Integrative Omics Strategies for Understanding and Combating Brown Planthopper Virulence in Rice Production: A Review
Abstract
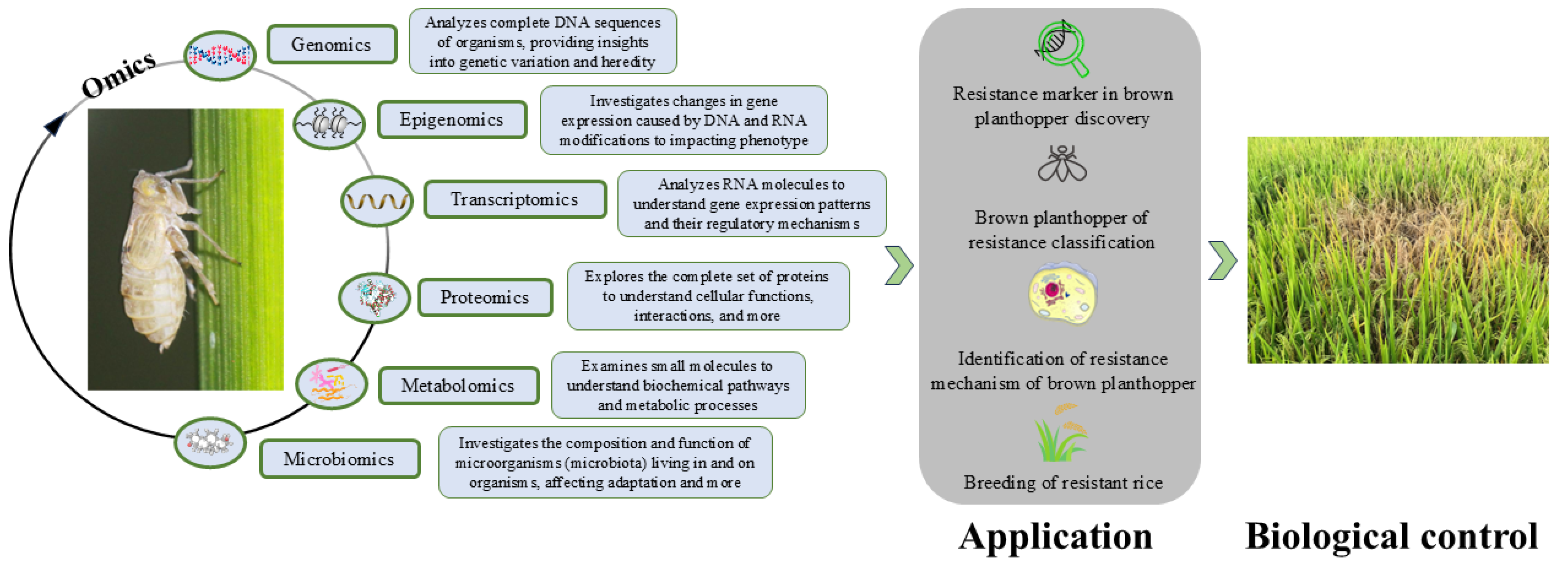
:1. Introduction
2. Genomic Characteristics and Their Applications in Evolutionary Ecology Studies
2.1. Genomic Structure and Characteristics of the BPH
2.2. Application of High-Throughput Sequencing in Population Genetics and Evolutionary Ecology Studies of the BPH
3. Transcriptomic Studies on BPH’s Response to Host Plant Defenses
3.1. Differential Gene Expression of the BPH to Resistant Rice Varieties
3.2. Non-Coding RNA Regulation of BPH Response Mechanisms to Feeding on Different Resistant Rice Varieties
4. Proteomics and Metabolomics Responses of BPHs to Resistant Rice
5. Diversities of Symbiotic Bacteria in BPHs and Their Role in Virulence
6. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Towards Understanding of Molecular Interactions between Rice and the Brown Planthopper. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Plant Health (PLH); Bragard, C.; Baptista, P.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Di Serio, F.; Gonthier, P.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; Justesen, A.F.; Magnusson, C.S.; Milonas, P.; et al. Pest Categorisation of Nilaparvata lugens. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.; Wan, P.J.; Yuan, S.Y.; Lai, F.X.; Wang, W.X.; Fu, Q. Differential Responses of OsMPKs in IR56 Rice to Two BPH Populations of Different Virulence Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Lu, H.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Jiao, B.; Tang, J. Seasonal Migration Pattern of an Important Rice Pest, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), on Hainan Island, China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, H. Biology and Epidemiology of Rice Viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sōgawa, K. The Rice Brown Planthopper: Feeding Physiology and Host Plant Interactions. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 27, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J. Rice Planthoppers in the Past Half Century in China. In Rice Planthoppers: Ecology, Management, Socio Economics and Policy; Heong, K.L., Cheng, J., Escalada, M.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-94-017-9535-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cabauatan, P.Q.; Cabunagan, R.C.; Choi, I.R. Rice Viruses Transmitted by the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. In Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability to of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Karthi, S.; Yang, H.; Li, C. A Review of Physiological Resistance to Insecticide Stress in Nilaparvata lugens. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Zhao, D.; Xue, J.; Zhang, B.Q.; Shen, Z.C.; Zhang, C.X. De Novo Intestine-Specific Transcriptome of the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Revealed Potential Functions in Digestion, Detoxification and Immune Response. Genomics 2012, 99, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ge, L.; Liu, F.; Song, Q.; Stanley, D. Pesticide-Induced Planthopper Population Resurgence in Rice Cropping Systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Peng, Y.X.; Wang, L.X.; Ye, W.N.; Pei, X.G.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.F.; Wu, S.F. Monitoring, Cross-Resistance, Inheritance, and Fitness Costs of Brown Planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens, Resistance to Pymetrozine in China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3980–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Xu, P.F.; Gong, P.-P.; Wan, H.; Li, J.H. Current Susceptibilities of Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens to Triflumezopyrim and Other Frequently Used Insecticides in China. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Xu, P.; Jin, R.; Li, Z.; Ma, K.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Resistance of Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) to Triflumezopyrim: Inheritance and Fitness Costs. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APRD Arthropod Pesticide Resistance Database. Available online: https://www.pesticideresistance.org/ (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Han, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y. Resistance to Nilaparvata lugens in Rice Lines Introgressed with the Resistance Genes Bph14 and Bph15 and Related Resistance Types. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Qin, L.; Wu, B.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Chen, C.; Ling, Y.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Q.; Huang, F.; et al. Resistance evaluation of rice variety ‘Guiyu 11’ to Nilaparvata lugens. J. South. China Agric. Univ. 2021, 42, 82–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jing, S.; Liu, B.; Peng, L.; Peng, X.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Q.; He, G. Development and Use of EST-SSR Markers for Assessing Genetic Diversity in the Brown Planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2012, 102, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Suetsugu, Y.; Kuwazaki, S.; Hattori, M.; Jairin, J.