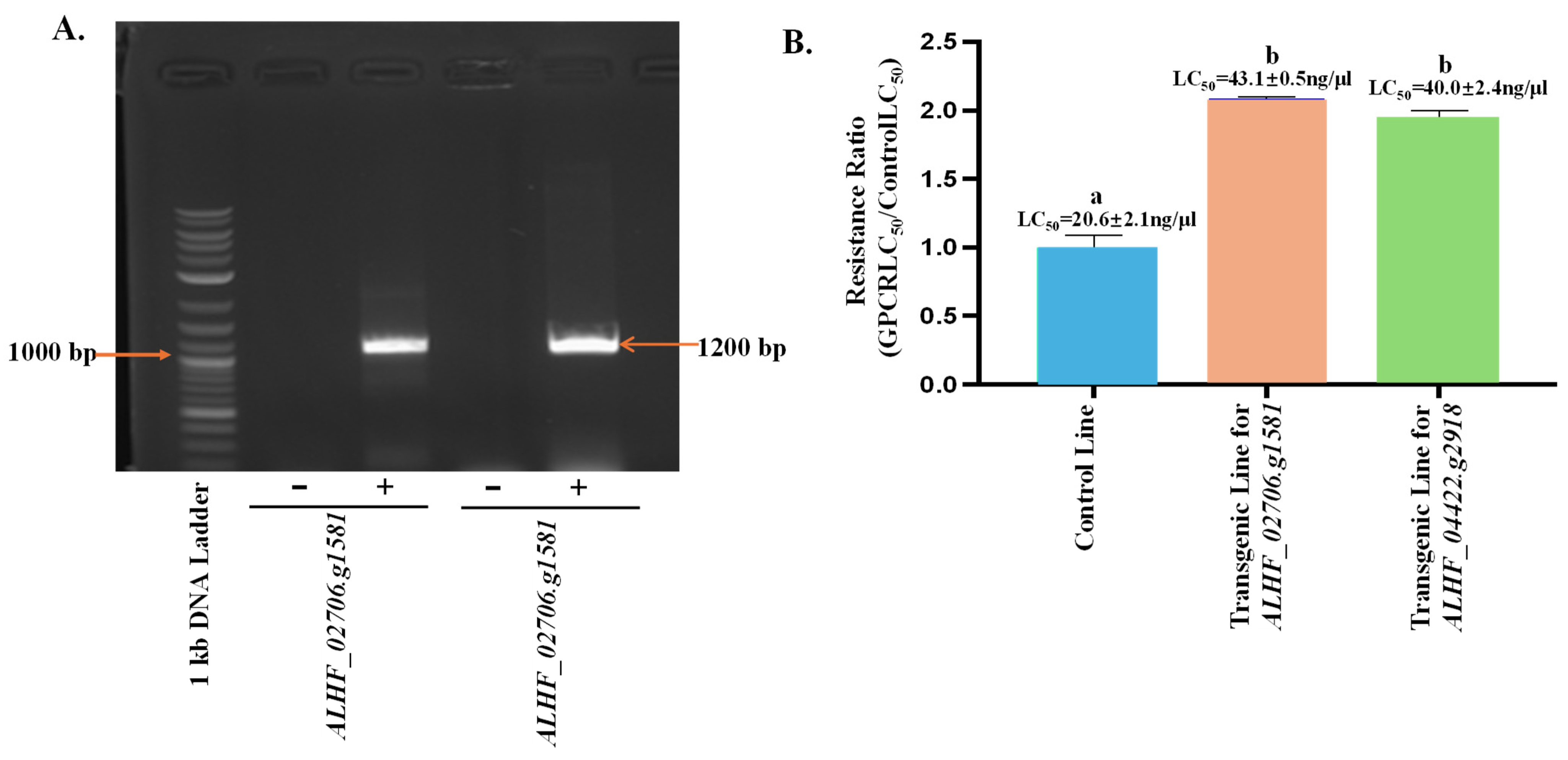
2.3. Up-Regulated House Fly Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Transgenic D. melanogaster—An Approach for Defining the House Fly Rhodopsin-like GPCR Gene Function
2.4. Relative Expression Levels of Drosophila P450 Genes in House Fly Rhodopsin-like GPCR Transgenic Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. House Flies
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Preparation
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.4. Autosome Assignment and Mapping of Overexpressed GPCR Genes in M. domestica
4.5. Amplification of Full Length of GPCR Genes
4.6. Construction of Transgenic Drosophila Flies
4.7. Toxicity of Permethrin on the Transgenic D. melanogaster
4.8. Expression of Drosophila Insecticide-Related P450 Genes in the House Fly GPCR Transgenic Drosophila Lines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geden, C.J.; Nayduch, D.; Scott, J.G.; Burgess, E.R.; Gerry, A.C.; Kaufman, P.E.; Thomson, J.; Pickens, V.; Machtinger, E.T. House fly (Diptera: Muscidae): Biology, pest status, current management prospects, and research needs. J. Integr. Pest. Manag. 2021, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, G.; Freeman, J.; Sipka, A.; Santisteban, C.; Wieland, M.; Gallardo, V.A.; Monistero, V.; Scott, J.G.; Moroni, P. Pathogens associated with houseflies from different areas within a New York State dairy. JDS Commun. 2022, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayduch, D.; Burrus, R.G. Flourishing in filth: House fly–microbe interactions across life history. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.C.; Ross, D.H.; Scott, J.G. Insecticide resistance monitoring of house fly populations from the United States. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 158, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Yue, X. Genetics of pyrethroid resistance in a strain (ALHF) of house flies (diptera: Muscidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2001, 70, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yue, X. Insecticide resistance and cross-resistance in the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.G. Cytochromes P450 and insecticide resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 757–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Reid, W.R.; Zhang, L.; Scott, J.G.; Gao, X.; Kristensen, M.; Liu, N. A whole transcriptomal linkage analysis of gene co-regulation in insecticide resistant house flies, Musca domestica. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P.; Freeman, J.C.; Asgari, D.; Llaca, V.; Fengler, K.A.; Mann, D.; Rastogi, A.; Loso, M.; Geng, C.; Scott, J.G. New insights into immune genes and other expanded gene families of the house fly, Musca domestica, from an improved whole genome sequence. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 114, e22049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Warren, W.C.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Bopp, D.; Clark, A.G.; Giers, S.D.; Hediger, M.; Jones, A.K.; Kasai, S.; Leichter, C.A.; et al. Genome of the house fly, Musca domestica L., a global vector of diseases with adaptations to a septic environment. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, X.; Reid, W.R.; Tang, F.; Liu, N. Multiple-P450 gene co-up-regulation in the development of permethrin resistance in the house fly, Musca domestica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect cytochrome P450. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: Impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Br, M.; Mk, S.; Mn, O.; Oc, J.; Ris, A.; Rd, F. Understanding the mechanisms involved in the regulation of cytochrome p450 gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Entomol. Ornithol. Herpetol. