Subduing the Inflammatory Cytokine Storm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
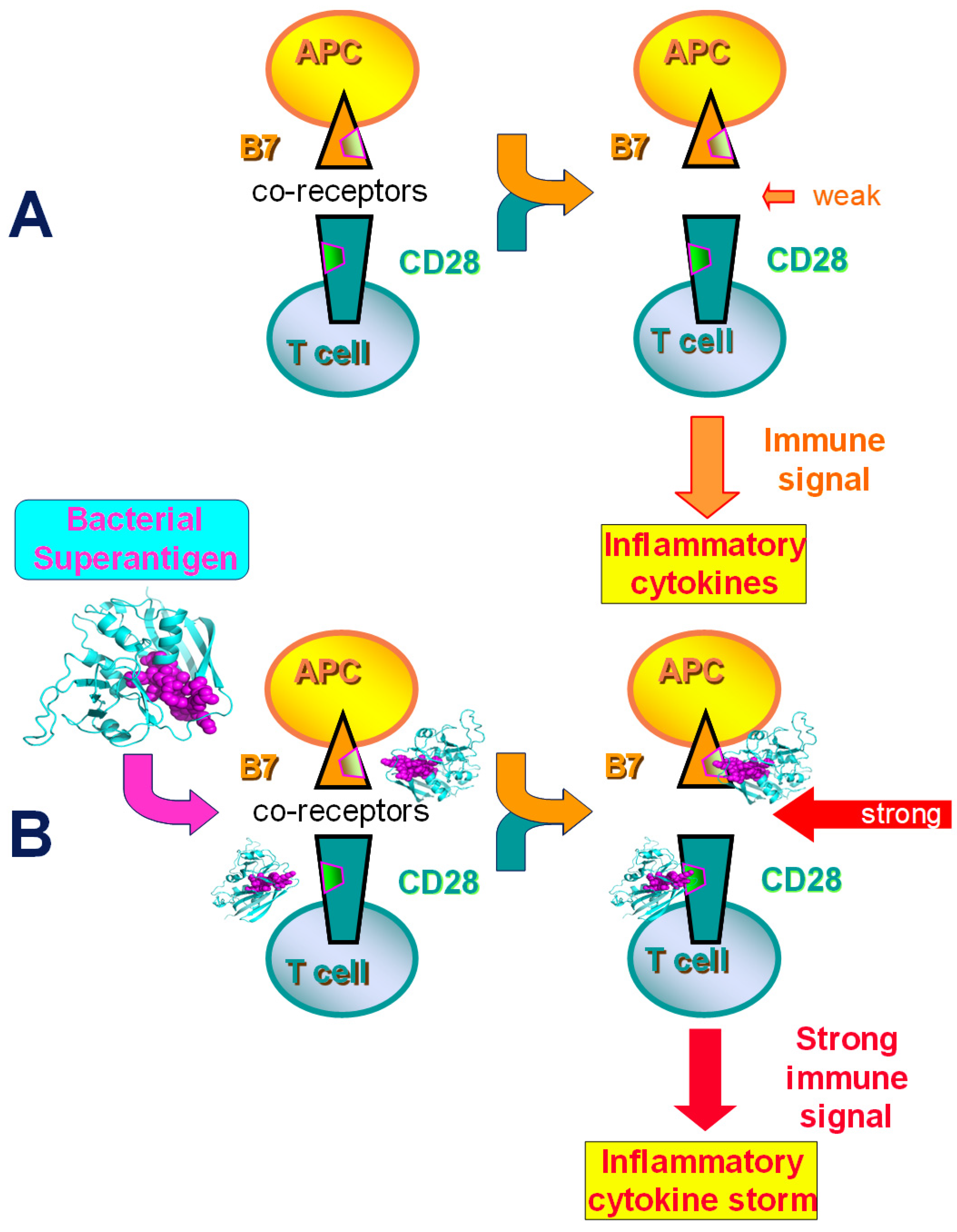
2.1. Superantigens Induce a Lethal Cytokine Storm by Directly Engaging B7 and CD28
2.2. Superantigen Toxins Trigger B7/CD28 Costimulatory Receptor Engagement
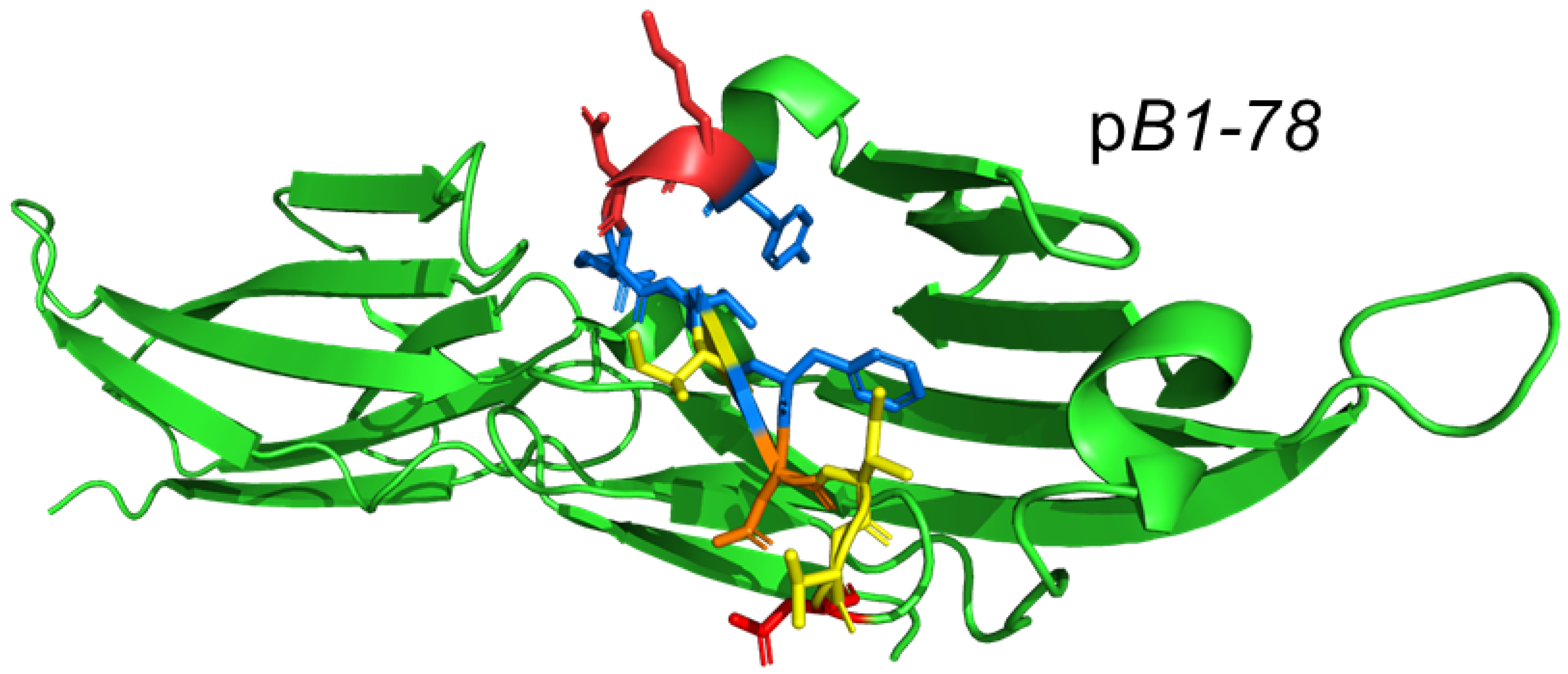
2.3. Design of Peptide Mimetics of the Human CD28 and B7 Receptor Homodimer Interfaces
2.4. The Homodimer Interface Mimetic Peptides Attenuate Intercellular B7/CD28 Engagement
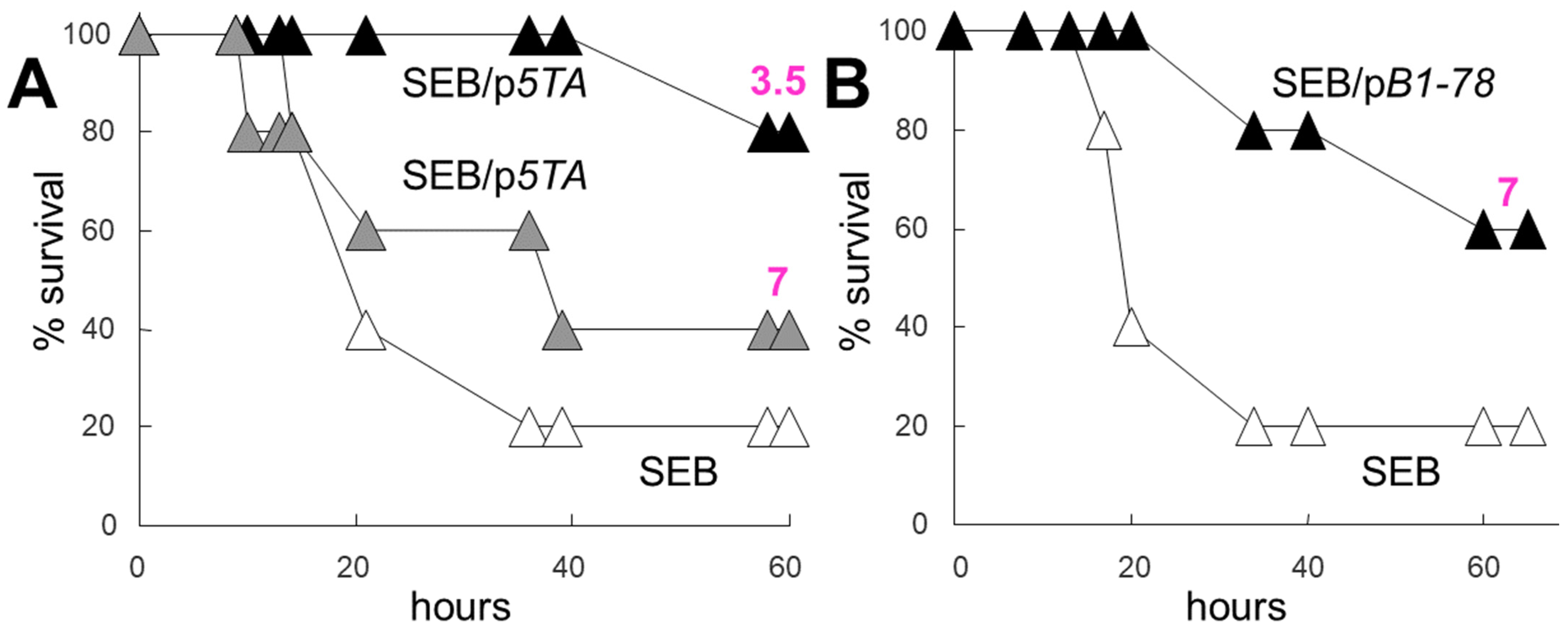
2.5. Dimer Interface Mimetic Peptides Protect Mice from Lethal Toxic Shock in Doses Far Sub-Molar to the Superantigen
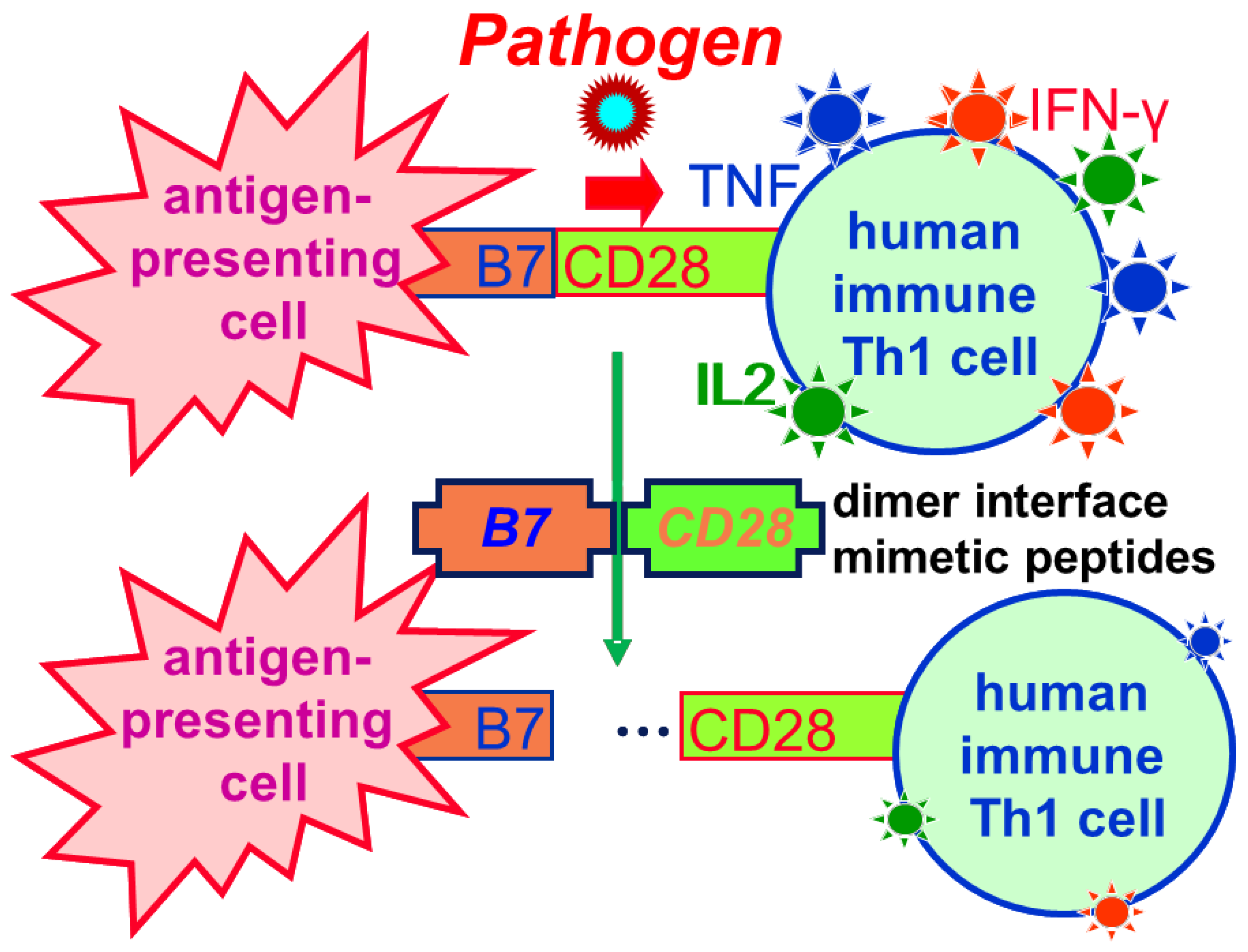
2.6. Subduing the Cytokine Storm: Beyond Superantigen Lethal Shock
2.7. Clinical Application of CD28 Dimer Interface Mimetic Peptide
3. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabler, S.S.; French, A.R.; Orvedahl, A. A cytokine circus with a viral ringleader: SARS-CoV-2-associated cytokine storm syndromes. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P.; Pullen, A.M. Superantigens: Mechanisms of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 745–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlievert, P.M. Role of superantigens in human disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohach, G.A.; Fast, D.J.; Nelson, R.D.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1990, 17, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrat, S.; Pilo, S.; Kaempfer, R. Kinetics of induction and molecular size of mRNA species encoding human interleukin-2 and gamma-interferon. Nature 1982, 297, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrat, S.; Kaempfer, R. Control of biologically active interleukin-2 messenger RNA formation in induced human lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2601–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebendiker, M.A.; Tal, C.; Sayar, D.; Pilo, S.; Eilon, A.; Banai, Y.; Kaempfer, R. Superinduction of the human gene encoding immune interferon. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, L.; Madar, L.; Arad, G.; Sharav, T.; Reshef, A.; Ketzinel, M.; Sayar, D.; Silberberg, C.; Kaempfer, R. Aberrant regulation of interleukin-2 but not of interferon-gamma gene expression in Down Syndrome (trisomy 21). Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1991, 58, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, L.; Madar, L.; Shkolnik, T.; Kristal, B.; Arad, G.; Reshef, A.; Steinberger, A.; Ketzinel, M.; Sayar, D.; Shasha, S.; et al. Regulation of interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma gene expression in renal failure. Kidney Int. 1991, 40, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaempfer, R.; Gerez, L.; Farbstein, H.; Madar, L.; Hirschman, O.; Nussinovich, R.; Shapiro, A. Prediction of response to treatment in superficial bladder carcinoma through pattern of interleukin-2 gene expression. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, L.; Shkolnik, T.; Hirschmann, O.; Lorber, M.; Arad, G.; Kaempfer, R. Hyperinducible expression of the interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) gene and its suppression in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 109, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arad, G.; Levy, R.; Hillman, D.; Kaempfer, R. Superantigen antagonist protects against lethal shock and defines a new domain for T-cell activation. