Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis Thermophilic Esterase in Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Acyl Substrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
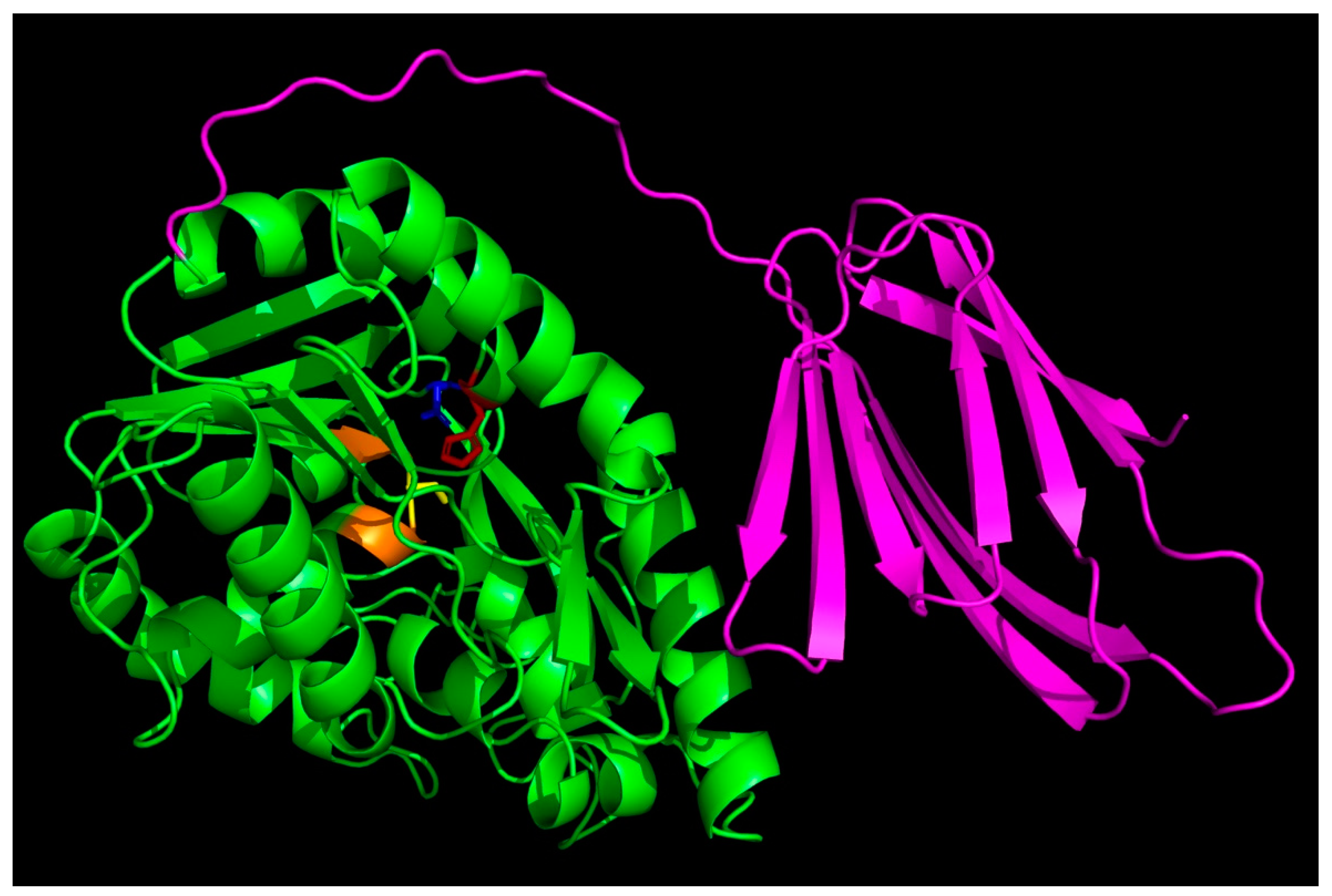
2.1. Alphafold-Predicted Structure of T. tengcongensis EstA3
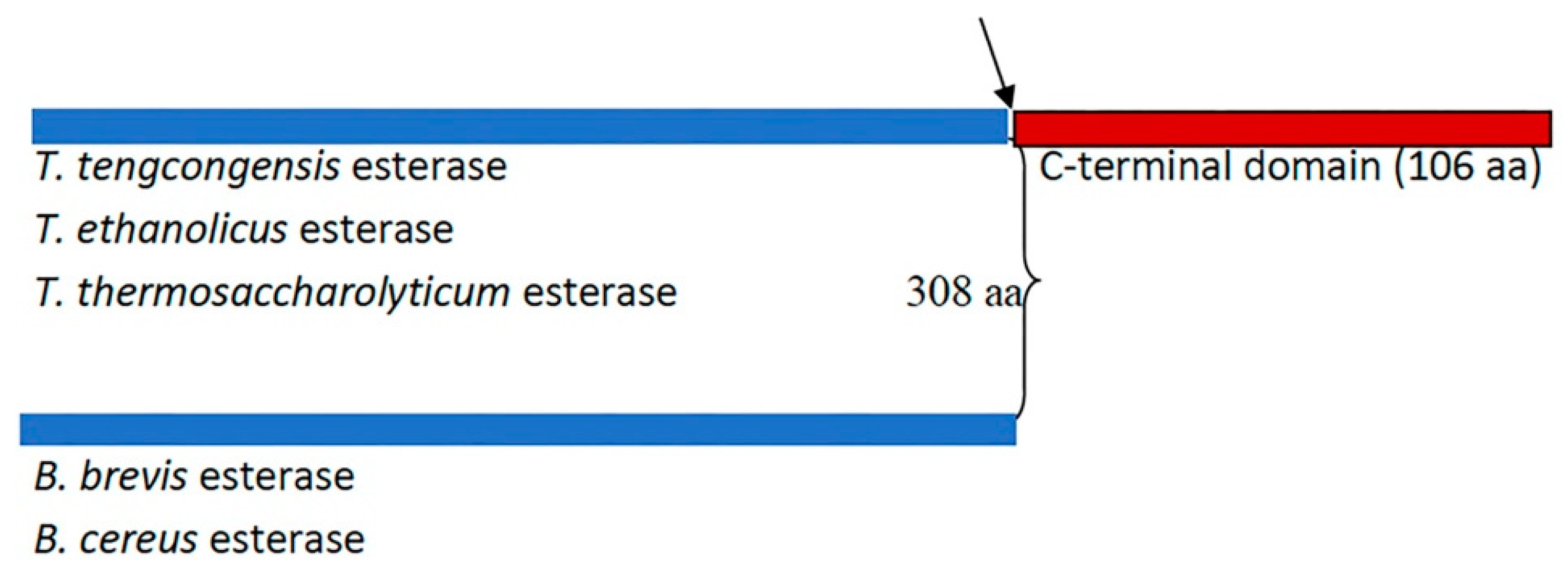
2.2. Design, Cloning, Expression, and Purification of Esterases
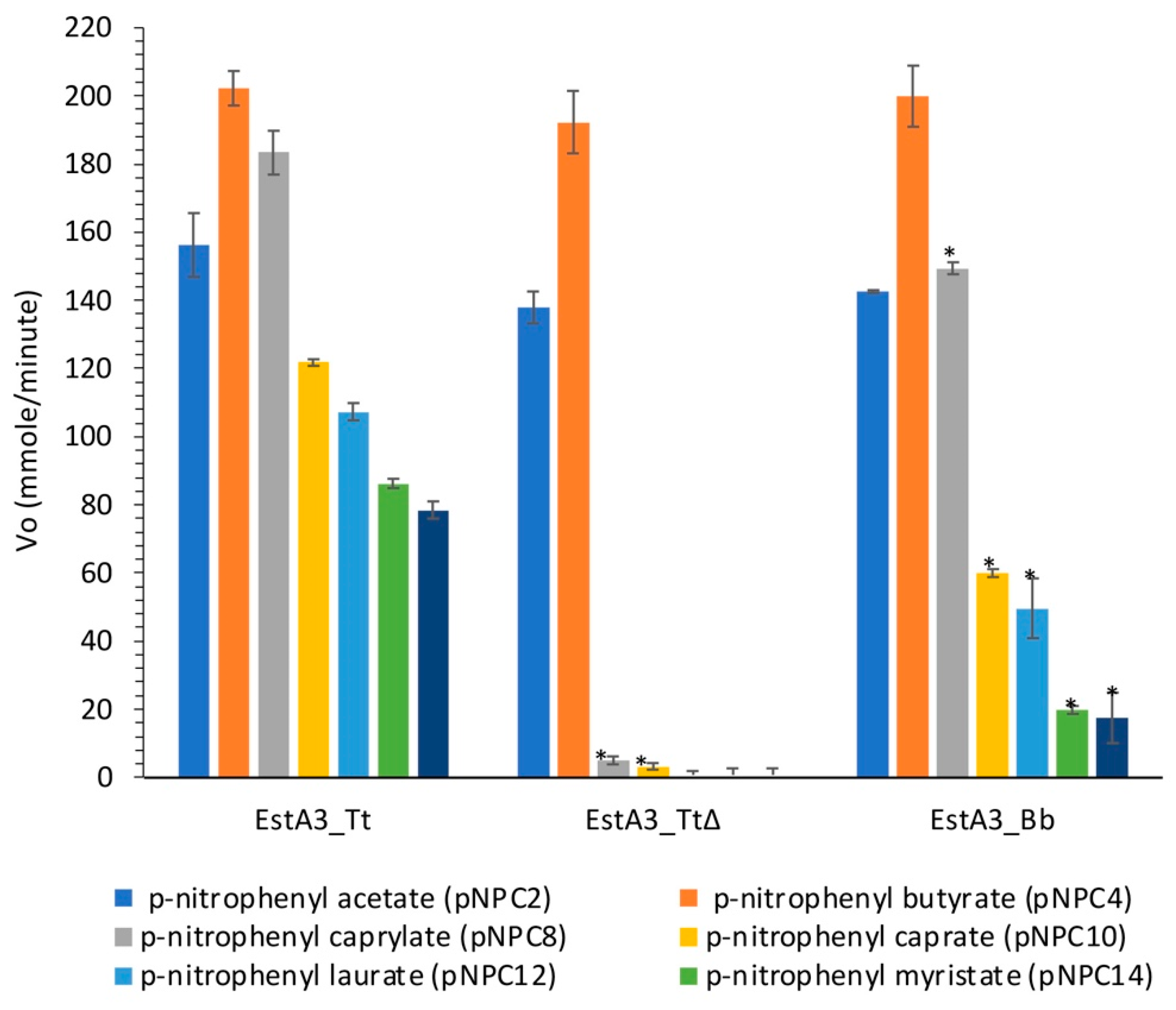
2.3. Hydrolytic Activities of Purified Esterases Reveal Different Substrate Preferences
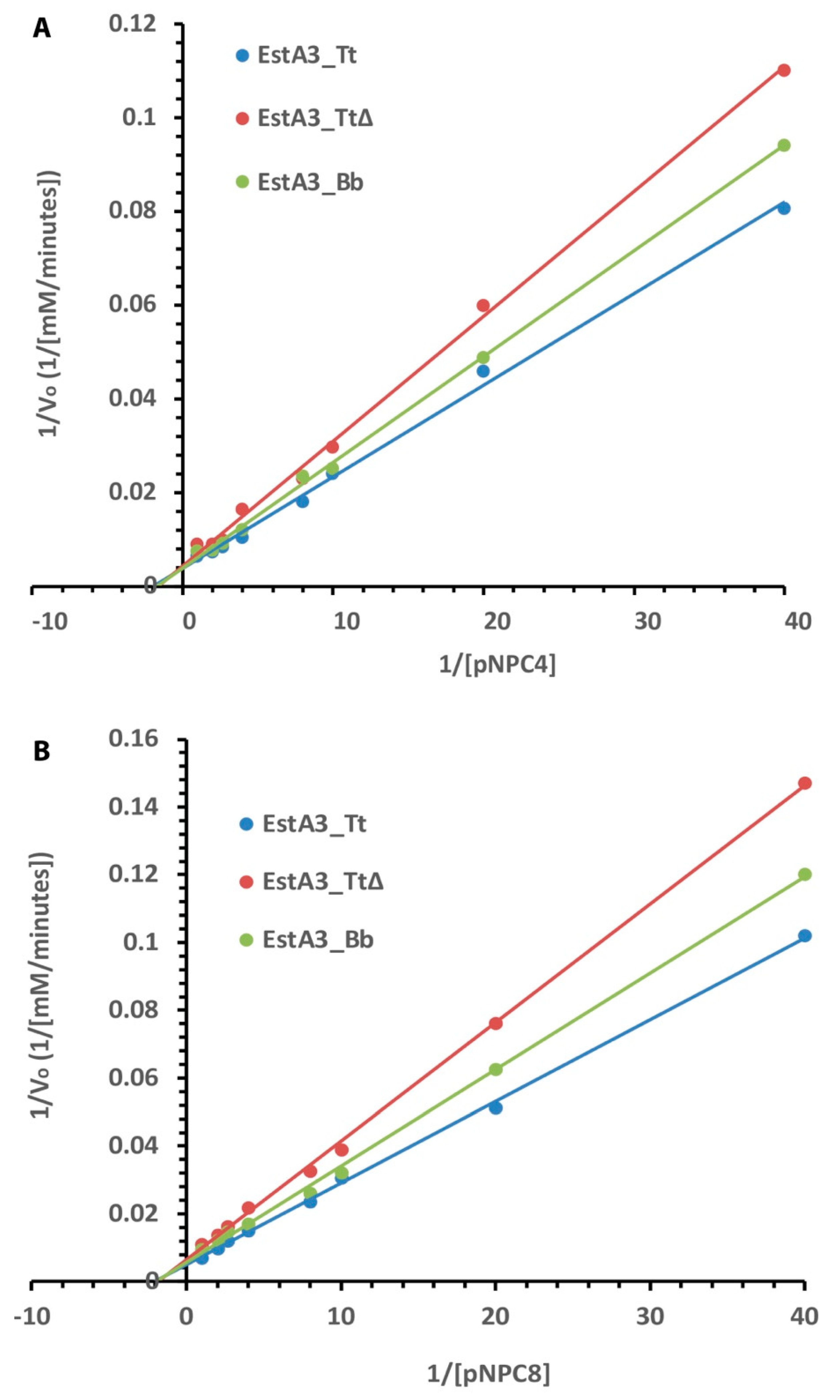
2.4. Kinetics of Activities of Purified Esterases on C4 and C8 Substrates
3. Discussion
3.1. Substrate Preferences of EstA3_Tt, EstA3_Tt∆, and EstA3_Bb
3.2. The C-Terminal Tail Contributes to the Stability of EstA3
3.3. Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich in Binding Long-Chain Acyl Substrates
3.4. Structure-Guided Engineering of Esterases Could Generate New Catalytic Flexibility for Industrial Applications
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids and Bacterial Strains
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Protein Expression and Purification
4.4. Determination of Esterase Activity
4.5. Determination of Substrate Preference and Kinetic Parameters
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barzkar, N.; Sohail, M.; Tamadoni Jahromi, S.; Gozari, M.; Poormozaffar, S.; Nahavandi, R.; Hafezieh, M. Marine Bacterial Esterases: Emerging Biocatalysts for Industrial Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 1187–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafeeq, H.; Hussain, A.; Shabbir, S.; Ali, S.; Bilal, M.; Sher, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Esterases as Emerging Biocatalysts: Mechanistic Insights, Genomic and Metagenomic, Immobilization, and Biotechnological Applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2176–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, P.; Gupta, R. Medical Aspects of Esterases: A Mini