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Matsumura, M. Genetic Mapping of the Rice Resistance-Breaking Gene of the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S.; Brar, D.S. Genetics Of Resistance To Insects In Crop Plants. In Advances in Agronomy; Brady, N.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; Volume 45, pp. 223–274. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Li, S.; Feng, Q. Advances in Silkworm Studies Accelerated by the Genome Sequencing of Bombyx mori. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 513–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Pang, R.; Tian, H.; Guan, Z.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, K. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Amino Acid Auxin Permease (AAAP) Gene Family and Identification of an AAAP Gene Associated with the Growth and Reproduction of the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Insects 2021, 12, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z.-D.; Li, D.-T.; Jiang, M.-X.; Zhang, C.-X. HSP70/DNAJ Family of Genes in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens: Diversity and Function. Genes 2021, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, H.; Bamu, A.; Lin, X. Peroxisome Biogenesis Factor PEX14 Is Crucial for Survival and Fecundity of Female Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 170, 104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Qu, L.Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, L.B.; Jin, H.Y.; Xu, L.M.; Cheng, J.A.; Zhang, C.X. The Genome- and Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Innate Immunity in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Ren, Z.; Li, W.; Cai, T.; Qin, X.; Wan, H.; Jin, B.R.; He, S.; Li, J. Carboxylesterase Genes in Nitenpyram-Resistant Brown Planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Li, Y.; Xiao, T.; Sun, Z. The Metabolic Resistance of Nilaparvata lugens to Chlorpyrifos Is Mainly Driven by the Carboxylesterase CarE17. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Kong, X.D.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Qin, Q.M.; Cai, Q.N. The Key Glutathione S-Transferase Family Genes Involved in the Detoxification of Rice Gramine in Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insects 2021, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, S.-H.; Huang, X.H.; Huang, H.J.; Liu, C.W.; Zhang, C.X.; Bao, Y.Y. Genomic and Transcriptomic Insights into the Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase Gene Repertoire in the Rice Pest Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Genomics 2015, 106, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xiao, T.; Lu, K. Contribution of UDP-Glycosyltransferases to Chlorpyrifos Resistance in Nilaparvata lugens. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 190, 105321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Zhao, Y.; Du, B.; Chen, R.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Genomics of Interaction between the Brown Planthopper and Rice. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 19, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Genetic and Molecular Understanding of Host Rice Resistance and Nilaparvata lugens Adaptation. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 45, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.E.; Hackett, K.J.; Purcell-Miramontes, M.; Brown, S.J.; Evans, J.D.; Goldsmith, M.R.; Lawson, D.; Okamuro, J.; Robertson, H.M.; Schneider, D.J. Creating a Buzz about Insect Genomes. Science 2011, 331, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.X.; Yu, L.L.; Fan, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Z.R.; Zhou, W.W.; et al. Genomes of the Rice Pest Brown Planthopper and Its Endosymbionts Reveal Complex Complementary Contributions for Host Adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Hua, H.; Chen, M.; Guo, M.; He, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, F. Chromosomal-Level Genomes of Three Rice Planthoppers Provide New Insights into Sex Chromosome Evolution. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, D.T.; Zhuo, J.C.; Shen, Y.; Hu, Q.L.; Zhang, C.X. Chromosome-Level Assembly of the Brown Planthopper Genome with a Characterized Y Chromosome. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Genome Assembly in the Telomere-to-Telomere Era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; He, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; et al. A Complete Assembly of the Rice Nipponbare Reference Genome. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Tan, K.; Huang, W.; Shi, J.; Li, T.; Hu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Xin, B.; et al. A Complete Telomere-to-Telomere Assembly of the Maize Genome. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Jiao, W.; Song, Q. A Telomere-to-Telomere Gap-Free Assembly of Soybean Genome. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Deng, L.; Qu, L.; Guo, D.; Hui, R.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. A Gap-Free Reference Genome Reveals Structural Variations Associated with Flowering Time in Rapeseed (Brassica napus). Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. A Near-Complete Genome Assembly of Brassica Rapa Provides New Insights into the Evolution of Centromeres. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xing, W.; Wang, A.; Zhang, N.; Jia, L.; Ma, S.; Xia, Q. Comparison of Long-Read Methods for Sequencing and Assembly of Lepidopteran Pest Genomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, M.; Butlin, R.K. The Genetic Basis of Host Plant Adaptation in the Brown Planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). Heredity 1998, 80, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.L.; Zhuo, J.C.; Fang, G.Q.; Lu, J.B.; Ye, Y.X.; Li, D.T.; Lou, Y.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.L.; et al. The Genomic History and Global Migration of a Windborne Pest. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Gilbert, C. Endogenous Viruses: Insights into Viral Evolution and Impact on Host Biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Ye, Z.X.; Li, L.L.; Hu, Q.L.; He, Y.J.; Qi, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Lu, G.; et al. Co-Option of a Non-Retroviral Endogenous Viral Element in Planthoppers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Guan, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Balancing Selection and Wild Gene Pool Contribute to Resistance in Global Rice Germplasm against Planthopper. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1695–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, M.K. How Does Adaptation Sweep through the Genome? Insights from Long-Term Selection Experiments. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Gordon, K.H.J. Going Global—Genomic Insights into Insect Invasions. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 31, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A Revolutionary Tool for Transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.; Ravindranath, N.; Gaikwad, D.; Nanda, S. Unveiling Nilaparvata lugens Stål Genes Defining Compatible and Incompatible Interactions with Rice through Transcriptome Analysis and Gene Silencing. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6790–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, K. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal the Responses of Brown Planthoppers to RH Resistant Rice Cultivar. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1018470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guan, W.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, R.; Du, B.; Zhu, L.; et al. Combining Next-Generation Sequencing and Single-Molecule Sequencing to Explore Brown Plant Hopper Responses to Contrasting Genotypes of Japonica Rice. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Yu, H.; Fu, Q.; Chen, H.; Ye, W.; Li, S.; Lou, Y. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Salivary Glands of Two Populations of Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, That Differ in Virulence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Ji, R.; Ye, W.; Chen, H.; Lai, W.; Fu, Q.; Lou, Y. Transcriptome Analysis of Fat Bodies from Two Brown Planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) Populations with Different Virulence Levels in Rice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Su, Q.; Kang, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.-X.; Zhang, W.Q.; Pang, R. Genome-Wide Analysis of Alternative Gene Splicing Associated with Virulence in the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 2512–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.J.; Zhou, R.N.; Nanda, S.; He, J.C.; Yuan, S.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Lai, F.X.; Fu, Q. Phenotypic and Transcriptomic Responses of Two Nilaparvata lugens Populations to the Mudgo Rice Containing Bph1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Shan, J.; Gao, M.; Guo, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Du, B.; Zhu, L.; et al. Bulked Segregant RNA Sequencing Revealed Difference Between Virulent and Avirulent Brown Planthoppers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 843227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, P.; Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Shi, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Long Non-Coding (lncRNA) in Nilaparvata lugens’s Adaptability to Resistant Rice. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zha, W. Expression profiles and potential functions of circRNAs in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) analyzed by high-throughput sequencin. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2024, 67, 431–442. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Hussain, S.; et al. Characterization and Comparative Profiling of the Small RNA Transcriptomes in the Hemipteran Insect Nilaparvata lugens. Gene 2016, 595, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; You, A. Comparative iTRAQ Proteomic Profiling of Proteins Associated with the Adaptation of Brown Planthopper to Moderately Resistant vs. Susceptible Rice Varieties. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Shangguan, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Comparative Metabolomics of the Interaction between Rice and the Brown Planthopper. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, B.; Hao, F.; Lei, H.; Wan, Q.; He, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Dynamic Metabolic Responses of Brown Planthoppers towards Susceptible and Resistant Rice Plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Kang, K.; Zhang, W. Metabolic Responses of Brown Planthoppers to IR56 Resistant Rice Cultivar Containing Multiple Resistance Genes. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 113, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Yue, L.; Yuan, L.; Kang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, R.; Zhang, W. Alanine Metabolism Mediates Energy Allocation of the Brown Planthopper to Adapt to Resistant Rice. J. Adv. Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xin, Y.; Peng, Y.; Shan, J.; Zhang, N.; Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Huang, J.; Guan, W.; Shi, S.; et al. Lipidomic Analyses Reveal Enhanced Lipolysis in Planthoppers Feeding on Resistant Host Plants. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1502–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.X.; Zhu, T.H.; Lai, F.X.; Fu, Q. Diversity and Infection Frequency of Symbiotic Bacteria in Different Populations of the Rice Brown Planthopper in China. J. Entomol. Sci. 2015, 50, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Pan, H.; Wu, W.; Li, M.Y.; Yu, X.P. The Gut Bacterial Flora Associated with Brown Planthopper Is Affected by Host Rice Varieties. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Shao, Y.; Iqbal, J. Insect Insights at the Single-Cell Level: Technologies and Applications. Cells 2023, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Sun, M.; Wu, B.; Shi, S.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Leaf Sheath Cells Reveals the Mechanism of Rice Resistance to Brown Planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1200014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, A.T.; Kumar, S. Computational Methods for Annotation of Plant Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Using RNA-Seq. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-D. Non-Coding RNA: A New Frontier in Regulatory Biology. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs and Its Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The Biogenesis, Biology and Characterization of Circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Shang, R.; Sun, W.; Dou, K.; Li, H. Circular RNA: A New Star of Noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015, 365, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Julie Li, Y.S.; Huang, H.D.; Shyy, J.Y.J.; Chien, S. microRNA: A Master Regulator of Cellular Processes for Bioengineering Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvortsova, K.; Iovino, N.; Bogdanović, O. Functions and Mechanisms of Epigenetic Inheritance in Animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Palli, S.R. RNA Modifications in Insects. Front. Insect Sci. 2024, 4, 1448766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, J.; Tang, S.; Shen, X. Low METTL3 Level in Midgut of the Bombyx mori Inhibit the Proliferation of Nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Pan, J.; Zhang, M.; Yan, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. N 6-Methyladenosine Level in Silkworm Midgut/Ovary Cell Line Is Associated With Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. RNA N6 -Methyladenosine Modification Suppresses Replication of Rice Black Streaked Dwarf Virus and Is Associated with Virus Persistence in Its Insect Vector. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Du, T.; Yin, C.; Fu, B.; Huang, M.; Liang, J.; Gong, P.; Liu, S.; et al. Epitranscriptomic Regulation of Insecticide Resistance. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Lai, Y.F.; Li, F.F.; Jiao, L.; Qiao, Q.X.; Li, S.Y.; Xiang, X.J.; Liao, H.; You, M.S.; He, W.Y. Functional Characterization of Two RNA Methyltransferase Genes METTL3 and METTL14 Uncovers the Roles of m6A in Mediating Adaptation of Plutella Xylostella to Host Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, J.X.; Feng, K.; Xu, Z.-S.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in Genomic, Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Metabolomic Approaches to Study Biotic Stress in Fruit Crops. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Baldwin, I.T. New Insights into Plant Responses to the Attack from Insect Herbivores. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, B.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G. Integration of Lipidomics and Metabolomics for In-Depth Understanding of Cellular Mechanism and Disease Progression. J. Genet. Genom. 