Diabetic Vasculopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Characteristics of Diabetic Vasculopathy in CVD
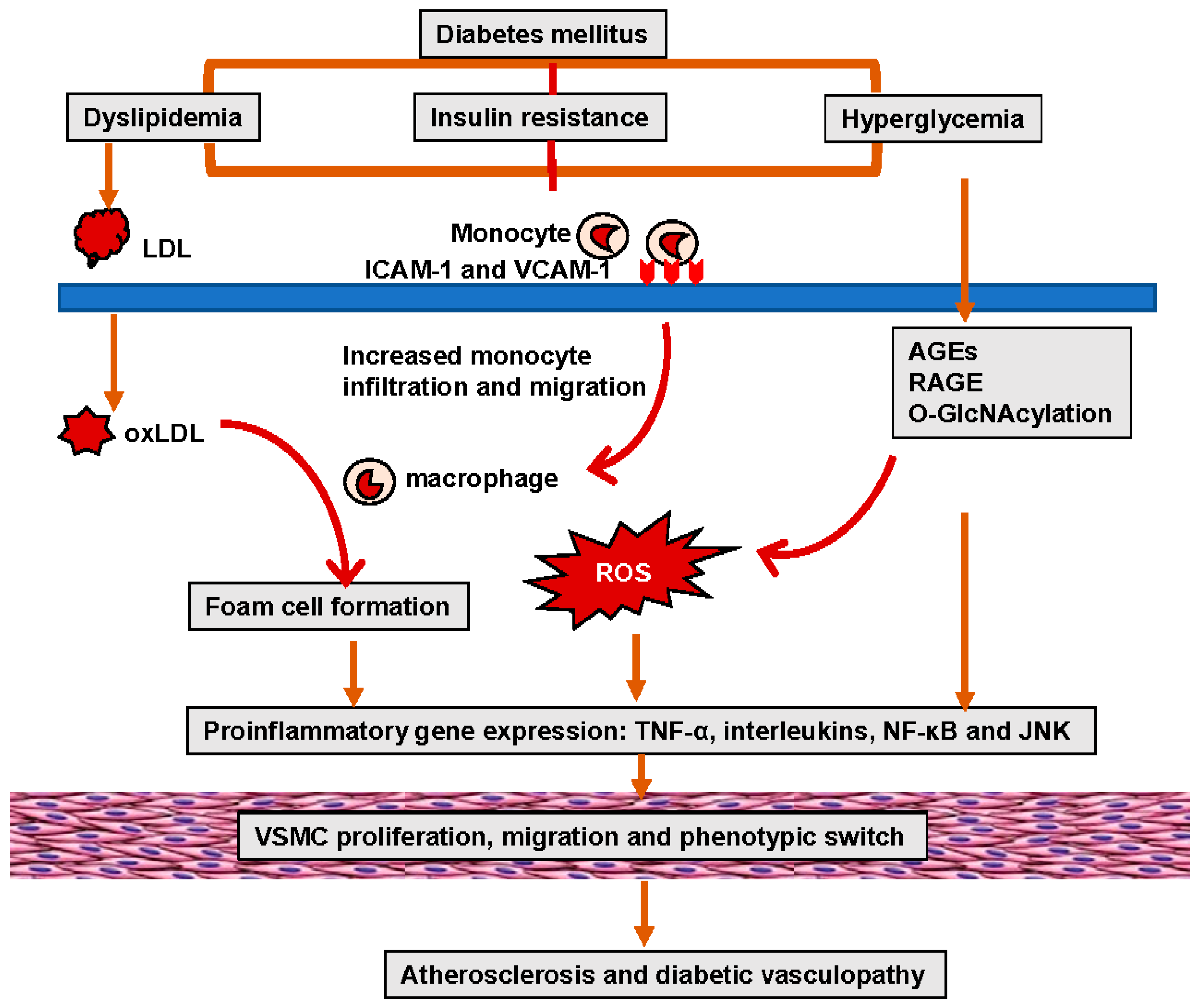
2.1. Atherosclerosis
2.2. CAD
2.3. Hypertension
2.4. PAD
3. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Vasculopathy
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Vasculopathy
4.1. Role of Renin Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS)
4.2. Mitochondria Dysfunction and Excessive Oxidative Stress
4.3. Inflammation
4.4. Dyslipidemia
4.5. Thrombosis
4.6. Endothelial Progenitor Cell (EPC) Dysfunction
4.7. Gut Dysbiosis
4.8. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Their microRNAs (miRs)
5. Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetic Vasculopathy
5.1. Lifestyle Management
5.2. Glycemic Control
5.3. Cardiovascular Drugs
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Mechanisms Contributing to This Clinical Entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.J.; Deedwania, P.; Acharya, T.; Aguilar, D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Chyun, D.A.; Di Palo, K.E.; Golden, S.H.; Sperling, L.S.; American Heart Association Diabetes Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; et al. Comprehensive Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e722–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juutilainen, A.; Lehto, S.; Ronnemaa, T.; Pyorala, K.; Laakso, M. Similarity of the impact of type 1 and type 2 diabetes on cardiovascular mortality in middle-aged subjects. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standl, E.; Balletshofer, B.; Dahl, B.; Weichenhain, B.; Stiegler, H.; Hormann, A.; Holle, R. Predictors of 10-year macrovascular and overall mortality in patients with NIDDM: The Munich General Practitioner Project. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keech, A.; Simes, R.J.; Barter, P.; Best, J.; Scott, R.; Taskinen, M.R.; Forder, P.; Pillai, A.; Davis, T.; Glasziou, P.; et al. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomaa, V.; Riley, W.; Kark, J.D.; Nardo, C.; Folsom, A.R. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and fasting glucose and insulin concentrations are associated with arterial stiffness indexes. The ARIC Study. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Circulation 1995, 91, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl-Jorgensen, K.; Larsen, J.R.; Hanssen, K.F. Atherosclerosis in childhood and adolescent type 1 diabetes: Early disease, early treatment? Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Vassy, J.L.; Ho, Y.L.; Song, R.J.; Gagnon, D.R.; Cho, K.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Phillips, L.S. Diabetes Mellitus-Related All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in a National Cohort of Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valensi, P.; Prevost, G.; Schnell, O.; Standl, E.; Ceriello, A. Targets for blood glucose: What have the trials told us. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.; O’Leary, D.H.; Zaccaro, D.; Haffner, S.; Rewers, M.; Hamman, R.; Selby, J.V.; Saad, M.F.; Savage, P.; Bergman, R. Insulin sensitivity and atherosclerosis. The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS) Investigators. Circulation 1996, 93, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomaa, B.; Almgren, P.; Tuomi, T.; Forsen, B.; Lahti, K.; Nissen, M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Groop, L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.M.; Lehto, S.; Ronnemaa, T.; Pyorala, K.; Laakso, M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B.; McGee, D.L. Diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors: The Framingham study. Circulation 1979, 59, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnohr, P.; Lange, P.; Scharling, H.; Jensen, J.S. Long-term physical activity in leisure time and mortality from coronary heart disease, stroke, respiratory diseases, and cancer. The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2006, 13, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajunen, P.; Taskinen, M.R.; Nieminen, M.S.; Syvanne, M. Angiographic severity and extent of coronary artery disease in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, S.L.; Lin, F.; Roberts, W.C. Composition of atherosclerotic plaques in the epicardial coronary arteries in juvenile (type I) diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 70, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaberi, R.; Schuijf, J.D.; Boersma, E.; Kroft, L.J.; Pereira, A.