Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
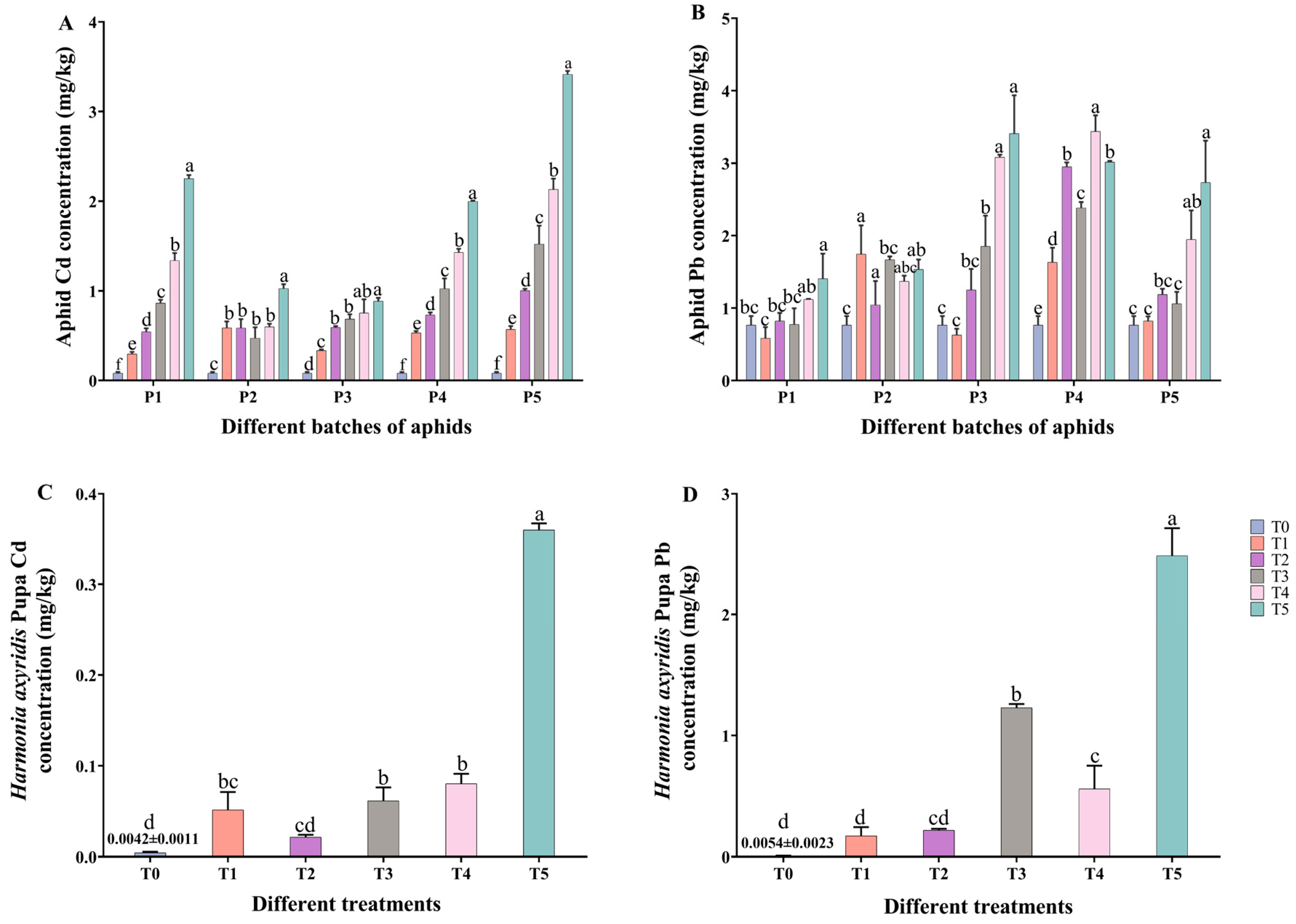
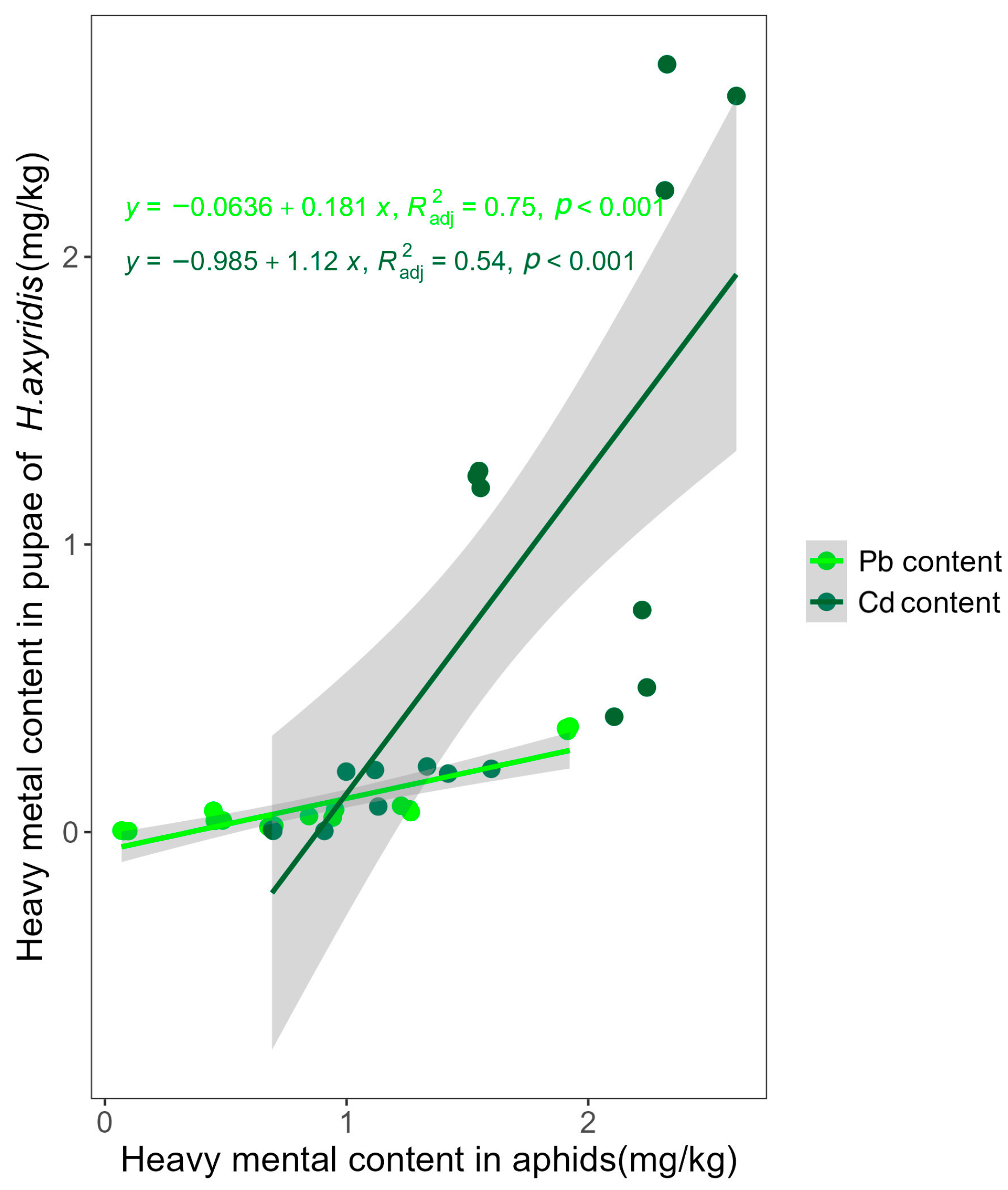
2.1. Cd, Pb Accumulation in M. crassicauda and Pupa of H. axyridis
2.2. Effect of Cd–Pb Stress on Carbohydrate Contents in Five Generations of Aphids
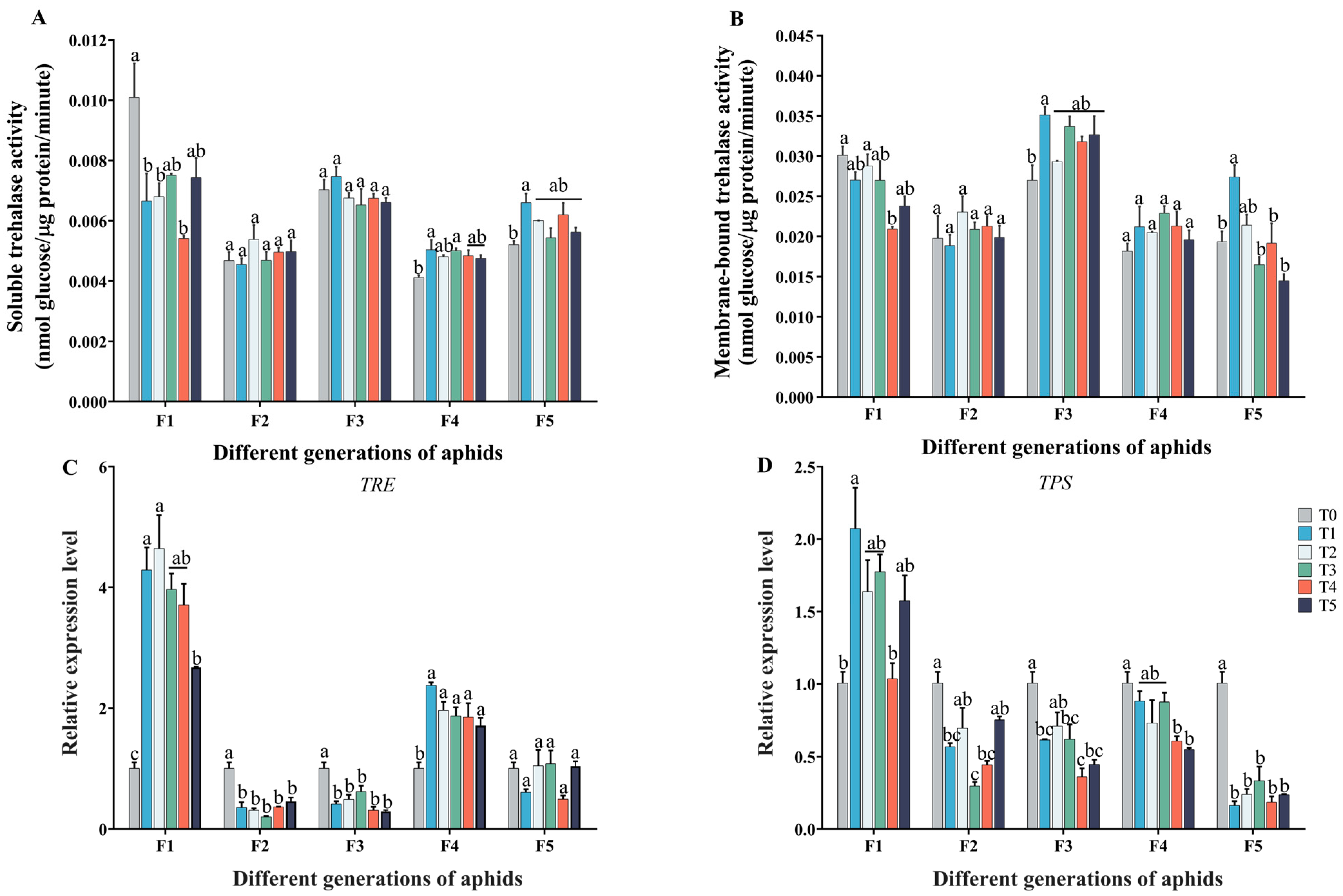
2.3. Effect of Cd–Pb Stress on Trehalose Metabolism in Five Generations of Aphids
2.4. Effects of Cd–Pb Treatment on Five Generations of Aphids’ Fertility
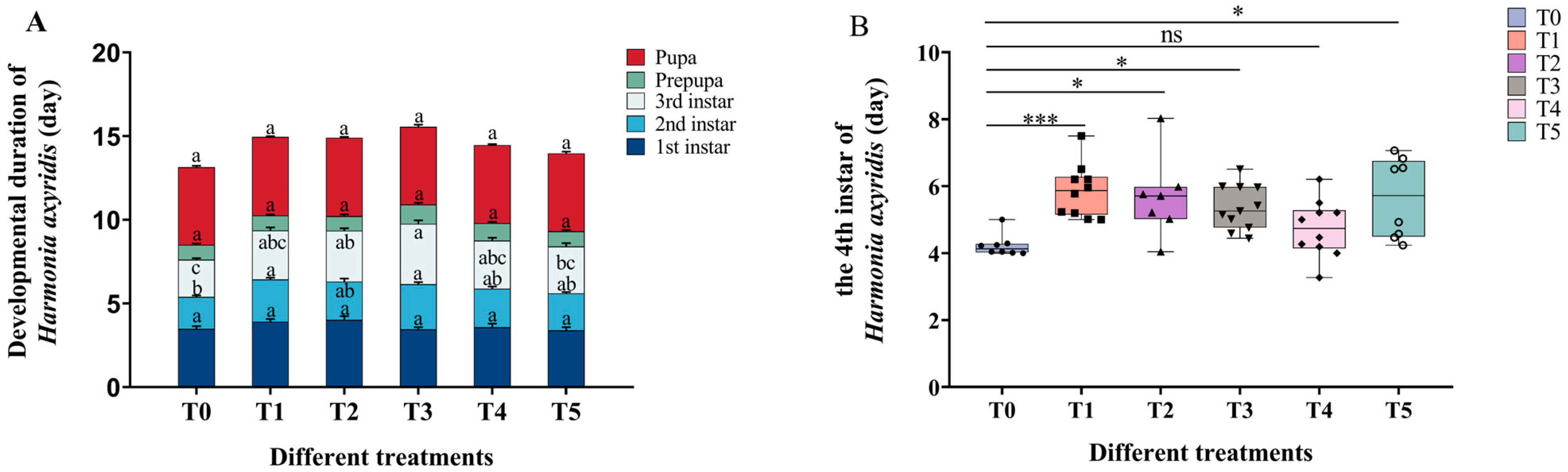
2.5. Effects of Cd–Pb Treatment on Ladybug Developmental Duration and Weight
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Determination of Heavy Metal Contents in Aphids and Ladybugs’ Pupae
4.4. Determination of Carbohydrate Content and Trehalase Activity in Aphids
4.5. Effects of Cadmium–Lead Treatment on Aphid Fecundity
4.6. Ladybug Developmental Duration, Weight
4.7. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannis, A.; Pentari, D.; Wang, J.Y.; Gidarakos, E. Application of sequential extraction analysis to electrokinetic remediation of cadmium, nickel and zinc from contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Tang, Z.; Song, J.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, P. Toxic metals and metalloids: Uptake, transport, detoxification, phytoremediation, and crop improvement for safer food. Mol. Plant. 2022, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection; Ministry of Land and Resources. National soil pollution survey bulletin. China Environ. Prot. Ind. 2014, 36, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.W.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.J. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s characteristics and speciation and environmental risks of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochars. Environ. Technol. 2022, 26, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Deng, H.; Jia, Z.M.; Wang, J.B.; Yu, F.; Zeng, Q.Q. Spatial distribution characteristics, pollution, and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals around mercury mining areas. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3018–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, M.M.; Harwood, J.D. Influence of heavy metal contamination on urban natural enemies and biological control. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2017, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Green, I.D.; Naikoo, M.I. The transfer and fate of Pb from sewage sludge amended soil in a multi-trophic food chain: A comparison with the labile elements Cd and Zn. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 16133–16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.C. Ecophysiological effects of heavy metals on insects. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2015, 58, 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.B.; Jiang, S.M.; Yan, X.P.; Qin, Z.X.; Jia, C.H.; Li, Z.B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, R.Z. The mobility of cadmium and lead in the soil-mulberry-silkworm system. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Noureldeen, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Sonne, C.; Rajakaruna, N.; Ahmad, P. Biotransfer, bioaccumulation and detoxification of nickel along the soil-faba bean-aphid-ladybird food chain. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 785, 147226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.I.; Raghib, F.; Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Hessini, K.; Ahmad, P. Uptake, accumulation and elimination of cadmium in a soil—Faba bean (Vicia faba)—Aphid (Aphis fabae)—Ladybird (Coccinella transversalis) food chain. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.I.; Green, I.D.; Naikoo, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A.; Lone, M.I. Assessment of biotransfer and bioaccumulation of cadmium, lead and zinc from fly ash amended soil in mustard-aphid-beetle food chain. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584–585, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.T.; Huang, C.S.; Chen, Z.H.; Bao, K. Distribution, ecological risk assessment, and bioavailability of cadmium in soil from Nansha, Pearl river delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, R.S.; Gautam, M.; Sengar, R.S.; Garg, S.K.; Sengar, K.; Chaudhary, R. Lead stress effects on physiobiochemical activities of higher plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 196, 73–93. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A. Lead tolerance and accumulation characteristics of Cubana Kordes rose in lead-contaminated soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tian, Y.B.; Liu, H.B.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Du, C.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, F.M. Heavy metal pollution analysis and health risk assessment of two medicinal insects of Mylabris. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2020, 200, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.H.; Noriega, F.G. Sub-lethal metal stress response of larvae of Aedes aegypti. Physiol. Entomol. 2014, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, C.; Krämer, U.; Müller, C. Heavy metal (hyper) accumulation in leaves of Arabidopsis halleri is accompanied by a reduced performance of herbivores and shifts in leaf glucosinolate and element concentrations. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 133, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Z.R.; Tariq, K.; Mavian, C.; Ali, A.; Ullah, F.; Zang, L.S.; Ali, F.; Nazir, T.; Ali, S. Trophic transfer and toxicity of heavy metals from dengue mosquito Aedes aegypti to predator dragonfly Tramea cophysa. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, B.L.; Ashraf, U.; Azad, R.; Wu, J.; Ali, S. Biotransfer of Cd along a soil-plant-mealybug-ladybird food chain: A comparison with host plants. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.M.; Ashraf, U.; Qiu, B.L.; Ali, S. Transfer of lead (Pb) in the soil-plant-mealybug-ladybird beetle food chain, a comparison between two host plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Xu, J.; Bashir, M.H.; Ali, S. Developmental responses of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri to heavy metals transferred across multi-trophic food chain. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.K.; Wang, S.S.; Pan, B.Y.; Liu, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.G.; Wang, S.; Tang, B. Effects of zinc acquired through the plant-aphid-ladybug food chain on the growth, development and fertility of Harmonia axyridis. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.S.; Si, H.R.; Wan, S.J.; Li, G.Y.; Shu, Y.H.; Dai, X.Y.; Wang, R.J.; Wang, S.G.; Zhai, Y.F.; et al. Responses of aphid and ladybird to lead transfer through soil and broad beans. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.; Qurat-Ul-Ain; Rehman, K.; Khan, M.X.; Hesselberg, T. Bioaccumulation of cadmium, lead, and zinc in agriculture-based insect food chains. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterenborg, I.; Vork, N.A.; Verkade, S.K.; van Gestel, C.A.; van Straalen, N.M. Dietary zinc reduces uptake but not metallothionein binding and elimination of cadmium in the springtail, Orchesella cincta. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.J.; Xie, Y.X.