Compound Heterozygous RYR1 Variants in a Patient with Severe Congenital Myopathy: Case Report and Comparison with Additional Cases of Recessive RYR1-Related Myopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
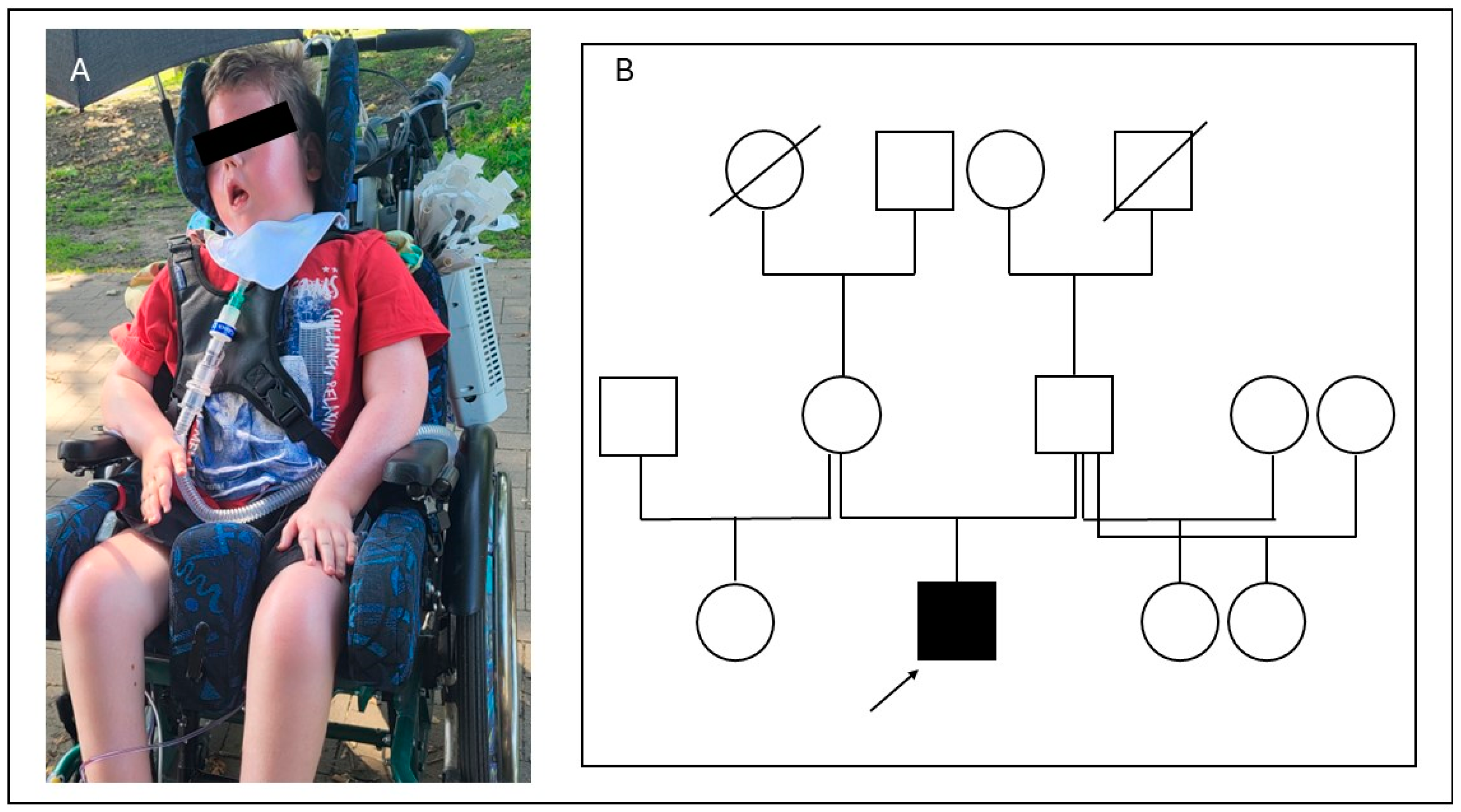
2.1. Case Report
2.2. Molecular Genetic Diagnostics
2.3. Phenotypic Presentation in Comparison to Other Compound Heterozygous Cases
| Patient | RYR1 Variants | Variation Type | ACMG Classification | Previous Report of Variant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c.14364+1G>A, p.(?) | Splice | Pathogenic | [11,12,13] |
| c.10441−48G>A, p.(?) | Splice | Likely pathogenic | [9] | |
| 2 + | c.6274+1G>A, p.(?) | Splice | Likely pathogenic | [9] |
| c.10441−48G>A, p.(?) | Splice | Likely pathogenic | [9] | |
| 3 | c.2505del, p.(Pro836Leufs*48) | Frameshift | Pathogenic | [14,15,16,17] |
| c.6197T>C, p.(Leu2066Pro) | Missense | Uncertain | - | |
| 4 | c.1951C>T, p.(Arg651*) | Nonsense | Pathogenic | - |
| c.11999_12001delATG, p.(Met4000del) | In-frame deletion | Uncertain | - | |
| 5 | c.1951C>T, p.(Arg651*) | Nonsense | Pathogenic | - |
| c.10883_10884delinsAA, p.(Arg3628Gln) | Missense/small indel | Uncertain | - | |
| 6 | c.1250T>C, p.(Leu417Pro) | Missense | Likely pathogenic | [4,18,19] |
| c.13677C>G, p.(Asn4559Lys) | Missense | Uncertain | - | |
| 7 | c.5470C>T, p.Gln1824* | Nonsense | Pathogenic | - |
| c.12138G>A, p.(Met4046Ile) | Missense | Uncertain | - |
| P1 | P2 * | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General information | ||||||||
| Current age (yrs) | 6 | Death in infancy | 28 | 14 | 9 | 14 | 42 | n.a. |
| Gender | m | m | f | m | m | m | f | n.a. |
| Age of onset (months) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% |
| Family history for myopathy | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Positive € | 14% |
| Neuromuscular symptoms | ||||||||
| Ventilation after birth required | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | 57% |
| Constant ventilation required | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | 29% |
| Feeding difficulties | + | + | + | - | + | - | - | 50% |
| Hypotonic facies | + | n.a. | + | - | + | - | - | 50% |
| Elevation of CK levels | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0% |
| Reduced endurance | n.a. | n.a. | - | + | + | - | + | 60% |
| Hypermobile joints | + | n.a. | + | - | - | + | - | 50% |
| Contractures | + | n.a. | + | - | - | + | + | 67% |
| Dysarthria | + | n.a. | + | - | + | - | - | 50% |
| Malignant hyperthermia | - | - | - | - | - | - | +(2 yrs) | 14% |
| Reduced nerve conduction vel. | - | + | - | - | n.a. | - | - | 17% |
| Muscular hypotonia | ||||||||