2020, 47, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harith Fadzilah, N.; Abdul-Ghani, I.; Hassan, M. Proteomics as a Tool for Tapping Potential of Entomopathogens as Microbial Insecticides. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 100, e21520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, S.P.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Uchikata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsubara, A.; Fukusaki, E. Current Metabolomics: Practical Applications. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldhaar, H.; Gross, R. Insects as Hosts for Mutualistic Bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 299, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, T.; Koga, R.; Kikuchi, Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Fukatsu, T. Wolbachia as a Bacteriocyte-Associated Nutritional Mutualist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.M.; Zheng, X.S.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, L.Z. Dynamics of Yeastlike Symbiote and Its Relationship with the Virulence of Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål, to Resistant Rice Varieties. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2004, 7, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Dong, S.Z.; Hou, Y.; Bian, Y.L.; Yang, K.; Yu, X.P. Cultivation, Identification and Quantification of One Species of Yeast-like Symbiotes, Candida, in the Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, Z.; Lizé, A. Insect Behaviour and the Microbiome. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 9, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The Gut Microbiota of Insects—Diversity in Structure and Function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E. Omics and the Metabolic Function of Insect-Microbial Symbioses. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Baweja, V.; Roy, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Singh, I.K. Molecular Rationale of Insect-Microbes Symbiosis-From Insect Behaviour to Mechanism. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frago, E.; Dicke, M.; Godfray, H.C.J. Insect Symbionts as Hidden Players in Insect-Plant Interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Lan, Y.; Sun, C.; Shao, Y. Insect Microbial Symbionts as a Novel Source for Biotechnology. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Genome Size (Mb) | Sequencing Platform | Chromosome | Scaffold N50 | Contig N50 | Protein Coding Genes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 1140 | Illumina Hiseq2000 | - | 356.6 kb | 24.2 kb | 27,571 | [34] |
| 2021 | 1087 | PacBio and Illumina PE150 | 16 | 77.63 Mb | 589.46 kb | 24,901 | [35] |
| 2021 | 955 | PacBio and ONT | 16 | 69.96 Mb | 1.01 Mb | 18,021 | [36] |
| Omics | BPH Population | Rice Variety | Key Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | 360 planthoppers from 90 geographical locations worldwide | They clarify the genetic sources of worldwide BPHs and illuminate a landscape of BPH migration showing that East Asian populations perform closed-circuit journeys between Indochina and the Far East. | [45] | |
| Transcriptomics | Susceptible: TN1 | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: PTB33 | The 1875 DEGs were identified of which many were annotated to be involved in cuticle development, sugar metabolism, detoxification, molting, and xenobiotics metabolism. | [52] |
| Susceptible: Huang Huazhan | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: RH | The DEGs identified in BPHs feeding on RH were mainly involved in energy metabolism, amino acid metabolism, hormone synthesis, and vitamin metabolism pathways. | [53] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Swarnalata | The DEGs related to BPH starvation response (Nlbmm), apoptosis and autophagy (caspase 8, ATG13, BNIP3, and IAP), active oxygen elimination (catalase, MSR, and ferritin), and detoxification (GST and CarE) were upregulated in BPHs’ responses to resistant rice. | [54] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Mudgo | Comparative analysis of the transcriptomes of the two populations revealed that the DEGs related to ‘metabolism’, ‘digestion and absorption’, and ‘salivary secretion’ might be associated with virulence. | [55] | ||
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Mudgo | The DEGs were identified in the fat bodies of the two populations, and these differentially expressed genes related to metabolism and immunity. | [56] | ||
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Mudgo | Genes encoding odorant receptor, secreted saliva protein, and xenobiotic metabolic P450 monooxygenase showed different splicing patterns between Mudgo and TN1 populations. | [57] | ||
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Mudgo | Resistant: Mudgo | Genes involved in cuticle formation, detoxification, metabolite transport, digestion, RNA processing, lipid or fatty acid metabolism, and proteolysis were significantly downregulated during the incompatible interaction, whereas genes involved in insulin signaling were significantly upregulated. | [58] | |