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Q.M.; Wan, S.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Wang, R.J.; Desneux, N.; Zhi, J.R.; et al. Bioaccumulation and transferreing for impacts on Cd and Pb by aphid consumption of the broad bean, Vicia faba L, in soil heavy metal pollution. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, M. Metal availability and bioconcentration in plants. In Heavy Metal Stress Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Naikoo, M.I.; Dar, M.I.; Khan, F.A.; Raghib, F.; Rajakaruna, N. Trophic transfer and bioaccumulation of lead along soil-plant-aphid-ladybird food chain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 23460–23470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, M.; Peterson, K.E.; Cantoral, A.; Song, P.X.K.; Jones, A.; Solano-González, M.; Meeker, J.D.; Basu, N.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M. Dietary predictors of urinary cadmium amng pregnant women and children. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meng, Z.J.; Yan, S.C. Effects of heavy metal (lead) stress on larval development and activity of detoxification enzymes in Lymantria dispar. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2018, 46, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Cao, H.M.; Fan, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.C.; Chen, J.X.; Chung, H.; Wei, H.Y. Bioaccumulation of cadmium affects development, mating behavior, and fecundity in the Asian Corn Borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. Insects 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilahi, I.; Yousafzai, A.M.; Ali, H. Effect of Pb, Cd and Cu on survival and development of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, T.M.Y.; Fouda, M.A.; Hassan, M.I.; Abd-Elghaphar, A.E.A.; Hasaballah, A.I. Toxicological effects of some heavy metal ions on Culex pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae). Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of copper on the development, protein and esterase isozymes of Drosophila melanogaster. Integr. Zool. 2006, 1, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, F.; Mao, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, F. Molecular cloning of the vitellogenin gene and the effects of vitellogenin protein expression on the physiology of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.L.; Tang, W.C.; Lu, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, G.R. Molecular characterization and expression pattern of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) vitellogenin, and its response to lead stress. J. Insect. Physiol. 