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Scholte, A.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Bax, J.J. Differences in atherosclerotic plaque burden and morphology between type 1 and 2 diabetes as assessed by multislice computed tomography. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, A.; Lacko, D.; Huttl, A.; Csobay-Novak, C.; Csavajda, A.; Sotonyi, P.; Merkely, B.; Nemes, B.; Ruzsa, Z. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Early Clinical Outcome and Stent Restenosis after Carotid Artery Stenting. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 4196195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Astor, B.C.; Stevens, L.A.; Coresh, J. Chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and hypertension: What’s in a name? Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, C.E.; Hansen, K.W.; Pedersen, M.M.; Christensen, C.K. Renal factors influencing blood pressure threshold and choice of treatment for hypertension in IDDM. Diabetes Care 1991, 14 (Suppl. 4), 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithovius, R.; Harjutsalo, V.; Mutter, S.; Gordin, D.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study, G. Resistant Hypertension and Risk of Adverse Events in Individuals With Type 1 Diabetes: A Nationwide Prospective Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hypertension in Diabetes Study Group. Prevalence of hypertension in newly presenting type 2 diabetic patients and the association with risk factors for cardiovascular and diabetic complications. J. Hypertens. 1993, 11, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S. Cardiovascular disease risk factors, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the Framingham Heart Study. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2010, 20, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; McAlister, F.A.; Walker, R.L.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Campbell, N.R. Cardiovascular outcomes in framingham participants with diabetes: The importance of blood pressure. Hypertension 2011, 57, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swislocki, A.L.; Hoffman, B.B.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in patients with hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1989, 2, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Spiering, W.; de Jong, P.A.; Bots, M.L.; Westerink, J.; SMART Study Group. Arterial stiffness as a risk factor for cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaze, A.D.; Musani, S.K.; Bidulescu, A.; Correa, A.; Bertoni, A.G.; Ahima, R.S.; Golden, S.H.; Abdalla, M.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Plasma Leptin and Blood Pressure Progression in Blacks: The Jackson Heart Study. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.M.; Valdez, R.; Morales, P.A.; Mitchell, B.D.; Hazuda, H.P.; Stern, M.P. Greater effect of glycemia on incidence of hypertension in women than in men. Diabetes Care 1992, 15, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Hiatt, W.R. Peripheral arterial disease in patients with diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.G.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; Aboyans, V.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; Norman, P.E.; Sampson, U.K.; Williams, L.J.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.D.; Langenberg, C.; Rapsomaniki, E.; Denaxas, S.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Gale, C.P.; Deanfield, J.; Smeeth, L.