| Upper extremities affected | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | 86% |
| Lower extremities affected | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 100% |
| Lower vs. upper extremities | = | = | > | > | > | >> | = | n.a. |
| Motor milestones | ||||||||
| Age at free walking | - | n.a. | 18 months | 18 months | 18 months | (only few steps) | 21 months | n.a. |
| Loss of ambulation | n.a. | n.a. | 20 yrs | - | - | 8 yrs | - | 40% |
| MRI pattern § | ||||||||
| AM > AD | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | + | n.a. | + | n.a. | 100% |
| V > RF | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | + | n.a. | + | n.a. | 100% |
| S > G | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | - | n.a. | + | n.a. | 50% |
| SO > GM | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | + | n.a. | + | n.a. | 100% |
| PG > TA | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | - | n.a. | + | n.a. | 50% |
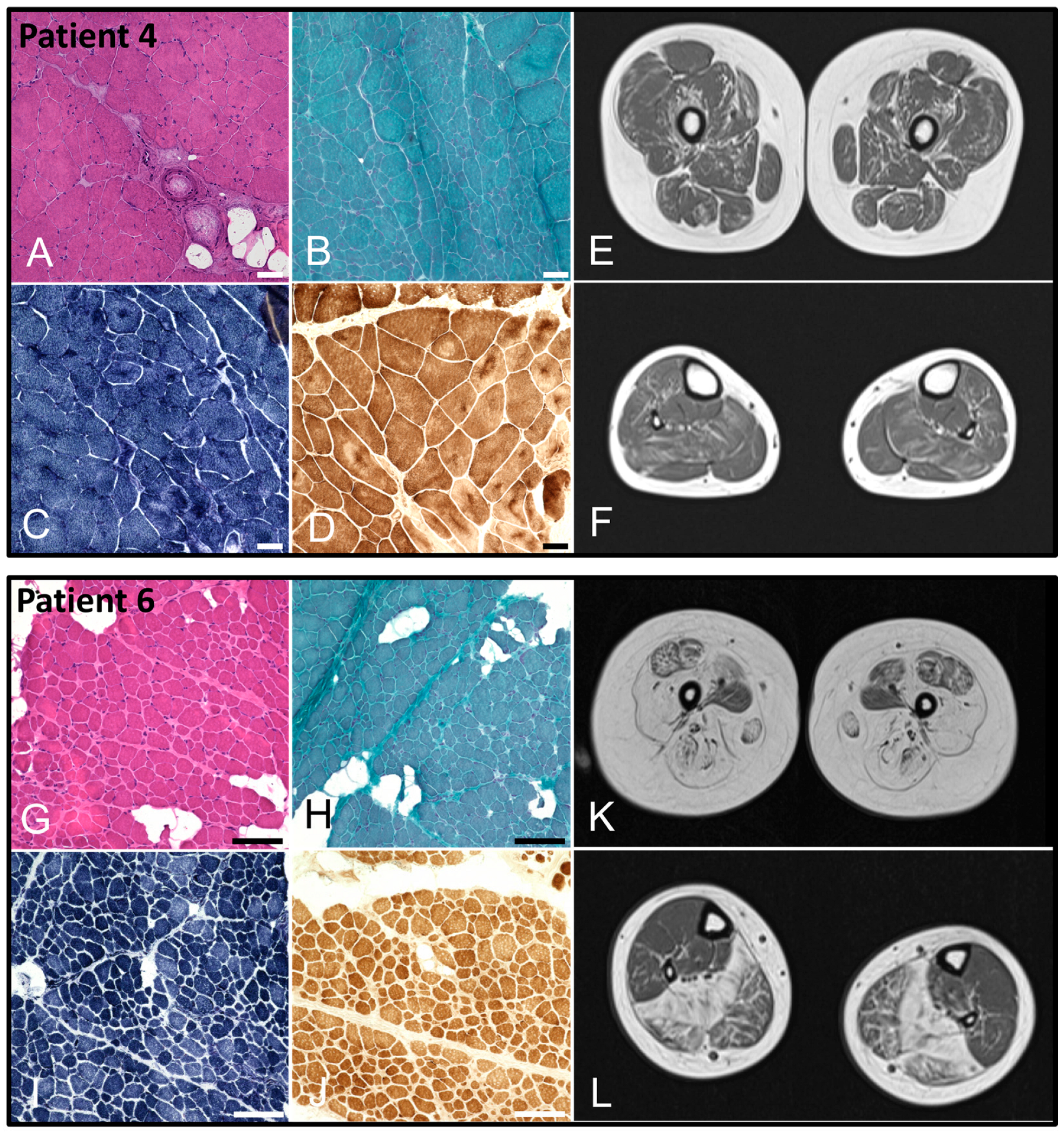
| Muscle biopsy | Fiber size variation, few internal nuclei (Figure 2) | Fiber size variation, numerous immature type 2C muscle fibers | Fiber size variation | Fiber size variation, centronuclear myopathy (Figure 3) | - | Fiber size variation, chronic active myopathy, reduced α-dystroglycan (Figure 3) | Fibrolipomatosis, internal nuclei | |
| Pregnancy issues | Gest. diabetes, preeclampsia; birth at 34 + 6 w | - | Polyhydramnion, reduced fetal movements | Birth at 32 weeks | Reduced fetal movements | Polyhydramnion | - | |
| Additional features | ||||||||
| Heart diseases | - | Transposition of great arteries | Preexcitation syndrome | - | - | - | - | |
| Lung diseases | Ventilation required since birth | Ventilation required since birth | Progressive restrictive ventilation disease | Ventilation required for 2 weeks after birth | - | - | - | |
| Orthopedic diseases | Contractures | n.a. | Scoliosis | Genu valgus | Pes planus valgus | Cong. bilateral hip dysplasia | - | |
| Neurological diseases | Secondary microcephaly | Intracerebral hemorrhages, motor axonal polyneuropathy | - | - | - | - | Progressive hearing loss | |
| Congenital malformations | - | Transposition of great arteries | - | - | - | Congenital hip and knee contractures | Cleft lip/palate | |
| Cognitive impairment | - | n.a. | - | - | - | - | - |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Whole Exome Sequencing and Segregation Analysis
4.2. Optical Genome Mapping
4.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