2009, 55, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Maymó, A.C.; Sendra, M.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Garcerá, M.D. Cadmium effects on development and reproduction of Oncopeltus fasciatus (Heteroptera: Lygaeidae). J. Insect. Physiol. 2004, 50, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Maymó, A.C.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Garcerá, M.D. Vitellogenin polypeptide levels in one susceptible and one cadmium-resistant strain of Oncopeltus fasciatus (Heteroptera: Lygaeidae), and its role in cadmium resistance. J. Insect. Physiol. 2006, 52, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płachetka-Bożek, A.; Chwiałkowska, K.; Augustyniak, M. Molecular changes in vitellogenin gene of Spodoptera exigua after long-time exposure to cadmium—Toxic side effect or microevolution? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płachetka-Bożek, A.; Kafel, A.; Augustyniak, M. Reproduction and development of Spodoptera exigua from cadmium and control strains under differentiated cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.H. Lead stress affects the reproduction of Spodoptera litura but not by regulating the vitellogenin gene promoter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.K.; Primicerio, R.; Amundsen, P.A. Diversity and structure of Chironomidae (Diptera) communities along a gradient of heavy metal contamination in a subarctic watercourse. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 307, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.Q.; Yi, Y.H. Effects of dietary heavy metals on the immune and antioxidant systems of Galleria mellonella larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 167, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, A.J.; Stachowicz, I. Costs of living in metal polluted areas: Respiration rate of the ground beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus from two gradients of metal pollution. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Ding, Y.J.; Hu, Y.W.; Tang, B.; Wang, S.G. Effects of heavy metal cadmium on the trehalose metabolism in Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2019, 62, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.J.; Si, H.R.; Wang, X.Z.; Chao, L.; Ma, W.; Sun, S.S.; Tang, B.; Tan, X.L.; Wang, S.G. Regulation of Vicia faba L. Response and Its Effect on Megoura crassicauda Reproduction under Zinc Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.K.