Degenerative Changes in the Claustrum and Endopiriform Nucleus after Early-Life Status Epilepticus in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
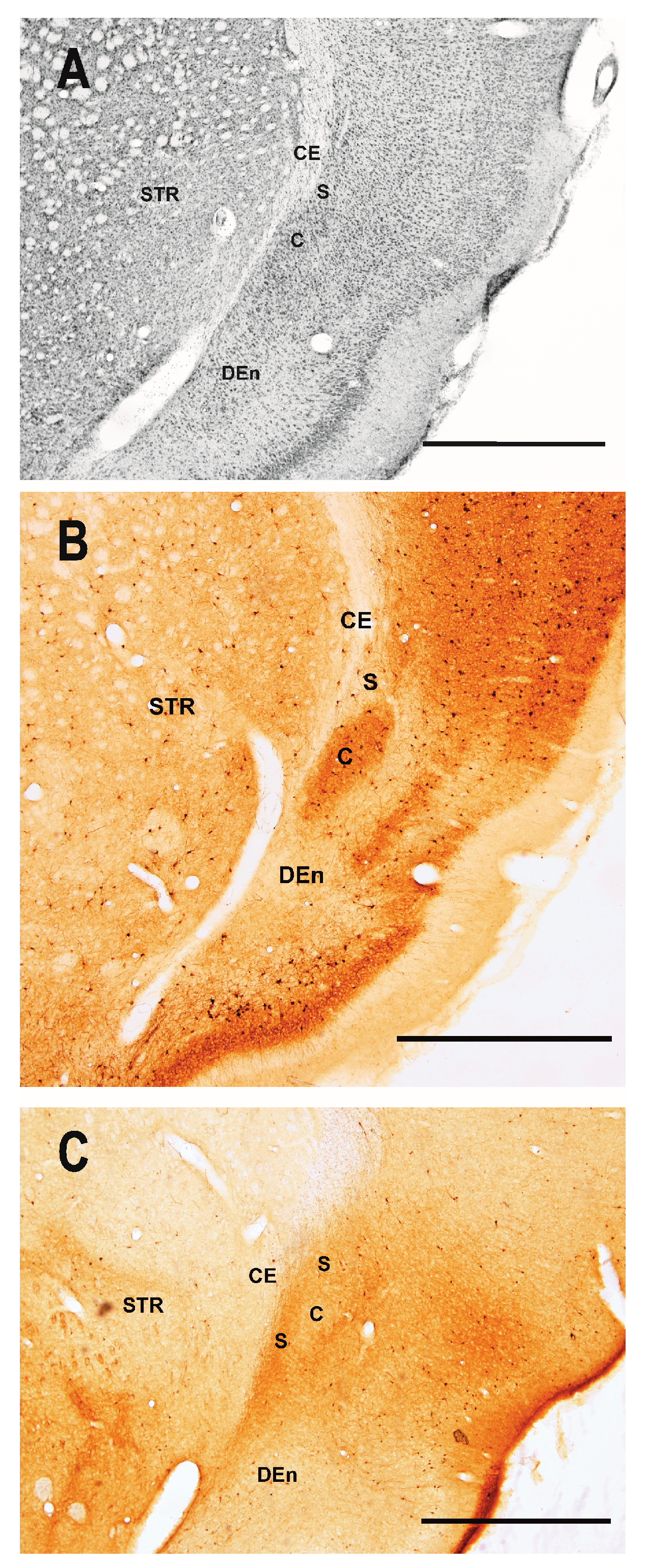
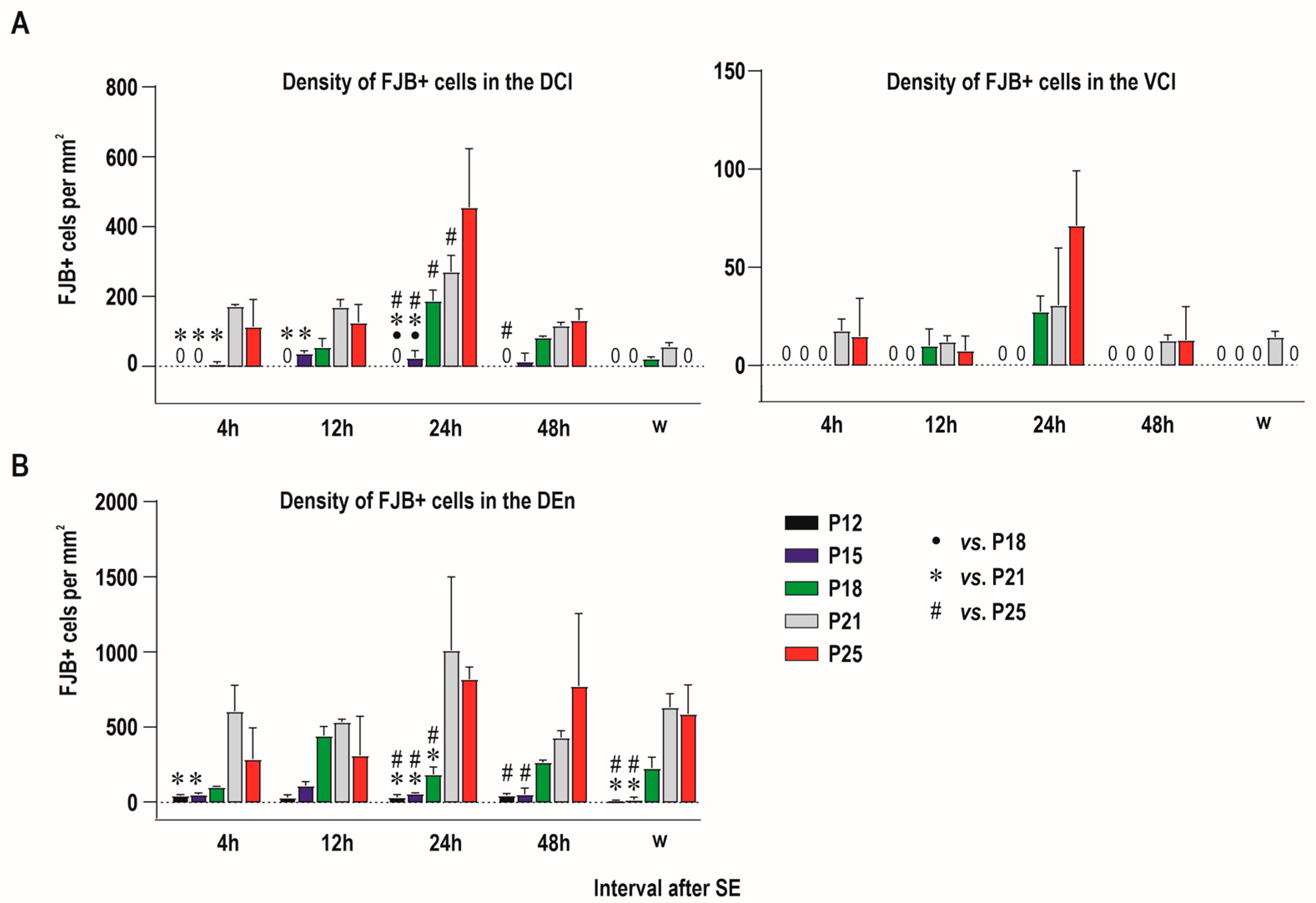
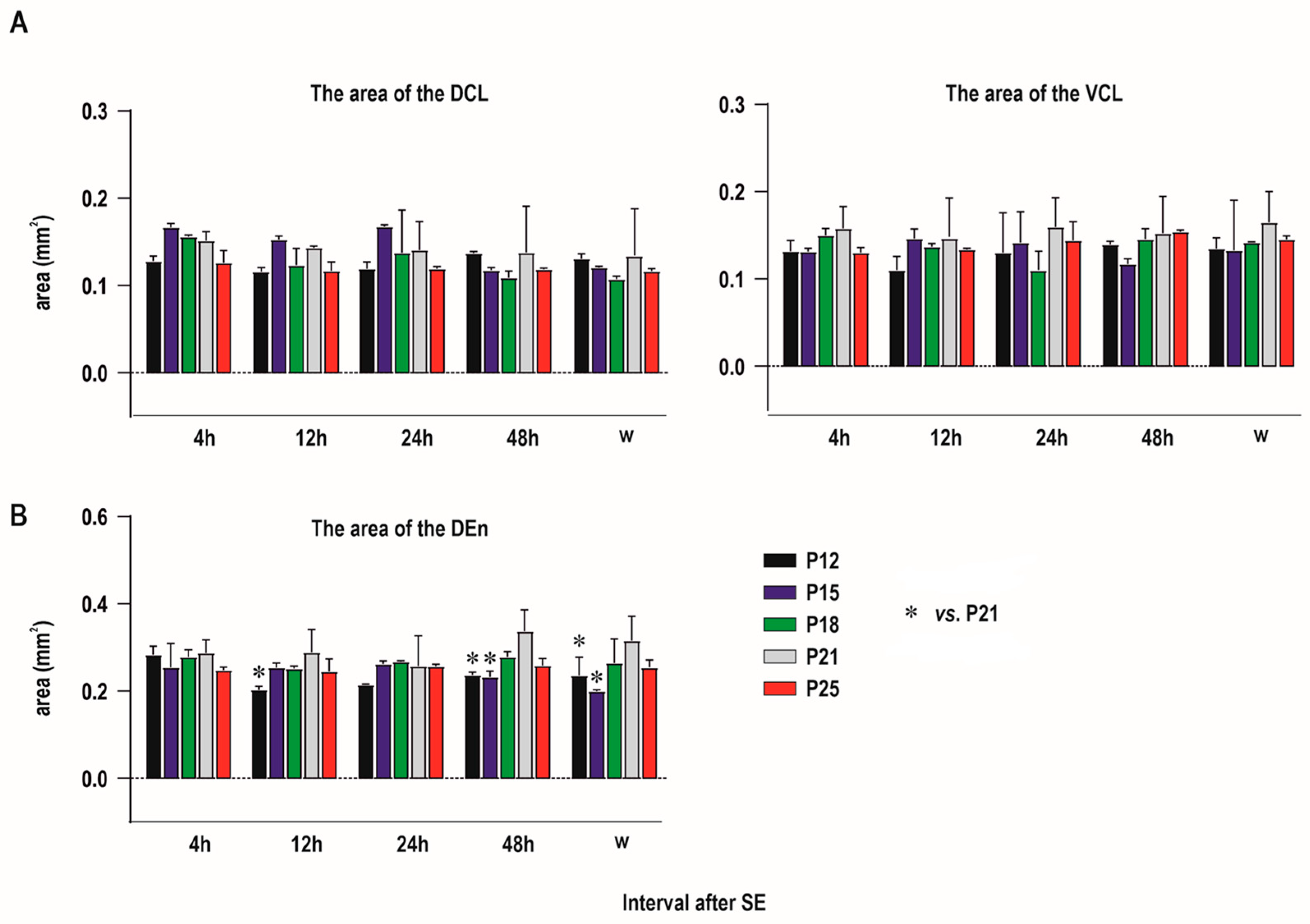
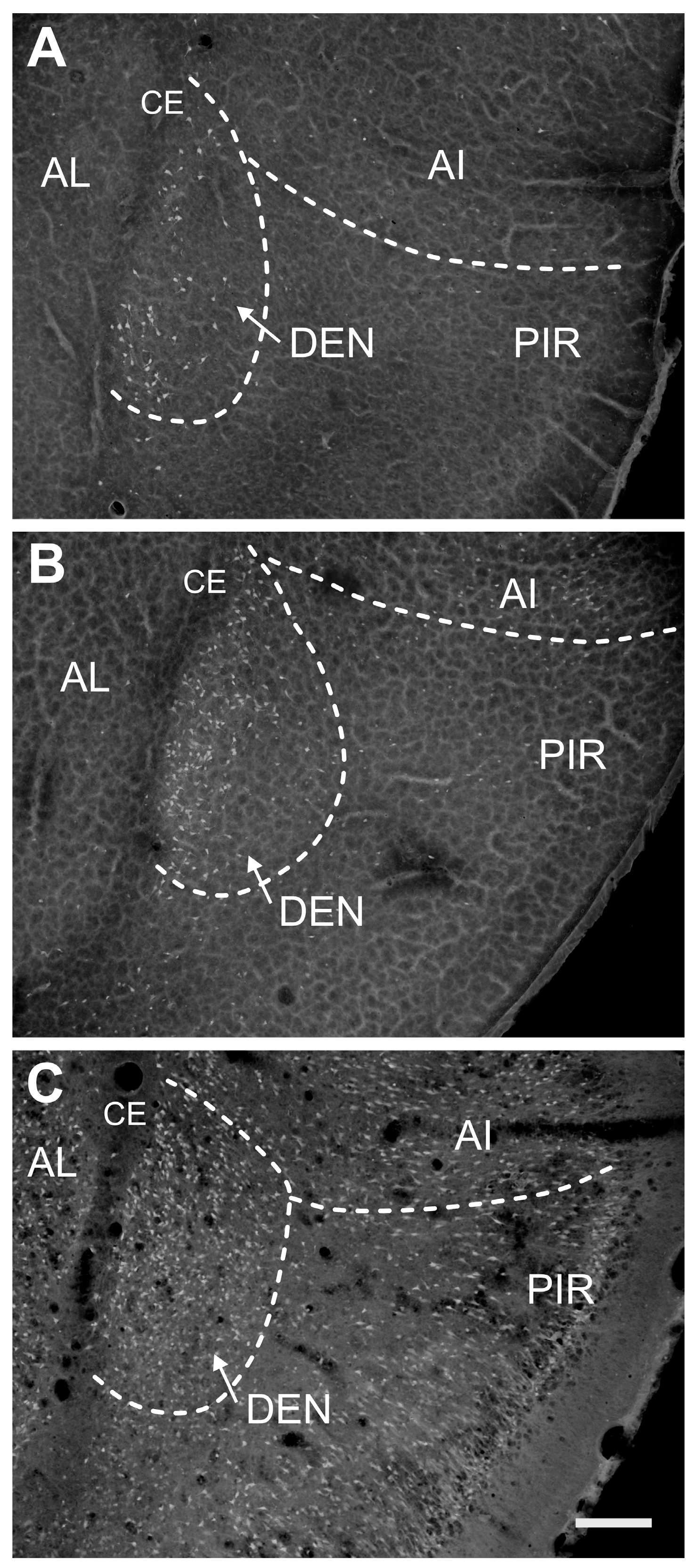
2.1. Distribution of Degenerating Neurons and Severity of Damage
2.1.1. Severity of Damage and Distribution of Degenerating Neurons in the Dorsal (Insular) Claustrum (CL) in SE Animals
2.1.2. Severity of Damage and Distribution of Degenerating Neurons in the Endopiriform Nucleus
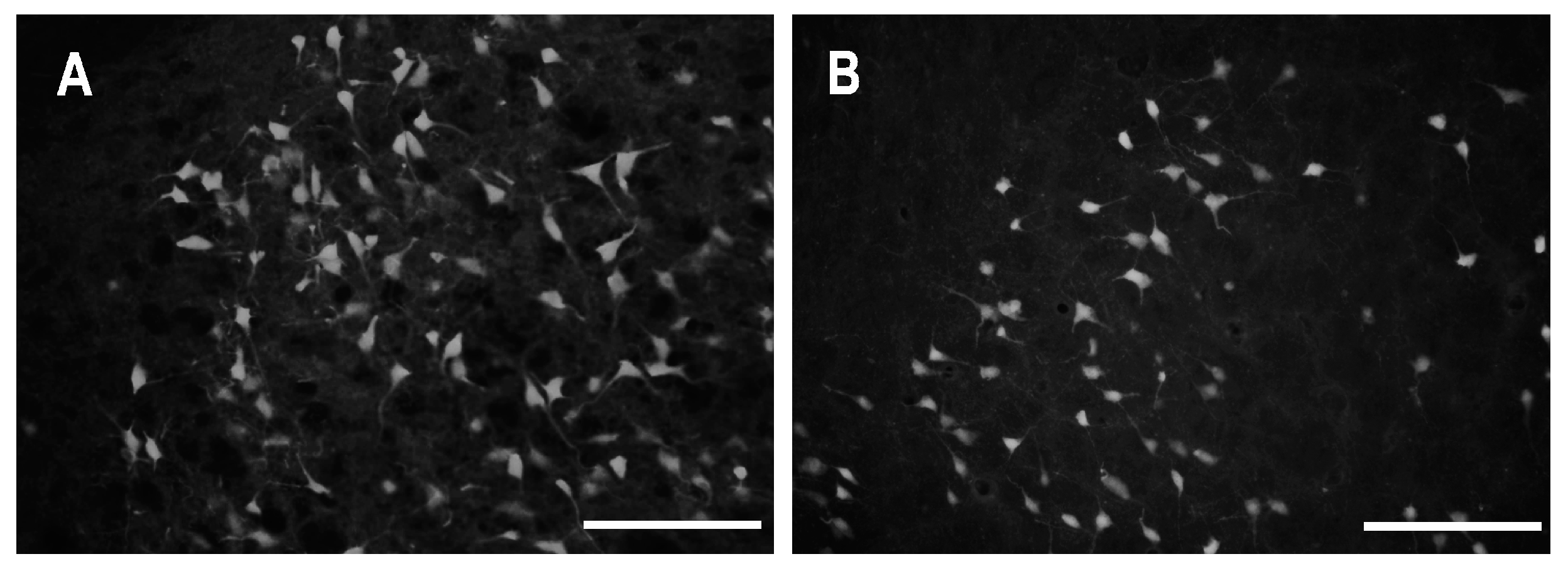
2.2. Characteristics of Degenerated Neurons
2.3. Distribution of Calretinin- and Parvalbumin-Positive Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Induction of Status Epilepticus
4.3. Histology
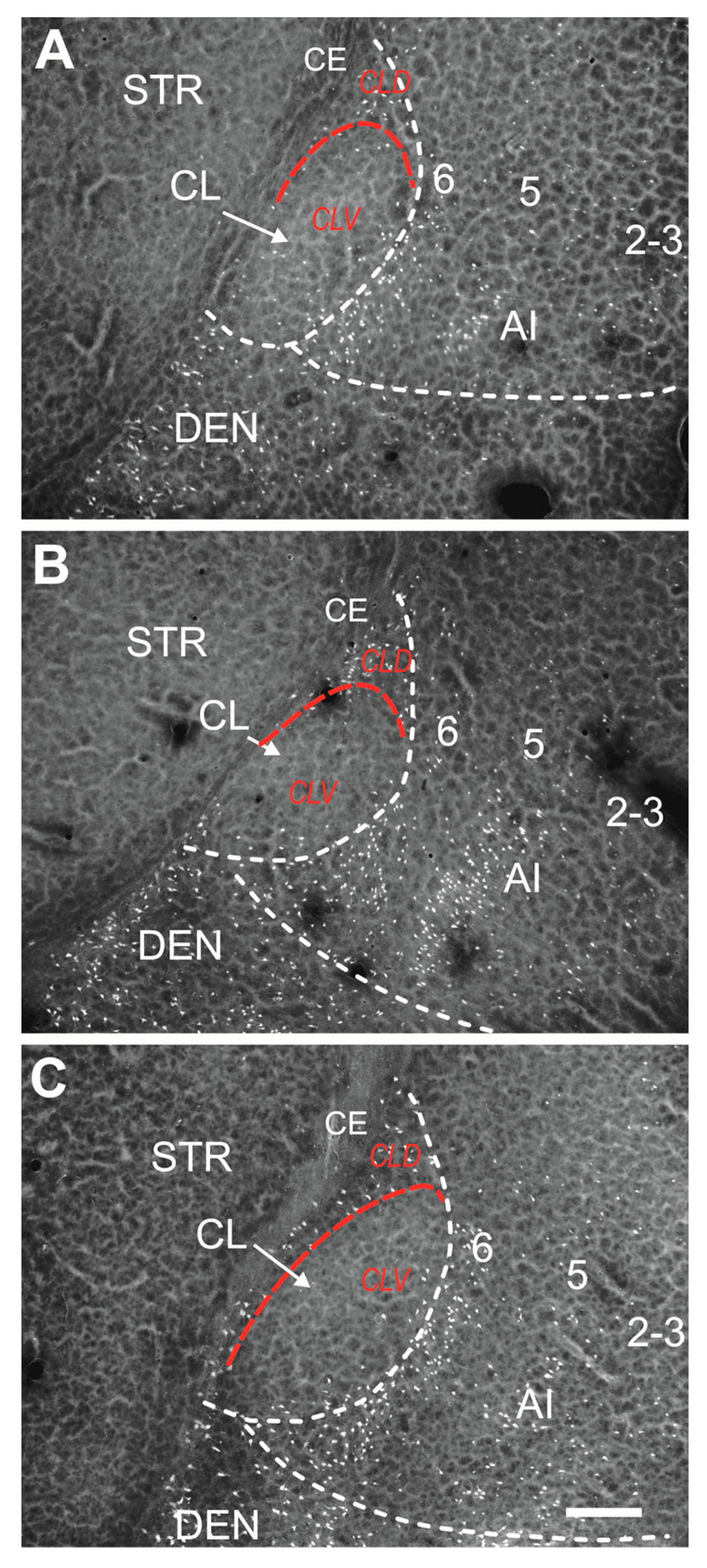
4.4. Parcellation of the Claustrum
4.5. Semiquantitative Analysis
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitkanen, A.; Kharatishvili, I.; Karhunen, H.; Lukasiuk, K.; Immonen, R.; Nairismägi, J.; Gröhn, O.; Nissinen, J. Epileptogenesis in experimental models. Epilepsia 2007, 48 (Suppl. 2), 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalheiro, E.A.; Silva, D.F.; Turski, W.A.; Calderazzo-Filho, L.S.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Turski, L. The susceptibility of rats to pilocarpine-induced seizures is age-dependent. Brain Res. 1987, 465, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covolan, L.; Mello, L.E. Temporal profile of neuronal injury following pilocarpine or kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 39, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, R.; Kubová, H.; Suchomelová, L.; Haugvicová, R. Lithium/pilocarpine status epilepticus-induced neuropathology of piriform cortex and adjoining structures in rats is age-dependent. Physiol. Res. 2003, 52, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druga, R.; Mares, P.; Otáhal, J.; Kubová, H. Degenerative neuronal changes in the rat thalamus induced by status epilepticus at different developmental stages. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 63, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubova, H.; Druga, R.; Haugvicová, R.; Suchomelová, L.; Pitkanen, A. Dynamic changes of status epilepticus-induced neuronal degeneration in the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus during postnatal development of the rat. Epilepsia 2002, 43 (Suppl. 5), 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubova, H.; Druga, R.; Lukasiuk, K.; Suchomelová, L.; Haugvicová, R.; Jirmanová, I.; Pitkänen, A. Status epilepticus causes necrotic damage in the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus in immature rats. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Mello, L.M.; Schwarz, M.; Turski, L. Seizures produced by pilocarpine in mice: A behavioral, electroencephalographic and morphological analysis. Brain Res. 1984, 321, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Schwarz, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Kleinrok, Z.; Turski, L. Limbic seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: Behavioural, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study. Behav. Brain Res. 1983, 9, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, K.W.; Hardman, C.; Paxinos, G. The claustrum is not missing from all monotreme brains. Brain Behav. Evol. 2004, 64, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, R. The claustrum of the cat (Felis domestica). Folia Morphol. 1966, 14, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Druga, R.; Salaj, M.; Barinka, F.; Edelstein, L.; Kubová, H. Calretinin immunoreactivity in the claustrum of the rat. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelstein, L.R.; Denaro, F.J. The claustrum: A historical review of its anatomy, physiology, cytochemistry and functional significance. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 675–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narkiewicz, O. Degenerations in the Claustrum after Regional Neocortical Ablations in the Cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1964, 123, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druga, R. The structure and connections of the claustrum. In The Claustrum. Structural, Functional and Clinical Neuroscience; Edelstein, L.R., Smythies, J.R., Ramachandran, V.S., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 29–84. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, L.; Legaz, I.; González, G.; De Castro, F.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Puelles, L. Expression of Dbx1, Neurogenin 2, Semaphorin 5A, Cadherin 8, and Emx1 distinguish ventral and lateral pallial histogenetic divisions in the developing mouse claustroamygdaloid complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 474, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, L.; Kuwana, E.; Puelles, E.; Bulfone, A.; Shimamura, K.; Keleher, J.; Smiga, S.; Rubenstein, J.L. Pallial and subpallial derivatives in the embryonic chick and mouse telencephalon, traced by the expression of the genes Dlx-2, Emx-1, Nkx-2.1, Pax-6, and Tbr-1. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 424, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davila, J.C.; Real, M.A.; Olmos, J.L.; Legaz, I.; Medina, L.; Guirado, S. Embryonic and postnatal development of GABA, calbindin, calretinin, and parvalbumin in the mouse claustral complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 481, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, R.; Chen, S.; Bentivoglio, M. Parvalbumin and calbindin in the rat claustrum: An immunocytochemical study combined with retrograde tracing frontoparietal cortex. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1993, 6, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, S.; Real, M.A.; Olmos, J.L.; Dávila, J.C. Distinct types of nitric oxide-producing neurons in the developing and adult mouse claustrum. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 465, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowianski, P.; Moryś, J.M.; Wójcik, S.; Dziewiatkowski, J.; Luczyńska, A.; Spodnik, E.; Timmermans, J.P.; Moryś, J. Neuropeptide-containing neurons in the endopiriform region of the rat: Morphology and colocalization with calcium-binding proteins and nitric oxide synthase. Brain Res. 2004, 996, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowianski, P.; Timmermans, J.P.; Morys, J. Differentiation in the immunocytochemical features of intrinsic and cortically projecting neurons in the rat claustrum—Combined immunocytochemical and axonal transport study. Brain Res. 2001, 905, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real, M.A.; Davila, J.C.; Guirado, S. Expression of calcium-binding proteins in the mouse claustrum. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003, 25, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowianski, P.; Dziewiatkowski, J.; Moryś, J.M.; Majak, K.; Wójcik, S.; Edelstein, L.R.; Lietzau, G.; Moryś, J. Colocalization of neuropeptides with calcium-binding proteins in the claustral interneurons during postnatal development of the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, S.R.; Sullivan, K.E.; Kendrick, R.M.; Marriott, B.; Wang, L.; Clements, J.; Lemire, A.L.; Jackson, J.; Cembrowski, M.S. Spatially patterned excitatory neuron subtypes and projections of the claustrum. Elife 2021, 10, e68967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Obst-Pernberg, K.; Medina, L.; Redies, C. Expression of R-cadherin and N-cadherin by cell groups and fiber tracts in the developing mouse forebrain: Relation to the formation of functional circuits. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 505–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, T.; Kollmar, R.; Ramzaoui, A.; Stewart, M.; Orman, R. Differential distribution of inhibitory neuron types in subregions of claustrum and dorsal endopiriform nucleus of the short-tailed fruit bat. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 1615–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narkiewicz, O.; Mamos, L. Relation of the insular claustrum to the neocortex in Insectivora. J. Hirnforsch. 1990, 31, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, B.N.; Caprioli, R.M.; Deutch, A.Y. Proteomic analysis illuminates a novel structural definition of the claustrum and insula. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majak, K.; Kowiánski, P.; Morýs, J.; Spodnik, J.; Karwacki, Z.; Wisniewski, H.M. The limbic zone of the rabbit and rat claustrum: A study of the claustrocingulate connections based on the retrograde axonal transport of fluorescent tracers. Anat. Embryol. 2000, 201, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minciacchi, D.; Molinari, M.; Bentivoglio, M.; Macchi, G. The organization of the ipsi- and contralateral claustrocortical system in rat with notes on the bilateral claustrocortical projections in cat. Neuroscience 1985, 16, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druga, R. Cortico-claustral connections. II. Connections from the parietal, temporal and occipital cortex to the claustrum. Folia Morphol. 1968, 16, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sherk, H.; LeVay, S. Contribution of the cortico-claustral loop to receptive field properties in area 17 of the cat. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, F.C.; Koch, C. What is the function of the claustrum? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Sugai, T.; Yoshimura, H.; Onoda, N. Convergence of olfactory and gustatory connections onto the endopiriform nucleus in the rat. Neuroscience 2004, 126, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majak, K.; Morys, J. Endopiriform nucleus connectivities: The implications for epileptogenesis and epilepsy. Folia Morphol. 