Review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, T.; Gowrishankar, B.S. Production and Applications of Esterases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivek, K.; Sandhia, G.S.; Subramaniyan, S. Extremophilic Lipases for Industrial Applications: A General Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.; Steiner, W. The Biocatalytic Potential of Extremophiles and Extremozymes. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Rigoldi, F.; Donini, S.; Redaelli, A.; Parisini, E.; Gautieri, A. Engineering of Thermostable Enzymes for Industrial Applications. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumorné, K.; Córdova, D.C.; Astorga-Eló, M.; Renganathan, P. Extremozymes: A Potential Source for Industrial Applications. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, M. Alpha Beta-Hydrolase Fold Enzymes Structures, Functions and Mechanisms. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tao, J.; Li, G.; Lu, J.R.; Ma, Y. A Thermostable Esterase from Thermoanaerobacter Tengcongensis Opening up a New Family of Bacterial Lipolytic Enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, P. Thermoanaerobacter Tengcongensis Sp. Nov., a Novel Anaerobic, Saccharolytic, Thermophilic Bacterium Isolated from a Hot Spring in Tengcong, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, D.M.; Walker, J.M. Thermostable Proteins. Life Chem. Rep. Ser. 1991, 8, 49–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Dai, X.; Xiang, H. Thermostable Esterase from Thermoanaerobacter Tengcongensis: High-Level Expression, Purification and Characterization. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J.; Döbeli, H.; Gentz, R.; Hochuli, E.; Stüber, D.; Henco, K. 6xHis-Ni-NTA Chromatography as a Superior Technique in Recombinant Protein Expressiod/Purification. In Protocols for Gene Analysis; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 31, pp. 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, J.R.; Ma, Y. A Novel Alkaliphilic Bacillus Esterase Belongs to the 13th Bacterial Lipolytic Enzyme Family. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.-B.V.; Horsfall, L.E.; Wardrope, C.; Togneri, P.D.; Marles-Wright, J.; Rosser, S.J. Characterisation of a New Family of Carboxyl Esterases with an OsmC Domain. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latip, W.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.; Leow, A.T.C.; Mohd Shariff, F.; Kamarudin, N.H.A.; Mohamad Ali, M.S. The Effect of N-Terminal Domain Removal towards the Biochemical and Structural Features of a Thermotolerant Lipase from an Antarctic Pseudomonas Sp. Strain AMS3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Fernández, J.; Barrero, J.J.; Benaiges, M.D.; Valero, F. Truncated Prosequence of Rhizopus Oryzae Lipase: Key Factor for Production Improvement and Biocatalyst Stability. Catalysts 2019, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, B. Culture Conditions for the Production of Esterase from Lactobacillus Casei CL96. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2001, 24, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Samoylova, Y.V.; Sorokina, K.N.; Romanenko, M.V.; Parmon, V.N. Cloning, Expression and Characterization of the Esterase estUT1 from Ureibacillus Thermosphaericus Which Belongs to a New Lipase Family XVIII. Extremophiles 2018, 22, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakruddin, M.; Mohammad Mazumdar, R.; Bin Mannan, K.S.; Chowdhury, A.; Hossain, M.N. Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Cloning, Expression, and Mass Production of Enzymes by Recombinant E. coli. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 590587. [Google Scholar]
- Bornscheuer, U.T.; Bessler, C.; Srinivas, R.; Krishna, S.H. Optimizing Lipases and Related Enzymes for Efficient Application. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levisson, M.; Van Der Oost, J.; Kengen, S.W.M. Characterization and Structural Modeling of a New Type of Thermostable Esterase from Thermotoga Maritima. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 2832–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, O.; Cerdan, M.E.; Gonzalez Siso, M.I. New Extremophilic Lipases and Esterases from Metagenomics. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.K. Enzymes: Principles and biotechnological applications. Essays Biochem. 2015, 59, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Martínez, M.; Coscolín, C.; Santiago, G.; Chow, J.; Stogios, P.J.; Bargiela, R.; Gertler, C.; Navarro-Fernández, J.; Bollinger, A.; Thies, S.; et al. The Inmare Consortium. Determinants and Prediction of Esterase Substrate Promiscuity Patterns. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Bargiela, R.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Mir, J.; Koch, R.; Golyshina, O.V.; Golyshin, P.N. Biodiversity for Biocatalysis: A Review of the α/β-Hydrolase Fold Superfamily of Esterases-Lipases Discovered in Metagenomes. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2015, 33, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpigny, J.L.; JAEGER, K.-E. Bacterial Lipolytic Enzymes: Classification and Properties. Biochem. J. 1999, 343, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, K.; Liu, J.; Oshima, Y.; Hirooka, K.; Shimanuki, S.; Yokota, Y.; Hemmi, H.; Nakayama, T.; Nishino, T. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Thermostable Carboxylesterase from an Archaeon, Sulfolobus Shibatae DSM5389: Non-Linear Kinetic Behavior of a Hormone-Sensitive Lipase Family Enzyme. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 98, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Ohta, H. A Novel Thermostable Esterase from the Thermoacidophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus Tokodaii Strain 7. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.; Raina, C.; Parshad, R.; Johri, S.; Verma, V.; Andrabi, K.I.; Qazi, G.N. A Novel Esterase from Bacillus Subtilis (RRL 1789): Purification and Characterization of the Enzyme. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 45, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, K.; Burcu Bakir Ateslier, Z.; Basbulbul, G.; Halil Biyik, H. Characterization of Esterase Activity in Geobacillus Sp. HBB-4. J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, H.; Ni, H.; Xiao, A.; Hou, L. Characterization of a New and Thermostable Esterase from a Metagenomic Library. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Chen, C.-S.; Liu, H.-T.; Chen, J.-L.; Xia, Y.; Wu, S.-J. Purification, Identification and Characterization of an Esterase with High Enantioselectivity to (S)-Ethyl Indoline-2-Carboxylate. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.M.; Godoy, A.S.; Kadowaki, M.A.S.; Polikarpov, I. The first structure of Bacillus licheniformis lipase BlEst2 in its propeptide and mature form revealing molecular details of inhibition by its C-terminal domains. RCSB 2021. to be submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; Frikha, F.; Miled, N.; Mtibaa, H.; Ali, Y.B.; Verger, R.; Gargouri, Y. N-Terminal Peptide of Rhizopus Oryzae Lipase Is Important for Its Catalytic Properties. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dai, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, M.; Yan, Y. Alteration of Chain-Length Selectivity and Thermostability of Rhizopus Oryzae Lipase via Virtual Saturation Mutagenesis Coupled with Disulfide Bond Design. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e01878-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, F.; Babic, N.; Krauss, U.; Jaeger, K.-E. Classification of Lipolytic Enzymes from Bacteria. Aerob. Util. Hydrocarb. Oils Lipids 2019, 24, 255–289. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T.; Wang, X.-R.; Zeng, Q.-Y. Structural and Functional Evolution of Positively Selected Sites in Pine Glutathione S-Transferase Enzyme Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24441–24451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Enzymes | EstA3_Tt | EstA3_Tt∆ | EstA3_Bb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 47,078 | 34,719 | 35,243 |