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, Q.Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.G.; Tang, B. Two novel soluble trehalase genes cloned from Harmonia axyridis and regulation of the enzyme in a rapid changing temperature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 198, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Wei, Y.; Ding, Y.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Wang, S.H.; Tang, B.; Wang, S.G. Effects of long-term cadmium exposure on trehalose metabolism, growth, and development of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.K.; Xu, C.D.; Zheng, X.S.; Chao, L.; Zhou, Y.F.; Li, G.Y.; Wu, Y.; Bai, X.L.; Zhou, T.; Tang, B.; et al. Zinc stress alters sugar content in rice plants and the reproduction and trehalose metabolism in Nilaparvata lugens. Agronomy 2023, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Chinese Soil Environmental Quality: Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB 15618-2018); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elbein, A.D.; Pan, Y.T.; Pastuszak, I.; Caroll, D. New insights on trehalose: A multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 17R–27R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.N. Trehalose—The Insect ‘Blood’ Sugar. Adv. Insect. Physiol. 2003, 31, 205–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.F.; Shi, Z.P.; Wu, J.C. Insecticide-induced enhancement of flight capacity of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop. Prot. 2011, 30, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.T.; Zhang, G.J.; Nan, J.L.; Cheng, W.N.; Zhu-Salzman, K. Characterization of trehalose metabolic genes and corresponding enzymatic activities during diapause of Sitodiplosis mosellana. J. Insect. Physiol. 2021, 135, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Quintana, A.; Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez, E.N.; Cremata, J.; Sánchez, J.C. Rapid and sensitive anthrone-sulfuric acid assay in microplate format to quantify carbohydrate in biopharmaceutical products: Method development and validation. Biologicals 2008, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Zhang, G.F.; Wan, F.H.; Ma, J. Effects of Plant Species Switching on Contents and Dynamics of Trehalose and Trehalase Activity of Bemisia tabaci B-biotype and Trialeurodes vaporariorum. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, L.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, H.J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, S.G.; Tang, B. Study on the effect of wing bud chitin metabolism and its developmental network genes in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, by knockdown of TRE gene. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Developmental Stage | Weight (mg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | Statistics | |
| 2nd instar | 1.42 ± 0.25 a | 1.42 ± 0.12 a | 1.40 ± 0.16 a | 1.23 ± 0.07 a | 1.35 ± 0.09 a | 1.31 ± 0.08 a | F5, 55 = 0.438, p = 0.820 |
| 3rd instar | 4.11 ± 0.20 a | 3.56 ± 0.23 ab | 3.11 ± 0.13 b | 3.33 ± 0.22 ab | 3.95 ± 0.14 a | 3.40 ± 0.19 ab | F5, 55 = 3.938, p = 0.004 |
| 4th instar | 11.71 ± 0.49 ab | 9.74 ± 0.48 b | 9.49 ± 0.72 b | 10.96 ± 0.64 ab | 12.80 ± 0.65 a | 10.50 ± 0.49 ab | F5, 54 = 6.078, p < 0.001 |
| Prepupa | 34.26 ± 1.28 a | 27.81 ± 1.27 bc | 25.63 ± 1.48 c | 27.05 ± 1.13 bc | 31.93 ± 1.27 ab | 29.40 ± 1.48 abc | F5, 48 = 5.704, p < 0.001 |
| Pupa | 32.46 ± 1.22 a | 25.50 ± 1.19 bc | 23.77 ± 1.30 c | 25.05 ± 1.03 bc | 29.89 ± 1.17 ab | 27.79 ± 1.40 abc | F5, 48 = 6.942, p < 0.001 |
| Adult | 27.91 ± 1.11 a | 21.61 ± 1.08 bc | 20.26 ± 1.17 c | 21.65 ± 0.99 bc | 25.72 ± 1.01 ab | 23.89 ± 1.07 abc | F5, 50 = 7.568, p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, S.; Dai, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011145
Wang S, Li Q, Li Y, Wan S, Yin Z, Zhao S, Dai X, Wang R, Wang S, Zhai Y, et al. Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):11145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011145
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shasha, Qimei Li, Yan Li, Sijing Wan, Zhenjuan Yin, Shan Zhao, Xiaoyan Dai, Ruijuan Wang, Shigui Wang, Yifan Zhai, and et al. 2024. "Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 11145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011145
APA StyleWang, S., Li, Q., Li, Y., Wan, S., Yin, Z., Zhao, S., Dai, X., Wang, R., Wang, S., Zhai, Y., Tan, X., & Tang, B. (2024). Stress Response of Aphid Population Under Combined Stress of Cadmium and Lead and Its Effects on Development of Harmonia axyridis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 11145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011145