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1.9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, J.S.; Katz, R.; Weisman, S.; Conte, M. Gender-specific risk factors for peripheral artery disease in a voluntary screening population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, E.; Heinke, P.; Reindel, J.; Kohnert, K.D.; Kairies, U.; Braun, J.; Eckel, L.; Kerner, W. Peripheral arterial disease in diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2: Are there different risk factors? Vasa 2002, 31, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, A.; Peter, O.A.; Cocoi, M.; Serban, A.; Mot, S.; Dadarlat-Pop, A.; Nemes, A.; Ruzsa, Z. Correlation between Coronary Artery Disease with Other Arterial Systems: Similar, Albeit Separate, Underlying Pathophysiologic Mechanisms. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, A.; Stanek, A.; Homorodean, C.; Spinu, M.; Onea, H.L.; Lazar, L.; Marc, M.; Ruzsa, Z.; Olinic, D.M. Approaches to Peripheral Artery Disease in Diabetes: Are There Any Differences? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Cederholm, J.; Nilsson, P.M.; Zethelius, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Gudbjornsdottir, S.; Eliasson, B. New aspects of HbA1c as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes: An observational study from the Swedish National Diabetes Register (NDR). J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, K.; Fecka, I.; Scheijen, J.; Ahles, S.; Vangrieken, P.; Schalkwijk, C.G. A Citrus and Pomegranate Complex Reduces Methylglyoxal in Healthy Elderly Subjects: Secondary Analysis of a Double-Blind Randomized Cross-Over Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.I. Role of Advanced Glycation Endproduct (AGE)-Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproduct (RAGE) Axis in Cardiovascular Disease and Its Therapeutic Intervention. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saku, K.; Tahara, N.; Takaseya, T.; Otsuka, H.; Takagi, K.; Shojima, T.; Shintani, Y.; Zaima, Y.; Kikusaki, S.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Pathological Role of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products in Calcified Aortic Valve Stenosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, N.; Feng, B.; Breton-Romero, R.; Inagaki, E.; Weisbrod, R.M.; Fetterman, J.L.; Hamburg, N.M. O-GlcNAcylation Mediates Glucose-Induced Alterations in Endothelial Cell Phenotype in Human Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byon, C.H.; Kim, S.W. Regulatory Effects of O-GlcNAcylation in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells on Diabetic Vasculopathy. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2020, 9, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Vascular endothelial mineralocorticoid receptors and epithelial sodium channels in metabolic syndrome and related cardiovascular disease. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2023, 71, e230066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobellis, G. Epicardial fat links obesity to cardiovascular diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 78, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, R.B.; Dahlof, B.; Gerdts, E.; Boman, K.; Nieminen, M.S.; Papademetriou, V.; Rokkedal, J.; Harris, K.E.; Edelman, J.M.; Wachtell, K. Regression of hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy by losartan compared with atenolol: The Losartan Intervention for Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension (LIFE) trial. Circulation 2004, 110, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study, I.; Yusuf, S.; Sleight, P.; Pogue, J.; Bosch, J.; Davies, R.; Dagenais, G. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilay, J.I.; Davis, B.R.; Cutler, J.A.; Pressel, S.L.; Whelton, P.K.; Basile, J.; Margolis, K.L.; Ong, S.T.; Sadler, L.S.; Summerson, J.; et al. Fasting glucose levels and incident diabetes mellitus in older nondiabetic adults randomized to receive 3 different classes of antihypertensive treatment: A report from the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, N.S.; McMurray, J.J.; Holman, R.R.; Haffner, S.M.; Bethel, M.A.; Holzhauer, B.; Hua, T.A.; Belenkov, Y.; Boolell, M.; Buse, J.B.; et al. Effect of valsartan on the incidence of diabetes and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1477–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, J.; Chen, D.; Hulse, J.L.