| Susceptible; TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | Resistant: YHY15 | Amino acid and nucleotide metabolism, the endocrine system, and signal transduction were upregulated in avirulent BPHs when they fed on YHY15 rice. | [59] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | A total of 157 differentially expressed lncRNA was identified. In metabolic-related pathways, arginine and proline metabolism, glutathione metabolism, and carbon metabolism categories were enriched 10 co-expression target genes of these lncRNAs. | [60] | ||
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | The abundance and expression level of circRNAs in YHY15 BPHs were higher than those in TN1, and 19 circRNAs have been identified as possibly involved in the autophagy process. | [61] | ||
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | The 26 miRNAs showed significantly differential expressions between two libraries. Moreover, it also determined that a majority of differential miRNAs were involved in the ’Metabolism’ pathway. | [62] | ||
| Proteomics | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | The 151 upregulated DEPs, which were involved in apoptosis metabolism, response to chemicals, response to oxygen-containing compounds, and regulation of the response to stress might be related in BPHs’ adaptation to rice resistance. | [63] | |
| Metabolomics | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | The levels of most amino acids in honeydew decreased, and the levels of succinic acid and malic acid were elevated in the BPHs of YHY15 compared with TN1. | [64] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: YHY15 | BPHs feeding on resistant plants had lower levels of amino acids, glucose, fatty acids, and TCA cycle intermediates than on the susceptible ones. The levels of these metabolites recovered after 24 h of feeding and were accompanied with increased levels of trehalose, choline metabolites, and nucleosides/nucleotides. | [65] | |
| Susceptible: Huang Huazhan | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: IR56 | BPHs feeding on IR56 plants exhibited significant decreases in concentrations of most of the detected sugars, vitamins, and some essential amino acids, but higher levels of most amides, free fatty acids, and some non-essential amino acids. | [66] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: IR36 | Resistant: IR36 | Alanine was one of the key biomarkers of BPH adaptation to the resistant rice variety IR36. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)-mediated alanine transfer to pyruvate was necessary and sufficient for the adaptation. | [67] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 | Susceptible: 9311 Resistant: NIL-Bph6, NIL-Bph9 | Insects that fed on resistant rice transformed triglyceride (TG) to phosphatidyl choline (PC) and digalactosyl diacylglycerol (DGDG), with these lipid classes showing significant alterations in fatty acid composition. | [68] | |
| Microbiomics | Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: Mudgo, ASD7, IR42, and IR56 | The composition of symbiotic bacteria within populations of different harmful brown planthopper species varies were evident, with ASD7 and Mudgo-resistant varieties having more symbiotic bacteria than the susceptible variety TN1. | [69] | |
| Susceptible: TN1 Resistant: ASD7 | Comparative analysis showed that significant differences in the profile of gut bacterial communities existed between the two BPH populations. We found the relative abundances of two subdominant phyla and two subdominant classes were significantly different. | [70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, J.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P. Integrative Omics Strategies for Understanding and Combating Brown Planthopper Virulence in Rice Production: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010981
Wang X, Wang Y, Yang H, Liu F, Cai Y, Xiao J, Fu Q, Wan P. Integrative Omics Strategies for Understanding and Combating Brown Planthopper Virulence in Rice Production: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):10981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010981
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinfeng, Yaxuan Wang, Houhong Yang, Fang Liu, Yubiao Cai, Jing Xiao, Qiang Fu, and Pinjun Wan. 2024. "Integrative Omics Strategies for Understanding and Combating Brown Planthopper Virulence in Rice Production: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 10981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010981
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Y., Yang, H., Liu, F., Cai, Y., Xiao, J., Fu, Q., & Wan, P. (2024). Integrative Omics Strategies for Understanding and Combating Brown Planthopper Virulence in Rice Production: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 10981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010981