2007, 66, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Majak, K.; Pikkarainen, M.; Kemppainen, S.; Jolkkonen, E.; Pitkänen, A. Projections from the amygdaloid complex to the claustrum and the endopiriform nucleus: A Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin study in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 451, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, W.H.; Haberly, L.B. Kindling-induced epileptiform potentials in piriform cortex slices originate in the underlying endopiriform nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y.; Tremblay, E.; Ottersen, O.P. Injections of kainic acid into the amygdaloid complex of the rat: An electrographic, clinical and histological study in relation to the pathology of epilepsy. Neuroscience 1980, 5, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperk, G.; Lassmann, H.; Baran, H.; Kish, S.J.; Seitelberger, F.; Hornykiewicz, O. Kainic acid induced seizures: Neurochemical and histopathological changes. Neuroscience 1983, 10, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmued, L.C.; Hopkins, K.J. Fluoro-Jade B: A high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res. 2000, 874, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, A.J.; Mott, D.D. Functional neuroanatomy of amygdalohippocampal interconnections and their role in learning and memory. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 797–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real, M.A.; Davila, J.C.; Guirado, S. Immunohistochemical localization of the vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT2 in the developing and adult mouse claustrum. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2006, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Matney, C.J.; Roth, R.H.; Brown, S.P. Synaptic Organization of the Neuronal Circuits of the Claustrum. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behan, M.; Haberly, L.B. Intrinsic and efferent connections of the endopiriform nucleus in rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 408, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, R.; Haberly, L.B.; Jackson, M.B. Voltage imaging of epileptiform activity in slices from rat piriform cortex: Onset and propagation. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 80, 2727–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, G.F.; Haberly, L.B. Deep neurons in piriform cortex. II. Membrane properties that underlie unusual synaptic responses. J. Neurophysiol. 1989, 62, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, R.; Haberly, L.B.; Jackson, M.B. Epileptiform discharges with in-vivo-like features in slices of rat piriform cortex with longitudinal association fibers. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Matney, C.J.; Roth, R.H.; Brown, S.P. Organization and development of corticocortical associative neurons expressing the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 466, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Kojima, M.; Ishida, M. Area- and lamina-specific organization of a neuronal subpopulation defined by expression of latexin in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 1999, 88, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Nihonmatsu, I.; Hatanaka, Y. Localization of latexin-immunoreactive neurons in the adult cat cerebral cortex and claustrum/endopiriform formation. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, Y.; Nihonmatsu, I.; Hirata, K.; Takiguchi-Hayashi, K. Cogeneration of neurons with a unique molecular phenotype in layers V and VI of widespread lateral neocortical areas in the rat. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubova, H.; Mares, P. Are morphologic and functional consequences of status epilepticus in infant rats progressive? Neuroscience 2013, 235, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, R.; Shin, D.H.; Liu, H.; Mazarati, A.; Pereira de Vasconcelos, A.; Wasterlain, C.G. Patterns of status epilepticus-induced neuronal injury during development and long-term consequences. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8382–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scantlebury, M.H.; Heida, J.G.; Hasson, H.J.; Velísková, J.; Velísek, L.; Galanopoulou, A.S.; Moshé, S.L. Age-dependent consequences of status epilepticus: Animal models. Epilepsia 2007, 48 (Suppl. 