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R.; Jia, G. Targeting mineralocorticoid receptors in diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R253–R262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, V.G.; Habibi, J.; Jia, G.; Aroor, A.R.; Ramirez-Perez, F.I.; Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Bender, S.B.; Garro, M.; Hayden, M.R.; Sun, Z.; et al. Low-Dose Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blockade Prevents Western Diet-Induced Arterial Stiffening in Female Mice. Hypertension 2015, 66, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, J.R.; Habibi, J.; Aroor, A.R.; Yang, Y.; Lastra, G.; Hill, M.A.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Jaisser, F.; Jia, G. Epithelial sodium channels in endothelial cells mediate diet-induced endothelium stiffness and impaired vascular relaxation in obese female mice. Metabolism 2019, 99, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Habibi, J.; Aroor, A.R.; Hill, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Jaisser, F.; Sowers, J.R. Epithelial Sodium Channel in Aldosterone-Induced Endothelium Stiffness and Aortic Dysfunction. Hypertension 2018, 72, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Aroor, A.R.; Ramirez-Perez, F.I.; Jia, G.; Habibi, J.; DeMarco, V.G.; Barron, B.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Nistala, R.; Sowers, J.R. Amiloride Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Vascular Stiffness in Female Mice Fed a Western Diet. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Habibi, J.; Aroor, A.R.; Hill, M.A.; DeMarco, V.G.; Lee, L.E.; Ma, L.; Barron, B.J.; Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Enhanced endothelium epithelial sodium channel signaling prompts left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in obese female mice. Metabolism 2018, 78, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ouweland, J.M.; Lemkes, H.H.; Ruitenbeek, W.; Sandkuijl, L.A.; de Vijlder, M.F.; Struyvenberg, P.A.; van de Kamp, J.J.; Maassen, J.A. Mutation in mitochondrial tRNA(Leu)(UUR) gene in a large pedigree with maternally transmitted type II diabetes mellitus and deafness. Nat. Genet. 1992, 1, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S. Body mass index, diabetes, and C-reactive protein among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, A.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Tracy, R.P.; Haffner, S.M.; Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis, S. Elevated levels of acute-phase proteins and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 predict the development of type 2 diabetes: The insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, C.; Hanley, A.J.; Haffner, S.M. Differential white cell count and incident type 2 diabetes: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaishi-Okano, R.; Yamasaki, Y.; Katakami, N.; Ohtoshi, K.; Gorogawa, S.; Kuroda, A.; Matsuhisa, M.; Kosugi, K.; Nishikawa, N.; Kajimoto, Y.; et al. Elevated C-reactive protein associates with early-stage carotid atherosclerosis in young subjects with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageno, W.; Becattini, C.; Brighton, T.; Selby, R.; Kamphuisen, P.W. Cardiovascular risk factors and venous thromboembolism: A meta-analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, K.Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Chen, H.J.; Liao, W.C.; Ho, W.C. Type 1 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism: A retrospective population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postula, M.; Janicki, P.K.; Rosiak, M.; Przybylkowski, A.; Kaplon-Cieslicka, A.; Grygorowicz, T.; Trzepla, E.; Filipiak, K.J.; Czlonkowski, A.; Opolski, G. Association of plasma concentrations of salicylic acid and high on ASA platelet reactivity in type 2 diabetes patients. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.J.; Sobel, B.E. PAI-1 and diabetes: A journey from the bench to the bedside. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruknudin, P.; Nazari, A.R.; Wirth, M.; Lahaie, I.; Bajon, E.; Rivard, A.; Chemtob, S.; Desjarlais, M. Novel Function of Nogo-A as Negative Regulator of Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenic Activity: Impact in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulwas, A.; Drela, E.; Jundzill, W.; Goralczyk, B.; Ruszkowska-Ciastek, B.; Rosc, D. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenic factors in diabetes complicated diabetic foot and without foot complications. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, L.; Lazarevic, V.; Derrien, M.; Everard, A.; Van Roye, M.; Knauf, C.; Valet, P.; Girard, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Francois, P.; et al. Altered gut microbiota and endocannabinoid system tone in obese and diabetic leptin-resistant mice: Impact on apelin regulation in adipose tissue. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Spor, A.; Felin, J.; Fak, F.; Stombaugh, J.; Tremaroli, V.; Behre, C.J.; Knight, R.; Fagerberg, B.; Ley, R.E.; et al. Human oral, gut, and plaque microbiota in patients with atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, V.; Su, J.; Hsu, A.; Gross, G.J.; Salzman, N.H.; Baker, J.E. Intestinal Microbial Metabolites Are Linked to Severity of Myocardial Infarction in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Santisteban, M.M.; Rodriguez, V.; Li, E.; Ahmari, N.; Carvajal, J.M.; Zadeh, M.; Gong, M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; et al. Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsar, B.; Vaziri, N.D.; Aslan, G.; Tarim, K.; Kanbay, M. Gut hormones and gut microbiota: Implications for kidney function and hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 10, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, H.; Du, H.; Yu, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Enterococcus faecalis contributes to hypertension and renal injury in Sprague-Dawley rats by disturbing lipid metabolism. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Meng, W.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ren, K.; Du, R.; et al. Cell-Derived Microparticles in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, D.W.; Noren Hooten, N.; Eitan, E.; Green, J.; Mode, N.A.; Bodogai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lehrmann, E.; Zonderman, A.B.; Biragyn, A.; et al. Altered Extracellular Vesicle Concentration, Cargo, and Function in Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Ni, Y. Circulating level of microparticles and their correlation with arterial elasticity and endothelium-dependent dilation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Tandon, N.N.; Nakamura, T.; Cone, J.; Fukuhara, S.; Kambayashi, J. High-shear-stress-induced activation of platelets and microparticles enhances expression of cell adhesion molecules in THP-1 and endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2001, 158, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Wang, H.; Przybilla, D.; Franklin, B.S.; Dolf, A.; Pfeifer, P.; Schmitz, T.; Flender, A.; Endl, E.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Vascular endothelial microparticles-incorporated microRNAs are altered in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Ammar, H.M.; Zhang, P.; Guo, R.; Liu, H.; Cheng, C.; Koroscil, T.M.; Chen, Y.; et al. The effects of microvesicles on endothelial progenitor cells are compromised in type 2 diabetic patients via downregulation of the miR-126/VEGFR2 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E828–E837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, J.R.; Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Insights and Vascular Mechanisms. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z. Effect of metformin on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with coronary artery diseases: A systematic review and an updated meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colca, J.R.; Tanis, S.P.; Kletzien, R.F.; Finck, B.N. Insulin sensitizers in 2023: Lessons learned and new avenues for investigation. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scirica, B.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Braunwald, E.; Steg, P.G.; Davidson, J.; Hirshberg, B.; Ohman, P.; Frederich, R.; Wiviott, S.D.; Hoffman, E.B.; et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Cannon, C.P.; Heller, S.R.; Nissen, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Bakris, G.L.; Perez, A.T.; Fleck, P.R.; Mehta, C.R.; Kupfer, S.; et al. Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.B.; Bethel, M.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; Buse, J.B.; Engel, S.S.; Garg, J.; Josse, R.; Kaufman, K.D.; Koglin, J.; Korn, S.; et al. Effect of Sitagliptin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Perkovic, V.; Johansen, O.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Kahn, S.E.; Marx, N.; Alexander, J.H.; Pencina, M.; Toto, R.D.; Wanner, C.; et al. Effect of Linagliptin vs Placebo on Major Cardiovascular Events in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk: The CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Kahn, S.E.; Johansen, O.E.; Zinman, B.; Espeland, M.A.; Woerle, H.J.; Pfarr, E.; Keller, A.; Mattheus, M.; Baanstra, D.; et al. Effect of Linagliptin vs Glimepiride on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: The CAROLINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Kober, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Orsted, D.D.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Tornoe, K.; Zinman, B.; Buse, J.B.; Committee, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Ryden, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Furtado, R.H.M.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; et al. Comparison of the Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Prevention of Major Adverse Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2019, 139, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethel, M.A.; Patel, R.A.; Merrill, P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Mentz, R.J.; Pagidipati, N.J.; Chan, J.C.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Drexel, H.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Pataky, Z.; Seferovic, P.M.; Wanner, C. Cardiovascular outcomes trials: A paradigm shift in the current management of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prato, S. Diabetes and vascular disease: New therapeutic avenues. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2023, 154, 107247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes, A. 8. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management. Diabetes Care 2016, 39 (Suppl. 1), S60–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignone, M.; Alberts, M.J.; Colwell, J.A.; Cushman, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Mukherjee, D.; Rosenson, R.S.; Williams, C.D.; Wilson, P.W.; Kirkman, M.S.; et al. Aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular events in people with diabetes: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association, a scientific statement of the American Heart Association, and an expert consensus document of the American College of Cardiology Foundation. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2011. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. S1), S11–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2013. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. S1), S11–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ 1998, 317, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, L.F.; Dixon, D.L.; Wohlford, G.F.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Baker, W.L.; Van Tassell, B.W. Effect of intensive blood pressure control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 9 years of follow-up: A subgroup analysis of high-risk ACCORDION trial participants. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, G.; Bai, H.; Mather, B.; Hill, M.A.; Jia, G.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic Vasculopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020804
Jia G, Bai H, Mather B, Hill MA, Jia G, Sowers JR. Diabetic Vasculopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020804
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, George, Hetty Bai, Bethany Mather, Michael A. Hill, Guanghong Jia, and James R. Sowers. 2024. "Diabetic Vasculopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Insights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020804
APA StyleJia, G., Bai, H., Mather, B., Hill, M. A., Jia, G., & Sowers, J. R. (2024). Diabetic Vasculopathy: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020804