4.4. Muscle Biopsy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.; Wei, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, J.; Qin, L.; Yan, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, H. Correlation of Phenotype-Genotype and Protein Structure in RYR1-Related Myopathy. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 870285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecevic, N.; Arsenijevic, V.; Manolakos, E.; Papoulidis, I.; Theocharis, G.; Sartsidis, A.; Tsagas, T.; Tziotis, I.; Dagklis, T.; Kalogeros, G.; et al. New Compound Heterozygous Splice Site Mutations of the Skeletal Muscle Ryanodine Receptor (RYR1) Gene Manifest Fetal Akinesia: A Linkage with Congenital Myopathies. Mol. Syndromol. 2020, 11, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, T.A.; Todd, J.J.; Witherspoon, J.W.; Bönnemann, C.G.; Dowling, J.J.; Hamilton, S.L.; Meilleur, K.G.; Dirksen, R.T. Ryanodine receptor 1-related disorders: An historical perspective and proposal for a unified nomenclature. Skelet. Muscle 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.; Lillis, S.; Munteanu, I.; Scoto, M.; Zhou, H.; Quinlivan, R.; Straub, V.; Manzur, A.Y.; Roper, H.; Jeannet, P.-Y.; et al. Clinical and genetic findings in a large cohort of patients with ryanodine receptor 1 gene-associated myopathies. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, I.; Lopez, M.A.; Marafi, D.; Pehlivan, D.; Calame, D.G.; Abid, F.; Lotze, T.E. Clinical exome sequencing in the diagnosis of pediatric neuromuscular disease. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-L.; Chuang, C.-K.; Chiu, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Tu, Y.-R.; Lo, Y.-T.; Lin, H.-Y.; Lin, S.-P. Application of whole exome sequencing in the diagnosis of muscular disorders: A study of Taiwanese pediatric patients. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1365729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilius-Eliliwi, V.; Gerding, W.M.; Schroers, R.; Nguyen, H.P.; Vangala, D.B. Optical Genome Mapping for Cytogenetic Diagnostics in AML. Cancers 2023, 15, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, L.S.; Hoffjan, S.; Janßen, S.; Kneifel, M.; Krause, K.; Gerding, W.M.; Döring, K.; Güttsches, A.-K.; Roos, A.; Buena Atienza, E.; et al. Exome Sequencing and Optical Genome Mapping in Molecularly Unsolved Cases of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Identification of a Causative X-Chromosomal Inversion Disrupting the DMD Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shillington, A.; Zea Vera, A.; Perry, T.; Hopkin, R.; Thomas, C.; Cooper, D.; Suhrie, K. Clinical RNA sequencing confirms compound heterozygous intronic variants in RYR1 in a patient with congenital myopathy, respiratory failure, neonatal brain hemorrhage, and d-transposition of the great arteries. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, T.A.; Todd, J.J.; Meilleur, K.G. Ryanodine Receptor 1-Related Myopathies: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuiman, G.J.; Küsters, B.; Eshuis, L.; Snoeck, M.; Lammens, M.; Heytens, L.; de Ridder, W.; Baets, J.; Scalco, R.S.; Quinlivan, R.; et al. The histopathological spectrum of malignant hyperthermia and rhabdomyolysis due to RYR1 mutations. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laquérriere, A.; Maluenda, J.; Camus, A.; Fontenas, L.; Dieterich, K.; Nolent, F.; Zhou, J.; Monnier, N.; Latour, P.; Gentil, D.; et al. Mutations in CNTNAP1 and ADCY6 are responsible for severe arthrogryposis multiplex congenita with axoglial defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, M.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Küsters, B.; Lammens, M.; Meijer, R.; Molenaar, J.P.F.; Raaphorst, J.; Verschuuren-Bemelmans, C.C.; Straathof, C.S.M.; Sie, L.T.L.; et al. RYR1-related myopathies: A wide spectrum of phenotypes throughout life. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1094–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa, M.; Blaska, M.; Hamm, M.; Czarniecka, A.; Krajewska, J.; Taczanowska-Niemczuk, A.; Zachurzok, A. A 4-Year-Old Boy with an Accidentally Detected Mutation in the RET Proto-Oncogene and Mutation in the Gene Encoding the Ryanodine Receptor1 (RyR1)—Case Report. Children 2023, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.R.; Lee, K.; Pfau, R.B.; Reshmi, S.C.; Corsmeier, D.J.; Hashimoto, S.; Dave-Wala, A.; Jayaraman, V.; Koboldt, D.; Matthews, T.; et al. Disease-associated mosaic variation in clinical exome sequencing: A two-year pediatric tertiary care experience. Cold Spring Harb Mol. Case Stud. 2020, 6, a005231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramensky, V.E.; Ershova, A.I.; Zaicenoka, M.; Kiseleva, A.V.; Zharikova, A.A.; Vyatkin, Y.V.; Sotnikova, E.A.; Efimova, I.A.; Divashuk, M.G.; Kurilova, O.V.; et al. Targeted Sequencing of 242 Clinically Important Genes in the Russian Population From the Ivanovo Region. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 709419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, Y.; Dushar, M.; Kovalyk, O.; Falion, R. Identification of the pathogenic variant in the RYR1 gene in a Ukrainian patient with severe muscle hypotonia. In Proceedings of the Conference NEUROPATHOLOGY, NEUROGENETICS 2019, Warsaw, Poland, 15 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.; Jungbluth, H.; Clement, E.; Lillis, S.; Abbs, S.; Munot, P.; Pane, M.; Wraige, E.; Schara, U.; Straub, V.; et al. Muscle magnetic resonance imaging in congenital myopathies due to ryanodine receptor type 1 gene mutations. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusto, A.; Cassandrini, D.; Fiorillo, C.; Codemo, V.; Astrea, G.; D’Amico, A.; Maggi, L.; Magri, F.; Pane, M.; Tasca, G.; et al. Expanding the clinical-pathological and genetic spectrum of RYR1-related congenital myopathies with cores and minicores: An Italian population study. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmer, M.K. Whole Genome Sequencing as a First-Line Clinical Test: Almost Ready for Prime Time. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1815–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, R.G.; Bryen, S.J.; Bahlo, M.; Cairns, A.; Chao, K.R.; Corbett, A.; Davis, M.R.; Ganesh, V.S.; Ghaoui, R.; Jones, K.J.; et al. Genome and RNA sequencing boost neuromuscular diagnoses to 62% from 34% with exome sequencing alone. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2024, 11, 1250–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, E.E. Genetic Variation, Comparative Genomics, and the Diagnosis of Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amburgey, K.; Bailey, A.; Hwang, J.H.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Bonnemann, C.G.; Medne, L.; Mathews, K.D.; Collins, J.; Daube, J.R.; Wellman, G.P.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in recessive RYR1-related myopathies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.J.; Dirksen, R.T.; Girard, T.; Gonsalves, S.G.; Hopkins, P.M.; Riazi, S.; Saddic, L.A.; Sambuughin, N.; Saxena, R.; Stowell, K.; et al. Variant curation expert panel recommendations for RYR1 pathogenicity classifications in malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha-Goebel, D.X.; Santi, M.; Medne, L.; Zukosky, K.; Dastgir, J.; Shieh, P.B.; Winder, T.; Tennekoon, G.; Finkel, R.S.; Dowling, J.J.; et al. Severe congenital RYR1-associated myopathy: The expanding clinicopathologic and genetic spectrum. Neurology 2013, 80, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, M.; Nishino, I. A review of core myopathy: Central core disease, multiminicore disease, dusty core disease, and core-rod myopathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Ibarra, M.C.A.; Malicdan, M.C.V.; Murayama, K.; Ichihara, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Nonaka, I.; Noguchi, S.; Hayashi, Y.K.; Nishino, I. Central core disease is due to RYR1 mutations in more than 90% of patients. Brain 2006, 129, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, M.; Geoffroy, M.; Pavani, G.; Guiraud, S. CRISPR-Based Gene Therapies: From Preclinical to Clinical Treatments. Cells 2024, 13, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, M.; Benetollo, A.; Dalla Barba, F.; Sandonà, D. Advanced therapeutic approaches in sarcoglycanopathies. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2024, 76, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, P.; Singh, S.; Ram, G.; Kapil, S.; Singh, A. Diving into progress: A review on current therapeutic advancements in spinal muscular atrophy. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1368658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbout, K.; Rousseau, J.; Tremblay, J.P. Successful Correction by Prime Editing of a Mutation in the RYR1 Gene Responsible for a Myopathy. Cells 2023, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Kurebayashi, N.; Ishida, R.; Kagechika, H. Drug development for the treatment of RyR1-related skeletal muscle diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2023, 69, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.T.; Wolfe, D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1180, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janßen, S.; Erbe, L.S.; Kneifel, M.; Vorgerd, M.; Döring, K.; Lubieniecki, K.P.; Lubieniecka, J.M.; Gerding, W.M.; Casadei, N.; Güttsches, A.-K.; et al. Compound Heterozygous RYR1 Variants in a Patient with Severe Congenital Myopathy: Case Report and Comparison with Additional Cases of Recessive RYR1-Related Myopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910867
Janßen S, Erbe LS, Kneifel M, Vorgerd M, Döring K, Lubieniecki KP, Lubieniecka JM, Gerding WM, Casadei N, Güttsches A-K, et al. Compound Heterozygous RYR1 Variants in a Patient with Severe Congenital Myopathy: Case Report and Comparison with Additional Cases of Recessive RYR1-Related Myopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910867
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanßen, Sören, Leoni S. Erbe, Moritz Kneifel, Matthias Vorgerd, Kristina Döring, Krzysztof P. Lubieniecki, Joanna M. Lubieniecka, Wanda M. Gerding, Nicolas Casadei, Anne-Katrin Güttsches, and et al. 2024. "Compound Heterozygous RYR1 Variants in a Patient with Severe Congenital Myopathy: Case Report and Comparison with Additional Cases of Recessive RYR1-Related Myopathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910867
APA StyleJanßen, S., Erbe, L. S., Kneifel, M., Vorgerd, M., Döring, K., Lubieniecki, K. P., Lubieniecka, J. M., Gerding, W. M., Casadei, N., Güttsches, A.-K., Heyer, C., Lücke, T., Nguyen, H. H. P., Köhler, C., & Hoffjan, S. (2024). Compound Heterozygous RYR1 Variants in a Patient with Severe Congenital Myopathy: Case Report and Comparison with Additional Cases of Recessive RYR1-Related Myopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910867