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carino, F.A.; Koener, J.F.; Plapp, F.W., Jr.; Feyereisen, R. Constitutive overexpression of the cytochrome P450 gene CYP6A1 in a house fly strain with metabolic resistance to insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 24, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsi, M.; Palli, S.R. Transcription factors, CncC and Maf, regulate expression of CYP6BQ genes responsible for deltamethrin resistance in Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 65, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, T. Cytochrome P450s—Their expression, regulation, and role in insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2015, 120, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Scott, J.G. Phenobarbital induction of CYP6D1 is due to a trans acting factor on autosome 2 in house flies, Musca domestica. Insect Mol. Biol. 1997, 6, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Scott, J.G. Genetics of resistance to pyrethroid insecticides in the house fly, Musca domestica. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1995, 52, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, C.M.; Brown, R.P.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Schuler, M.A. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of two allelochemical-inducible cytochrome P450 genes differentially regulate transcription. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Denholm, I.; Han, Z. Multiple cis-acting elements involved in up-regulation of a cytochrome P450 gene conferring resistance to deltamethrin in smal brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 78, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Tyagi, R.; Kasai, S.; Scott, J.G. CYP-mediated permethrin resistance in Aedes aegypti and evidence for trans-regulation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, J.; Wu, S.; Ling, L.; Danao, J.; Li, Y.; Yeh, W.C.; Tian, H.; Baribault, H. G-protein-coupled receptor GPR21 knockout mice display improved glucose tolerance and increased insulin response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, R.P.; Newton, C.L. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovatkina, V.; Alegre, K.O.; Dey, R.; Huang, X.Y. Regulation, signaling, and physiological functions of G-proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3850–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zhu, F.; Shah, K.; Palli, S.R. Large-scale RNAi screen of G protein-coupled receptors involved in larval growth, molting and metamorphosis in the red flour beetle. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhzaz, S.; Cabrero, P.; Robben, J.H.; Radford, J.C.; Hudson, B.D.; Milligan, G.; Dow, J.A.; Davies, S.A. Mechanism and function of Drosophila capa GPCR: Adesiccation stress-responsive receptor with functionalhomology to human neuromedinU receptor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersch, C.N.; Pietrantonio, P.V. Mosquito Aedes aegypti (L.) leucokinin receptor is critical for in vivo fluid excretion post blood feeding. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3507–3512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Cao, C.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Xi, Z.; Bian, G.; Liu, N. A G-protein-coupled receptor regulation pathway in cytochrome P450-mediated permethrin-resistance in mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N. Role of G-protein-coupled receptor-related genes in insecticide resistance of the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in insects—A potential target for new insecticide development. Molecules 2021, 26, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Feng, X. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs): Signaling pathways, characterization, and functions in insect physiology and toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, N. Role of the G-protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in insecticide resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, N. The function of G-protein-coupled receptor-regulatory cascade in southern house mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, N. Regulation of P450-mediated permethrin resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus by the GPCR/Gαs/AC/cAMP/PKA signaling cascade. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.P.; Scott, J.G. Using genomic data to study insecticide resistance in the house fly, Musca domestica. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2018, 151, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, S.W. Muller “Elements” in Drosophila: How the search for the genetic basis for speciation led to the birth of comparative genomics. Genetics 2018, 210, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, N.C.; Elgin, S.C.R. The Drosophila dot chromosome: Where genes flourish amidst repeats. Genetics 2018, 210, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, S.W.; Bhutkar, A.; McAllister, B.F.; Matsuda, M.; Matzkin, L.M.; O’Grady, P.M.; Rohde, C.; Valente, V.L.; Aguadé, M.; Anderson, W.W.; et al. Polytene chromosomal maps of 11 Drosophila species: The order of genomic scaffolds inferred from genetic and physical maps. Genetics 2008, 179, 1601–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C. BLAST plus: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Liu, N. Differential expression of CYP6A5 and CYP6A5v2 in pyrethroid-resistant house flies, Musca domestica. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 67, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daborn, P.J.; Lumb, C.; Boey, A.; Wong, W.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Batterham, P. Evaluating the insecticide resistance potential of eight Drosophila melanogaster cytochrome P450 genes by transgenic over-expression. Insect Biochem. Mole. Biol. 2007, 37, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palli, S.R. CncC/Maf-mediated xenobiotic response pathway in insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 104, e21674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Norris, E.J.; Jiang, S.; Bernier, U.R.; Linthicum, K.J.; Bloomquist, J.R. Reduced effectiveness of repellents in a pyrethroid-resistant strain of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) and its correlation with olfactory sensitivity. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, S.; Ren, M.; Wei, Q.; Tian, X.; Elzaki, M.E.A.; Bass, C.; Su, J.; Palli, S.R. Changes in both trans- and cis-regulatory elements mediate insecticide resistance in a lepidopteron pest, Spodoptera exigua. PLOS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Sun, L.; Du, H.; Moural, T.W.; Bai, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, F. Physiological functions of a methuselah-like G protein coupled receptor in Lymantria dispar Linnaeus. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zou, P.; Yu, X.Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Shi, L.N.; Hong, S.C.; Zhou, D.; Chang, X.L.; Wang, W.J.; et al. Functional characterization of an arrestin gene on insecticide resistance of Culex pipiens pallens. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; You, C.; Zeng, X.; Gao, X. The role of G protein-coupled receptor-related genes in cytochrome P450-mediated resistance of the house fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae), to imidacloprid. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Bogwitz, M.R.; McCart, C.; Andrianopoulos, A.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Batterham, P.; Daborn, P.J. Cis-regulatory elements in the Accord retrotransposon result in tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila melanogaster insecticide resistance gene Cyp6g1. Genetics 2007, 175, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Dombrowski, S.M.; Waters, L.C.; Ganguly, R. Three second chromosome-linked clustered Cyp6 genes show differential constitutive and barbital-induced expression in DDT-resistant and susceptible strains of Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 1996, 180, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Cao, C.; He, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, N. Autosomal interactions and mechanisms of pyrethroid resistance in house flies, Musca domestica. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Scott, J.G. Role of the transcriptional repressor mdGfi-1 in CYP6D1v1-mediated insecticide resistance in the house fly, Musca domestica. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L. Differential expression of genes in pyrethroid resistant and susceptible mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus (S.). Gene 2007, 394, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.L.; Gonzales, M.I.; Topalian, S.L. Selection of appropriate control genes to assess expression of tumor antigens using real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques 2004, 36, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, M.; Liu, N. Carboxylesterase genes in pyrethroid resistant house flies, Musca domestica. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 92, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strode, C.; Wondji, C.S.; David, J.P.; Hawkes, N.J.; Lumjuan, N.; Nelson, D.R.; Drane, D.R.; Karunaratne, S.H.; Hemingway, J.; Black, W.C.; et al. Genomic analysis of detoxification genes in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.G.; Whitten, M.J.; Konovalov, C.; Arnold, J.T.A.; Maffi, G. Autosomal genetic maps of the Australian Sheep Blowfly, Lucilia cuprina dorsalis R.-D. (Diptera: Calliphoridae), and possible correlations with the linkage maps of Musca domestica L. and Drosophila melanogaster (Mg.). Genet. Res. 1981, 37, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicoso, B.; Bachtrog, D. Numerous transitions of sex chromosomes in Diptera. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Maeda, R.K.; Hediger, M.; Karch, F.; Basler, K. An optimized transgenesis system for Drosophila using germ-line-specific φC31 integrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3312–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.H.; Perrimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993, 118, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, J.R.; Lee, A.M.; Wu, C.T. Site-specific transformation of Drosophila via ϕC31 integrase-mediated cassette exchange. Genetics 2006, 173, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, M. Prsentation d’un programme basic d’analyse log-probit pour micro-ordinateur. ORSTOM Ser. Entomol. Med. Parasitol. 1985, 23, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner, M. Drosophila: A Laboratory Handbook; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 52, 1448p. [Google Scholar]


| Gene Name | GeneBank ID | qRT Primers (5′-3′); F (Forward), R (Reverse) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| qRT-PCR | ALHF_02706.g1581 | LOC101898316 | qRT 1581F: CAAAATCTCTGCGTACACCTGC qRT 1581R: AACCGGCATAGACATCACACAT |
| ALHF_04422.g2918 | LOC101888328 | qRT 2918F: GTCCTCAATTTGGCCTTTTCCG qRT 2918R: CGATCCAGGGCTATCATACACA | |
| CYP6A2 | qRT 6a2F: TGGACGGAAAGAAGTGGAAGGAC qRT 6a2R: AGTTCATGTTCCCGACGGTGATCA | ||
| CYP12D1 | qRT 12d1F: GCTCGGCTCAAATGTGCTGATGAA qRT 12d1R: TGACCTGCATCTTCTTTCCGGTCT | ||
| CYP6A8 | qRT 6a8F: ACGAGTGCACCAAGGATCTGAAG qRT 6a8R: ATTGACCAGCCTCGATGACGAAGT | ||
| CYP6G1 | qRT 6g1F: CGGCTGAAGGACGAGGCTG qRT 6g1R: GCTATGCTGTCCGTGGAGAACTGA | ||
| β-actin | actinF: ATGAGGCTCAGAGCAAACGTGG actinR: AGTCATCTTCTCGCGATTGGCCT | ||
| Full Length Clone | ALHF_02706.g1581 | LOC101898316 | Full-1581F: CCGGAATTCCAAAATGGAAAGATTCGCTGAACA Full-1581R: CTAGTCTAGATGCCTTTGATTCGGACTCAGT |
| ALHF_04422.g2918 | LOC101888328 | Full-2918F: CCGGAATTCCAAAATGAGAGATGACATGGCG Full-2918R: CTAGTCTAGAAGCCTGGGACTCTGCCTGT | |
| Allele-Specific PCR | ALHF_02706.g1581 | LOC101898316 | Allele-F: AGATTATTTTCGTTTGGGCCATGG Allele-R: TGTGGCGTCACTGCCCGA |
| GPCR Gene [8] | Gene_ID | Accession Number | Drosophila Chromosome (Mullers Element) | Drosophila Homologous Gene | House Fly Autosome [36] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALHF_02706.g1581 | LOC101898316 | XP_005182983.1 | 3R (E) | Dm Rh1 * | 2 |
| ALHF_04422.g2918 | LOC101888328 | XP_005191160.1 | 3R (E) | Dm Rh2 ** | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xin, J.; Brown, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Liu, N. Unveiling the Role of Two Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Insecticide-Resistant House Flies, Musca domestica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910618
Xin J, Brown D, Wang Y, Wang X, Li M, Li T, Liu N. Unveiling the Role of Two Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Insecticide-Resistant House Flies, Musca domestica. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910618
Chicago/Turabian StyleXin, Juanjuan, Dylan Brown, Yifan Wang, Xin Wang, Ming Li, Ting Li, and Nannan Liu. 2024. "Unveiling the Role of Two Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Insecticide-Resistant House Flies, Musca domestica" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910618
APA StyleXin, J., Brown, D., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Li, M., Li, T., & Liu, N. (2024). Unveiling the Role of Two Rhodopsin-like GPCR Genes in Insecticide-Resistant House Flies, Musca domestica. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910618