| Molar Extinction Coefficient (M−1cm−1) | 71,280 | 58,330 | 48,820 |
| A280 (1000 μg/mL) | 1.514 | 1.680 | 1.385 |
| Protein Concentration (μg/mL) | 1250 | 950 | 990 |
| Protein Concentration (μM) | 26.6 | 27.4 | 28.09 |
| Enzymes | Km (mM) | Vmax (mM/Minutes) | Kcat × 105 (S−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pNPC4 | |||
| EstA3_Tt | 0.53 | 263.17 | 2.94 |
| EstA3_Bb | 0.59 | 256.41 | 1.51 |
| EstA3_Tt∆ | 0.64 | 238.10 | 1.50 |
| pNPC8 | |||
| 0.49 | 204.08 | 2.28 | |
| EstA3_Tt | 0.51 | 181.82 | 1.07 |
| EstA3_Bb | 0.56 | 158.73 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joel, E.B.; Aberuagba, A.; Bello, A.J.; Akanbi-Gada, M.; Igunnu, A.; Malomo, S.O.; Olorunniji, F.J. Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis Thermophilic Esterase in Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Acyl Substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021272
Joel EB, Aberuagba A, Bello AJ, Akanbi-Gada M, Igunnu A, Malomo SO, Olorunniji FJ. Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis Thermophilic Esterase in Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Acyl Substrates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021272
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoel, Enoch B., Adepeju Aberuagba, Adebayo J. Bello, Mariam Akanbi-Gada, Adedoyin Igunnu, Sylvia O. Malomo, and Femi J. Olorunniji. 2024. "Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis Thermophilic Esterase in Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Acyl Substrates" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021272
APA StyleJoel, E. B., Aberuagba, A., Bello, A. J., Akanbi-Gada, M., Igunnu, A., Malomo, S. O., & Olorunniji, F. J. (2024). Role of the C-Terminal β Sandwich of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis Thermophilic Esterase in Hydrolysis of Long-Chain Acyl Substrates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021272