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arad, G.; Levy, R.; Nasie, I.; Hillman, D.; Rotfogel, Z.; Barash, U.; Supper, E.; Shpilka, T.; Minis, A.; Kaempfer, R. Binding of superantigen toxins into the CD28 homodimer interface is essential for induction of cytokine genes that mediate shock. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Rotfogel, Z.; Hillman, D.; Popugailo, A.; Arad, G.; Supper, E.; Osman, F.; Kaempfer, R. Superantigens hyperinduce inflammatory cytokines by enhancing the B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6437–E6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popugailo, A.; Rotfogel, Z.; Supper, E.; Hillman, D.; Kaempfer, R. Staphylococcal and streptococcal superantigens trigger B7/CD28 costimulatory receptor engagement to hyperinduce inflammatory cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popugailo, A.; Rotfogel, Z.; Hillman, D.; Levy, M.; Turgeman, O.; Levy, R.; Arad, G.; Shpilka, T.; Kaempfer, R. The homodimer interfaces of costimulatory receptors B7 and CD28 control their engagement and pro-inflammatory signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earhart, C.A.; Mitchell, D.T.; Murray, D.L.; Pinheiro, D.M.; Matsumura, M.; Schlievert, P.M.; Ohlendorf, D.H. Structures of five mutants of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 with reduced biological activity. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7194–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.B.; Lindsten, T.