2), 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrotti, A.; Mazzocchetti, C. Epilepsy: Timely treatment of refractory convulsive status epilepticus. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klitgaard, H.; Matagne, A.; Vanneste-Goemaere, J.; Margineanu, D.G. Pilocarpine-induced epileptogenesis in the rat: Impact of initial duration of status epilepticus on electrophysiological and neuropathological alterations. Epilepsy Res. 2002, 51, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarati, A.M.; Baldwin, R.A.; Sankar, R.; Wasterlain, C.G. Time-dependent decrease in the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs during the course of self-sustaining status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1998, 814, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torolira, D.; Suchomelova, L.; Wasterlain, C.G.; Niquet, J. Phenobarbital and midazolam increase neonatal seizure-associated neuronal injury. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubova, H.; Mares, P.; Suchomelová, L.; Brozek, G.; Druga, R.; Pitkänen, A. Status epilepticus in immature rats leads to behavioural and cognitive impairment and epileptogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Druga, R.; Mares, P.; Salaj, M.; Kubova, H. Degenerative Changes in the Claustrum and Endopiriform Nucleus after Early-Life Status Epilepticus in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021296
Druga R, Mares P, Salaj M, Kubova H. Degenerative Changes in the Claustrum and Endopiriform Nucleus after Early-Life Status Epilepticus in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021296
Chicago/Turabian StyleDruga, Rastislav, Pavel Mares, Martin Salaj, and Hana Kubova. 2024. "Degenerative Changes in the Claustrum and Endopiriform Nucleus after Early-Life Status Epilepticus in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021296