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Kunkel, S.L.; Young, H.A.; Emerson, S.G.; Leiden, J.M.; June, C.H. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.J.; Esnouf, R.M.; Manso-Sancho, R.; Gilbert, R.J.; James, J.R.; Yu, C.; Fennelly, J.A.; Vowles, C.; Hanke, T.; Walse, B.; et al. Crystal structure of a soluble CD28-Fab complex. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemizu, S.; Gilbert, R.J.; Fennelly, J.A.; Collins, A.V.; Harlos, K.; Jones, E.Y.; Stuart, D.I.; Davis, S.J. Structure and dimerization of a soluble form of B7-1. Immunity 2000, 12, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.C.; Zhang, X.; Fedorov, A.A.; Nathenson, S.G.; Almo, S.C. Structural basis for co-stimulation by the human CTLA-4/B7-2 complex. Nature 2001, 410, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamper, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tobin, J.F.; Erbe, D.V.; Ikemizu, S.; Davis, S.J.; Stahl, M.L.; Seehra, J.; Somers, W.S.; Mosyak, L. Crystal structure of the B7-1/CTLA-4 complex that inhibits human immune responses. Nature 2001, 410, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.J.; Ikemizu, S.; Evans, E.J.; Fugger, L.; Bakker, T.R.; van der Merwe, P.A. The nature of molecular recognition by T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.; Tulapurkar, M.E.; Harris, K.M.; Arad, G.; Shirvan, A.; Shemesh, R.; DeTolla, L.J.; Benazzi, C.; Opal, S.M.; Kaempfer, R.; et al. A peptide antagonist of CD28 signaling attenuates toxic shock and necrotizing soft tissue infection induced by Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.; Kaempfer, R.; Chung, C.-S.; Chahin, A.B.; Palardy, J.E.; Parejo, N.A.; Chen, Y.; Whitford, M.; Arad, G.; Hillman, D.; et al. CD28 homodimer interface mimetic peptide acts as preventive and therapeutic agent in models of severe bacterial sepsis and Gram-negative bacterial peritonitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoeva, S.; Paunesku, T.; Wanzer, M.B.; Shirvan, A.; Kaempfer, R.; Woloschak, G.E.; Small, W., Jr. Single administration of p2TA (AB103), a CD28 antagonist peptide, prevents inflammatory and thrombotic reactions and protects against gastrointestinal injury in total-body irradiated mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulger, E.M.; Maier, R.V.; Sperry, J.; Joshi, M.; Henry, S.; Moore, F.A.; Moldawer, L.L.; Demetriades, D.; Talving, P.; Schreiber, M.; et al. A novel drug for treatment of necrotizing soft-tissue infections: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulger, E.M.; May, A.K.; Robinson, B.R.H.; Evans, D.C.; Henry, S.; Green, J.M.; Toschlog, E.; Sperry, J.L.; Fagenholz, P.; Martin, N.D.; et al. A novel immune modulator for patients with necrotizing soft tissue infections (NSTI). Results of a multicenter, phase 3 randomized controlled trial of reltecimod (AB 103). Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Li, J.; Chang, W. Systemic toxicity of CAR-T therapy and potential monitoring indicators for toxicity prevention. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1422591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandström, K.; Xu, Z.; Forsberg, G.; Nygren, P.-Å. Inhibition of the CD28—CD80 co-stimulation signal by a CD28-binding affibody ligand developed by combinatorial protein engineering. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2003, 16, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heninger, A.K.; Wentrup, S.; Al-Saeedi, M.; Schiessling, S.; Giese, T.; Wartha, F.; Meuer, S.; Schröder-Braunstein, J. Immunomodulation of human intestinal T cells by the synthetic CD80 antagonist RhuDex®. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2014, 2, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.C.; Chuang, P.H.; Chang, K.C.; Jan, P.S.; Hwang, P.I.; Wu, H.B.; Yi, M.; Zhou, H.X.; Chen, H.M. Blocking effect of an immuno-suppressive agent, cynarin, on CD28 of T-cell receptor. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.J.; Xiang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Davies, A.M.; Erbe, D.; Tam, S.; Tobin, J.F. Structure-activity studies of a series of dipyrazolo [3,4-b:3′,4′-d]pyridin-3-ones binding to the immune regulatory protein B7.1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 2991–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaempfer, R. Subduing the Inflammatory Cytokine Storm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011194
Kaempfer R. Subduing the Inflammatory Cytokine Storm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):11194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011194
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaempfer, Raymond. 2024. "Subduing the Inflammatory Cytokine Storm" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 11194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011194
APA StyleKaempfer, R. (2024). Subduing the Inflammatory Cytokine Storm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 11194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011194





